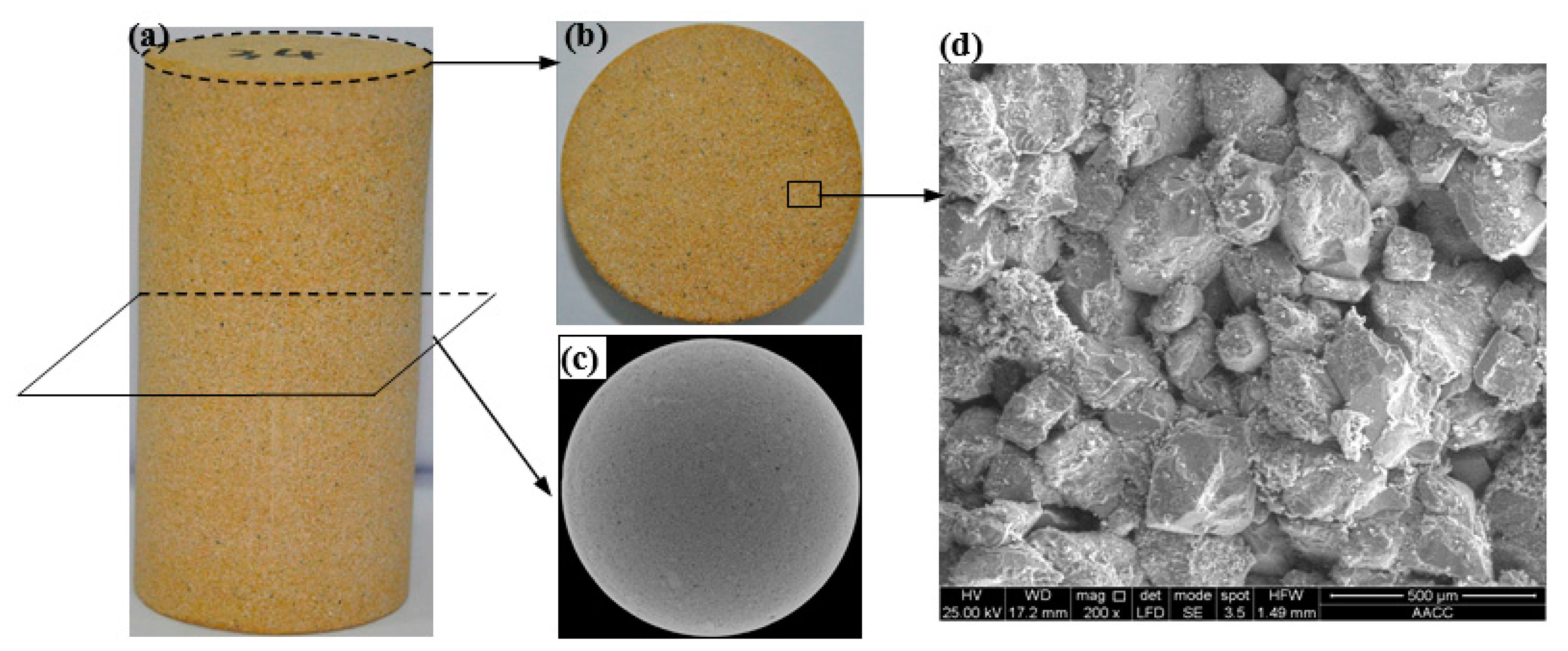
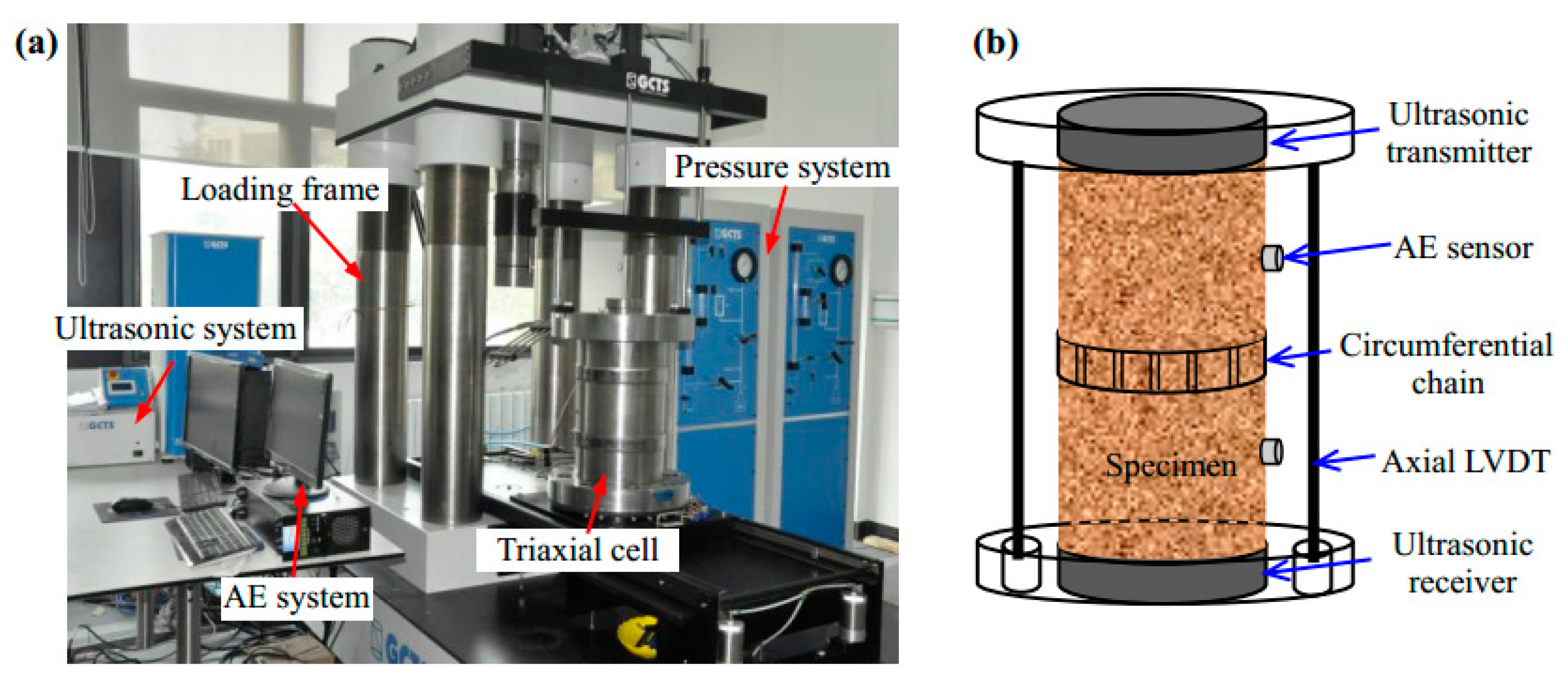
3.1. Mechanical Properties
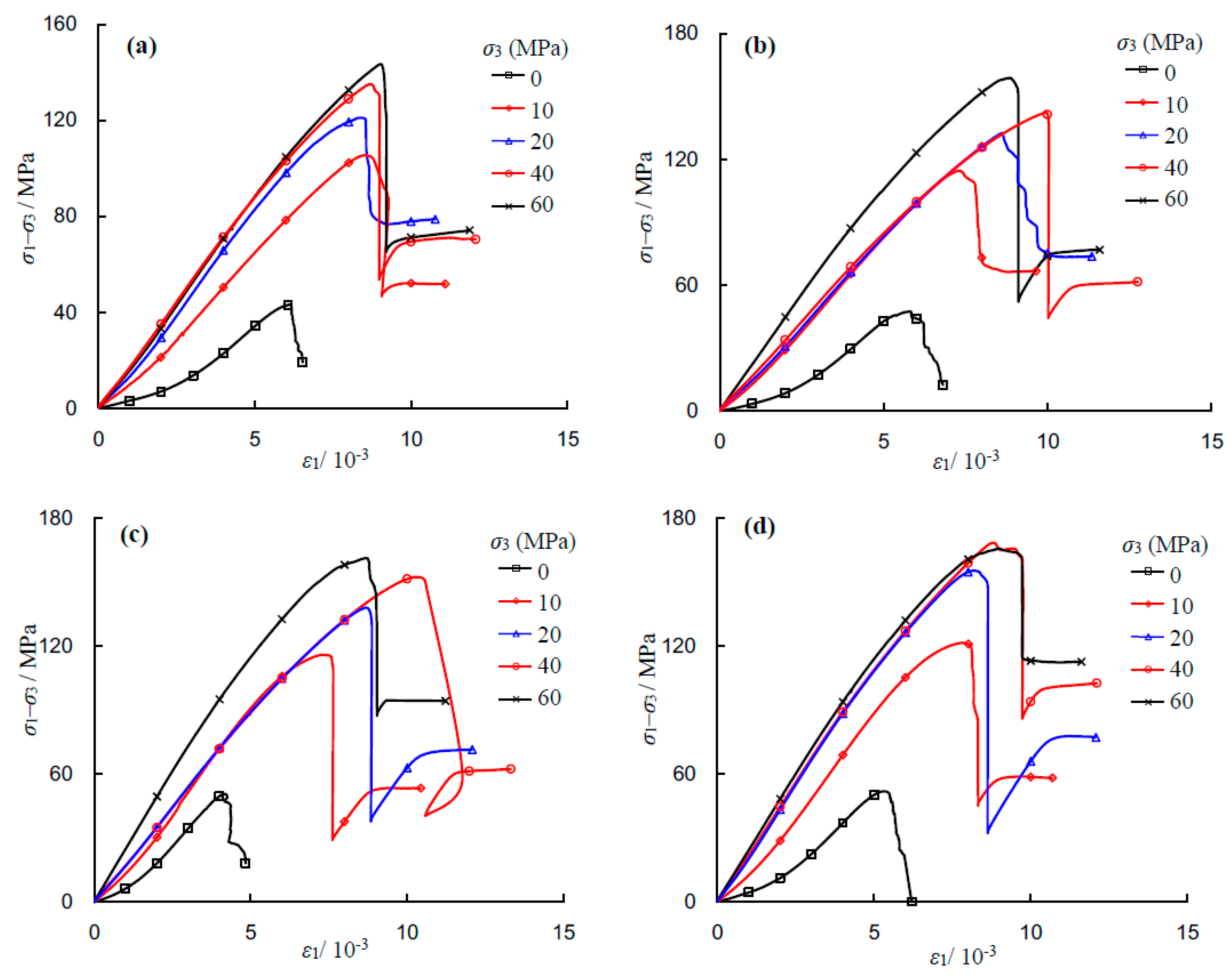
Figure 5 shows the axial deviatoric stress–strain curves of the saturated sandstone specimens under conventional triaxial compression. As seen from
Figure 5, the NaCl concentration and confining pressure affect the stress–strain response and can be summarized as follows. (1) Under uniaxial compression (i.e.,
σ3 = 0 MPa), the sandstone specimen firstly undergoes initial compression, then elastic deformation, nonlinear deformation, and post-peak failure. However, under triaxial compression, besides those above stages, there is a residual strength stage. This finding is similar to those from previous studies [
11,
20]; (2) The characteristics of the post-peak curve depend upon the applied confining pressure. Under low confining pressures (e.g., 0, 10 and 20 MPa) multiple stress drops can be observed. However, under relatively high confining pressures (e.g., 40 and 60 MPa), the curve drops abruptly, which is typical of brittle failure. The brittleness of the sandstone increases with the increase of confining pressure regardless of NaCl concentration values; (3) The mechanical parameters, such as peak compressive strength and elastic modulus, are greatly influenced by NaCl concentration and confining pressure, which will be analyzed in the following section.
