Atomization of Gel Fuels with Solid Particle Addition Utilizing an Air Atomizing Nozzle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Data Processing Method
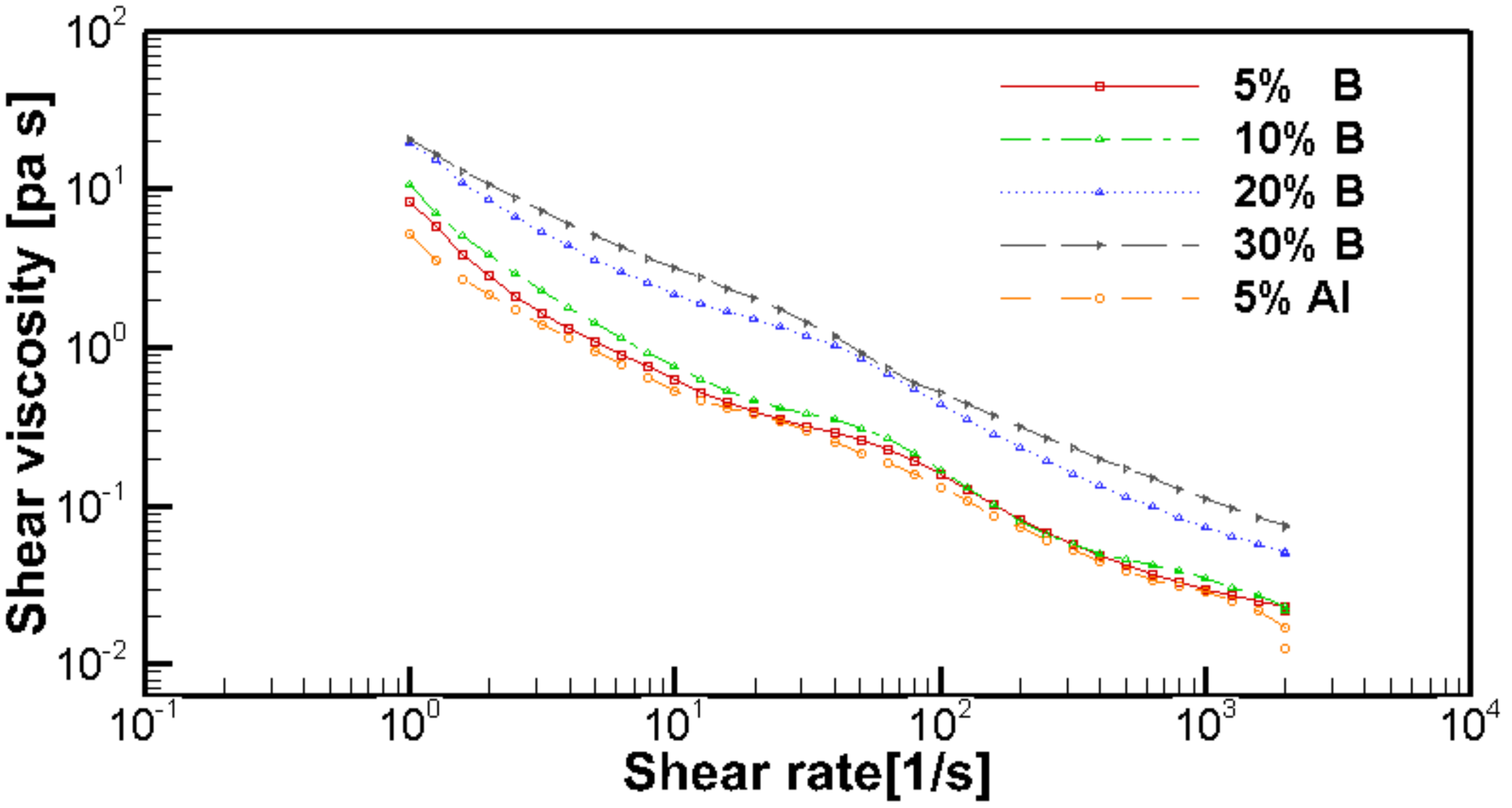
2.1. Gel Preparation and Characteristics
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Data Processing Method
2.4. Calibration Experiment and Error Analysis.
3. Results and Analysis
- The gas mass flow rate.
