Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Attained by Bimetallic Heterogeneous PdAg Catalytic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
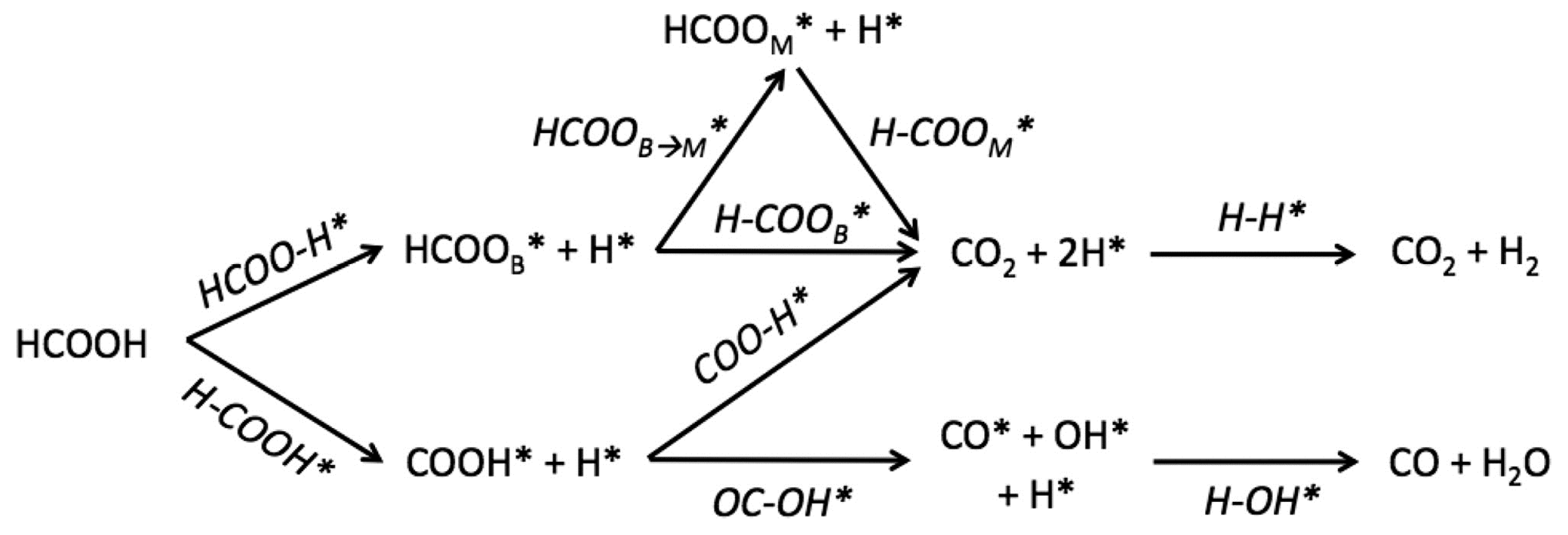
2. Decomposition of Formic Acid
3. Decomposition of Formic Acid over PdAg Bimetallic Catalysts
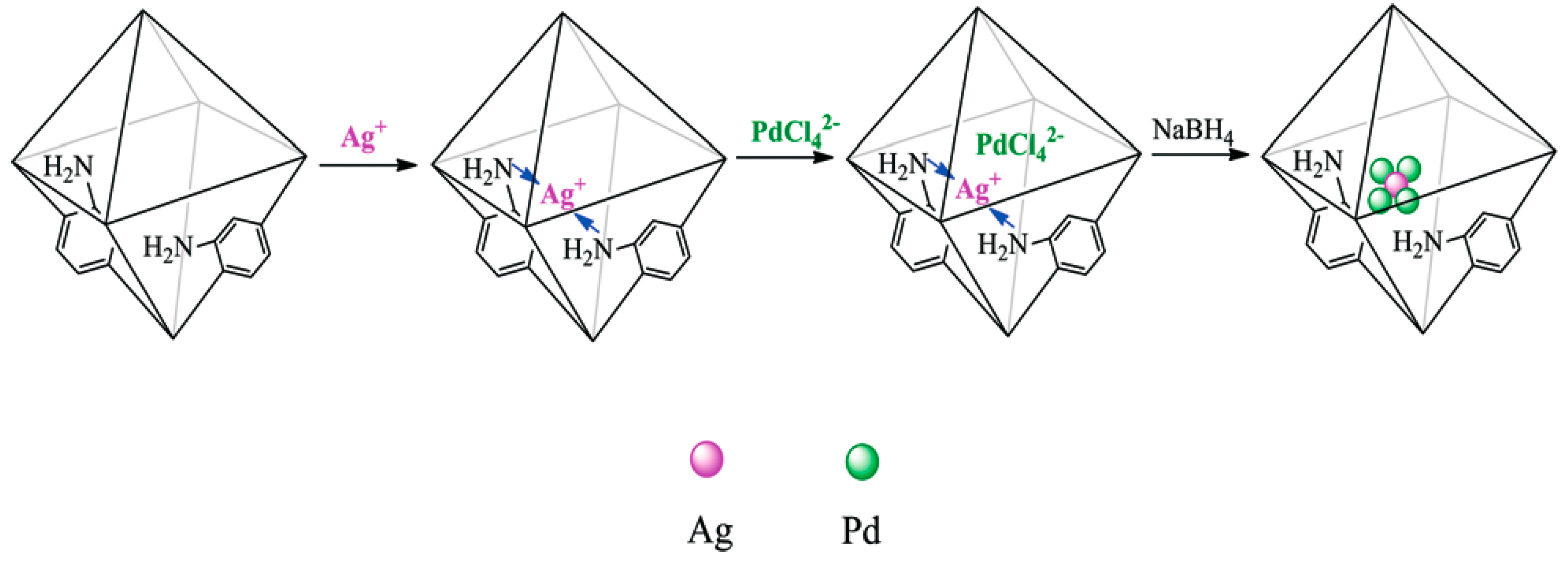
3.1. Carbon-supported PdAg Catalysts
3.2. N-doped Carbon-based PdAg Catalysts
3.3. Metal Oxide-containing Carbon-based PdAg Catalysts
3.4. PdAg Catalysts Supported on Non-carbon Materials
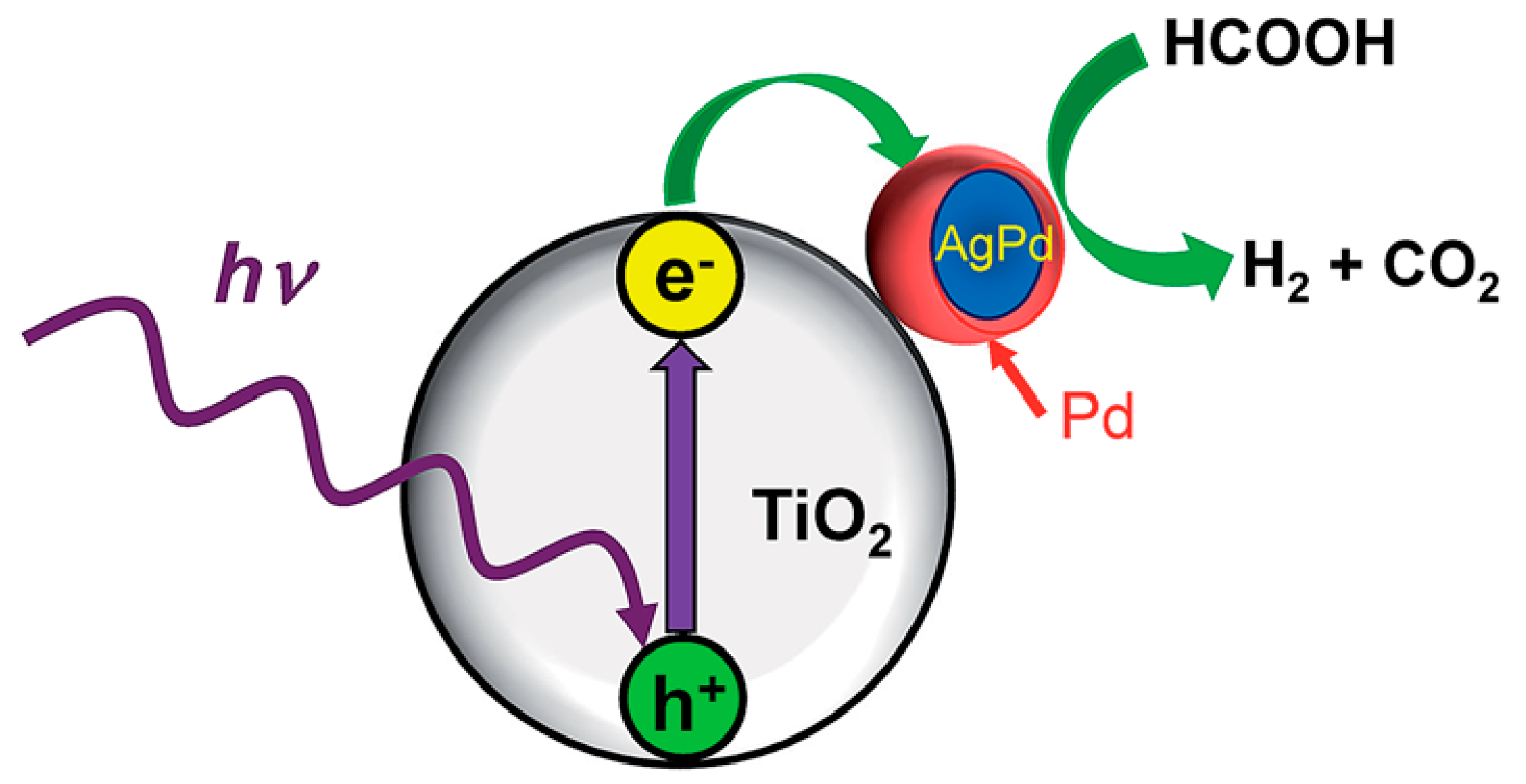
3.5. Photocatalytic Decomposition of Formic Acid
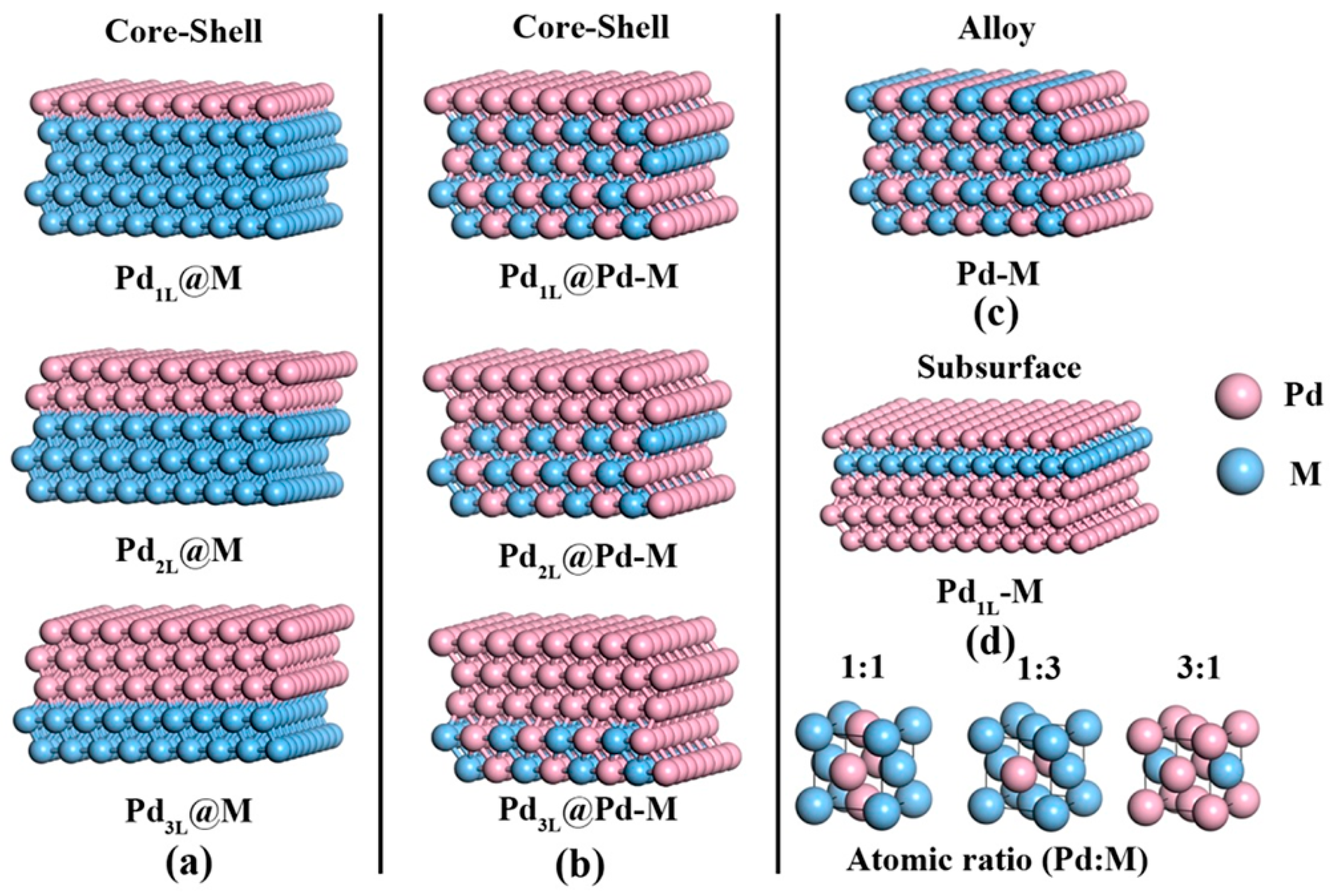
3.6. Theoretical Investigations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/understanding-global-warming-potentials (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Arrhenius, S. XXXI. On the influence of carbonic acid in the air upon the temperature of the ground. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1896, 41, 237–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, M.; Tang, X. Depletion of fossil fuels and anthropogenic climate change-A review. Energy Policy 2013, 52, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, N.; Kalair, A.; Khan, N. Review of fossil fuels and future energy technologies. Futures 2015, 69, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Bansode, A.; Urakawa, A.; Bavykina, A.V.; Wezendonk, T.A.; Makkee, M.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Challenges in the Greener Production of Formates/Formic Acid, Methanol, and DME by Heterogeneously Catalyzed CO2 Hydrogenation Processes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9804–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artz, J.; Muller, T.E.; Thenert, K.; Kleinekorte, J.; Meys, R.; Sternberg, A.; Bardow, A.; Leitner, W. Sustainable Conversion of Carbon Dioxide: An Integrated Review of Catalysis and Life Cycle Assessment. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 434–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ajmal, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L. Efficient nanomaterials for harvesting clean fuels from electrochemical and photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 510–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.M.; Hossain, S.; Nisfindy, O.B.; Azad, A.T.; Dawood, M.; Azad, A.K. Hydrogen production, storage, transportation and key challenges with applications: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 165, 602–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Marco-Lozar, J.P.; Cazorla-Amoros, D. Hydrogen Storage in Porous Materials: Status, Milestones, and Challenges. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Jo, Y.S.; Lee, W.J.; Shin, B.S.; Sohn, H.; Jeong, H.; Jang, S.C.; Kwak, S.K.; Kang, J.W.; Yoon, C.W. A High-Capacity, Reversible Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier: H2 —Release Properties and an Application to a Fuel Cell. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, M.; Drunert, S.; Kaltschmitt, M.; Bonhoff, K. Liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs)—Techno-economic analysis of LOHCs in a defined process chain. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modisha, P.M.; Ouma, C.N.M.; Garidzirai, R.; Wasserscheid, P.; Bessarabov, D. The Prospect of Hydrogen Storage Using Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2778–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuster, P.; Papp, C.; Wasserscheid, P. Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs): Toward a Hydrogen-free Hydrogen Economy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enthaler, S.; Von Langermann, J.; Schmidt, T. Carbon dioxide and formic acid—The couple for environmental-friendly hydrogen storage? Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Mori, K.; Futamura, Y.; Yamashita, H. PdAg Nanoparticles Supported on Functionalized Mesoporous Carbon: Promotional Effect of Surface Amine Groups in Reversible Hydrogen Delivery/Storage Mediated by Formic Acid/CO2. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Torres, D.; Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Nitrogen-doped carbon materials as a promising platform toward the efficient catalysis for hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 571, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinger, J.; Huang, K.-W. Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Energy Carrier. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, R.S. The decomposition of formic acid catalysed by soluble metal complexes. Chem. Commun. 1967, 18, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellay, C.; Dyson, P.J.; Laurenczy, G. A viable hydrogen-storage system based on selective formic acid decomposition with a ruthenium catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3966–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loges, B.; Boddien, A.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Controlled generation of hydrogen from formic acid amine adducts at room temperature and application in H2/O2 fuel cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3962–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.; Oro, L.A. Mechanistic Considerations on Homogeneously Catalyzed Formic Acid Dehydrogenation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasemann, M.; Laurenczy, G. Formic acid as a hydrogen source—Recent developments and future trends. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Q. Metal-Nanoparticle-Catalyzed Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, N.; Iguchi, M.; Yang, X.; Kanega, R.; Kawanami, H.; Xu, Q.; Himeda, Y. Development of Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Storage Technology Using Formic Acid. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordakis, K.; Tang, C.; Vogt, L.K.; Junge, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Beller, M.; Laurenczy, G. Homogeneous Catalysis for Sustainable Hydrogen Storage in Formic Acid and Alcohols. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 372–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedsree, K.; Li, T.; Jones, S.; Chan, C.W.A.; Yu, K.M.K.; Bagot, P.A.J.; Marquis, E.A.; Smith, G.D.W.; Tsang, S.C.E. Hydrogen production from formic acid decomposition at room temperature using a Ag-Pd core-shell nanocatalyst. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, N.; Laurenczy, G.; Beller, M.; Himeda, Y. Recent progress for reversible homogeneous catalytic hydrogen storage in formic acid and in methanol. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 373, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellmann, D.; Sponholz, P.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Formic acid as a hydrogen storage material-development of homogeneous catalysts for selective hydrogen release. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3954–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Kitta, M.; Tsumori, N.; Himeda, Y.; Autrey, T.; Xu, Q. Immobilization of highly active bimetallic PdAu nanoparticles onto nanocarbons for dehydrogenation of formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18835–18839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Tsumori, N.; Kitta, M.; Xu, Q. Phosphate-Mediated Immobilization of High-Performance AuPd Nanoparticles for Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid at Room Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tsumori, N.; Kitta, M.; Xu, Q. Fast Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid over Palladium Nanoparticles Immobilized in Nitrogen-Doped Hierarchically Porous Carbon. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 12041–12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Zhu, Q.L.; Yang, X.; Zhan, W.W.; Pachfule, P.; Tsumori, N.; Xu, Q. Metal–Organic Framework Templated Porous Carbon-Metal Oxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide as Superior Support of Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Efficient Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-J.; Wen, Y.-H.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Wu, X.-T. Surface-Amine-Implanting Approach for Catalyst Functionalization: Prominently Enhancing Catalytic Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 4808–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Tsumori, N.; Liu, Z.; Himeda, Y.; Autrey, T.; Xu, Q. Tandem Nitrogen Functionalization of Porous Carbon: Toward Immobilizing Highly Active Palladium Nanoclusters for Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Dojo, M.; Yamashita, H. Pd and Pd-Ag nanoparticles within a macroreticular basic resin: An efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from formic acid decomposition. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martis, M.; Mori, K.; Fujiwara, K.; Ahn, W.S.; Yamashita, H. Amine-functionalized MIL-125 with imbedded palladium nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid at ambient temperature. J. Phys. Chem.C 2013, 117, 22805–22810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Naka, K.; Masuda, S.; Miyawaki, K.; Yamashita, H. Palladium Copper Chromium Ternary Nanoparticles Constructed In situ within a Basic Resin: Enhanced Activity in the Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3456–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Enhanced formic acid dehydrogenation by the synergistic alloying effect of PdCo catalysts supported on graphitic carbon nitride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Martis, M.; Lozano-Castello, D.; Cazorla-Amoros, D.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Investigation of Pd nanoparticles supported on zeolites for hydrogen production from formic acid dehydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Wen, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamshita, H. Size Effect of Carbon-Supported Pd Nanoparticles in the Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 1370, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Tanaka, H.; Dojo, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Yamashita, H. Synergic Catalysis of PdCu Alloy Nanoparticles within a Macroreticular Basic Resin for Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 12085–12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Nozaki, A.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Investigation of Size Sensitivity in the Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid over Carbon-Supported Pd Nanoparticles. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Nozaki, A.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Screening of Carbon-Supported PdAg Nanoparticles in the Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7612–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Navlani-Garcia, M.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Cazorla-Amoros, D. Evolution of the PVP-Pd surface interaction in nanoparticles through the case study of formic acid decomposition. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12110–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Plasmonic Au@Pd nanoparticles supported on a basic metal-organic framework: Synergic boosting of H2production from formic acid. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wen, M.; Navlani-Garcia, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Palladium nanoparticles supported on titanium doped graphitic carbon nitride for formic acid dehydrogenation. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Jia, L.; Beloshapkin, S.; Ross, J.R.H. Improved hydrogen production from formic acid on a Pd/C catalyst doped by potassium. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4184–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Beloshapkin, S.; Plyusnin, P.E.; Shubin, Y.V.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I.; Korenev, S.V.; Ross, J.R.H. Vapour phase formic acid decomposition over PdAu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of composition of metallic particles. J. Catal. 2013, 299, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Sobolev, V.I.; Pirutko, L.V.; Starostina, A.V.; Asanov, I.P.; Modin, E.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Gupta, N.; Okotrub, A.V.; Bulusheva, L.G. Hydrogen production from formic acid over au catalysts supported on carbon: Comparison with Au catalysts supported on SiO2 and Al2O3. Catalysts 2019, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Bulushev, D.A.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Boronin, A.I.; Kibis, L.S.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Beloshapkin, S.; Seryak, I.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Ross, J.R.H. Pt nanoclusters stabilized by N-doped carbon nanofibers for hydrogen production from formic acid. J. Catal. 2013, 307, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharska, M.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Kibis, L.S.; Boronin, A.I.; Senkovskiy, B.V.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Taran, O.P.; Ayusheev, A.B.; Parmon, V.N.; Leahy, J.J.; et al. Ruthenium Clusters on Carbon Nanofibers for Formic Acid Decomposition: Effect of Doping the Support with Nitrogen. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2910–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharska, M.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Kriventsov, V.V.; Beloshapkin, S.; Estrada, M.; Simakov, A.; Bulushev, D.A. Support effect for nanosized Au catalysts in hydrogen production from formic acid decomposition. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 6853–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Zacharska, M.; Shlyakhova, E.V.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Guo, Y.; Beloshapkin, S.; Okotrub, A.V.; Bulusheva, L.G. Single Isolated Pd2+ Cations Supported on N-Doped Carbon as Active Sites for Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Decomposition. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Zacharska, M.; Lisitsyn, A.S.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Hage, F.S.; Ramasse, Q.M.; Bangert, U.; Bulusheva, L.G. Single Atoms of Pt-Group Metals Stabilized by N-Doped Carbon Nanofibers for Efficient Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharska, M.; Bulusheva, L.G.; Lisitsyn, A.S.; Beloshapkin, S.; Guo, Y.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Shlyakhova, E.V.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Leahy, J.J.; Okotrub, A.V.; et al. Factors Influencing the Performance of Pd/C Catalysts in the Green Production of Hydrogen from Formic Acid. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulushev, D.A.; Zacharska, M.; Beloshapkin, S.; Guo, Y.; Yuranov, I. Catalytic properties of PdZn/ZnO in formic acid decomposition for hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 561, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podyacheva, O.Y.; Bulushev, D.A.; Suboch, A.N.; Svintsitskiy, D.A.; Lisitsyn, A.S.; Modin, E.; Chuvilin, A.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Sobolev, V.I.; Parmon, V.N. Highly Stable Single-Atom Catalyst with Ionic Pd Active Sites Supported on N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes for Formic Acid Decomposition. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 3724–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Recent strategies targeting efficient hydrogen production from chemical hydrogen storage materials over carbon-supported catalysts. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Mori, K.