Fault Tolerant and Optimal Control of Wind Turbines with Distributed High-Speed Generators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Wind Turbine Model with Distributed Generators
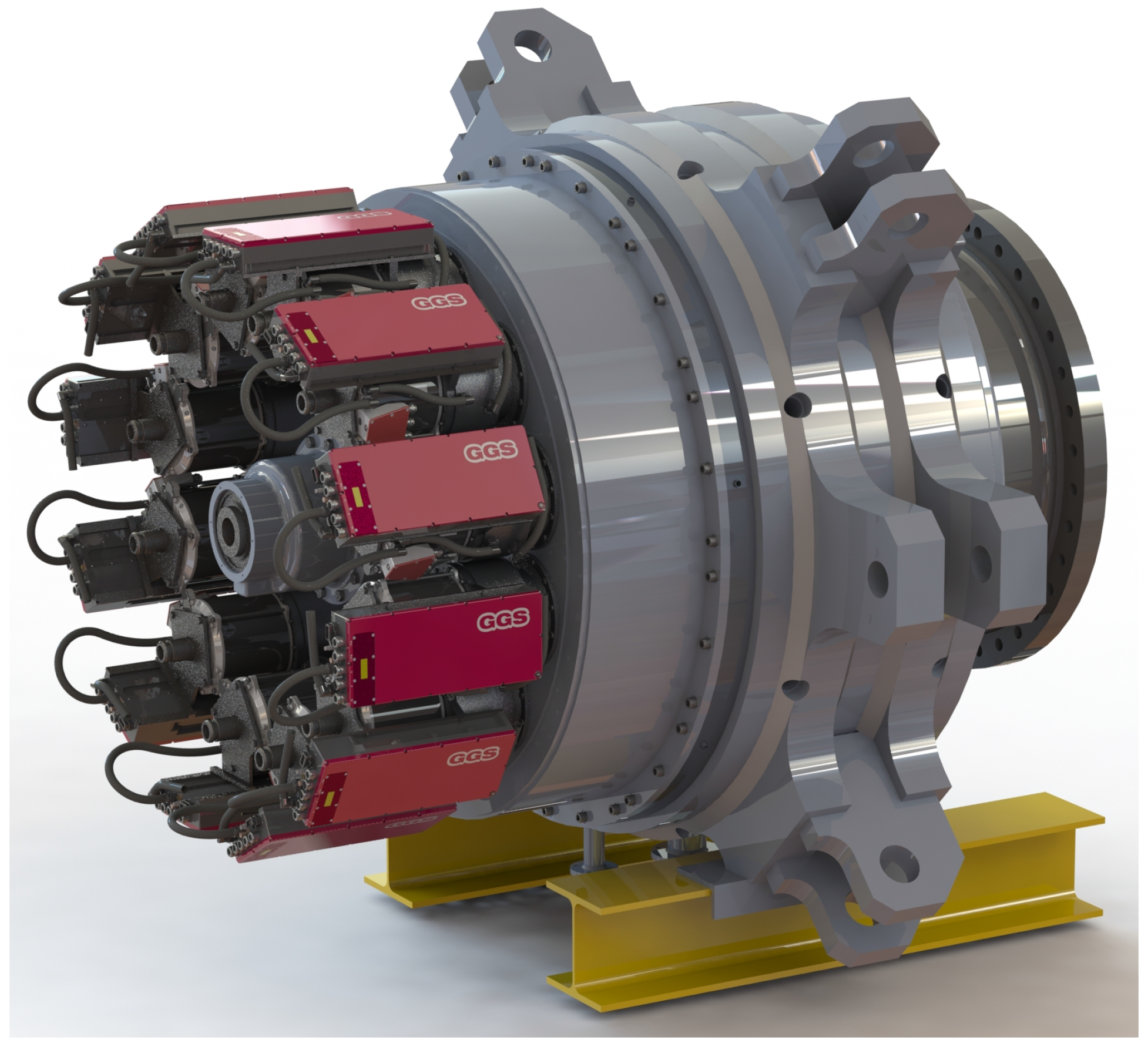
2.1. Drive Train Concept and Reduced-Order Model
2.2. Baseline Controller
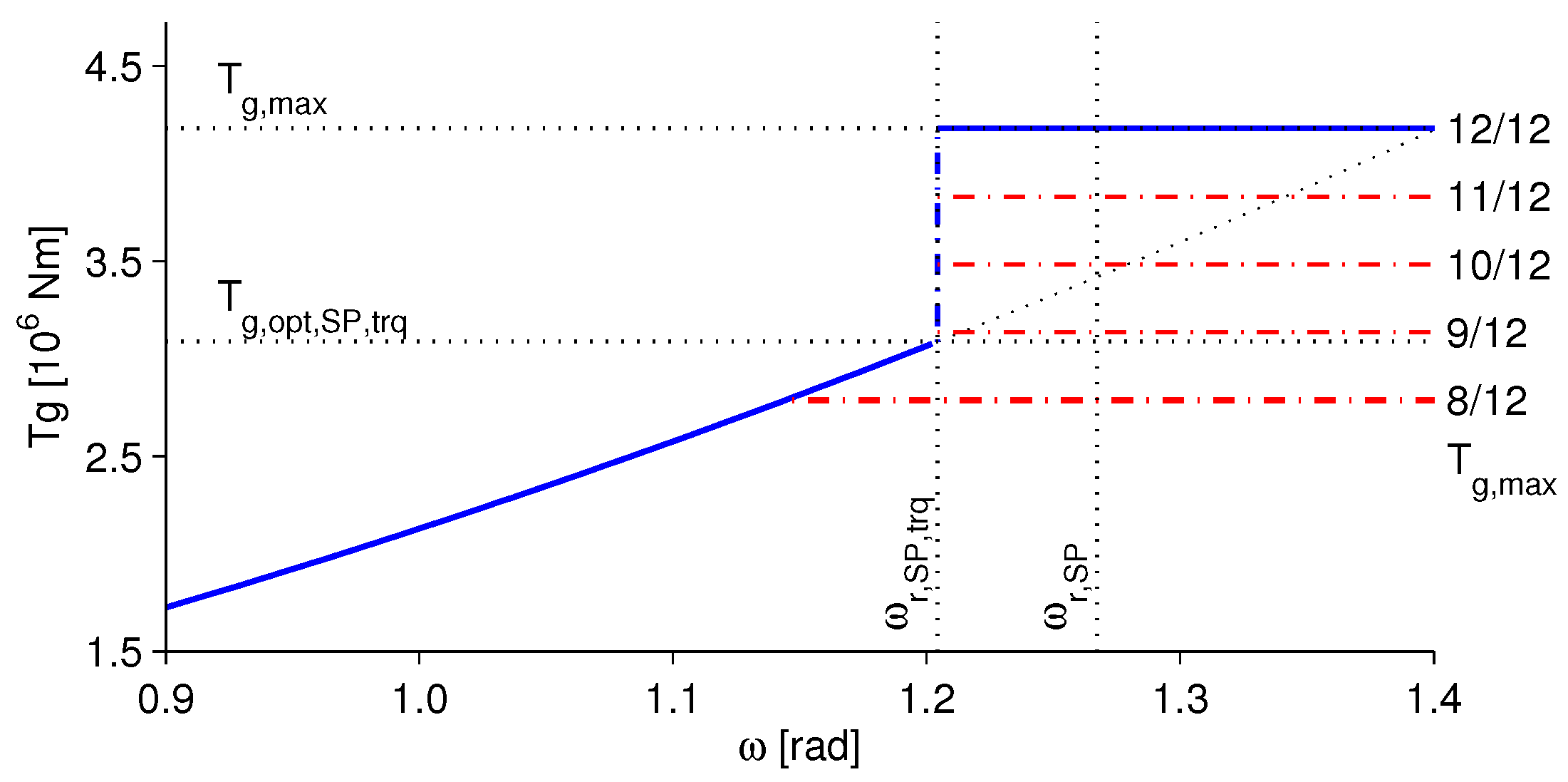
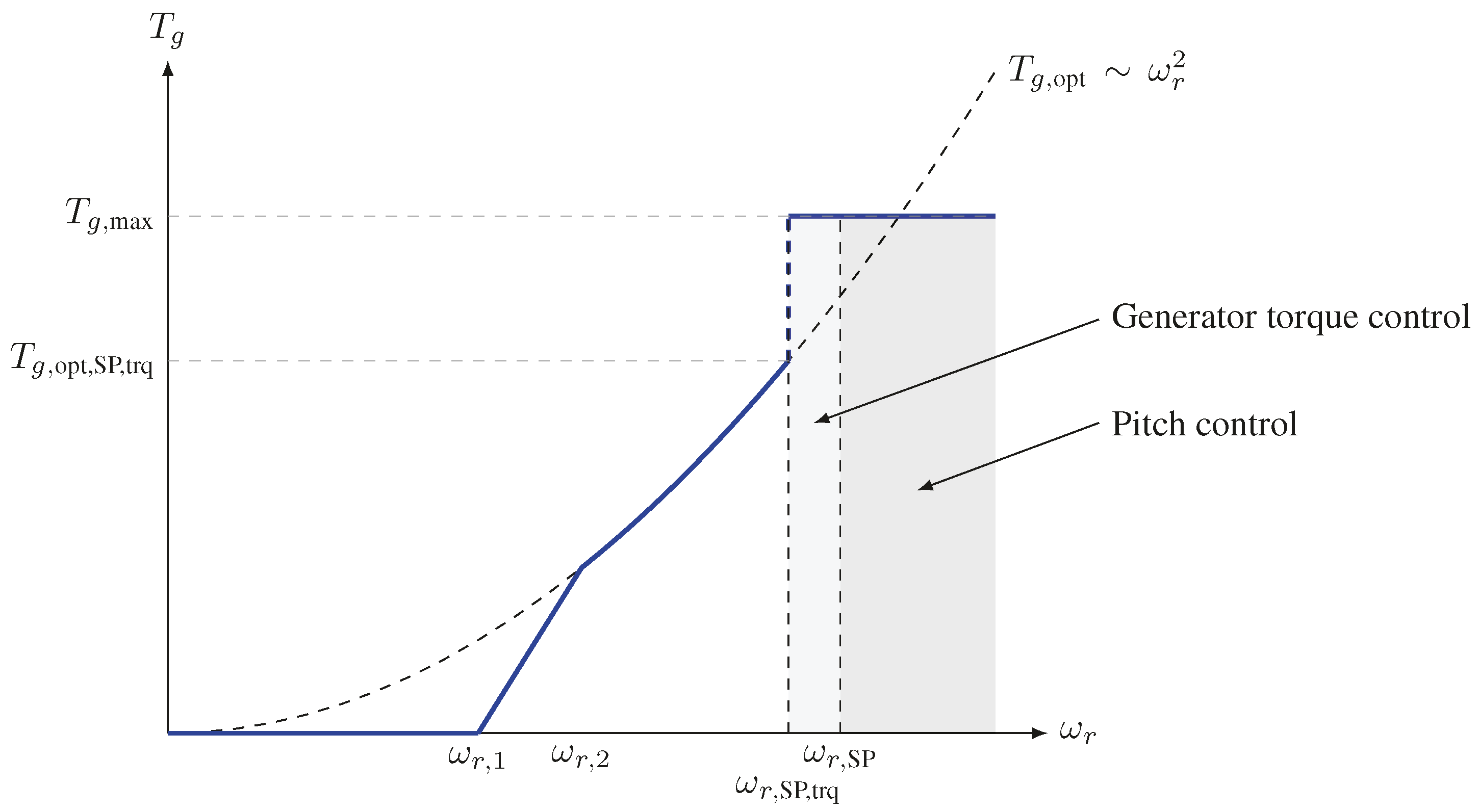
2.3. Optimal Controller Design for the Full-Load Region