- The boron particle content.
- The species of the solid particle.
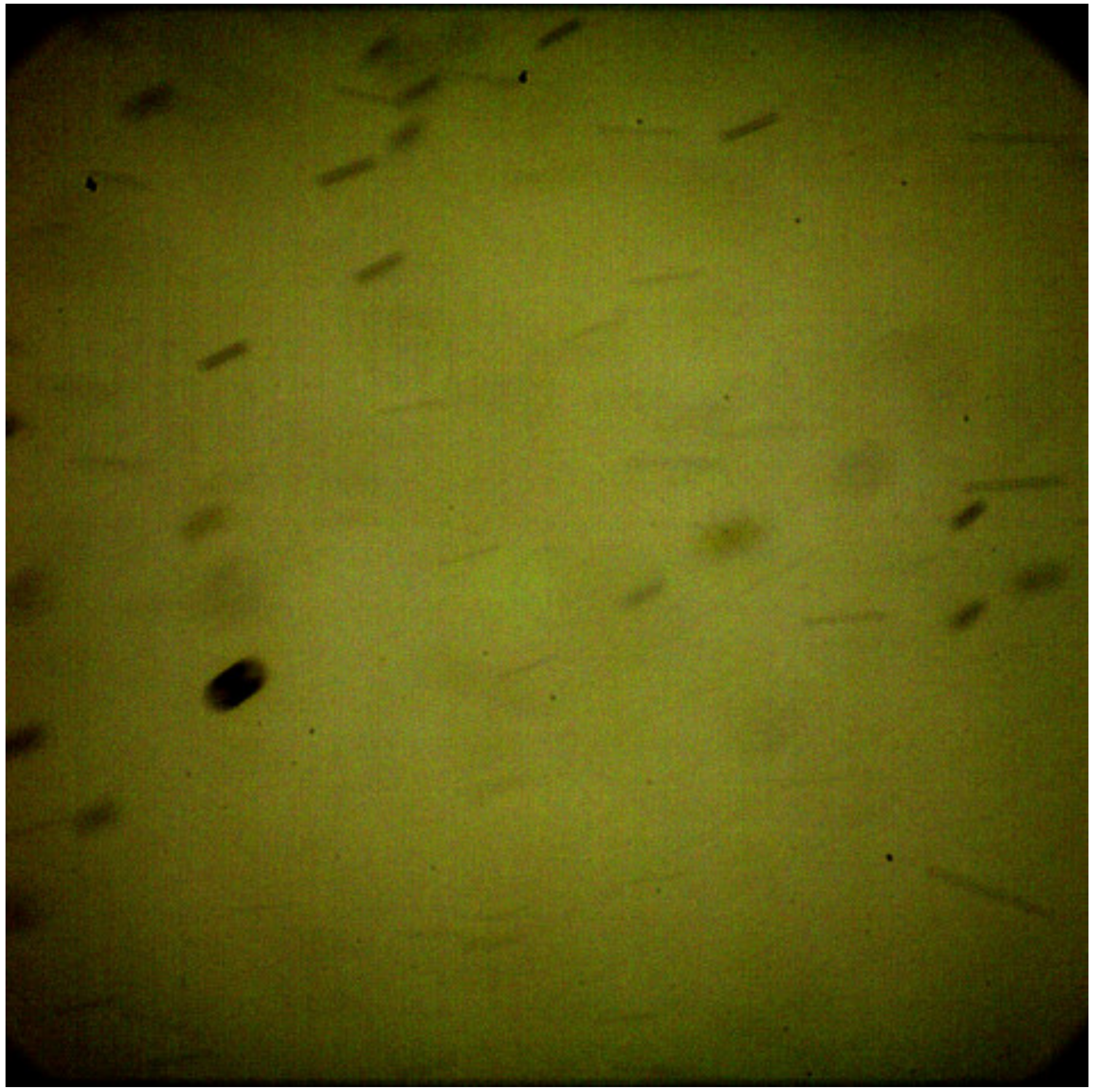
3.1. Analysis of the Spray