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. New Approaches Toward the Hydrogen Production From Formic Acid Dehydrogenation Over Pd-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Jang, J.H.; Han, J.; Yoon, S.P.; Nam, S.W.; Lim, T.H.; Ham, H.C. Impact of d-Band Occupancy and Lattice Contraction on Selective Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid in the Bimetallic Pd3M (M = Early Transition 3d Metals) Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-S.; Song, J.; Song, M.; Goo, B.S.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, S.W. Core–Shell Engineering of Pd–Ag Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Decomposition. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, A.; Yurderi, M.; Karatas, Y.; Say, Z.; Kivrak, H.; Kaya, M.; Gulcan, M.; Ozensoy, E.; Zahmakiran, M. MnOx-Promoted PdAg Alloy Nanoparticles for the Additive-Free Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid at Room Temperature. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6099–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. An efficient room temperature core-shell AgPd@MOF catalyst for hydrogen production from formic acid. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8321–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Long, T.; Shuai, Q.; Li, Q. Reducing agent-structure-activity relationship of PdAg/C catalysts in formic acid decomposition for hydrogen generation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3798–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Yan, J.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, H.L.; Jiang, Q. Ag0.1-Pd0.9/rGO: An efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from formic acid/sodium formate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12188–12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Mu, X.; Fan, J.; Ma, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, N. Interfacial effects in PdAg bimetallic nanosheets for selective dehydrogenation of formic acid. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiu, H. An effective low Pd-loading catalyst for hydrogen generation from formic acid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18375–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fan, X.; Xiao, X.; Qin, T.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Ge, H.; Chen, L. Novel AgPd hollow spheres anchored on graphene as an efficient catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 4, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabid, M.R.; Bide, Y.; Etemadi, B. Ag@Pd nanoparticles immobilized on a nitrogen-doped graphene carbon nanotube aerogel as a superb catalyst for the dehydrogenation of formic acid. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10773–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hua, X.; Su, J.; Luo, W.; Chen, S.; Cheng, G. Highly efficient hydrogen generation from formic acid-sodium formate over monodisperse AgPd nanoparticles at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Shang, N.; Wang, C. Hydrogen generation at ambient conditions: AgPd bimetal supported on metal-organic framework derived porous carbon as an efficient synergistic catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2016, 78, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Yao, Q.; Qing, S.; Lu, Z.-H. A PdAg-CeO2 nanocomposite anchored on mesoporous carbon: A highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from formic acid at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 21438–21446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Metin, O.; Su, D.; Sun, S. Monodisperse AgPd alloy nanoparticles and their superior catalysis for the dehydrogenation of formic acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3681–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Li, X.; Wan, C.; Xu, L.; An, Y.; Ye, M.; Lei, Z. Highly efficient hydrogen release from formic acid using a graphitic carbon nitride-supported AgPd nanoparticle catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jang, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Sharma, S.; Basavaraju, K.C.; Kim, M.