A Virtual Synchronous Generator Based Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
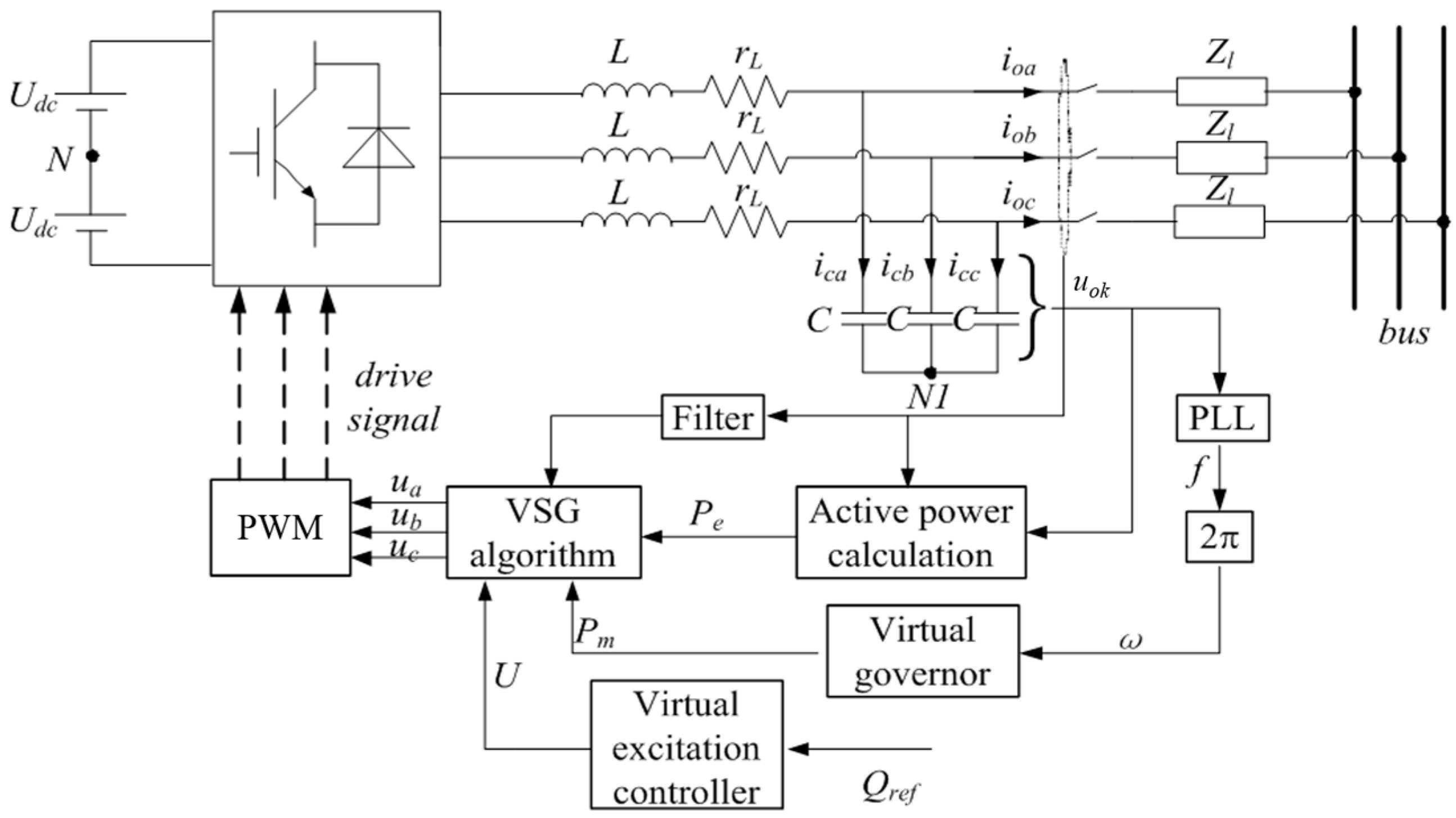
2. The VSG-Based Inverter Control
2.1. System Structure of VSG-Based Control
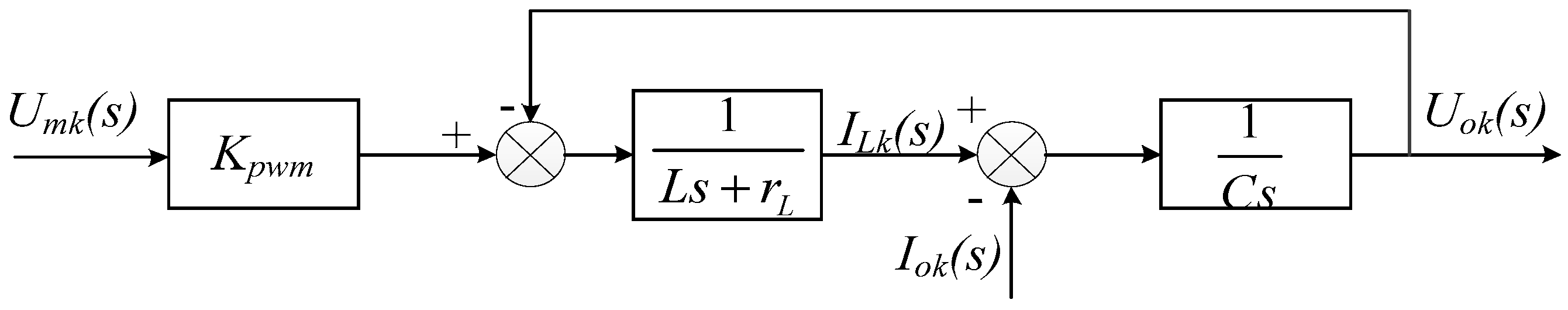
2.2. VSG-Based Control Algorithm
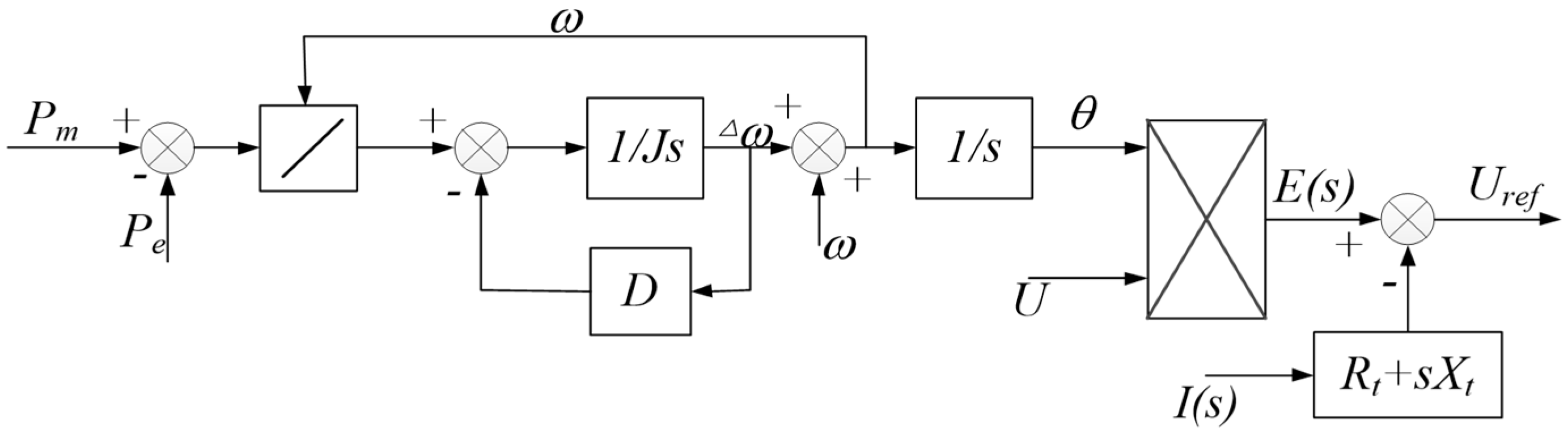
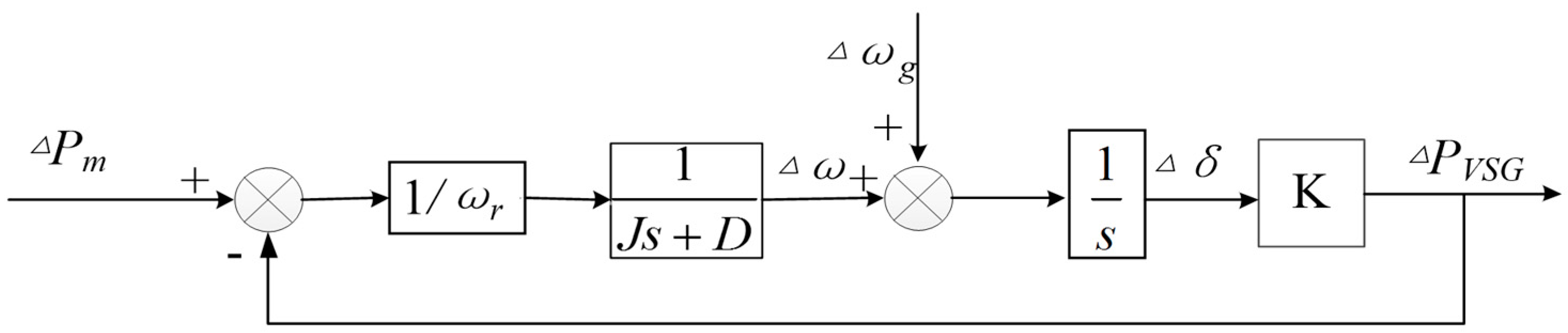
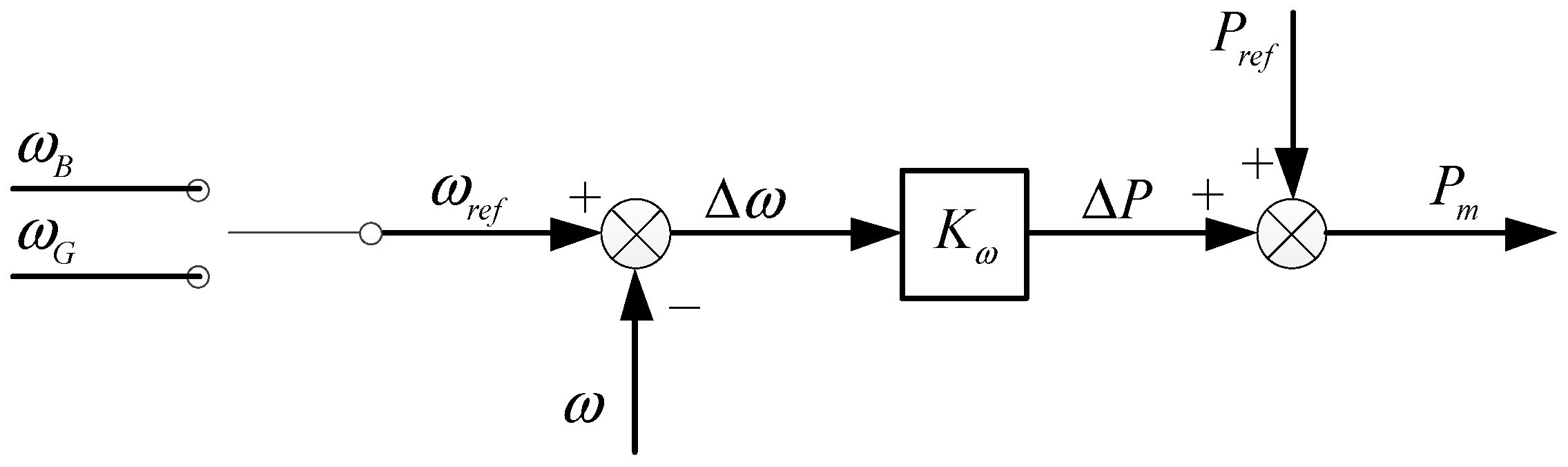
2.3. Virtual Speed Regulator Design
