PMU’s Behavior with Flicker-Generating Voltage Fluctuations: An Experimental Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Voltage Fluctuations and PMU Requirements
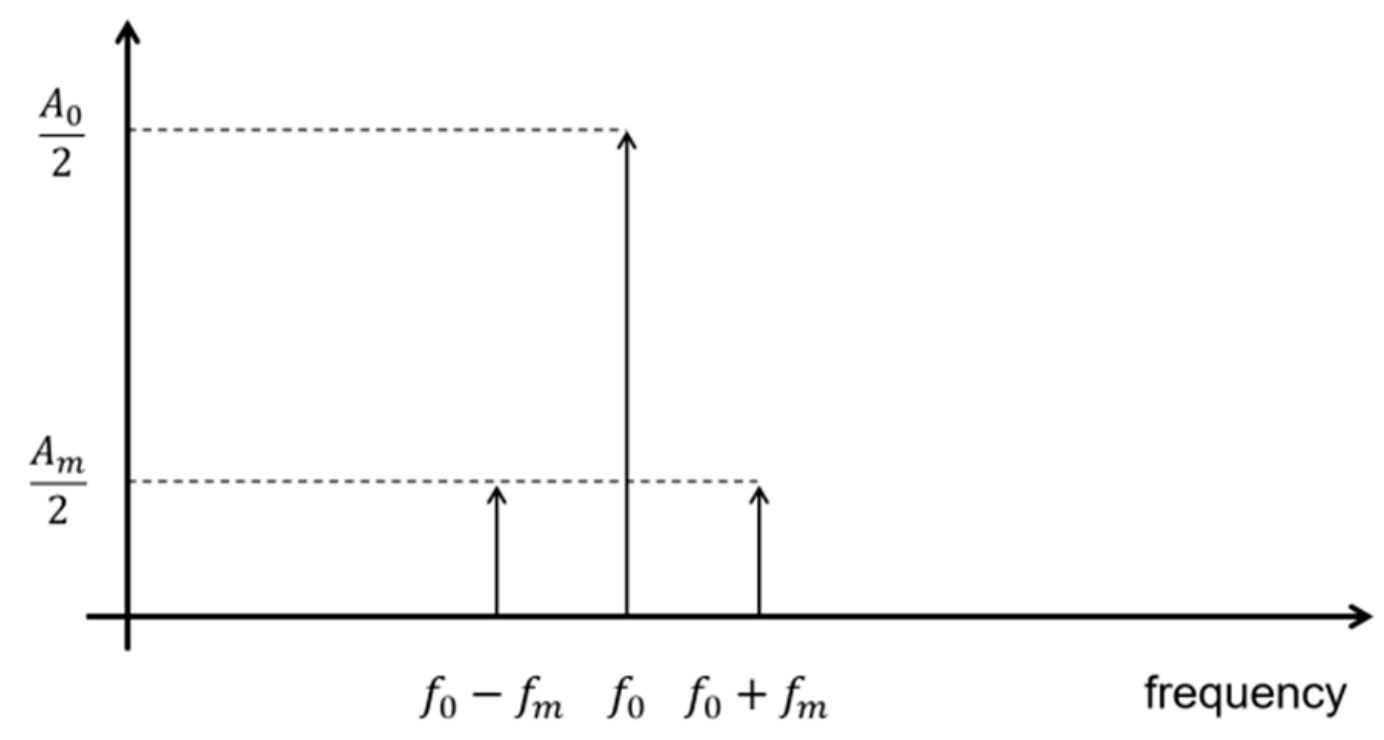
2.1. Models of Voltage Fluctuations
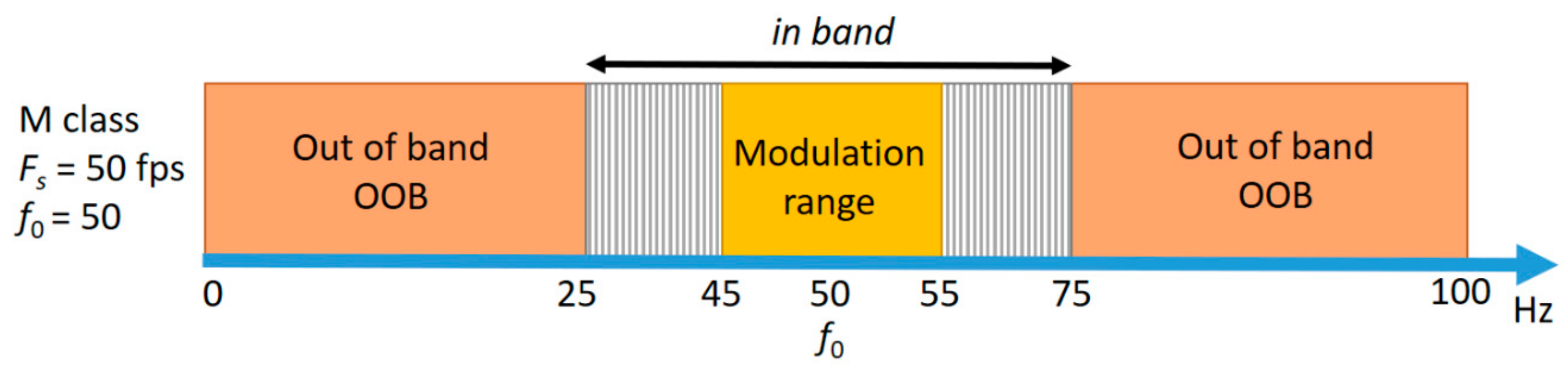
2.2. Modulations and Out-of-Band Signals in Standard PMU Testing
- The amplitude modulation test, in which the signal at nominal frequency has a time-varying cosinusoidal amplitude. This test signal is introduced to be representative of a dynamic condition that the PMU must be able to measure. Thus, the synchrophasor magnitudes estimated in this condition are expected to follow the signal amplitude evolution. According to [1], to guarantee the interoperability of PMUs from different manufacturers, the device performance must remain within the given TVE, FE, and RFE limits when the modulation frequency is up to 2 Hz, in the case of a p-class device, and 5 Hz for M-class PMUs.
