Design and Materials
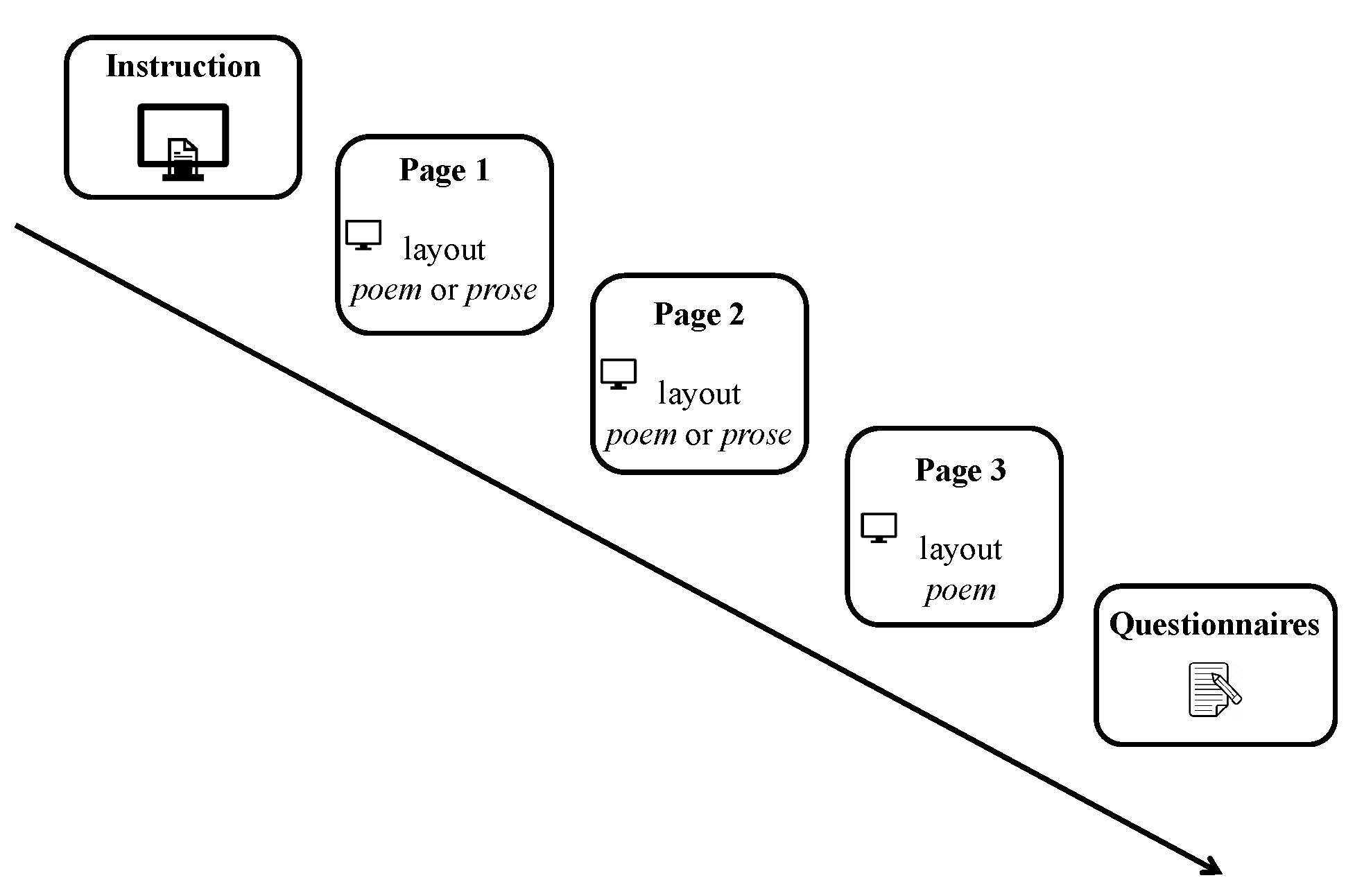
Stimuli consist of eight German poems that were each manipulated according to a 2x2 design, comprising the factors layout (poem vs. prose) and version (original poems vs. versions that included rhythm and rhyme violations). The 8x4 (items x condition) texts were then distributed to four presentation lists following a Latin square rotation scheme, such that each participant was presented with two texts for each condition, and each item occurred only once per list.
