Direct Printing of a Multi-Layer Sensor on Pet Substrate for CO2 Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
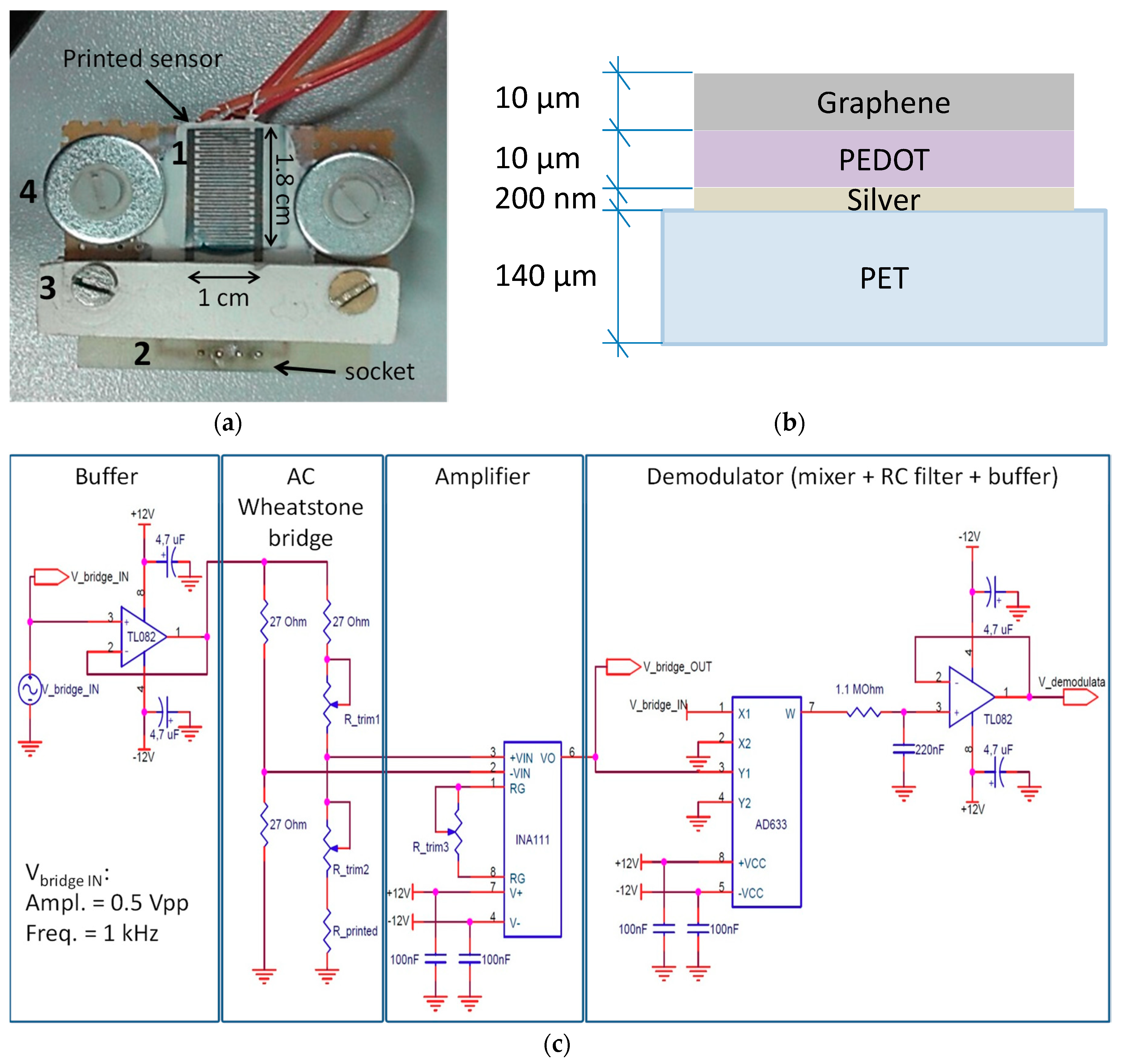
2. The Developed Sensor and the Experimental Set-Up
2.1. Description of the Device Structure and Material Properties
- to realize a uniform layer over the IDT electrodes guaranteeing continuity of the resistive contact between IDT fingers.