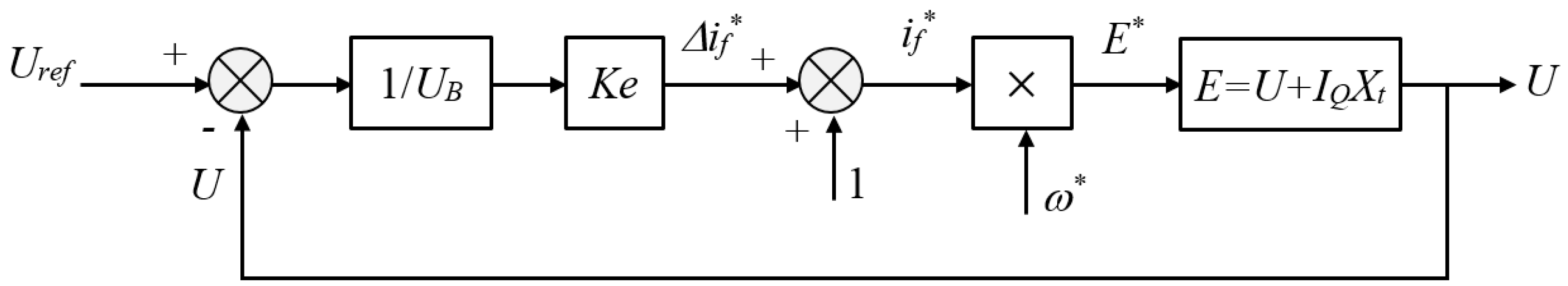
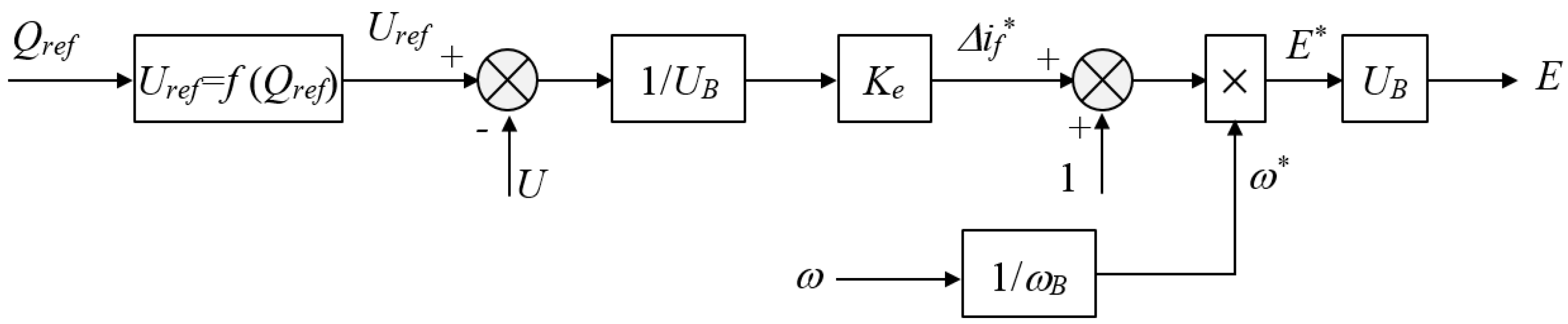
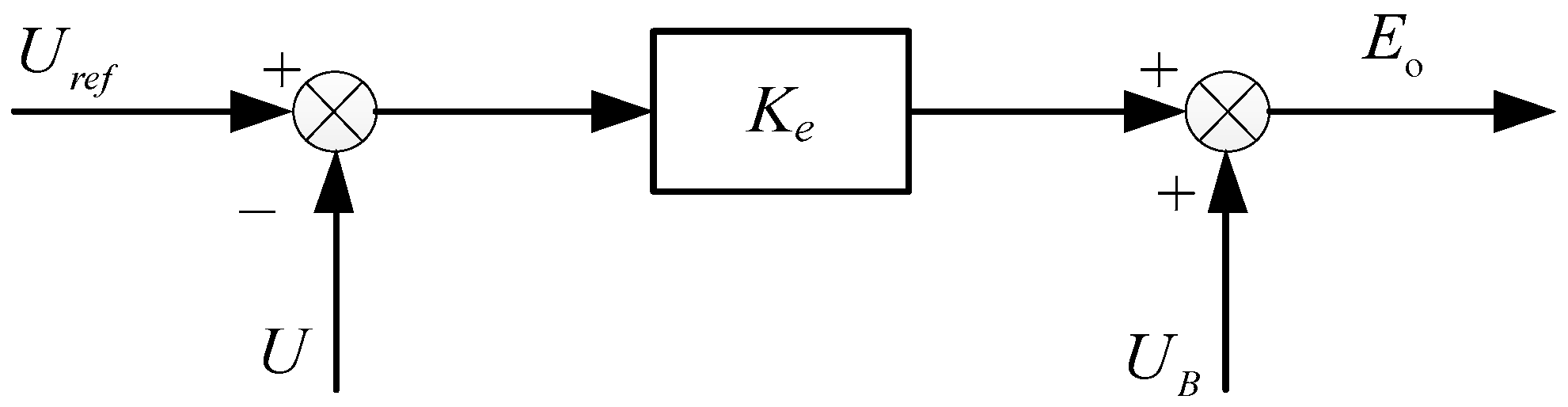
2.4. Virtual Excitation System Design
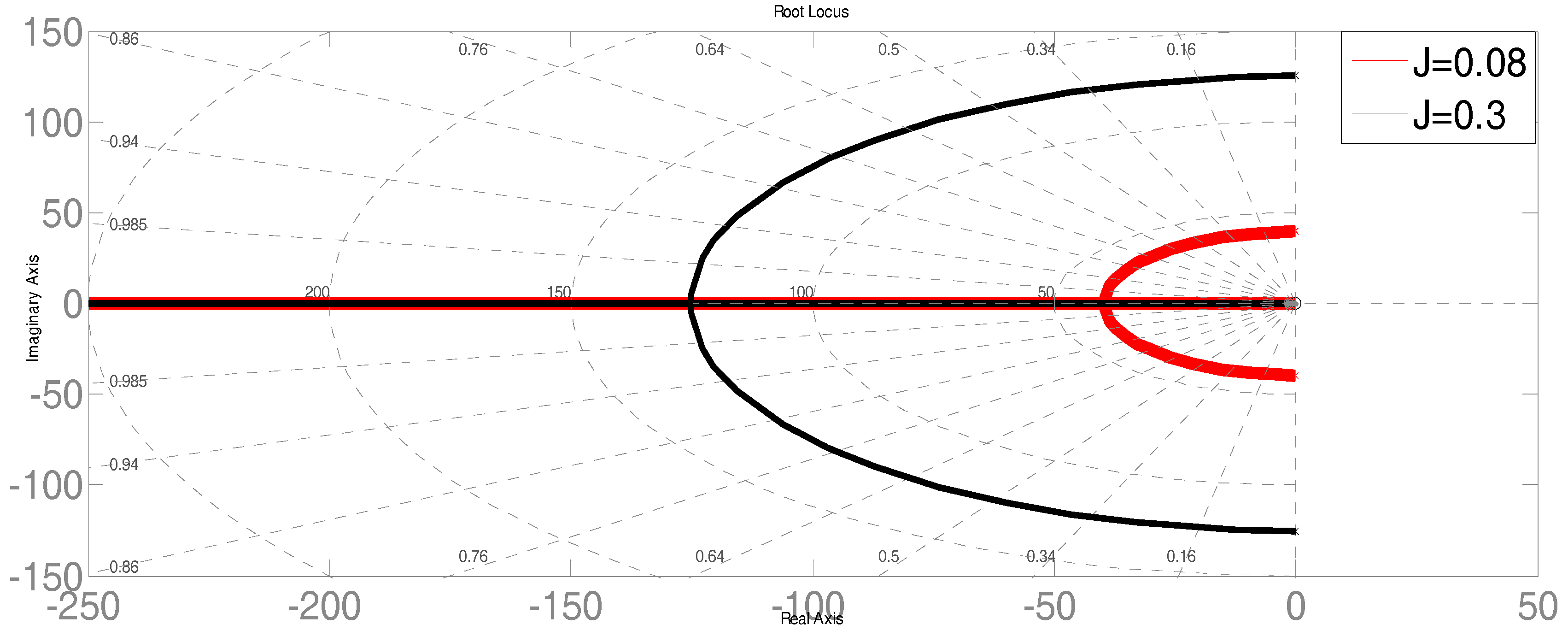
2.5. Stability Analysis of the VSG Algorithm
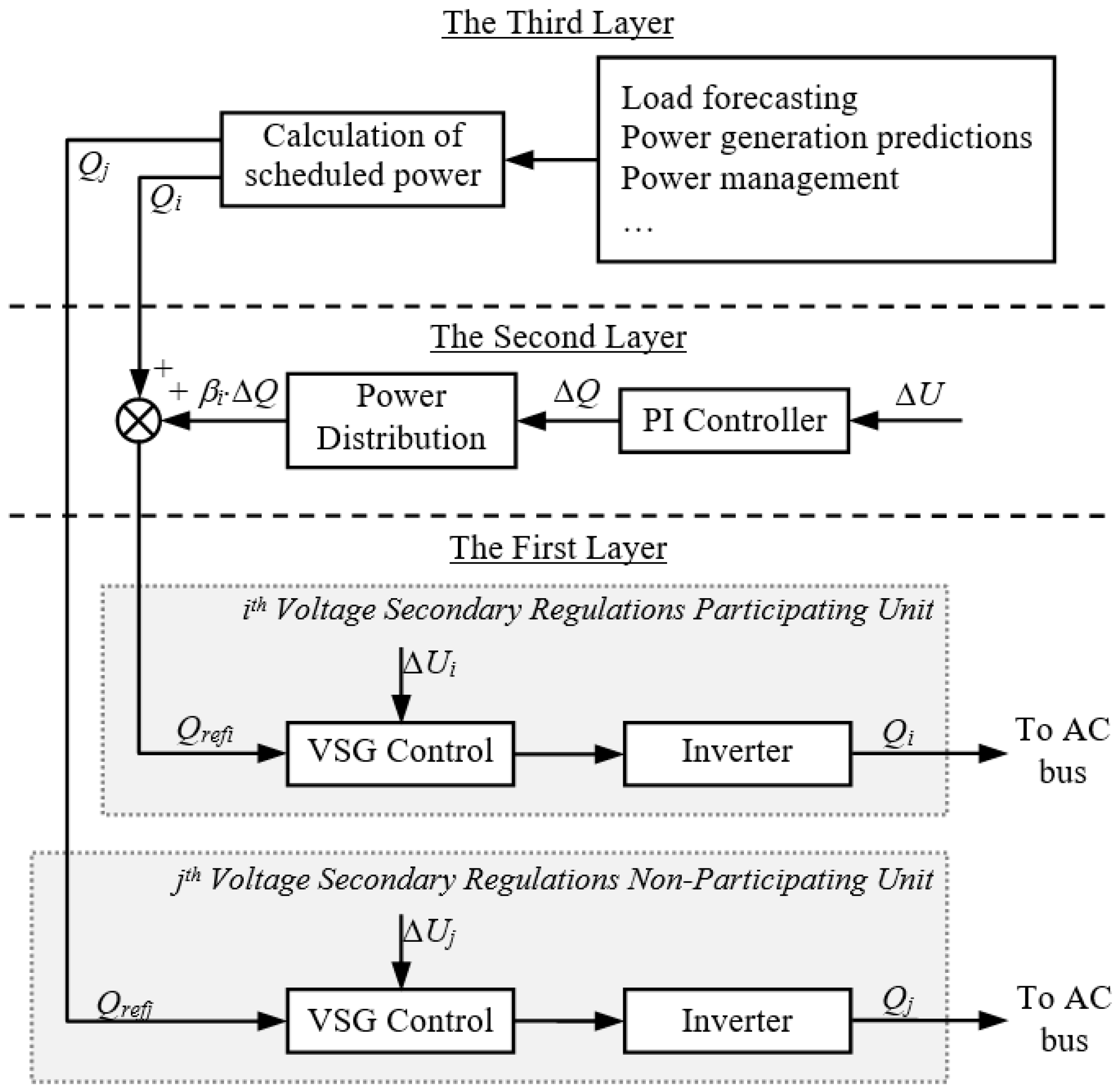
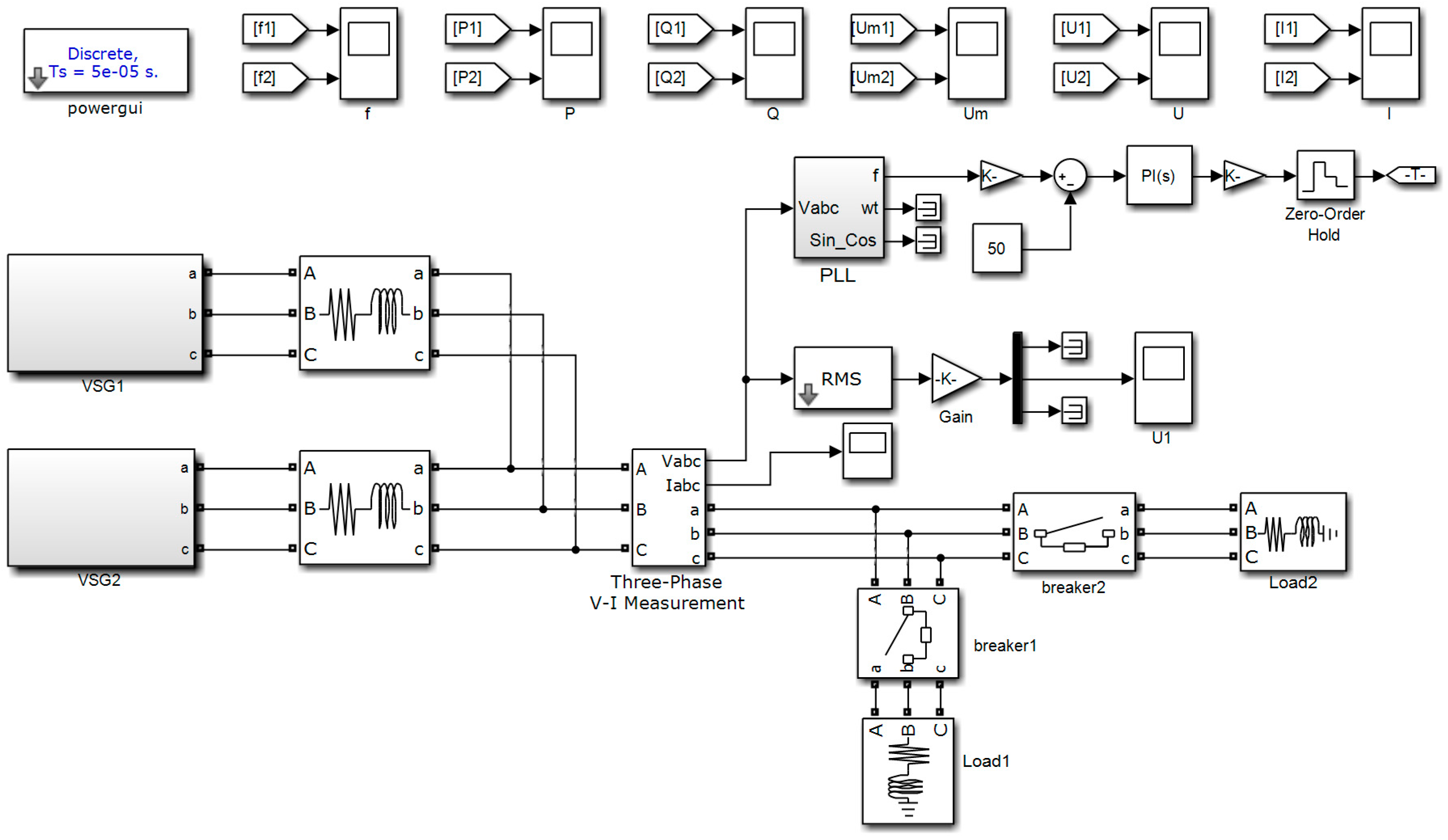
3. Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems
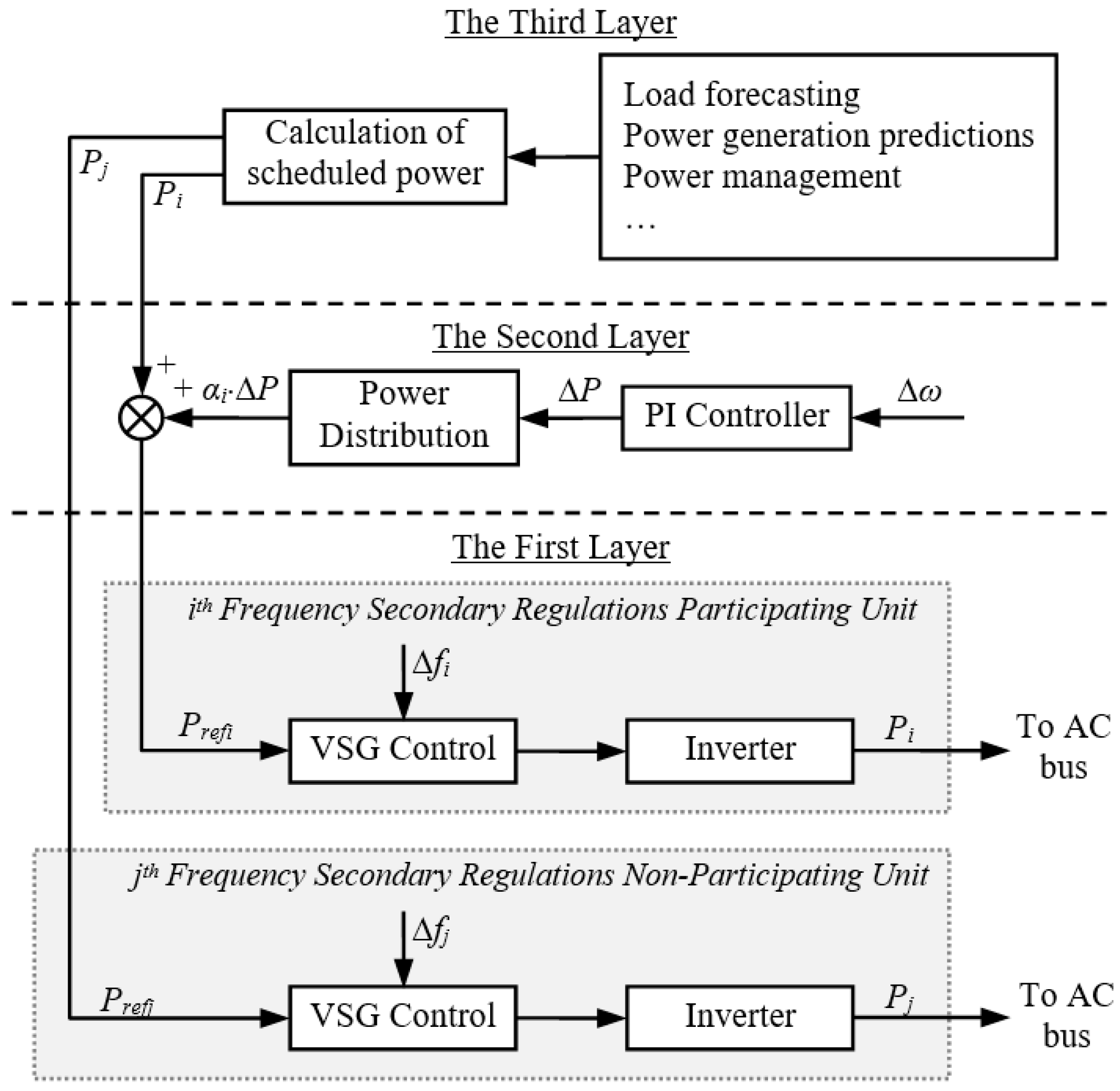
3.1. Hierarchical Control Structure Design
- The first layer is in the lowest position of the control architecture, and mainly realizes the real-time control of inverters, such as the primary frequency and voltage control in both islanding and grid-connected modes, pre-coordinating of inverters, and etc. To be the bottom layer, its response speed is the fastest and adjusting time is shortest among the three layers.