The order of presentation of stimuli was randomized. Stimuli were presented in Trebuchet MS, with a font size of 30. The display resolution was 1920 (width) x 1080 (height) pixels, leaving space for up to 13 lines of text with a 1.5 line spacing. Stimuli were split over max. 3 pages of the screen (for poem versions: page one presented stanza 1-3, page two stanza 3-6, page 3 stanza 7; for prose versions: page 1 presented the first two text blocks, consisting of stanza 1-4 and page 2 presented the second two text blocks consisting of stanza 5-7).
Although the prose version caused one critical region to coincide with the position of the last word on the screen, which is commonly known to be a problematic area regarding eye-movement behavior, we decided to keep this structure to examine effects caused by a disruption of expected rhythm at the end of the rhythmic system (auditive gestalt) of the prose version, as well as the poem version. This decision was also based on results reported by
Wassiliwizky et al. (
2017), who measured skin conductance to investigate emotion and aesthetic appreciation while listening to poems and found that chills occurred at the end of line, end of stanza and end of a poem.
The three types of experimental manipulations (
meter rhyme,
rhyme&meter; see appendix for all stimuli) are shown
Figure 3.
The first stanza of a poem introduced its rhythm, so participants had the chance to pick it up while reading silently and to potentially build rhythmic expectations. The rhythm of each poem was closely aligned to its main metrical grid to make sure MRRL was strongly metrical (compare
Figure 2 in
Ravignani & Madison, 2017), thus allowing for ‘quasi-isochrony’. We also added combined rhyme and metric anomalies (manipulation 4). These anomalies presumably impede the accommodation of the rhyme scheme into an ABAC pattern.
Stanzas 3 and 5 were in accordance with the rhythmic constraints so that readers might pick up the rhythm again. Manipulations (2) and (4) in stanza 7 allowed for complete deviation from the ABAB rhyme-scheme. In the present study, ABAB scheme implies perfect as well as imperfect, but acoustically close rhymes. Findings by (
Knoop et al., 2019, 10f) suggest “that imperfect rhymes benefit from metered verse context” and “are harder to distinguish from perfect rhymes as distances increase”, presumably depending on the “degree of phonological similarity”.
Note that we introduced the different rhythmic deviations on the basis of the constraints named above (for details see Appendix).
Figure 3.
Illustration of poem layout and prose layout: (1) original text, (2) rhyme anomaly: substitution of rhyme with original number of syllables, (3) metric anomaly: change of prominent metrical figure by adding one or two syllables with rhyme being maintained, (4) rhyme and metric (rm) anomaly: change of prominent metrical figure by adding one or two syllables, with substitution of rhyme.
Figure 3.
Illustration of poem layout and prose layout: (1) original text, (2) rhyme anomaly: substitution of rhyme with original number of syllables, (3) metric anomaly: change of prominent metrical figure by adding one or two syllables with rhyme being maintained, (4) rhyme and metric (rm) anomaly: change of prominent metrical figure by adding one or two syllables, with substitution of rhyme.
Rhyme anomaly. Since the first stanza introduces the ABAB scheme, readers may use it as a default for the upcoming stanzas. Rhyme anomalies such as begehrt/aufgebraucht instead of begehrt/aufgezehrt do not violate a potentially superimposed regular beat distribution but they may collide with the expected rhyme scheme. This holds true for imperfect rhymes, too.
