Numerical Study of Bubble Coalescence and Breakup in the Reactor Fuel Channel with a Vaned Grid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Models
2.1. Eulerian Two-Fluid Model
2.2. MUSIG Model
2.3. Phasic Interaction Models
2.3.1. Drag Force
2.3.2. Lift Force
2.3.3. Wall Lubrication Force
2.3.4. Turbulent Dispersion Force
2.3.5. Virtual Mass Force
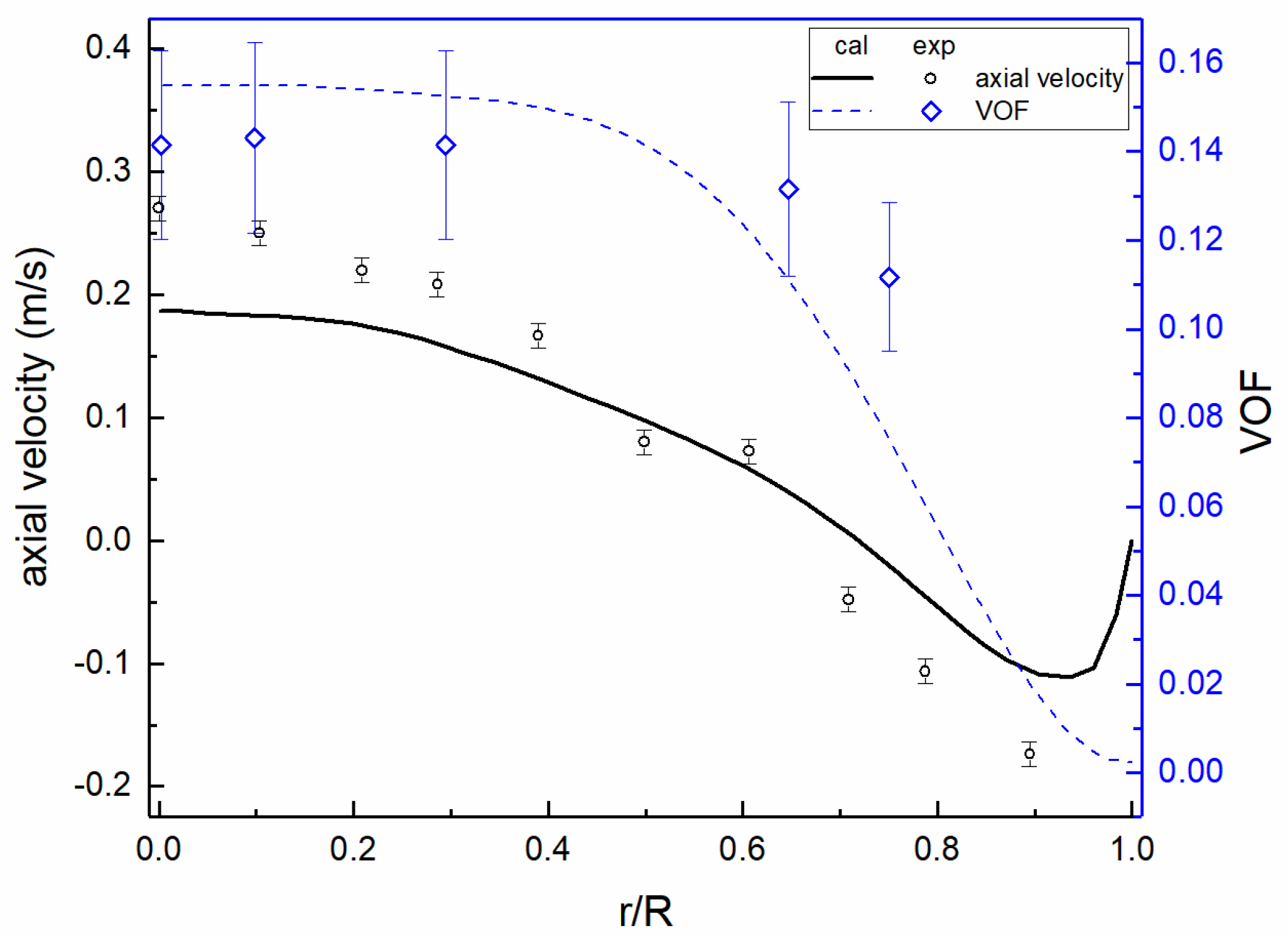
3. Model Validation
4. Two-Phase Flow in the Fuel Assembly with Two Channels
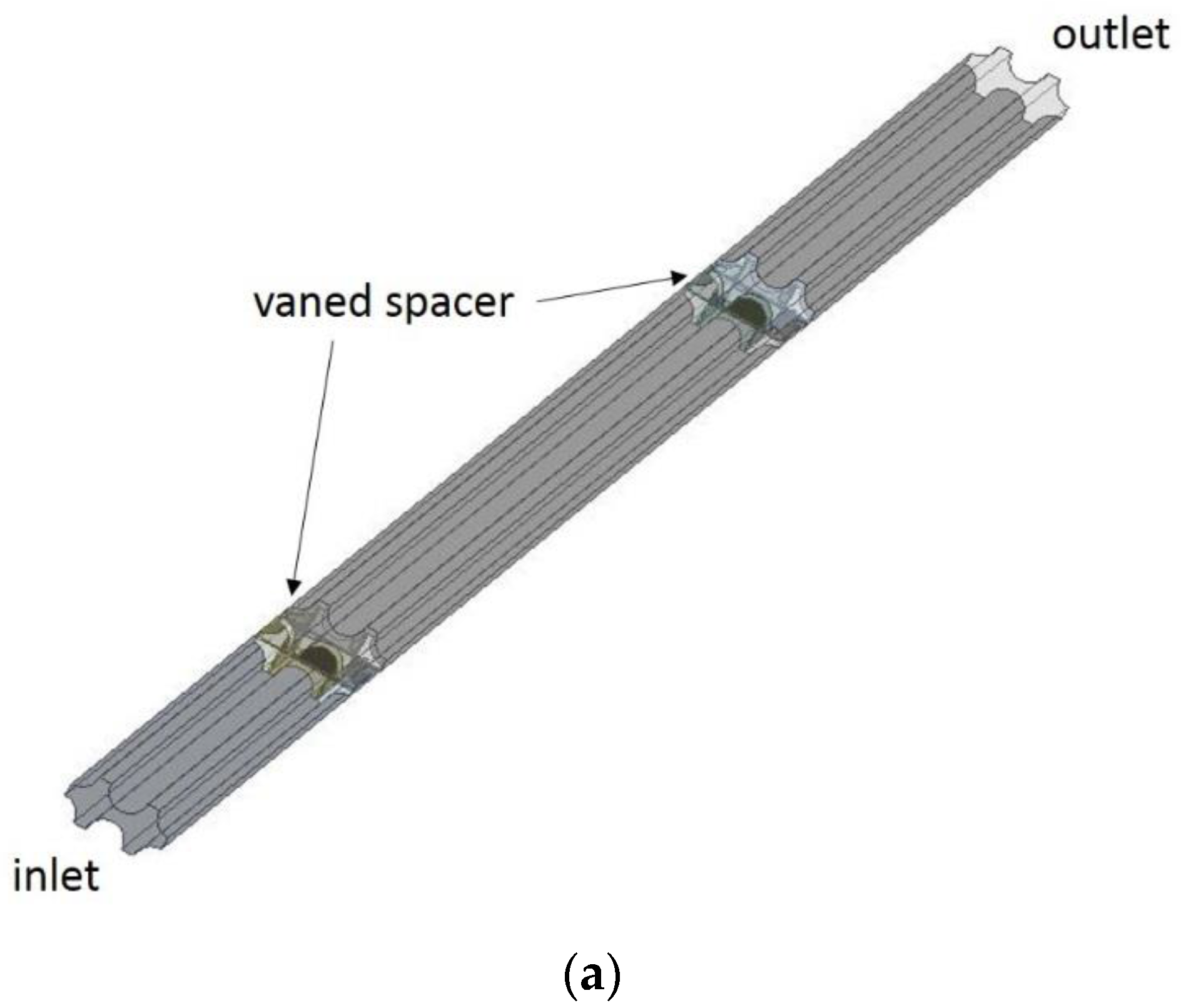
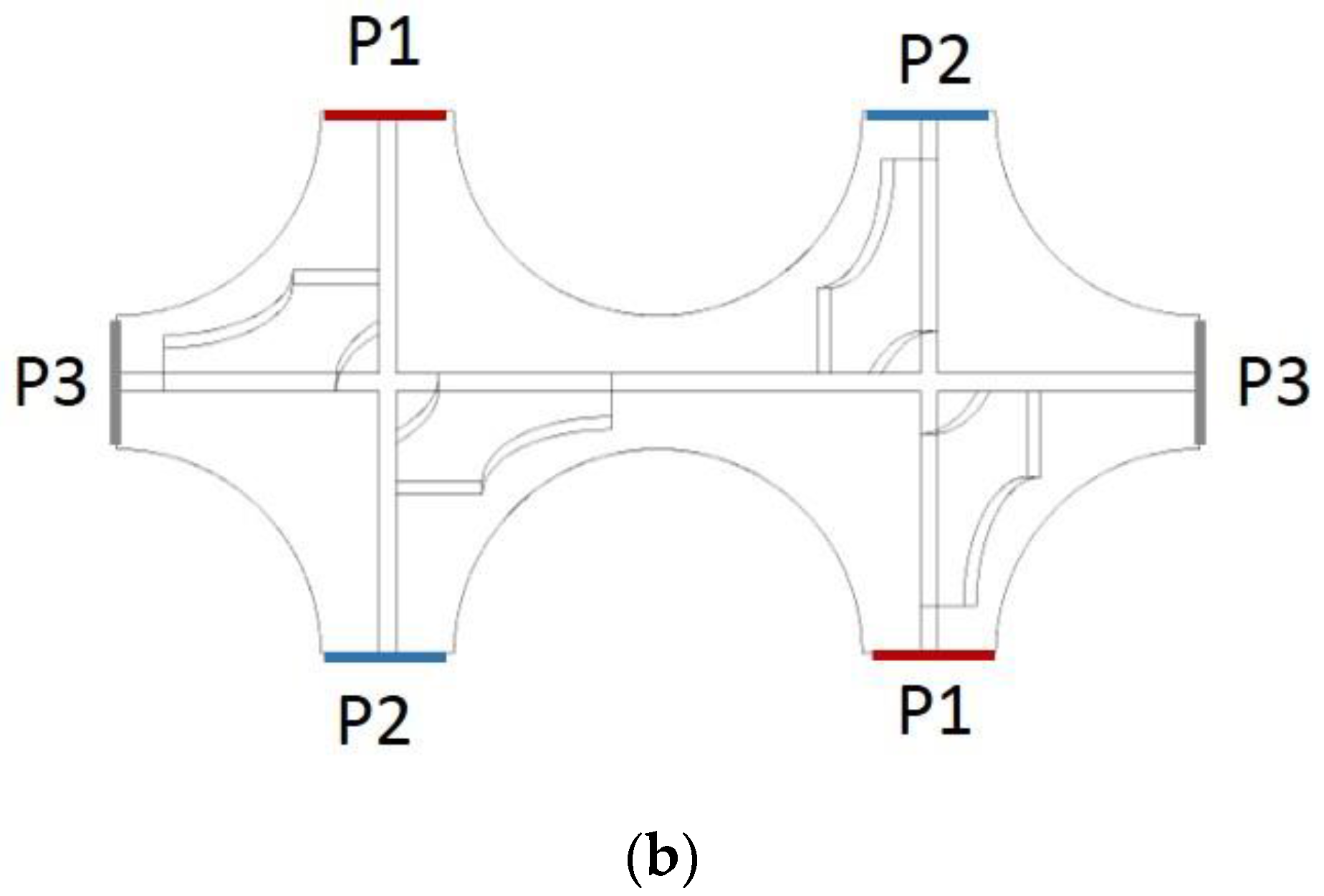
4.1. Geometry, Grid, Boundary Conditions and Numerical Scheme
4.2. Analysis on the Two-Phase Parameters in the Fuel Assembly
4.2.1. Cases Setup
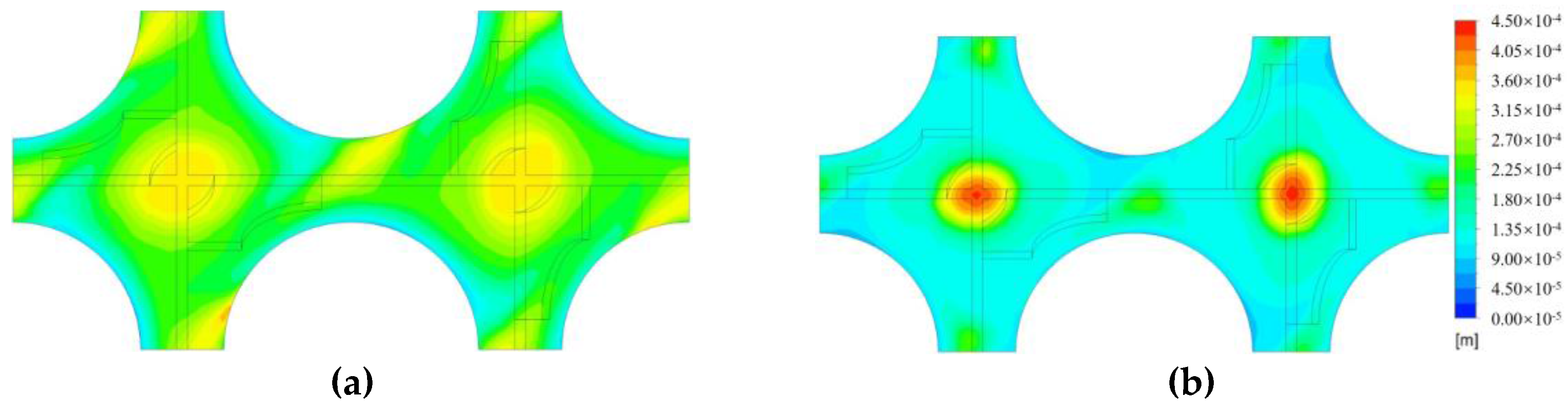
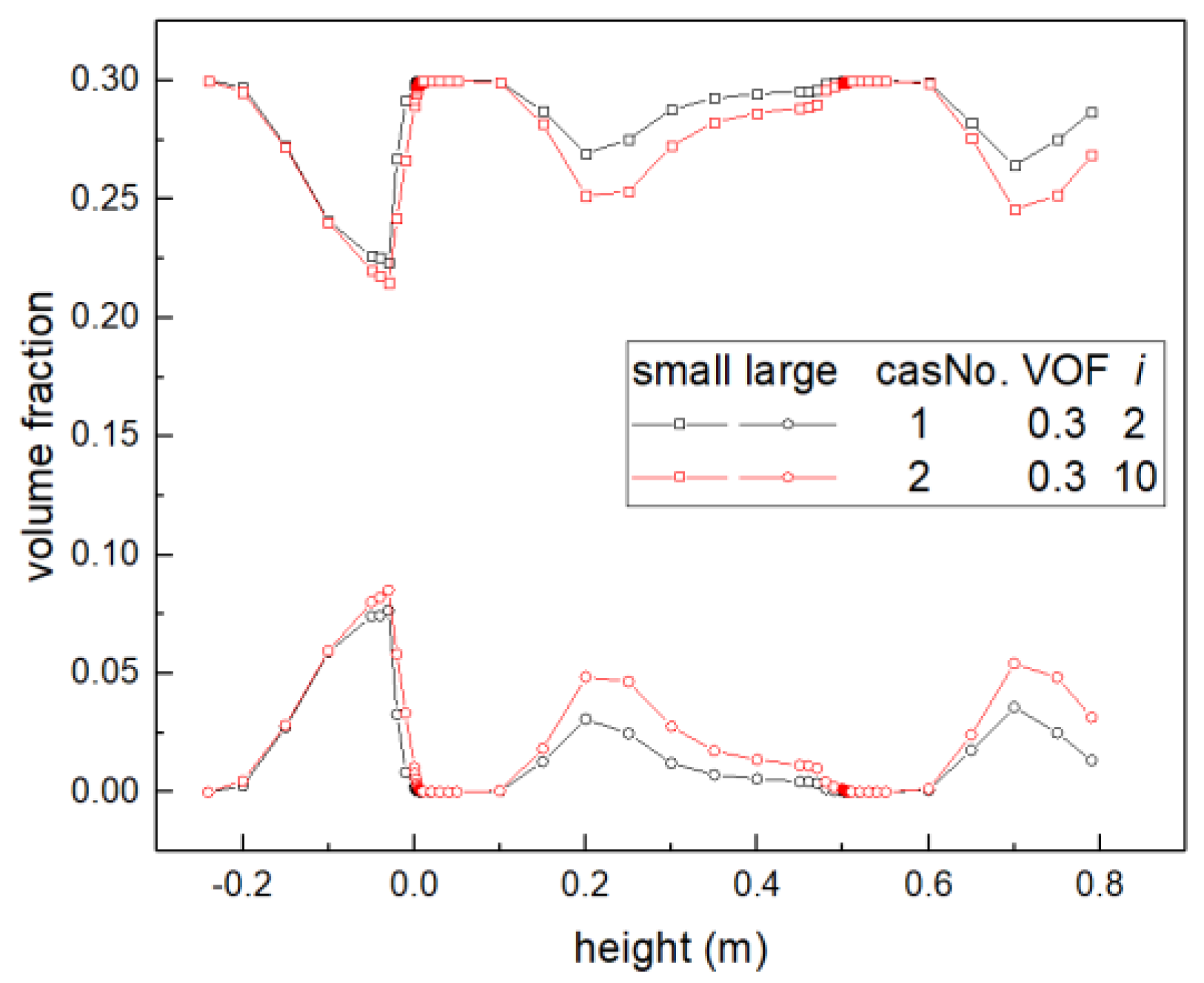
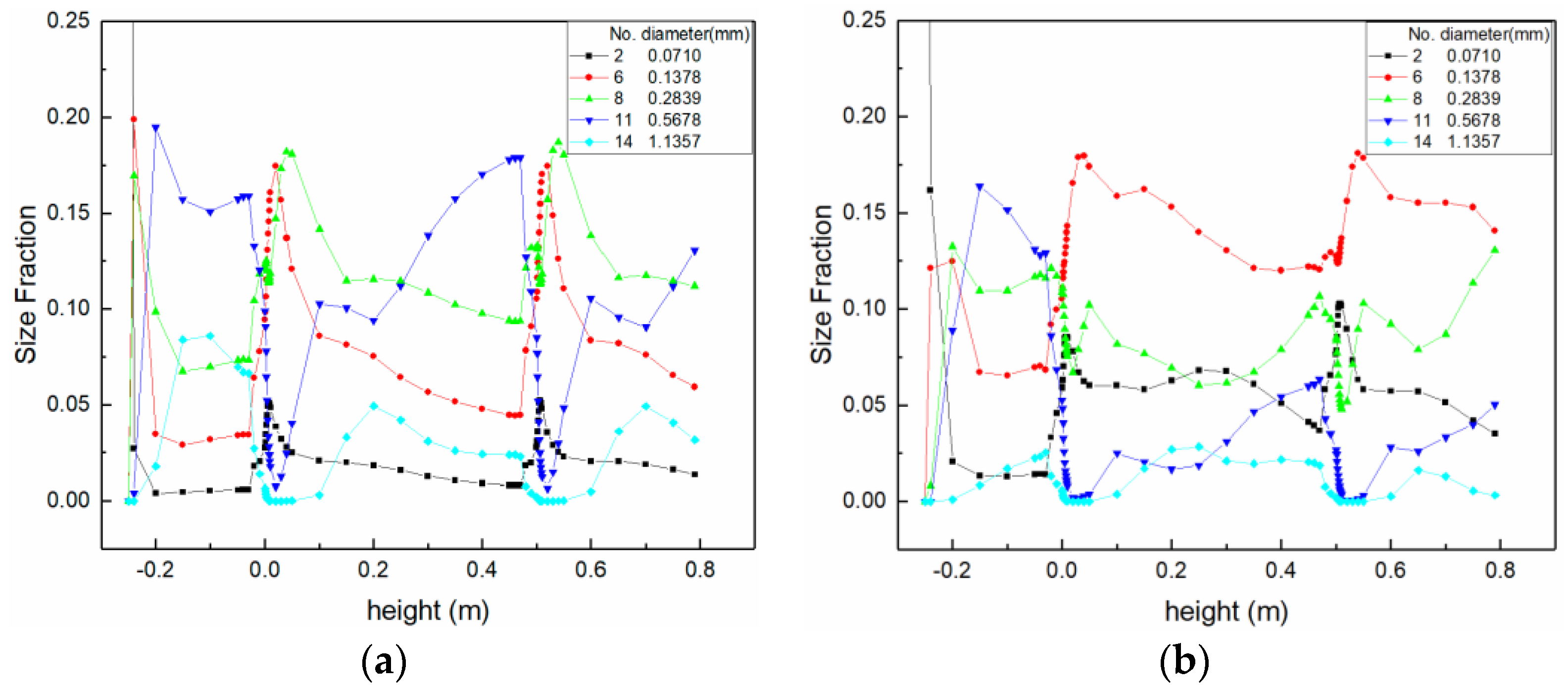
4.2.2. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
