Innovative Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Fabrication for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
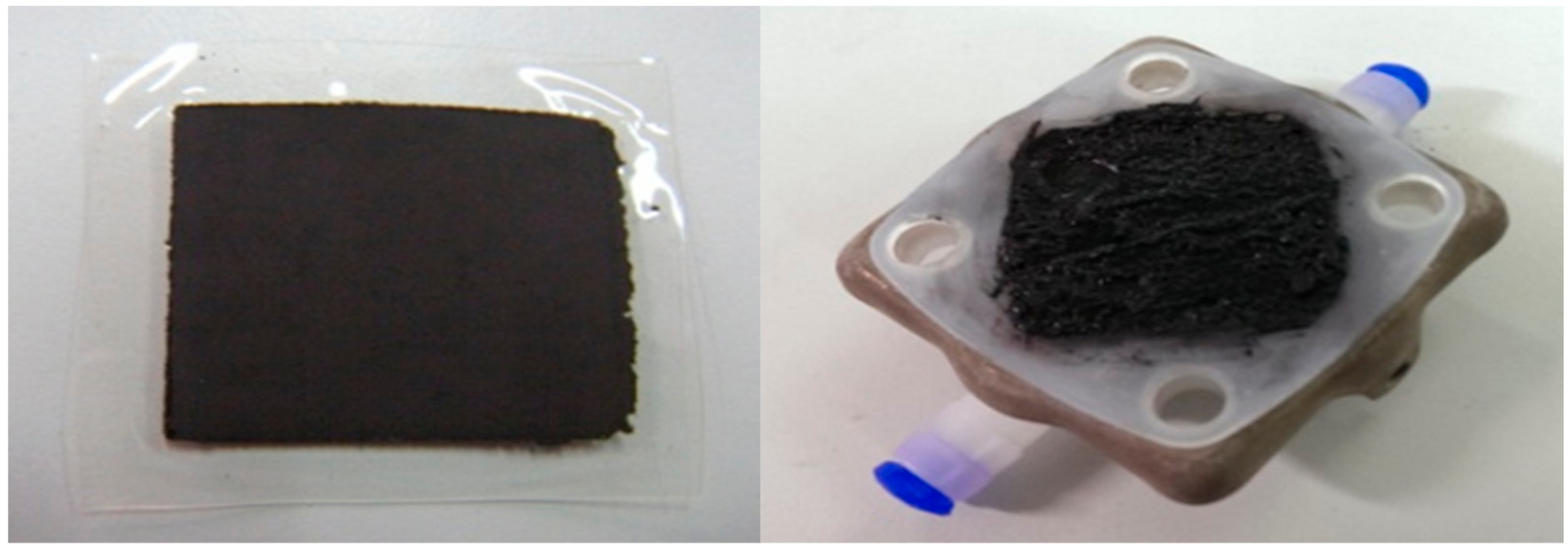
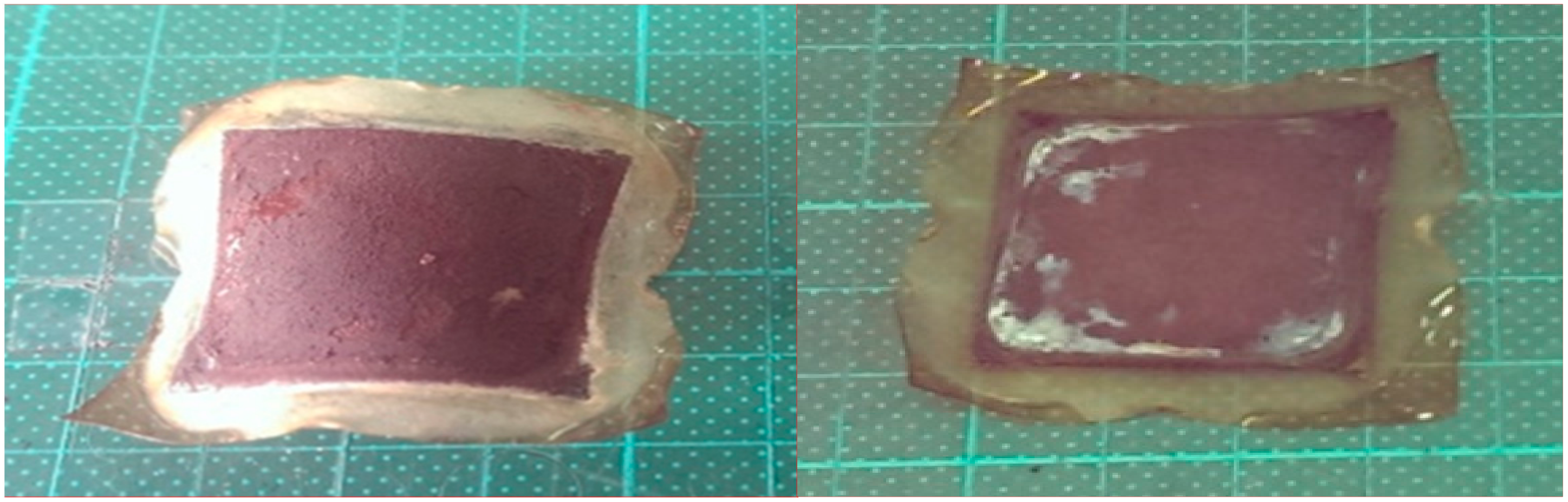
2.1. Anode Preparation
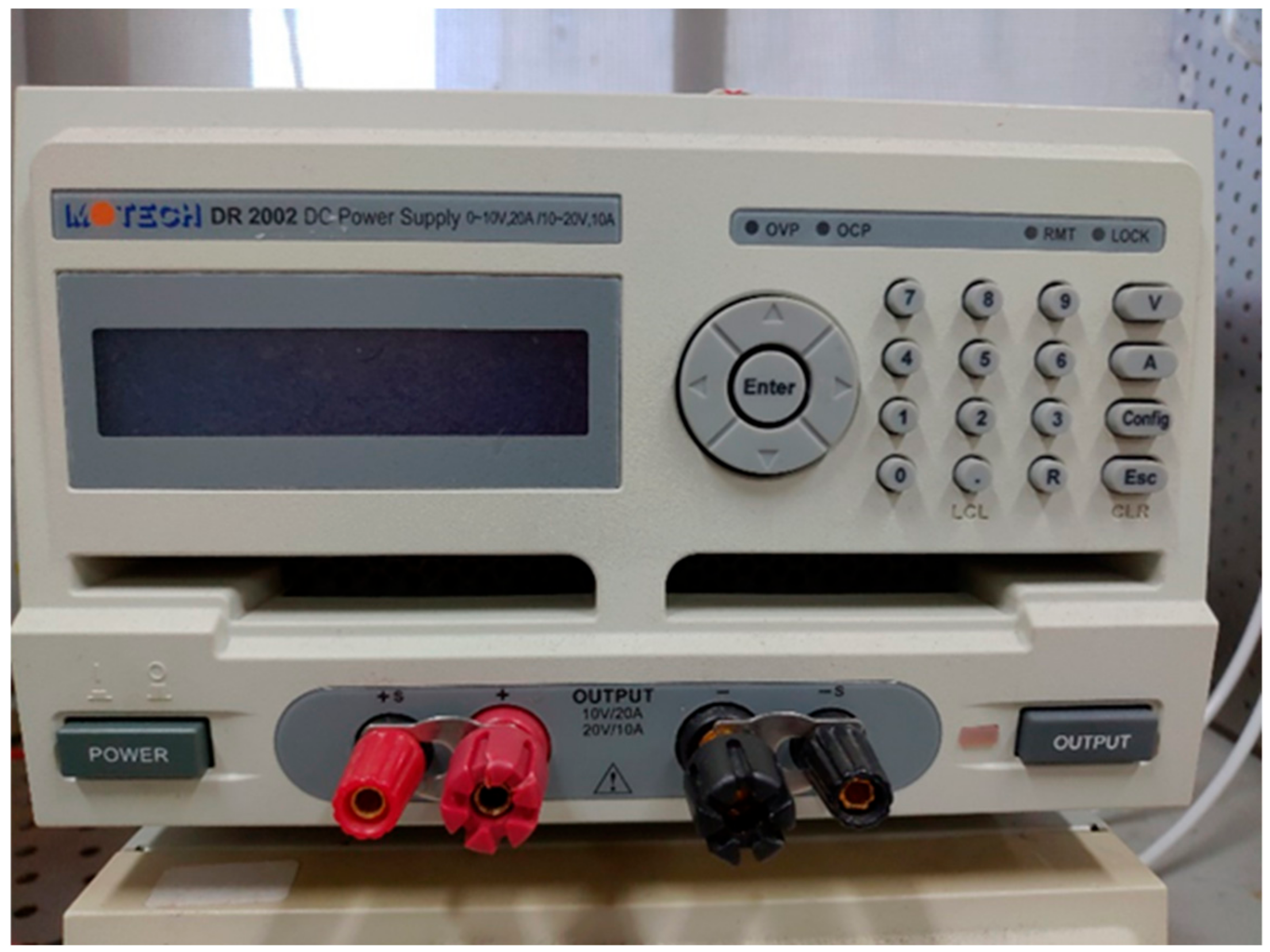
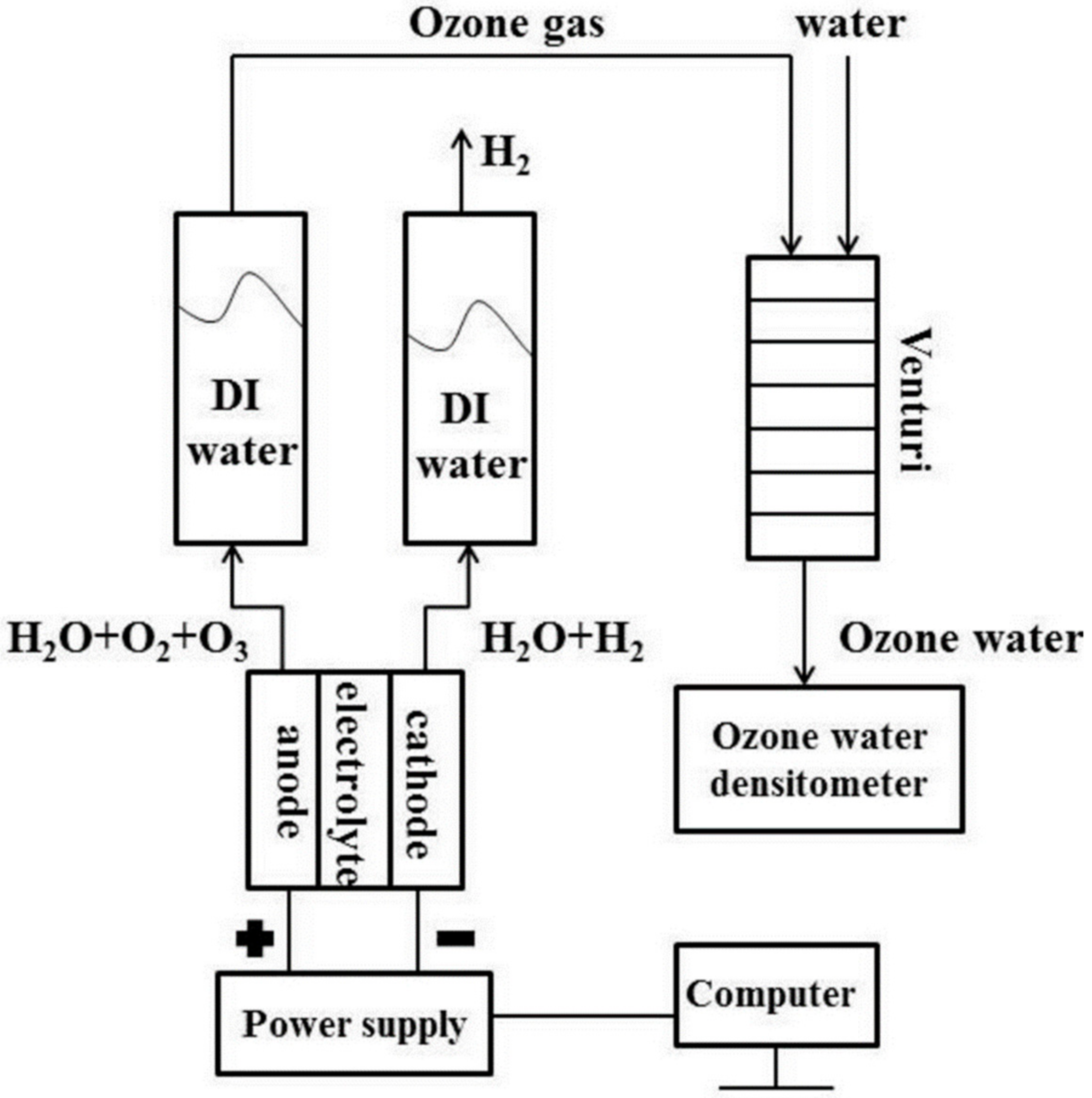
2.2. Electrolysis Test
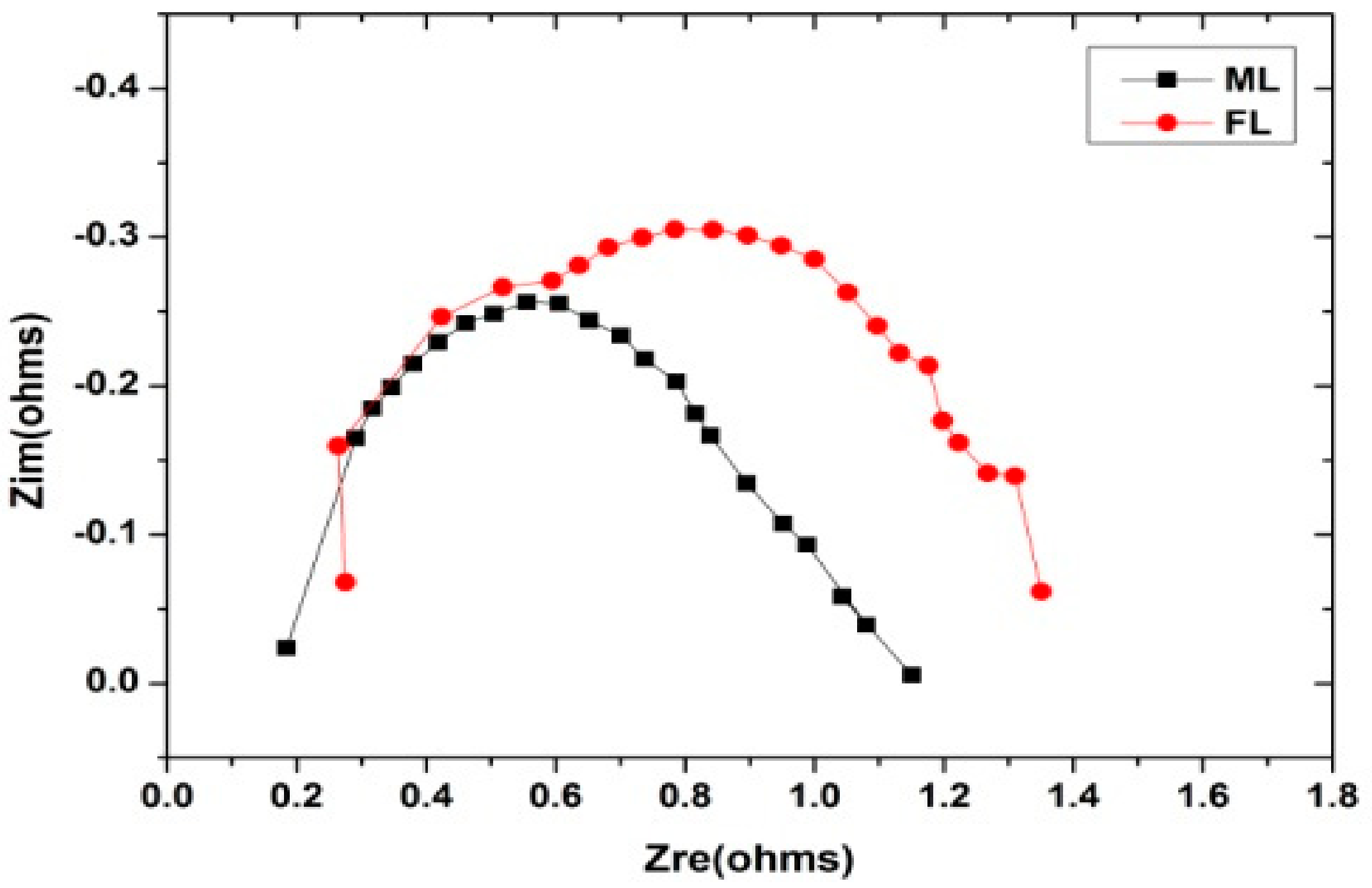
2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Analysis
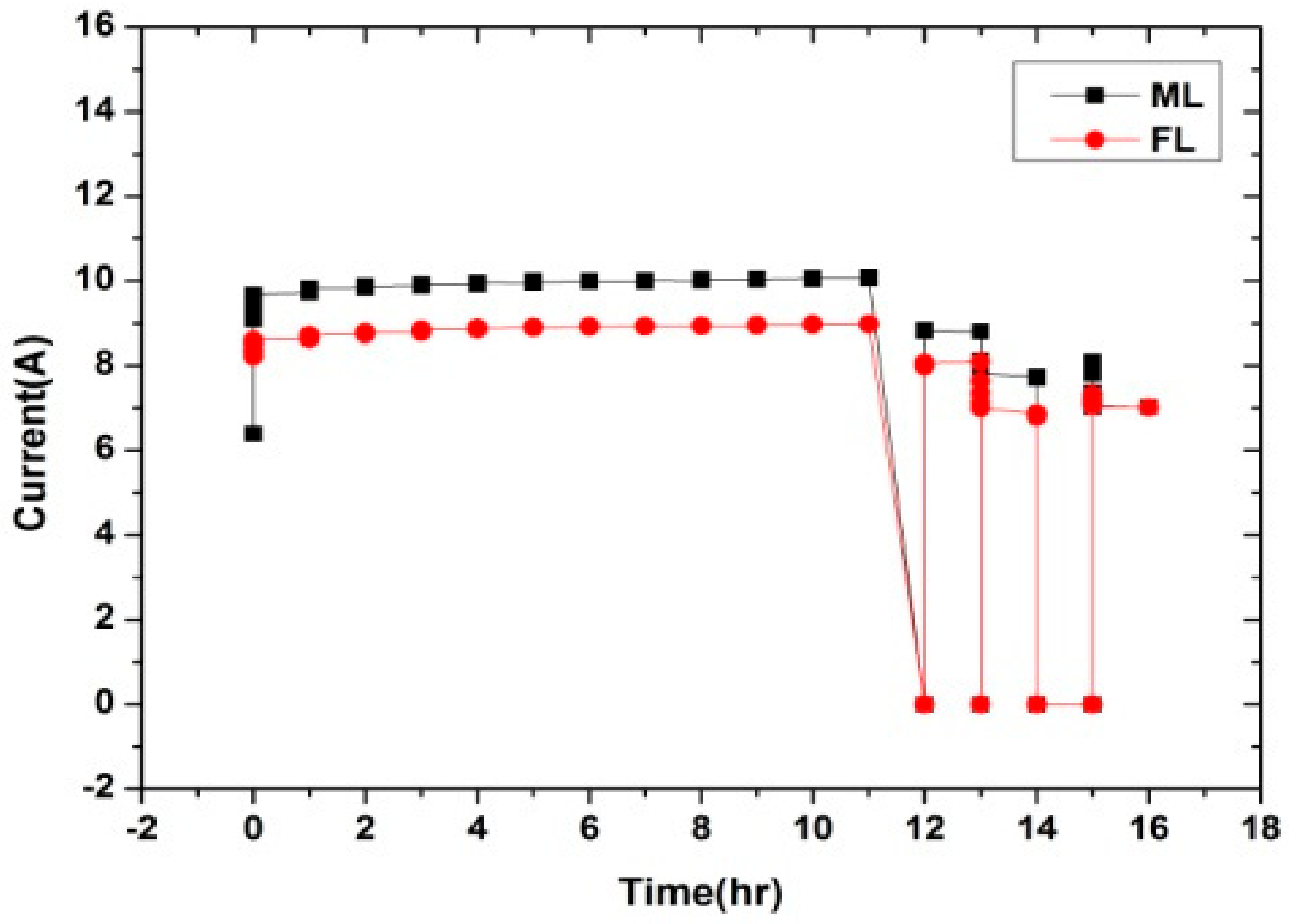
2.4. Accelerated Aging
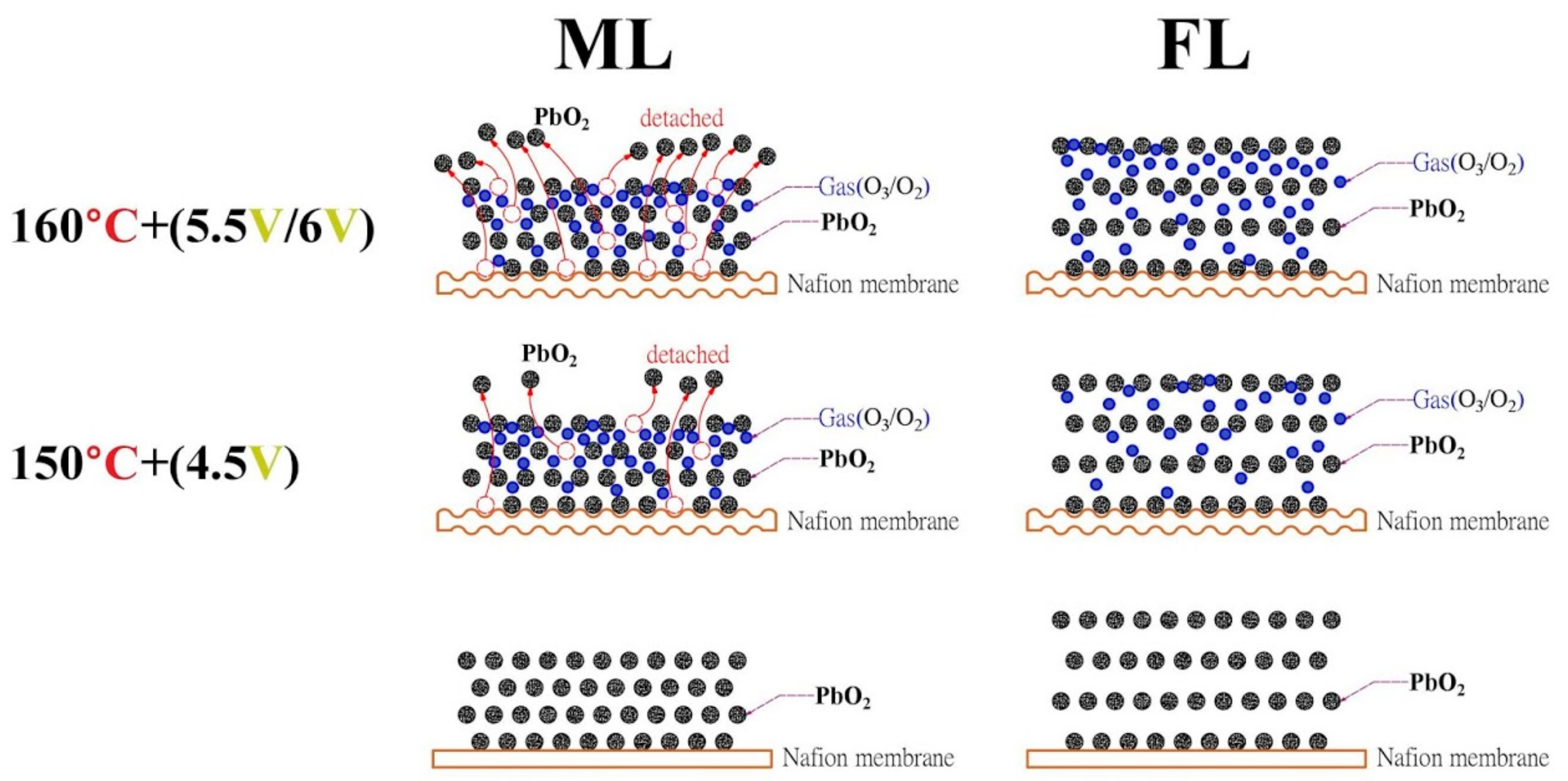
2.4.1. High-Temperature Effect
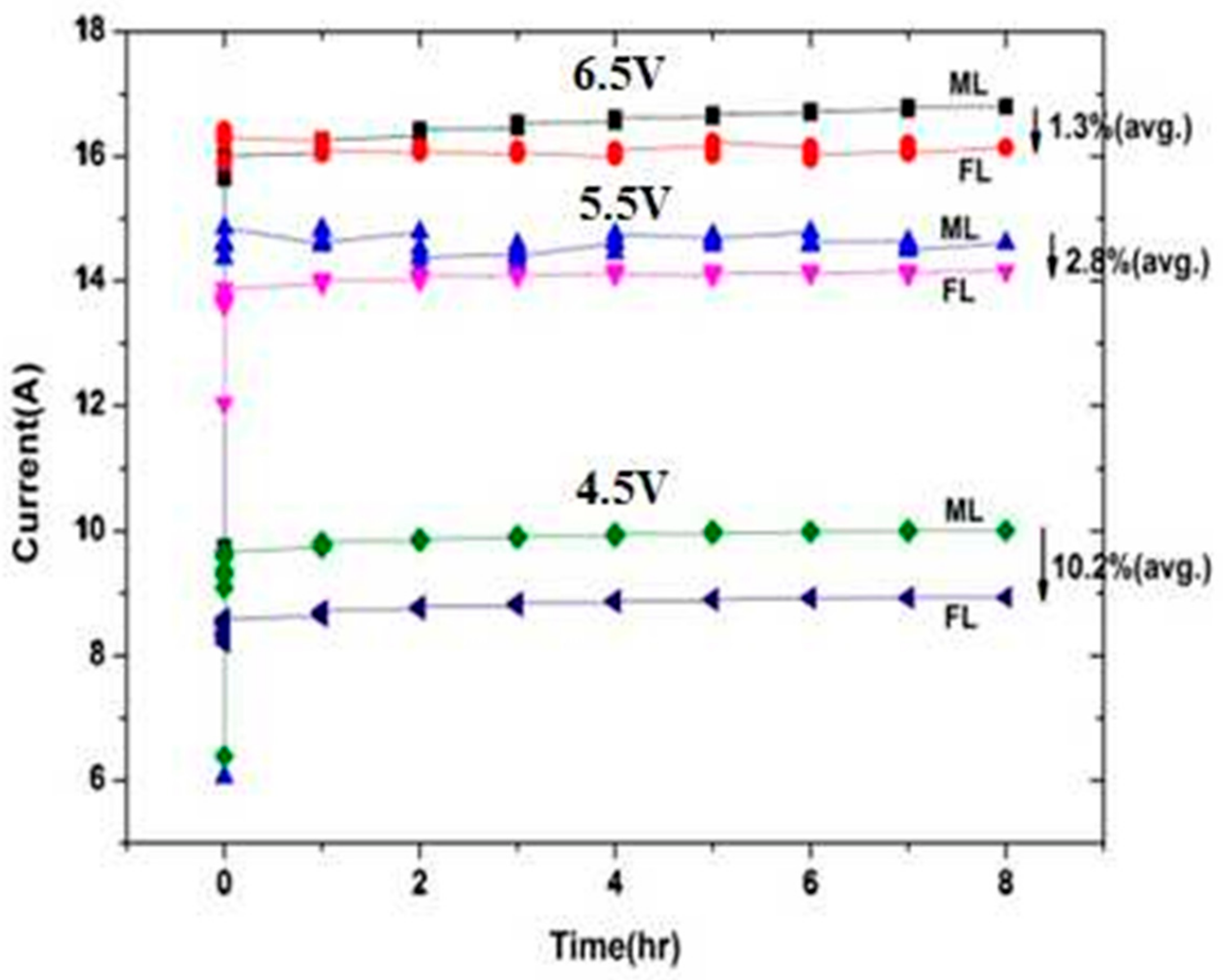
2.4.2. High-Voltage Effect
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buttler, A.; Spliethoff, H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallisch, A.; Schellhase, L.; Fresko, J.; Zechmeister, M.; Zedda, M.; Ohlmann, J.; Zielke, L.; Paust, N.; Smolinka, T. Investigation on pem water electrolysis cell design and components for a hycon solar hydrogen generator. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13544–13553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, M.; Coleman, D.; Scheppat, B.; Stiller, C.; Scheffer, K.; Aichinger, J. Energiepark mainz: Technical and economic analysis of the worldwide largest power-to-gas plant with pem electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13311–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, F. Pem electrolysis for production of hydrogen from renewable energy sources. Sol. Energy 2005, 78, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on pem water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, F.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X. Synthesis and application of lead dioxide nanowires for a pem ozone generator. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 192, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussayajarn, N.; Ming, H.; Hoong, K.K.; Ming Stephen, W.Y.; Hwa, C.S. Planar air breathing pemfc with self-humidifying mea and open cathode geometry design for portable applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7761–7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Sui, S.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Q.; Cao, G.; Hong, X.; Tu, H. A 10 kw class pem fuel cell stack based on the catalyst-coated membrane (ccm) method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.H.; Park, K.T.; Park, S.H.; Jo, D.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.H.; Jyoung, J.-Y. Development of a novel hydrophobic/hydrophilic double micro porous layer for use in a cathode gas diffusion layer in pemfc. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8422–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Ko, T.-H.; Shen, J.-W.; Chang, S.-I.; Chang, S.-I.; Liao, Y.-K. Effect of hydrophobic gas diffusion layers on the performance of the polymer exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.; Manthiram, A. Effect of non-active area on the performance of subgasketed meas in pemfc. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 7400–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cho, E.; Lim, T.-H.; Yoon, S.P.; Hwang, I.C.; Jang, J.H. The effects of nafion® ionomer content in pemfc meas prepared by a catalyst-coated membrane (ccm) spraying method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cho, E.; Lim, T.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Yoon, S.P.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, T.W.; Jang, J.H. The effects of relative humidity on the performances of pemfc meas with various nafion® ionomer contents. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 13104–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-F.; Cheng, C.-H.; Su, A.; Yu, T.-L.; Hourng, L.