Metric anomalies were construed by adding one to two syllables, disturbing the grouping structure of the previous syllabic material in the stanza. This was done by e.g., violation of expected stress/accent, by missing and/or delayed accent or by preponed and/or added accent. Examples are e.g., Gang/lang vs. Gang/entlang, leading to an additional floating stress moment, or grad/Waldesnaht vs. grad/Waldesziernaht, leading to preponed stressing of “zier” and stress diffraction on the last syllable “naht”. Adding a syllable could also shift the projected number of beats if introducing one more syllable which requires stress, thus locally disturbing the overall stress distribution within the stanza.
Metric & rhyme anomaly should most clearly lead to irritation within the overall rhythmically structured ‘gestalt’, either by realizing possibilities listed above combined with deviation from the rhyme scheme, or, by implying a stress clash, e.g. gegeben/(gut) durchleben vs. gegeben/(gut) überstehen (see Appendix for further details). However, our focus was not to analyze the different sub-types of metrical anomalies or rhyme anomalies, but more so the general eye-movement reactions elicit by the anomalies.
The corresponding prose version which includes experimental manipulations had the same pattern (adjusted interpunction marked red). Content-wise, both prose versions, original and manipulated, were in line with the corresponding poem versions. Changes in prose versions were undertaken for two purposes: a) line breaks should not coincide with the position of pre-rhymes, and b), when line breaks coincided with clause boundaries in the poem layout, interpunction and capitalization was adjusted to preserve the clause structure.
Seven poems were composed by the first author specifically for the purpose of the experiment. One more poem was an original, “Auf hohem Gerüste” (
Ringelnatz, 1997, p. 63). Hence, the stimuli have not been used in previous research. These seven poems followed a preset poetic rhythm structure as close as possible. This was obtained by adherence to the rhythmical matrix of classical originals, i.e., 1)
Dancing Queen, 2)
Flüstern, as in “Der Pilgrim” by Friedrich Schiller, 3)
Klimawandel as in “Der Wanderer in der Sägemühle” by Justinus Kerner, 4)
9 Leben as in “Auf hohem Gerüste” by Joachim Ringelnatz, 5)
Normal as in “Am Waldessaume träumt die Föhre” by Theodor Fontane, 6)
Im Hüteland and 7)
Glühwürmchen were authored following preponderantly the rhythmic matrix (rhyme, meter, phonological relatedness) of those named above. They all had to rhyme according to the ABAB-scheme, which could also include imperfect, yet acoustically close rhymes.
The semantic field of words was chosen from commonly known topics such as nature, summer, youth, desperation, etc. Poems mostly contained familiar and high frequency words, such as luck, stars, sky, forest, breathing, etc., function words as well as some low frequency or antiquated words, and neologisms.
The seven new poems included parallistic dictions and a higher level of difficulty (
Castiglione, 2019;
Yaron, 2002,
2008) compared to “Auf hohem Gerüste” by Ringelnatz, i.e., they presented a moderate number of stylistic devices such as assonances, alliterations, comparisons, e. g. “die Sterne wie Glitzerstuck am Himmel” (the stars like glittering stucco in the sky) or neologisms, e.g. “Hügelzwerg” (hill dwarf), etc. We did not exclude any non-standard syntactic patterns, because word order is an important stylistic feature contributing to the multilayered meaning and rhythm construct of a MRRL-poem (
Schrott & Jacobs, 2011).
Although stimuli were written in a sound-familiar metrically regular and rhymed style (such as quatrains, nursery rhymes, etc.), the choice of words and the occasionally complicated syntax should prohibit complete and deep sentence comprehension. At the same time, we expected readers to grasp the narrative of a poem quickly (
Castiglione, 2017), i.e., global comprehension of content. For this reason, we assumed fluent reading, which in turn was presumed to enhance rhythmic subvocalization. Also, participants were not allowed to move back to earlier pages, which also made full sentence comprehension within the course of a poem more difficult. This ensured that rhythm became a more salient feature.
Data Analysis
Fixation reports of the raw data were generated using the SR-Research Data-Viewer. Blink durations were not included in fixation durations. Fixations occurring directly before or after a blink were not excluded from the data set. Rectangular interest areas (IA) were defined automatically around each word on a page. Every computational step from here, including interest area assignment, was taken in the R programming language. The code is available upon email request.
