Distribution System Operation with Electric Vehicle Charging Schedules and Renewable Energy Resources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
2.1. Objective Function
2.2. First-Step Restrictions Stage
2.3. Second-Step Restrictions Stage
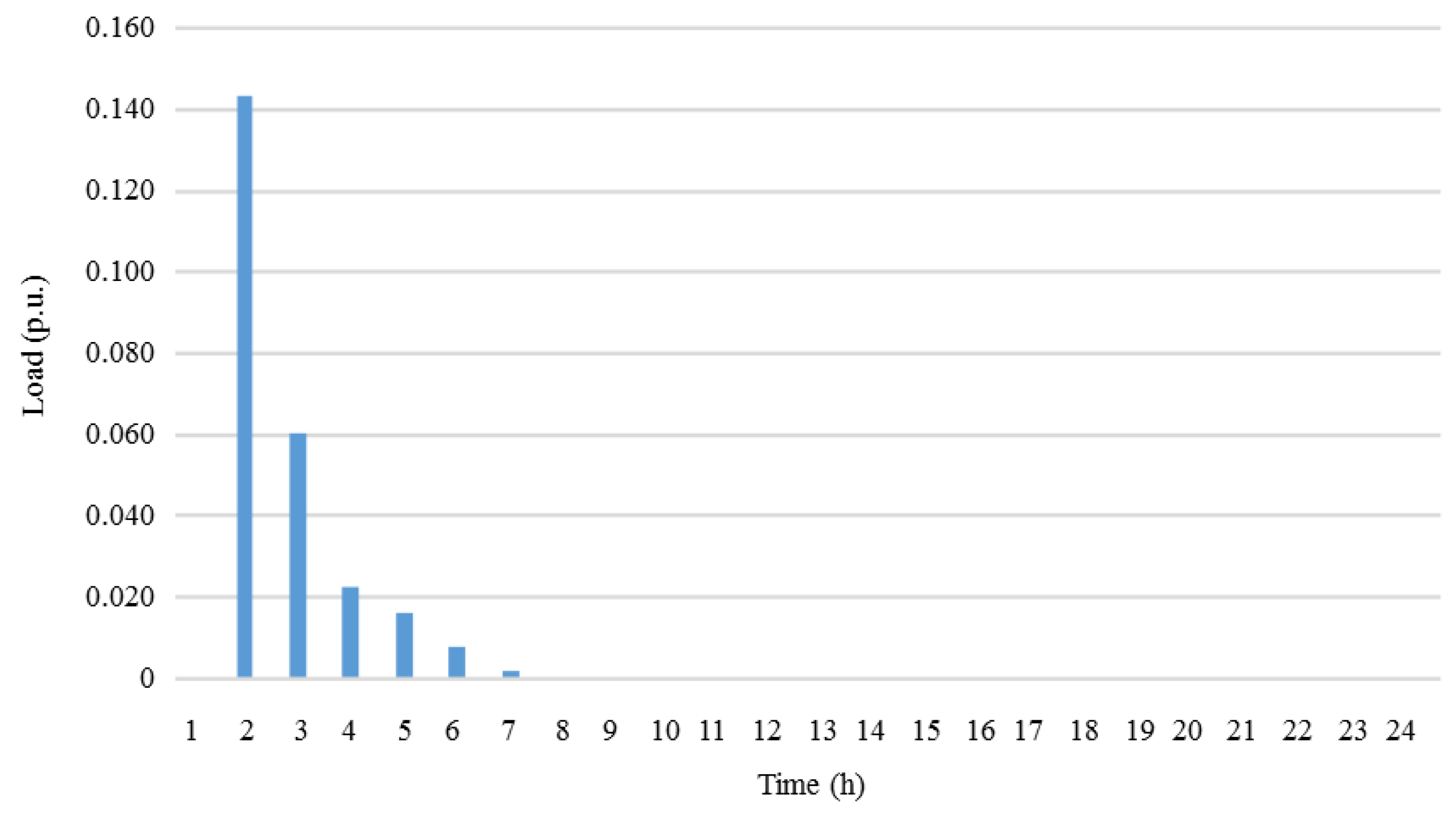
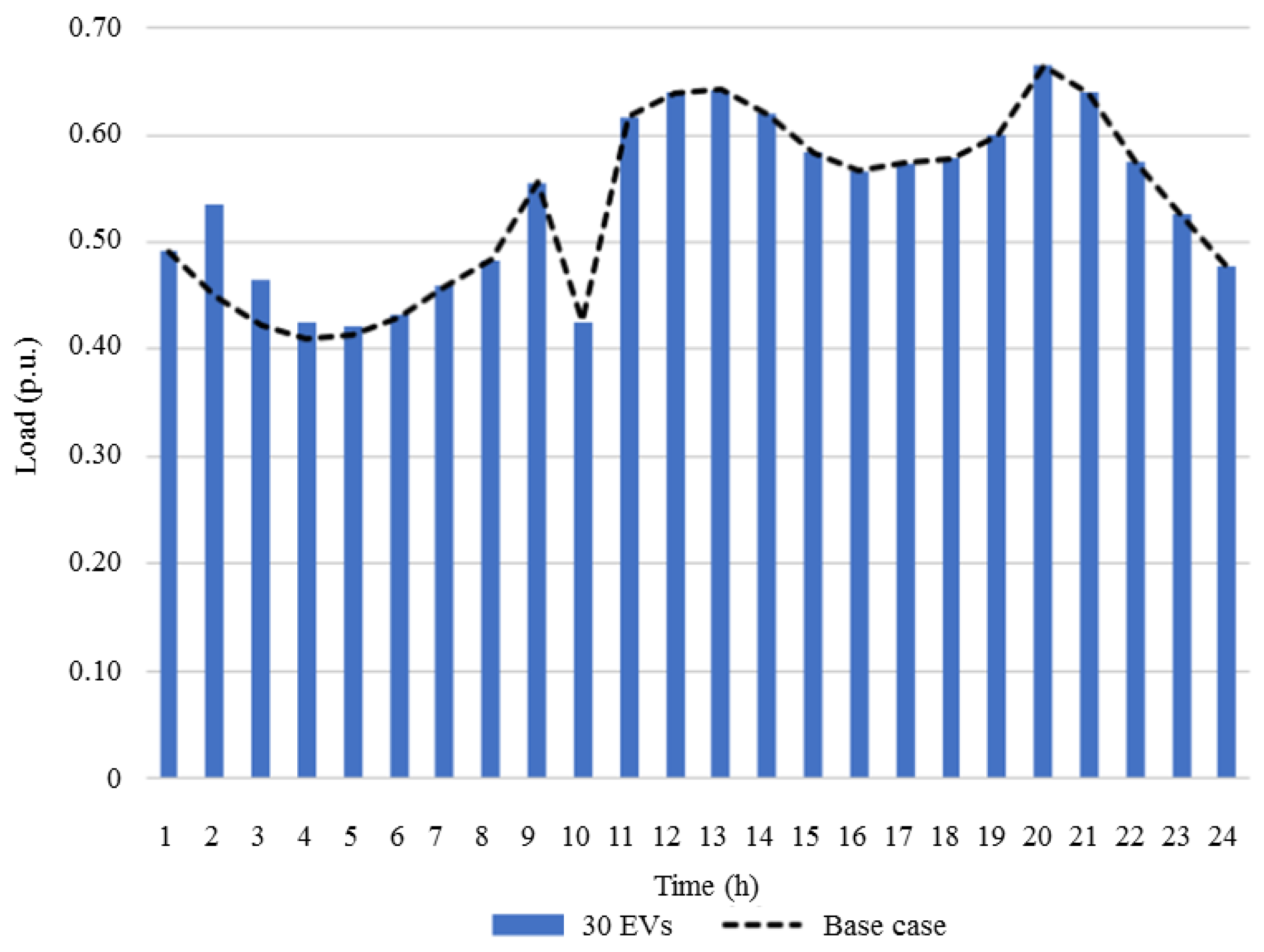
