Properties of Gasoline Stored in Various Containers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis of Storage Gasoline and PE Surface
3. Results
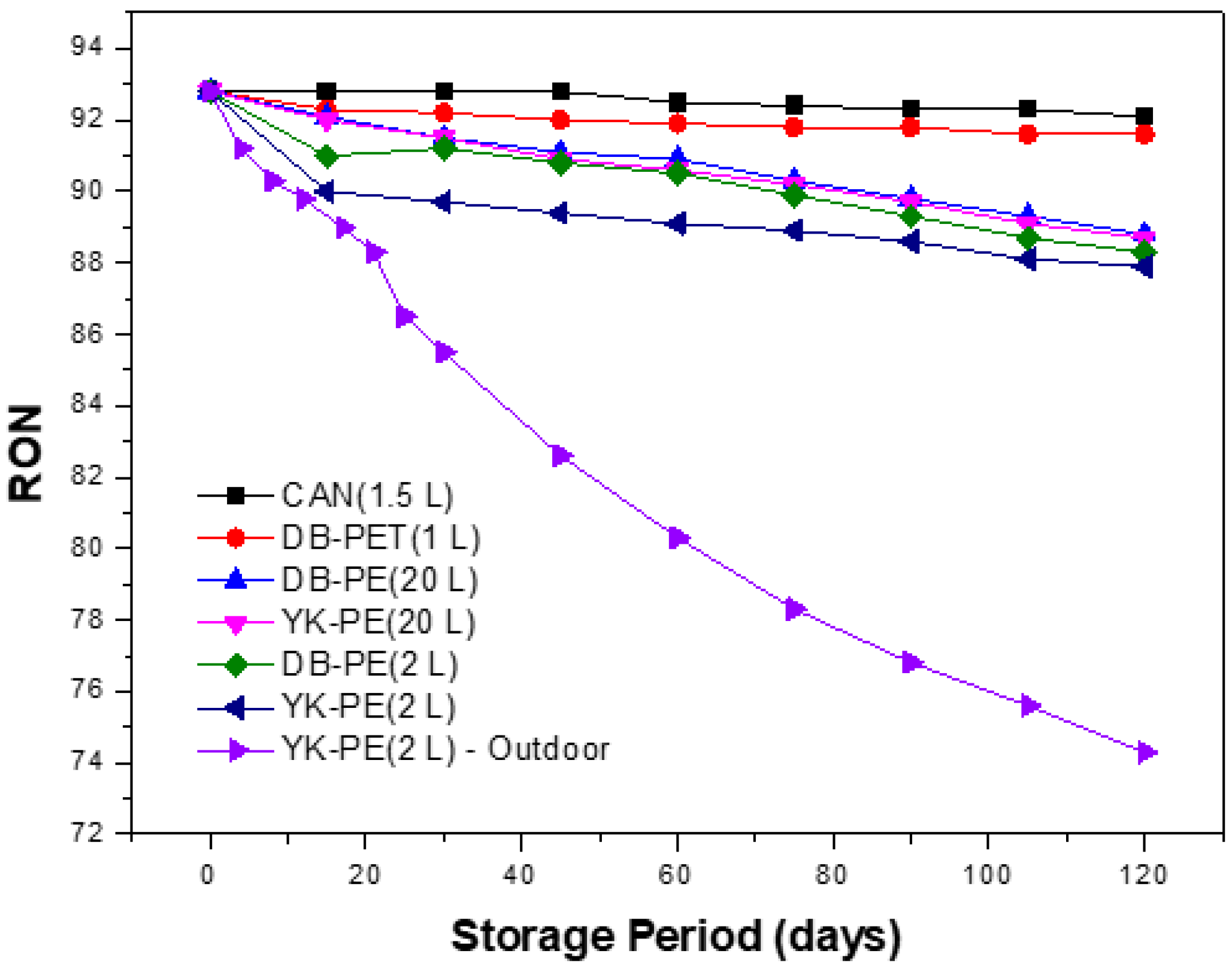
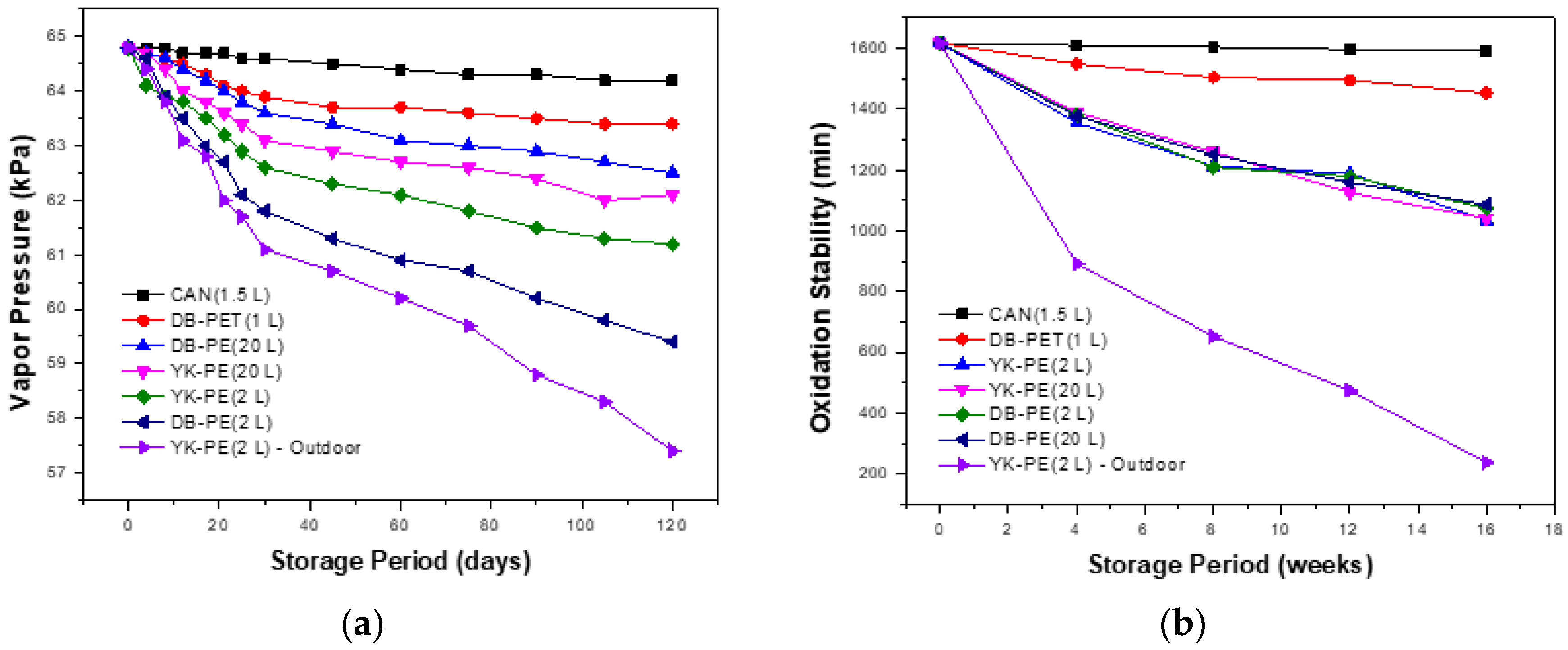
3.1. Variation of Fuel Quality Depending on Storage Containers’ Type
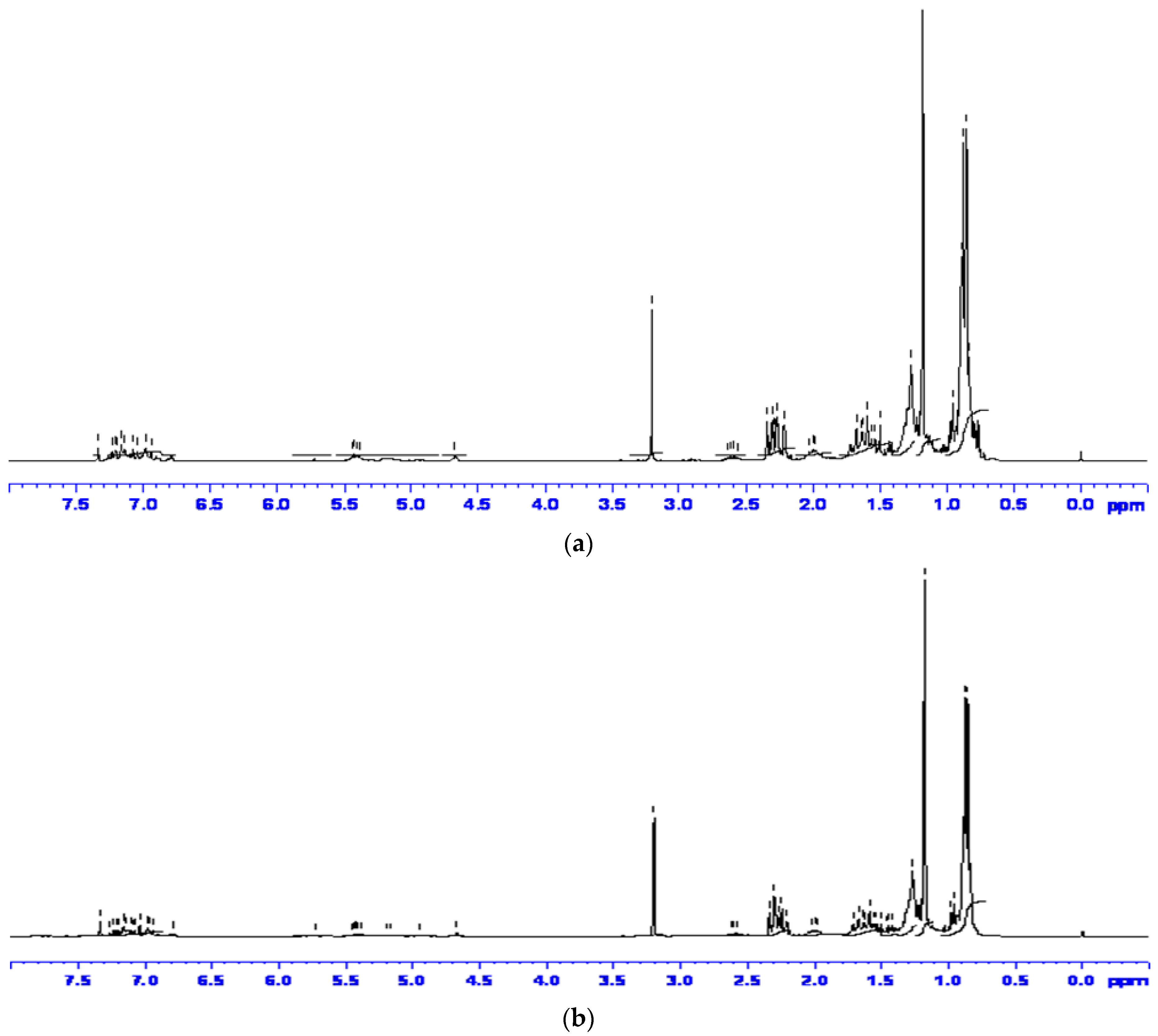
3.2. Analysis of the Surfaces of Storage Containers
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveria, F.S.; Teixerira, L.S.G.; Araújo, M.C.U.; Korn, M. Screening analysis to detect adulterations in Brazilian gasoline samples using distillation curves. Fuel 2004, 83, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE). Quality Standard for Autotomobile Gasoline. 2017. Available online: http://www.motie.go.kr/motie/ms/nt/gosi/bbs/bbsView.do?bbs_seq_n=62709&bbs_cd_n (accessed on 11 June 2017).
- Min, K.I.; Yim, E.S.; Jung, C.-S.; Kim, J.-K. Study on the characterization of oxidative degradation of automotive gasoline. Korean Chem. Eng. Res 2013, 51, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Zheng, D. A chemical mechanism for ignition and oxidation of multi-component gasoline surrogate fuels. Fuel 2014, 128, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhan, O. Change in the properties of gasoline in storage in underground tanks. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2008, 44, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, E.L.; Yabroff, D.L.; Minor, H.B. Correlation of Predicted and Observed Storage Stability of Cracked Gasoline. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1948, 40, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, J.M.; Joshi, G.C.; Singh, J. Gum forming olefinic precursors in motor gasoline, A model compound study. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 1994, 12, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanier, A. Thermal-oxidative stability of motor gasolines by pressure d.s.c. Fuel 1998, 77, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Saito, A.; Matsushita, S.; Shibata, H.; Niwa, Y. Study of deposit formation mechanism on gasoline injection nozzle. JSAE 1998, 19, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.T.; Jou, W.S.; Su, Y.S. Permeation barrier properties of polyethylene/modified blends of polyamide and polyvinylalcohol containers against methanol/gasoline fuels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 2158–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.T.; Huang, S.S.; Yao, W.H. Gasoline permeation resistance of containers of polyethylene, polyethylene/modified polyamide and polyethylene/blends of modified polyamide and ethylene vinyl alcohol. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2002, 287, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Storage Container 1 | Capacity (L) | Number of Samples | Storage Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CAN | 1.5 | 20 | Indoor |
| 2 | YK-PE | 2 | 15 | Indoor |
| 3 | YK-PE | 20 | 2 | Indoor |
| 4 | YK-PE | 2 | 15 | Outdoor |
| 5 | DB-PE | 2 | 15 | Indoor |
| 6 | DB-PE | 20 | 2 | Indoor |
| 7 | DB-PET | 1 | 30 | Indoor |