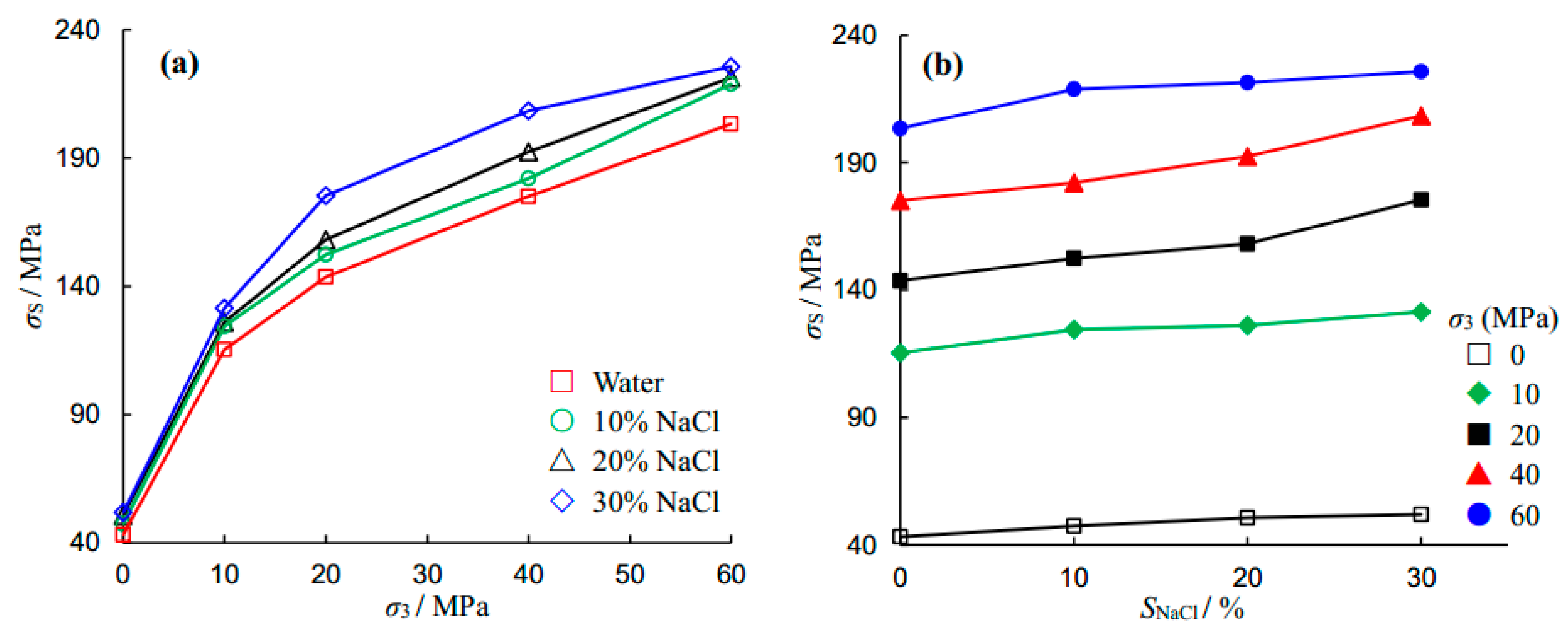
The effects of confining pressure and NaCl concentration on the triaxial compressive strength of a sandstone specimen are shown in
Figure 6. It is clear from
Figure 6a that as the confining pressure increases, the peak strength increases, regardless of saturation conditions. The relationship between peak strength and confining pressure shows nonlinear characteristics and is dependent upon both the confining pressure and NaCl concentration values. Under low confining pressures all four curves are nonlinear. This perhaps results from the low strength of sandstone under uniaxial compression. Similar experimental results have been reported in Rathnaweera et al. [
12] in which a series of conventional triaxial compression tests were conducted at confining pressures of 0–20 MPa. The study reported that when the NaCl concentration was relatively high (i.e., 20 wt % and 30 wt %), the strength envelope was non-linear; without considering uniaxial compressive strength (UCS). However, in the present study much higher confining pressures than this were also taken into account. In the range of 20–60 MPa confining pressures, the curves of NaCl concentrations of 0%, 10% and 20% appear linear. However, NaCl-saturated sandstone specimens at 30% NaCl concentration exhibit non-linear responses, which is perhaps due to a significant increase in local NaCl crystallization, as indicated in
Figure 3.