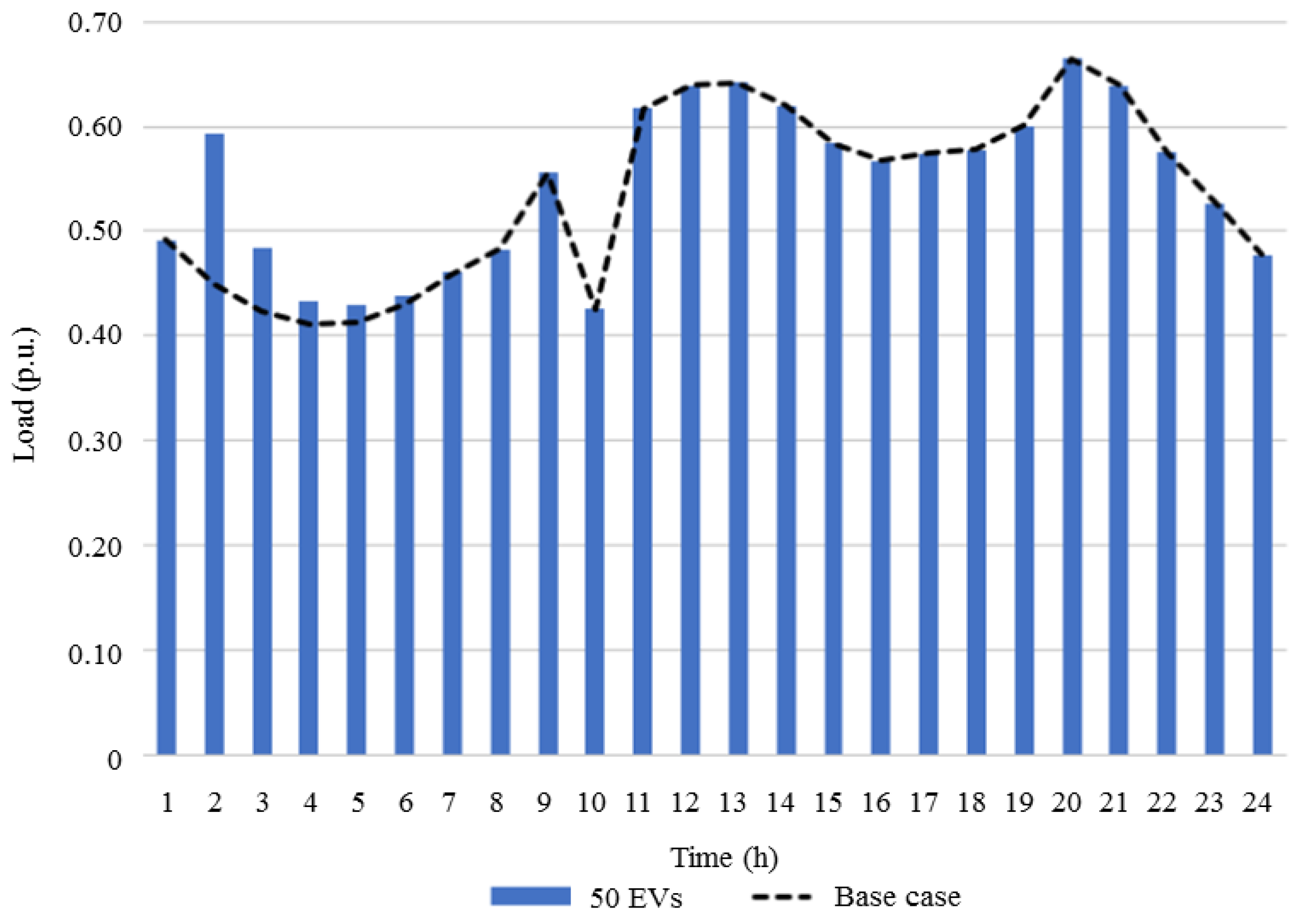
3. Numerical Study and Results
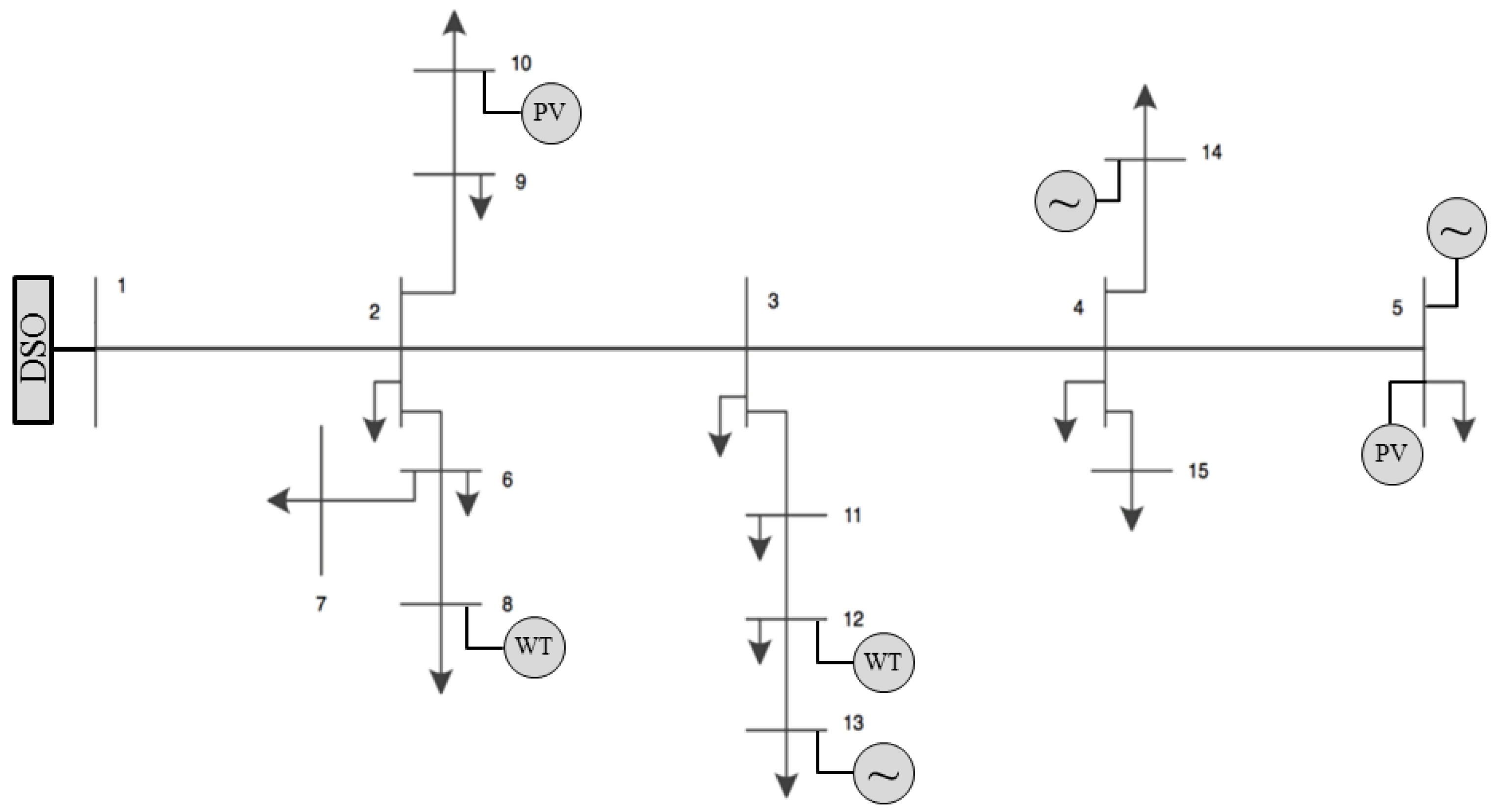
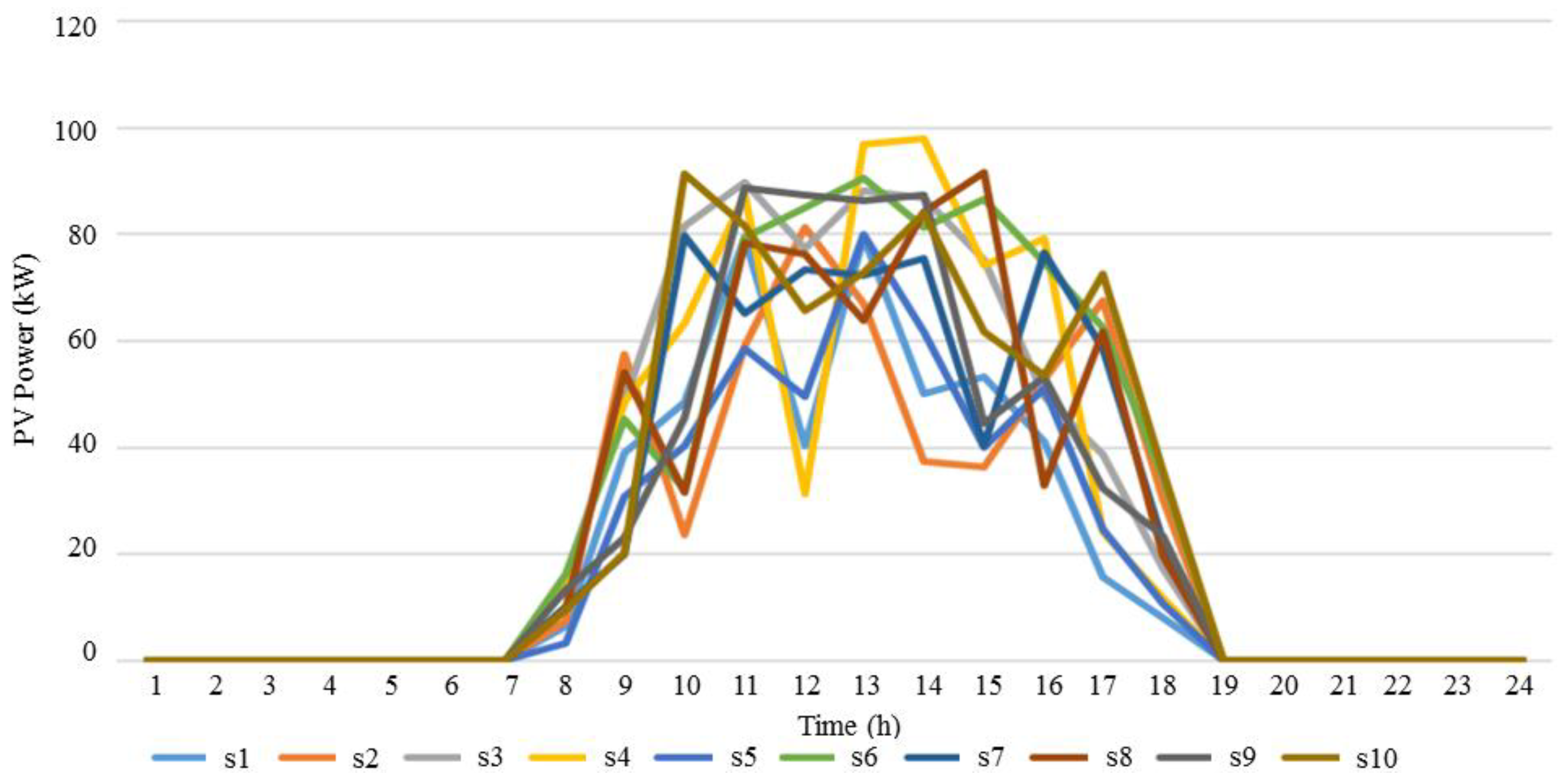