For each fixation, we assigned an IA based on the fixation’s x and y coordinates. Fixations’ start times were used to identify the page one out of three that was read. The completed fixation reports were then transformed into IA-reports, with each row representing a consecutive IA/word in an item, including variables for eye tracking measures, lexical features and other IA related variables that would potentially affect reading measures, including the design factors.
Word reading time measures, especially in longer texts, are affected by many variables that are not in the main focus of our study. However, to control for these variables, we consider it mandatory to account for their influence. This should be done on as many data as possible, namely on all words in the texts, with the exception of the first word.
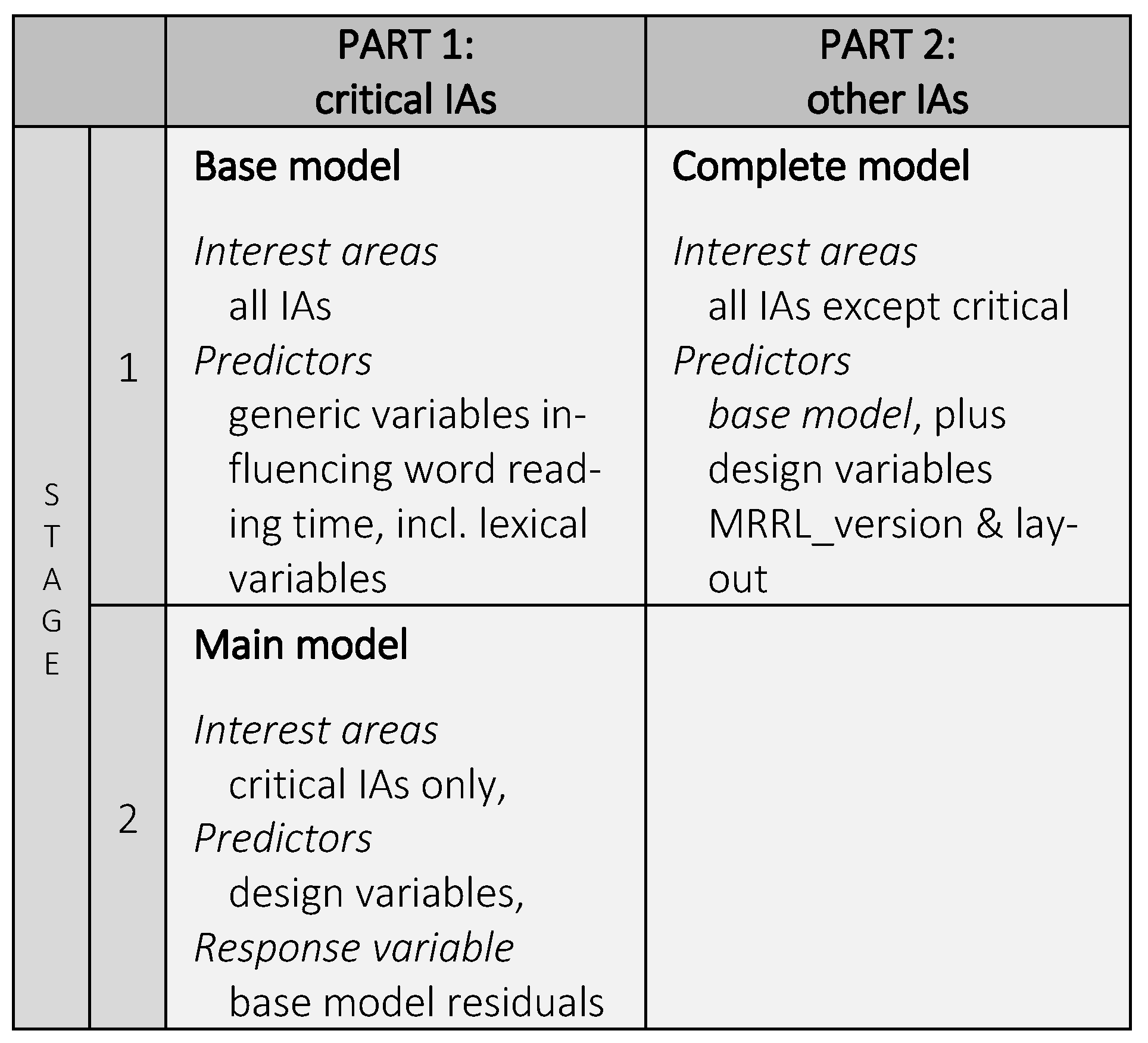
For the data analysis of the critical IAs, we hence chose a two-stage approach, where the analysis of critical IAs was based on residuals derived from all IAs.