- The out-of-band (OOB) interference test, in which the signal is affected by a single interharmonic component. Interharmonics are considered as disturbances and M class PMUs (the only PMUs for which OOB test specifications are given) must properly filter them out.
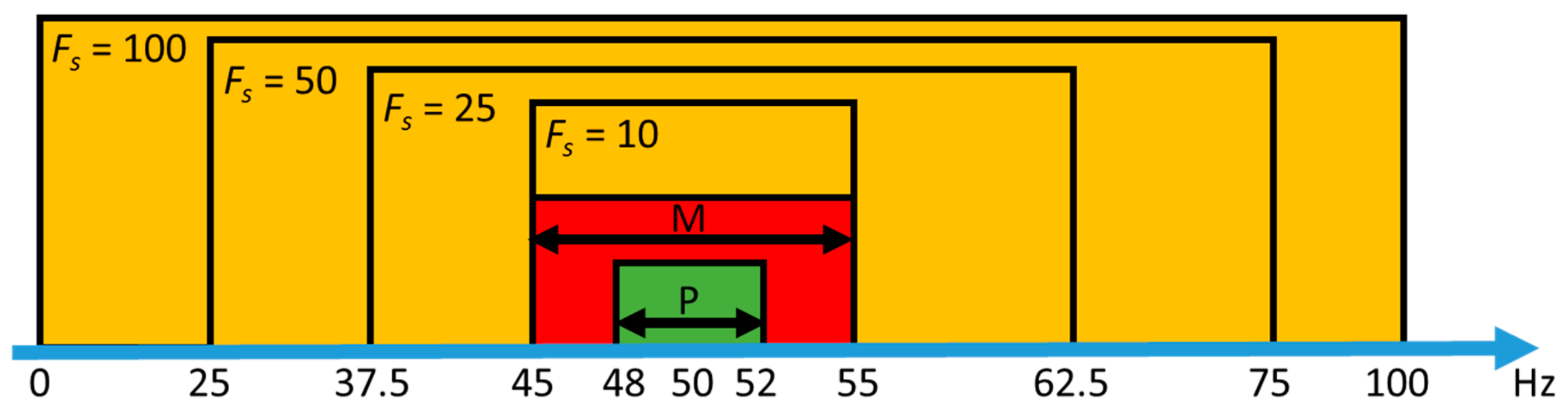
2.3. Voltage Fluctuations and PMU Specifications
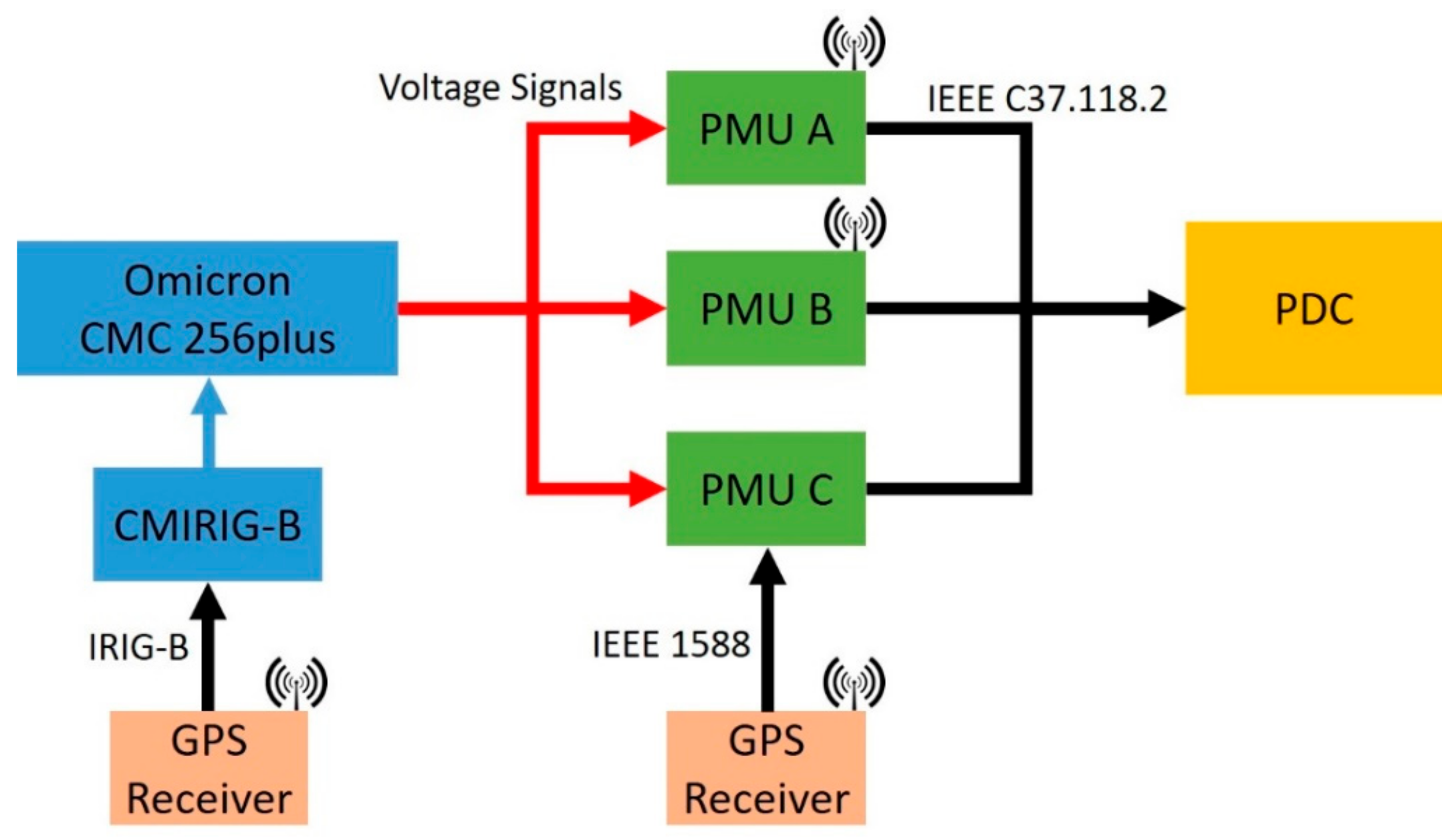
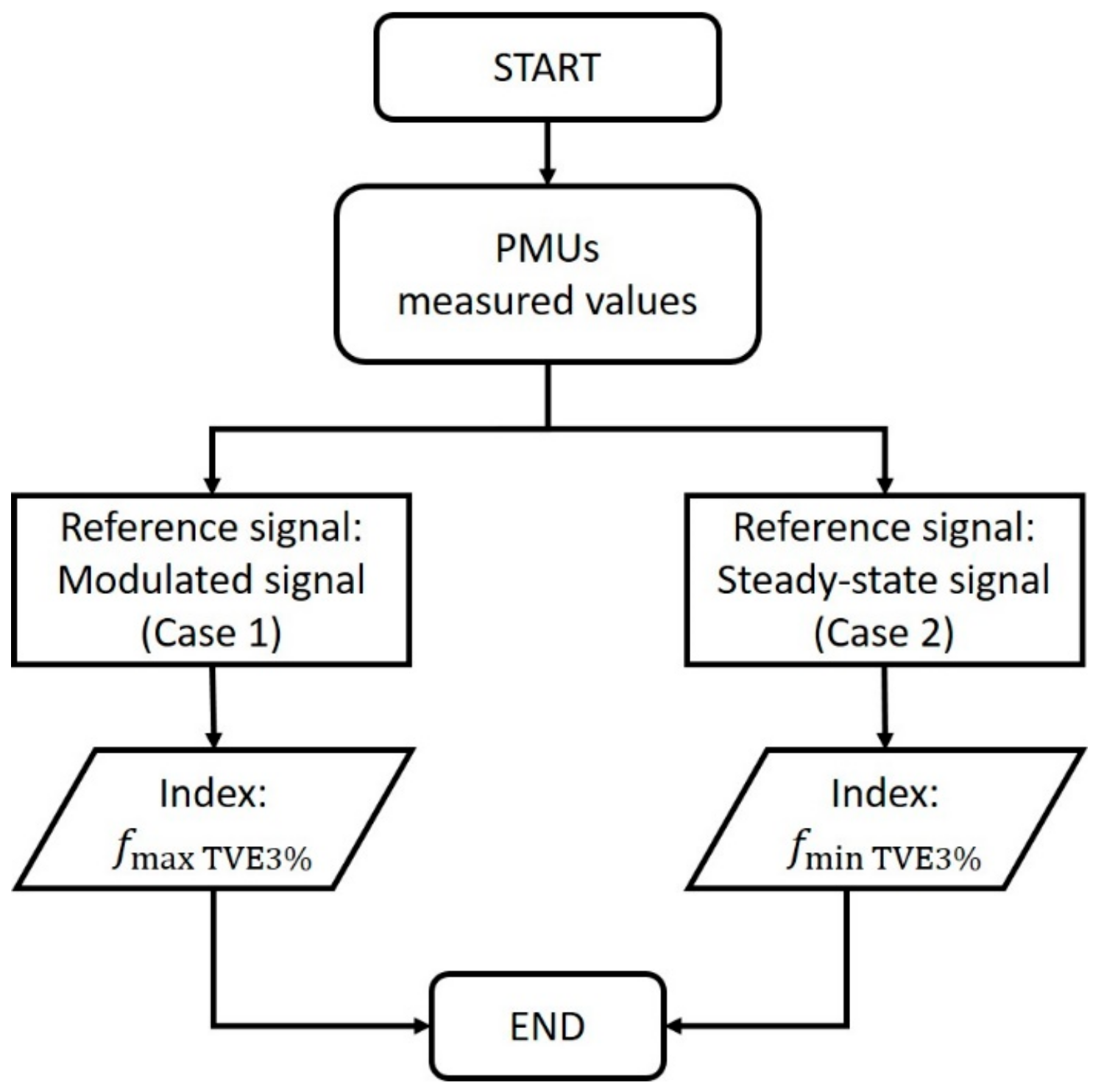
3. Test Setup
- P-like configuration: Window type: triangular; window length: two cycles at nominal frequency.