It can be seen from
Figure 6b that the triaxial compressive strength of the sandstone specimen increases with NaCl concentration. For example, under unconfined compression, the UCS increases from 43.24 MPa to 47.33 MPa and 50.67 MPa to 51.83 MPa, when the NaCl concentration is increased from 0% to 10% and 20% to 30%, respectively. This implies that the maximum increase in peak strength is 19.86%, when the NaCl concentration increases from 0% to 30%. Under triaxial compression, the corresponding increments are 13.94%, 20.07%, 19.05% and 10.97% for
σ3 = 10, 20, 40 and 60 MPa. The above analysis indicates that the NaCl solution strengthens the sandstone significantly.
The crack damage threshold (
σcd) is axial deviatoric stress when the volumetric strain switches from compaction to dilation [
13,
21,
22].
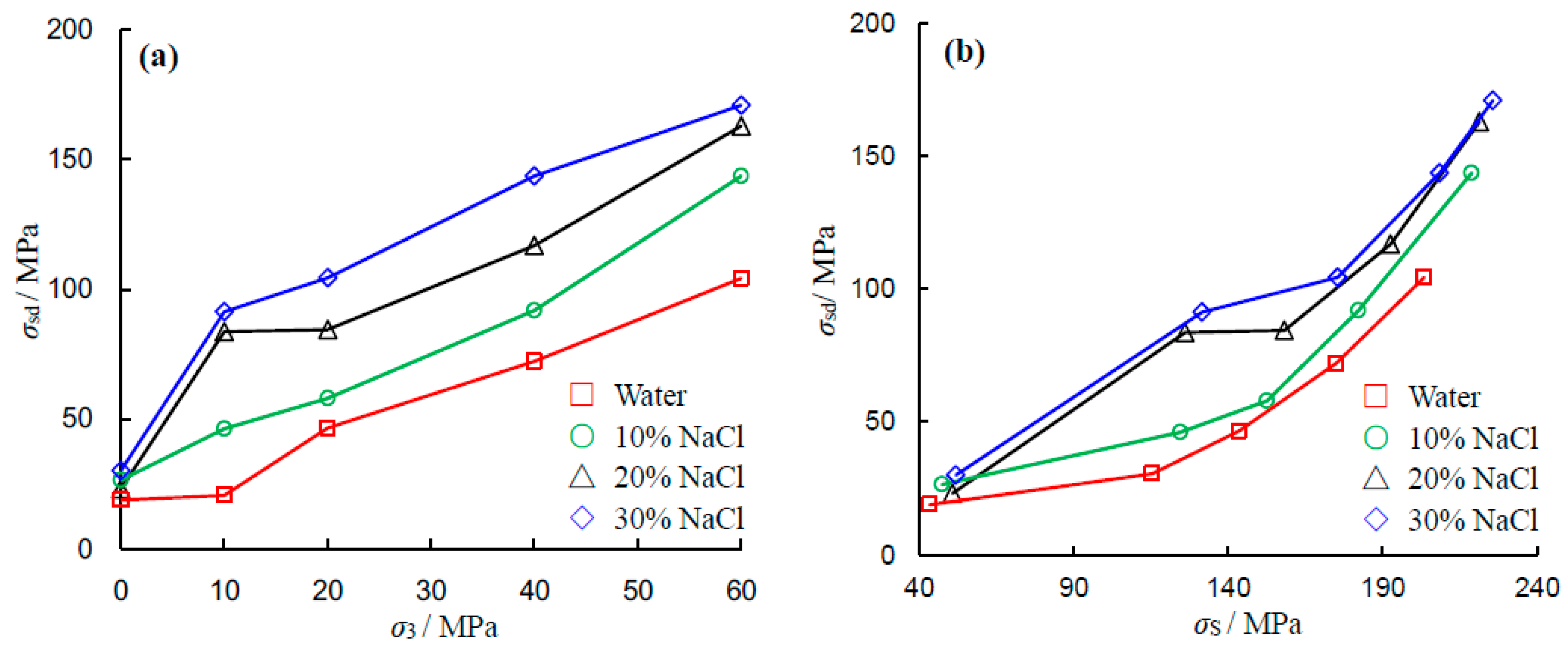
Figure 7a depicts the influence of confining pressure and NaCl concentration on the crack damage threshold of the sandstone specimen. As the confining pressure and the NaCl concentration increase, the crack damage threshold increases. The change trend of the crack damage threshold is similar to that of peak strength. Under low confining pressures, NaCl-saturated sandstone specimens exhibit non-linear responses. However, under high confining pressures, the crack damage threshold is linearly related to the confining pressure.
The crack damage threshold versus the corresponding triaxial compressive strength is displayed in
Figure 7b. As the triaxial compressive strength increases, the crack damage threshold of sandstone also increases. In other words, the increase in crack damage strength is greater than the increase in triaxial compressive strength along with the confining pressure.
Although the strength of the sandstone specimen shows a nonlinear response to the confining pressure, the Mohr–Coulomb criterion was used to analyze the evolution of cohesion and internal friction angle. The Mohr–Coulomb criterion can be expressed as the following equation [
23]:
where
σ3 is the UCS,
q is an influence coefficient of
σ3 on
σS,
C is the cohesion, and
ϕ is the internal friction angle.
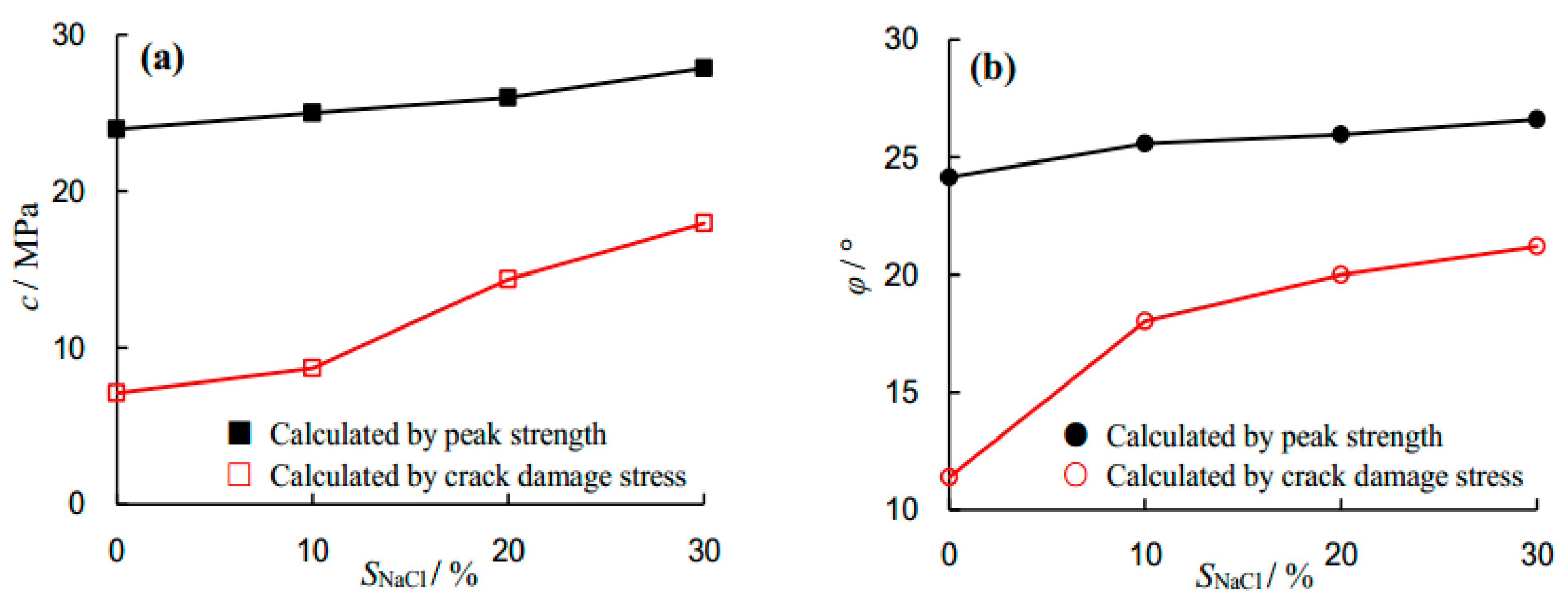
The calculated cohesion and internal friction angle results are presented in
Figure 8. As can be seen from
Figure 8a, the cohesions calculated by peak strength and crack damage threshold increase with increasing NaCl concentration. The cohesions calculated by peak strength were 23.99, 25.03, 25.99 and 27.88 MPa for the 0, 10%, 20% and 30% NaCl-saturated sandstone specimens, respectively. This indicates that the increment of cohesion calculated by peak strength is 16.22%, when the NaCl concentration increases from zero to 30%. However, the increment of cohesion calculated by crack damage threshold was 152.44%.
