A High-Gain Reflex-Based Bidirectional DC Charger with Efficient Energy Recycling for Low-Voltage Battery Charging-Discharging Power Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
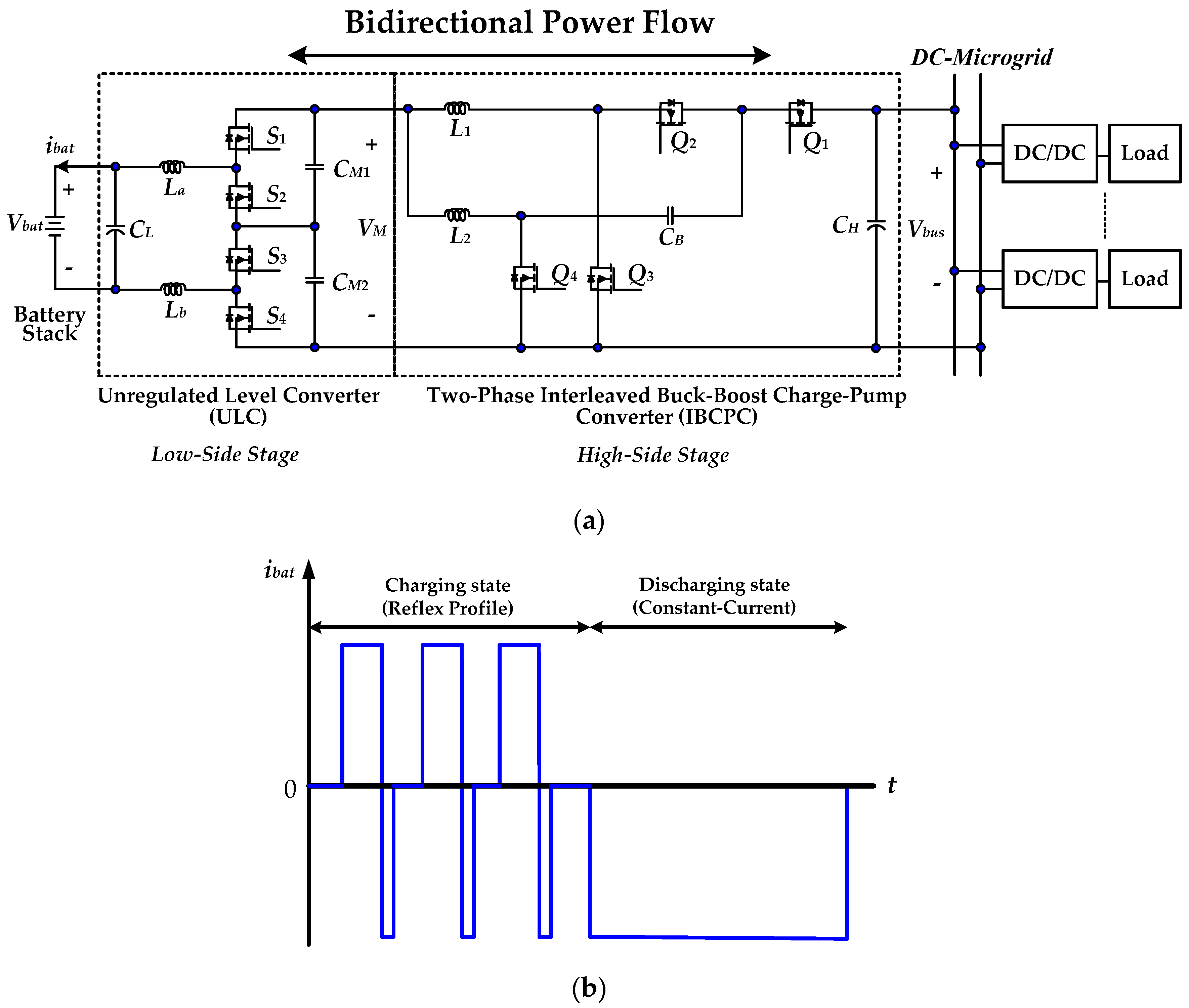
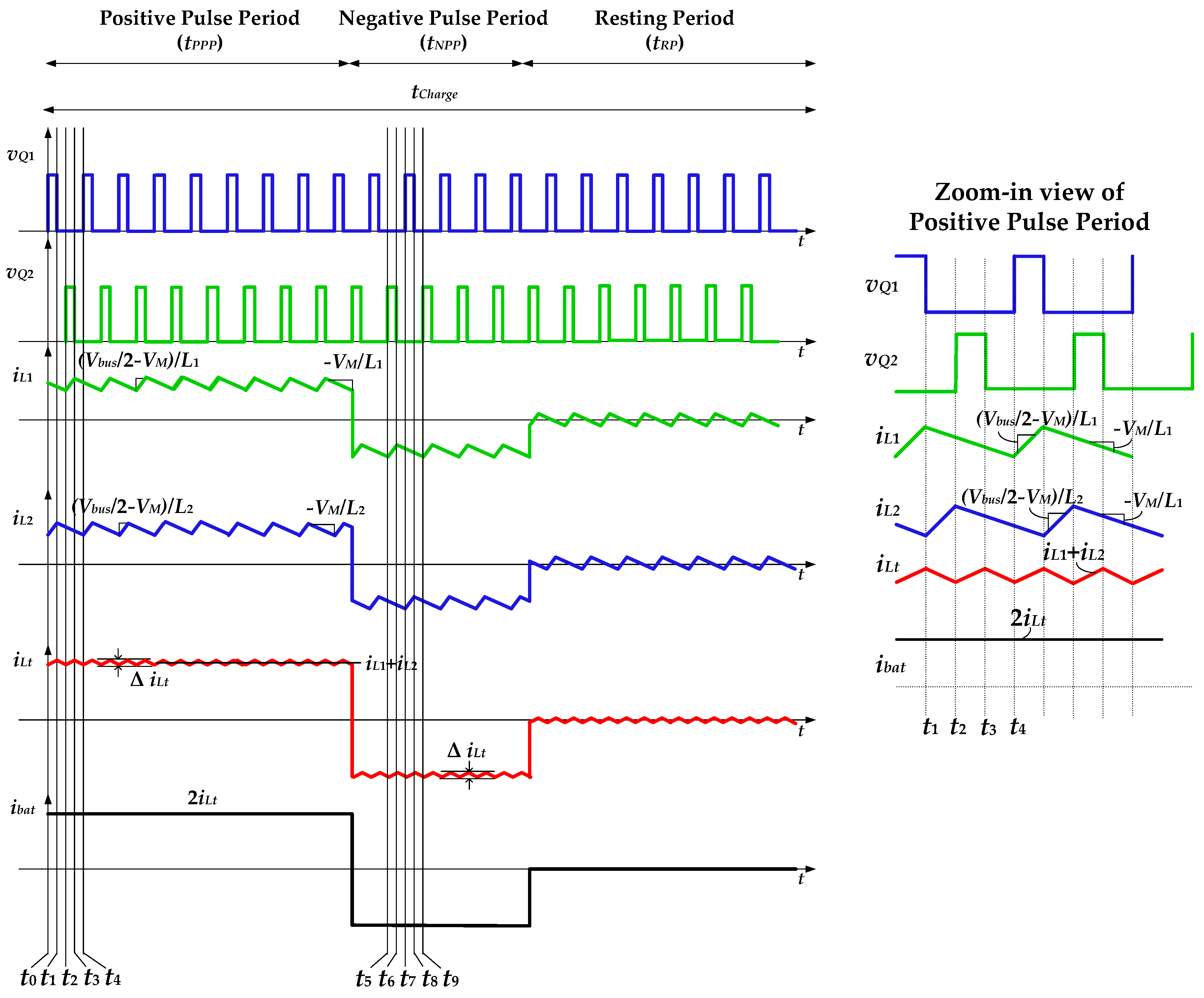
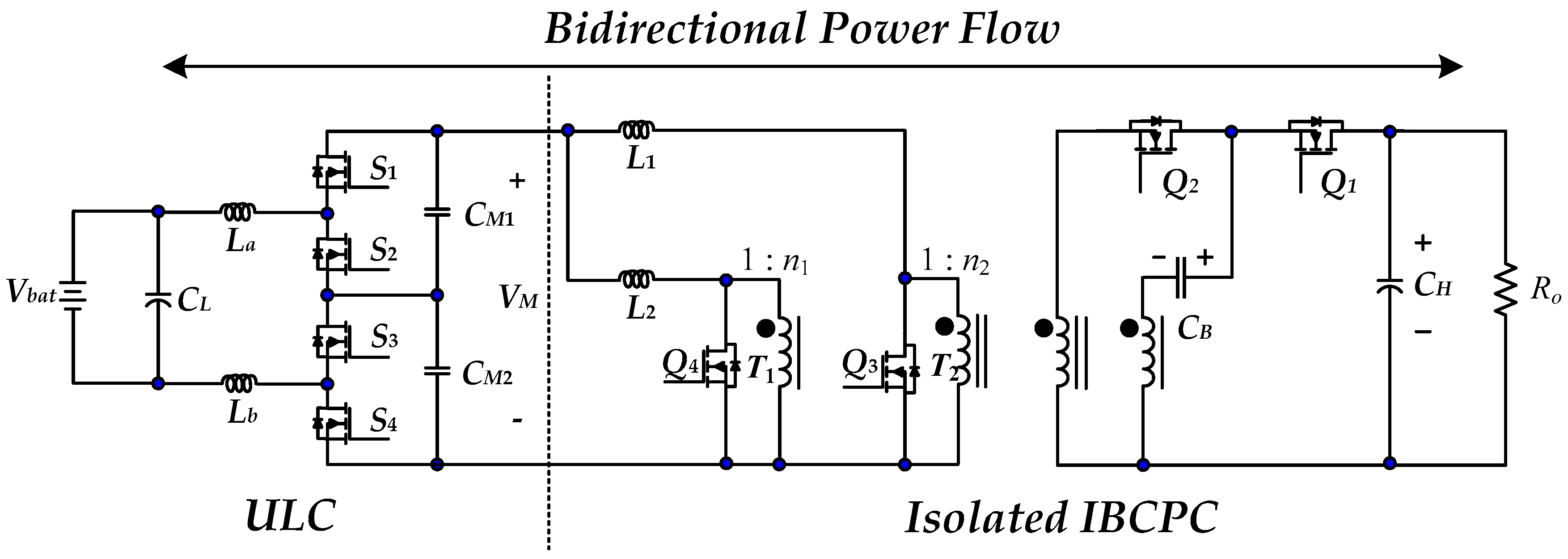
2. Operation Principles of the Proposed High-Gain RC-BDC
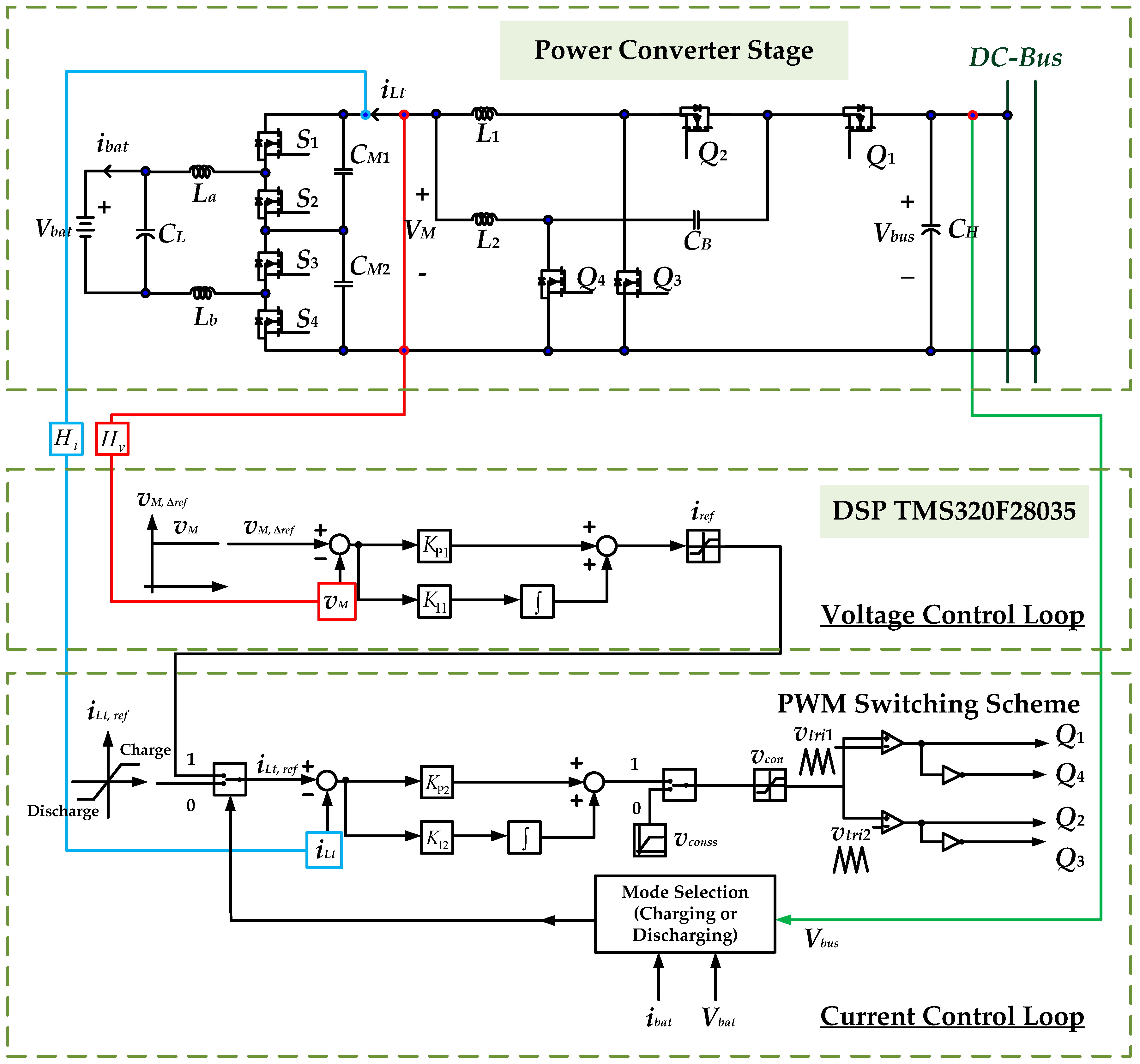
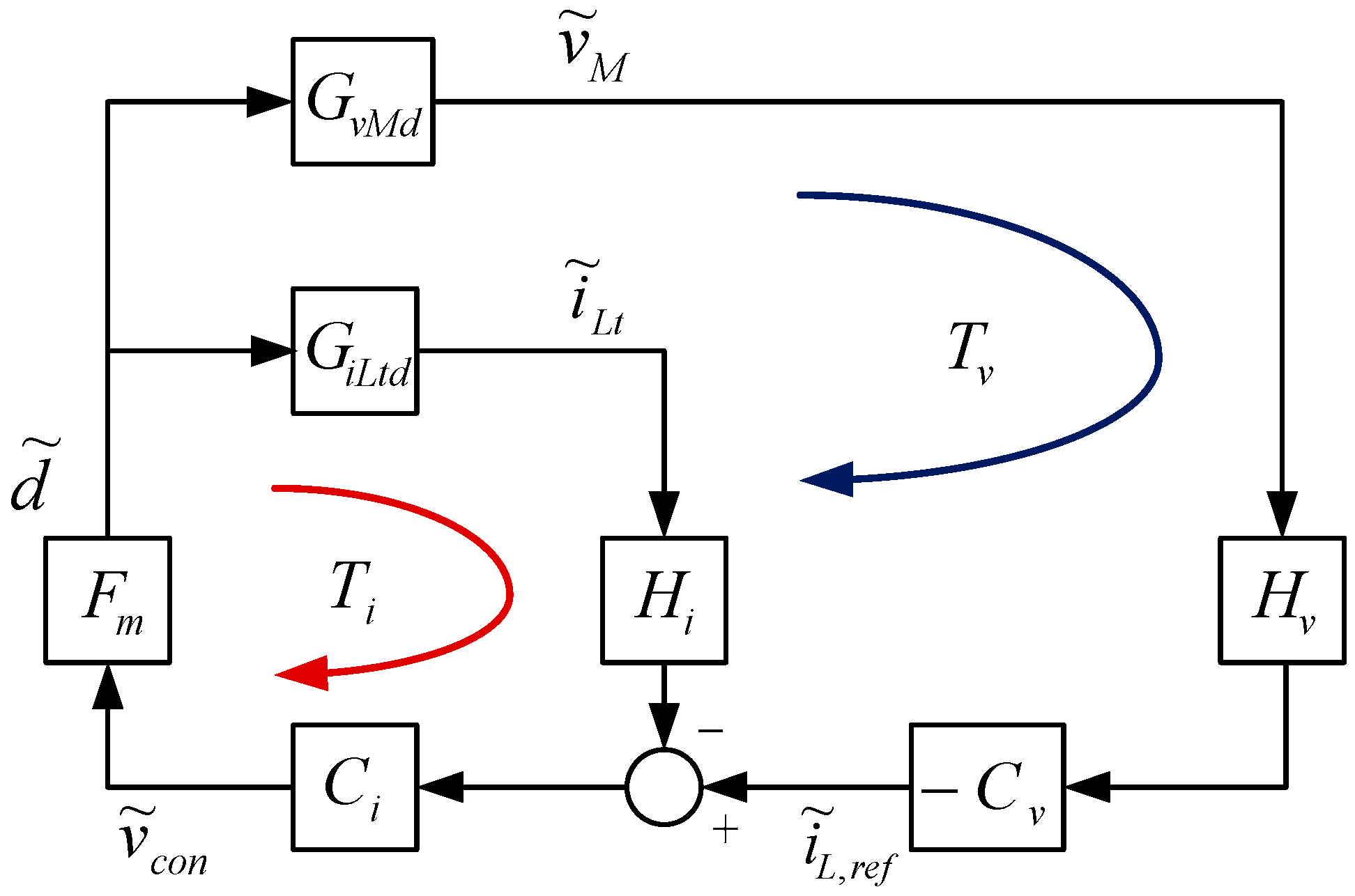
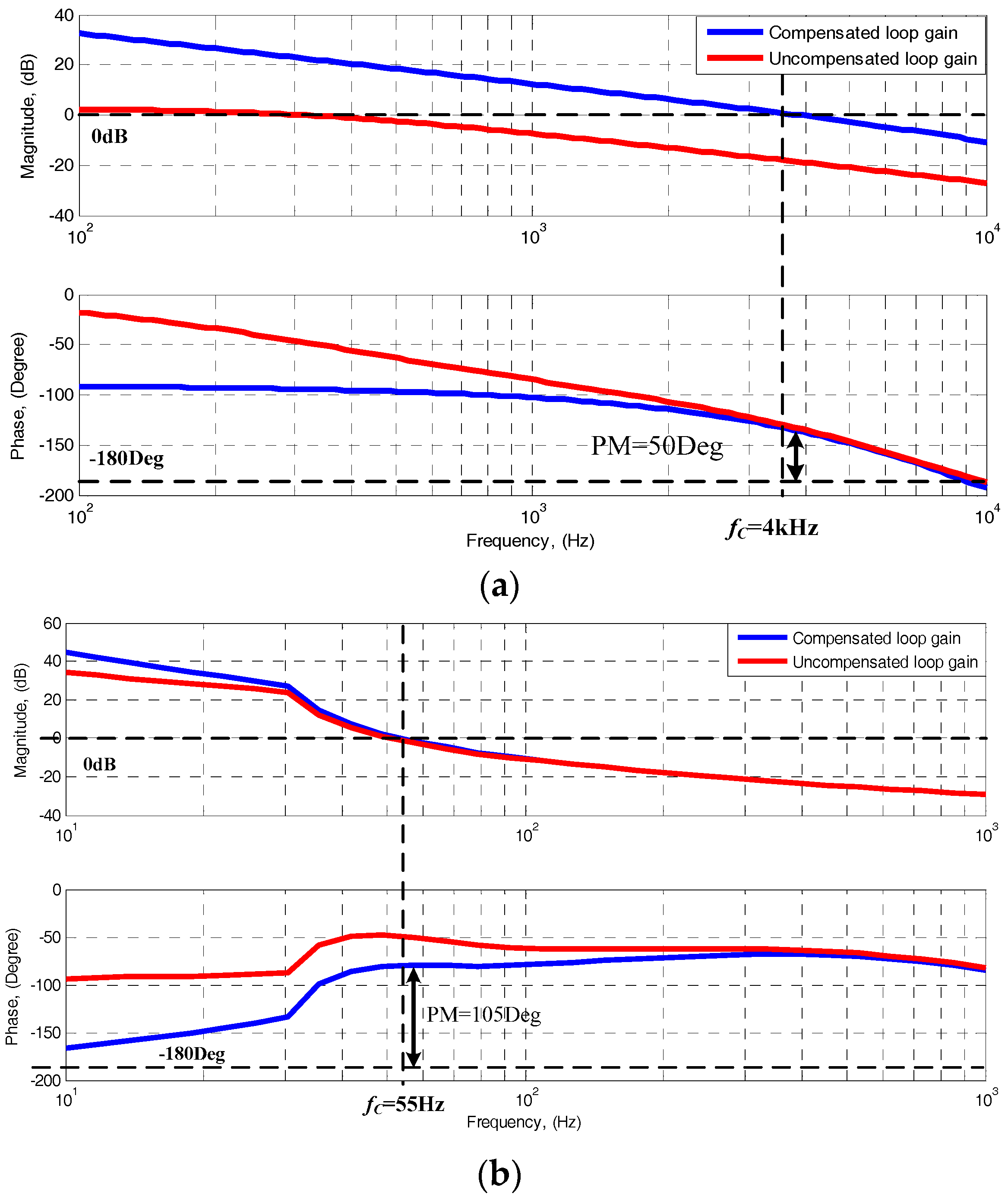
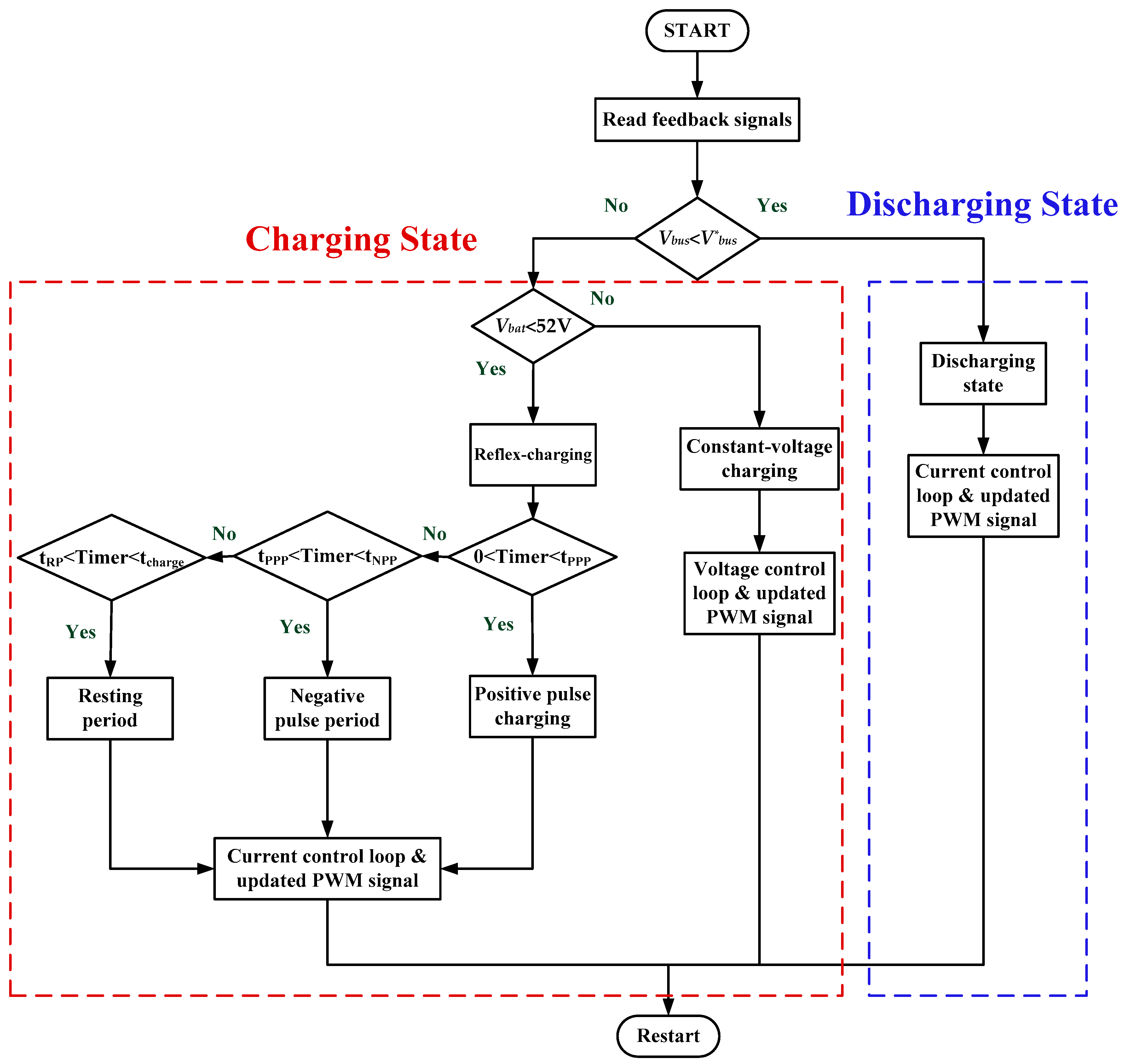
3. Controller Descriptions of the Proposed High-Gain RC-BDC
- (1)
- power switches and diodes are ideal;
- (2)
- equivalent series resistances (ESRs) of all the inductors and capacitors of the converter have precise dynamic model; and,
- (3)
- the converter works under continuous conduction mode (CCM) and ESRs (rL1 = rL2 = 180 mΩ; rCH = rCL = rCB = 60 mΩ). The circuit parameters for 500 W rating are L1 = L2 = 800 μH, CL = CH = 100 μF, CB = 10 μF.
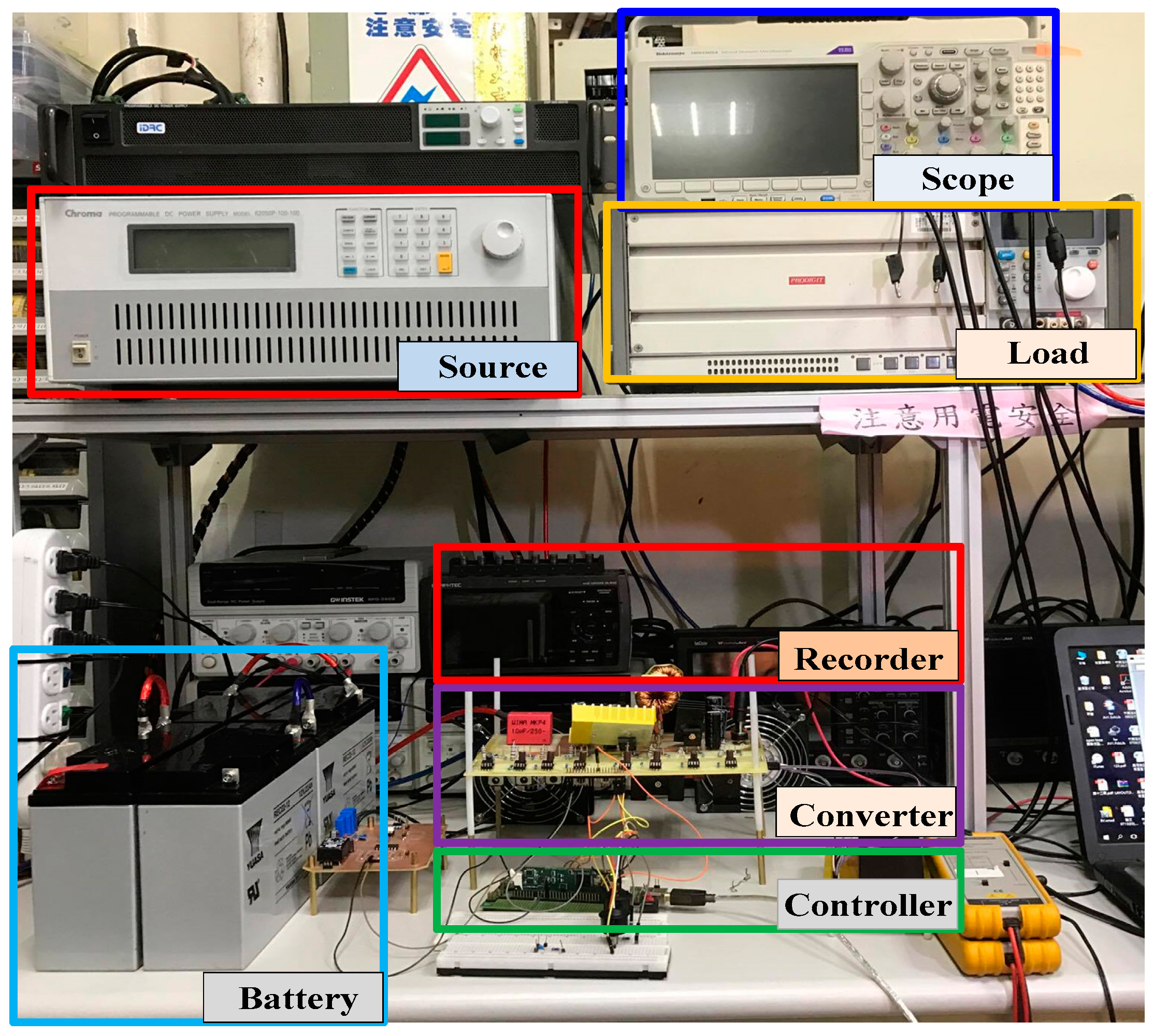
4. System Design and Implementations
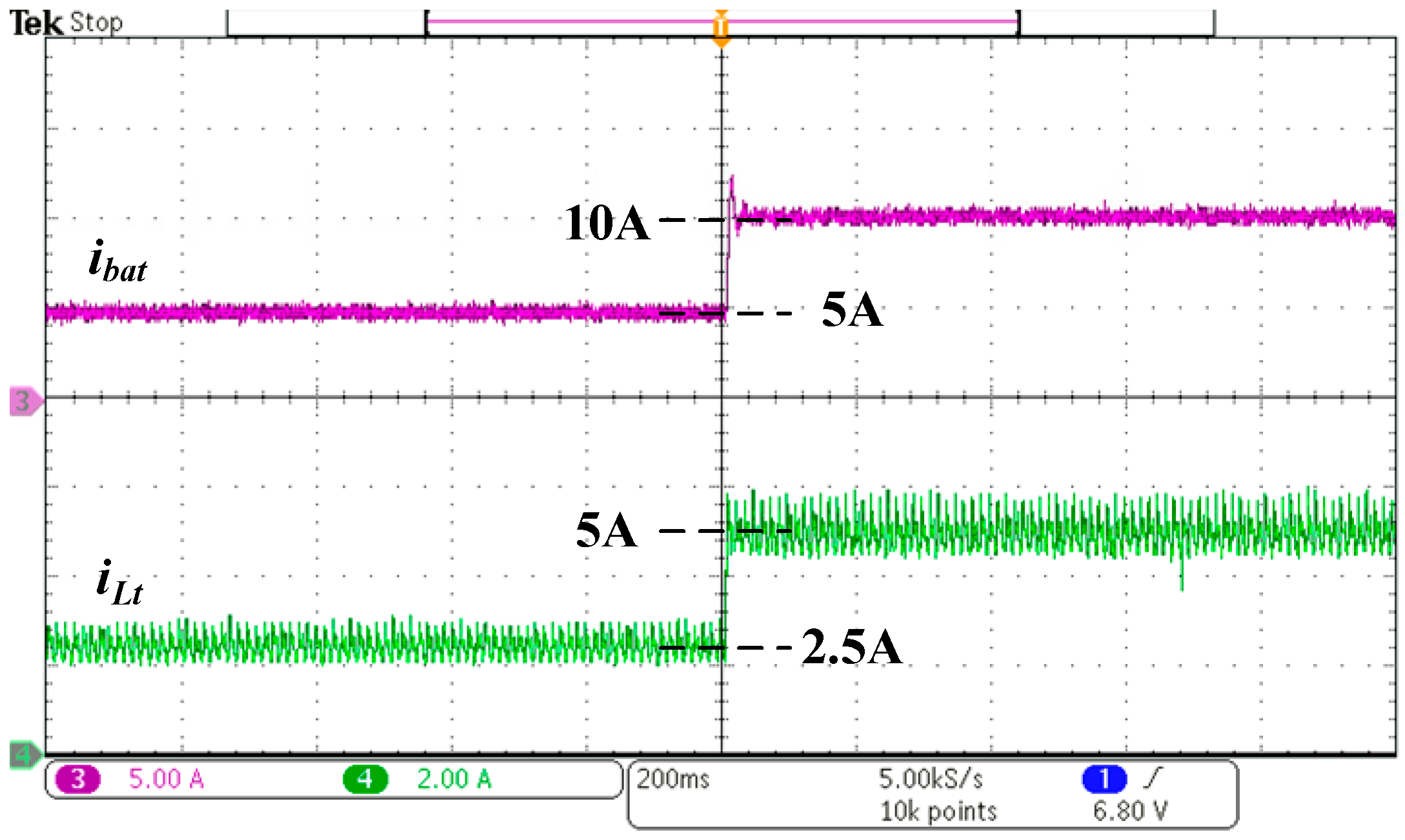