However, we were also interested in general eyetracking signatures of subvocalization on areas other than the critical IAs. We therefore chose to analyze the IA-reports in two parts (except for skipping probability and load-contributions; see
Figure 4).
Part 1 focused on the reading of the critical IAs themselves. This analysis has been carried out in two stages. In stage 1 we fitted a base model over all IAs (words). The purpose of the base model is to eliminate all effects that are not (related to) the design factors, which are included in the main model, namely
layout, anomaly_type and
MRRL_version. The base model includes a wide variety of general predictors that are known or very likely to influence eye-movements and word reading times. Among those were
i. lexical features, such as word length, frequency (
Just & Carpenter, 1980;
Kliegl et al., 2004;
Schuster et al., 2016), and the word category (noun, verb, adjective, closed class words),
ii. structural features, such as whether an interest area (word) occurred at the end or the beginning of a line (
Koops van ’t Jagt et al., 2014) or verse (rhyme indicator) (
Carminati et al., 2006). Finally, we also included
iii. oculomotor behavior variables, such as whether or not a first pass regression is launched, and gaze durations of the predecessor word. These variables can strongly affect all duration measures independently of our design factor manipulations and should thus be accounted for, either in the base or main model. Accounting for them in the base model has the advantage of almost completely detaching them from the critical IAs, where the effect of the design variables should be as pure as possible.
The base model was only fitted to produce residuals (
Trueswell et al., 1994), which were then used as the response variables in the second stage models. Using residual reading times is a common technique to account for, and eliminate, irrelevant influences before looking at the effects of the design factors. Note that the base-model was fitted across
all interest areas.
The residuals were then used in stage 2 (i.e., the main model) to analyze a reduced data set, where all but the critical interest areas (IAs) were excluded. Because distractor influences were eliminated in stage 1, the main model only included the design factors as fixed effects predictors. Critical interest areas were those target words that have been manipulated in the experimental conditions, i.e., replaced with other words inducing a meter or rhyme anomaly, or both.
The two-stage approach was chosen for two reasons: First, we could include a plethora of variables influencing reading times in the base model without sacrificing power in the main model. The main model could thus be based on residual eye-tracking parameter values that were fitted over the entirety of the poems, consisting of about 160 words each. Had we chosen to include all predictors in a single model, not only would we have lost power by analyzing only five interest areas (words) per poem. Secondly, estimates of lexical variables would have been obscured by any manipulation that disrupts reading, particularly so the anomalies. Only results from the main model of part 1 will be reported.