As can be seen from
Figure 8b, as the NaCl concentration increases, the internal friction angles calculated by peak strength and crack damage threshold also increase. The evolution of the internal friction angle is similar to that of cohesion. The internal friction angles calculated by peak strength were 24.15°, 25.59°, 25.99° and 26.62° for the 0, 10%, 20% and 30% NaCl-saturated sandstone specimens, respectively. A total increment of 10.22% in internal friction angle calculated by peak strength was observed by increasing the NaCl concentration from zero to 30%. However, the increment of internal friction angle calculated by crack damage threshold was 86.55%. The observation of cohesion and internal friction angle can be explained as follows. In distilled-water-saturated specimens, the irregular boundaries among grains become smoother due to frictional abrasion. Moreover, during the loading process, the lubricating effect of water reduces the inter-particle friction. However, in brine-saturated specimens, NaCl depositions in the pore structure of rock appear to enhance the inter-particle friction and the enhancement effect increases with the increase of salinity level.
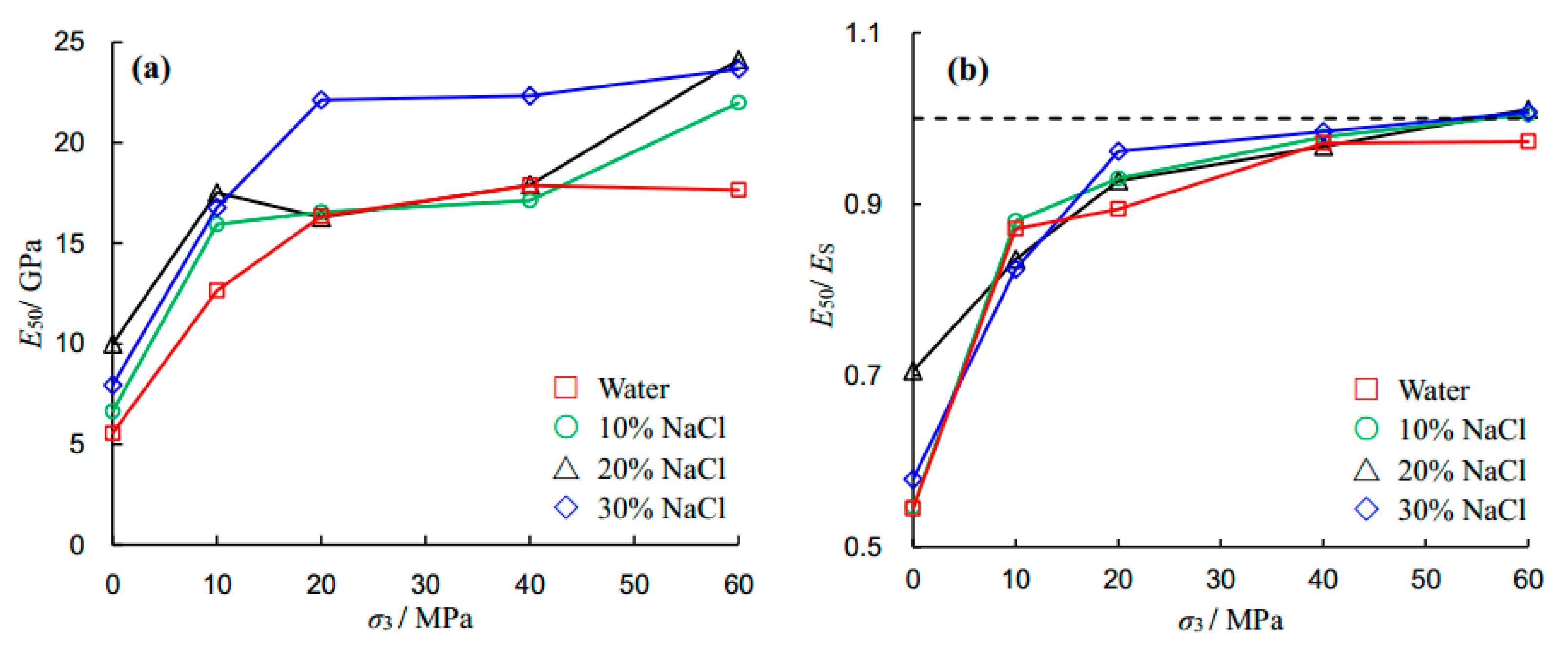
Figure 9 depicts the effects of salinity and confining pressure on the Young’s modulus of the sandstone specimen under triaxial compression. The elastic modulus (
ES) was determined from the linear component of the stress–strain curves, and the deformation modulus (
E50) was calculated from the slope between zero and 50% peak strength. It is clear that the deformation modulus increases with increasing confining pressure. For example, the deformation moduli for 30% NaCl-saturated sandstone specimens under confining pressures of 0, 10, 20, 40 and 60 MPa were 7.94, 16.78, 22.14, 22.33 and 23.66 GPa, respectively. The deformation modulus increased as
σ3 increased from 0 to 20 MPa. However, they remained relatively constant as
σ3 increased from 20 to 60 MPa. Overall, the deformation modulus of the sandstone specimen increased with increasing salinity.
Further, to compare the elastic modulus and deformation modulus, the
E50 to
ES ratio was plotted against the confining pressure, as shown in
Figure 9b. As the confining pressure increases from zero to 60 MPa, the value of
E50 to
ES varies from 0.54 to 0.97 under water saturation, 0.55 to 1.00 under 10% salinity level, 0.71 to 1.01 at 20% salinity, and 0.58 to 1.01 at 30% salinity. The
E50 to
ES ratio demonstrates that it increases with confining pressure, which results in the tested sandstone specimens exhibiting nonlinear behavior at the initial stage under a relatively low confining pressure (see
Figure 5).
