Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Coal Gasification—An Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
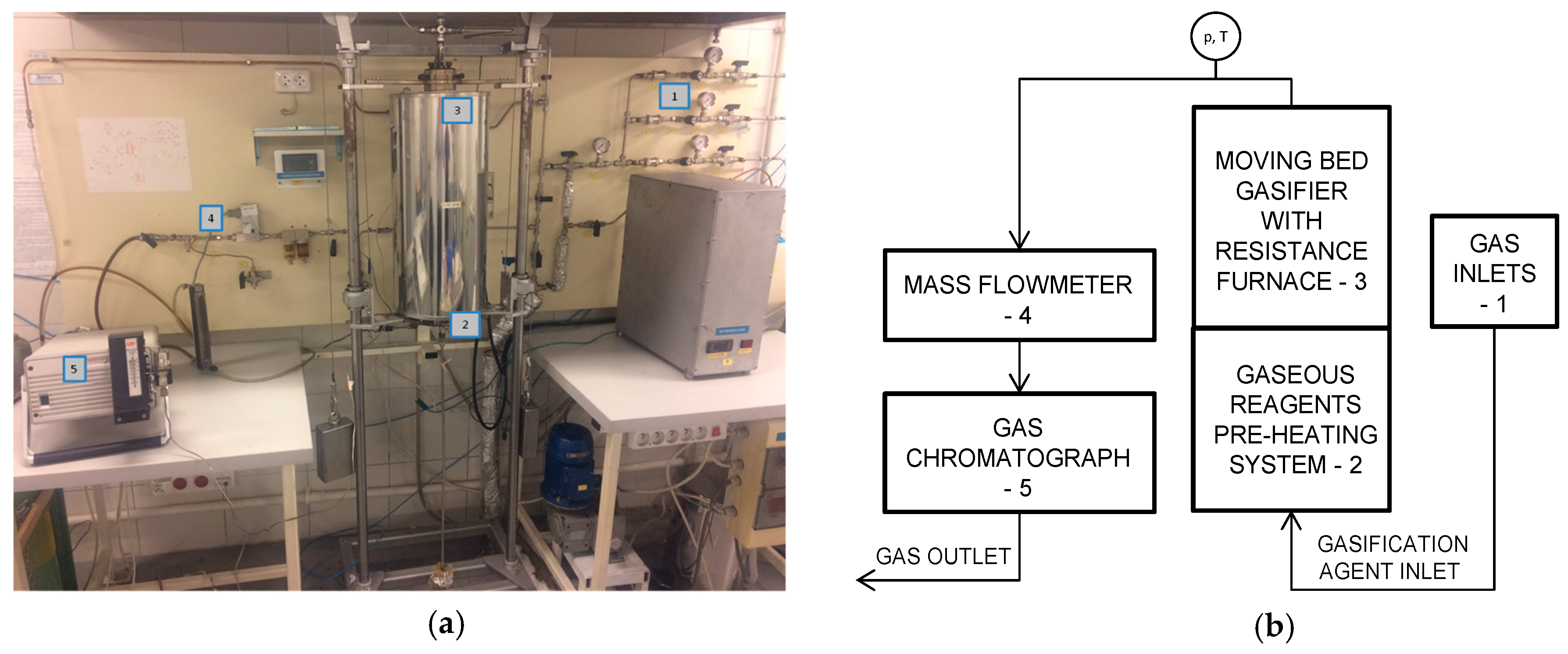
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.2. Materials
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
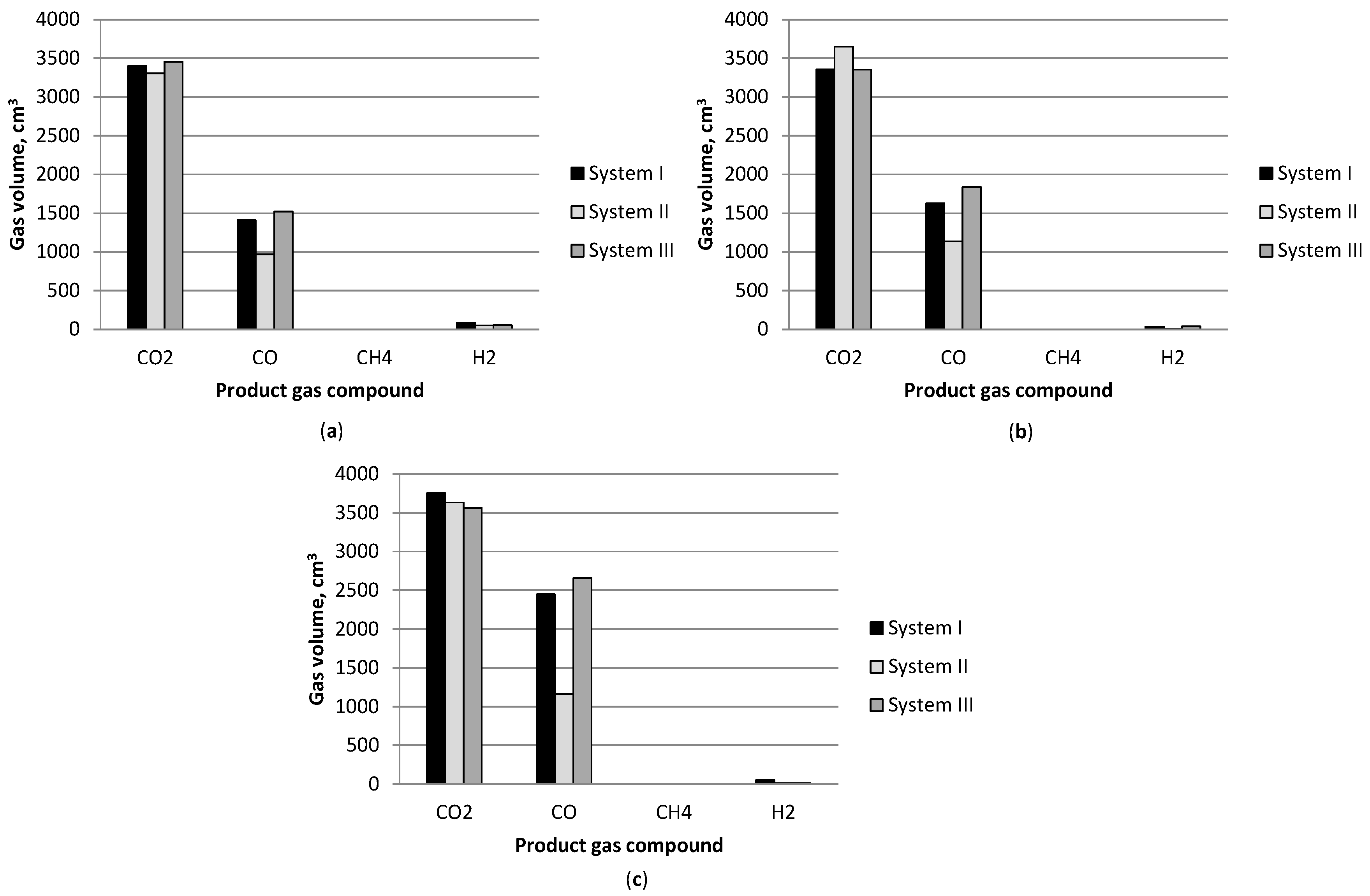
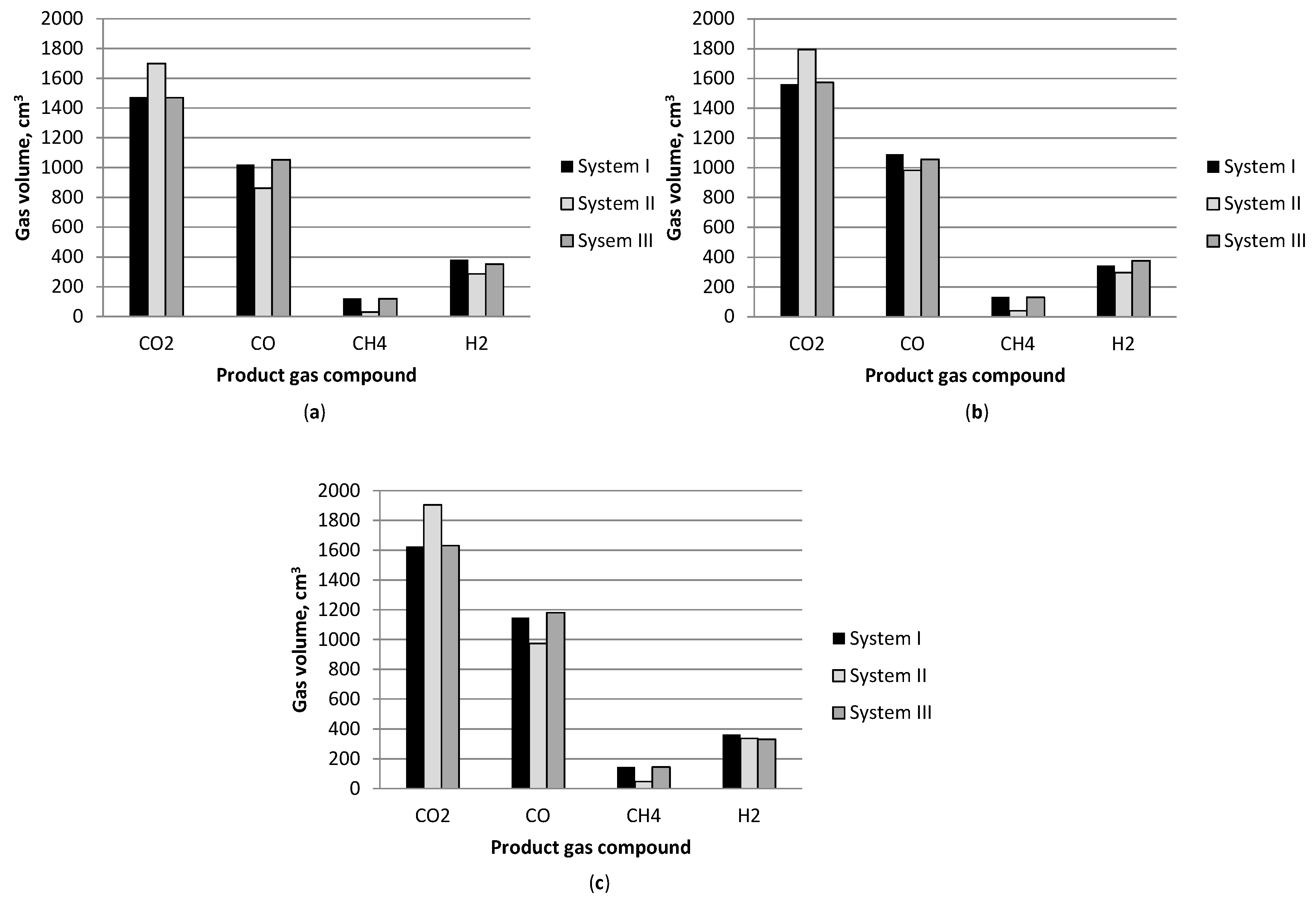
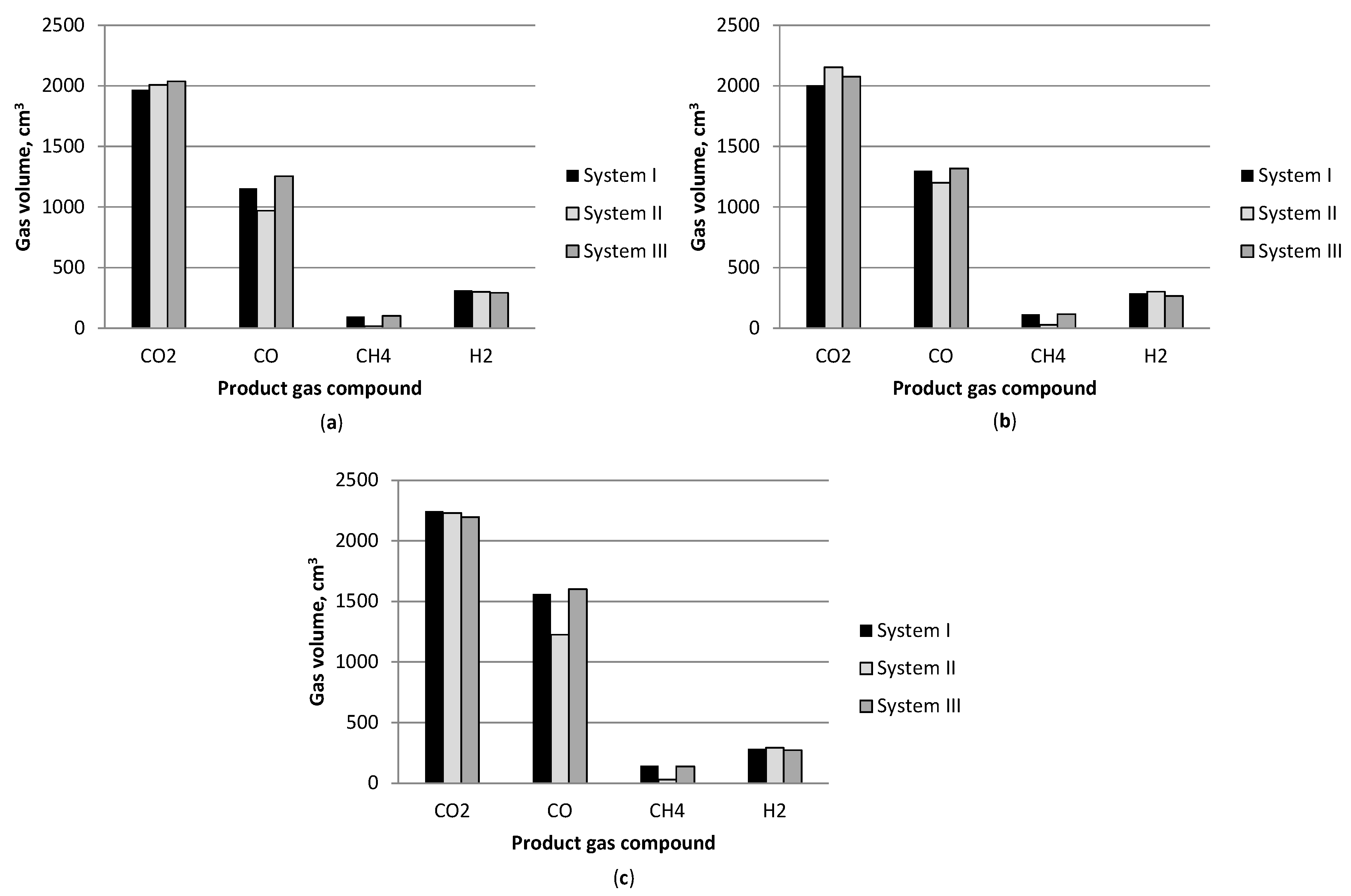
3.1. Effect of Temperature
3.2. Gasification Products
3.3. Principal Components Analysis in Exploration of the Combined Effects of Temperature, Gasification Agent Composition and Waste Heat Utilization on Gasification Process Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BP, 2018. BP Statistical Review of World Energy June 2018. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/en/corporate/pdf/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2018-full-report.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- European Commission. A Policy Framework for Climate and Energy in the Period from 2020 to 2030. Brussels, 22.1.2014. COM (2014) 15 Final. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52014DC0015&from=EN (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources (Recast) COM/2016/0767 Final/2—2016/0382 (COD). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52016PC0767R%2801%29 (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directive 2012/27/EU on Energy Efficiency COM/2016/0761 Final—2016/0376 (COD). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1485938766830&uri=CELEX:52016PC0761 (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Energy Information Administration, Office of Integrated Analysis and Forecasting, U.S. Department of Energy. International Energy Outlook 2017; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Bell, D.A.; Towler, B.F.; Fan, M. Coal Gasification and Its Applications; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mahinpey, N.; Gomez, A. Review of gasification fundamentals and new findings: Reactors, feedstock, and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 148, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormos, C.C. Integrated assessment of IGCC power generation technology with carbon capture and storage (CCS). Energy 2012, 42, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansaniwal, S.K.; Pal, K.; Rosen, M.A.; Tyagi, S.K. Recent advances in the development of biomass gasification technology: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.; Artetxe, M.; Amutio, M.; Alvarez, J.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Recent advances in the gasification of waste plastics. A critical overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howaniec, N.; Smoliński, A. Biowaste utilization in the process of co-gasification with bituminous coal and lignite. Energy 2017, 118, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howaniec, N.; Smoliński, A. Influence of fuel blend ash components on steam co-gasification of coal and biomass—Chemometric study. Energy 2015, 78, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoback, M.D.; Gorelick, S.M. Earthquake triggering and large-scale geologic storage of carbon dioxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10164–10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; Schneider, M.; Winkler, A. Threats to the quality of water resources by geological CO2 storage: Hydrogeochemical and other methods of investigation: A review. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 40, pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tola, V.; Pettinau, A. Power generation plants with carbon capture and storage: A techno-economic comparison between coal combustion and gasification technologies. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Franca, R.M.; Azapagic, A. Carbon capture, storage and utilisation technologies: A critical analysis and comparison of their life cycle environmental impacts. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 9, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhasyima, R.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Advances in CO2 utilization technology: A patent landscape review. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 26, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koytsoumpa, E.I.; Bergins, C.; Kakaras, E. The CO2 economy: Review of CO2 capture and reuse technologies. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 132, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. In Novel Carbon Capture and Utilization Technologies; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guizani, C.; Escudero Sanz, F.J.; Salvador, S. The gasification reactivity of high-heating-rate chars in single and mixed atmospheres of H2O and CO2. Fuel 2013, 108, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.P.; Agnew, J.B.; Zhang, D.K. Gasification of a South Australian low rank coal with carbon dioxide and steam: Kinetics and reactivity studies. Fuel 1998, 77, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, T.; Yadav, M.V.; Pushpavanam, S.; Voolapalli, R.K.; Cho, Y.S. CO2 utilization for gasification of carbonaceous feedstock: A thermodynamic analysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 83, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everson, E.C.; Neomagus, H.W.J.P.; Kaitano, R.; Falcon, R.; Cann, V.M. Properties of high ask coal-char particles derived from inertinite-rich coal: II. Gasification kinetics with carbon dioxide. Fuel 2008, 87, 3403–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bell, D.A. Reaction kinetics of Powder River Basin coal gasification in carbon dioxide using a modified drop tube reactor. Fuel 2015, 140, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porada, S.; Czerski, G.; Grzywacz, P.; Makowska, D.; Dziok, T. Comparison of the gasification od coals and their chars with CO2 based on the formation kinetics of gaseous products. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 653, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahijani, P.; Zainal, Z.