3. Fault Tolerant Control Using Adaption of Reference Signals
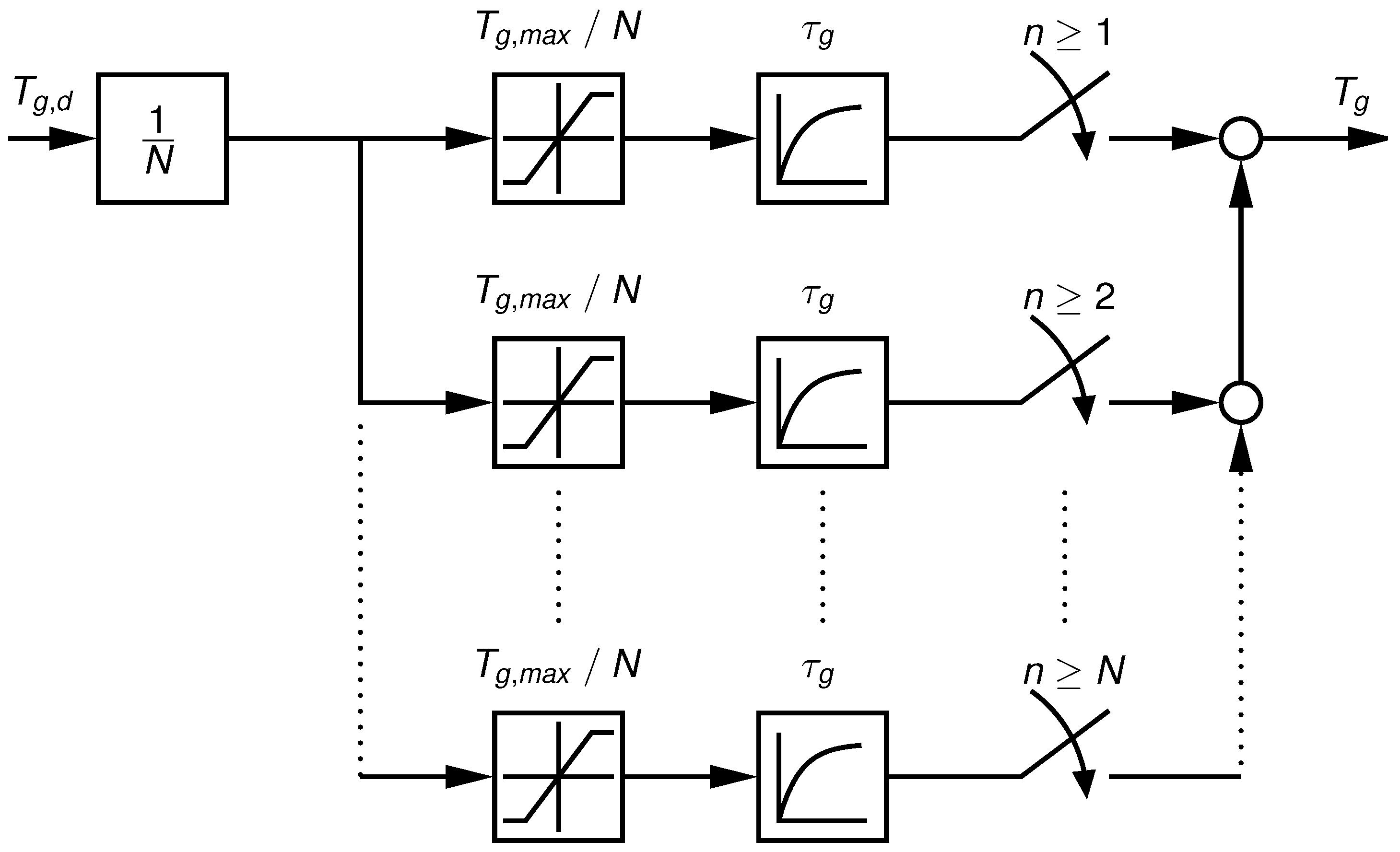
3.1. Fault Dependent Adaptation of the Reference Signals
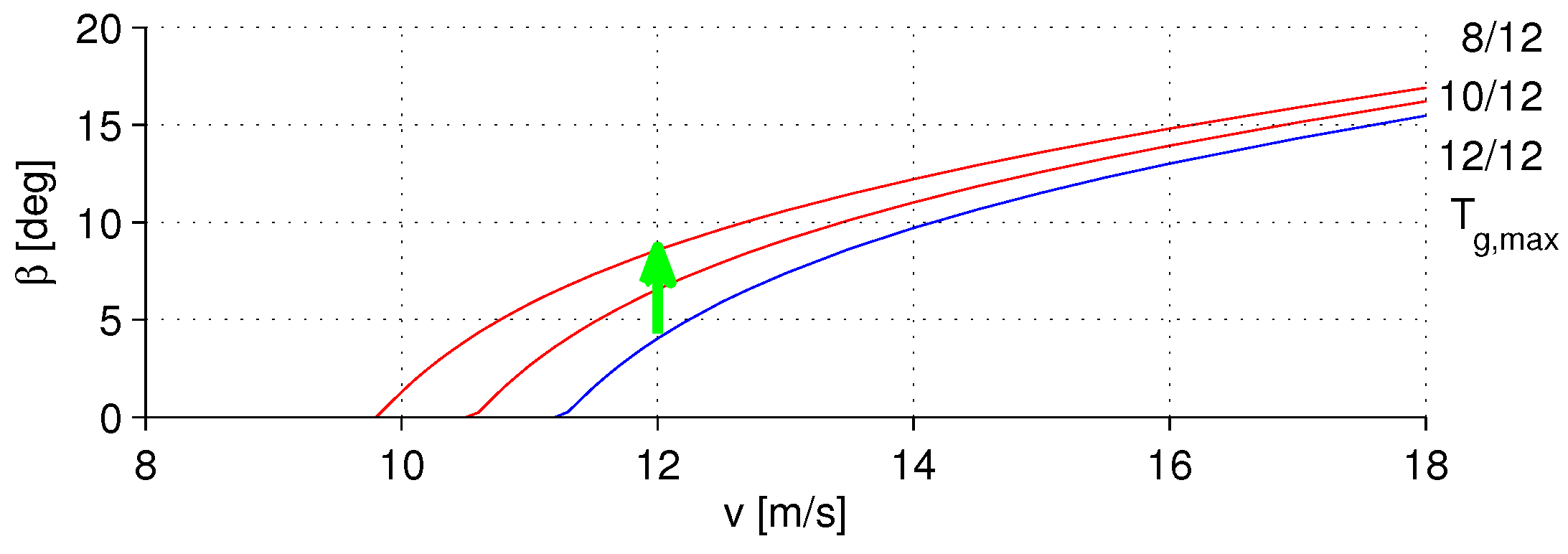
3.2. Fault Tolerant Interaction between the Partial and Full Load Region
| Algorithm 1: FTC hybrid wind turbine control scheme |
 |
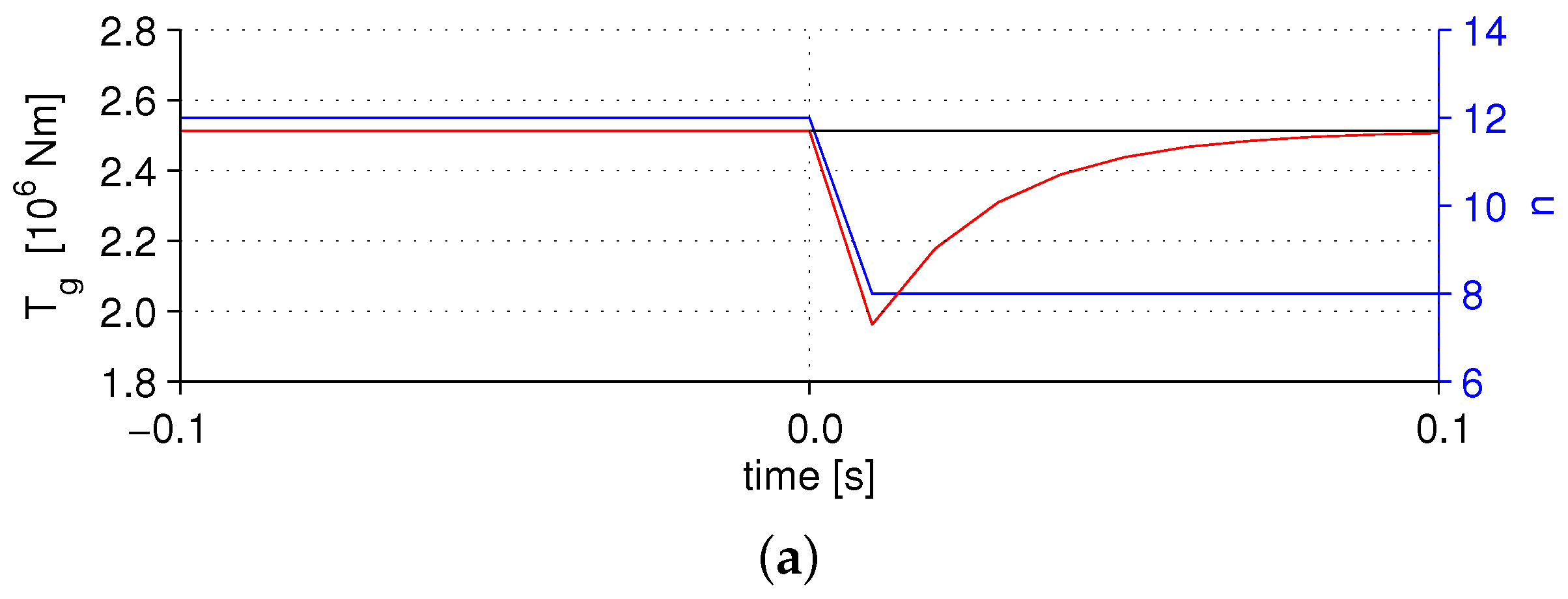