- M-like configuration: Window type: Hanning; window length: seven cycles at nominal frequency.
4. Test Results
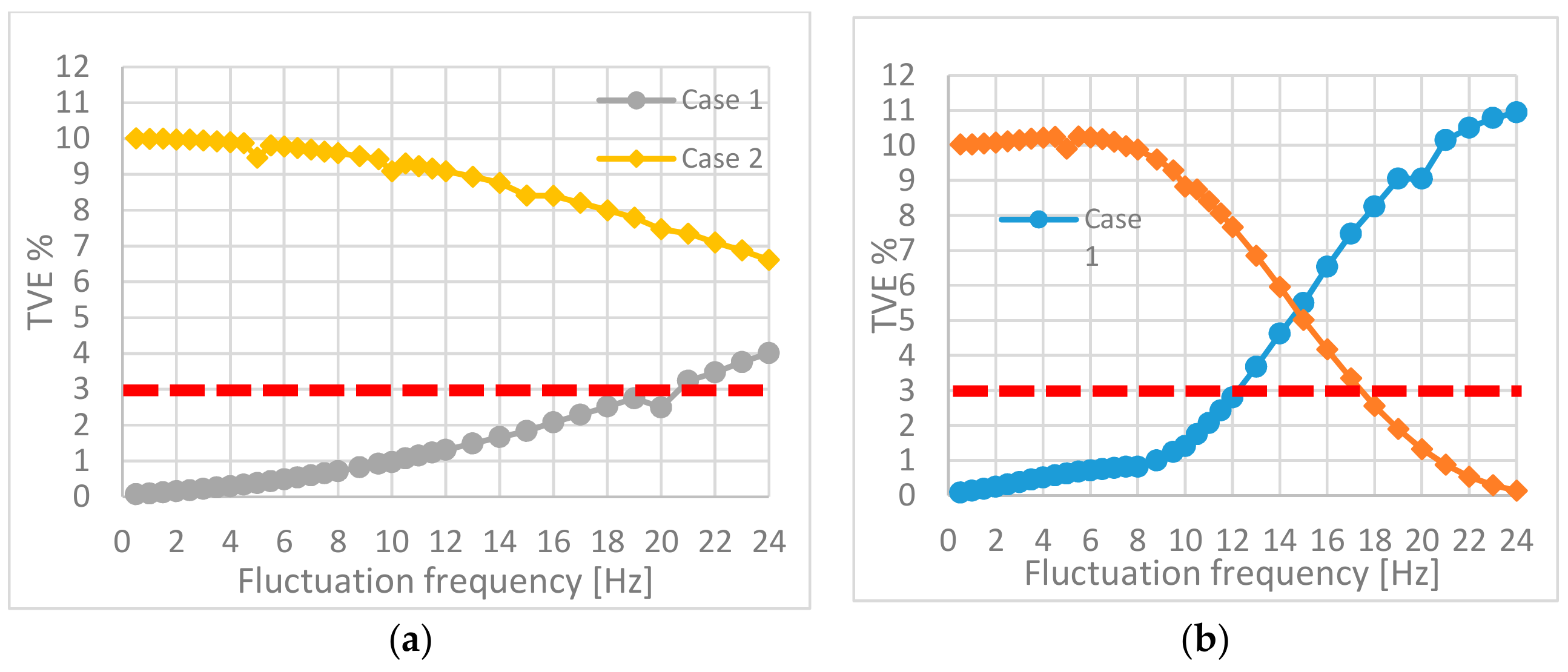
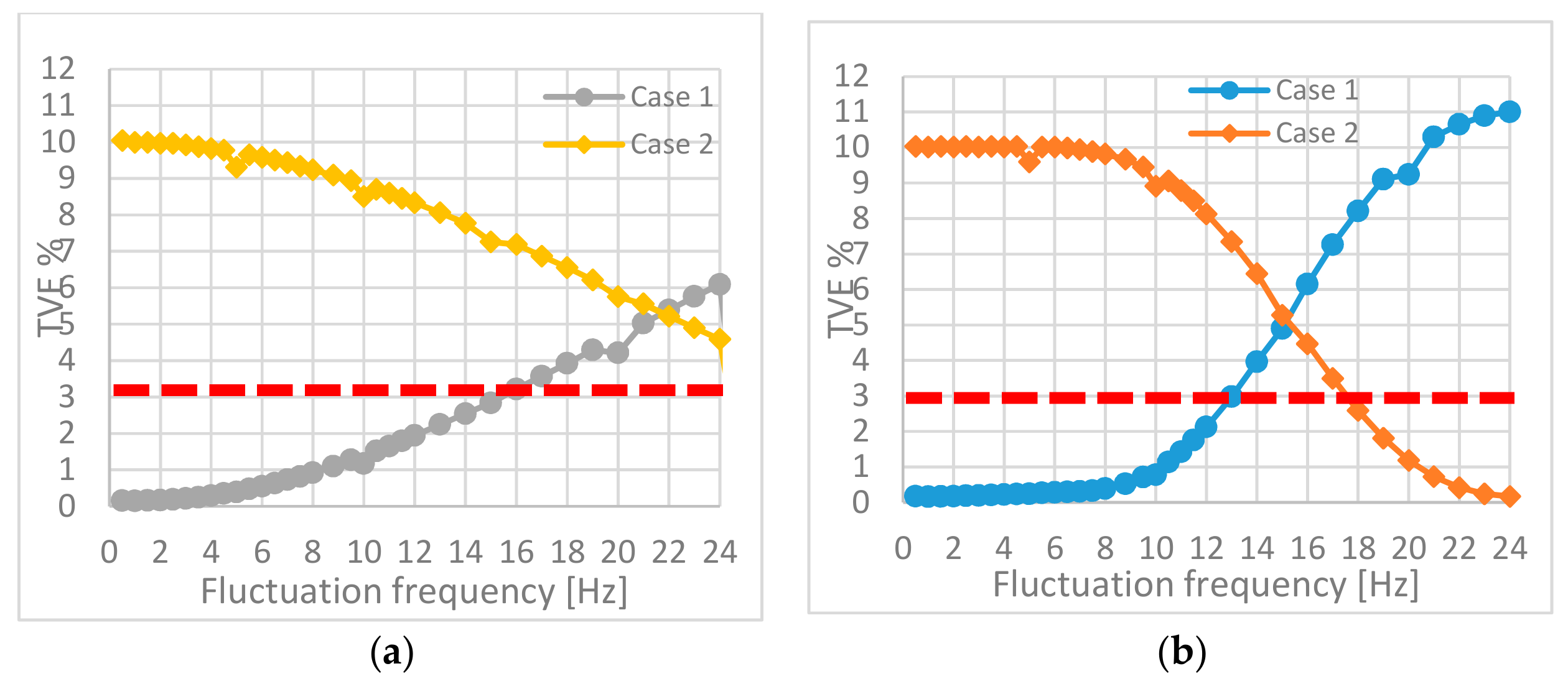
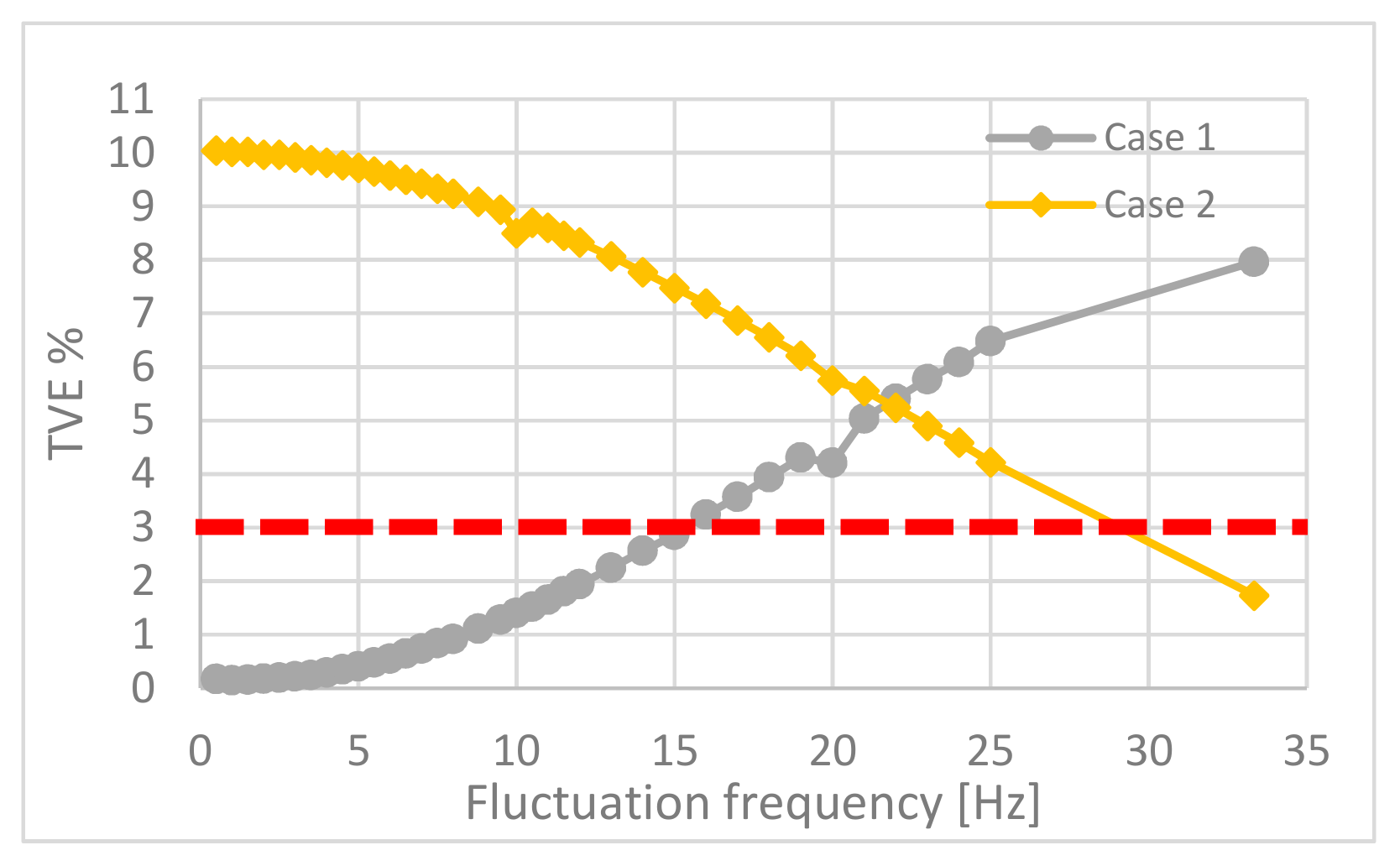
4.1. TVE Results
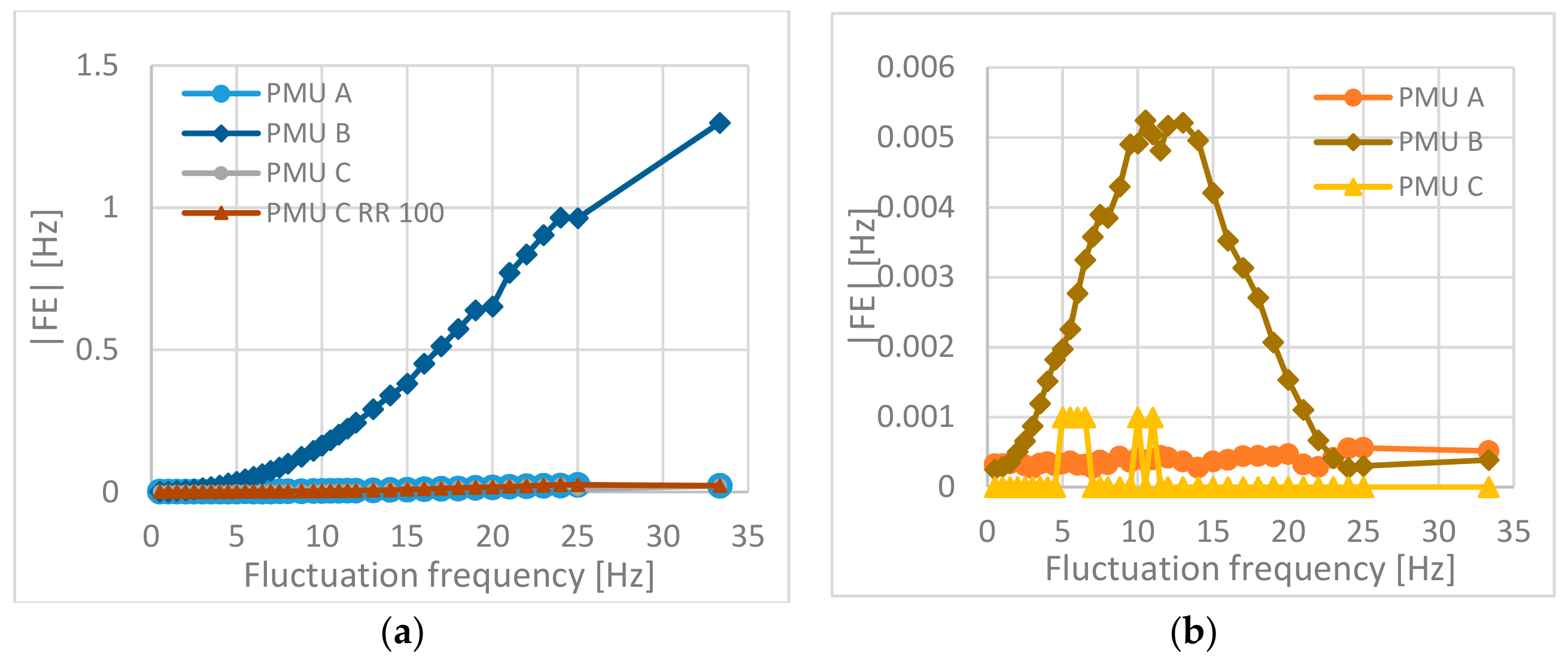
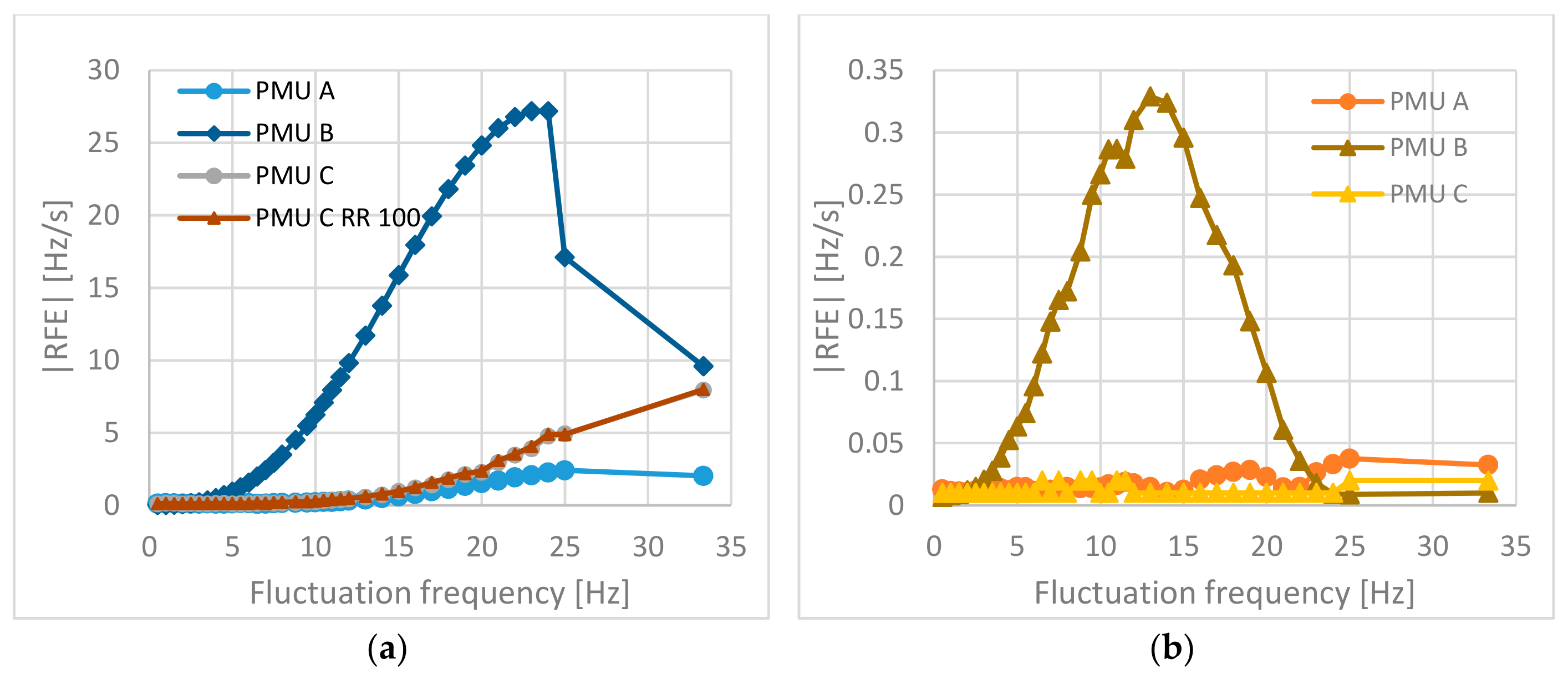
4.2. Frequency and ROCOF Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE/IEC International Standard—Measuring Relays and Protection Equipment—Part 118-1: Synchrophasor for Power Systems—Measurements, in IEC/IEEE 60255-118-1:2018; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Guide for Phasor Data Concentrator Requirements for Power System Protection, Control, and Monitoring, IEEE Std C37.244-2013; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Guide for Synchronization, Calibration, Testing, and Installation of Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs) for Power System Protection and Control, IEEE Std C37.242-2013; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Standard for Synchrophasors for Power Systems, IEEE Std C37.118-2005; Revision of IEEE Std 1344-1995; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Measurements for Power Systems, in IEEE Std C37.118.1-2011; Revision of IEEE Std C37.118-2005; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Measurements for Power Systems—Amendment 1: Modification of Selected Performance Requirements, in IEEE Std C37.118.1a-2014; Amendment to IEEE Std C37.118.1-2011; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, A.; Muscas, C.; Ponci, F. Phasor Measurement Units and Wide Area Monitoring Systems, 1st ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchi, G.; Macii, D.; Petri, D. Phasor Measurement Units for Smart Grids: Estimation Algorithms and Performance Issues. In Proceedings of the AEIT Annual Conference 2013, Mondello, Palermo, Italy, 3–5 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, P.; Ferrari, P.; Flammini, A.