- to realize a layer with a resistance value higher than a pure layer of conductive material (such as the silver ink used to realize IJP IDT electrodes). This allows for making dominant the effect of the resistance variation of the graphene layer, super-imposed to the PEDOT layer, as a consequence of a variation of the concentration of CO2 molecules adsorbed into the sensing layer.
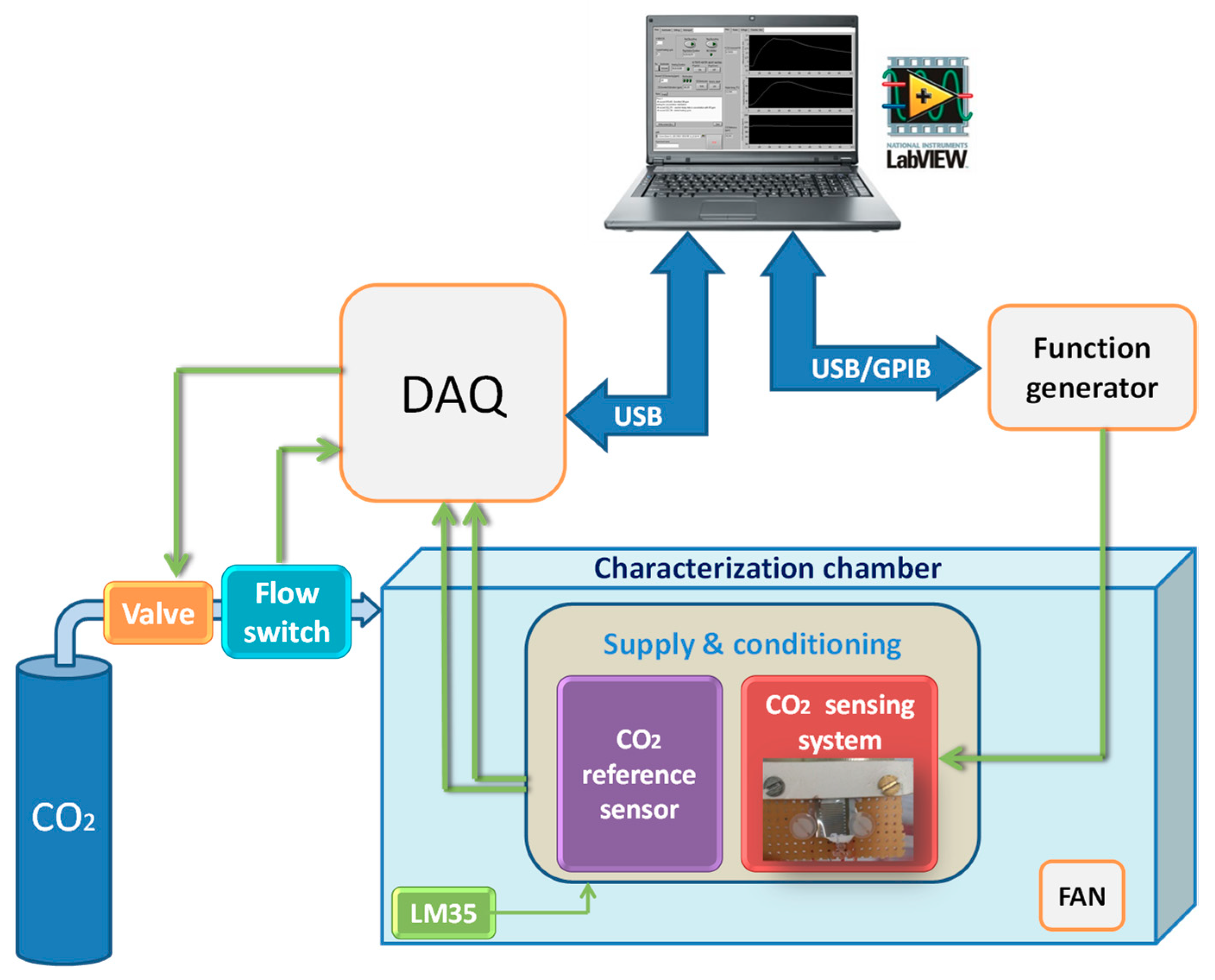
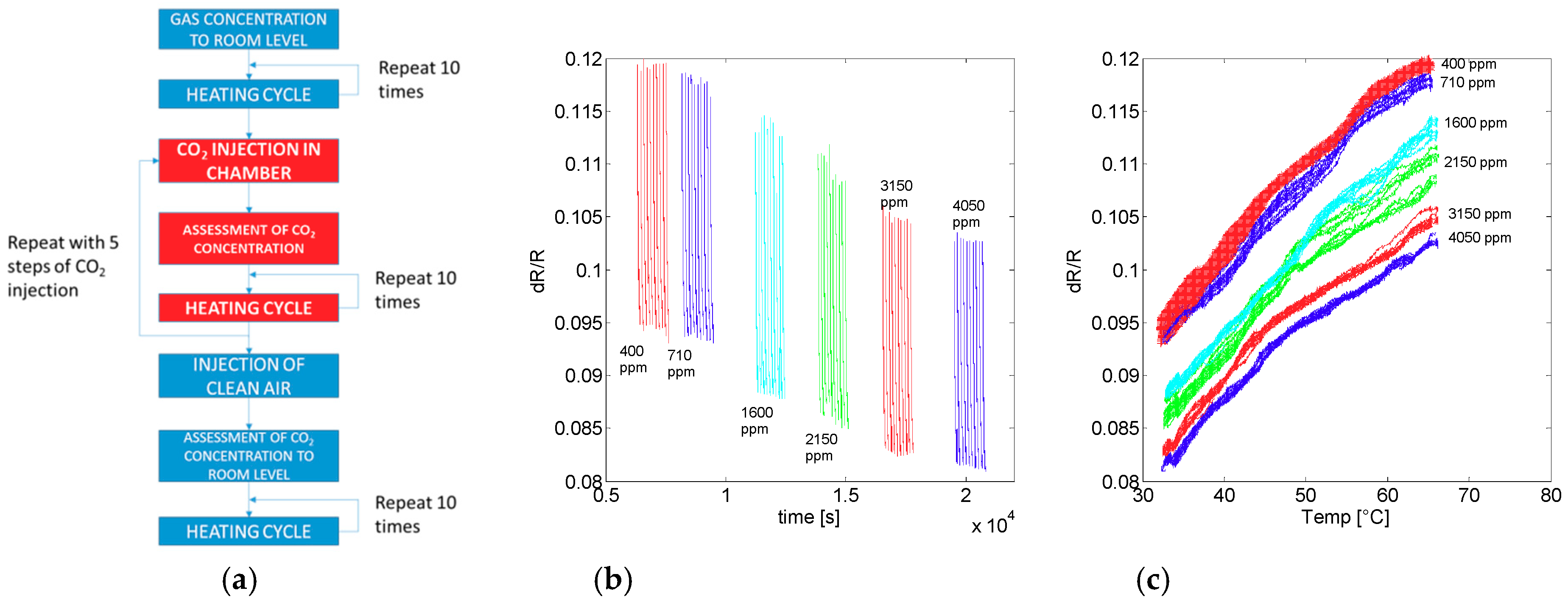
2.2. Experimental Set up and Procedure
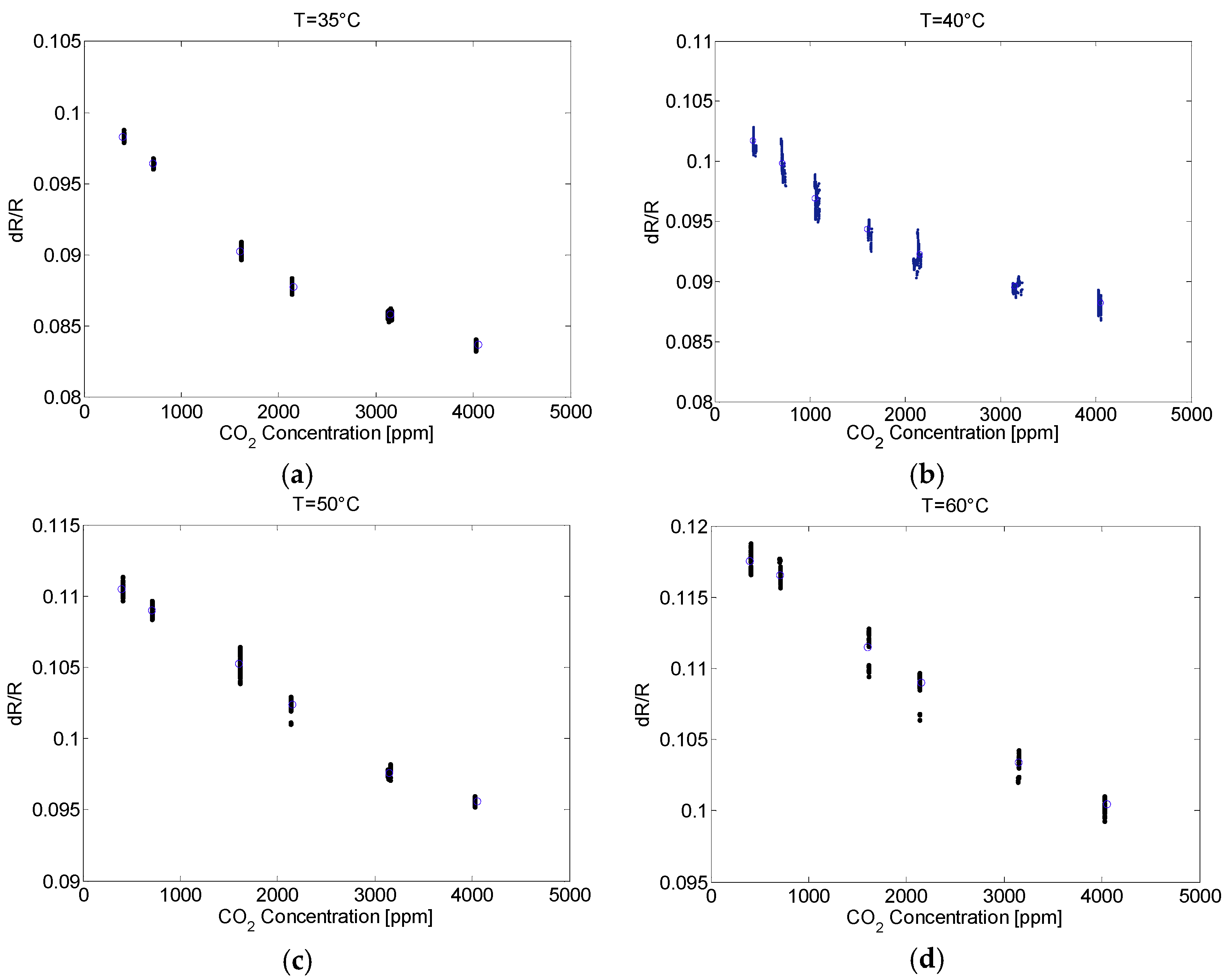
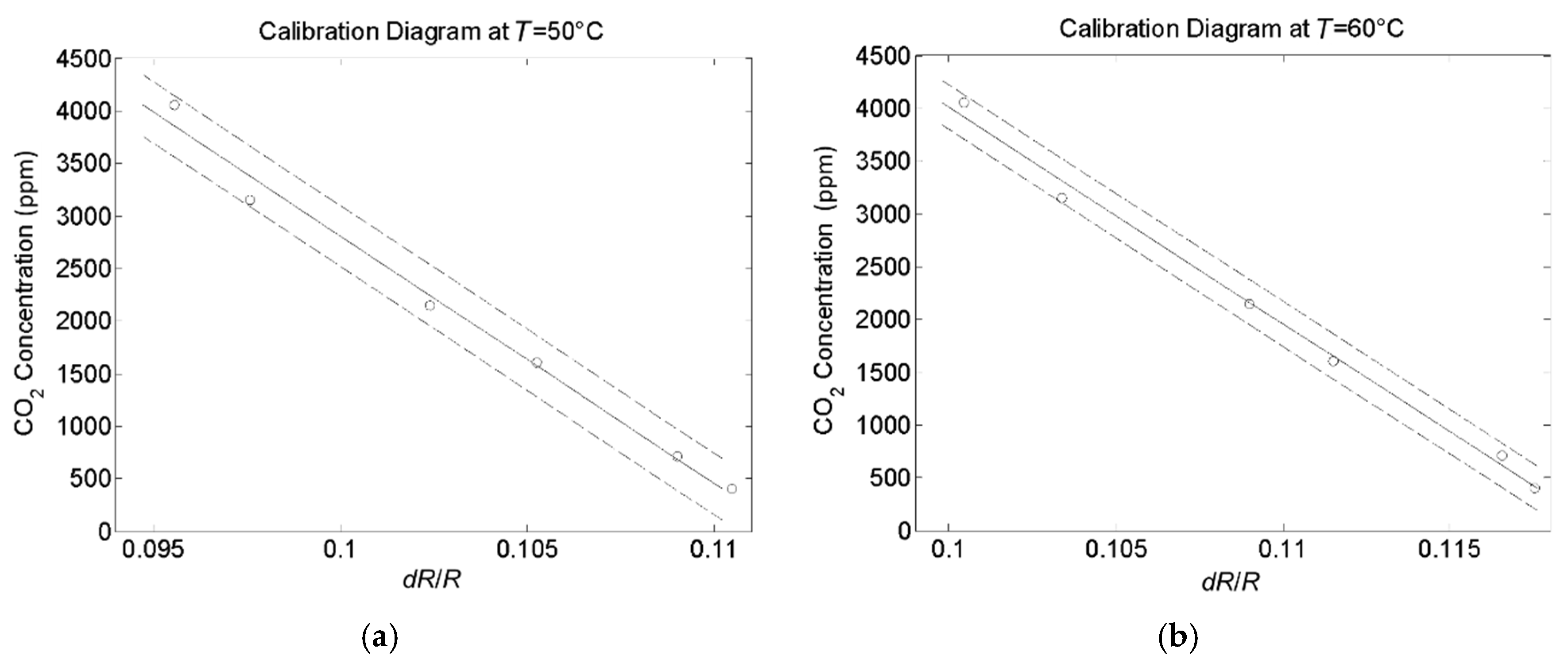
3. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yunusa, Z.; Hamidon, M.N.; Kaiser, A.; Awang, Z. Gas Sensors: A Review. Sens. Transducers 2014, 168, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pearton, S.J.; Ren, F. Gallium nitride-based gas, chemical and biomedical sensors. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2012, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutzler, C.; Unger, A.; Marhold, H.; Fricke, T.; Conrad, T.; Schütze, A. Influence of MOS gas-sensor production tolerances on pattern recognition techniques in electronic noses. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponara, S.; Petri, E.; Fanucci, L.; Terreni, P. Sensor modeling, low-complexity fusion algorithms, and mixed-signal IC prototyping for gas measures in low-emission vehicles. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, F.; Heywang, G. Technical applications for conductive polymers. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendaal, L.B.; Jonas, F.; Freitag, D.; Pielartzik, H.; Reynolds, J.R. Poly (34-ethylenedioxythiophene) and Its Derivatives: Past Present and Future. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Hwang, D.H.; Woo, S.L. Thermoelectric properties of nanocomposite thin films prepared with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) poly(styrenesulfonate) and grapheme. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 3530–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.W.; Vijayaragahvan, A.; Novoselov, K. Graphene Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.D.; Allen, M.J.; Tung, V.C.; Yang, Y.; Kaner, R.B.; Weiller, B.H. Practical chemical sensors from chemically derived graphene. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, V.; Surwade, S.P.; Ammu, S.; Agnihotra, S.R.; Jain, S.; Roberts, K.E.; Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S.; Manohar, S.K. All-organic vapor sensor using inkjet-printed reduced graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, S.; Satrapinski, A.; Lebedeva, N.; Iisakka, I. Sensitivity optimization of epitaxial graphene-based gas sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Jun, D.H.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S.S.; Cheng, M.M.-C. Carbon dioxide gas sensor using a graphene sheet. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, S.M.; Ritikos, R.; Whitcher, T.J.; Razib, N.M.; Bien, D.C.S.; Chanlek, N.; Nakajima, H.; Saisopa, T.; Songsiriritthigul, P.; Huang, N.M.; et al. A practical carbon dioxide gas sensor using room-temperature hydrogen plasma reduced graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntysalo, M.; Pekkanen, V.; Kaija, K.; Niittynen, J.; Koskinen, S.; Halonen, E.; Mansikkamäki, P.; Hämeenoja, O. Capability of Inkjet Technology in Electronics Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Electronic Components and Technology Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dimatix Material Printer DMP-2850. Available online: www.fujifilmusa.com/shared/bin/dimatix_materials_printer_dmp-2850.