Identification Method for Voltage Sags Based on K-means-Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Support Vector Machine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of Voltage Sags
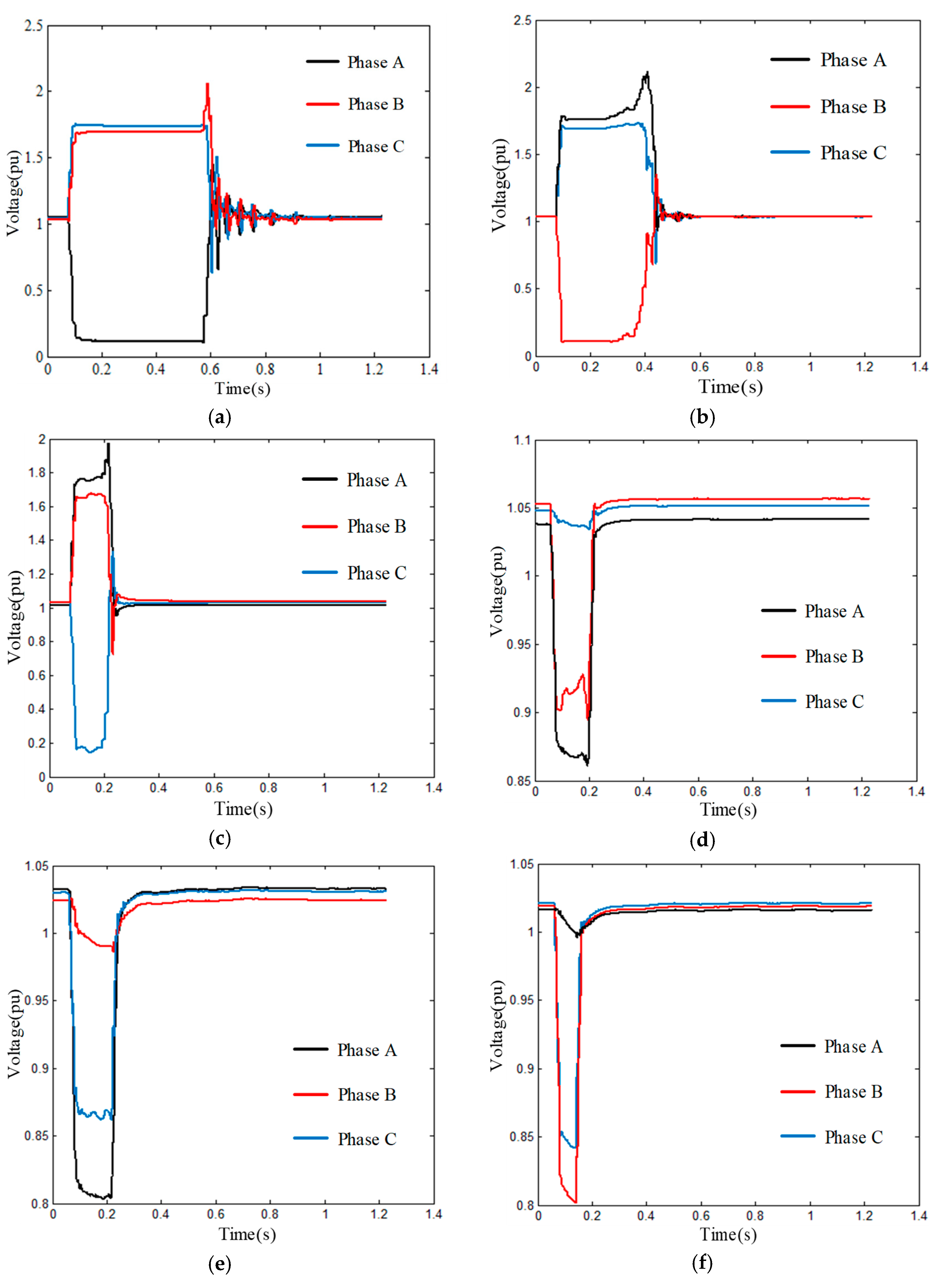
2.1. Short-Circuit Faults