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Rinaldi, S. A Distributed PMU for Electrical Substations with Wireless Redundant Process Bus. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, S.; Tan, G.; Haddad, A. Low-Cost Monitoring of Synchrophasors Using Frequency Modulation. Energies 2019, 12, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distribution Task Team, Synchrophasor Monitoring for Distribution Systems—Technical Foundations and Applications, 2018, NASPI-2018-TR-001. Available online: https://www.naspi.org/node/688 (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Shen, Y.; Abubakar, M.; Liu, H.; Hussain, F. Power Quality Disturbance Monitoring and Classification Based on Improved PCA and Convolution Neural Network for Wind-Grid Distribution Systems. Energies 2019, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Meier, A.; Stewart, E.; McEachern, A.; Andersen, M.; Mehrmanesh, L. Precision Micro-Synchrophasors for Distribution Systems: A Summary of Applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2017, 8, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifredo-Chacón, M.-Á.; Perez-Peña, F.; Quirós-Olozábal, Á.; González-de-la-Rosa, J.-J. Implementation of Processing Functions for Autonomous Power Quality Measurement Equipment: A Performance Evaluation of CPU and FPGA-Based Embedded System. Energies 2019, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization. Voltage Characteristics of Electricity Supplied by Public Distribution Systems; European Standard CENELEC EN 50160; European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano, U.; Braun, J.P.; Voljč, B.; Lapuh, R. Software platform for PMU algorithm testing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bi, T.; Yang, Q. The evaluation of phasor measurement units and their dynamic behavior analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, P.; Liu, J.