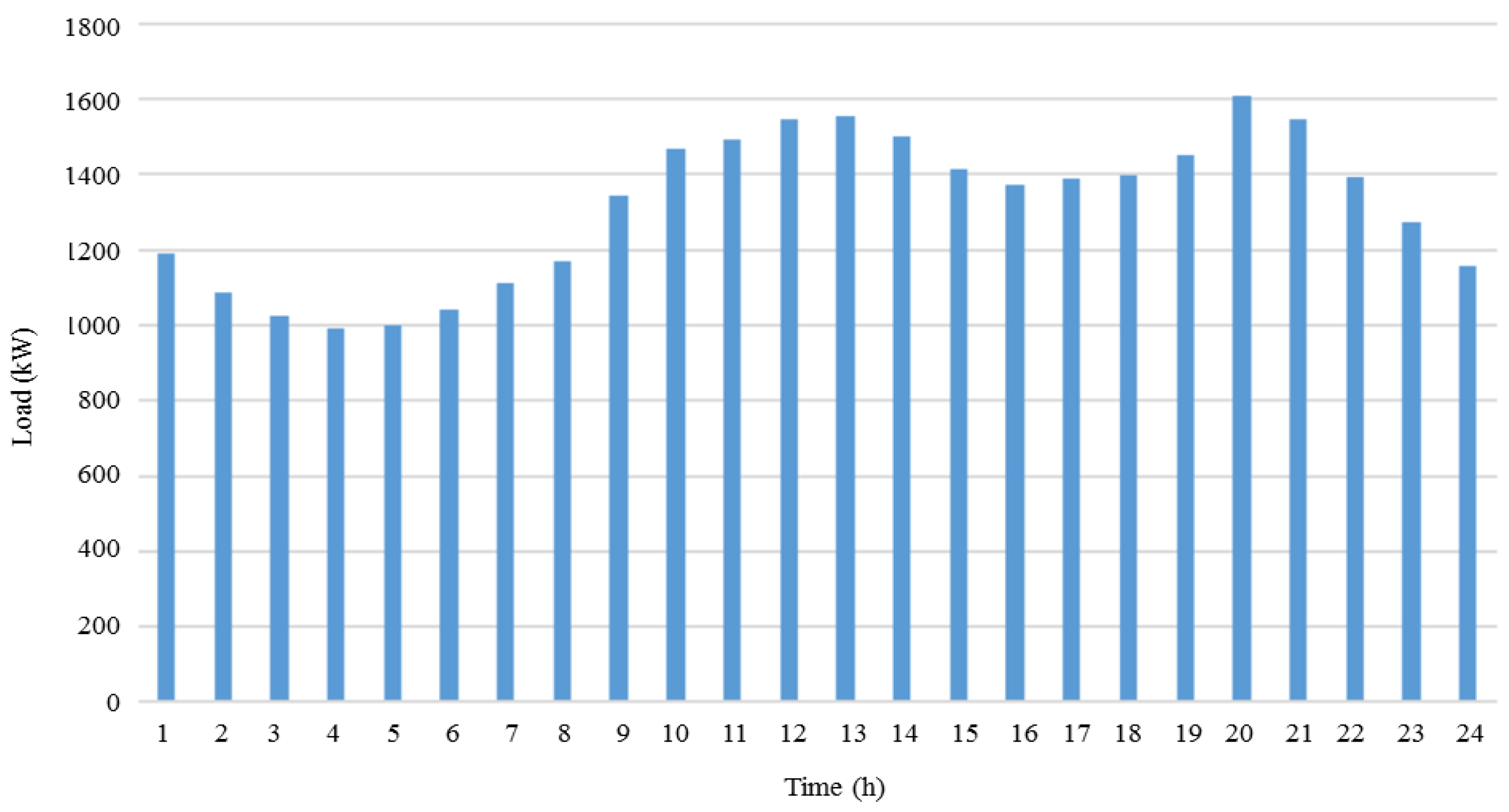
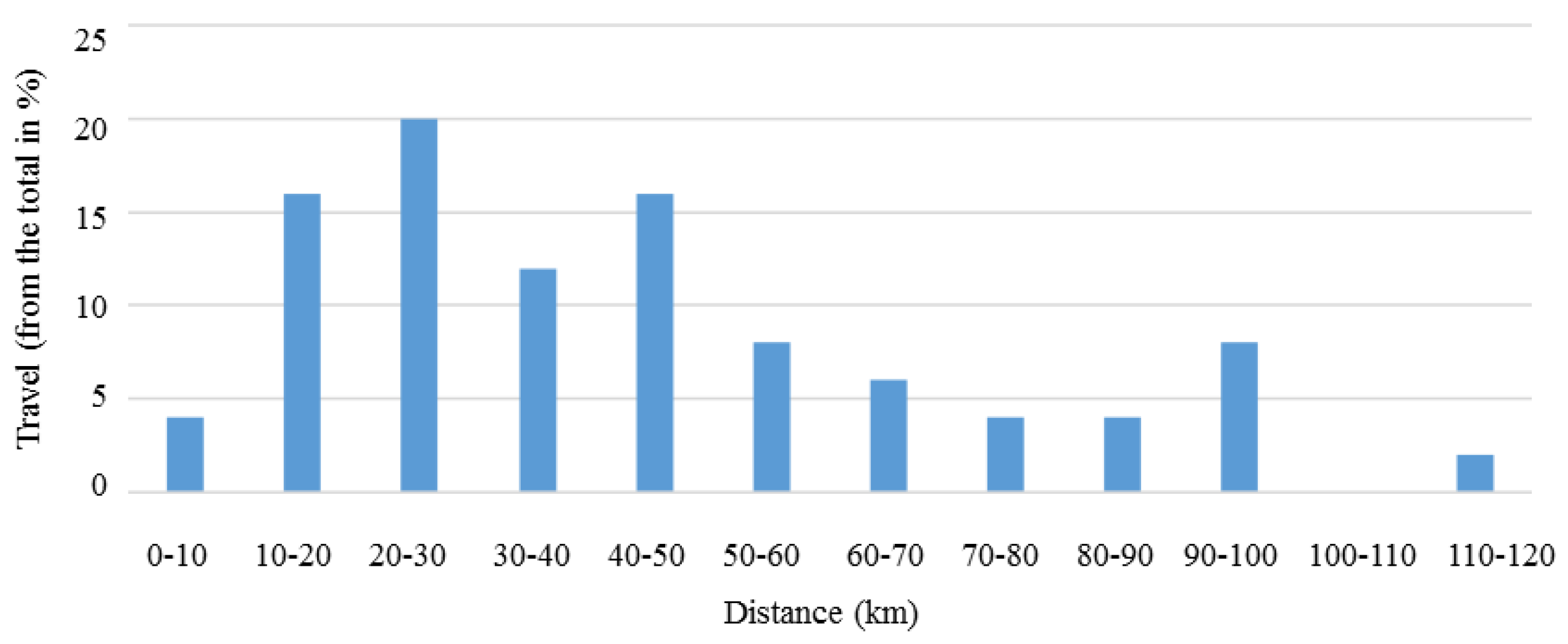
3.1. Numerical Study
- Charging efficiency is 85% for all EVs.