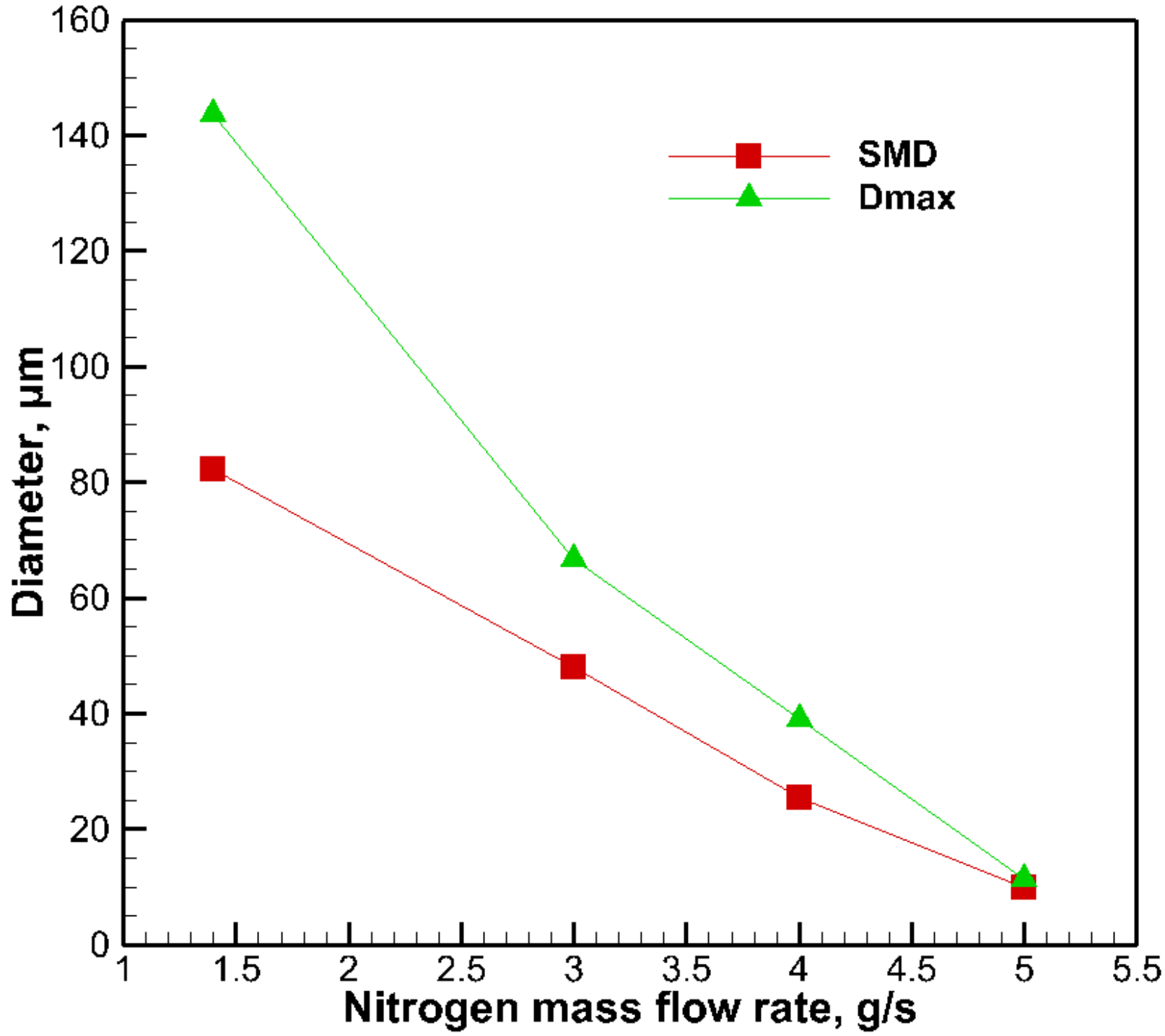
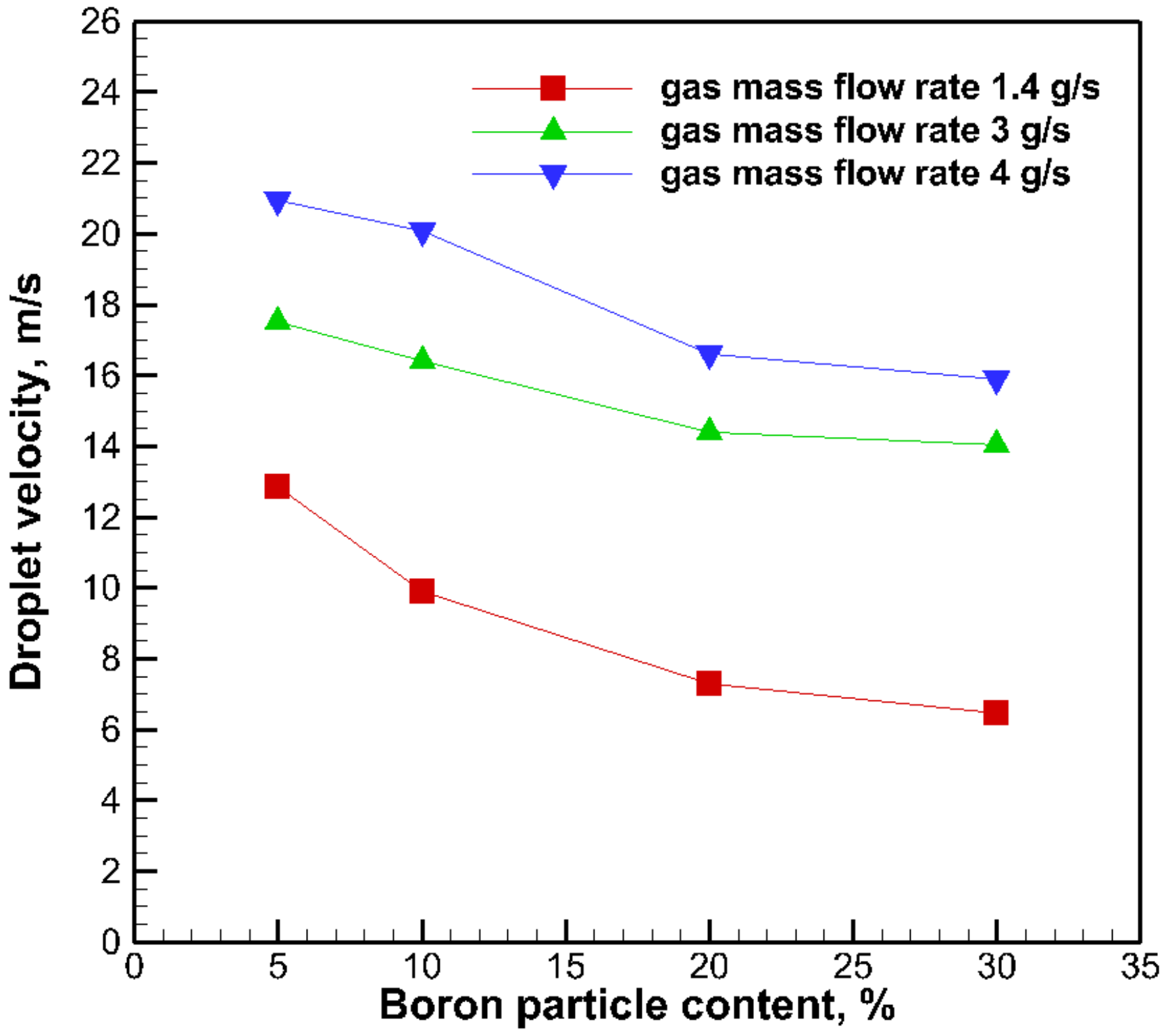
3.2. The Effect of Gas Mass Flow