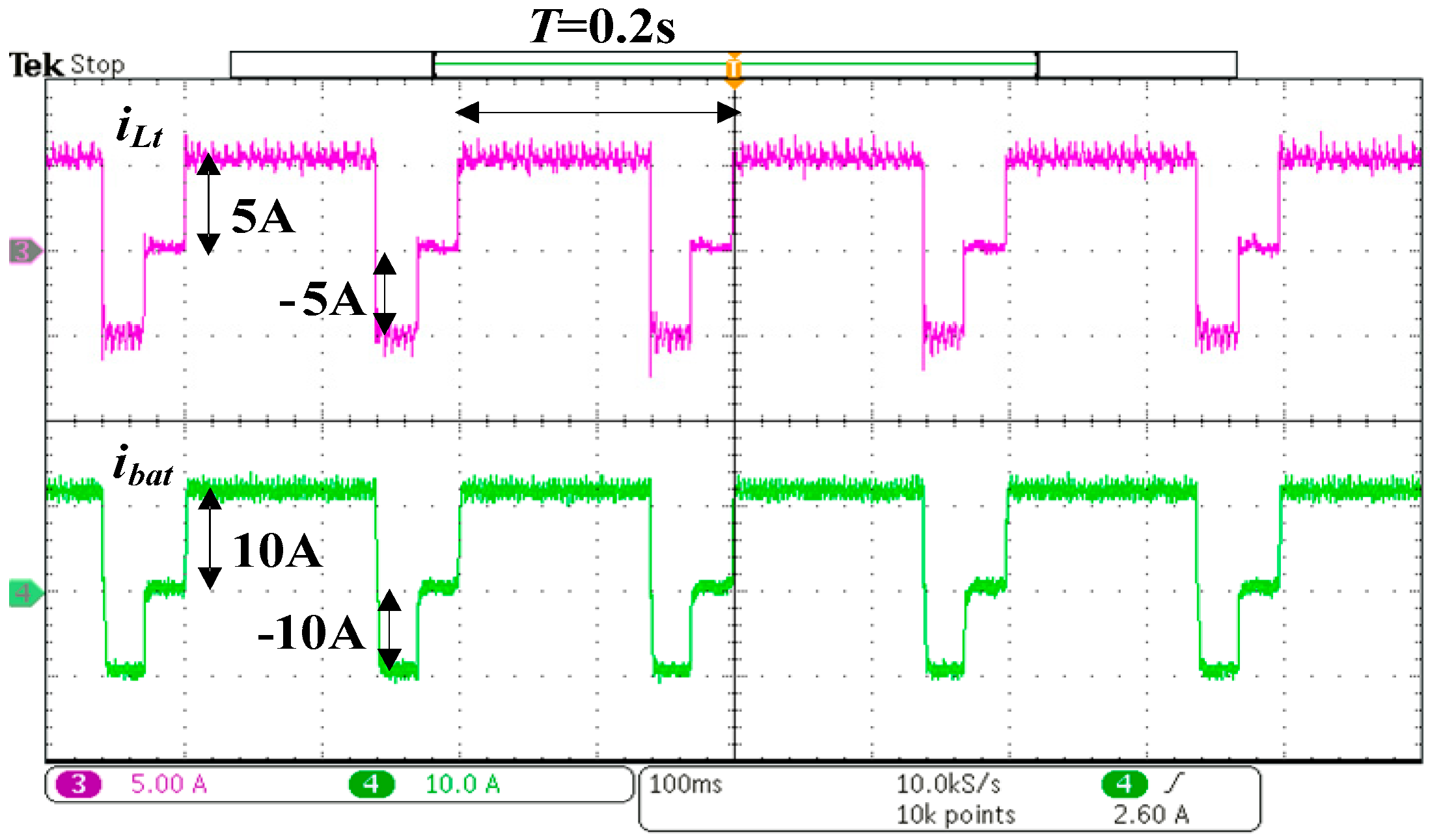
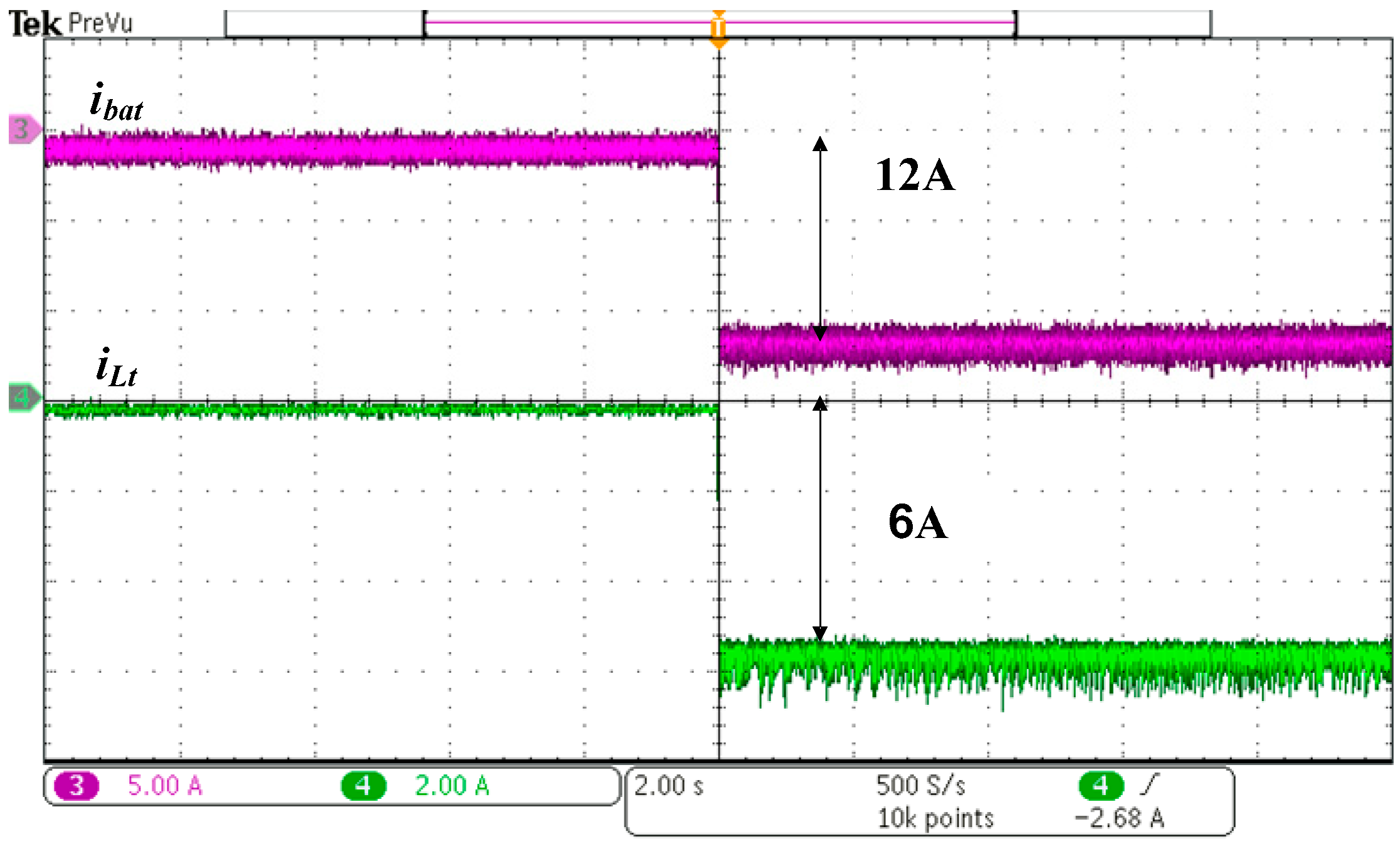
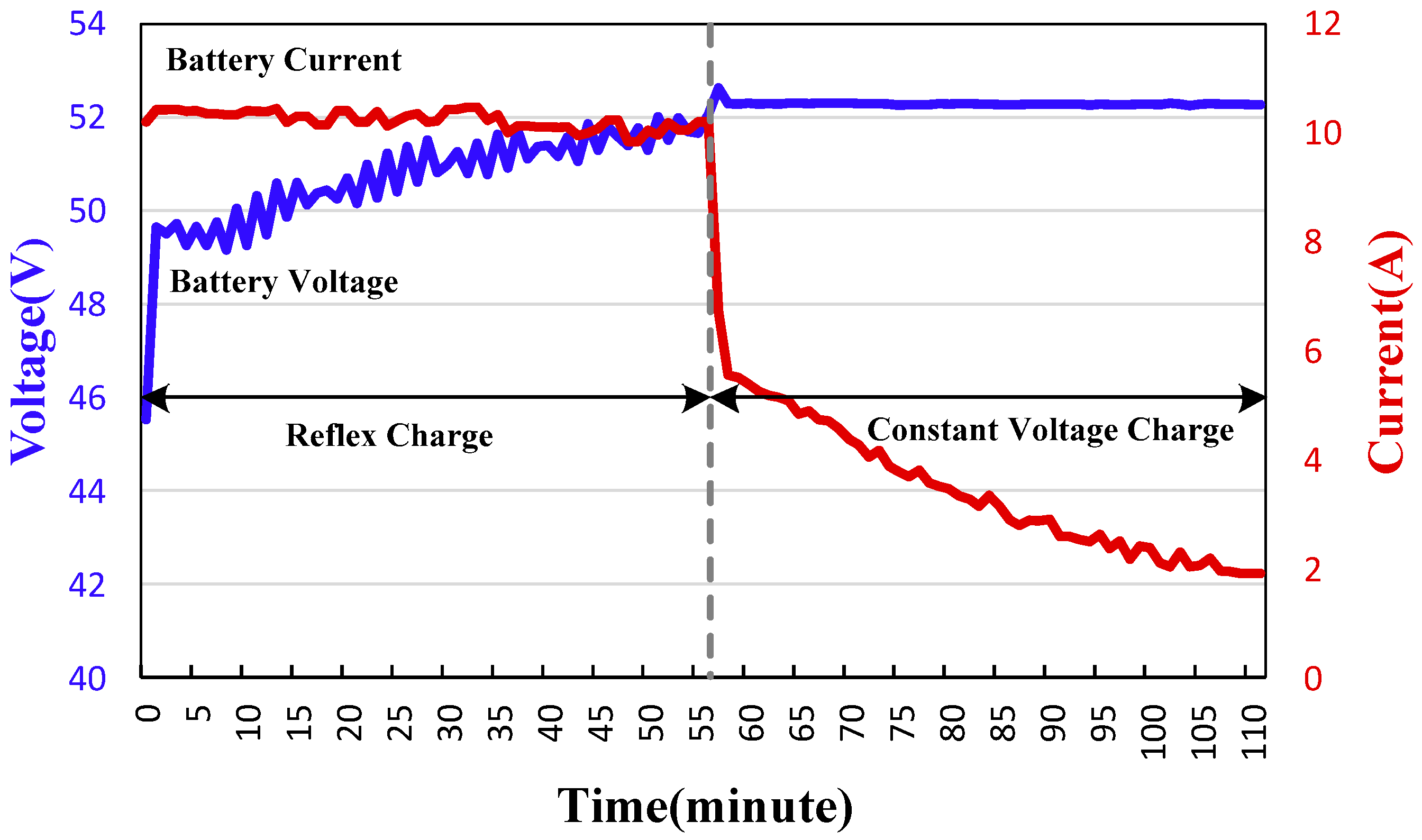
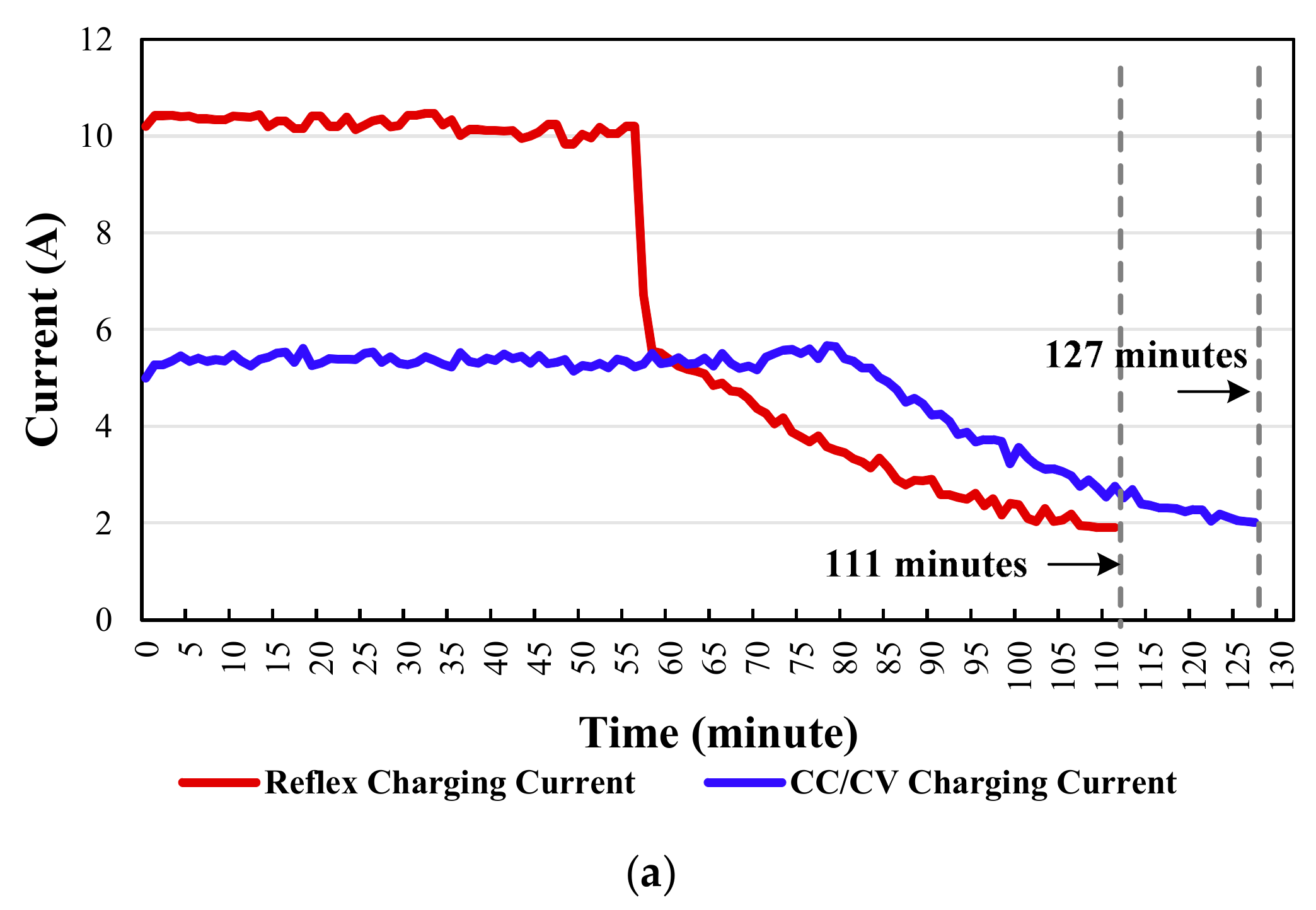
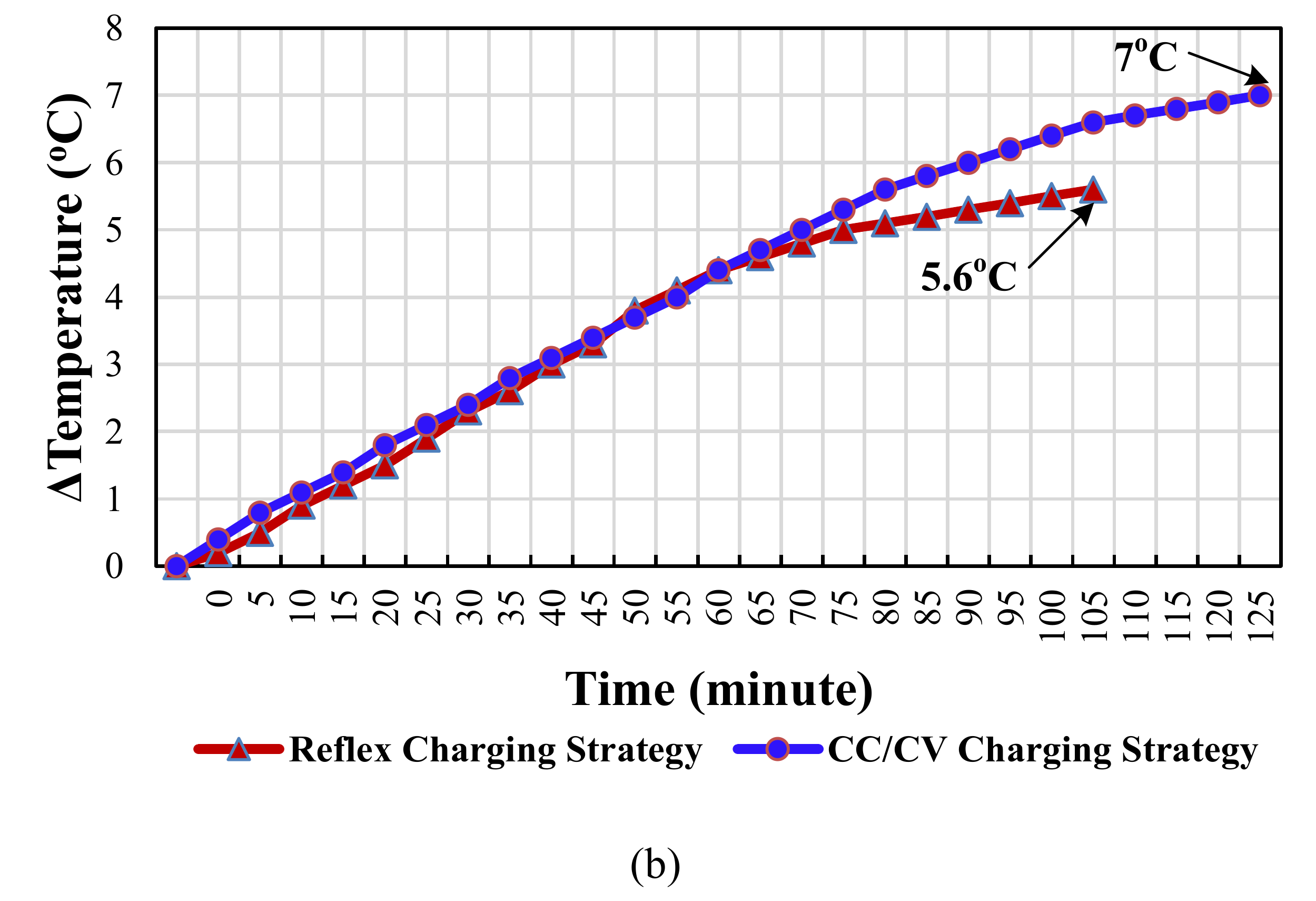
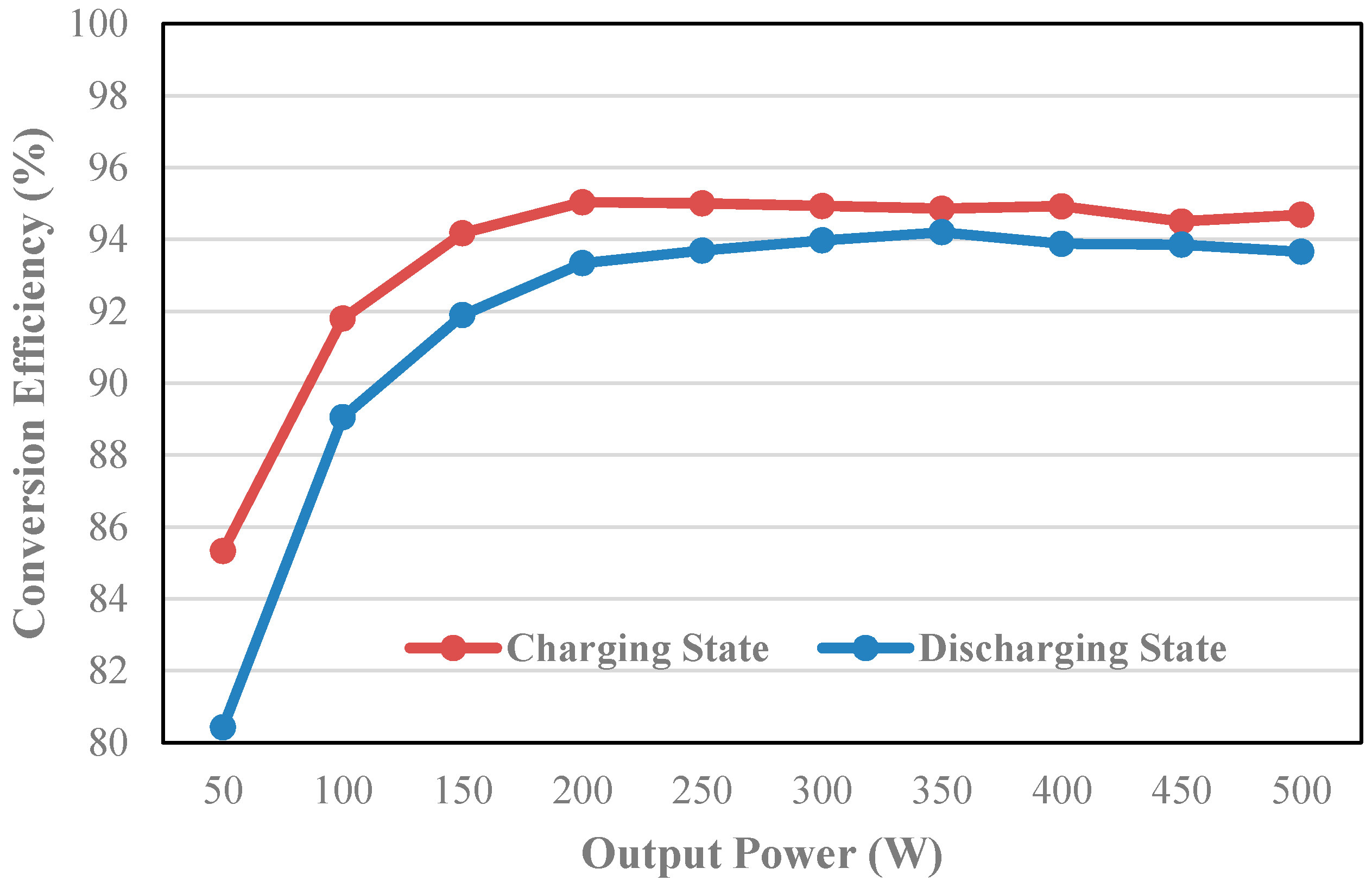
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatziargyriou, N.; Asano, H.; Iravani, R.; Marnay, C. Microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.T.; Lai, C.M.; Cheng, M.C.; Hsu, L.T. A Low Switch Voltage Stress Interleaved Boost Converter for Power Factor Correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–5 November 2009; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.M.; Pan, C.T.; Cheng, M.C. High-efficiency modular high step-up interleaved boost converter for dc-microgrid applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, U.C.; Mahajan, S.M. Real-time management of power systems with V2G facility for smart-grid applications. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Krein, P.T. Review of the impact of vehicle-to-grid technologies on distribution systems and utility interfaces. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5673–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Bialasiewicz, J.T.; Galván, E.; Guisado, R.C.P.; Prats, M.Á.M.; Leon, J.I.; Moreno-Alfonso, N. Power-electronic systems for the grid integration of renewable energy sources: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Zhelev, T.; Hemmes, K.; Monmasson, E.; Jemei, S.; Comech, M.P.; Granadino, R.; Frau, J.I. Distributed generation: Toward a new energy paradigm. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2010, 4, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.T.; Lai, C.M.; Cheng, M.C. A novel integrated single-phase inverter with auxiliary step-up circuit for low-voltage alternative energy source applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Gajanayake, C.J.; Loh, P.C. Modulation and control of three-phase paralleled Z-source inverters for distributed generation applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.D.; Kang, J.W. A single-phase battery charger design for LEV based on DC-SRC with resonant valley-fill circuit. IEEE Trans Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, D.S. Study and implementation of a two-phase interleaved bidirectional DC/DC converter for vehicle and dc-microgrid systems. Energies 2015, 8, 9969–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.W.; Liaw, C.M. Incorporated operation control of DC microgrid and electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Hung, Y.C.; Hwang, J.C.; Chang, I.P.; Tsai, M.T. Digital signal processor-based probabilistic fuzzy neural network control of in-wheel motor drive for light electric vehicle. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.L.; Chuang, Y.C.; Kang, M.S.; Wu, Y.K.; Lai, C.M.; Yu, C.C. Solar Power Battery Charger with a Parallel-Load Resonant Converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–13 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.J.; Wen, T.; Tseng, K.C.; Chen, J.F. Implementation of a regenerative pulse charger using hybrid buck-boost converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Denpasar, Indonesia, 25 October 