- Minimum and maximum SoC is 0.2 and 1, respectively.
- The bidirectional capability of EVs (V2G), to inject power to the network has not been considered. EV charging can only be carried out at the owner's residence.
- The BMW i3 and Tesla S vehicles include the BMW i wallbox and Tesla wall connectors, respectively, which increase charge power capacity.
- The EVs are loaded to their maximum SoC.
3.2. Case Study and Results
3.2.1. Base Case Study Comparison with Cases 2, 3, and 4
3.2.2. Base Case Study Comparison with Cases 5, 6 and 7
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Distributed generation index | |
| Electrical vehicle index | |
| Node index | |
| Connection point index with the upstream network | |
| Photovoltaic farm index | |
| Scenario index | |
| Time (in hours) index | |
| Arrival time index | |
| Linear partitions index in the linearization process | |
| Power Index () | |
| Wind farm index | |
| Unit generation cost | |
| EV battery charging efficiency (%) | |
| EV battery capacity (kW) | |
| Regulation cost in the day-ahead and real-time markets | |
| Daily distance traveled by EV (km) | |
| Upper limit in quadratic flow discretization (kVA) | |
| EV driving efficiency (km/kWh) | |
| Maximum current capacity in the line | |
| Planned active and reactive power, respectively | |
| Market compensation price | |
| EV power charging (kW) | |
| Probability of each scenario | |
| Maximum power capacity of each | |
| Day-ahead, and real-time markets regulation, respectively | |
| Distribution line resistance and inductance, respectively | |
| Maximum, minimum and nominal voltage, respectively | |
| Current flow, and quadratic current flow, for the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively (A) | |
| Active and reactive power that flows in upstream direction in the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively (kW) | |
| Active power in the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively | |
| Active and reactive power that flows in downstream direction in the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively (kW) | |
| Reactive power in the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively | |
| EV state-of-charge | |
| Power factor | |
| Voltage, and quadratic voltage, for the day-ahead and real-time markets, respectively (V) |
References
- Llamas, J.; Bullejos, D.; Barranco, V.; de Adana, M.R. Regulation Issues for Renewable Energy Integration into Electrical Markets. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2017 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Milan, Italy, 6–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Yaici, W.; Foiadelli, F. Electric Vehicles Charged with Residential’s Roof Solar Photovoltaic System: A Case Study in Ottawa. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, C.K. On the Synergy between Large Electric Vehicle Fleet and High Wind Penetration—An Analysis of the Danish Case. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, G.R.C.; Venugopal, P.; Bauer, P. Future of Electric Vehicle Charging. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Power Electronics (Ee), Novi Sad, Serbia, 19–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Su, C.; Chen, Z.; Bak-Jensen, B. Optimal Operation of Plug-In Electric Vehicles in Power Systems with High Wind Power Penetrations. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Mortazavi, H.; Mehrjerdi, H.; Saad, M.; Lefebvre, S.; Asber, D.; Lenoir, L. A Monitoring Technique for Reversed Power Flow Detection with High PV Penetration Level. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Han, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Demand Response Capability of V2G Based Electric Vehicles in Distribution Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), Torino, Italy, 26–29 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi-Fard, A.; Niknam, T.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. Stochastic Reconfiguration and Optimal Coordination of V2G Plug-in Electric Vehicles Considering Correlated Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.W.; Al -Awami, A.T.; Sortomme, E. Stochastic-Programming-Based Bidding Strategy for V2G Services. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES ISGT Europe 2013, Lyngby, Denmark, 6–9 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradijoz, M.; Parsa Moghaddam, M.; Haghifam, M.R.; Alishahi, E. A Multi-Objective Optimization Problem for Allocating Parking Lots in a Distribution Network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 46, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venayagamoorthy, G. Dynamic, Stochastic, Computational, and Scalable Technologies for Smart Grids. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2011, 6, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, L. Integration of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles into Residential Distribution Grid Based on Two-Layer Intelligent Optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureri, F.; Puliga, L.; Robba, M.; Delfino, F.; Bulto, G.O. An Optimization Model for the Integration of Electric Vehicles and Smart Grids: Problem Definition and Experimental Validation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Trento, Italy, 12–15 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Zhou, C.; Allan, M.; Yuan, Y. Modeling of Load Demand Due to EV Battery Charging in Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, R.; Viola, F. Designing a Sustainable University Recharge Area for Electric Vehicles: Technical and Economic Analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, Y.G.; Trindade, F.C.L.; Cebrian, J.C.; Teixeira, W.W. Investigation of Infrastructural Solutions to Mitigate the Impacts of EV Recharging at LV Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference—Latin America (ISGT Latin America), Quito, Ecuador, 20–22 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakarami, A.; Farahani, H.F.; Aghaei, J. Stochastic Characterization of Electricity Energy Markets Including Plug-in Electric Vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, O.; Paterakis, N.G.; Mendes, T.D.P.; Bakirtzis, A.G.; Catalao, P.S.J. Smart Household Operation Considering Bi-Directional EV and ESS Utilization by Real-Time Pricing-Based DR. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Flynn, D.; Keane, A. Local Versus Centralized Charging Strategies for Electric Vehicles in Low Voltage Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, A.; Bibeau, E.; Shahidinejad, S.; Molinski, T. PEV Charging Profile Prediction and Analysis Based on Vehicle Usage Data. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalfati, A.; Iannuzzi, D.; Fantauzzi, M.; Roscia, M. Optimal Sizing of Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Microgrids: A Mixed Integer Linear Programming Formulation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAMS Development Corp.; GAMS Software GmbH. General Algebraic Modeling System (GAMS) —Cutting Edge Modeling. Available online: https://www.gams.com/ (accessed on 2 November 2018).