3.2. Ultrasonic Velocity and AE Behavior
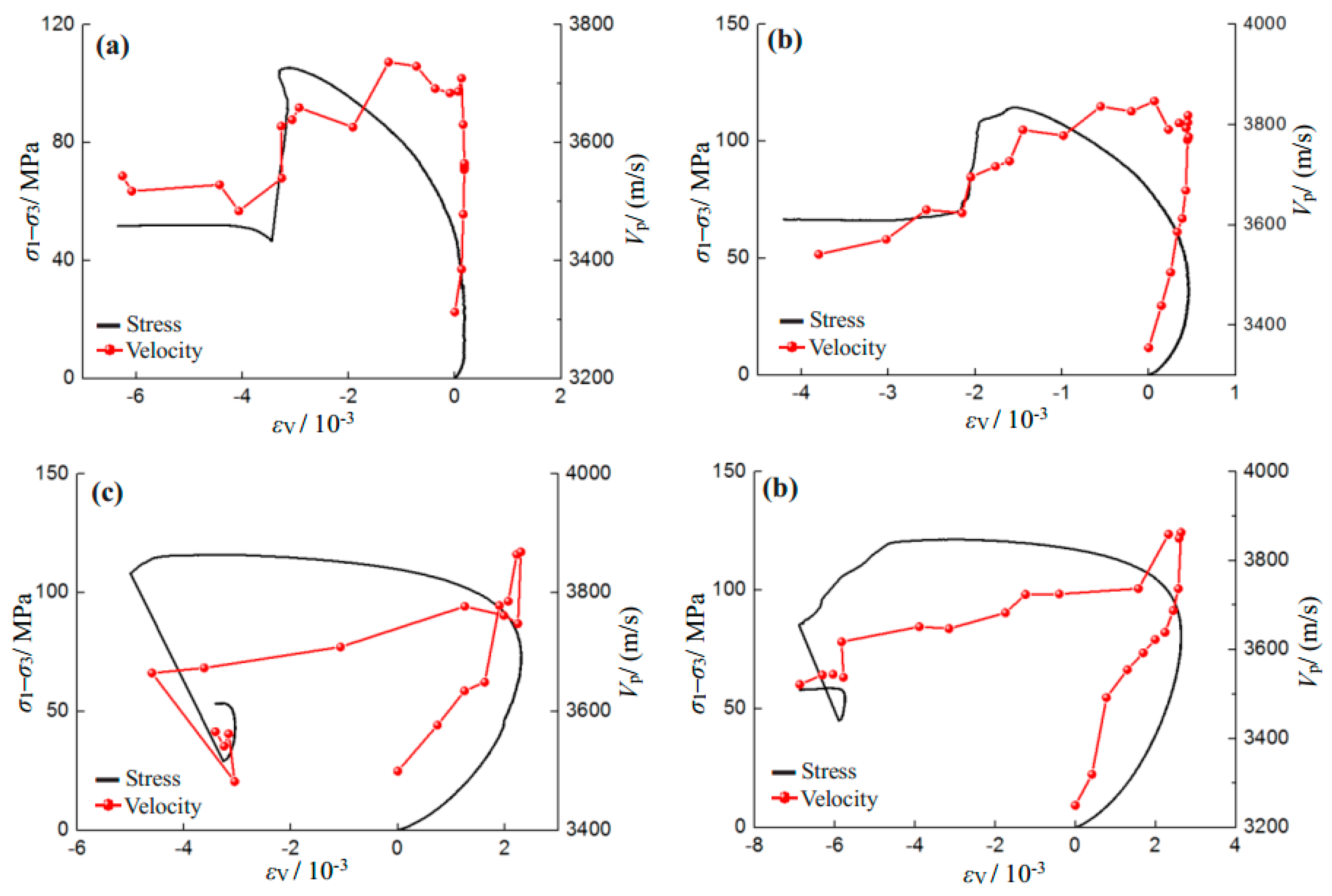
Figure 10 shows the evolution process of P-wave velocity for the sandstone specimens during the whole deformation. In general, similar variation trends were observed for various confining pressures and salinity levels.
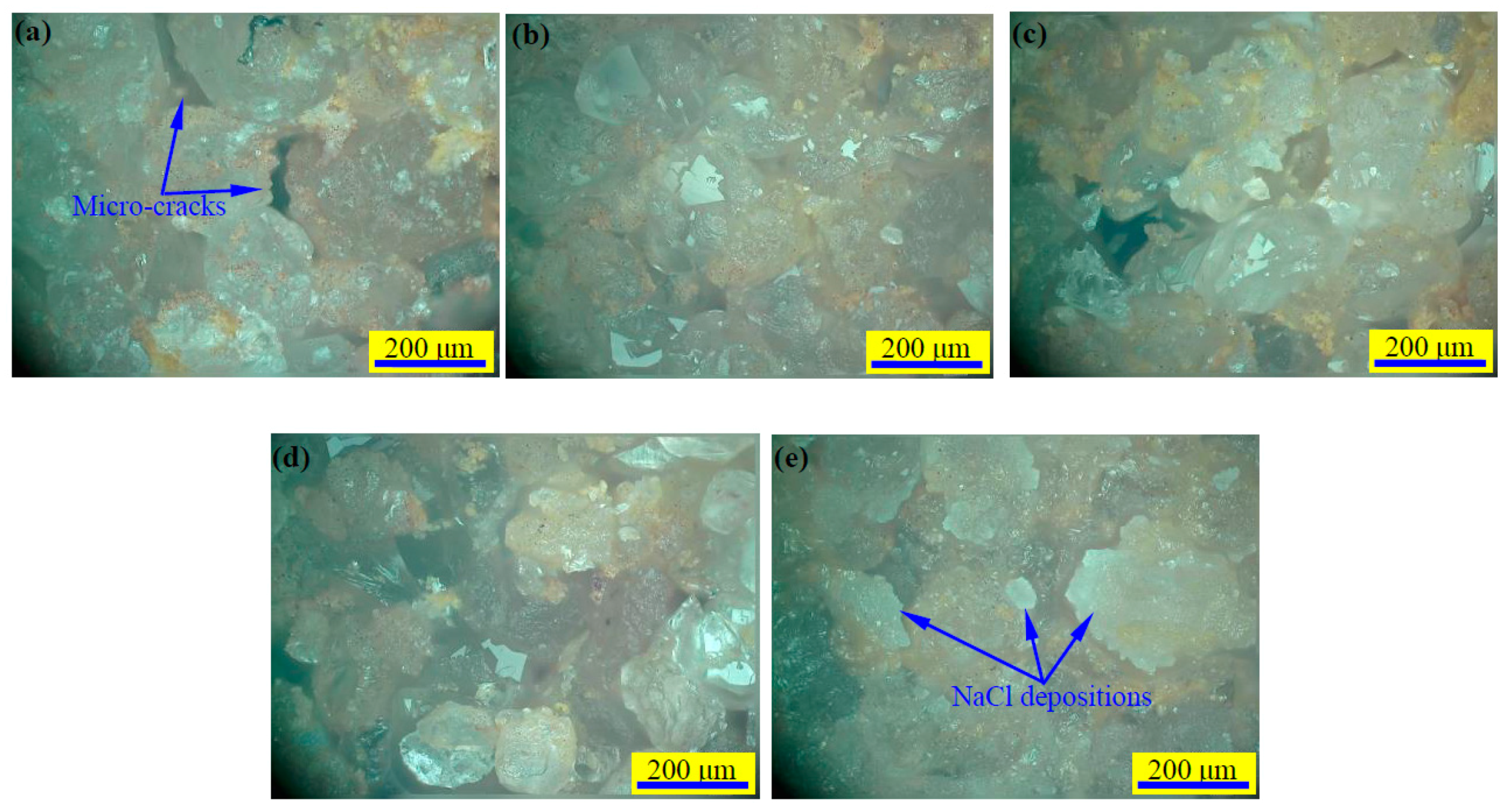
In the initial compaction stage, P-wave velocity increased. This mainly occurs as a result of the closure of the original micro-cracks in the sandstone material (see
Figure 1 and
Figure 3). After that, the linear elastic deformation starts to dominate the stress–strain curve, and the increase rate of P-wave velocity reduces. When the specimen reaches the nonlinear deformation stage, the P-wave velocity shows fluctuations due to the initiation and propagation of cracks. After the peak stress, macro fractures form in the specimen, leading the P-wave velocity to fall rapidly. During the stress drops, the P-wave velocity also suddenly drops. However, at the residual strength stage, the P-wave velocity remained constant, possibly due to the macro failure mode that had already formed.