-G.; Kim, K.-R.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, D.-P. One-Pot Defunctionalization of Lignin-Derived Compounds by Dual-Functional Pd50Ag50/Fe3O4/N-rGO Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6964–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S. Decomposition of formic acid using tungsten(VI) oxide supported AgPd nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Jin, B.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, D.-G.; Chen, F.; An, Y.; Cui, P.; Wan, C. Efficient hydrogen generation from formic acid using AgPd nanoparticles immobilized on carbon nitride-functionalized SBA-15. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46908–46914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yao, F.; Li, X.; Hu, K.; Ye, M.; Xu, L.; An, Y. Bimetallic AgPd Nanoparticles Immobilized on Amine-Functionalized SBA-15 as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 6907–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shang, N.; Shang, H.; Du, T.; Zhou, X.; Feng, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Nitrogen-decorated porous carbon supported AgPd nanoparticles for boosting hydrogen generation from formic acid. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shang, N.; Zhou, X.; Feng, C.; Gao, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. AgPd-MnOxsupported on carbon nanospheres: An efficient catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3443–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Gao, S.; Shang, N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C. Super Nanoteragonal ZrO2 Embedded in Carbon as Efficient Support of PdAg Nanoparticle for Boosting Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.-F.; Xin, J.-J.; Ma, S.-K.; Cui, F.-J.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Jia, L.-H. Hydrogen Production from the Decomposition of Formic Acid over Carbon Nitride-Supported AgPd Alloy Nanoparticles. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 2374–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Xia, B.; Wen, L.; Du, C.; Su, J.; Luo, W.; Cheng, G. Synergistic catalysis of AgPd@ZIF-8 on dehydrogenation of formic acid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Cao, N.; Yang, L.; Su, J.; Luo, W.; Cheng, G. AgPd nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high performance catalysts for catalytic dehydrogenation of formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 11060–11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-T.; Liu, W.; Feng, C.; Shang, N.-Z.; Wang, C. A Ag-Pd alloy supported on an amine-functionalized UiO-66 as an efficient synergetic catalyst for the dehydrogenation of formic acid at room temperature. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shang, N.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. AgPd nanoparticles supported on zeolitic imidazolate framework derived N-doped porous carbon as an efficient catalyst for formic acid dehydrogenation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39878–39883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Xu, K.; Zou, S.; Cai, W.-B. B-doped pd catalyst: Boosting room-temperature hydrogen production from formic acid-formate solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4861–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Mori, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Tailoring the Size and Shape of Colloidal Noble Metal Nanocrystals as a Valuable Tool in Catalysis. Catal. Surv. Asia 2019, 23, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-Garcia, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Mori, K.; Leonard, A.F.; Kuwahara, Y.; Job, N.; Yamashita, H. Insights on palladium decorated nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels for the hydrogen production from formic acid. Catal. Today 2019, 324, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Vladimir, F.; Ge, J.; Xing, W. Surface interaction between Pd and nitrogen derived from hyperbranched polyamide towards highly effective formic acid dehydrogenation. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 40, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Qiu, H.; Cao, W.; Fu, H.; Wan, H.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, S. Ultrafine Pd Particles Embedded in Nitrogen-Enriched Mesoporous Carbon for Efficient H2 Production from Formic Acid Decomposition. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Xing, W.; Liu, C.; Liao, J.; Lu, T. High-quality hydrogen from the catalyzed decomposition of formic acid by Pd-Au/C and Pd-Ag/C. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3540–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, M.; Shimamoto, D.; Ago, H.; Tsuji, M. AgPd@Pd/TiO2 nanocatalyst synthesis by microwave heating in aqueous solution for efficient hydrogen production from formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10666–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, T.; Demirci, U.B.; Gul, F.; Ata, A. Pd-MnO2-Fe/C as electrocatalyst for the formic acid electrooxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 6920–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Guo, S. Enhanced electron transfer and light absorption on imino polymer capped PdAg nanowire networks for efficient room-temperature dehydrogenation of formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1979–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Shimamoto, D.; Uto, K.; Hattori, M.; Ago, H. Enhancement of catalytic activity of AgPd@Pd/TiO2 nanoparticles under UV and visible photoirradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14649–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Jun, Y.-S.; Wu, B.; Liu, D.; Chuong, T.T.; Fan, J.; Stucky, G.D. Carbon nitride supported AgPd alloy nanocatalysts for dehydrogenation of formic acid under visible light. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6382–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Shen, M.; Geng, S.; Yu, C.; Shen, B.; Yu, Y. Photocatalytic dehydrogenation of formic acid promoted by a superior PdAg@g-C3N4 Mott–Schottky heterojunction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, N.; Zhou, M.; Hanchett, M.K.; Chen, J.; Liu, B. Practical principles of density functional theory for catalytic reaction simulations on metal surfaces—From theory to applications. Mol. Simul. 2017, 43, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameera, W.M.C.; Maseras, F. Transition metal catalysis by density functional theory and density functional theory/molecular mechanics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norskov, J.K.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Studt, F.; Bligaard, T. Density functional theory in surface chemistry and catalysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Li, S.; Carrasquillo-Flores, R.; Alba-Rubio, A.C.; Dumesic, J.A.; Mavrikakis, M. Formic acid decomposition on Au catalysts: DFT, microkinetic modeling, and reaction kinetics experiments. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Ting, S.-W.; Chan, K.-Y.; Huang, W. Reaction pathways derived from DFT for understanding catalytic decomposition of formic acid into hydrogen on noble metals. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15956–15965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Norskov, J.K.; Studt, F. Theoretical analysis of transition-metal catalysts for formic acid decomposition. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Lee, S.; Han, J.; Yoon, S.P.; Nam, S.W.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Ham, H.C. Importance of Ligand Effect in Selective Hydrogen Formation via Formic Acid Decomposition on the Bimetallic Pd/Ag Catalyst from First-Principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22553–22560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Cao, D.; Zeng, X.C.; Cheng, D. Hydrogen Production via Efficient Formic Acid Decomposition: Engineering the Surface Structure of Pd-Based Alloy Catalysts by Design. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