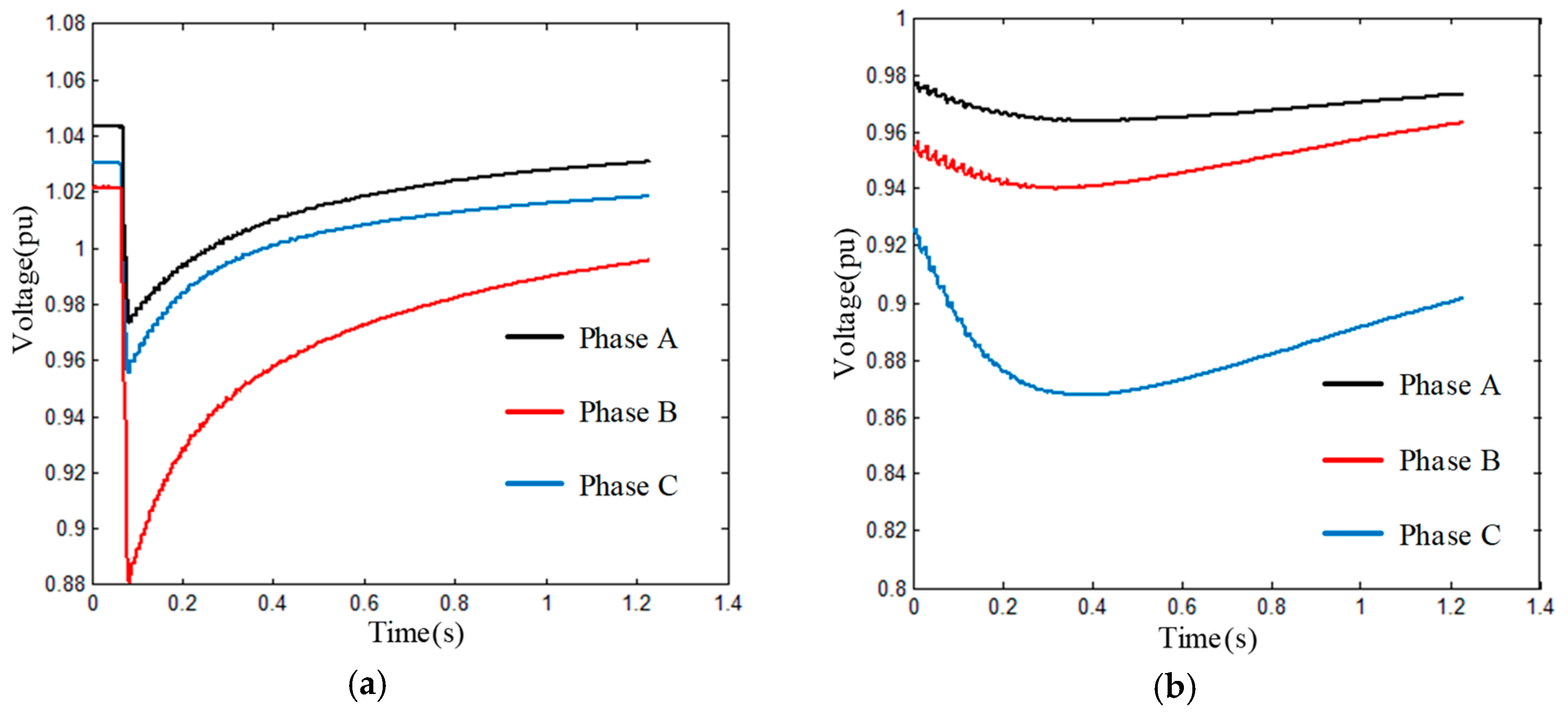
2.2. Transformer Energizing and Motor Starting
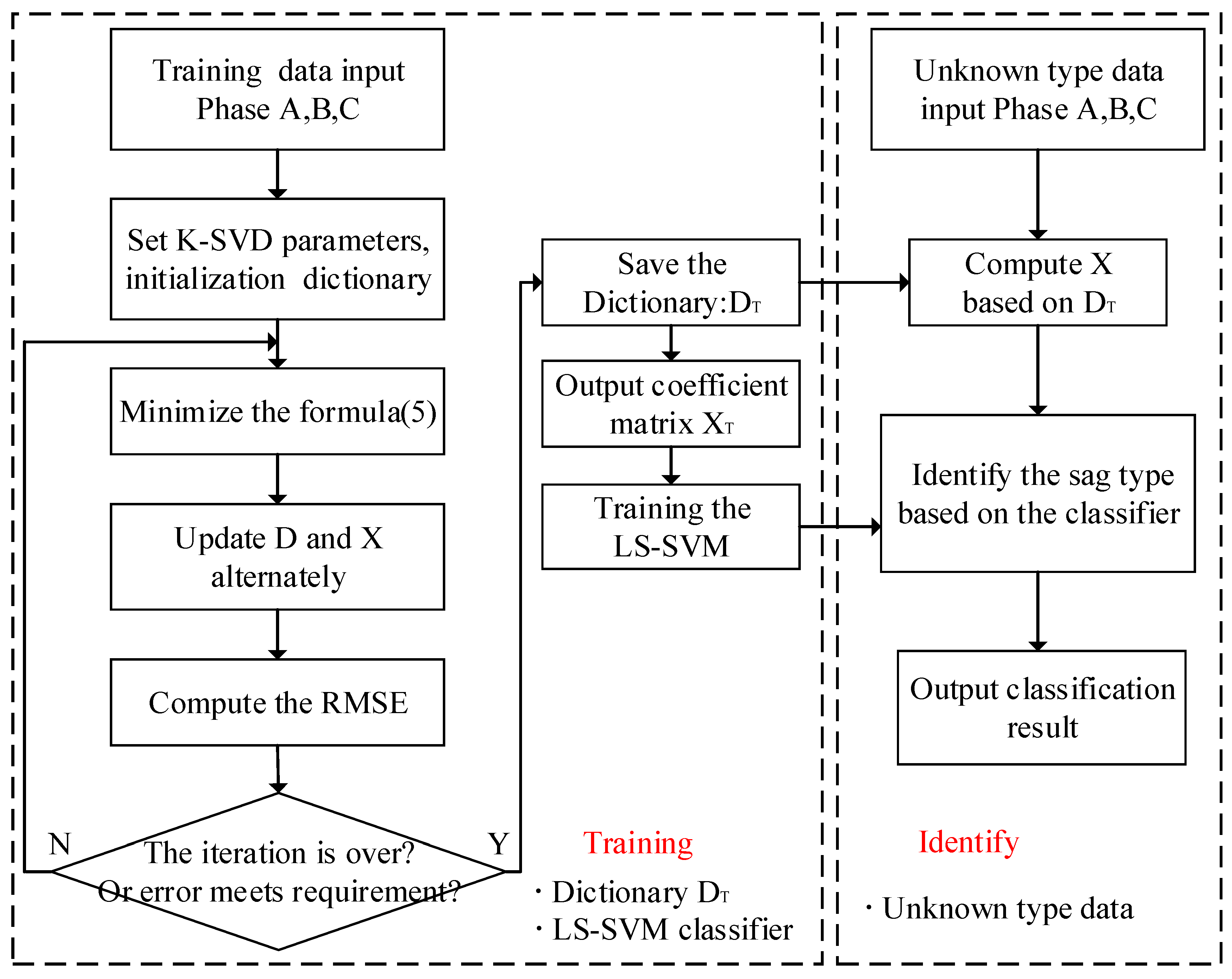
3. Classification of Sag Type Based on K-SVD and LS-SVM
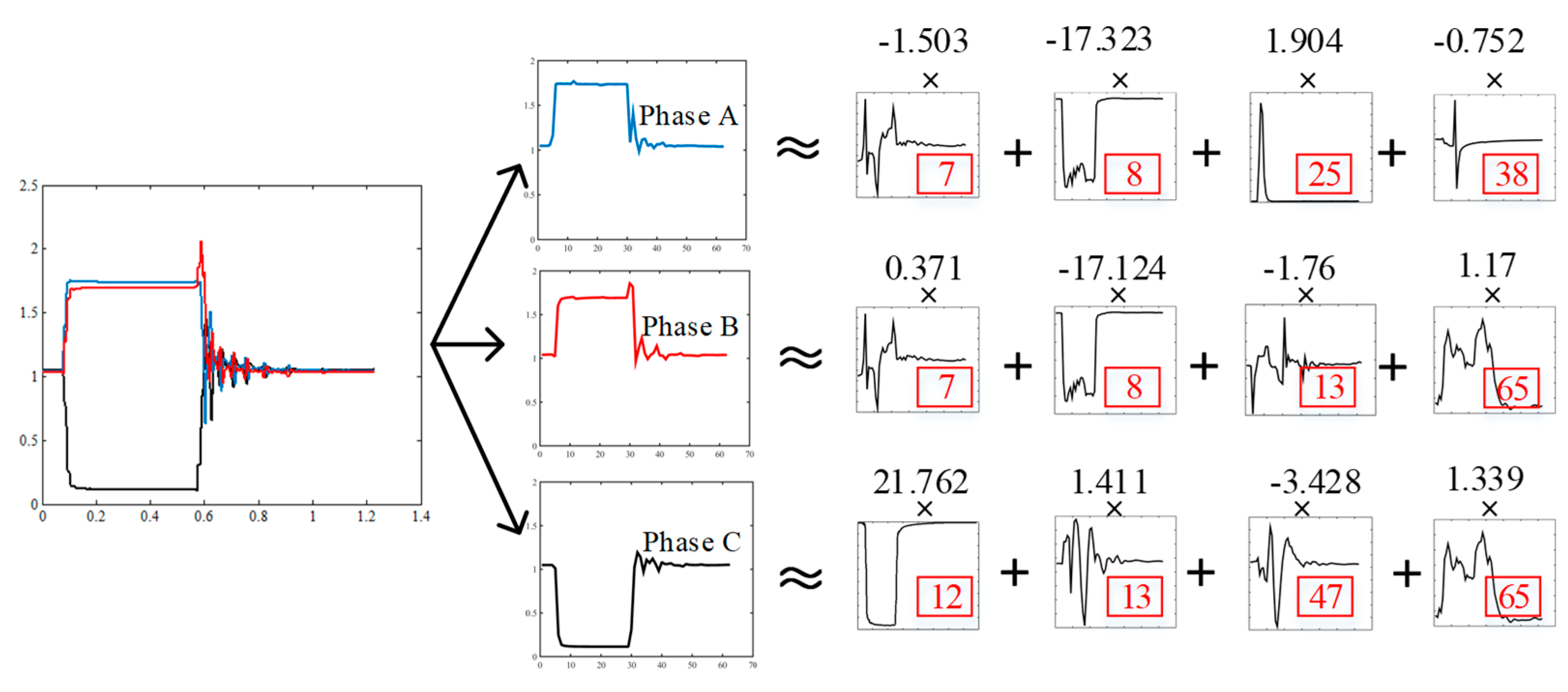
3.1. K-SVD Algorithm
- Self-Learning. This algorithm is a self-learning algorithm, rather than extracting hand-crafted features, and reducing the dependence on artificial experience. All features are extracted directly from the RMS waveform without complex feature extraction algorithms.