2001; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, C.C.; Lin, M.Y. A study of charging control of lead-acid battery for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Cholula, Puebla, Mexico, 4–8 December 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.R.; Chu, N.Y.; Wang, C.S.; Liang, R.H. Design of a reflex-based bidirectional converter with the energy recovery function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3022–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.W.; Yang, M.J.; Shyu, K.K.; Lai, C.M. Design Fuzzy SOC Estimation for Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries of Electric Vehicle in ReflexTM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Vigo, Spain, 4–7 June 2007; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.T.; Kuo, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.P.; Hsieh, C.T. A Reflex Charger with ZVS and Non-Dissipative Cells for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion. Energies 2015, 8, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M. Development of a novel bidirectional DC/DC converter topology with high voltage conversion ratio for electric vehicles and DC-microgrids. Energies 2016, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M.; Cheng, Y.H.; Li, Y.S.; Li, J.T.; Lin, Y.C. A Reflex-Charging Based Bidirectional DC Charger for Light Electric Vehicle and DC-Microgrid. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference, Penang, Malaysia, 5–8 November 2017; pp. 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Micro Hybrid & Hybrid Vehicles Explained-Yuasa. Available online: https://www.yuasa.co.uk/info/technical/micro-hybrid-hybrid-vehicles-explained (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- Schaeck, S.; Stoermer, A.O.; Hockgeiger, E. Micro-hybrid electric vehicle application of valve-regulated lead-acid batteries in absorbent glass mat technology: Testing a partial-state-of-charge operation strategy. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenciano, J.; Fernndez, M.; Trinidad, F.; Sanz, L. Lead-acid batteries for micro- and mild-hybrid applications. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.R. A design of an optimal battery pulse charge system by frequency-varied technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Yau, H.T.; Lu, J.H. Chaos embedded particle swarm optimization algorithm-based solar optimal ReflexTM frequency charge. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2015, 13, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Rong, Y.; Li, Z.; Fantao, L. Study on the Optimal Charring Method for Lithium-ion Batteries Used in Electric Vehicles. Energy Procedia 2016, 88, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Specifications | |
| VH (DC-bus Voltage) | 380–410 V |
| VL (Battery Voltage) | 44–56 V Nominal: 48 V (four 12 V cells in series) |
| Power rating | Po: 500-W |
| Switching frequency | fs: 20 kHz |
| Parameters | |
| Capacitors | CH = CL = 400 μF, CM1 = CM2 = 100 μF, CB = 10 = 0 μF; |
| Inductors | L1 = L2 = Ls = 800 μH; La = Lb = 1.5 μH |
| MOSFET | S1–S4: IXFH160N15T2, Q1–Q4: W25NM60 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-M.; Li, Y.-H.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Teh, J. A High-Gain Reflex-Based Bidirectional DC Charger with Efficient Energy Recycling for Low-Voltage Battery Charging-Discharging Power Control. Energies 2018, 11, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030623
Lai C-M, Li Y-H, Cheng Y-H, Teh J. A High-Gain Reflex-Based Bidirectional DC Charger with Efficient Energy Recycling for Low-Voltage Battery Charging-Discharging Power Control. Energies. 2018; 11(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030623
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Ching-Ming, Yun-Hsiu Li, Yu-Huei Cheng, and Jiashen Teh. 2018. "A High-Gain Reflex-Based Bidirectional DC Charger with Efficient Energy Recycling for Low-Voltage Battery Charging-Discharging Power Control" Energies 11, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030623
APA StyleLai, C.-M., Li, Y.-H., Cheng, Y.-H., & Teh, J. (2018). A High-Gain Reflex-Based Bidirectional DC Charger with Efficient Energy Recycling for Low-Voltage Battery Charging-Discharging Power Control. Energies, 11(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030623