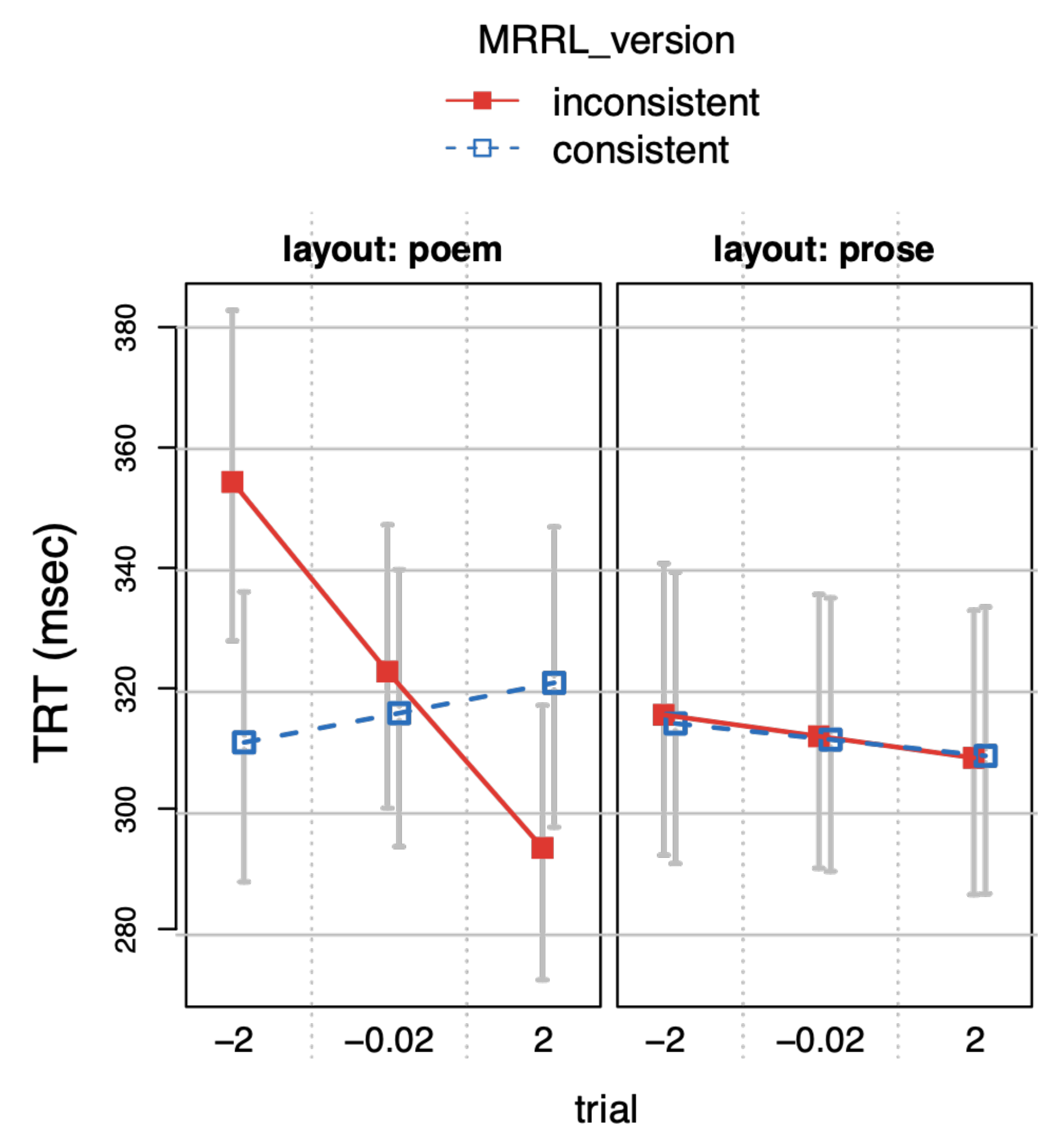
Complete model. However, we were also interested in how our design manipulations affected reading in general not only at the target words, but throughout the entire poem. Hence, part 2 focused on the effects of our manipulations on all but the critical IAs. This complete model included all predictors from the base model in stage 1, plus the design factors layout (layout: poem vs. prose) and MRRL_version (consistent vs. inconsistent). Factor anomaly_type was not included, because it was only defined for critical IAs, as all manipulated stimuli contained all three types of anomalies (anomaly_type metric, anomaly_type rhyme, anomaly_type r&m).
For the complete models, we used stepwise elimination to yield a minimal model, which only included predictors that significantly increase the model quality. For this, we used the function step() from the lmerTest package, which applies backward elimination of random-effect terms followed by backward elimination of fixed-effect terms in linear mixed models.