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Mohamed, A.R. Conversion of the greenhouse gas CO2 to the fuel gas CO via the Boudouard reaction: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.F.; Usman, M.R.; Kusakabe, K. Coal gasification in CO2 atmosphere and its kinetics since 1948: A brief review. Energy 2011, 36, 12–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billaud, J.; Valis, S.; Peyrot, M.; Salvador, S. Influence of H2O, CO2 and O2 addition on biomass gasification in entrained flow gasifier reactor conditions: Experiments and modelling. Fuel 2016, 166, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lin, B.J. Hydrogen and synthesis gas production from activated carbon and steam via reusing carbon dioxide. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Khordehgah, N.; Almahmoud, S.; Delpech, B.; Chauhan, A.; Tassou, S.A. Waste heat recovery technologies and applications. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 6, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, E.; Luo, Y.; Simeone, A. Industrial waste heat recovery: A systematic approach. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 29, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, F.; Dobson, R.; Harms, T. Simulation of syngas from coal production plant coupled to a high temperature nuclear reactor. J. Energy South Afr. 2013, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Howaniec, N.; Smoliński, A.; Cempa-Balewicz, M. Experimental study on application of high temperature reactor excess heat in the process of coal and biomass co-gasification to hydrogen-rich gas. Energy 2015, 84, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howaniec, N.; Smoliński, A. Co-gasification of coal/sewage sludge blends to hydrogen-rich gas with the application of simulated high temperature reactor excess heat. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 8154–8158. [Google Scholar]
- Viklund, S.B.; Johansson, M.T. Technologies for utilization of industrial excess heat: Potentials for energy recovery and CO2 emission reduction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 77, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoliński, A. Coal char reactivity as a fuel selection criterion