Figure 11 shows the evolution process of P-wave velocity with the volumetric strain of saturated sandstone specimens under various salinity conditions. It is clear from
Figure 11 that the P-wave velocity is closely related to the volumetric strain. During the volumetric compaction (before the crack damage stress), P-wave velocity shows an increase trend due to the closure of pre-existing micro-defects. During the stage of volumetric dilation, the initiation and coalescence of micro-cracks and initiation of macro-cracks lead to decreasing P-wave velocity.
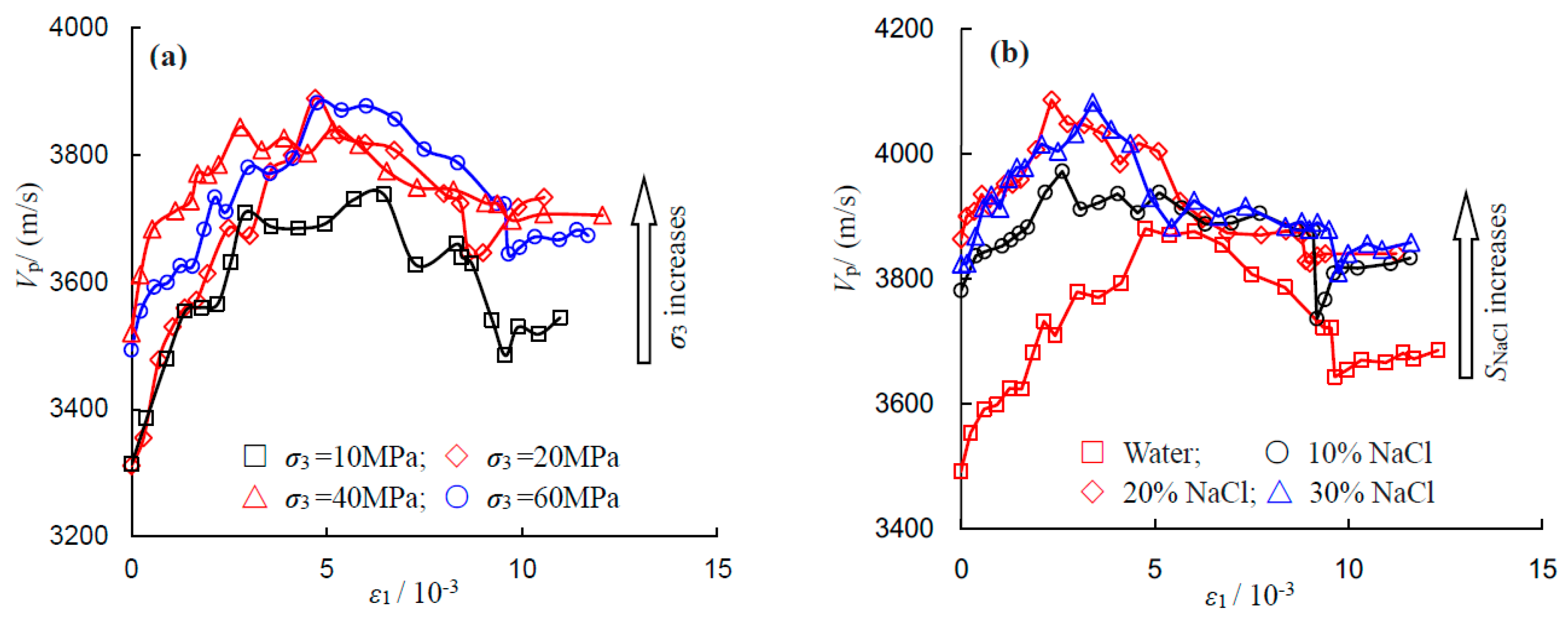
To investigate the influences of confining pressure and NaCl concentration on the ultrasonic wave velocity, the relationship between P-wave velocity and confining pressure and that between P-wave velocity and NaCl concentration are shown in
Figure 12a,b, respectively. Under the same salinity level, e.g., 0% in
Figure 12a, increments in P-wave velocity were clearly observed when the applied confining pressure increases from 10 to 60 MPa. The reason for the P-wave velocity increment can be explained by the densification of the particle assembly within the rock under increased confining pressure.
As can be seen from
Figure 12b, the P-wave velocity increases with NaCl concentration. An apparent enhancement in P-wave velocity was observed when the saturation condition changes from distilled water to 10% brine concentration. However, the rates of increase were reduced when the salinity level moved from 10% to 30%, which indicated that the enhancement effect of brine in the pore space is limited.
Figure 13 shows the evolution of AE events of sandstone specimens during the whole deformation process under conventional triaxial compression. From
Figure 13, it is clear that the AE characteristic can be divided into two phases according to the active extent. Before peak strength, especially at the initial deformation stage, very few AE counts were recorded. At the nonlinear deformation stage (close to the peak strength), some AE events were observed. However, the magnitude of the AE events during this stage was relatively low compared to the post-peak stage. With the increase of deformation, the corresponding AE events became active, which indicates that the extent of fracturing within the specimen will most likely increase. When the specimen reached the post-peak stage, multiple abrupt AE counts were observed due to the initiation and coalescence of fractures. Moreover, the characteristics of the AE count under unconfined compression are quite different from those recorded under triaxial compression. In the 30% brine-saturated sandstone specimens shown in
Figure 13e,f several AE counts can be seen at the post-peak strength stage during UCS, which correspond to the stress drops in the stress–strain curve. However, under a confining pressure of 40 MPa, only one huge AE count was observed during the whole deformation process. These AE phenomena confirm the observation that the sandstone fails progressively under low confining pressures, but fails abruptly under high confining pressures from the stress–strain curves shown in
Figure 5.
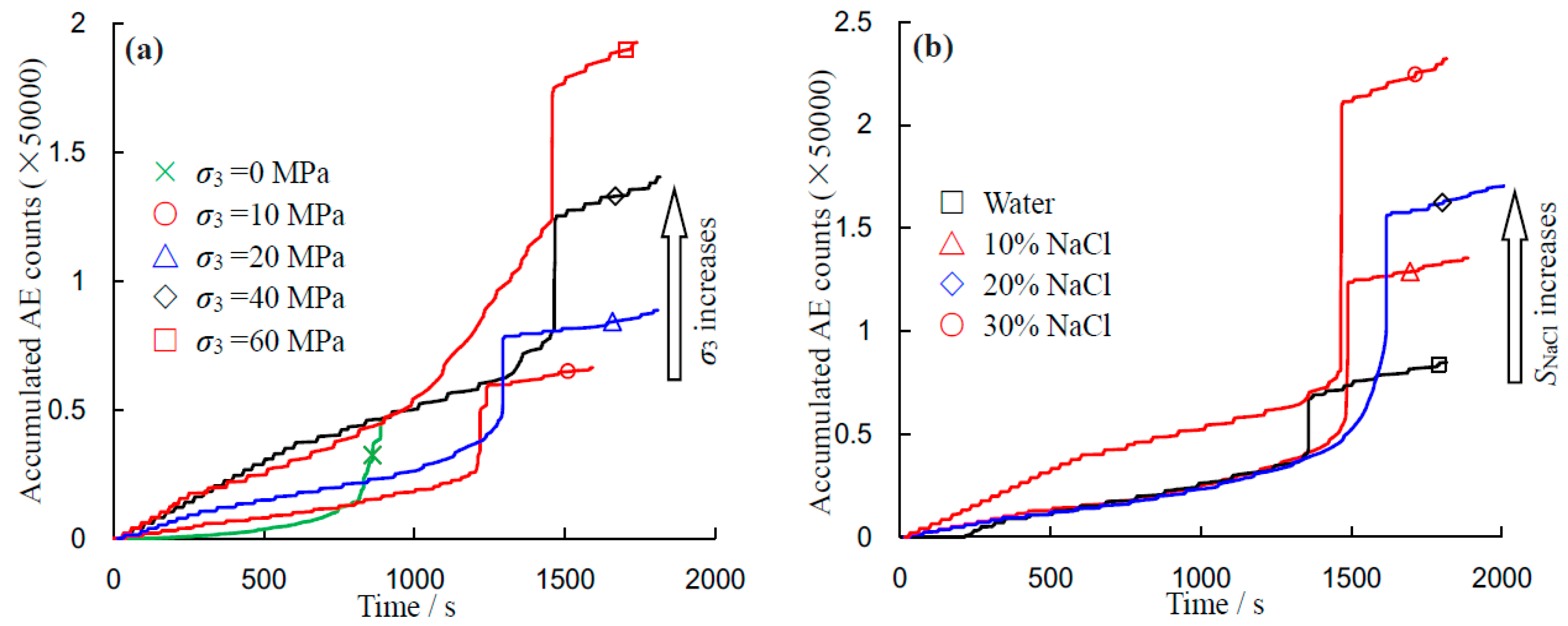
Figure 14 illustrates the evolution process of accumulated AE counts for sandstone specimens under triaxial compression. Generally, similar variation trends of AE can be observed for different applied confining pressures. With the increase of confining pressure, the rate of increase in the accumulated AE count before peak stress increased, along with the accumulated AE counts. However, the rate of increase in the accumulated AE counts before peak stress appeared to be independent of the salinity. The accumulated AE counts at the failure point increase with the NaCl concentration, as did the total accumulated AE counts. This again indicates that the increasing NaCl concentration strengthens the sandstone specimen. These phenomena correspond to the observed effect of the salinity level on the strength and Young’s modulus (see
Figure 6 and
Figure 9).