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- Functional Polymer/Printed Electronics. Available online: www.microdrop.de/functional-polymer-printed-electronics.html (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- Al-Chami, H.; Cretu, E. Inkjet printing of microsensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Mixed-Signals, Sensors, and Systems Test Workshop, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 10–12 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Cook, C.; Derby, B. Fabrication of a Glucose Biosensor by Piezoelectric Inkjet Printing. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, Athens, Greece, 18–23 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, B.; Chen, Q.; Amin, Y.; Hllstedt, J.; Liu, R.; Tenhunen, H.; Zheng, L. Process-dependence of inkjet printed folded dipole antenna for 2.45 GHz RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Rodriguez, S.; Shao, B. Design and implementation of a fully reconfigurable chipless RFID tag using Inkjet printing technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, Y.; Prokkola, S.; Botao, S.; Hallstedt, J.; Tenhunen, H.; Zheng, L. Inkjet printed paper based quadrate bowtie antennas for UHF RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, Phoenix Park, Korea, 15–18 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, H.; Manuilskiy, A.; Unander, T.; Lidenmark, C.; Forsberg, S.; Nilsson, H.-E. Inkjet printed silver nanoparticle humidity sensorwith memory effect on paper. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12–16, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S. Inkjet-Printed Sensors: A Useful Approach for Low Cost, Rapid Prototyping. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2011, 14, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S. All-Inkjet Printed Strain Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4874–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Baù, M.; Bulsara, A.R.; Ferrari, V.; Ferrari, M.; L’Episcopo, G. A Nonlinear Energy Harvester by Direct Printing Technology. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Bulsara, A.R.; Marletta, V.; Ferrari, V.; Ferrari, M. A Low-Cost Snap-Through Buckling Inkjet Printed Device for Vibrational Energy Harvesting. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3209–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Lombardo, C.O.; Marletta, V.; Pistorio, A. A Low-Cost Accelerometer Developed by Inkjet Printing Technology. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Bulsara, A.R.; Emery, T.; Marletta, V.; Pistorio, A. Low-Cost Inkjet Printing Technology for the Rapid Prototyping of Transducers. Sensors 2017, 17, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichan, C.; Saikrajang, T.; Lomas, T.; Jomphoak, A.; Maturos, T.; Phokaratkul, D.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Tuantranont, A. Inkjet printing PEDOT:PSS using desktop inkjet printer. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Pattaya, Thailand, 6–9 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, T.; Varahramyan, K. All-polymer capacitor fabricated with inkjet printing technique. Solid State Electron. 2003, 47, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.B.; Wilhelm, E.J.; Jacobson, J.M. Ink-jet Printed Nanoparticle Microelectromechanical Systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghuley, S.A.; Yenorkar, S.M.; Yawale, S.S.; Yawale, S.P. SnO2/PPy Screen-Printed Multilayer CO2 Gas Sensor. Sens. Transducers J. 2007, 79, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; di Pasquale, G.; Pollicino, A.; D’Agata, S.; Gugliuzzo, C.; Lombardo, C.; Re, G. An Inkjet Printed CO2 Gas Sensor. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Elgammal, K.; Fan, X.; Lemme, M.C.; Delin, A.; Råsander, M.; Bergqvist, L.; Schröder, S.; Fischer, A.C.; Niklaus, F.; et al. Graphene-based CO2 sensing and its cross-sensitivity with humidity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22329–22339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T (°C) | Responsivity (Ω/Ω/ppm) | Resolution (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 4.01 × 10–6 | 400 |
| 60 | 4.75 × 10–6 | 420 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andò, B.; Baglio, S.; Di Pasquale, G.; Pollicino, A.; Graziani, S.; Gugliuzzo, C.; Lombardo, C.; Marletta, V. Direct Printing of a Multi-Layer Sensor on Pet Substrate for CO2 Detection. Energies 2019, 12, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030557
Andò B, Baglio S, Di Pasquale G, Pollicino A, Graziani S, Gugliuzzo C, Lombardo C, Marletta V. Direct Printing of a Multi-Layer Sensor on Pet Substrate for CO2 Detection. Energies. 2019; 12(3):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030557
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndò, Bruno, Salvatore Baglio, Giovanna Di Pasquale, Antonio Pollicino, Salvatore Graziani, Chiara Gugliuzzo, Cristian Lombardo, and Vicenzo Marletta. 2019. "Direct Printing of a Multi-Layer Sensor on Pet Substrate for CO2 Detection" Energies 12, no. 3: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030557
APA StyleAndò, B., Baglio, S., Di Pasquale, G., Pollicino, A., Graziani, S., Gugliuzzo, C., Lombardo, C., & Marletta, V. (2019). Direct Printing of a Multi-Layer Sensor on Pet Substrate for CO2 Detection. Energies, 12(3), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030557