for coal-based hydrogen-rich gas production in the process of steam gasification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04502:2014-11 Węgiel Kamienny i Brunatny—Pobieranie i Przygotowanie Próbek do Badań Laboratoryjnych—Metody Podstawowe (Bituminous Coal and Lignite—Sampling and Preparation for Laboratory Tests—Basic Methods); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04560:1998 Paliwa Stałe—Oznaczanie Zawartości Wilgoci, Części Lotnych Oraz Popiołu Analizatorem Automatycznym (Solid Fuels—Determination of Moisture, Volatiles and Ash with the Application of Automatic Analyzer); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04513:1981 Paliwa Stałe—Oznaczanie Ciepła Spalania i Obliczanie Wartości Opałowej (Solid Fuels—Determination of Heat of Combustion and Calorific Value); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04535:1982 Paliwa Stałe—Oznaczanie Charakterystycznych Temperatur Topliwości Popiołu (Solid Fuels—Determination of Ash Fusion Temperatures); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04584:2001 Paliwa Stałe—Oznaczanie Zawartości Siarki Całkowitej i Popiołowej Automatycznymi Analizatorami (Solid Fuels—Determination of total Sulfur and Ash Sulfur with the Application of Automatic Analyzers); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- PCS (Polish Committee for Standardization). PN-G-04571:1998 Paliwa Stałe—Oznaczanie Zawartości Węgla, Wodoru i Azotu Automatycznymi Analizatorami—Metoda Makro (Solid Fuels—Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen Content with the Application of Automatic Analyzers); Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Components Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Massart, D.L.; Vandeginste, B.G.M.; Buydens, L.M.C.; De Jong, S.; Lewi, P.J.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J. Handbook of Chemometrics and Qualimetrics: Part A; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S. Principal Components Analysis. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1987, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | Parameter, unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moisture, %w/w | 7.4 |