- Response to the characteristics of the signal directly. Each signal has a linear combination of one atom with the highest similarity, that is, the atom with the highest absolute coefficient which is called Dominating Atom (DA) in this paper, and its corresponding coefficient x is called Dominating Coefficient (DC). DA and DC reflect the characteristics of the signal, so the DA’s number and DC can be used as the basis for its classification.
- Data visualization. The waveform of each dictionary atom is part of the sag voltage waveform. This visualization can show how the original profiles are transformed into other forms, which can help with coding accuracy analysis.
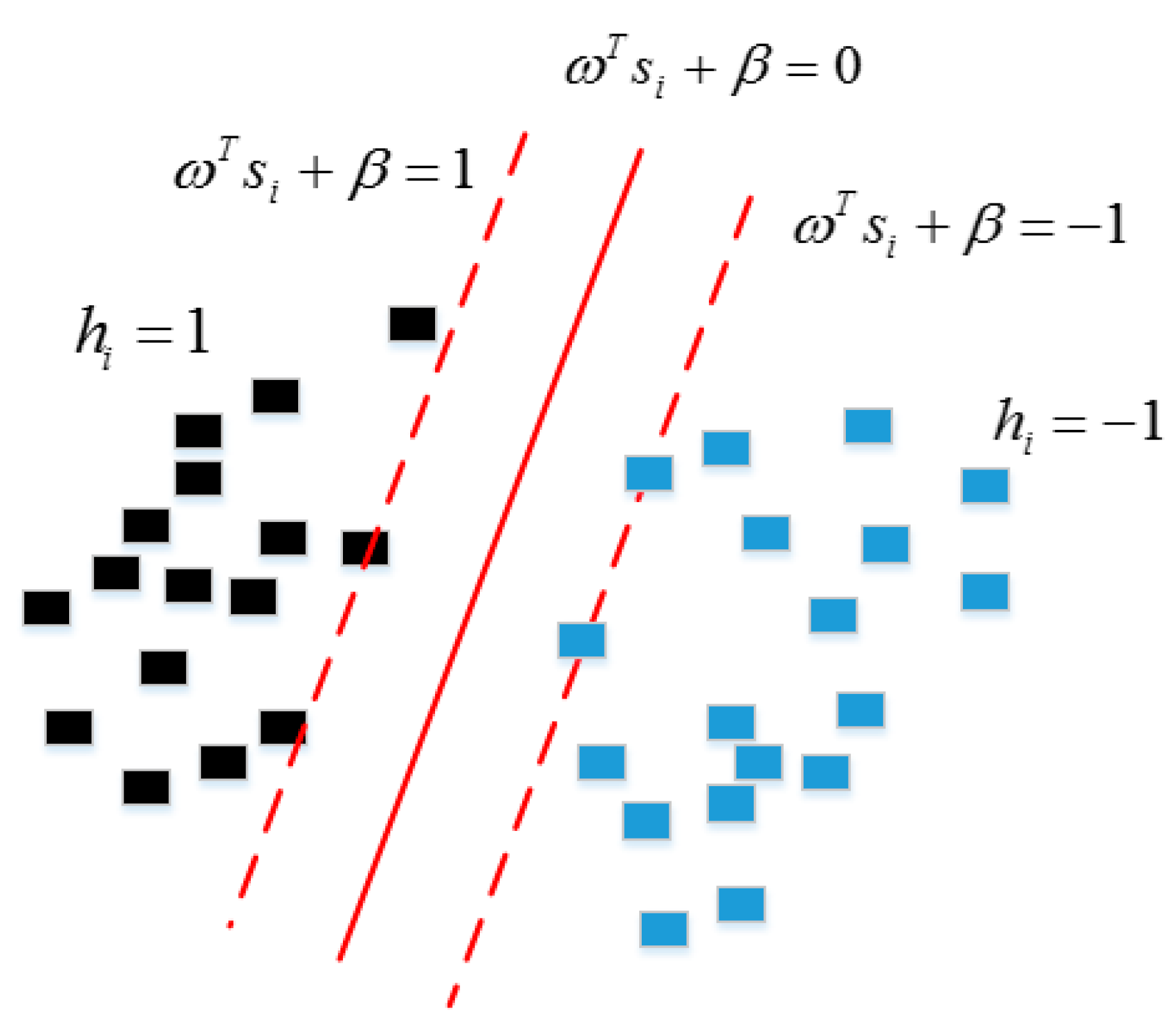
3.2. Classification Algorithm
3.3. Dip Type Classification Method
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Data Description
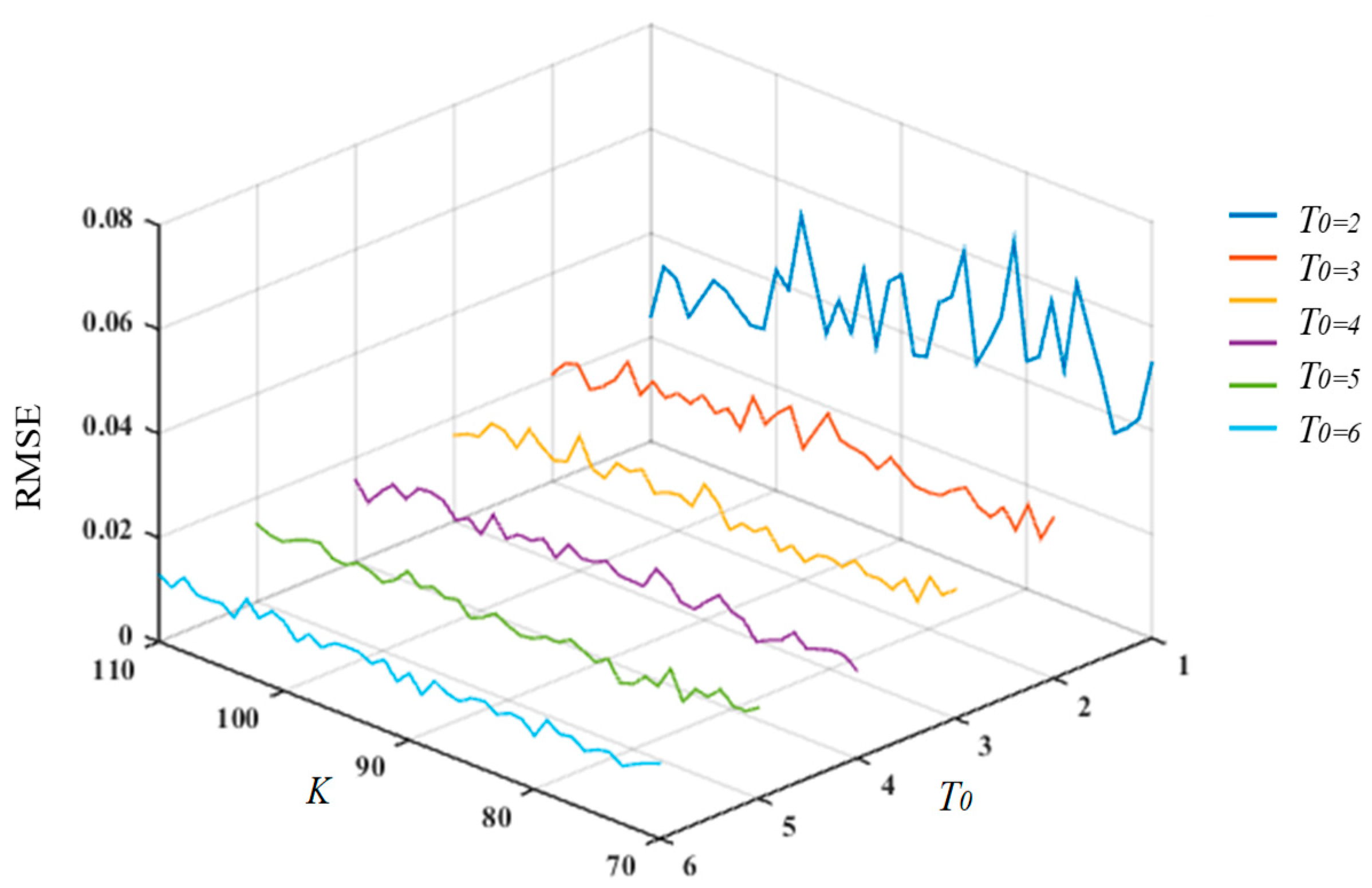
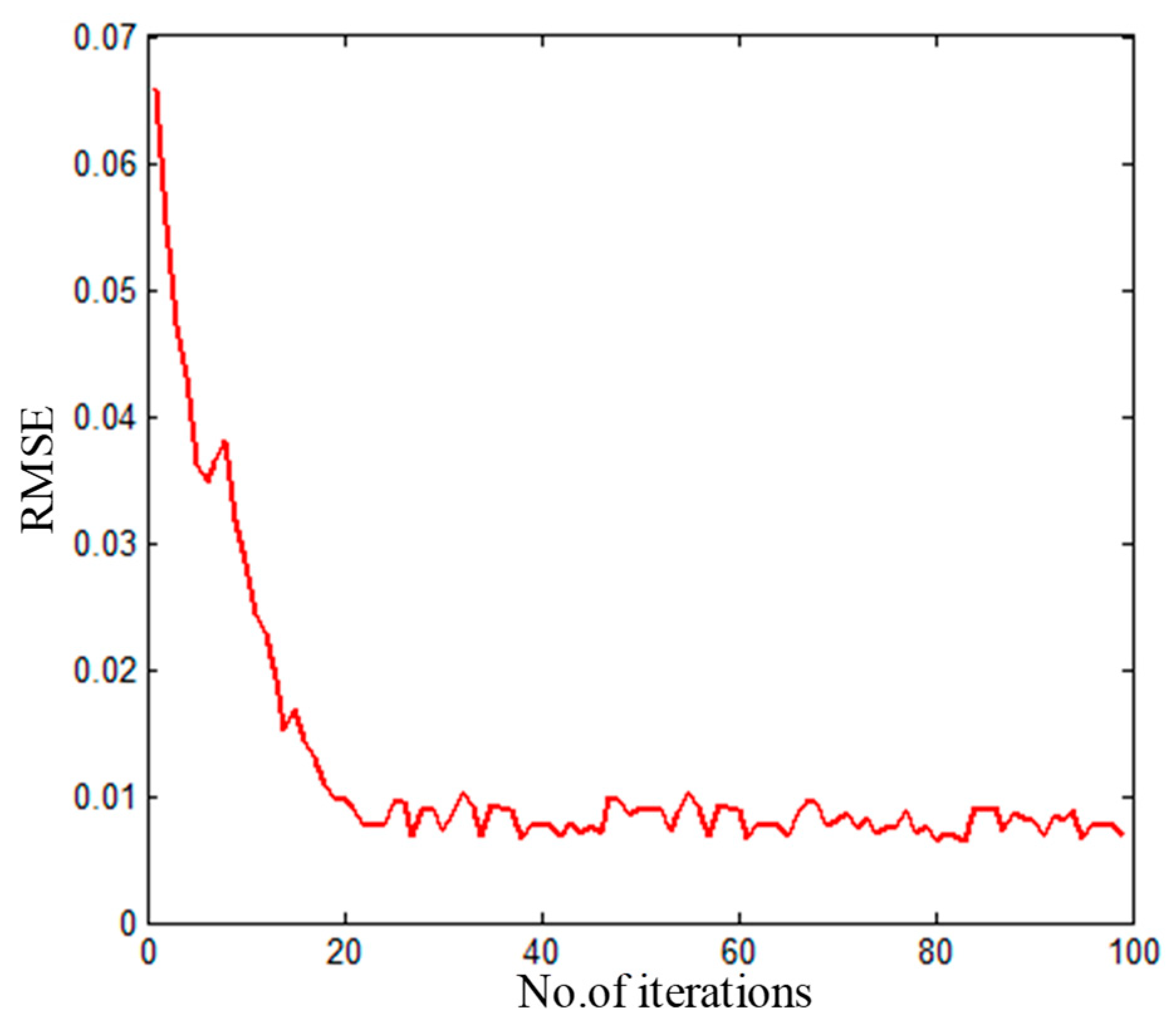
4.2. Parameter Selection
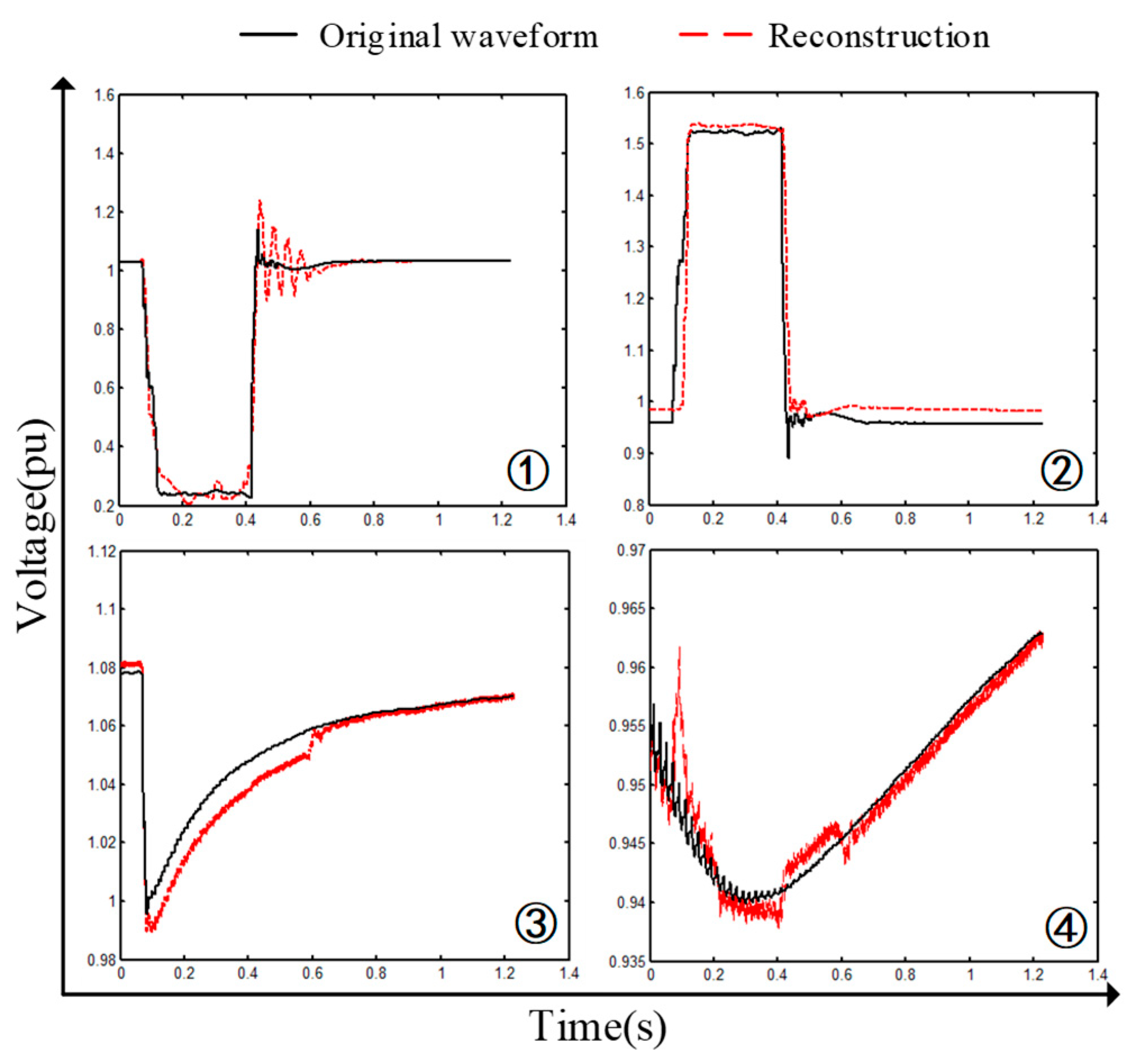
4.3. Sag Classification Experiment Example
4.3.1. Experiment 1
4.3.2. Experiment 2
4.3.3. Experiment 3
4.4. Comparative Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Pan, Z. Voltage sag state estimation for power distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Guzmán, S.; Ruiz-Guzmán, O.A.; Garcia-Arías, L.F.; Jaramillo-Gonzáles, M.; Cardona-Orozco, P.D.; Ustariz-Farfán, A.J.; Cano-Plata, E.A.; Salazar-Jiménez, A.F. Analysis of Voltage Sag Severity Case Study in an Industrial Circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Singh, A.K. Unbalance voltage sag fault-type characterization algorithm for recorded waveform. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekke, K.; Esteves, J.; Bollen, M.; Lo Schiavo, L.; Villa, F.; Reti, G.; Haber, A.; Falcao, A.; Westergaard, T.; Kolessar, R. The CEER and the 4th Benchmarking Report on Quality of Electricity Supply. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Lisbon, Portugal, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldemariam, L.; Cuk, V.; Cobben, S.; van Waes, J. Regulation and classification of voltage dips. CIRED—Open Access Proc. J. 2017, 1, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranaghan, M.F.; Mueller, D.R.; Samotyj, M.J. Voltage sags in industrial systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.A.; de Vicuña, J.L.; Miret, J.; Castilla, M.; Guzmán, R. Control Strategy for Grid-ConnectedThree-Phase Inverters During Voltage Sags to Meet Grid Codes and to Maximize Power Delivery Capability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9360–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.Q. Multi-attribute analysis on voltage sag insurance mechanisms and their feasibility for sensitive customers. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 3892–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Bollen, M.H. Characteristic of voltage dips (sags) in power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2000, 15, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styvaktakis, E.; Bollen, M.H.; Gu, I.Y.H. Expert system for classification and analysis of power system events. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2002, 17, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelberg, P.G.; Gu, I.Y.H.; Bollen, M.H. Support vector machine for classification of voltage disturbances. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2007, 22, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hao, X.; Lin, J. Interference Source of Voltage Sag in Distribution System Automatic Identification and Classification Using Wavelet and Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Faiz, J.; Lotfi-fard, S.; Bollen, M.H.J. Wavelet-based Mann and Morrison algorithm for improvement of three-phase unbalanced voltage dips characterization. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2007, 1, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.B.; Driesen, J. Assessment of voltage sag indices based on scaling and wavelet coefficient energy analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2013, 28, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.M.