| Properties | Specification | Value | Test Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Octane No. (RON) | 91–94 | 92.8 | ASTM D2699 | |
| Distillation | T10 (°C), max | 70 | 53.1 | ASTM D86 |
| T50 (°C), max | 125 | 82.2 | ||
| T90 (°C), max | 170 | 157.3 | ||
| FBP (°C), max | 225 | 203.5 | ||
| Residue, vol %, max | 2.0 | 1.0 | ||
| Water and sediment (vol %), max | 0.01 | 0.005 | ASTM D2709 | |
| Copper corrosion (50 °C, 3 h), max | 1 | 1a | ASTM D130 | |
| Vapor pressure (37.8 °C, kPa) | 44–82 (summer: 44–60, winter: 44–96) | 64.8 | ASTM D5191 | |
| Oxidation stability (min), min | 480 | 480 | ASTM D525 | |
| Washed gums (mg/100 mL), max | 5 | 0.01 | ASTM D381 | |
| Sulfur content (mg/kg), max | 10 | 6.03 | ASTM D5453 | |
| Color | Yellow | Yellow | - | |
| Lead content (g/L), max | 0.013 | 0.001 | ASTM D3237 | |
| Phosphorus content (g/L), max | 0.0013 | 0.0001 | ASTM D3231 | |
| Aromatic content (vol %), max | 22 (19) | 18.96 | JIS K 2536-2 | |
| Benzene content (vol %), max | 0.7 | 0.52 | JIS K 2536-2 | |
| Olefin content (vol %), max | 16 (19) | 13.91 | JIS K 2536-2 | |
| Oxygen content (wt %), max | 2.3 | 2.10 | JIS K 2536-2 | |
| Methanol content (wt %), max | 0.1 | 0.00 | JIS K 2536-2 | |
| Distill. Temp. | Initial Value | CAN | YK-PE | YK-PE | YK-PE | DB-PE | DB-PE | DB-PET |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1.5 L) | (2 L) | (20 L) | (2 L) 1 | (2 L) | (20 L) | (1 L) | ||
| T10 (°C) | 53.1 | 52.5 | 56.4 | 52.4 | 54.9 | 54.8 | 52.6 | 53.9 |
| T50 (°C) | 82.2 | 81.8 | 86.3 | 81.6 | 85.0 | 84.4 | 81.8 | 83.0 |