| 2 | Ash, %w/w | 7.2 |
| 3 | Volatiles, %w/w | 32.4 |
| 4 | Heat of combustion, kJ/kg | 27,815 |
| 5 | Calorific value, kJ/kg | 26,626 |
| 6 | Sintering point, °C | 940 |
| 7 | Softening point, °C | 1280 |
| 8 | Melting point, °C | 1360 |
| 9 | Flow temperature, °C | 1430 |
| 10 | Sulfur, %w/w | 1.9 |
| 11 | Carbon, %w/w | 67.4 |
| 12 | Hydrogen, %w/w | 4.1 |
| 13 | Nitrogen, %w/w | 0.9 |
| No | Gasification Agent | Temperature, °C | Qg, MJ/m3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System I | System II | System III | |||
| 1 | carbon dioxide | 700 | 3.50 | 2.70 | 3.59 |
| 2 | carbon dioxide | 800 | 3.81 | 2.75 | 4.12 |
| 3 | carbon dioxide | 900 | 4.59 | 2.80 | 4.92 |
| 4 | oxygen | 700 | 6.73 | 4.88 | 6.73 |
| 5 | oxygen | 800 | 6.72 | 5.12 | 6.65 |
| 6 | oxygen | 900 | 6.80 | 5.06 | 6.78 |
| 7 | 30 vol.% carbon dioxide in oxygen | 700 | 5.70 | 4.56 | 5.77 |
| 8 | 30 vol.% carbon dioxide in oxygen | 800 | 5.97 | 4.91 | 5.87 |
| 9 | 30 vol.% carbon dioxide in oxygen | 900 | 6.17 | 4.86 | 6.26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdeb, J.; Howaniec, N.; Smoliński, A. Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Coal Gasification—An Experimental Study. Energies 2019, 12, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010140
Zdeb J, Howaniec N, Smoliński A. Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Coal Gasification—An Experimental Study. Energies. 2019; 12(1):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010140
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdeb, Janusz, Natalia Howaniec, and Adam Smoliński. 2019. "Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Coal Gasification—An Experimental Study" Energies 12, no. 1: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010140
APA StyleZdeb, J., Howaniec, N., & Smoliński, A. (2019). Utilization of Carbon Dioxide in Coal Gasification—An Experimental Study. Energies, 12(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010140