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Ponci, F.; Monti, A. A Fast and Accurate PMU Algorithm for P+M Class Measurement of Synchrophasor and Frequency. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscani, S.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A. Design and Performance Prediction of Space Vector-Based PMU Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, P.; Paolone, M. Enhanced Interpolated-DFT for Synchrophasor Estimation in FPGAs: Theory, Implementation, and Validation of a PMU Prototype. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y. Flicker Mitigation by Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator Variable-Speed Wind Turbines. Energies 2013, 6, 3807–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodetti, S.; Azcarate, I.; Gutiérrez, J.J.; Leturiondo, L.A.; Redondo, K.; Sáiz, P.; Melero, J.J.; Bruna, J. Flicker of Modern Lighting Technologies Due to Rapid Voltage Changes. Energies 2019, 12, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIGRE. Review of LV and MV Compatibility Levels for Voltage Fluctuations; Working Group C4.111; CIGRE: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Castello, P.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Sulis, S. Analysis of PMU Response Under Voltage Fluctuations in Distribution Grids. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Applied Measurements for Power Systems (AMPS), Aachen, Germany, 28–30 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)—Part 4-15: Testing and Measurement Techniques—Flickermeter—Functional and Design Specifications; IEC Int. Std. 61000-4-15; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wiczyński, G. Estimation of Pst Indicator Values on the Basis of Voltage Fluctuation Indices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, F.; Langella, R.; Sollazzo, A.; Testa, A. On the interharmonic components generated by adjustable speed drives. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 2005, 20, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langella, R.; Testa, A. Amplitude and Phase Modulation Effects of Waveform Distortion in Power Systems. Electr. Power Qual. Util. 2007, 13, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Reliability Guideline, PMU Placement and Installation, December 2016. Available online: https://www.nerc.com/comm/PC_Reliability_Guidelines_DL/Reliability%20Guideline%20%20PMU%20Placement.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Stenbakken, G.; Nelson, T.; Zhou, M.; Centeno, V. Reference values for dynamic calibration of PMUs. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Fu, H.J.; Bo, B.; Dong, Z.Y. Application of Phasor Measurement Unit on Locating Disturbance Source for Low-Frequency Oscillation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2010, 1, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanfretti, L.; Baudette, M.; Domínguez-García, J.-L.; Almas, M.S.; White, A.; Gjerde, J.O. A Phasor Measurement Unit Based Fast Real-time Oscillation Detection Application for Monitoring Wind-farm-to-grid Sub–synchronous Dynamics. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2016, 44, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems, in IEEE Std 1588-2008; Revision of IEEE Std 1588-2002; IEEE Power & Energy Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.G.; Thorp, J.S. Synchronized Phasor Measurements and Their Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hz | Hz | Hz | Hz | Hz | Hz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 4 | 7.5 | 8.8 | 13 | 20 |