-W. Numerical analysis of the manipulated high performance catalyst layer design for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2014, 38, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Scott, K. The effects of ionomer content on pem water electrolyser membrane electrode assembly performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12029–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Shao, Z.; Baker, R.T.; Yi, B. Electrochemical investigation of electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in pem water electrolyzers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4955–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Linkov, V.; Bladergroen, B.J. Membrane electrode assemblies with low noble metal loadings for hydrogen production from solid polymer electrolyte water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 9601–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Miao, R.; Zhao, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. A novel catalyst layer with hydrophilic–hydrophobic meshwork and pore structure for solid polymer electrolyte water electrolysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 437–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozain, C.; Mayousse, E.; Guillet, N.; Millet, P. Influence of iridium oxide loadings on the performance of pem water electrolysis cells: Part I—Pure iro2-based anodes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-W.; Jung, G.-B.; Su, Y.-J.; Yeh, C.-C.; Kan, M.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lai, C.-J. Proton exchange membrane water electrolysis system-membrane electrode assembly with additive. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15721–15726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdzik, A.; Stähler, M.; Friedrich, I.; Carmo, M.; Stolten, D. Homogeneity analysis of square meter-sized electrodes for pem electrolysis and pem fuel cells. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, S.A.; Neyerlin, K.C.; Yang-Neyerlin, A.C.; More, K.L.; Ulsh, M. Gravure coating for roll-to-roll manufacturing of proton-exchange-membrane fuel cell catalyst layers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, K.; Ohba, T.; Kusunoki, H.; Takezawa, S.; Sunakawa, D.; Araki, T. Improving characteristics of ozone water production with multilayer electrodes and operating conditions in a polymer electrolyte water electrolysis cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, P.; Ranjbari, A.; De Guglielmo, F.; Grigoriev, S.A.; Auprêtre, F. Cell failure mechanisms in pem water electrolyzers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17478–17487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, G.-B.; Chan, S.-H.; Lai, C.-J.; Yeh, C.-C.; Yu, J.-W. Innovative Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Fabrication for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Energies 2019, 12, 4218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214218
Jung G-B, Chan S-H, Lai C-J, Yeh C-C, Yu J-W. Innovative Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Fabrication for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Energies. 2019; 12(21):4218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214218
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Guo-Bin, Shih-Hung Chan, Chun-Ju Lai, Chia-Chen Yeh, and Jyun-Wei Yu. 2019. "Innovative Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Fabrication for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis" Energies 12, no. 21: 4218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214218
APA StyleJung, G.-B., Chan, S.-H., Lai, C.-J., Yeh, C.-C., & Yu, J.-W. (2019). Innovative Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Fabrication for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Energies, 12(21), 4218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214218