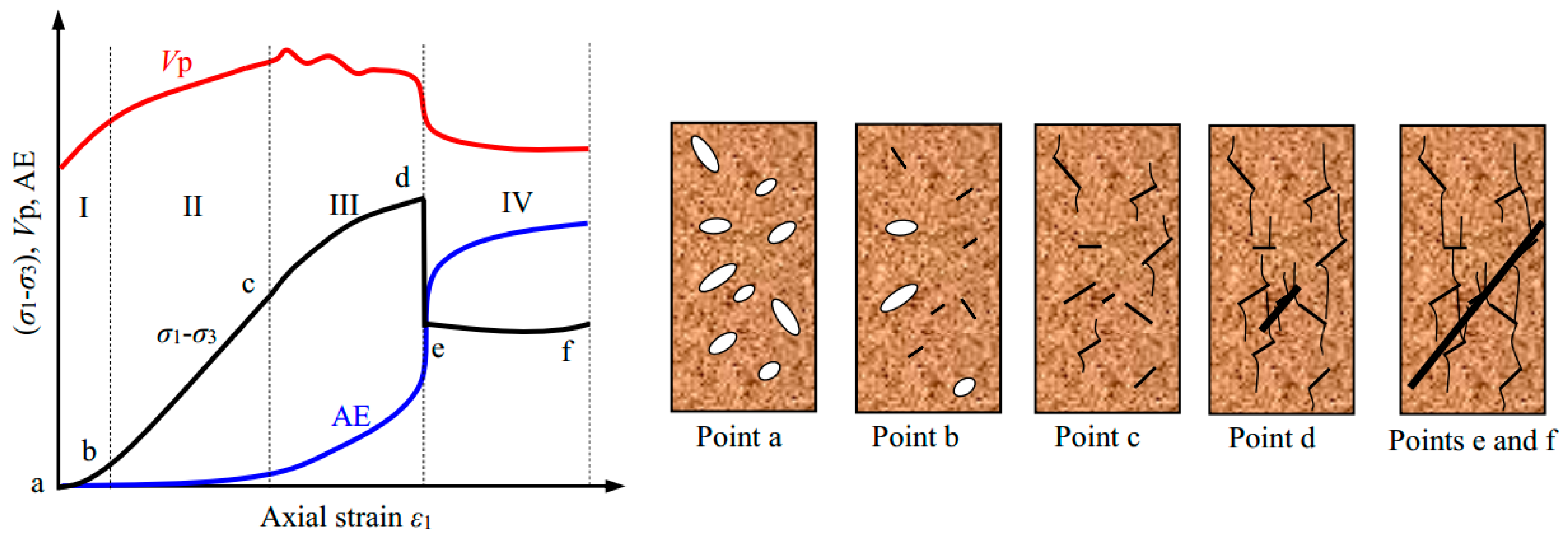
On the basis of the above observations, the evolution of P-wave velocity and AE event can be characterized as having four stages during the triaxial failure process (
Figure 15). It is clear that the P-wave velocity and number of AE events evolve during the deformation process, and that both are dependent on the stress level. At the initial compressive deformation stage (from point a to point b), the P-wave velocity increased rapidly, while very few or no AE counts appeared. At the linear elastic deformation stage (from point b to point c), the P-wave velocity and the accumulated AE counts increased stably. At the nonlinear deformation stage (from point c to point d), the P-wave velocity decreased unstably, while the accumulated AE counts increased exponentially. At the residual strength stage (from point e to point f), the P-wave velocity remained constant, whilst the accumulated AE counts increased stably.
3.3. Fracture Behavior
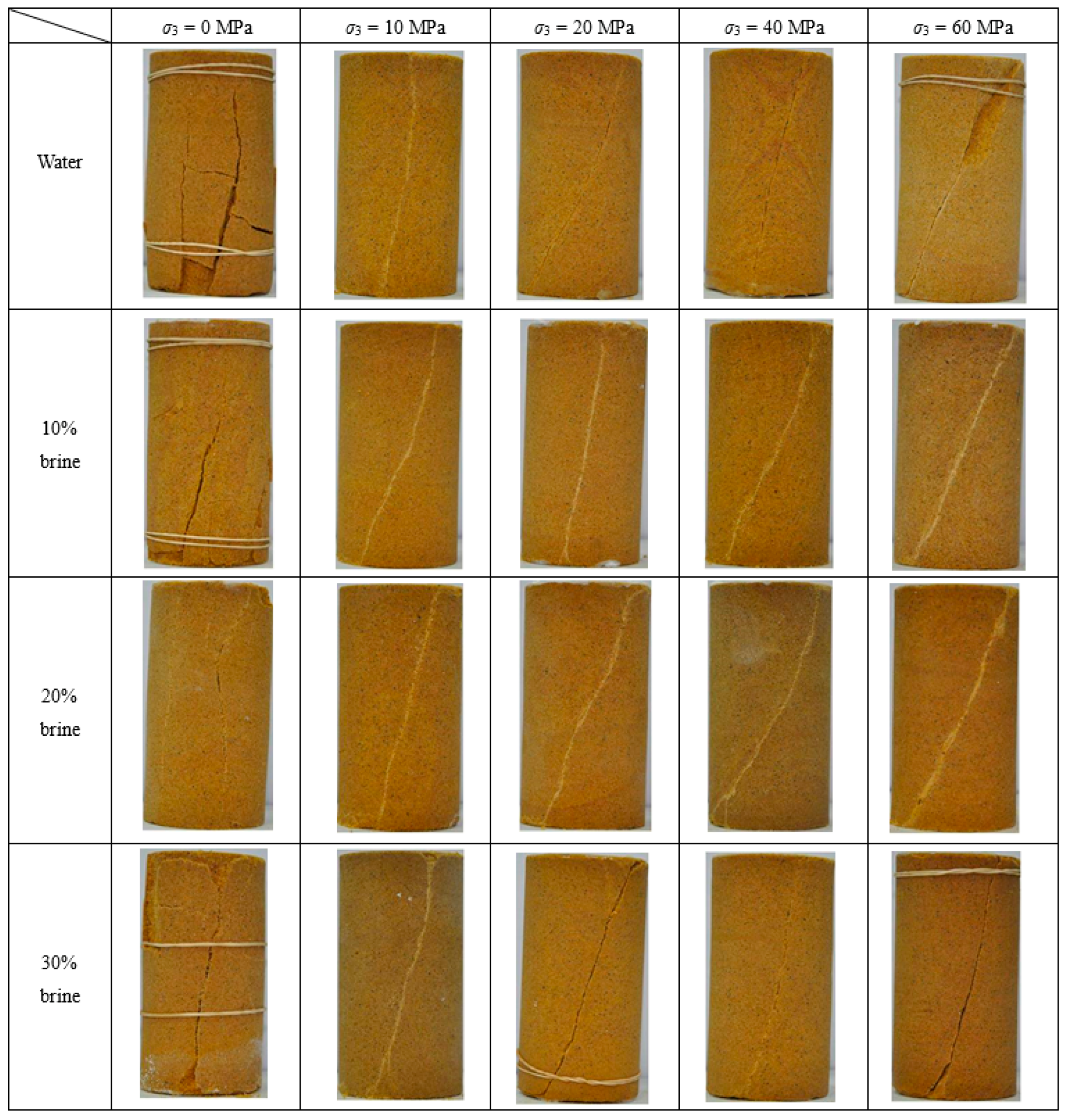
The failure patterns of specimens can provide some important information on their mechanical behaviour [
24,
25]. To better understand the failure mechanisms of brine-saturated sandstone specimens under conventional triaxial compression, the images of failed specimens under each confining pressure and salinity level are shown in
Figure 16.