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Bouzerdoum, A. A new approach for classification and characterization of voltage dips and swells using 3-D polarization ellipse parameters. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2015, 30, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, T.; Gómez-Lázaro, E.; Muljadi, E.; Kessler, M.; Molina-García, A. Approach to fitting parameters and clustering for characterising measured voltage dips based on two-dimensional polarisation ellipses. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharon, M.; Elad, M.; Bruckstein, A. K-SVD: An algorithm for de-signing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4311–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, Y.C.; Rezaiifar, R.; Krishnaprasad, P.S. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit: Recursive Function Approximation with Applications to Wavelet Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1–3 November 1993; pp. 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, T.; Suykens, J.A.; Baesens, B.; Viaene, S.; Vanthienen, J.; Dedene, G.; De Moor, B.; Vandewalle, J. Benchmarking least squares support vector machine classifiers. Mach. Learn. 2004, 54, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.W.; Sun, Y. Forecasting dissolved gases content in power transformer oil based on support vector machine with genetic algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Ye, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H. Grid search optimized SVM method for dish-like underwater robot attitude prediction. In Proceedings of the 5th International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, Harbin, China, 23–26 June 2012; pp. 839–843. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lin, C.J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kang, C.; Xia, Q.; Luo, M. Sparse and Redundant Representation-Based Smart Meter Data Compression and Pattern Extraction. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gan, D.; Yang, J.; Kirschen, D.S.; Kang, C. Deep Learning-Based Socio-demographic Information Identification from Smart Meter Data. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Number | Training | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fault-induced | A-phase short circuit | 465 | 348 | 117 |
| B-phase short circuit | 369 | 276 | 93 | |
| C-phase short circuit | 201 | 150 | 51 | |
| A- and B-phase short circuit | 72 | 54 | 18 | |
| B- and C-phase short circuit | 45 | 33 | 12 | |
| A- and C-phase short circuit | 120 | 90 | 30 | |
| Three-phase short circuit | 123 | 92 | 31 | |
| No-Fault-induced | Motor starting | 90 | 67 | 23 |
| Transformer energizing | 69 | 51 | 18 | |
| Total | 1554 | 1161 | 393 | |
| Sag Type | Single 1 | Two 1 | Three 1 | Q (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single 1 (261) | 257 | 4 | - | 98.85 |
| Two 1 (60) | 2 | 58 | - | 95.07 |
| Three 1 (31) | - | - | 31 | 100 |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||
| 97.97 | ||||
| Sag Type | Single 1 | Two 1 | Three 1 | M 2 | T 2 | Q (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single 1 (261) | 258 | 3 | - | - | - | 98.23 |
| Two 1 (60) | 1 | 59 | - | - | - | 92.92 |
| Three 1 (31) | - | - | 27 | 4 | - | 92.03 |
| M 2 (23) | - | - | 1 | 22 | - | 88.91 |
| T 2 (18) | - | - | - | - | 18 | 100 |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||||
| 95.14 | ||||||
| Sag Type | A | B | C | AB | BC | AC | ABC | M 1 | T 1 | Q (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (117) | 117 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| B (93) | - | 93 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 98.43 |
| C (51) | - | 51 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 95.34 | |
| AB (18) | - | 2 | 16 | - | - | - | - | - | 94.18 | |
| BC (12) | - | 1 | 2 | - | 9 | - | - | - | - | 85.71 |
| AC (30) | - | - | 3 | - | - | 27 | - | - | - | 94.74 |