3.3. Rotor Acceleration Test of the Multi-Generator Drive Train
- partial load: remaining healthy generators compensate the occurred generator faults
- full load: previous engagement of pitch control compensates for the decreased maximum total torque
4. Transient Behavior of Fault Tolerant Control Scheme
4.1. Transient Behavior in the Partial Load Region
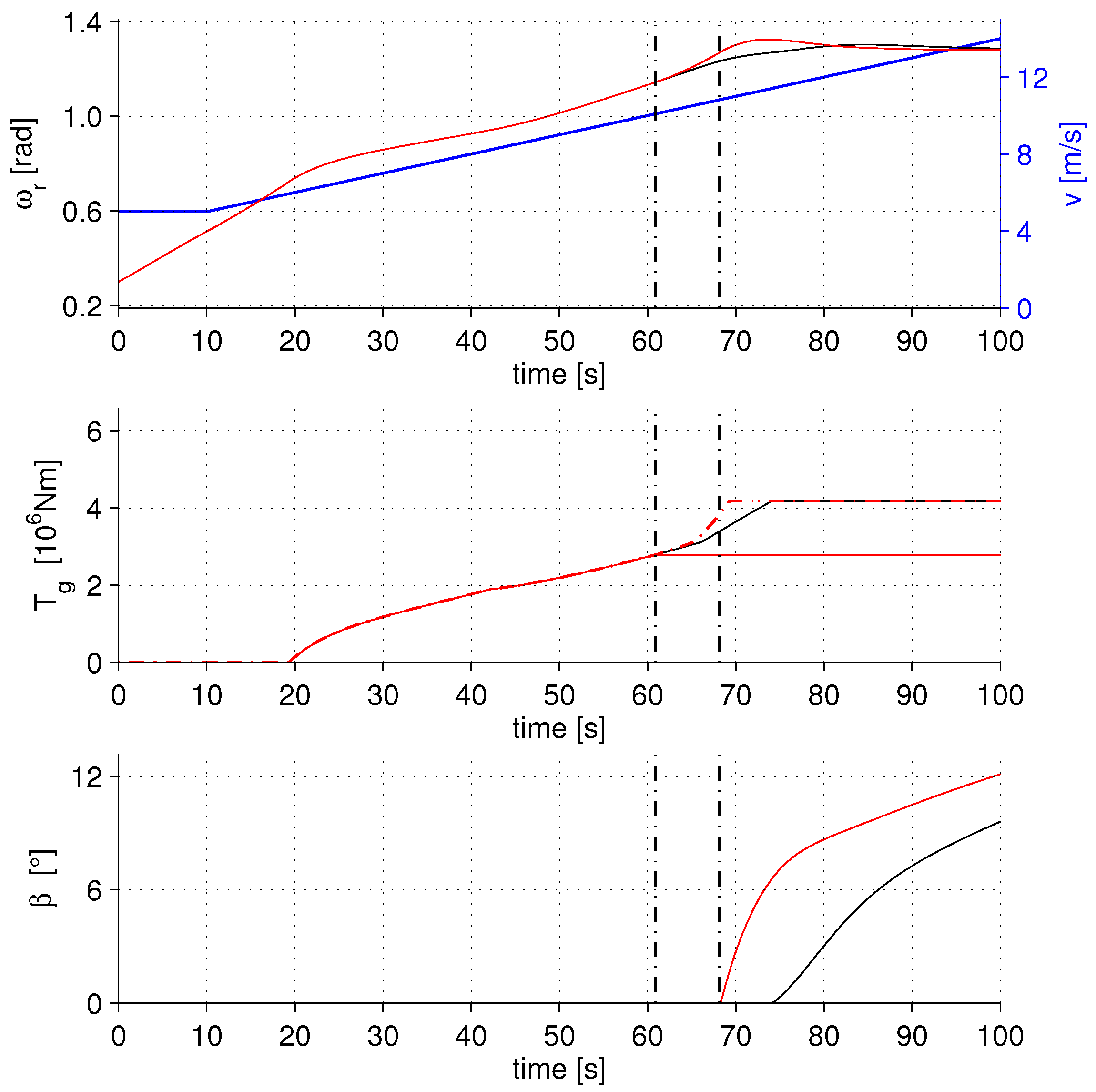
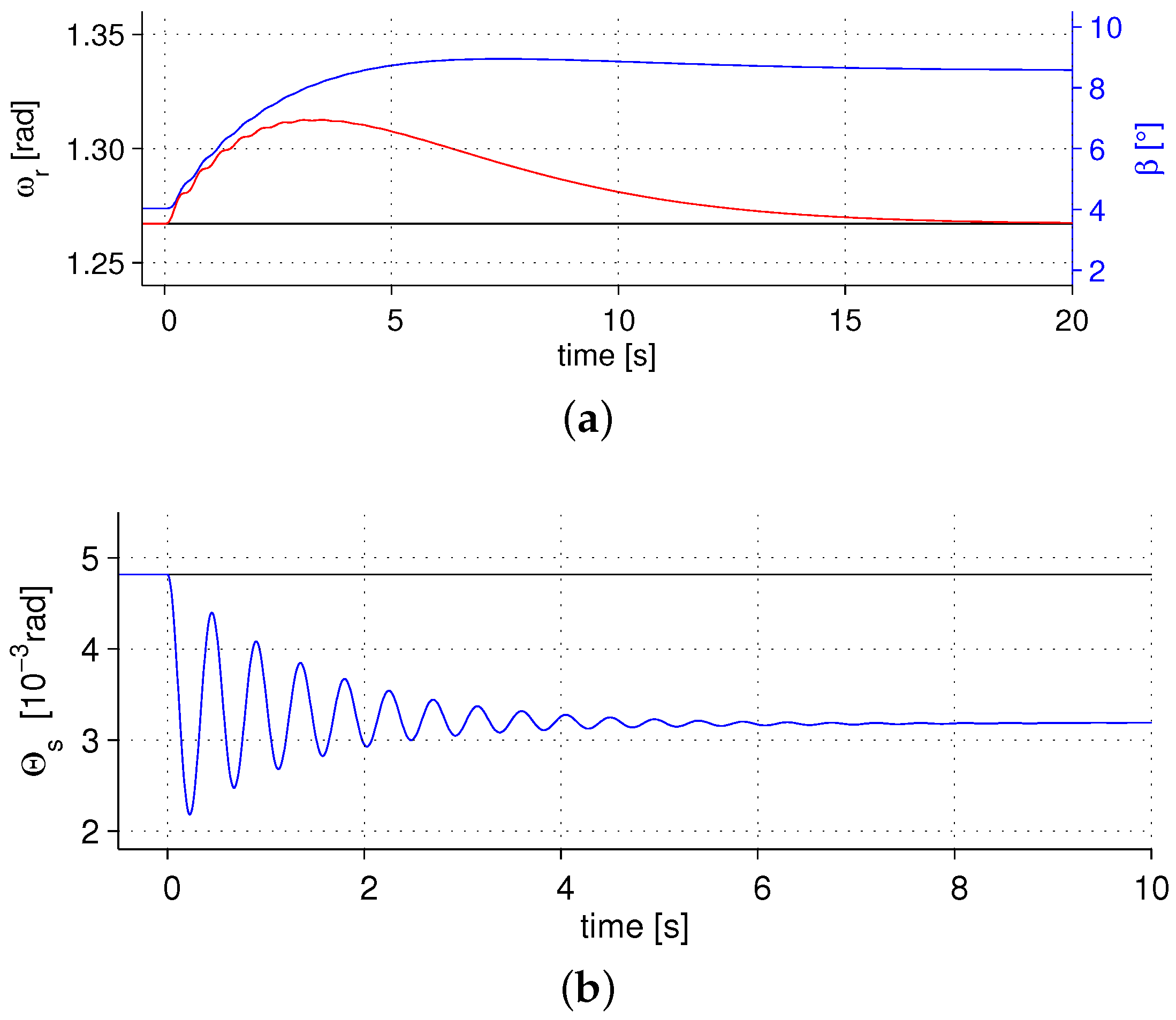
