Continuously Variable-Frequency Energy-Encrypted Wireless Power Transfer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Topology and Operating Principle
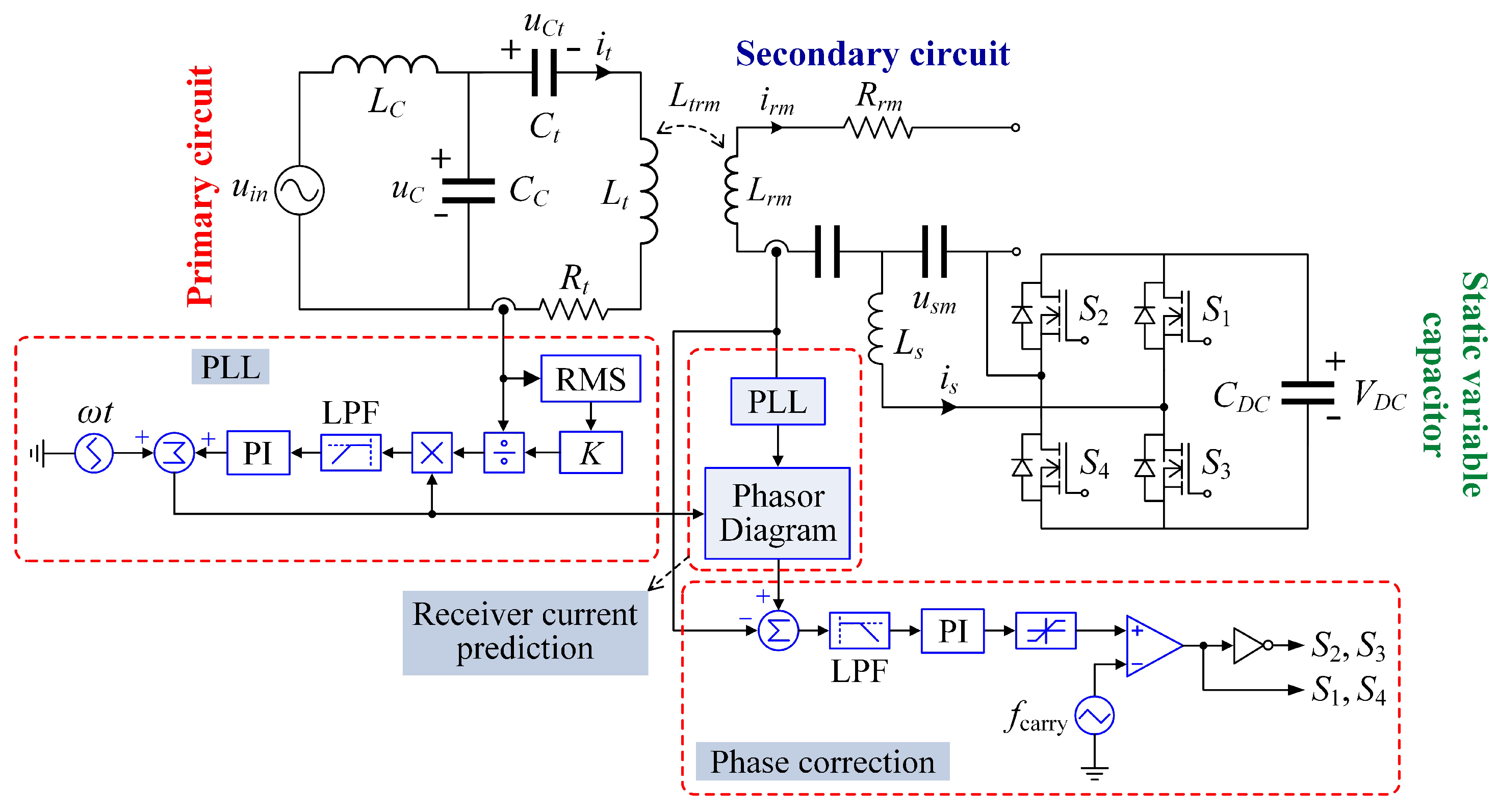
2.1. System Topology
2.2. Operating Principle
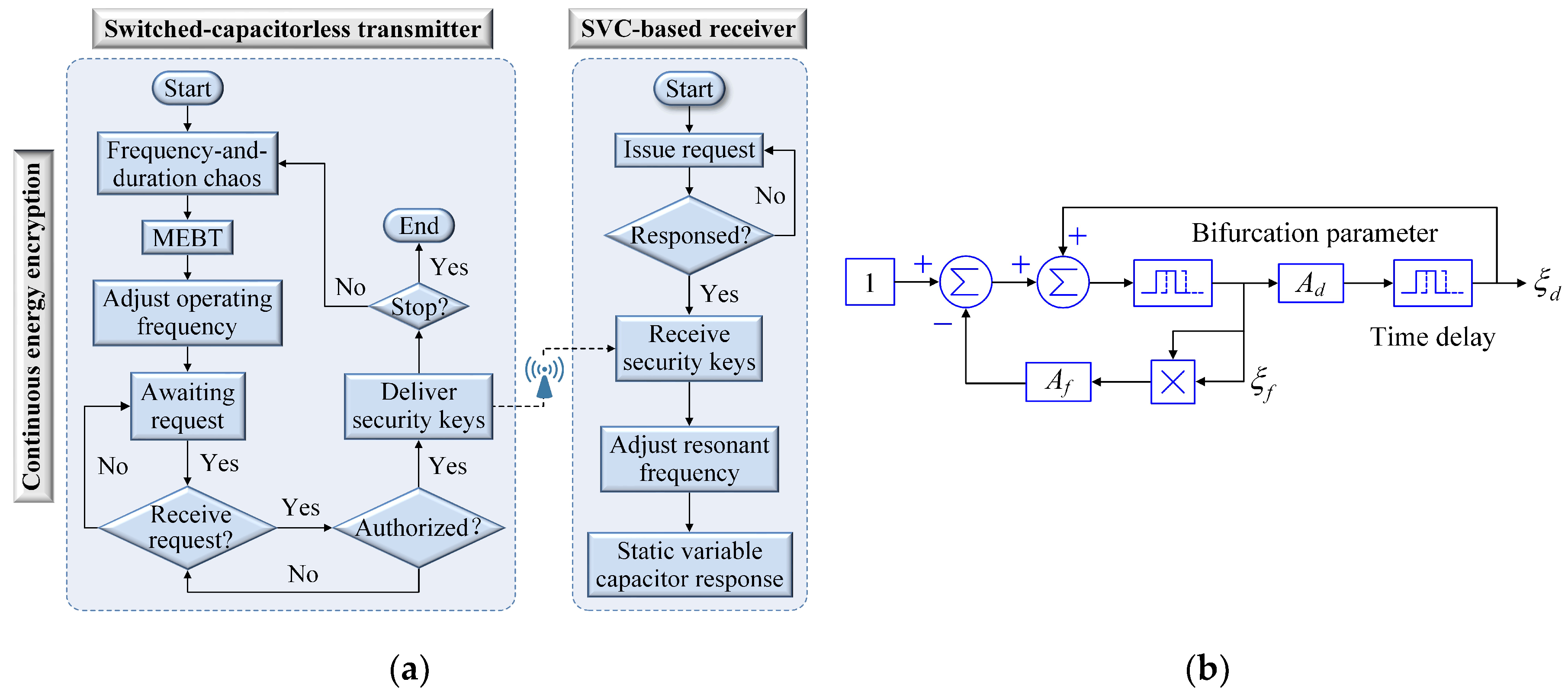
3. Frequency-and-Duration Encryption and Static Variable Capacitor Decryption
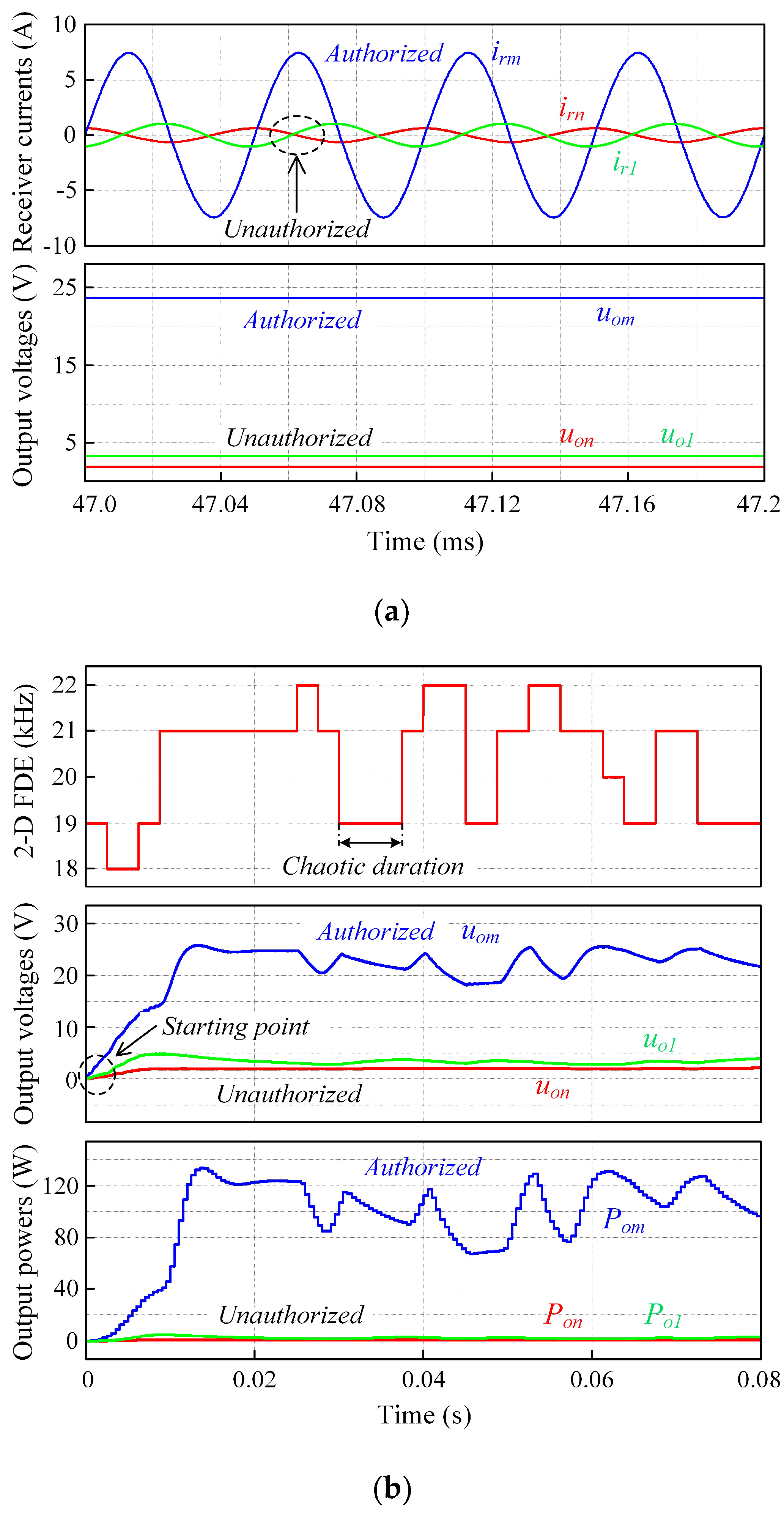
3.1. Chaotic 2-D Frequency-and-Duration Encryption
3.2. Static Variable Capacitor Decryption
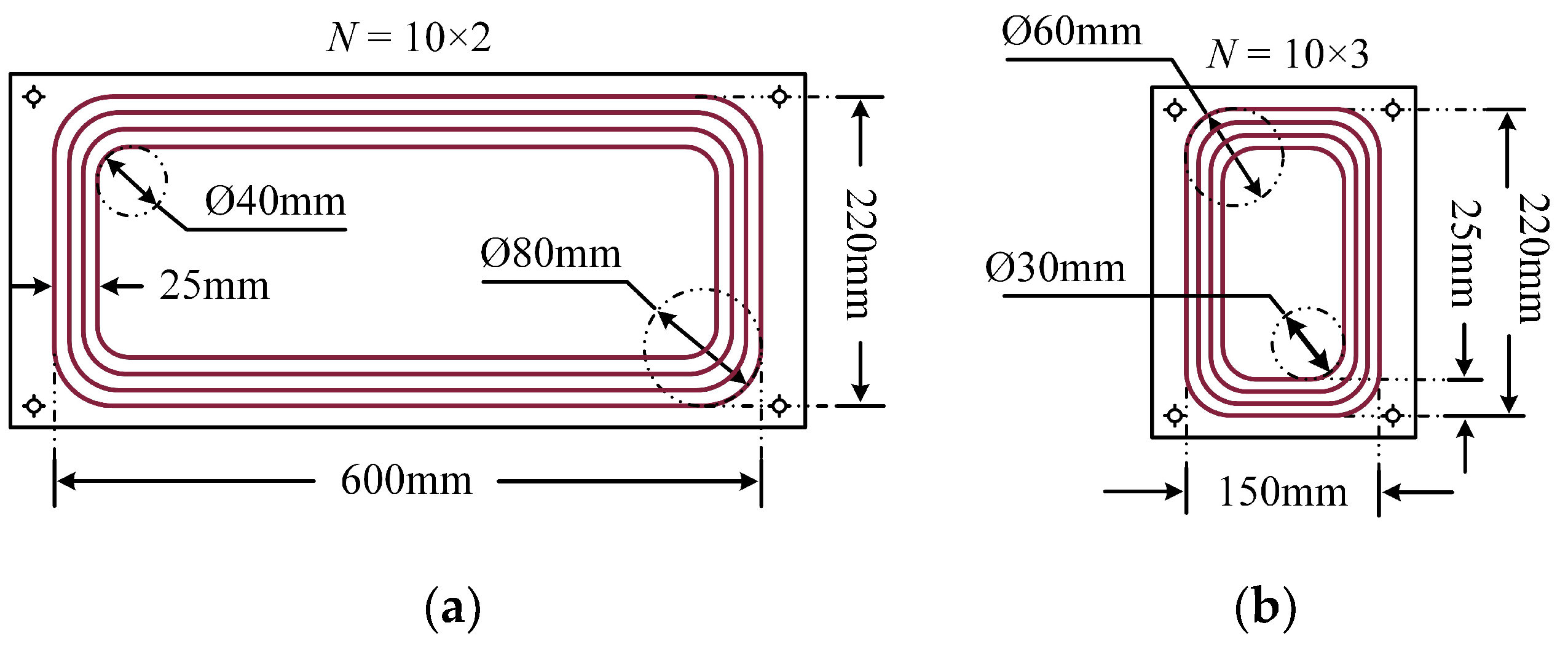
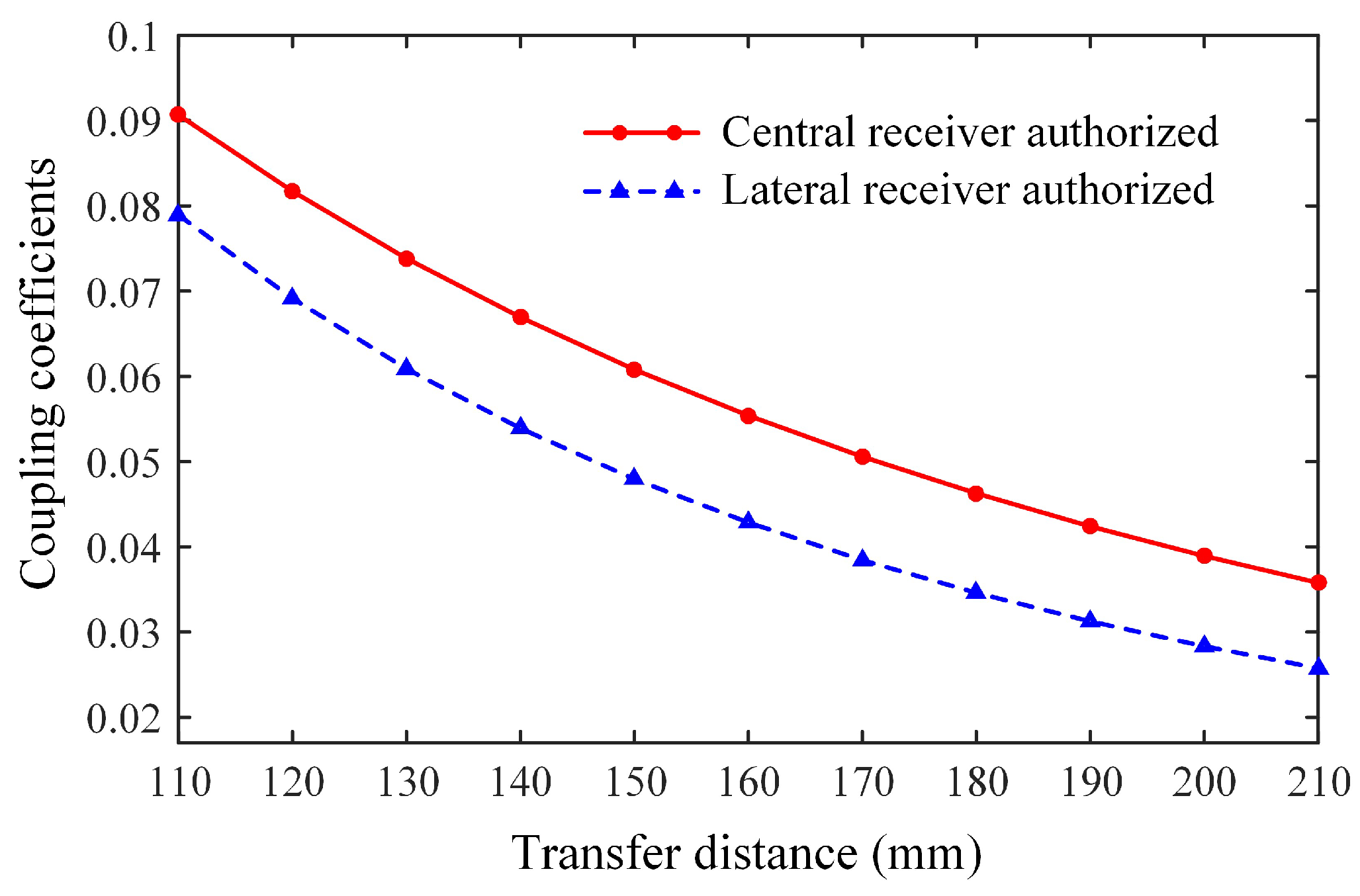
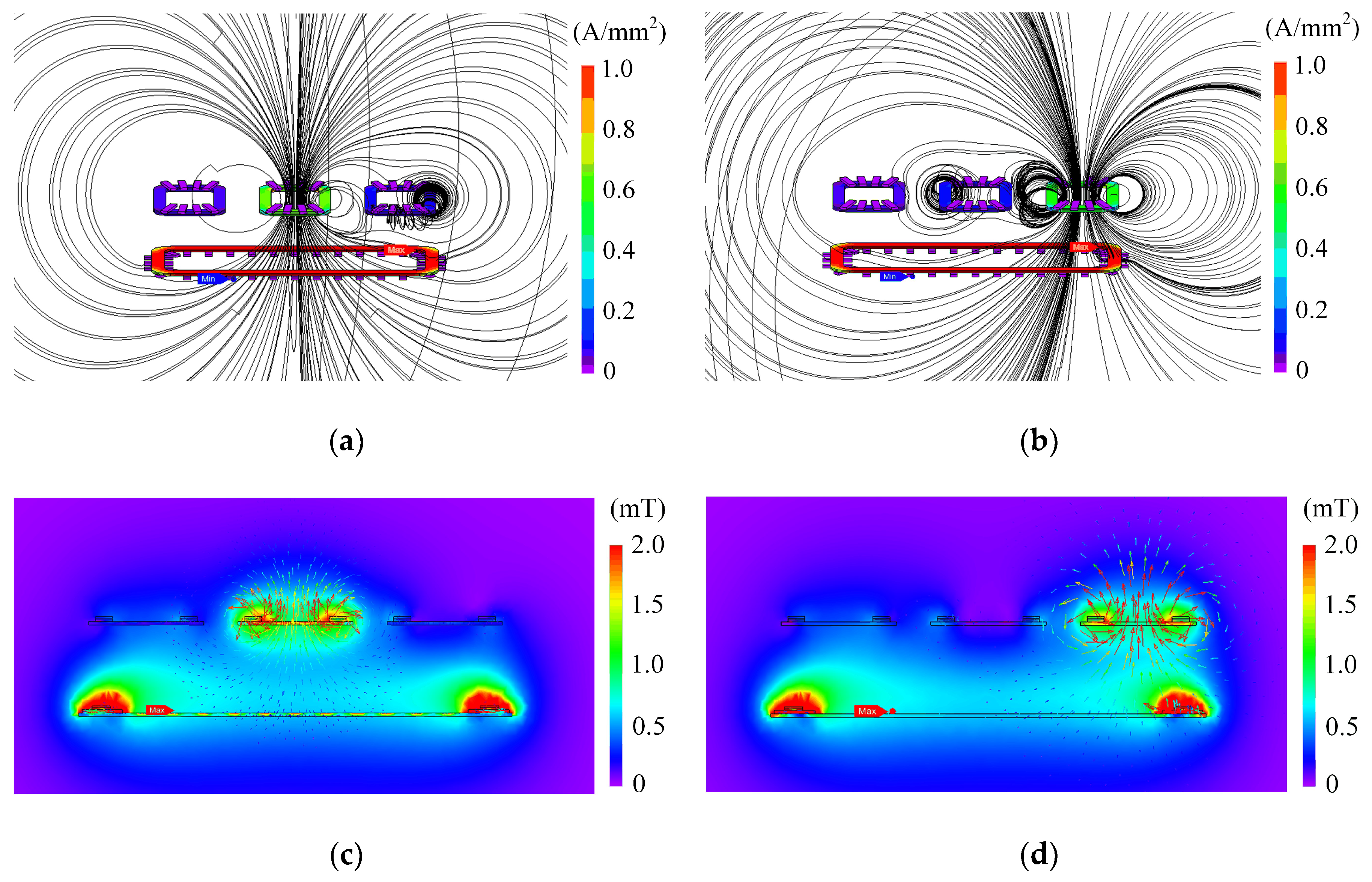
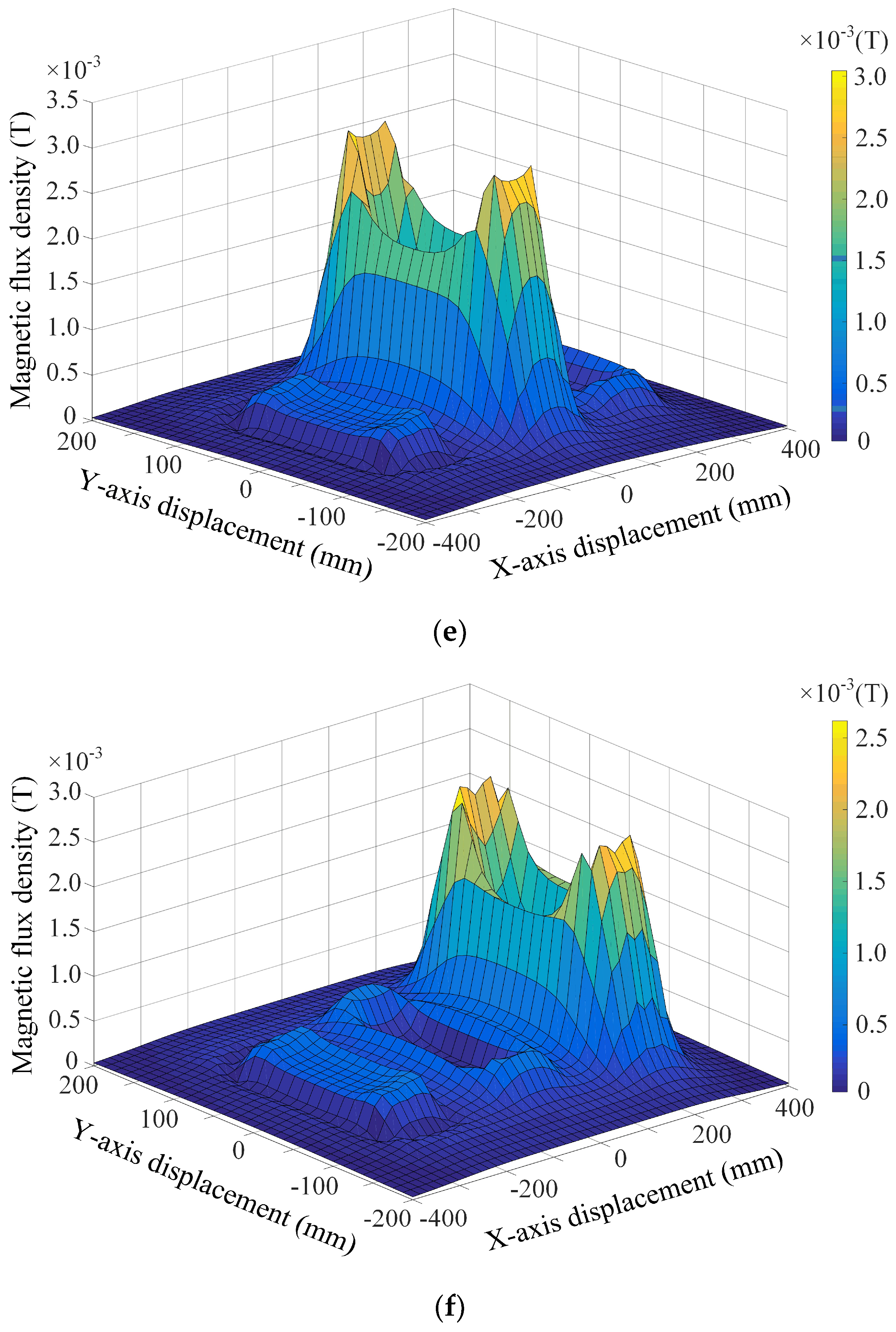
4. Computational Simulation
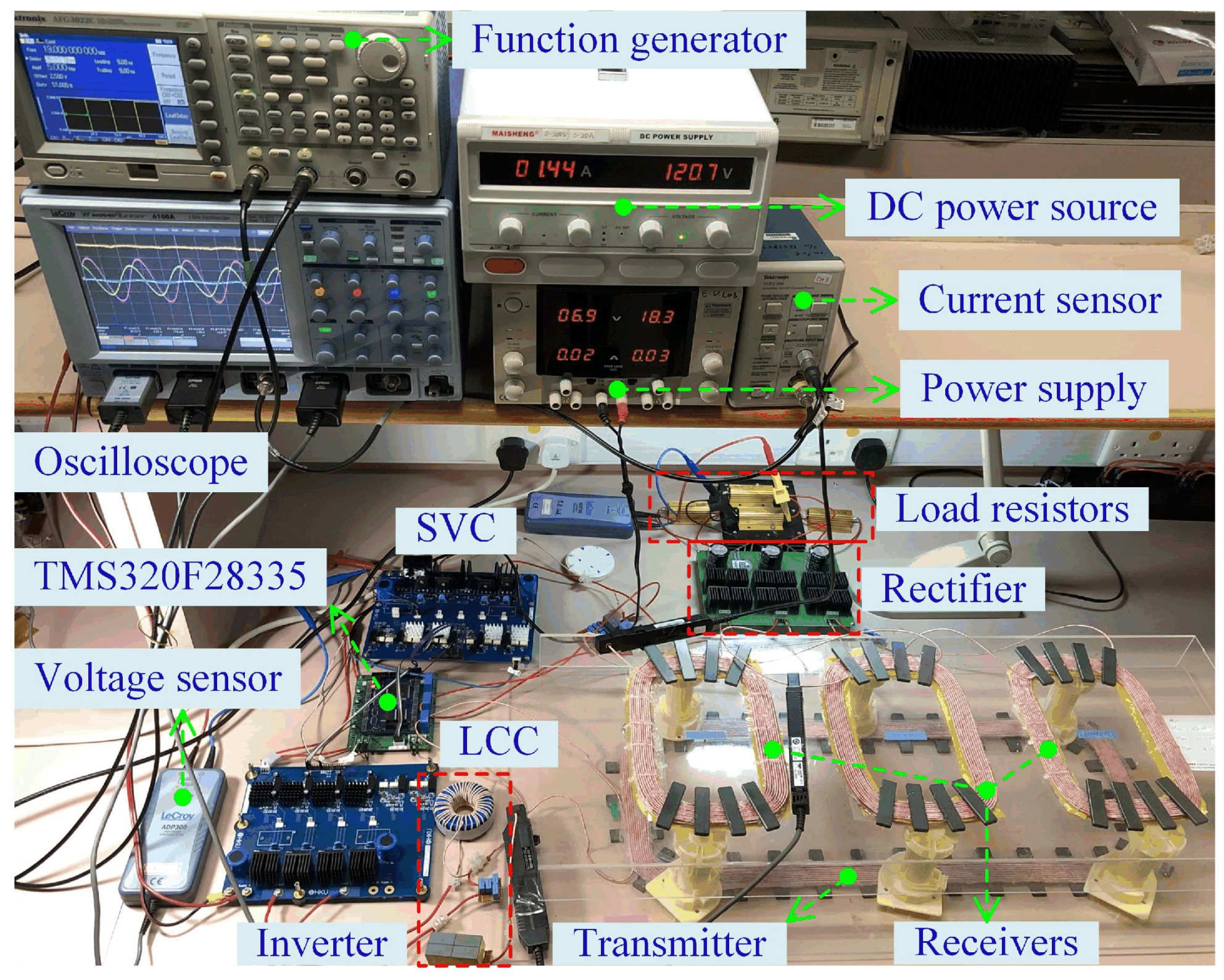
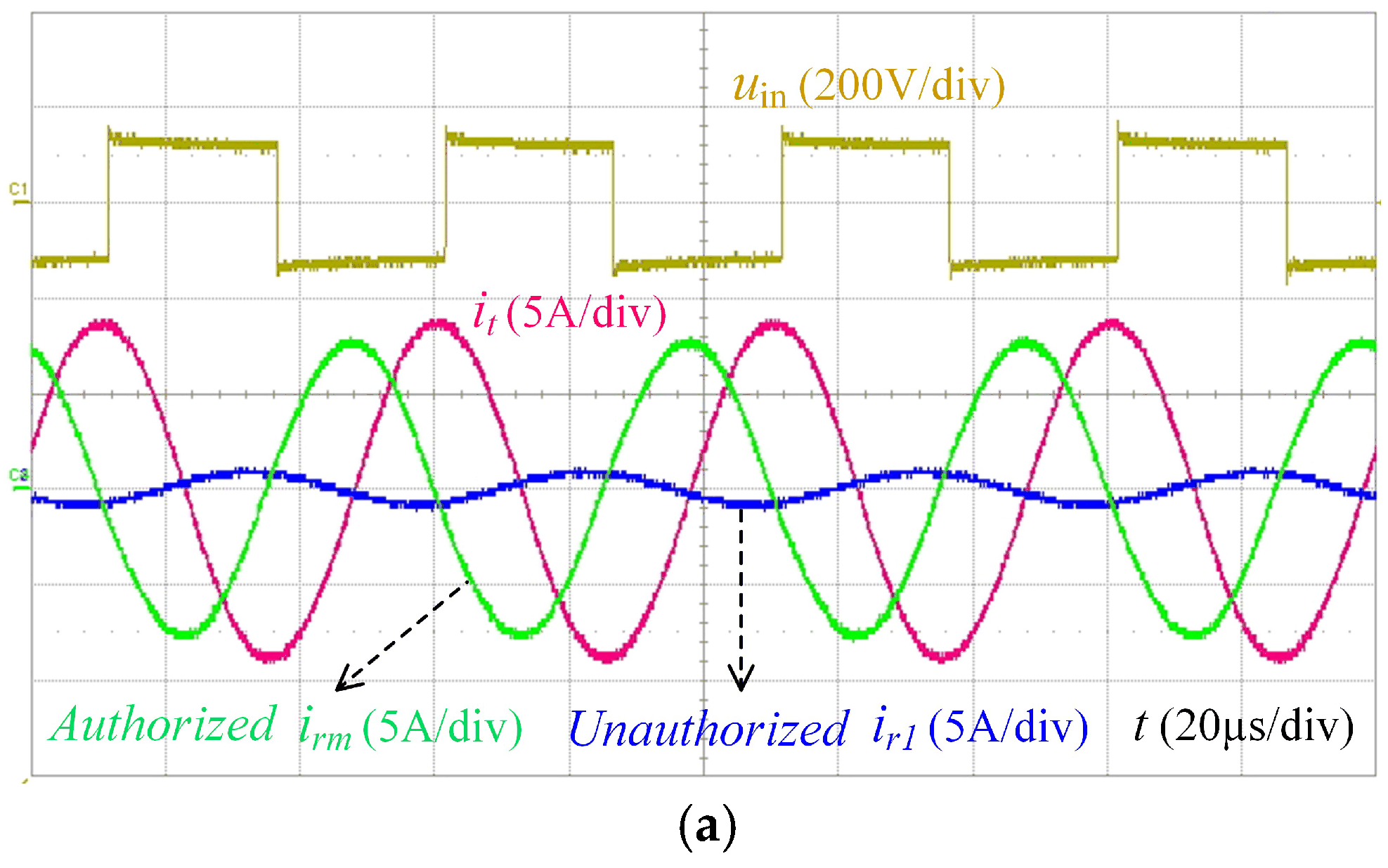
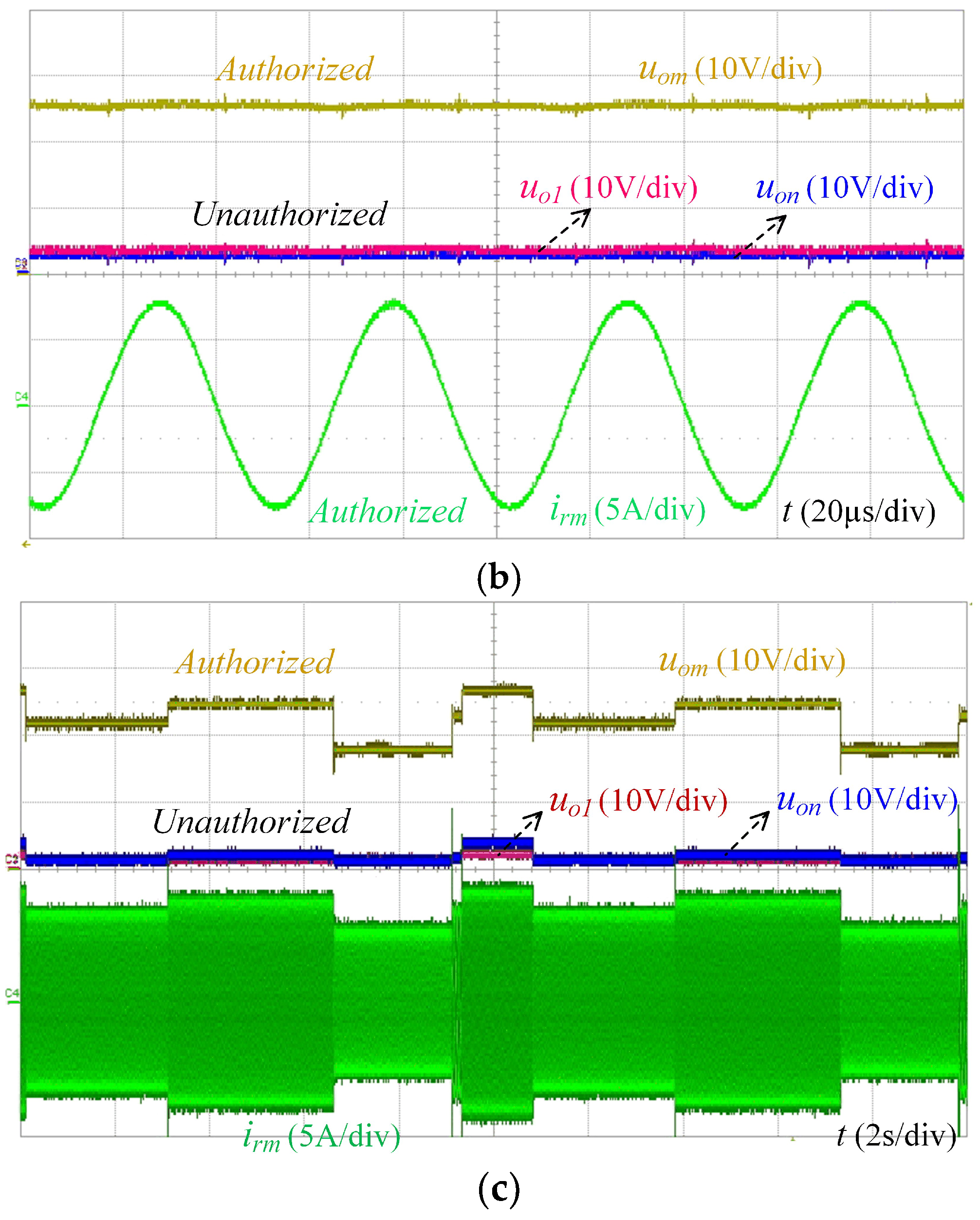
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Tesla, N. Apparatus for Transmitting Electrical Energy. U.S. Patent 119 732, 1 December 1914. [Google Scholar]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Inductive power transfer. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H.T. An overview of resonant circuits for wireless power transfer. Energies 2017, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.C.; Buja, G.; Choi, S.Y.; Rim, C.T. Modern advances in wireless power transfer systems for roadway powered electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6533–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chau, K.T.; Zhang, Z. Flexible induction heating using magnetic resonant coupling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Leung, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H.T.; Han, W. Design and analysis of wireless ballastless fluorescent lighting. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4065–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chau, K.T.; Lee, C.H.T.; Jiang, C.; Han, W.; Lam, W.H. Multi-frequency multi-power one-to-many wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, F. Applying LCC compensation network to dynamic wireless EV charging system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6557–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chau, K.T.; Lee, C.H.T.; Jiang, C.; Han, W. A switched-capacitorless energy-encrypted transmitter for roadway-charging electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Gu, B.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Rim, C.T. Advances in wireless power transfer systems for roadway-powered electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Han, W. Wireless DC motor drives with selectability and controllability. Energies 2017, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Yamamoto, G.; Gunji, D.; Imura, T.; Fujimoto, H. Development of wireless in-wheel motor using magnetic resonance coupling. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5270–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chau, K.T.; Qiu, C.; Liu, C. Energy encryption for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 5237–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Qiu, C.; Lin, F. An efficient wireless power transfer system with security considerations for electric vehicle applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurs, A.; Karalis, A.; Moffatt, R.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fisher, P.; Soljačić, M. Wireless power transfer via strongly coupled magnetic resonances. Science 2007, 317, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhao, Z.; He, F.; Chen, K.; Yuan, L. Selective wireless power transfer to multiple loads using receivers of different resonant frequencies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6001–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Hu, A.P. A DC-voltage-controlled variable capacitor for stabilizing the ZVS frequency of a resonant converter for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2312–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, R. Modelling and control of a novel zero-current-switching inverter with sinusoidal current output. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.C.; Zeng, Y. Control of inverters via a virtual capacitor to achieve capacitive output impedance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5568–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Tan, S.C.; Lee, C.K.; Hui, S.Y.R. Mitigating voltage and frequency fluctuation in microgrids using electric springs. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2015, 6, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, F.Z. An H-bridge-based single-phase var generator with minimum DC capacitance. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Choe, G.-Y.; Lee, B.K. Integrated control strategy for inductive power transfer systems with primary-side LCC network for load-average efficiency improvement. Energies 2019, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Zhang, K.; Kan, T.; Mi, C. An LCC-P compensated wireless power transfer system with a constant current output and reduced receiver size. Energies 2019, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Clare, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. A design method for making an LCC compensation two-coil wireless power transfer system more energy efficient than an SS counterpart. Energies 2017, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.T.; Wang, Z. Chaos in Electric Drive Systems—Analysis, Control. and Application; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hénon, M. A two-dimensional mapping with a strange attractor. Comm. Math. Phys. 1976, 50, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, B.T.; Kato, M.; Imura, T.; Sehoon, O.; Hori, Y. Automated impedance matching system for robust wireless power transfer via magnetic resonance coupling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3689–3698. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.; Tang, H.; Lim, S.; Park, J. An adaptive impedance-matching network based on a novel capacitor matrix for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4403–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Items | Value |
|---|---|
| Digital signal processer | TMS320F28335 |
| Transmitter compensated inductance (Lf) | 150 μH |
| Transmitter compensated capacitance (Cf) | 250 nF |
| Transmitter capacitance (Ct) | 100 nF |
| Transmitter coil inductance (Lt) | 566.80 μH |
| Transmitter coil turns (nt) | 20 (2 layers) |
| Transmitter coil internal resistance (Rt) | 0.3 Ω |
| Receiver capacitances (Crk) | 81.43, 185.23, 850.00 nF |
| Receiver coil inductances (Lr1, Lrm, Lrn) | 345.65, 355.30, 348.63 μH |
| Receiver coil turns (nrk) | 30 (3 layers) |
| Receiver coil internal resistance (Rrk) | 0.2 Ω |
| Mutual inductances (Ltr1, Ltrm, Ltrn) | 26.72, 33.11, 28.59 μH |
| SVC AC inductance (Lsk) | 10 μH |
| SVC AC capacitance (Csk) | 2 μF |
| Output filter capacitance (Co) | 2000 μF |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Chau, K.T.; Lam, W.H.; Zhang, Z. Continuously Variable-Frequency Energy-Encrypted Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2019, 12, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071286
Liu W, Chau KT, Lam WH, Zhang Z. Continuously Variable-Frequency Energy-Encrypted Wireless Power Transfer. Energies. 2019; 12(7):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071286
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, K. T. Chau, W. H. Lam, and Zhen Zhang. 2019. "Continuously Variable-Frequency Energy-Encrypted Wireless Power Transfer" Energies 12, no. 7: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071286
APA StyleLiu, W., Chau, K. T., Lam, W. H., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Continuously Variable-Frequency Energy-Encrypted Wireless Power Transfer. Energies, 12(7), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071286