Overall, the failure modes of the sandstone specimens were closely related to the confining pressure, but appeared to be independent of NaCl concentration. There are two typical categories of failure patterns: splitting under uniaxial compression, and single shear failure under triaxial compression, which is consistent with the observation of previous studies [
16,
19,
20,
25]. In distilled-water-saturated specimens, the fracture angles between the fracture and the direction of minor principal stress (i.e.,
σ3) under confining pressures of 0, 10, 20, 40 and 60 MPa, were 90°, 81°, 78°, 79° and 71°, respectively. A similar trend of reduction in the fracture angle in water-saturated Hawkesbury sandstone specimens was reported by Wasantha and Ranjith [
26]. This phenomenon indicates that the friction angle of the sandstone specimen decreases with increasing confining pressure, and possibly results from the more quasi-brittle behavior of sandstone specimens under higher confining pressures [
26]. However, the trend of reduction in the fracture angle in brine-saturated sandstone specimens was less obvious than that using distilled water. The reduction of fracture angle implies an increase in the quasi-brittle behavior of the sandstone with increased confining pressure. This observation was supported by the observed characteristics of stress–strain response shown in
Figure 5.
Microscopic observation tests were also carried out for the fracture surface of failed sandstone specimens. The fracture surfaces of distilled-water-saturated specimens and 30% NaCl-solution-saturated specimens under confining pressures of 0, 20 and 60 MPa were selected in the present study, as shown in
Figure 17 and
Figure 18.
From
Figure 17, in the distilled-water-saturated sandstone specimens, the fracture surface is rough. Under higher resolution, the grains on the surface can be clearly observed. However, under a confining pressure of 20 MPa, frictional sliding was observed along the direction of the shear fracture plane. This was identified by the observation of rock flour at higher resolutions. Under a high confining pressure (e.g., 60 MPa), sliding is distinct, and a considerable amount of fault gouges were seen. The effect of confining pressure on the microstructure of the specimen under saline conditions (see
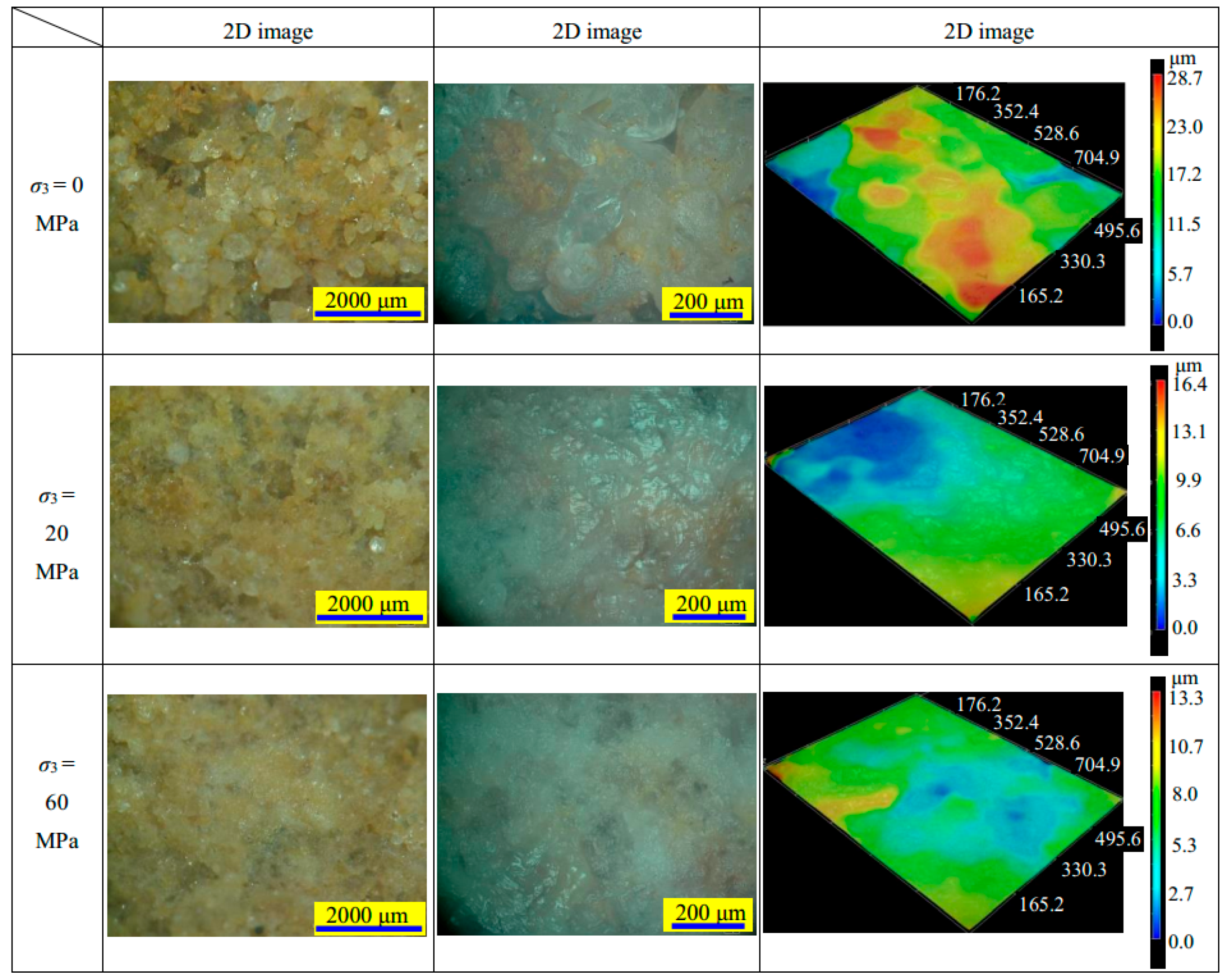
Figure 18) is very similar to that of the specimen under water saturation.
Furthermore, in the distilled-water-saturated sandstone specimens, under confining pressures of 0, 20 and 60 MPa, the maximum height values were 26.7, 24.5 and 15.9 μm, respectively (see the third column in
Figure 17). The height values were 28.7, 16.4 and 13.3 μm for the brine-saturated sandstone specimens (see the third column in
Figure 18). The observed height reduction indicates that the friction increases with confining pressure. It needs to be noted that the micro-observations were conducted on a relatively small sub-sample of each sandstone specimen after conducting the triaxial compression tests. The height values are merely indicative and used as a qualitative comparison between the fracture plane surfaces. The indicative trend was that a reduction in height (surface roughness) was observed across the fracture surface as confining pressures were increased.