4.2. Transient Behavior in the Full Load Region
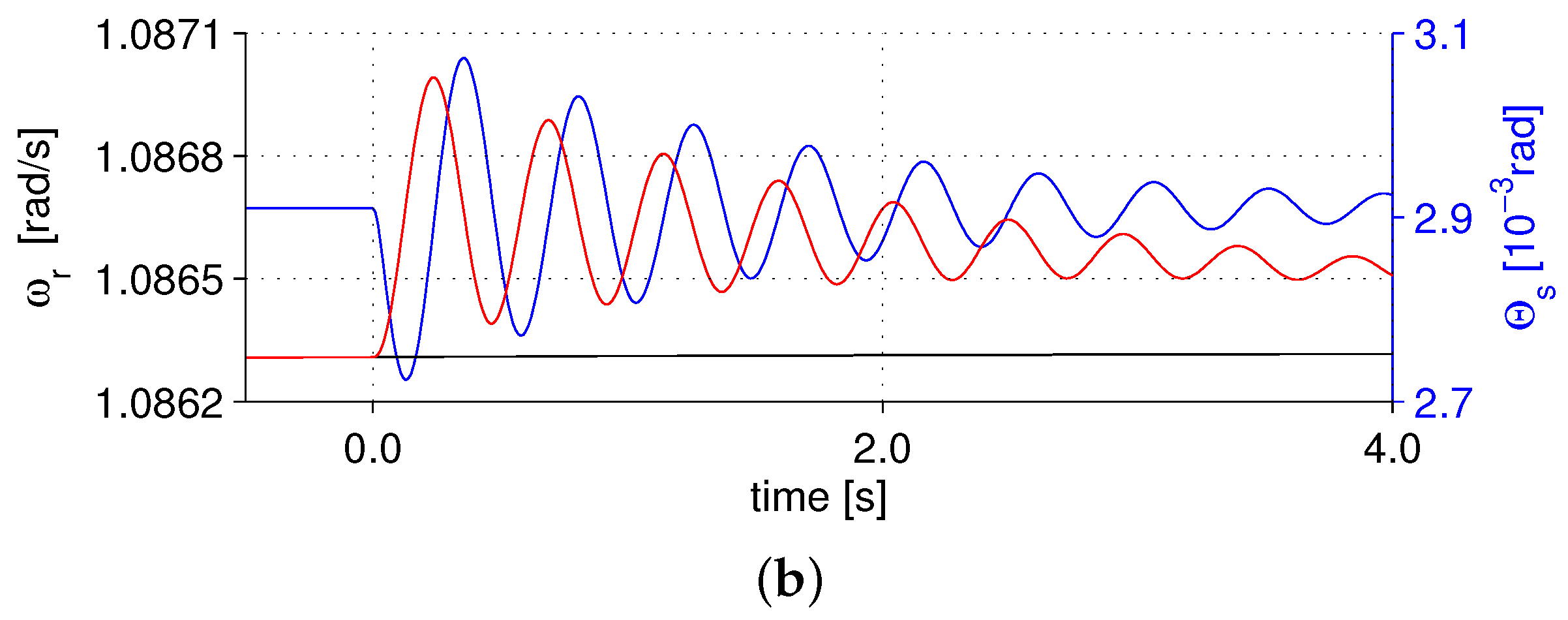
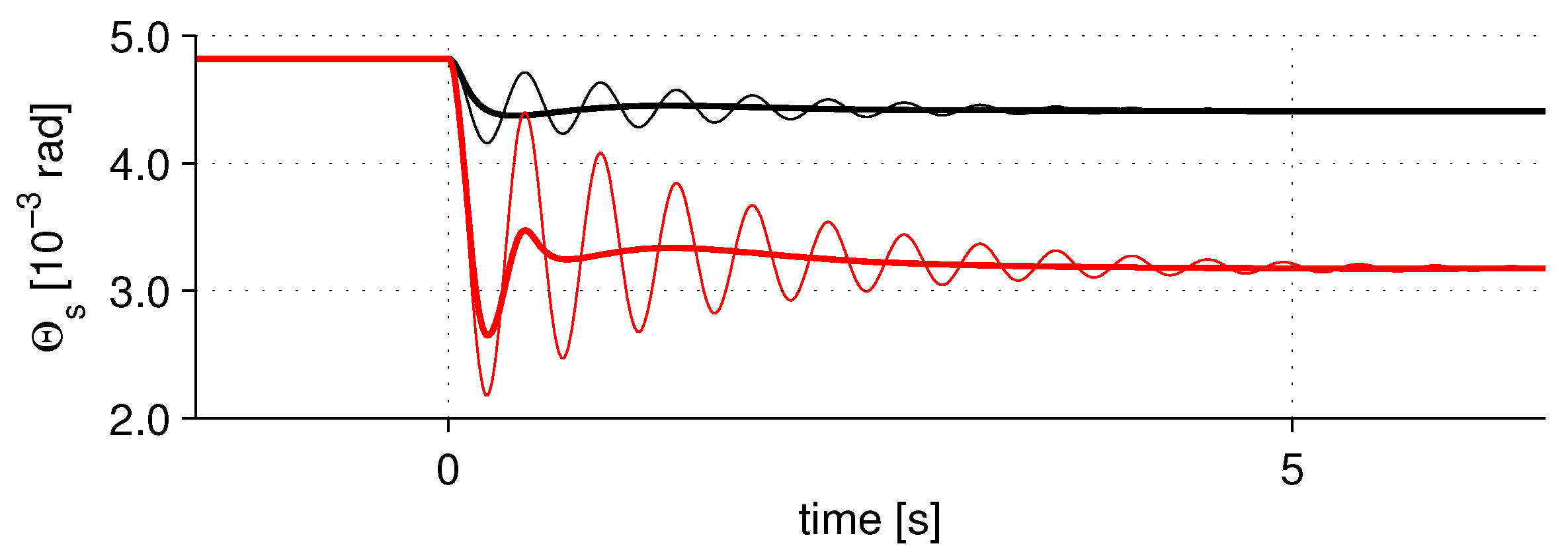
4.3. Active Vibration Damping
5. Conclusions and Future Works
References
- Cohen, J.; Schweizer, T.; Laxson, A.; Butterfield, S.; Schreck, S.; Fingersh, L.; Veers, P.; Ashwill, T. Technology Improvement Opportunities for Low Wind Speed Turbines and Implications for Cost of Energy Reduction; NREL/TP-500-41036; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Robb, D. The return of the Clipper Liberty wind turbine. Power 2008, 152, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Giger, U.; Arnaudov, K. New drive train design for ultra large 15 MW wind turbines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Gears, Garching, Germany, 7–9 October 2013.
- Sloth, C.; Esbensen, T.; Stoustrup, J. Robust and fault-tolerant linear parameter-varying control of wind turbines. Mechatronics 2011, 21, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgaard, P.F.; Stoustrup, J. Fault tolerant control of wind turbines using unknown input observers. In Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety of Technical Processes, Mexico City, Mexico, 29–31 August 2012; pp. 313–318.
- Odgaard, P.F.; Stoustrup, J.; Kinnaert, M. Fault Tolerant control of wind turbines—A benchmark model. In Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety of Technical Processes, Barcelona, Spain, 30 June–3 July 2009; pp. 155–160.
- Sami, M.; Patton, R.J. An FTC approach to wind turbine power maximisation via T-S fuzzy modelling and control. In Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety of Technical Processes, Mexico City, Mexico, 29–31 August 2012; pp. 349–354.