Rate on Droplet Size
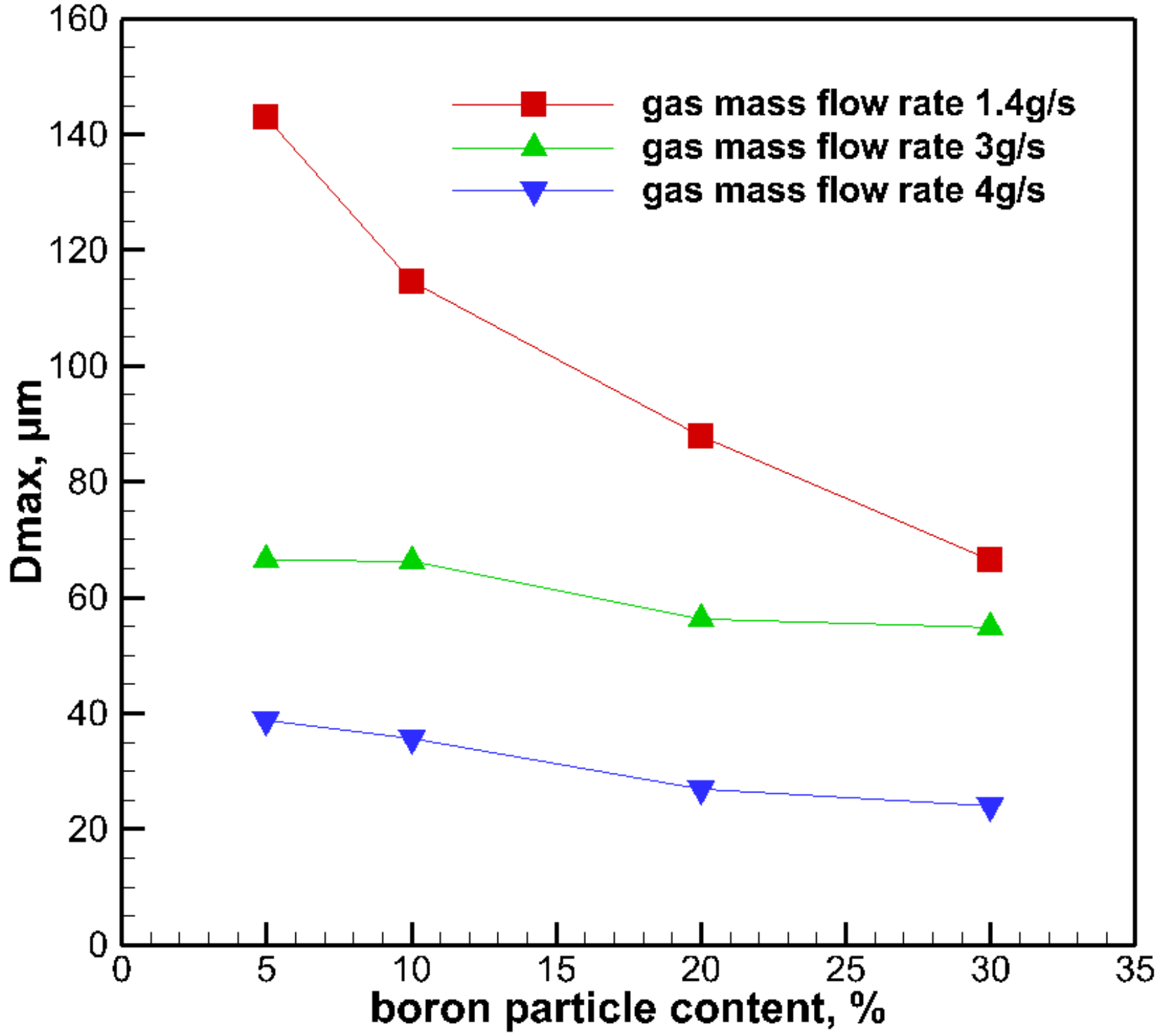
3.3. The Effect of Boron Particle Content on Droplet Size