- The second layer is the coordination layer which focuses on the control of the parallel inverters in a microgrid, and its response speed is slower and adjusting time is longer than those of the lower layer. This layer executes functions including the power control of connecting lines, secondary frequency and voltage regulations in the island mode, per-coordinating of the microgrid, islanding detection, etc.
- The third layer is in the top of the control architecture, and is mainly dedicated to energy management and economic power scheduling. Its response speed is the slowest and adjusting time is the longest among the three layers. According to the energy output forecasting, energy consumption of load, energy exchange plan and operation modes, the active and reactive power outputs of scheduling power generation units are calculated.
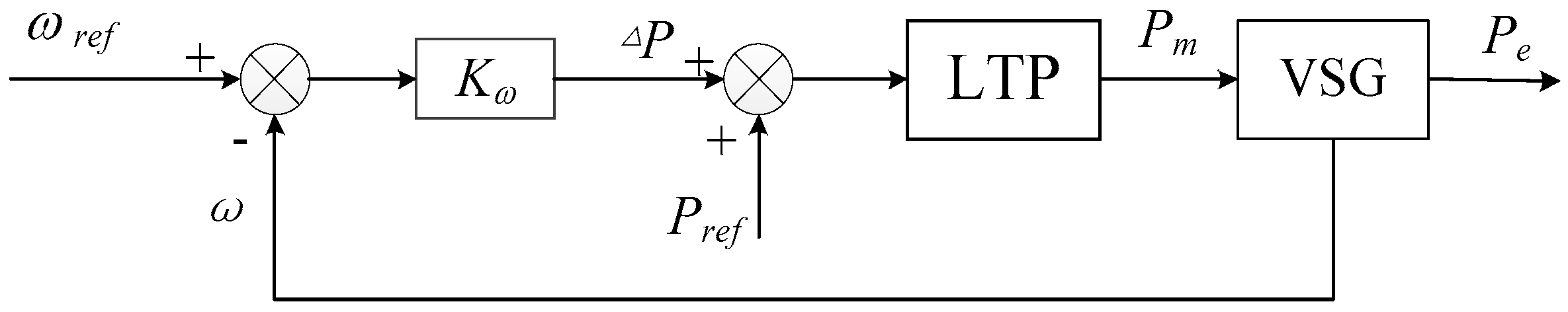
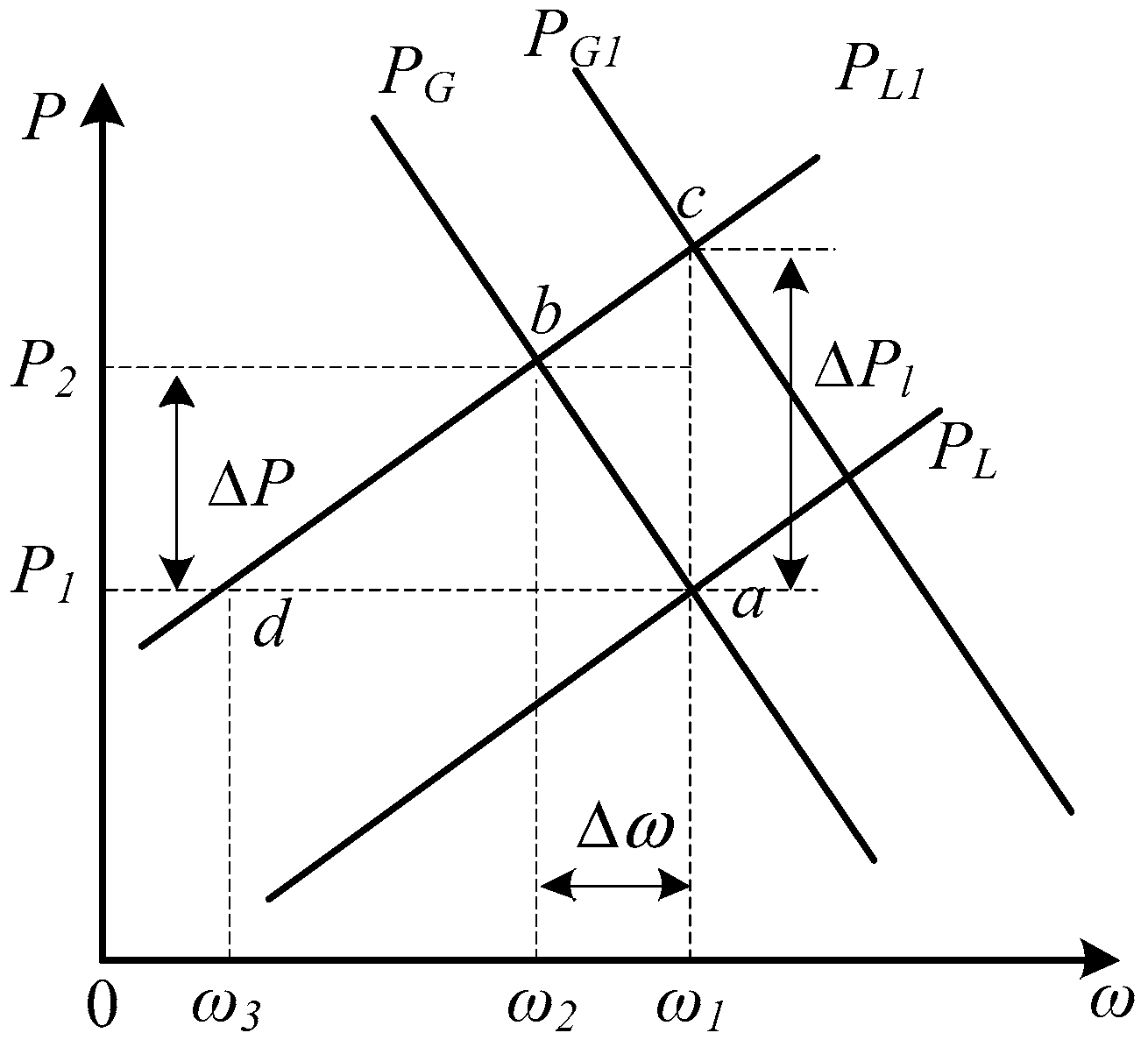
3.2. Frequency Hierarchical Control In Island Mode
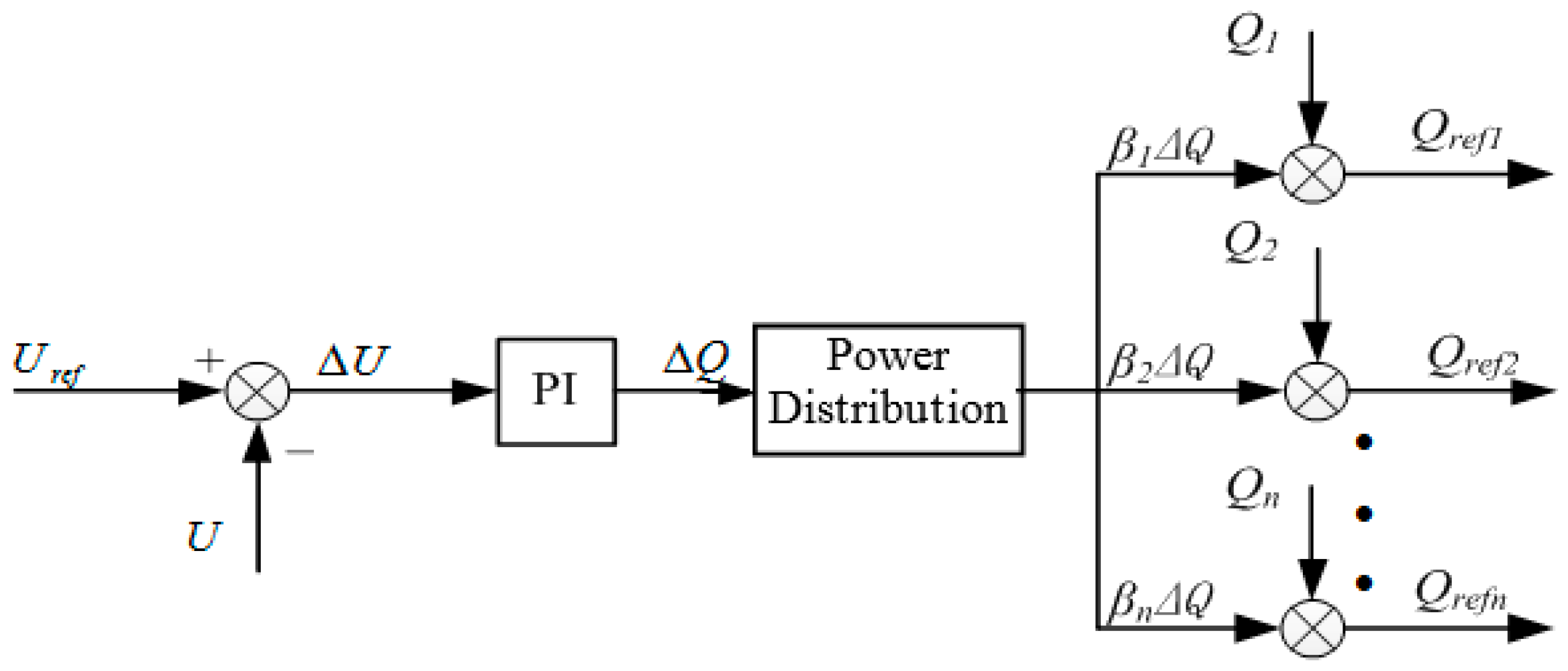
3.3. Voltage Hierarchical Control In Island Mode
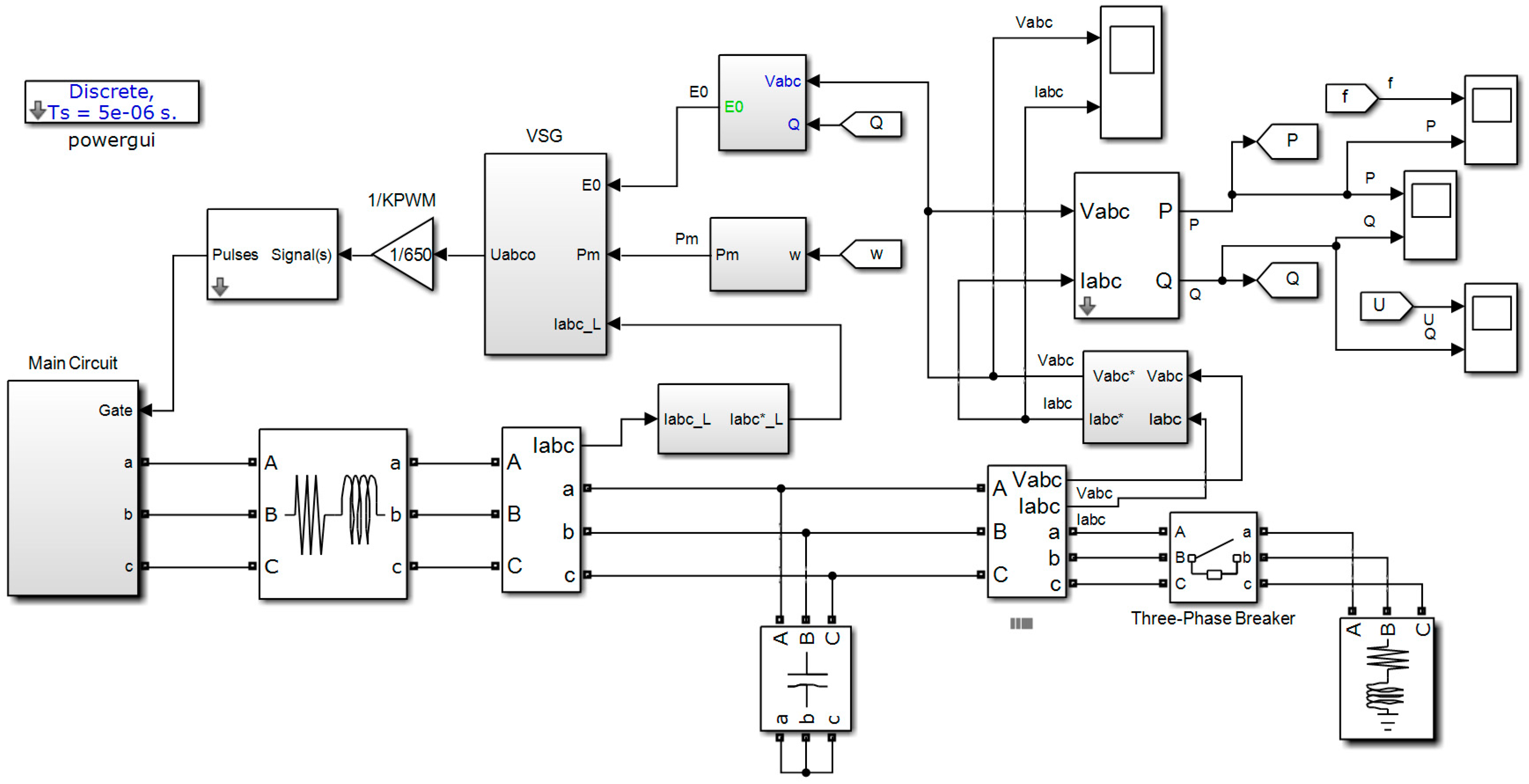
4. Simulations and Results Analysis
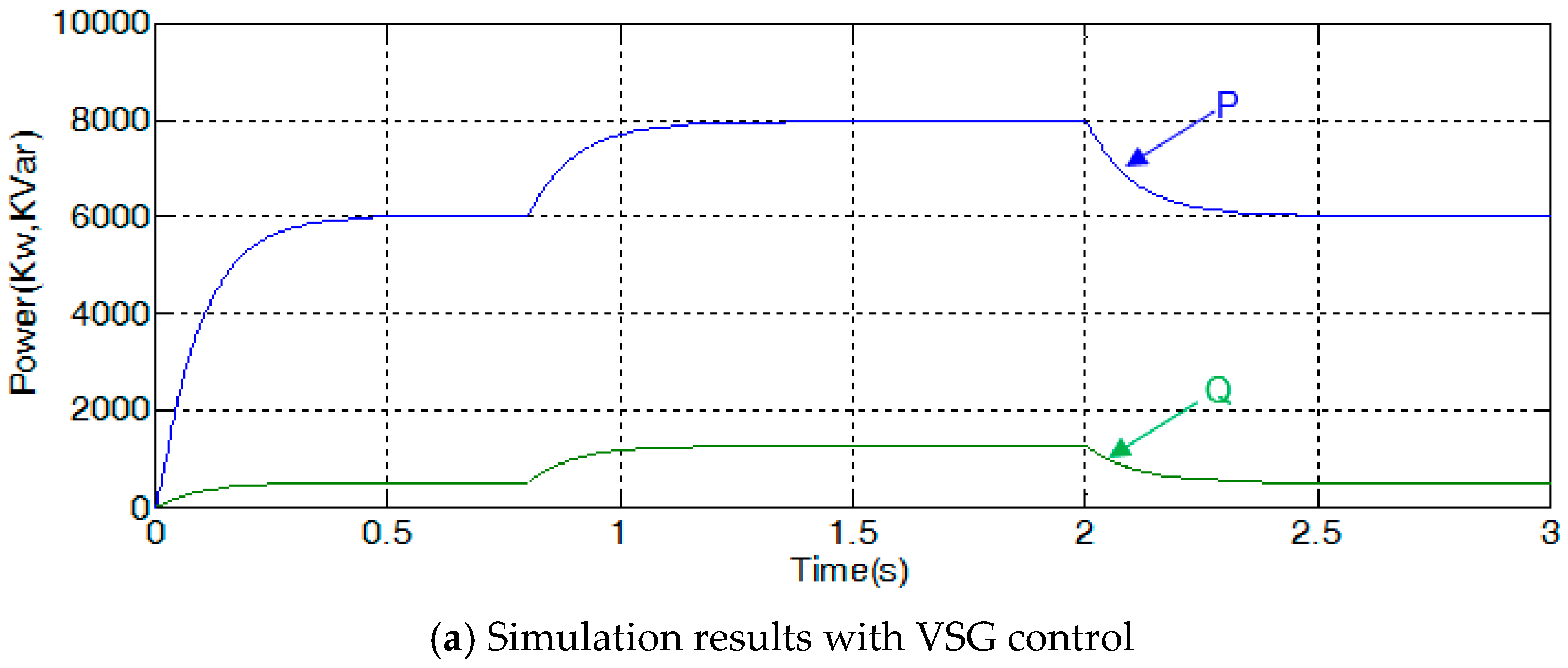
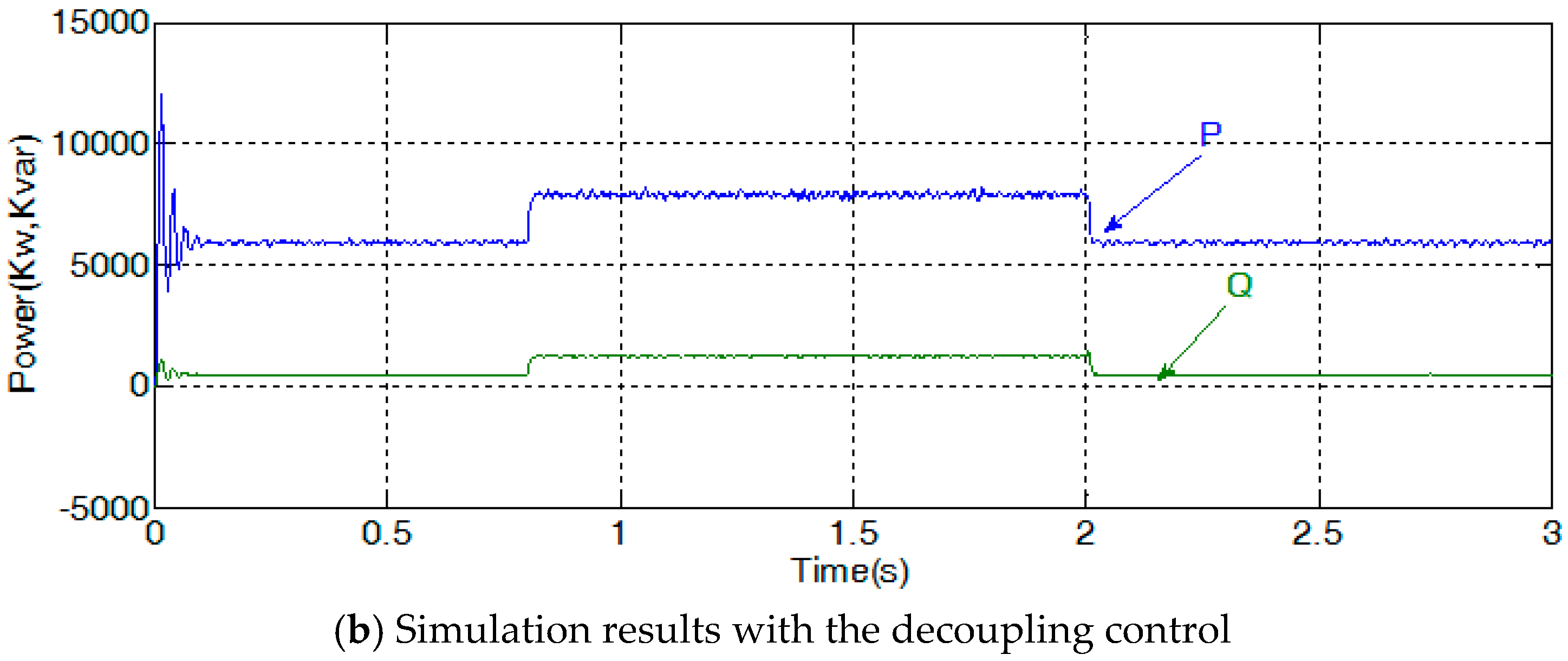
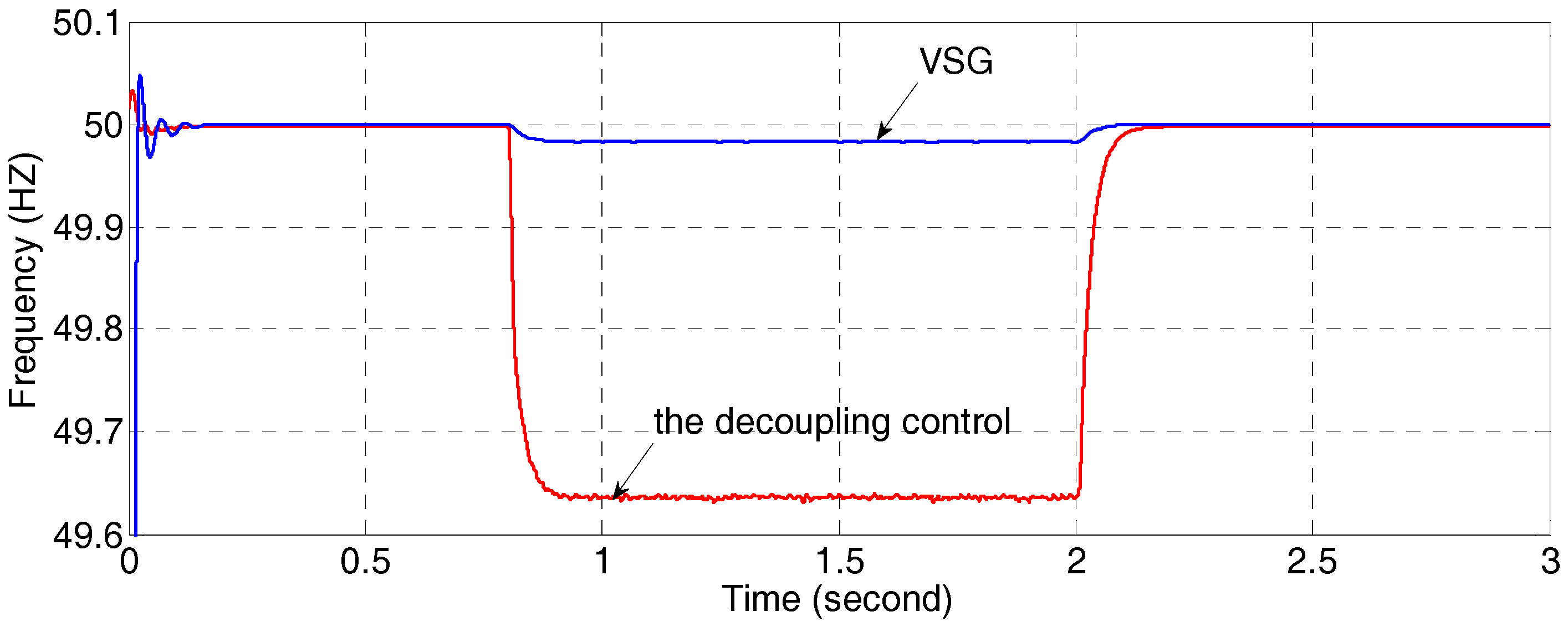
4.1. Comparision between VSG Control and Classical Decoupling Control
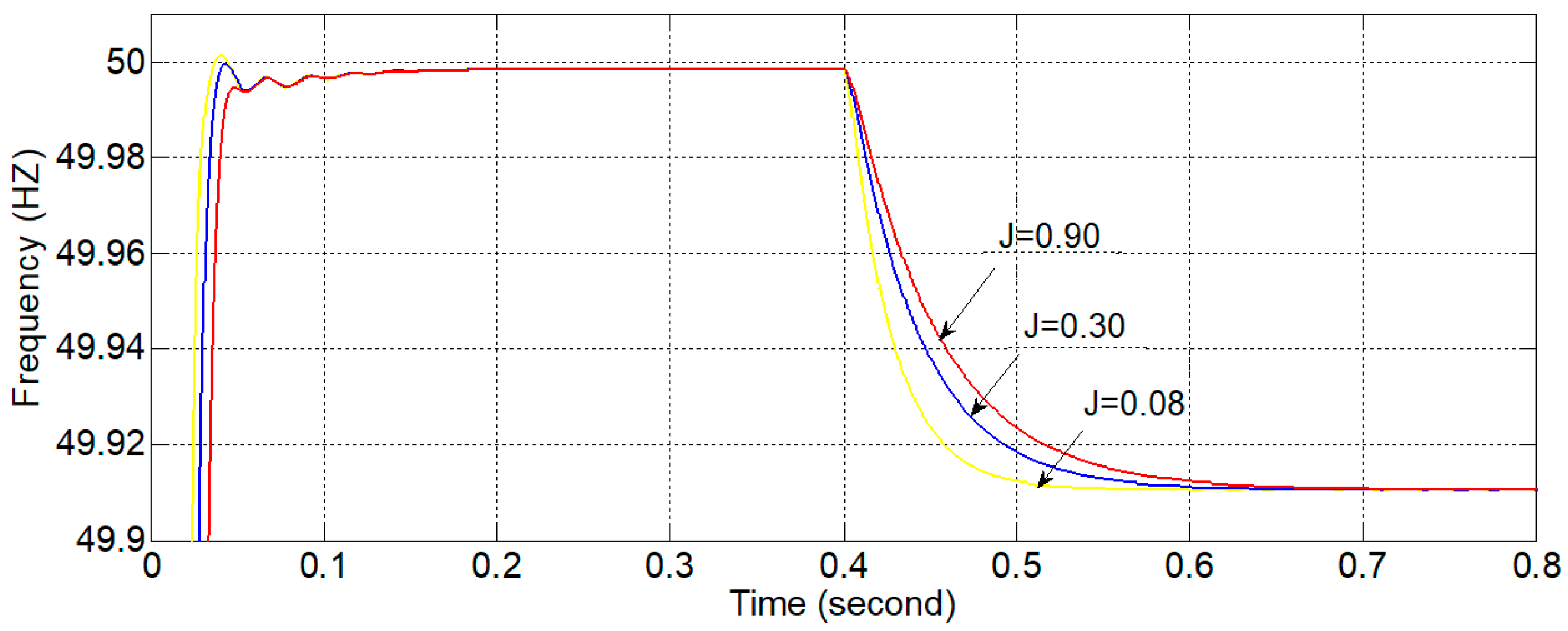
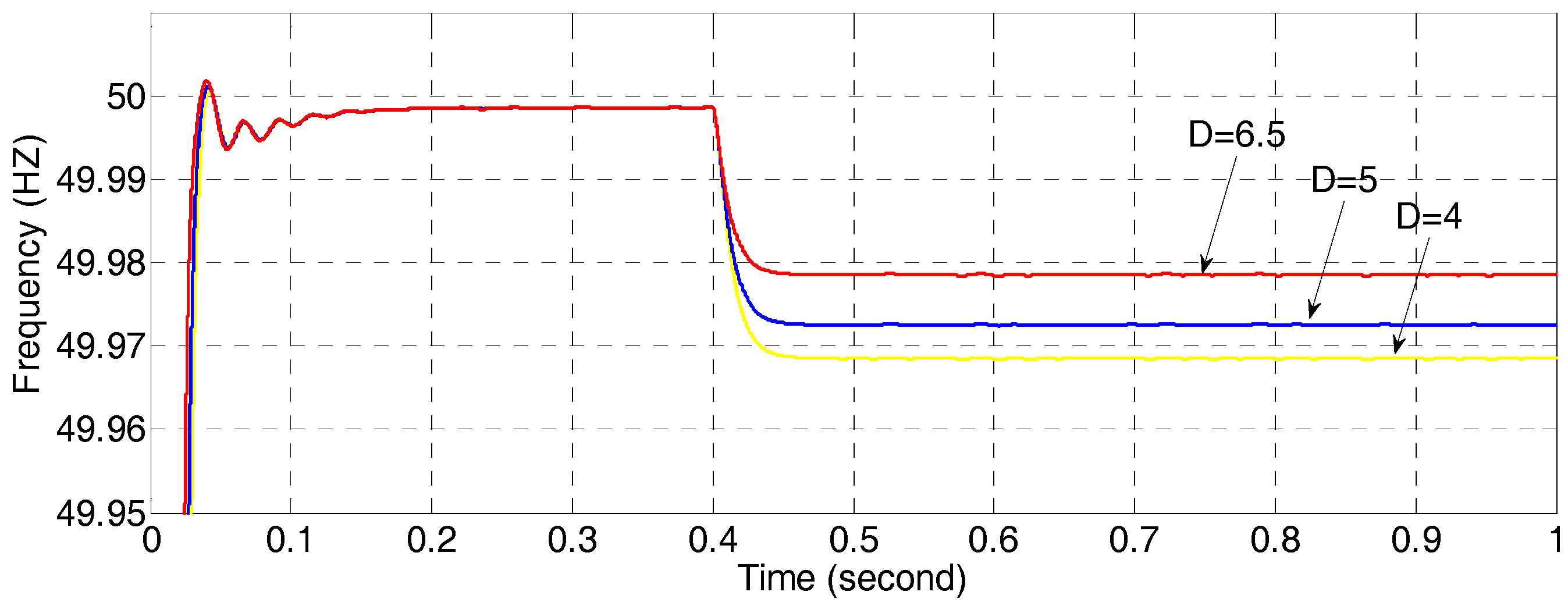
4.2. Simulations for Parameters Analysis of a VSG Controller
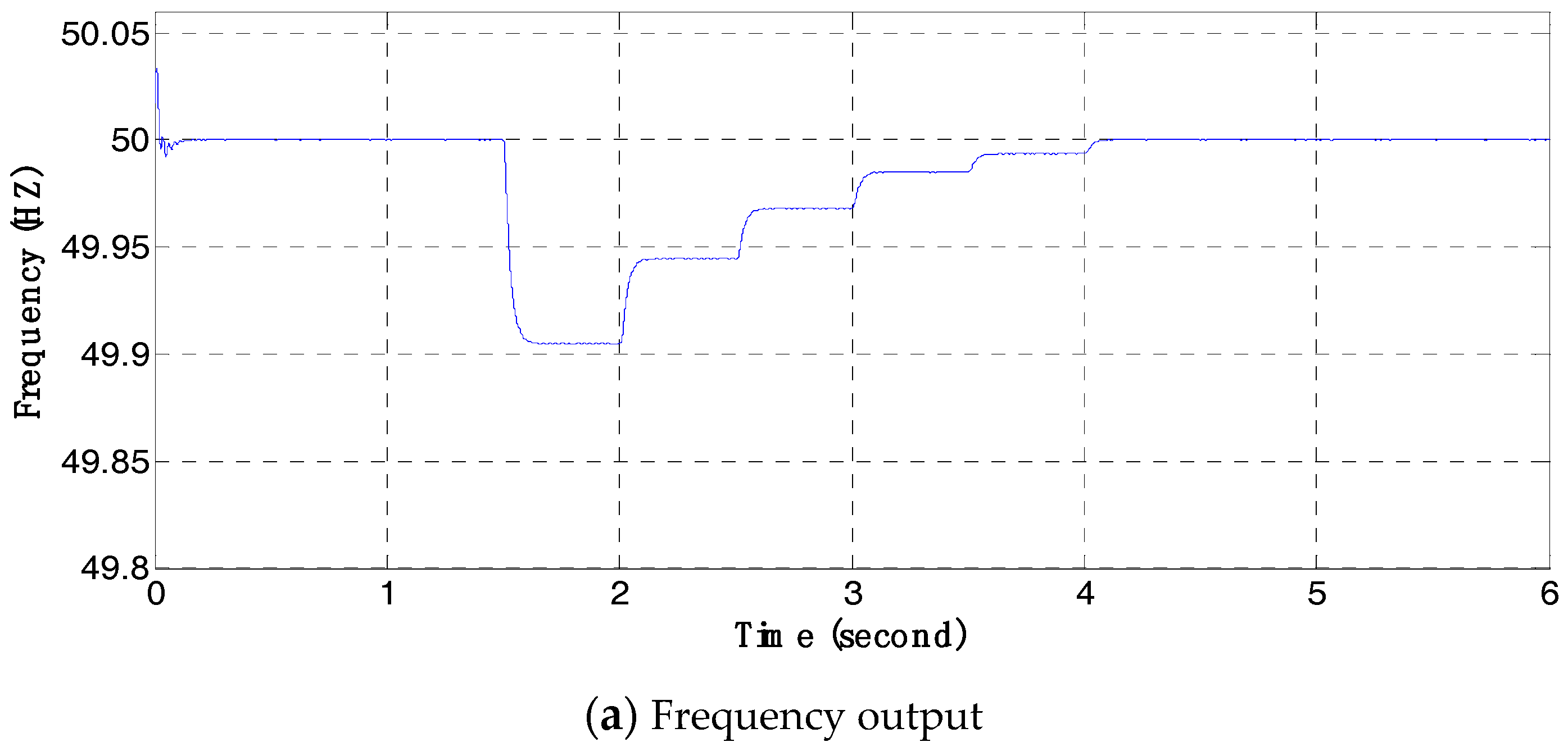
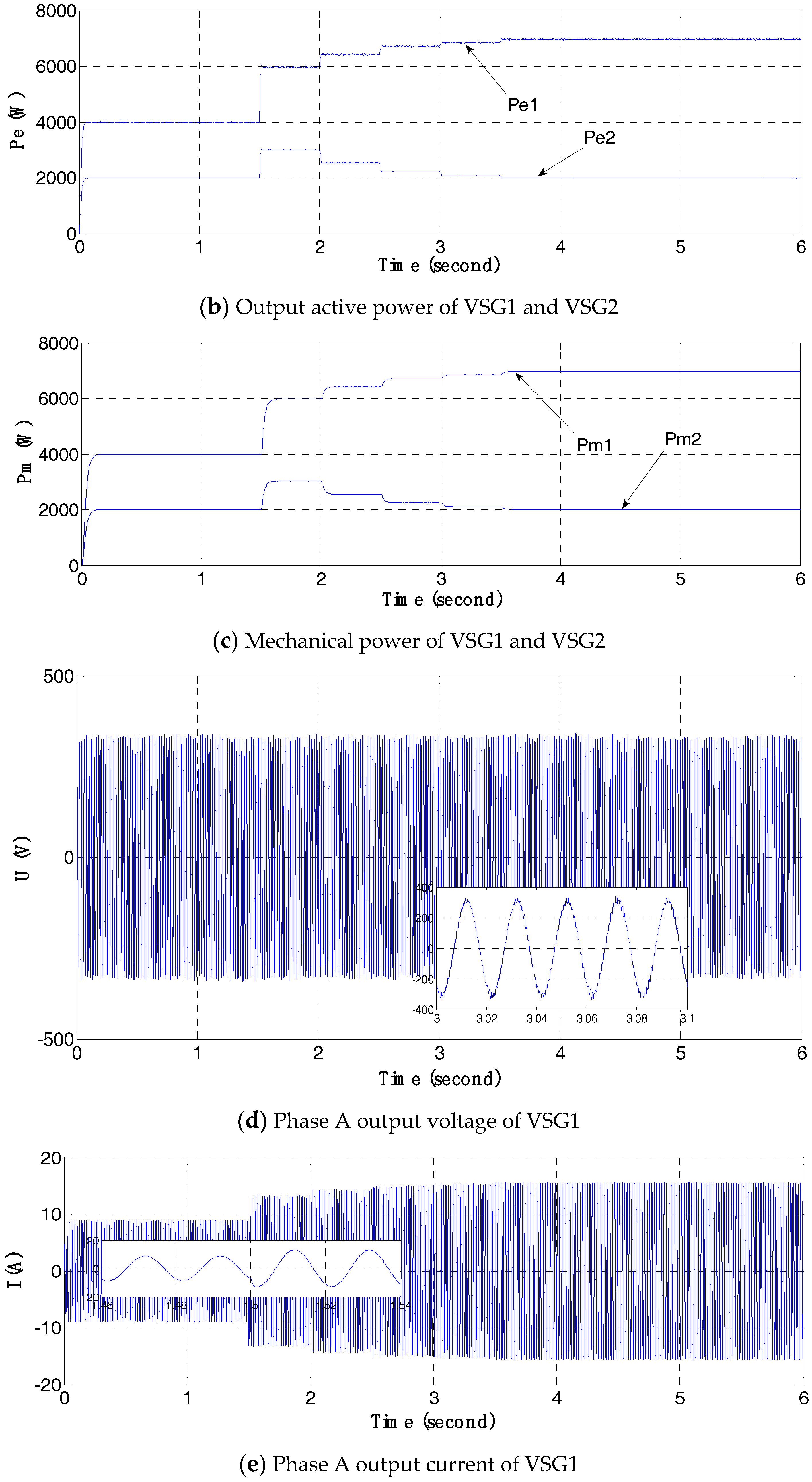
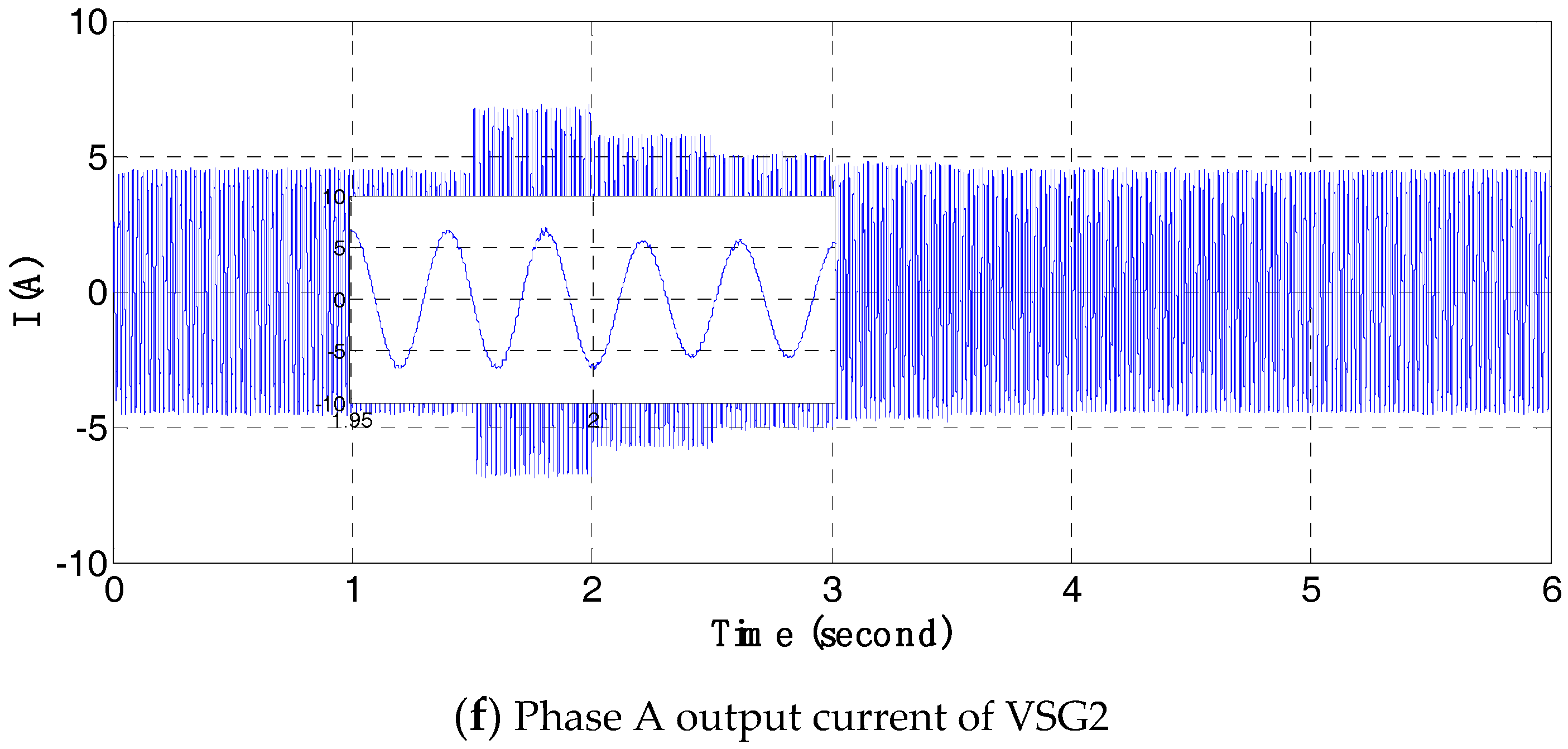
4.3. Simulations of the Frequency Hierarchical Control
4.4. Simulations of the Voltage Hierarchical Control
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, G.; Lu, Y.; Tang, T.; Benbouzid, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, T. A central control strategy of parallel inverters in AC microgrid. In Proceedings of the IECON 2013—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 7112–7117. [Google Scholar]