- Sami, M.; Patton, R.J. Active sensor fault tolerant output feedback tracking control for wind turbine systems via T-S model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2014, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sami, M.; Patton, R.J. Fault tolerant adaptive sliding mode controller for wind turbine power maximisation. In Proceedings of the 7th IFAC Symposium on Robust Control Design, Aalborg, Denmark, 20–22 June 2012; pp. 499–504.
- Rotondo, D.; Nejjari, F.; Puig, V.; Blesa, J. Fault tolerant control of the wind turbine benchmark using virtual sensors/actuators. In Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety of Technical Processes, Mexico City, Mexico, 29–31 August 2012; pp. 114–119.
- Simani, S.; Castaldi, P. Active actuator fault-tolerant control of a wind turbine benchmark model. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2014, 24, 1283–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badihi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, H. Fuzzy gain-scheduled active fault tolerant control of a wind turbine. J. Frankl. Inst. 2014, 351, 3677–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badihi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, H. Wind turbine fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant torque load control against actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 1351–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georg, S.; Schulte, H. Actuator fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of wind turbines using a Takagi-Sugeno sliding mode observer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (Sys-Tol), Nice, France, 9–11 October 2013; pp. 516–522.
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its application to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1985, 15, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.M.; Buhl, M.L., Jr. FAST User’s Guide; Technical Report NREL/EL-500-38230; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Georg, S.; Schulte, H.; Aschemann, H. Control-oriented modelling of wind turbines using a Takagi-Sugeno model structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Brisbane, Australia, 11–15 June 2012; pp. 1737–1744.
- Tanaka, K.; Sano, M. A robust stabilization problem of fuzzy control systems and its application to backing up control of a truck-trailer. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1994, 2, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georg, S. Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control of Wind Turbines Nonlinear Takagi-Sugeno and Sliding Mode Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Maschinenbau und Schiffstechnik, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte, H.; Georg, S. Hardware-in-the-Loop Test-Bed for benchmarking of fault tolerant control schemes for wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 9th IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety of Technical Processes, Paris, France, 2–4 September 2015.
- Burton, T.; Jenkins, N.; Sharpe, D.; Bossanyi, E. Wind Energy Handbook, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Odgaard, P.F.; Johnson, K. Wind turbine fault detection and fault tolerant control—An enhanced benchmark challenge. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 4447–4452.
- van der Hooft, E.L.; Schaak, P.; van Engelen, T.G. Wind Turbine Control Algorithms; Technical Report DOWEC-F1W1-EH-03-094/0; Energy Research Center of the Netherlands (ECN): Delft, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
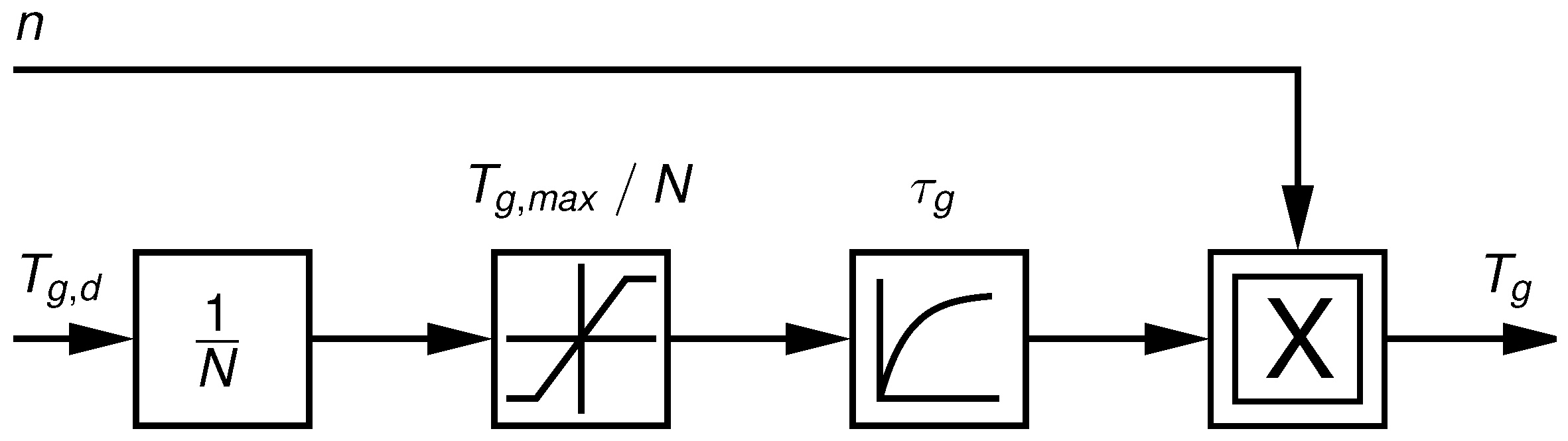

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giger, U.; Kühne, P.; Schulte, H. Fault Tolerant and Optimal Control of Wind Turbines with Distributed High-Speed Generators. Energies 2017, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020149
Giger U, Kühne P, Schulte H. Fault Tolerant and Optimal Control of Wind Turbines with Distributed High-Speed Generators. Energies. 2017; 10(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020149
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiger, Urs, Patrick Kühne, and Horst Schulte. 2017. "Fault Tolerant and Optimal Control of Wind Turbines with Distributed High-Speed Generators" Energies 10, no. 2: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020149
APA StyleGiger, U., Kühne, P., & Schulte, H. (2017). Fault Tolerant and Optimal Control of Wind Turbines with Distributed High-Speed Generators. Energies, 10(2), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020149