- GM-Volt.com LLC. Chevy Volt Specs—GM-VOLT: Chevy Volt Electric Car Site GM-VOLT: Chevy Volt Electric Car Site. Available online: https://gm-volt.com/full-specifications/ (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- Sustainable Enterprises Media Inc. 2018 Nissan Leaf Specs. Available online: https://evobsession.com/2018-nissan-leaf-specs/ (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- BMW of North America. BMW i3-Features & Specifications—BMW USA. Available online: https://www.bmwusa.com/vehicles/bmwi/bmw-i3/bmw-i3-features-and-specs.html (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- Tesla. Model S Specifications | Tesla. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/support/model-s-specifications (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- SoftNews NET. RENAULT ZOE Specs & Photos—2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018—Autoevolution. Available online: https://www.autoevolution.com/cars/renault-zoe-2013.html#aeng_renault-zoe-2013-65kw-88-hp (accessed on 9 April 2018).



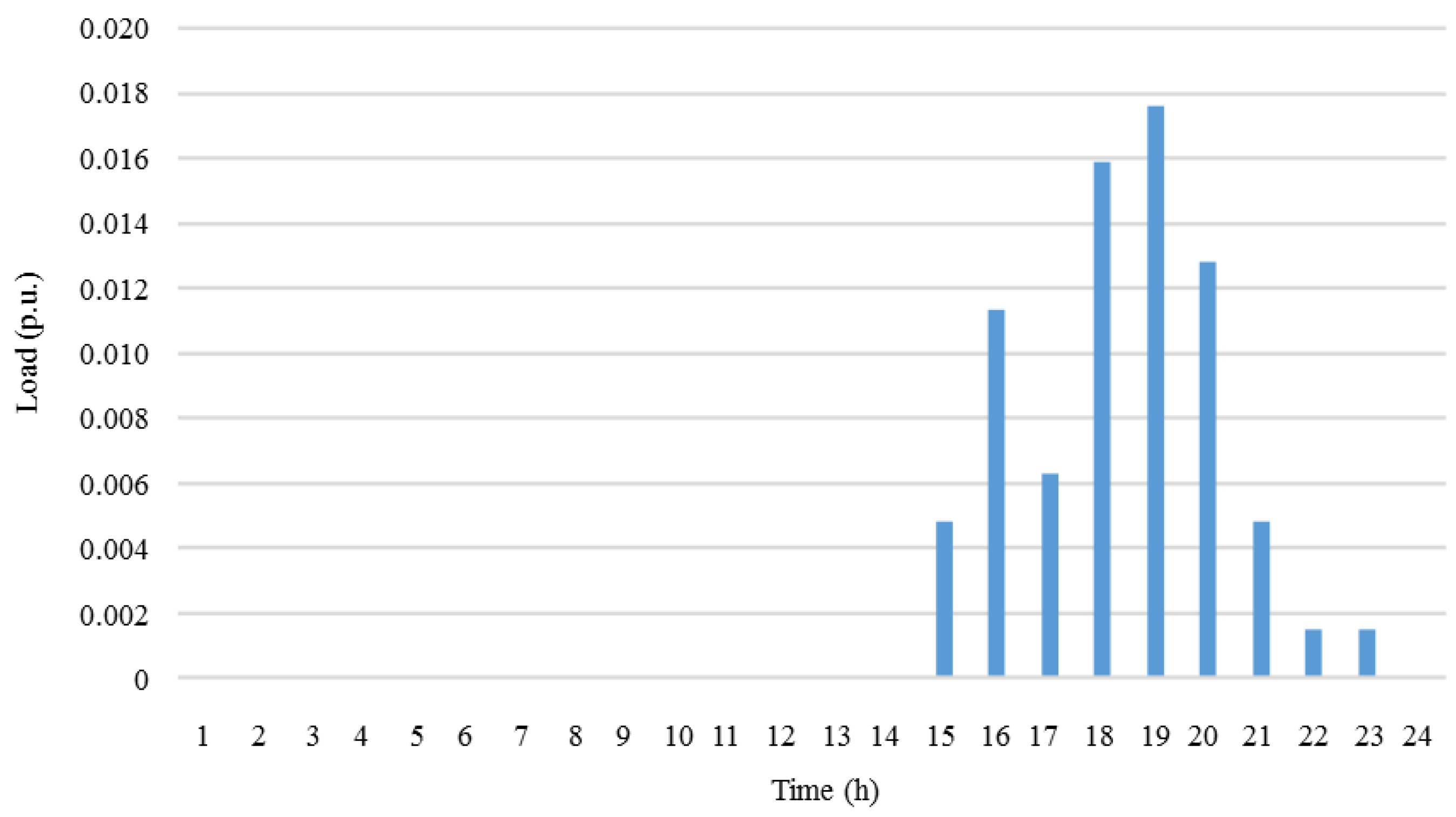

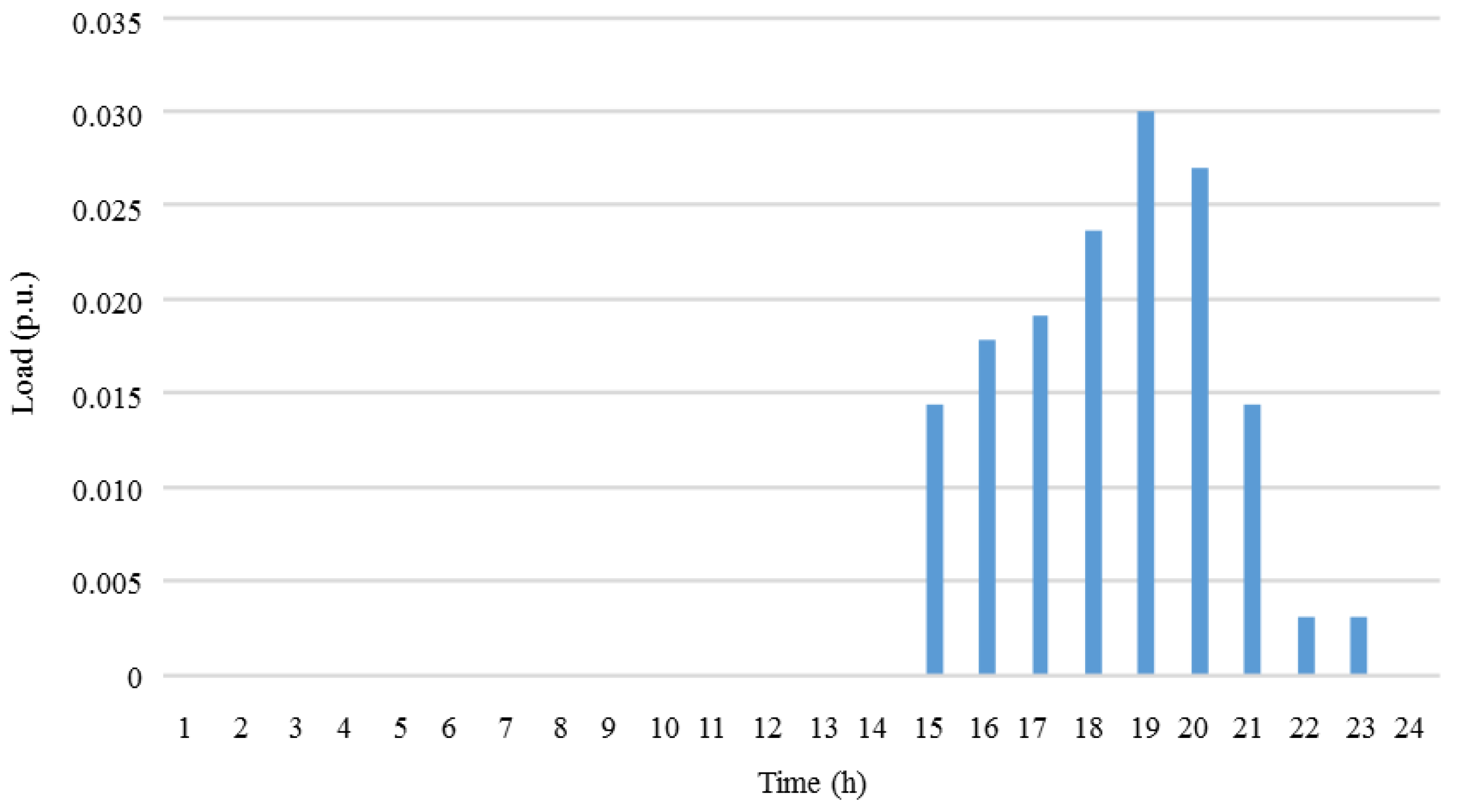

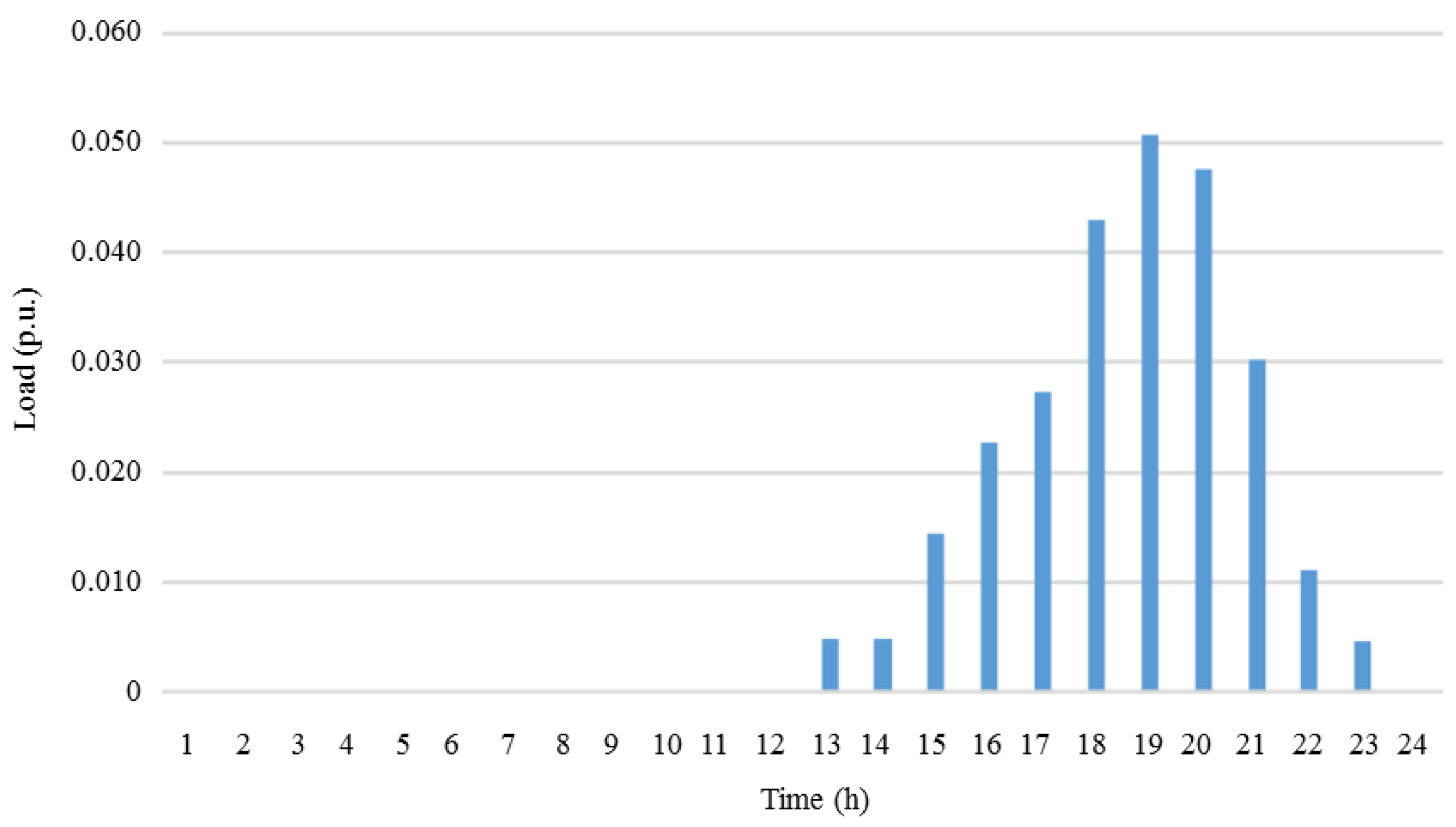

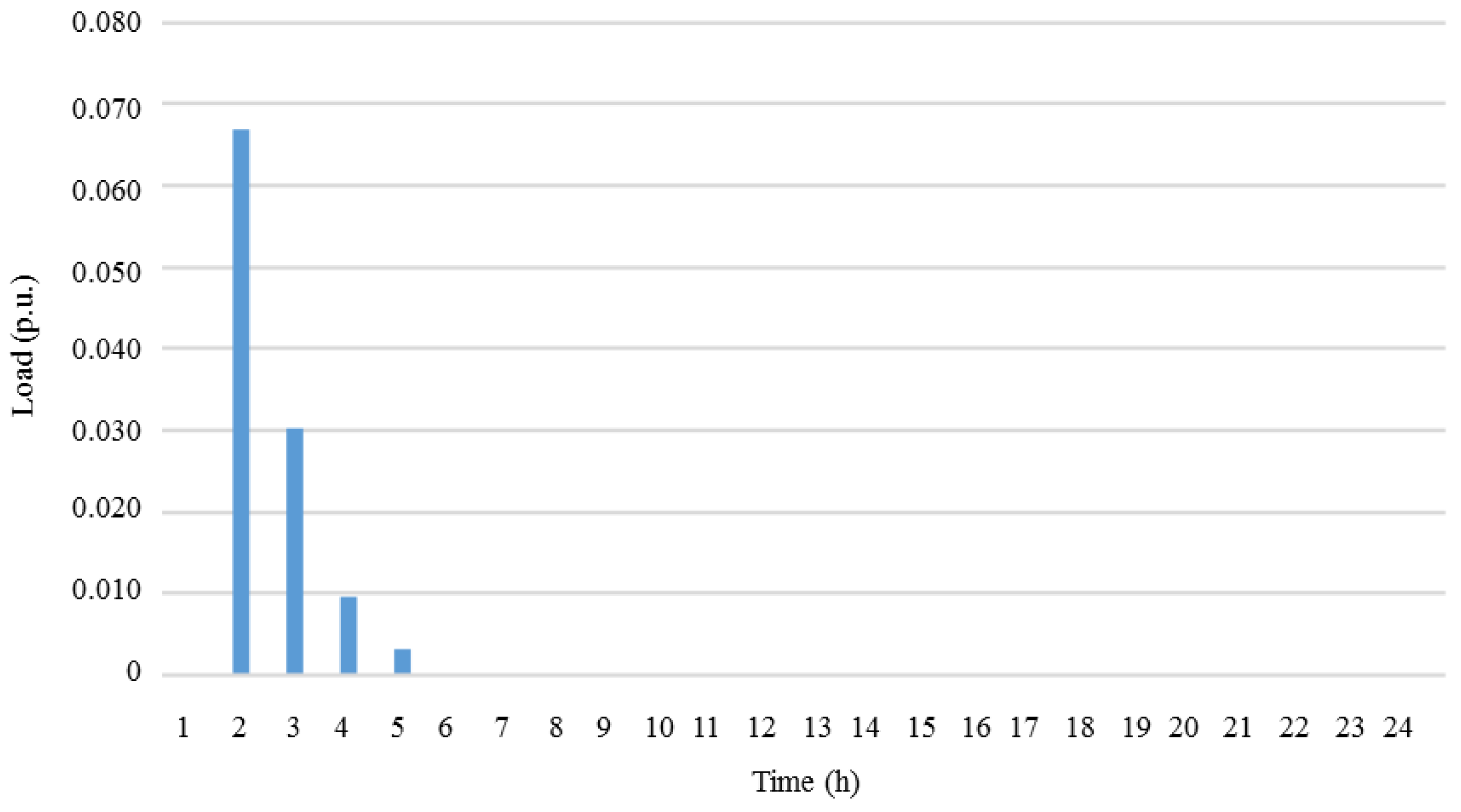


| Generator | Power (kW) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (Bus 05) | 23.00 | 230.00 |
| 2 (Bus 13) | 69.00 | 690.00 |
| 3 (Bus 14) | 46.00 | 460.00 |