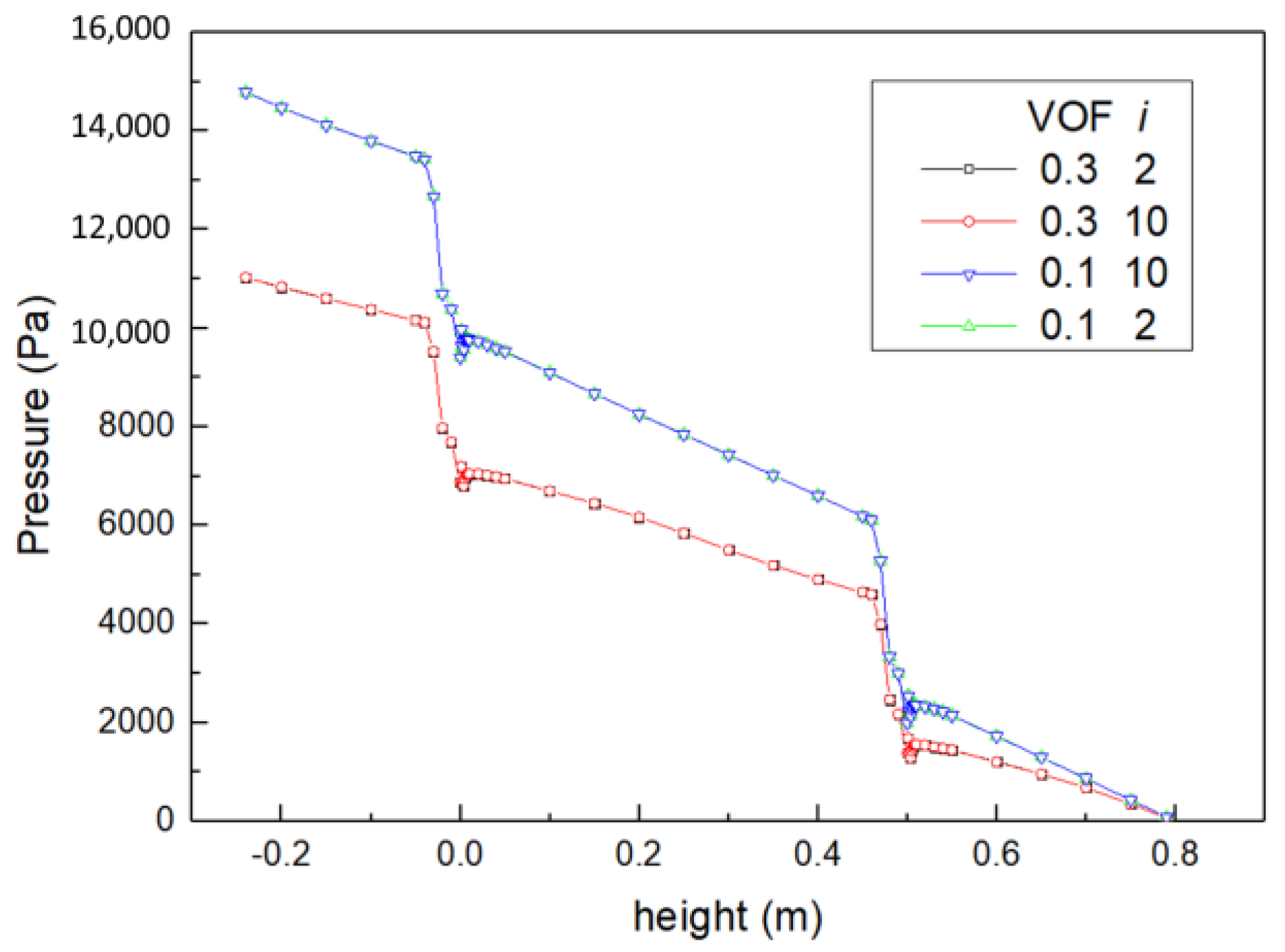
- Vaned spacers caused sharp pressure drop, which is associated with the vapor volume fraction, rather than the inlet bubble size.
- (2)
- Vapor phase crowded at the rod surface for the higher inlet vapor fraction case, but crowded in the channel center for the lower inlet vapor fraction cases, i.e., increasing the inlet fraction can increase the risk of bubble aggregation at the rod surface, which might anticipate the critical heat flux under the condition of boiling two-phase flow.
- (3)
- Mixing vanes can reduce the average bubble size by breakup. However, the bubble size distribution downstream of the mixing vane was related to the inlet vapor fraction, rather than the inlet bubble size.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krepper, E.; Končar, B.; Egorov, Y. CFD modelling of subcooled boiling—Concept, validation and application to fuel assembly design. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2007, 237, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cong, T.; Tian, W.; Qiu, S.; Su, G. CFD analysis on subcooled boiling phenomena in PWR coolant channel. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2015, 81, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cong, T.; Tian, W.; Qiu, S.; Su, G. Effects of turbulence models on forced convection subcooled boiling in vertical pipe. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 80, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Yap, Y.F.; Lou, J.; Chai, J.C.; Shang, Z. Conjugate heat transfer in stratified two-fluid flows with a growing deposit layer. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Rzehak, R.; Lucas, D.; Krepper, E. Baseline closure model for dispersed bubbly flow: Bubble coalescence and breakup. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestion, D.; Anglart, H.; Mahaffy, J.; Lucas, D.; Song, C.-H.; Scheuerer, M.; Zigh, G.; Andreani, M.; Kasahara, F.; Heitsch, M.; et al. Extension of CFD Codes Application to Two-Phase Flow Safety Problems. Phase 2; NEA/CSNI/R(2010)2; OECD: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS CFX-Solver Theory Guide, 14 ed.; ANSYS Inc.: Cononsburg, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Narayanan, C.; Lakehal, D.; Gong, Y. Multiphase Flow Simulation of Subcooled Boiling Using the N-Phase Approach in TransAT. In Proceedings of the 2013 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering, Chengdu, China, 29 July–2 August 2013; p. V003T10A015. [Google Scholar]
- Lifante, C.; Reiterer, F.; Frank, T.; Burns, A. Coupling of wall boiling with discrete population balance model. J. Comput. Multiph. Flows 2012, 4, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, D.; Frank, T.; Lifante, C.; Zwart, P.; Burns, A. Extension of the inhomogeneous MUSIG model for bubble condensation. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 4359–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, A.; Tamai, H.; Zun, I.; Hosokawa, S. Transverse migration of single bubbles in simple shear flows. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Svendsen, H.F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.J.; Blanch, H.W. Bubble coalescence and break-up in air-sparged bubble columns. AIChE J. 1990, 36, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Zuber, N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows. AIChE J. 1979, 25, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.; Shi, J.; Burns, A.D. Validation of Eulerian multiphase flow models for nuclear safety application. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Two-Phase Modelling and Experimentation, Pisa, Italy, 22–25 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Antal, S.; Lahey, R., Jr.; Flaherty, J. Analysis of phase distribution in fully developed laminar bubbly two-phase flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1991, 17, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.D.; Frank, T.; Hamill, I.; Shi, J.M. The favre averaged drag model for turbulent dispersion in Eulerian multi-phase flows. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Multiphase Flow, Yokohama, Japan, 30 May–4 June 2004; JSME: Yokohama, Japan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vial, C.; Laine, R.; Poncin, S.; Midoux, N.; Wild, G. Influence of gas distribution and regime transitions on liquid velocity and turbulence in a 3-D bubble column. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y. Methods of simulating large-scale rod bundle and application to a 17 × 17 fuel assembly with mixing vane spacer grid. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2014, 267, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffy, J.; Chung, B.; Dubios, F.; Ducros, F.; Graffard, E.; Heitsch, M.; Henriksson, M.; Komen, E.; Moretti, F.; Morii, T.; et al. Best Practice Guidelines for the Use of CFD in Nuclear Reactor Safety Applications; NEA/CSNI/R(2007)5; OECD/NEA: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
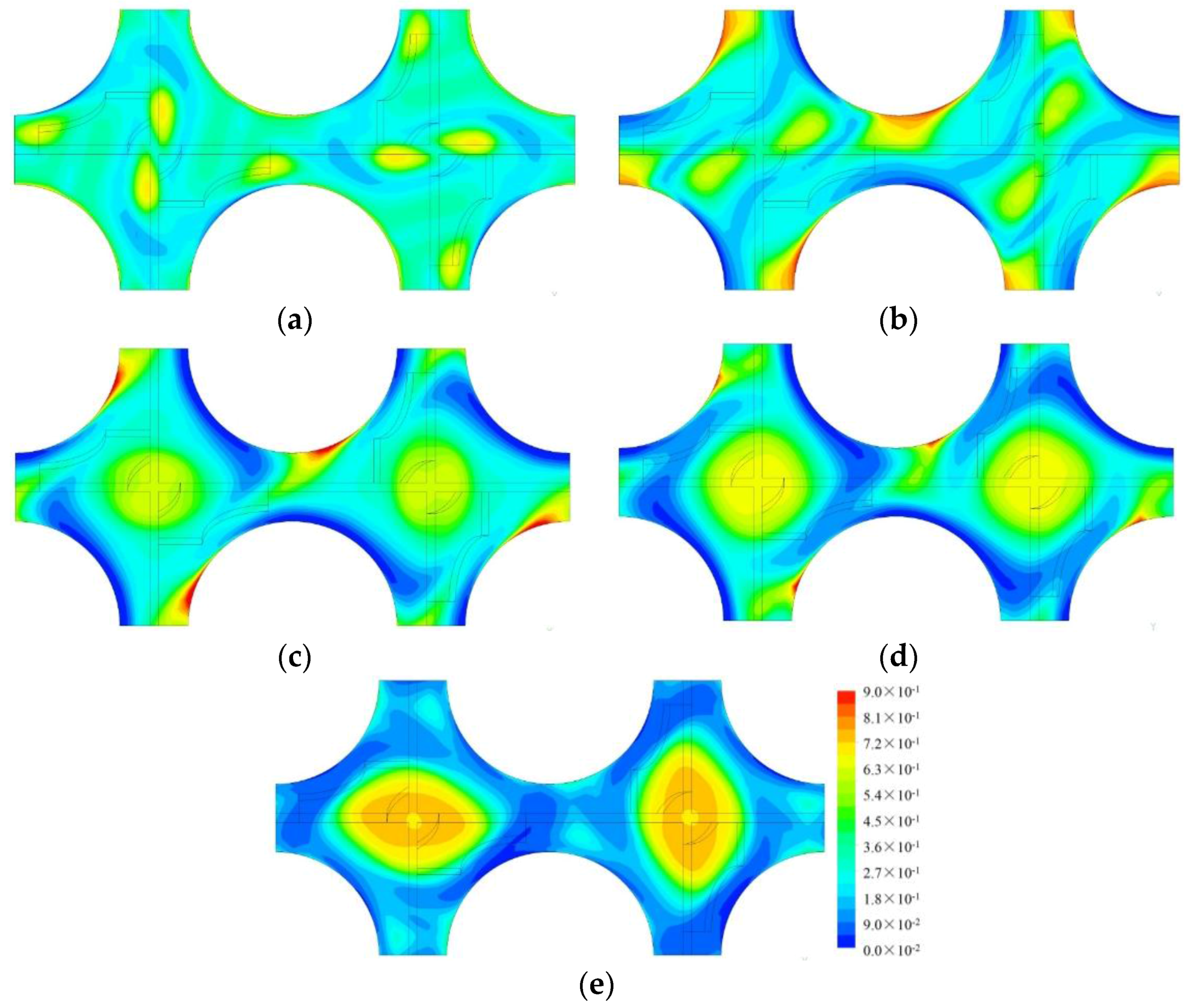
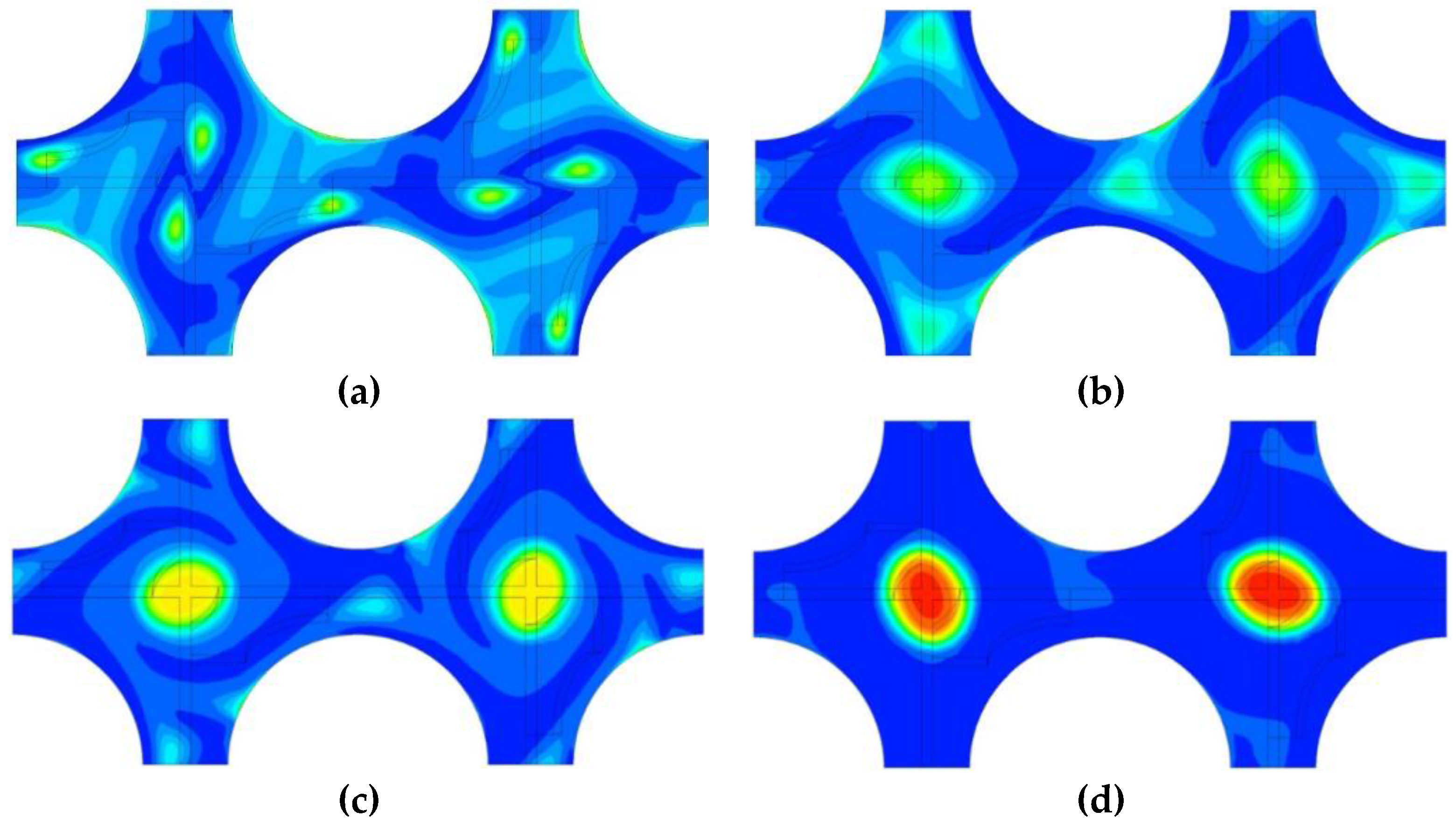
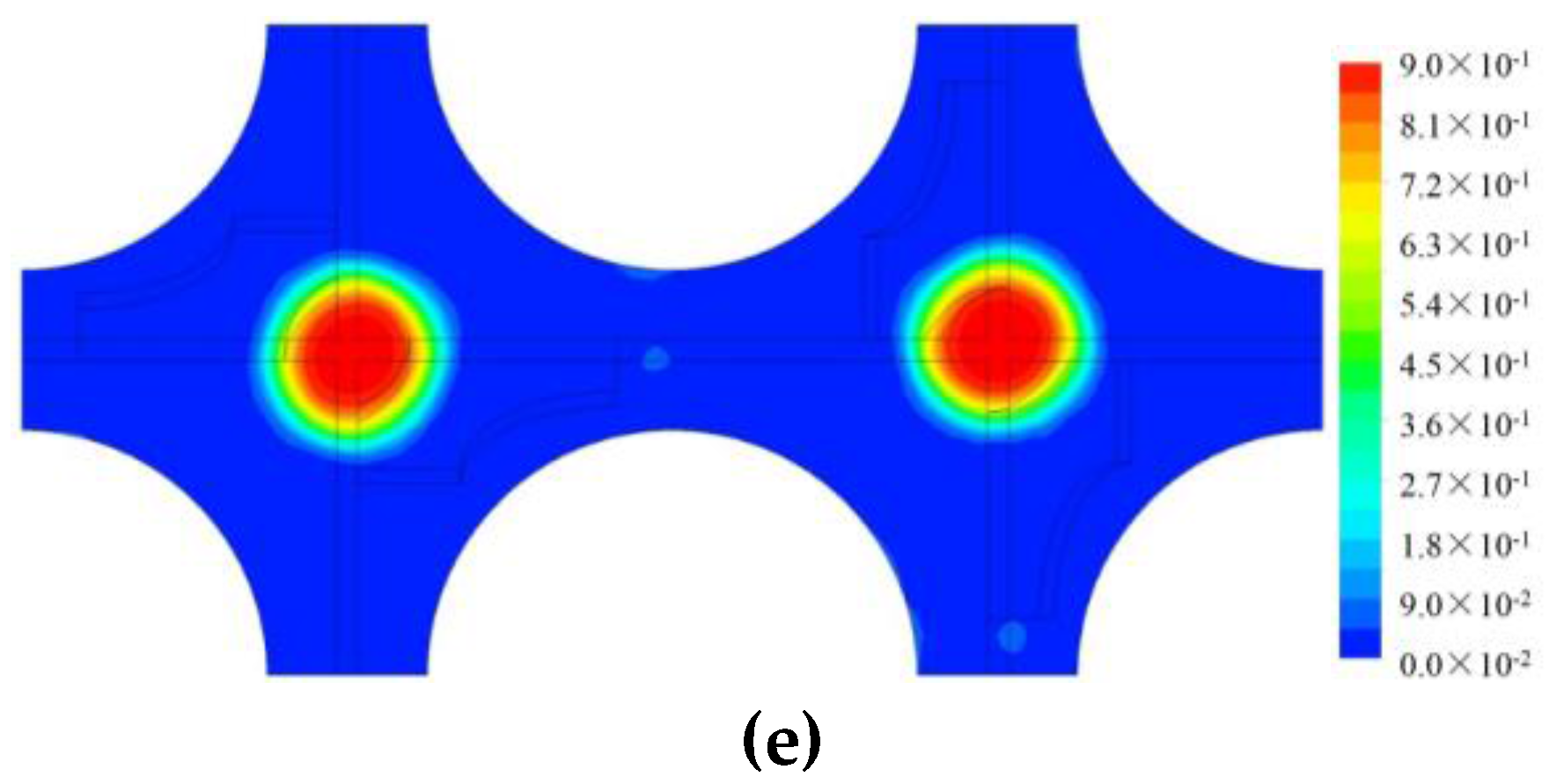
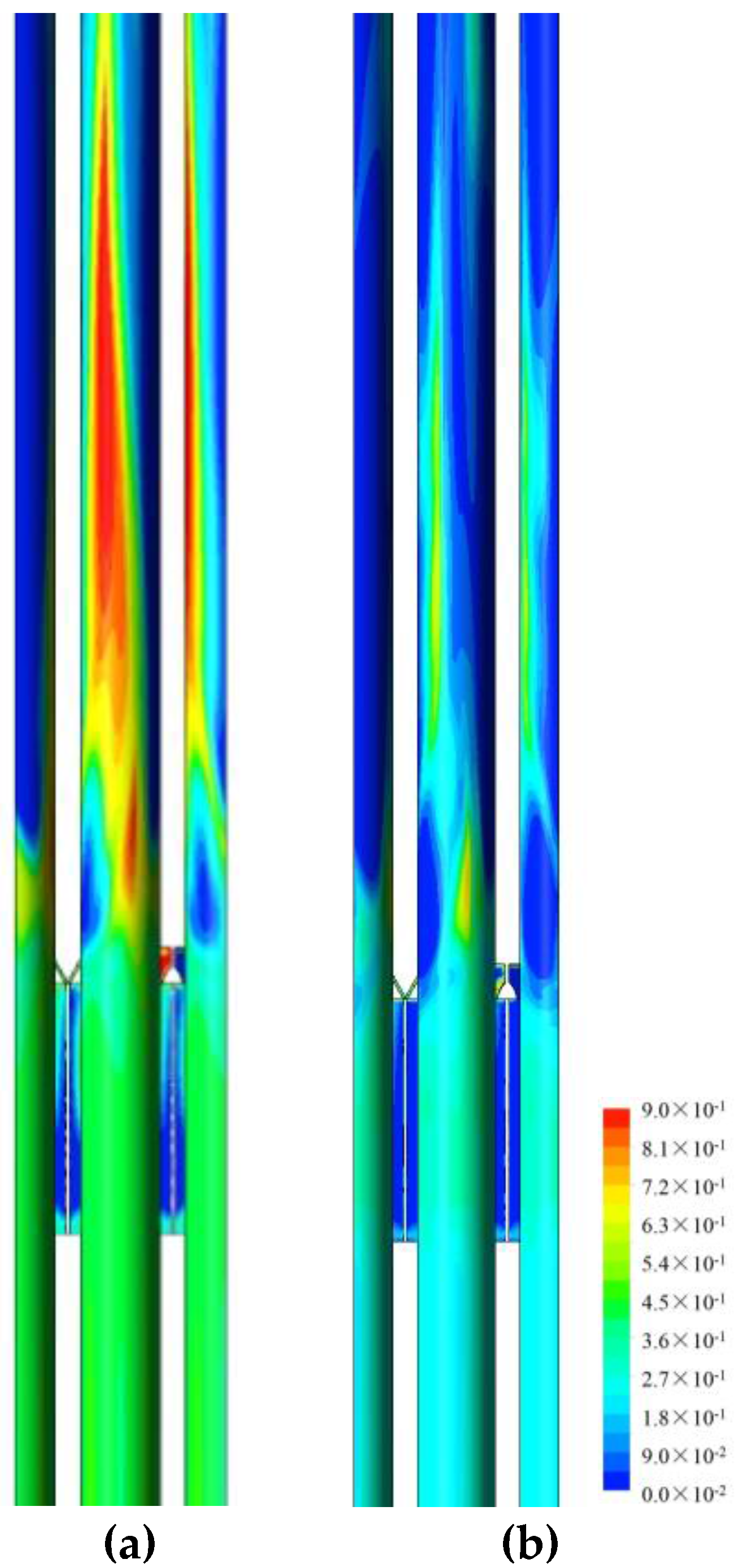

| Case No. | Inlet VOF | Inlet Bubble Size |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3 | All in group 2 |
| 2 | 0.3 | All in group 10 |
| 3 | 0.1 | All in group 10 |
| 4 | 0.1 | All in group 2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cong, T.; Zhang, X. Numerical Study of Bubble Coalescence and Breakup in the Reactor Fuel Channel with a Vaned Grid. Energies 2018, 11, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010256
Cong T, Zhang X. Numerical Study of Bubble Coalescence and Breakup in the Reactor Fuel Channel with a Vaned Grid. Energies. 2018; 11(1):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010256
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Tenglong, and Xiang Zhang. 2018. "Numerical Study of Bubble Coalescence and Breakup in the Reactor Fuel Channel with a Vaned Grid" Energies 11, no. 1: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010256
APA StyleCong, T., & Zhang, X. (2018). Numerical Study of Bubble Coalescence and Breakup in the Reactor Fuel Channel with a Vaned Grid. Energies, 11(1), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010256