| T90 (°C) | 157.3 | 156.5 | 159.0 | 157.1 | 158.9 | 158.1 | 156.8 | 157.1 |
| FBP (°C) | 203.5 | 204.3 | 206.1 | 200.9 | 198.9 | 203.4 | 205.4 | 205.0 |
| Content (vol %) | Initial Value | CAN | YK-PE | YK-PE | YK-PE | DB-PE | DB-PE | DB-PET |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1.5 L) | (2 L) | (20 L) | (2 L) 2 | (2 L) | (20 L) | (1 L) | ||
| Aromatic | 18.96 | 19.15 | 19.76 | 18.79 | 19.40 | 19.33 | 18.77 | 19.19 |
| Olefin | 13.91 | 14.04 | 12.27 | 14.02 | 11.92 | 12.90 | 13.80 | 14.01 |
| n-Parffin | 11.01 | 10.84 | 10.63 | 10.94 | 10.13 | 10.70 | 10.97 | 10.92 |
| iso-Paraffin | 38.86 | 38.93 | 39.87 | 39.12 | 40.50 | 39.78 | 39.05 | 38.82 |
| Naphtene | 6.79 | 6.99 | 7.20 | 6.84 | 6.88 | 7.04 | 6.79 | 6.86 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, C.-H.; Park, C.-K.; Na, B.-K.; Kim, J.-K. Properties of Gasoline Stored in Various Containers. Energies 2017, 10, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091307
Jeon C-H, Park C-K, Na B-K, Kim J-K. Properties of Gasoline Stored in Various Containers. Energies. 2017; 10(9):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091307
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Cheol-Hwan, Cheon-Kyu Park, Byung-Ki Na, and Jae-Kon Kim. 2017. "Properties of Gasoline Stored in Various Containers" Energies 10, no. 9: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091307
APA StyleJeon, C.-H., Park, C.-K., Na, B.-K., & Kim, J.-K. (2017). Properties of Gasoline Stored in Various Containers. Energies, 10(9), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091307