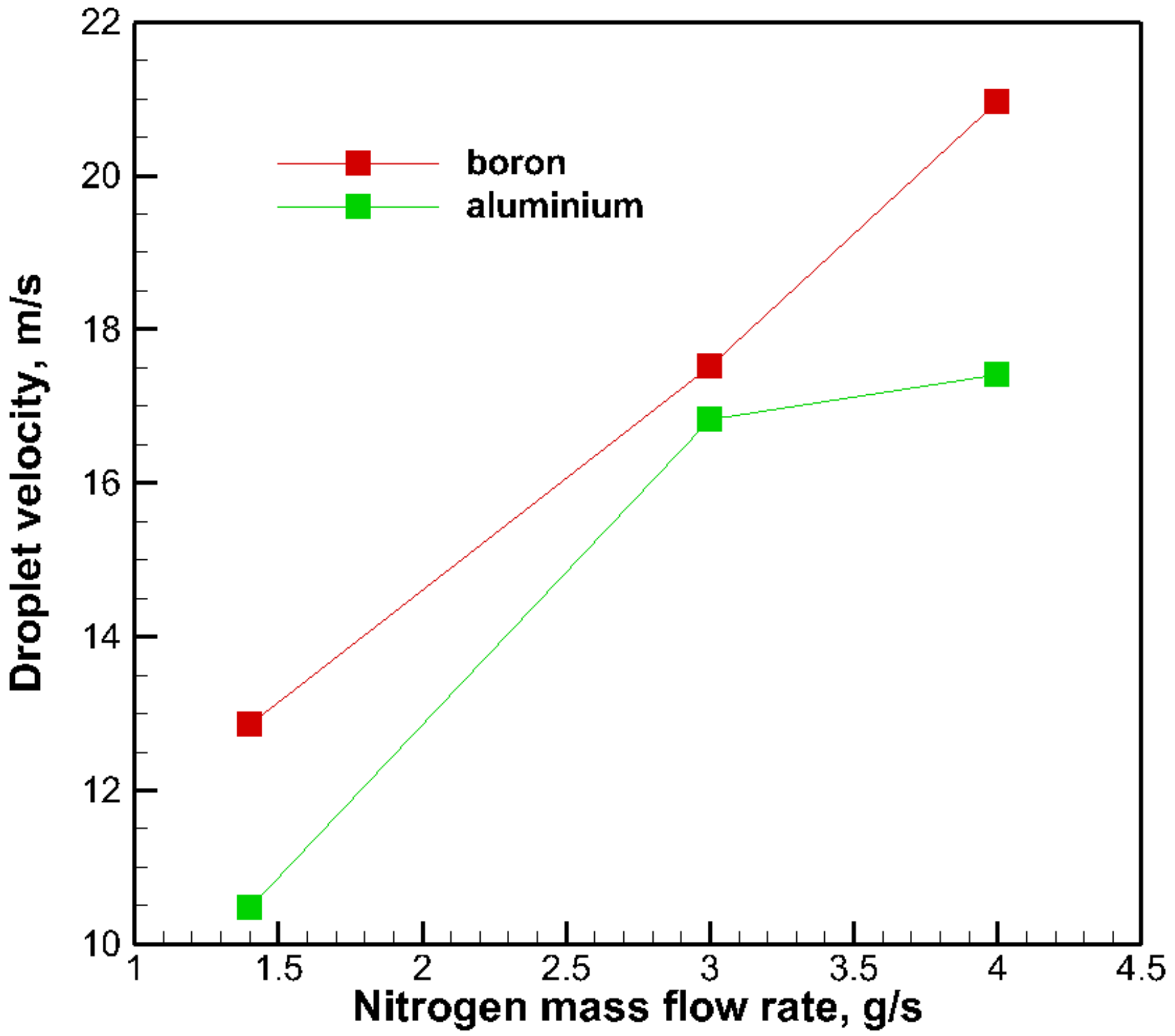
3.4. The Effect of Solid Particle Species on Droplet Size
4. Summary and Conclusions
- The droplet diameters of gel fuels with a boron particle addition decrease with the increasing of the gas mass flow rate.