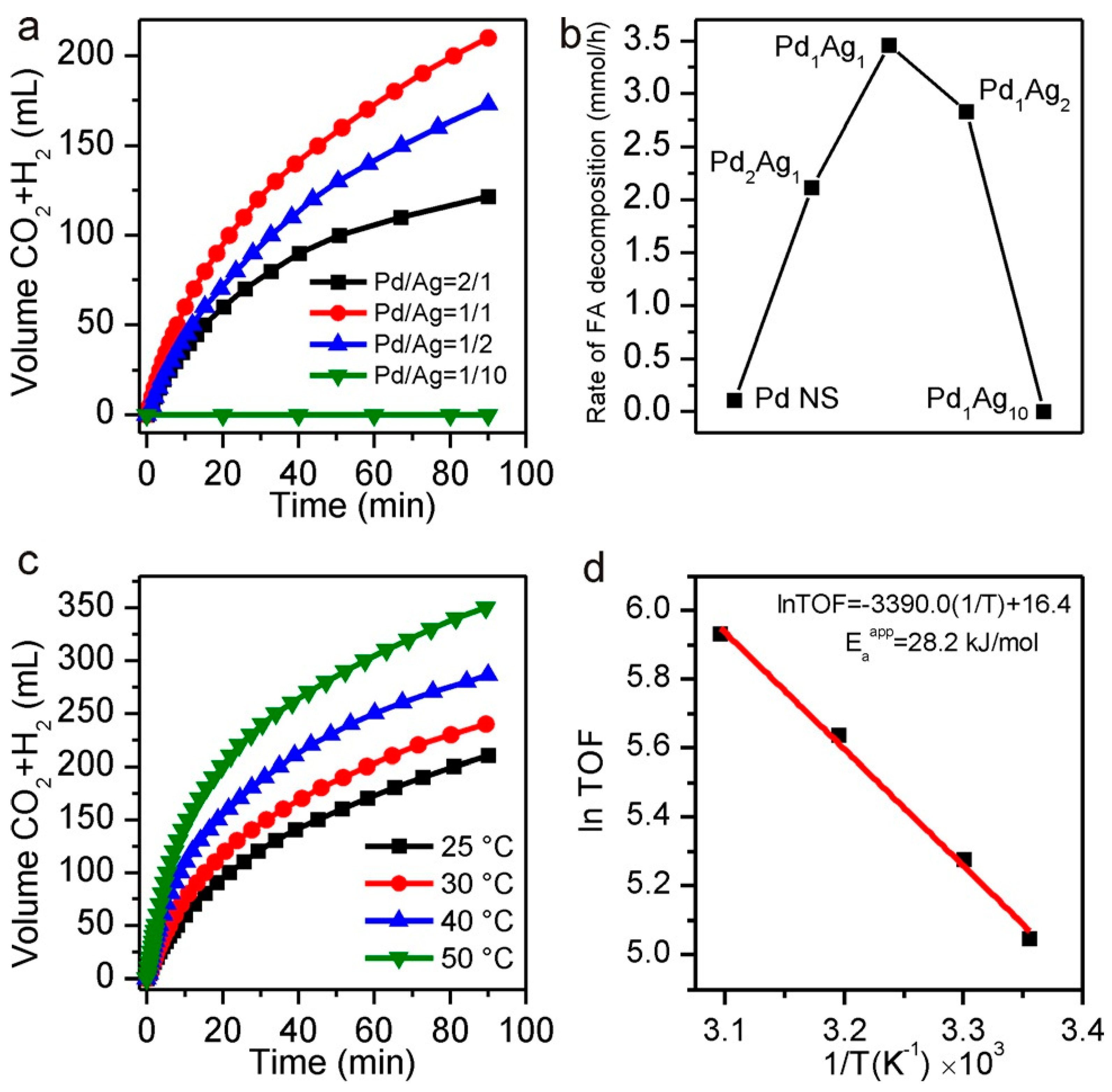
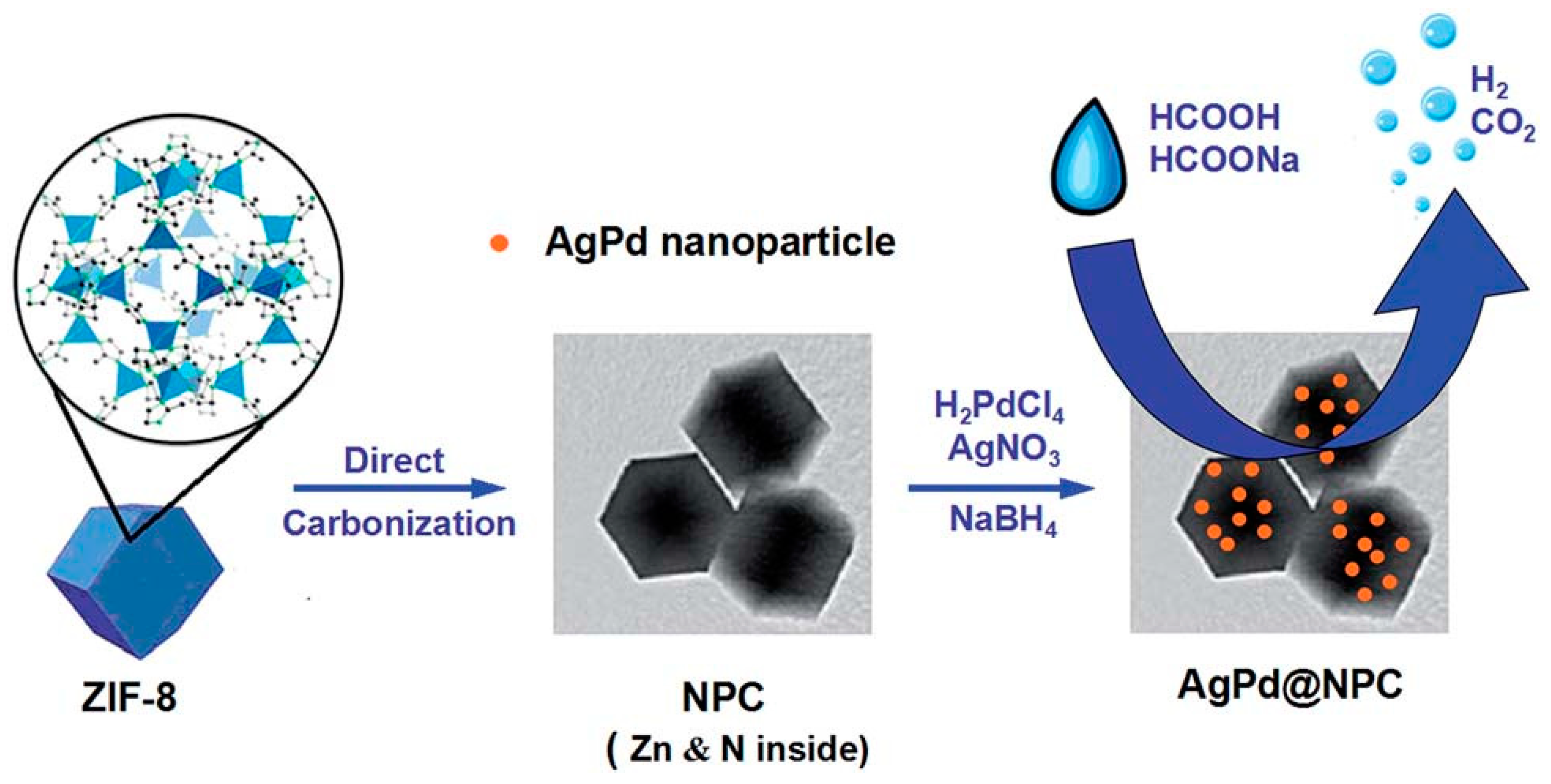
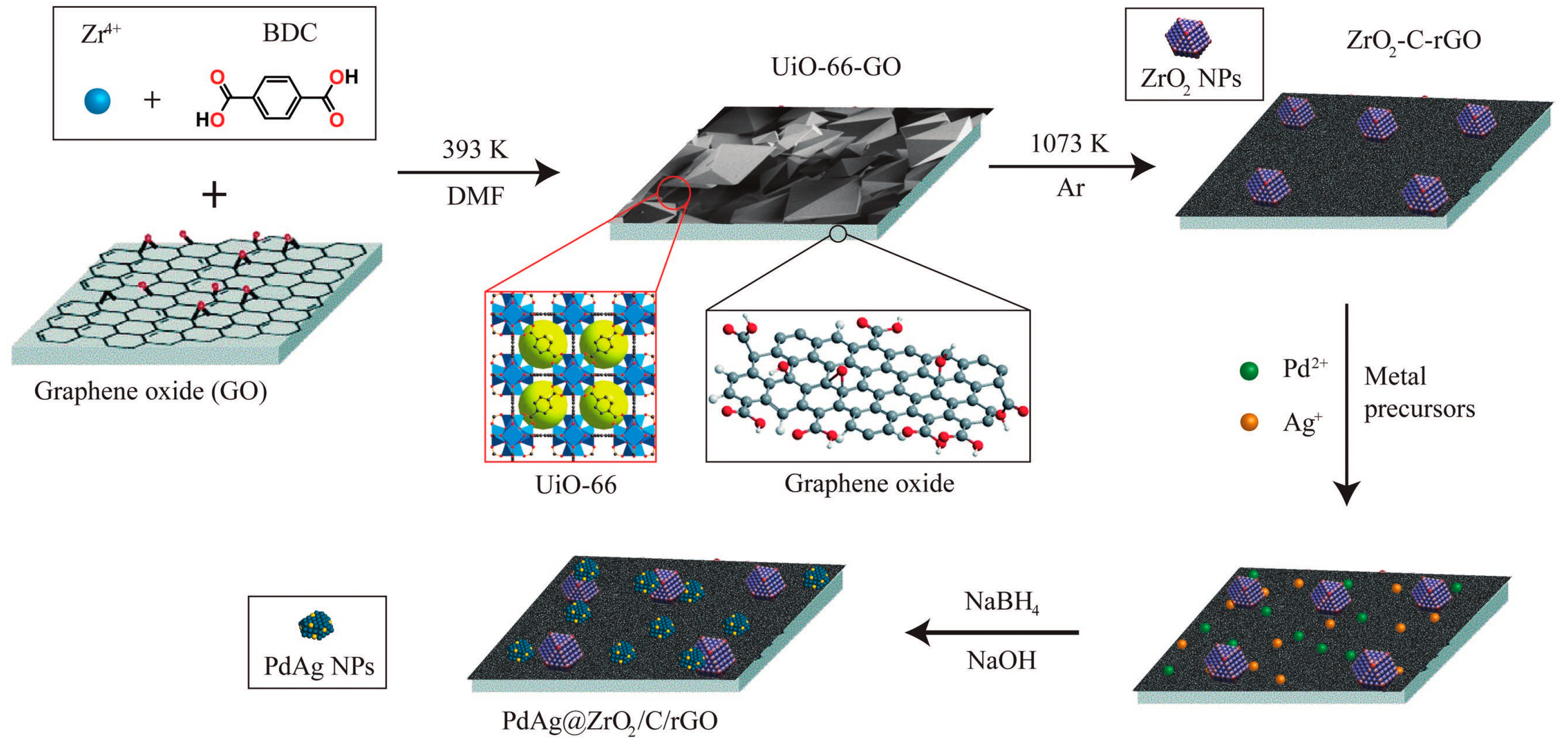

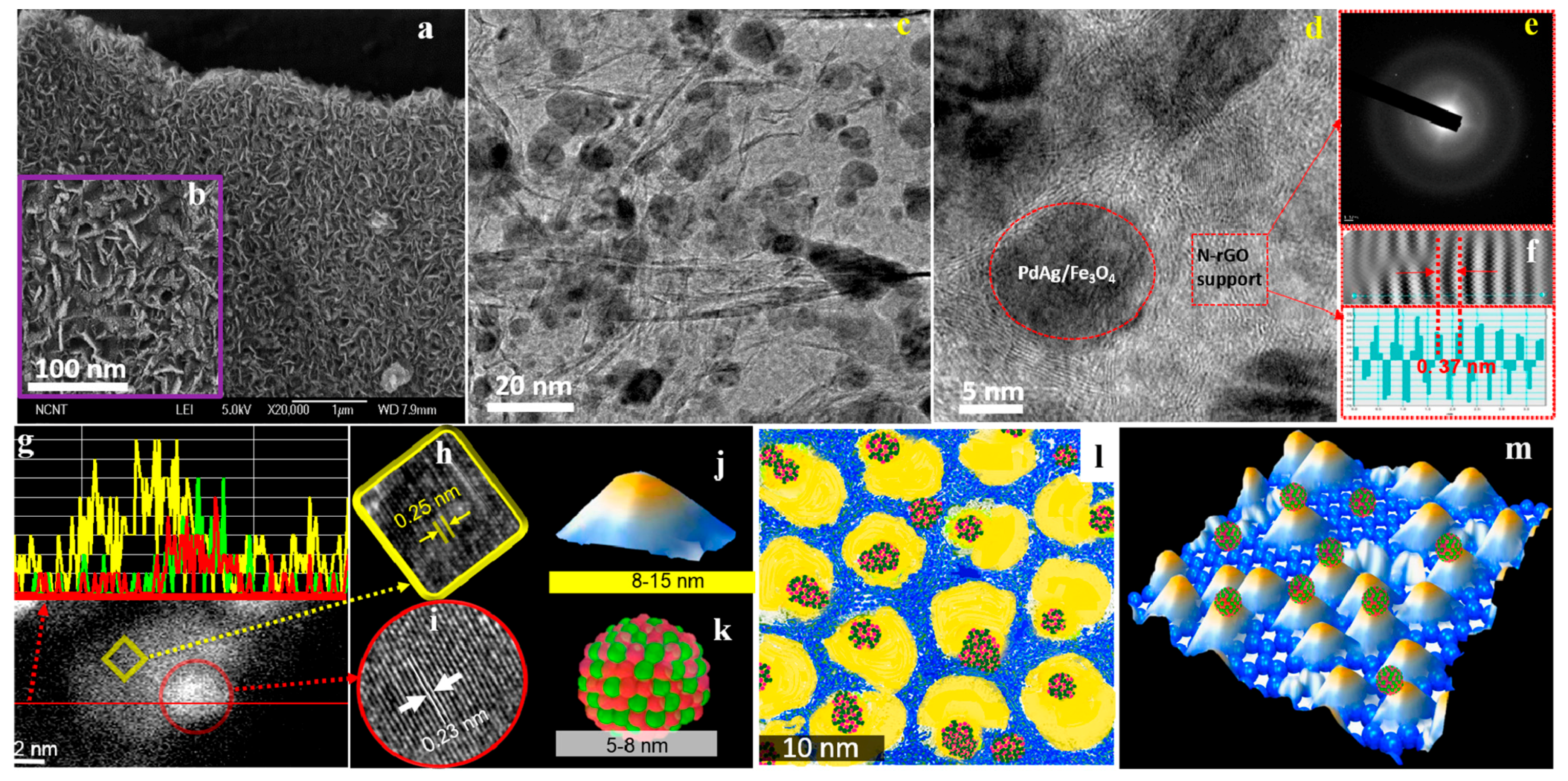
| Catalysts | Temperature(°C) | Additive | Concentration of FA and Additive (a) | TOF (h−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgPd@MIL-100(Fe) | 25 | - | 1 M | 58 | [63] |
| PdAg/C–FA | 25 | HCOONa | 5 M + 5 M | 90 (b) | [64] |
| Ag0.1-Pd0.90/rGO | 25 | HCOONa | 1 M + 0.67 M | 105 (b) | [65] |
| C-Pd1Ag1 BNSs | 25 | HCOONa | 1 M + 0.5 M | 156 | [66] |
| Ag6Pd1/N-rGO | 25 | - | 5 M | 171 | [67] |
| PdAg-MnOx/N-SiO2 | 25 | - | 0.25 M | 330 (b) | [62] |
| AgPd-Hs/G | 25 | HCOONa | 2.5 M + 2.5 M | 333 | [68] |
| Ag@Pd/N-GCNT | 25 | - | N/A | 413 | [69] |
| Ag74Pd26/graphene | 25 | HCOONa | 0.9 M + 0.1 M | 572 | [70] |
| PdAg-MnOx/N-SiO2 | 30 | - | 0.25 M | 530 (b) | [62] |
| AgPd/MOF-5-C | 30 | HCOONa | 1.25 M + 3.75 M | 854 | [71] |
| PdAg-CeO2/MC | 30 | HCOONa | N/A | 2272 | [72] |
| PdAg-MnOx/N-SiO2 | 35 | - | 0.25 M | 700 (b) | [62] |
| PdAg-MnOx/N-SiO2 | 40 | - | 0.25 M | 1430 (b) | [62] |
| C-Pd1Ag1 BNSs | 50 | HCOONa | 1 M + 0.5 M | 378 | [66] |
| C-Ag42Pd58 | 50 | - | 1 M | 382 (b) | [73] |
| Ag9Pd91/g-C3N4 | 50 | HCOONa | 1.5 M + 0.5 M | 480 | [74] |
| Pd50Ag50/Fe3O4/N-rGO | 50 | - | 1.33 M | 497 | [75] |
| Ag0.25Pd/WO3 | 50 | HCOONa | 0.15 M + 1.2 M | 683 | [76] |
| Ag10Pd90/0.2CND/SBA-15 | 50 | HCOONa | 1.5 M + 0.5 M | 893 | [77] |
| Ag1Pd9/SBA-15-Amine | 50 | HCOONa | 1.5 M + 0.5 M | 964 | [78] |
| Ag1Pd9@NPC | 50 | HCOONa | N/A | 3000 | [79] |
| Ag1Pd9–MnOx/carbonspheres | 50 | HCOOK | 5 M + 15 M | 3558 | [80] |
| PdAg@ZrO2/C | 50 | HCOOK | 2.5 M + 10 M | 9206 | [81] |
| Ag74Pd26/graphene | 60 | HCOONa | 0.9 M + 0.1 M | 572 | [70] |
| PdAg@ZrO2/C/rGO | 60 | HCOONa | 3 M + 7.5 M | 4500 | [32] |
| Ag1Pd2/CN | 75 | - | 2 M | 621 (b) | [82] |
| Pd1Ag2/C(1) | 75 | HCOONa | 0.9 M + 0.1 M | 855 (b) | [43] |
| PdAg/amine-MSC | 75 | HCOONa | 0.9 M + 0.1 M | 5638 | [15] |
| Ag18Pd82@ZIF-8 | 80 | HCOONa | N/A | 580 | [83] |
| Ag20Pd80@MIL-101 | 80 | HCOONa | N/A | 848 | [84] |
| Ag1Pd4@NH2–UiO-66 | 80 | - | 1.25 M | 893 (b) | [85] |
| AgPd@NPC | 80 | HCOONa | 0.25 M + 0.25 M | 936 | [86] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navlani-García, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Cazorla-Amorós, D. Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Attained by Bimetallic Heterogeneous PdAg Catalytic Systems. Energies 2019, 12, 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214027
Navlani-García M, Salinas-Torres D, Cazorla-Amorós D. Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Attained by Bimetallic Heterogeneous PdAg Catalytic Systems. Energies. 2019; 12(21):4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214027
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavlani-García, Miriam, David Salinas-Torres, and Diego Cazorla-Amorós. 2019. "Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Attained by Bimetallic Heterogeneous PdAg Catalytic Systems" Energies 12, no. 21: 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214027
APA StyleNavlani-García, M., Salinas-Torres, D., & Cazorla-Amorós, D. (2019). Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Attained by Bimetallic Heterogeneous PdAg Catalytic Systems. Energies, 12(21), 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214027