| 1 | 4.5 | 8 | 9.5 | 14 | 21 |
| 1.5 | 5 | 8.8 | 10 | 15 | 22 |
| 2 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 10.5 | 16 | 23 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 10 | 11 | 17 | 24 |
| 3 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 11.5 | 18 | 25 |
| 3.5 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 19 | 33 1/3 |
| DUT | Configuration | (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMU A 50 fps | P | 15 | - |
| M | 5 | 9.5 | |
| PMU B 50 fps | P | 20 | - |
| M | 12 | 18 | |
| PMU C 50 fps | P | 15 | - |
| M | 13 | 18 | |
| PMU C 100 fps | P | 15 | 33.33 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castello, P.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Sulis, S. PMU’s Behavior with Flicker-Generating Voltage Fluctuations: An Experimental Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173355
Castello P, Muscas C, Pegoraro PA, Sulis S. PMU’s Behavior with Flicker-Generating Voltage Fluctuations: An Experimental Analysis. Energies. 2019; 12(17):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173355
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastello, Paolo, Carlo Muscas, Paolo Attilio Pegoraro, and Sara Sulis. 2019. "PMU’s Behavior with Flicker-Generating Voltage Fluctuations: An Experimental Analysis" Energies 12, no. 17: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173355
APA StyleCastello, P., Muscas, C., Pegoraro, P. A., & Sulis, S. (2019). PMU’s Behavior with Flicker-Generating Voltage Fluctuations: An Experimental Analysis. Energies, 12(17), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173355