| ABC (31) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 27 | 4 | - | 91.51 |
| M 1 (23) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 22 | - | 89.81 |
| T 1 (18) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 18 | 100 |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||||||||
| 92.98 | ||||||||||
| Sag Type | Expert System | SVM | The Proposed Method | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R% | P% | Q% | A% | R% | P% | Q% | A% | R% | P% | Q% | A% | |
| Single 1 (261) | 95.8 | 98.8 | 97.28 | 91.88 | 93.9 | 98.8 | 96.29 | 90.22 | 96.9 | 99.6 | 98.23 | 95.14 |
| Two 1 (60) | 93.3 | 87.5 | 90.31 | 86.7 | 85.2 | 85.94 | 98.3 | 88.1 | 92.92 | |||
| Three 1 (31) | 87.1 | 84.4 | 85.73 | 90.3 | 87.5 | 88.88 | 93.5 | 90.6 | 92.03 | |||
| M 2 (23) | 91.3 | 80.8 | 85.73 | 91.3 | 77.8 | 84.01 | 87 | 90.9 | 88.91 | |||
| T 2 (18) | - | - | - | 88.9 | 64 | 74.42 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sha, H.; Mei, F.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, J. Identification Method for Voltage Sags Based on K-means-Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Energies 2019, 12, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061137
Sha H, Mei F, Zhang C, Pan Y, Zheng J. Identification Method for Voltage Sags Based on K-means-Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Energies. 2019; 12(6):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061137
Chicago/Turabian StyleSha, Haoyuan, Fei Mei, Chenyu Zhang, Yi Pan, and Jianyong Zheng. 2019. "Identification Method for Voltage Sags Based on K-means-Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Support Vector Machine" Energies 12, no. 6: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061137
APA StyleSha, H., Mei, F., Zhang, C., Pan, Y., & Zheng, J. (2019). Identification Method for Voltage Sags Based on K-means-Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Energies, 12(6), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061137