- Alipoor, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Stability Assessment and Optimization Methods for Microgrid with Multiple VSG Units. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.M.A.; Lopes, L.A.C.; Morán, T.L.A.; Espinoza, C.J.R. Self-Tuning Virtual Synchronous Machine: A Control Strategy for Energy Storage Systems to Support Dynamic Frequency Control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.C.; Weiss, G. Static synchronous generators for distributed generation and renewable energy. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–18 March 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Yuan, X.; Sun, L. On Inertial Dynamics of Virtual-Synchronous-Controlled DFIG-Based Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanos, V.; de Haan, S.; Zwetsloot, K. Real time simulation of a power system with VSG hardware in the loop. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011—37th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Melbourne, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 3748–3754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.C.; Weiss, G. Synchronverters: Inverters That Mimic Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, M.F.M.; El-Saadany, E.F. Implementing Virtual Inertia in DFIG-Based Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Pan, W.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, X. Synchronous Generator Emulation Control Strategy for Voltage Source Converter (VSC) Stations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, A.D.; Divan, D.M. Virtual Impedance Current Limiting for Inverters in Microgrids with Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Comparison of Dynamic Characteristics between Virtual Synchronous Generator and Droop Control in Inverter-Based Distributed Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3600–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhong, Q.C. Small-Signal Modeling and Parameters Design for Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Lu, Z.; Benbouzid, M.; Tang, T.; Han, J. A virtual synchronous generator based inverter control method for distributed generation systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 2112–2117. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, C.X.; Liu, B. Multi-Agent Based Hierarchical Hybrid Control for Smart Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica-Nava, E.; Macana, C.A.; Quijano, N. Dynamic Population Games for Optimal Dispatch on Hierarchical Microgrid Control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2014, 44, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shen, P.; Zhao, X.; Guerrero, J.M. Control Strategies for Islanded Microgrid Using Enhanced Hierarchical Control Structure With Multiple Current-Loop Damping Schemes. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Sun, K.; Guan, Y.; Guerrero, J.; Xiao, X. Active Power Quality Improvement Strategy for Grid-connected Microgrid Based on Hierarchical Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintuglu, M.H.; Youssef, T.; Mohammed, O.A. Development and Application of a Real-Time Testbed for Multiagent System Interoperability: A Case Study on Hierarchical Microgrid Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbouzid, M.E.H.; Beltran, B.; Amirat, Y.; Yao, G.; Han, J.; Mangel, H. Second-order sliding mode control for DFIG-based wind turbines fault ride-through capability enhancement. ISA Trans. 2014, 53, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipoor, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Power System Stabilization Using Virtual Synchronous Generator with Alternating Moment of Inertia. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C. A Coherency-Based Equivalence Method for MMC Inverters Using Virtual Synchronous Generator Control. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Q. Virtual Synchronous Motor Based Contrl Scheme of Fast Charger for Electric Vehicle Application. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Fu, C.; Li, P. Control Strategy and Parameter Analysis of Distributed Inverters Based on VSG. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2014, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.Y.; Chu, C.C. Consensus-Based Secondary Frequency and Voltage Droop Control of Virtual Synchronous Generators for Isolated AC Micro-Grids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2015, 5, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobierajski, M.; Rojewski, W. Primary and secondary frequency control in a small power system (SPS) with rotating and static sources after islanding. In Proceedings of the 2015 Modern Electric Power Systems (MEPS), Wroclaw, Poland, 6–9 July 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Xia, J.; Du, Z. New Algorithm for Dynamic Optimal Reactive Power and Voltage Control. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2006, 40, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Liu, N.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, G. A novel frequency control strategy of micro-grid based on the secondary frequency regulation of power system. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2013, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Frack, P.F.; Mercado, P.E.; Molina, M.G.; Watanabe, E.H.; de Doncker, R.W.; Stagge, H. Control Strategy for Frequency Control in Autonomous Microgrids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, G.; Bao, W.; Sun, Y.; Hao, M. A hierarchical control strategy of micro-grid based on grid-friendly distributed generation technology. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Power System Technology (POWERCON), Chengdu, China, 20–22 October 2014; pp. 3181–3185. [Google Scholar]




| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damping coefficient D | 4 | Kω | 2000 |