- The droplet diameters were found to decrease by increasing the boron particle content. The steady-shear rheology data did not correlate to the atomization data in this study.
- The gel fuels with an aluminum particle addition were observed to produce smaller droplet diameters at a low gas mass flow rate than that with a boron particle addition. The differences of the density and the surface properties between the boron and the aluminum particles are supposed to be the cause of this.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natan, B.; Rahimi, S. The status of gel propellants in year 2000. Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2002, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafni, G.; Kuznetsov, A.; Har-Lev, D.; Natan, B. Experimental investigation of a ramjet combustor using an aluminized gel fuel. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.P.; Patyal, A.; Padhwal, M. Effects of gellant concentration on the burning and flame structure of organic gel propellant droplets. Fuel 2011, 90, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, Y.; Dan, G.; Natan, B. Pyrotechnic dispersion and ignition of boron particles in gels. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, C.; Kou, Z. Experimental studies on the spraying pattern of a swirl nozzle for coal dust control. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.H. Airblast atomization. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1980, 6, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Y.; Takeno, K.; Hashiguchi, K.; Lu, J. Mixing and atomization characteristics in an internal-mixing twin-fluid atomizer. Fuel 2012, 97, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.; Rapp, D.; Roncace, J. Flow visualization of a rocket injector spray using gelled propellant simulants. In Proceedings of the 27th AIAA/SAE/ASME/ ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 24–26 June 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciezki, H.; Robers, A.; Schneider, G. Investigation of the spray behavior of gelled Jet-A1 fuels using an air blast and an impinging jet atomizer. In Proceedings of the 38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 7–10 July 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Natan, B. Atomization of gel propellants through an air-blast triplet atomizer. At. Spray. 2006, 16, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, V.; Natan, B. Effect of Periodic Disturbances on Non-Newtonian Fluid Sprays. At. Spray. 2008, 18, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, S.; Han, J.; Kim, C. Atomization characteristics of impinging jets of gel material containing nanoparticles. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2011, 166, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ko, T.; Kim, S.; Yoon, W. Spray characteristics of aluminized-gel fuels sprayed using pressure-swirl atomizer. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2017, 249, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurkar, S.Y.; Yadav, G.; Mishra, D.P. Visualizations of sheet breakup of non-Newtonian gels loaded with nanoparticles. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 100, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, J.V.; Alberio, F.; Ciezki, H.K. Spray and combustion characteristics of aluminized gelled fuels with an impinging jet injector. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2007, 11, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, P.; Stamper, J.A.; Giles, J.K. Pneumatic atomization of laundry detergent slurries as affected by solid particle size and concentration. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–18 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vysokomornaya, O.V.; Piskunov, M.V.; Strizhak, P.A. Breakup of heterogeneous water drop immersed in high-temperature air. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strizhak, P.A.; Piskunov, M.V.; Volkov, R.S.; Legros, J.C. Evaporation, boiling and explosive breakup of oil–water emulsion drops under intense radiant heating. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 127, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, R.S.; Kuznetsov, G.V.; Strizhak, P.A. Water droplet deformation in gas stream: Impact of temperature difference between liquid and gas. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.Q.; Mullen, J.C. Burning-rate behavior in aluminized wide-distribution AP composite propellants. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2011, 47, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
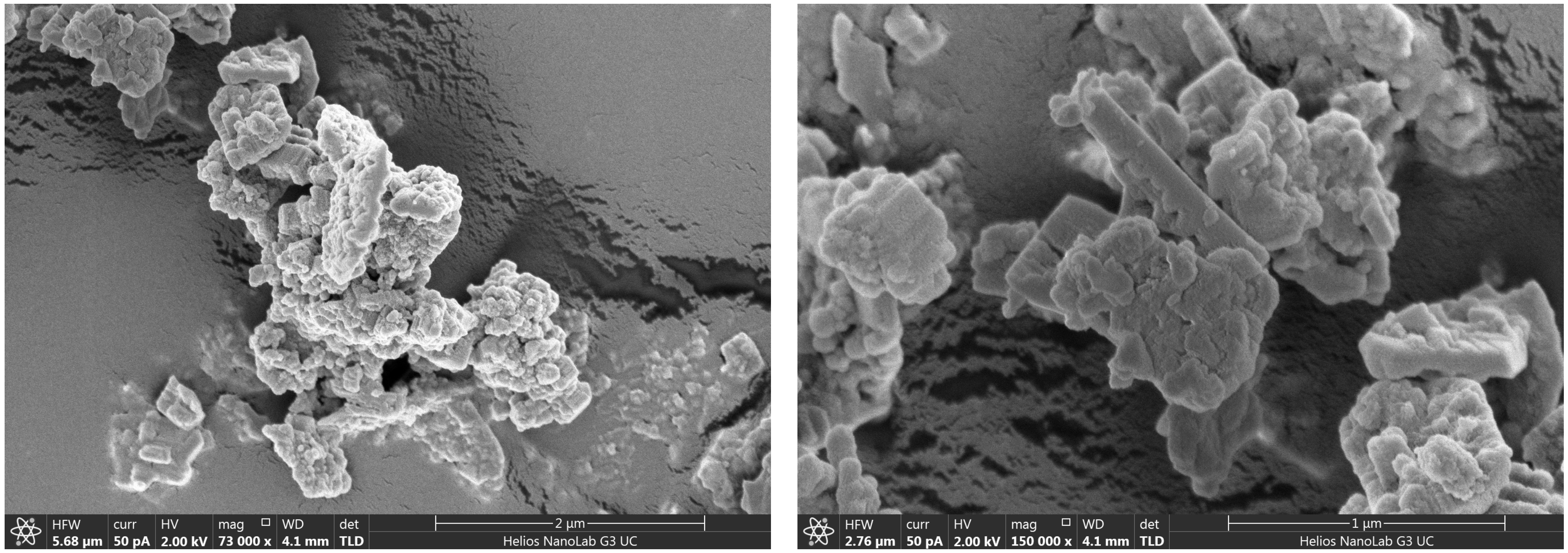









| YB [wt.%] | YAl [wt.%] | Power Law Coefficients | Herschel–Bulkley Coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K(Pl) [Pa s] | n(Pl) [-] | K(HB) [Pa s] | n(HB) [-] | τ0 [Pa] | ||
| 5 | - | 2.835 | 0.3506 | 0.5564 | 0.5557 | 5.587 |
| 10 | - | 3.741 | 0.3186 | 0.5137 | 0.5681 | 7.294 |
| 20 | - | 13.06 | 0.2574 | 5.161 | 0.3667 | 12.39 |
| 30 | - | 14.26 | 0.3001 | 4.847 | 0.4314 | 17.48 |
| - | 5 | 2.982 | 0.3142 | 2.124 | 0.3544 | 1.520 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Xia, Z.; Huang, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, D. Atomization of Gel Fuels with Solid Particle Addition Utilizing an Air Atomizing Nozzle. Energies 2018, 11, 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112959
Xiao Y, Xia Z, Huang L, Ma L, Yang D. Atomization of Gel Fuels with Solid Particle Addition Utilizing an Air Atomizing Nozzle. Energies. 2018; 11(11):2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112959
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yunlei, Zhixun Xia, Liya Huang, Likun Ma, and Dali Yang. 2018. "Atomization of Gel Fuels with Solid Particle Addition Utilizing an Air Atomizing Nozzle" Energies 11, no. 11: 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112959
APA StyleXiao, Y., Xia, Z., Huang, L., Ma, L., & Yang, D. (2018). Atomization of Gel Fuels with Solid Particle Addition Utilizing an Air Atomizing Nozzle. Energies, 11(11), 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112959