| EV Model | Battery Capacity (kWh) | Charging Power (kW) | Electrical Driving Efficiency (km/kWh) | EV number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chevrolet Volt | 16.00 | 3.50 | 3.75 | 01; 06; 11; 16; 21; 26; 31; 36; 41; 46 |
| Nissan Leaf | 24.00 | 4.00 | 6.70 | 02; 07; 12; 17; 22; 27; 32 37; 42; 47 |
| BMW i3 | 22.00 | 11.00 | 7.20 | 03; 08; 13; 18; 23; 28; 33; 38; 43; 48 |
| Tesla S | 60.00 | 11.00 | 6.70 | 04; 09; 14; 19; 24; 29; 34; 39; 44; 49 |
| Renault Zoe | 22.00 | 3.50 | 6.70 | 05; 10; 15; 20; 25; 30; 35; 40; 45; 50 |
| Time (h) | BUS | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| 06:00 a.m. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 07:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| 08:00 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| 09:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| 10:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| 11:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 12:00 a.m. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 01:00 p.m. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 02:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 03:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| 04:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 05:00 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| 06:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 07:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| 08:00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| 09:00 p.m. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Case | Penetration (# of EVs) | Controlled/Uncontrolled |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (base case) | 0 | - |
| 2 | 15 | uncontrolled |
| 3 | 30 | uncontrolled |
| 4 | 50 | uncontrolled |
| 5 | 15 | controlled |
| 6 | 30 | controlled |
| 7 | 50 | controlled |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osório, G.J.; Shafie-khah, M.; Coimbra, P.D.L.; Lotfi, M.; Catalão, J.P.S. Distribution System Operation with Electric Vehicle Charging Schedules and Renewable Energy Resources. Energies 2018, 11, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113117
Osório GJ, Shafie-khah M, Coimbra PDL, Lotfi M, Catalão JPS. Distribution System Operation with Electric Vehicle Charging Schedules and Renewable Energy Resources. Energies. 2018; 11(11):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113117
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsório, Gerardo J., Miadreza Shafie-khah, Pedro D. L. Coimbra, Mohamed Lotfi, and João P. S. Catalão. 2018. "Distribution System Operation with Electric Vehicle Charging Schedules and Renewable Energy Resources" Energies 11, no. 11: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113117
APA StyleOsório, G. J., Shafie-khah, M., Coimbra, P. D. L., Lotfi, M., & Catalão, J. P. S. (2018). Distribution System Operation with Electric Vehicle Charging Schedules and Renewable Energy Resources. Energies, 11(11), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113117