| Rotational inertia J | 0.33 Kg·m2 | Kω | 0.5 |
| Phase voltage U | 220 V | Rated frequency f | 50 Hz |
| DC bus voltage VDC | 700 V | Line impedance Zl | 0.3 Ω + 0.3 mH |
| Lf | 3 mH | Cf | 15 μF |
| Object Names | Parameters and Values |
|---|---|
| VSG1 | VDC = 700 V, Lf = 2.32 mH, rL = 0.1 Ω, Cf = 300 μF, f = 50 Hz, Pref = 4 KW, Kω = 40,000, Ke = 0.001, D = 2 |
| VSG2 | VDC = 700 V, Lf = 2.32 mH, rL = 0.1 Ω, Cf = 300 μF, f = 50 HZ, Pref = 2 KW, Kω = 20,000, Ke = 0.001, D = 5 |
| Line1, Line2 | 0.3 Ω + 0.3 mH |
| Loads | Sload1 = 6 KW, Sload2 = 3 KW |
| Object Names | Parameters and Values |
|---|---|
| VSG1 | VDC = 700 V, Lf = 2 mH, rL = 0.1 Ω, Cf = 500 μF, f = 50 Hz, Qref = 4 Kvar, Kω = 40,000, Ke = 0.001, D = 2 |
| VSG2 | VDC = 700 V, Lf = 2 mH, rL = 0.1 Ω, Cf = 500 μF, f = 50 Hz, Qref = 2 Kvar, Kω = 20,000, Ke = 0.001, D = 5 |
| Line1, Line2 | 0.3 Ω + 0.3 mh |
| Loads | Sload1 = 1 Kvar, Sload2 = 1 Kvar |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, G.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Benbouzid, M.; Moreau, L. A Virtual Synchronous Generator Based Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122049
Yao G, Lu Z, Wang Y, Benbouzid M, Moreau L. A Virtual Synchronous Generator Based Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems. Energies. 2017; 10(12):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122049
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Gang, Zhichong Lu, Yide Wang, Mohamed Benbouzid, and Luc Moreau. 2017. "A Virtual Synchronous Generator Based Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems" Energies 10, no. 12: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122049
APA StyleYao, G., Lu, Z., Wang, Y., Benbouzid, M., & Moreau, L. (2017). A Virtual Synchronous Generator Based Hierarchical Control Scheme of Distributed Generation Systems. Energies, 10(12), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122049