The variance inflation factors of all predictors in both the main and complete models were below 5.
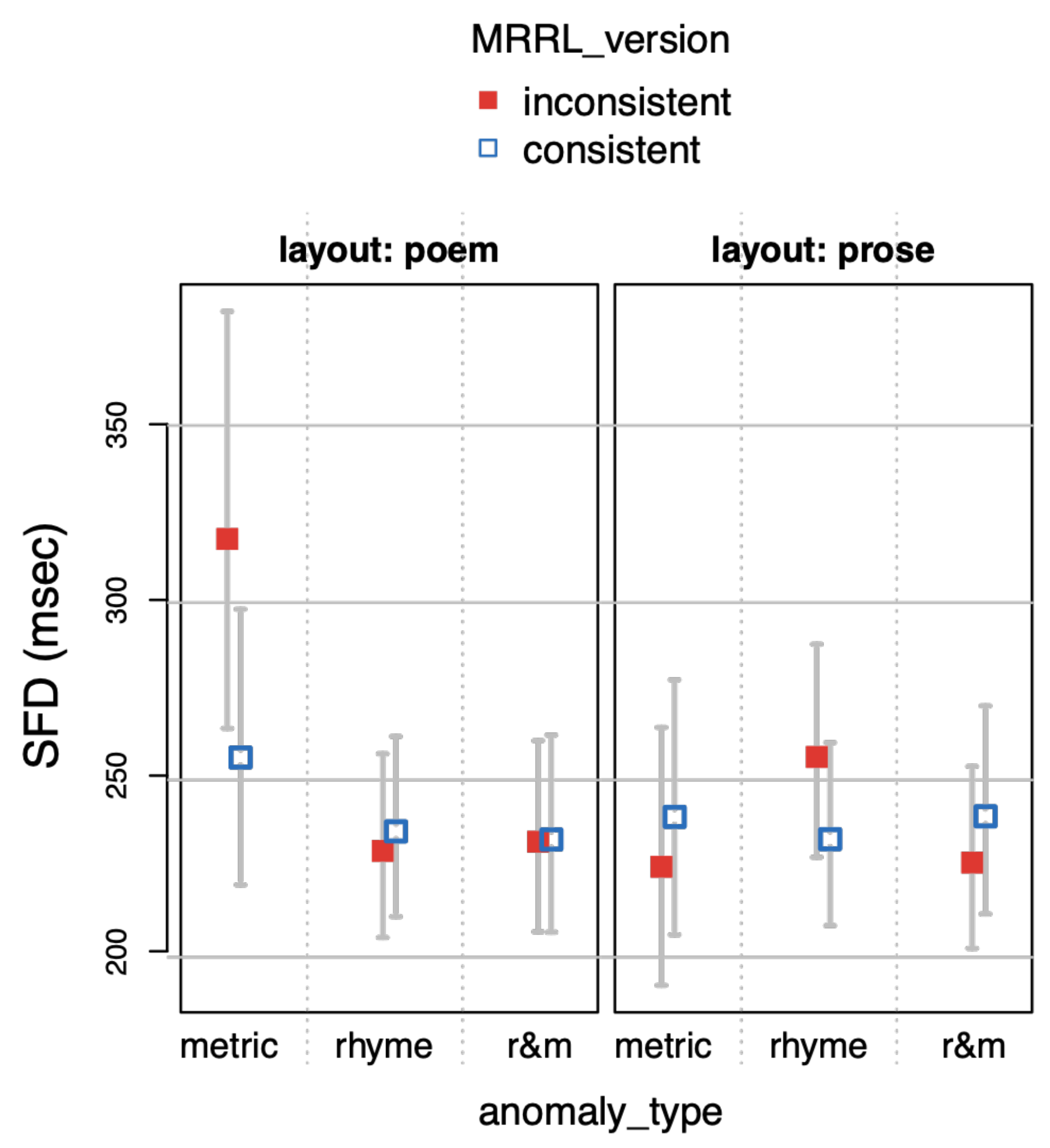
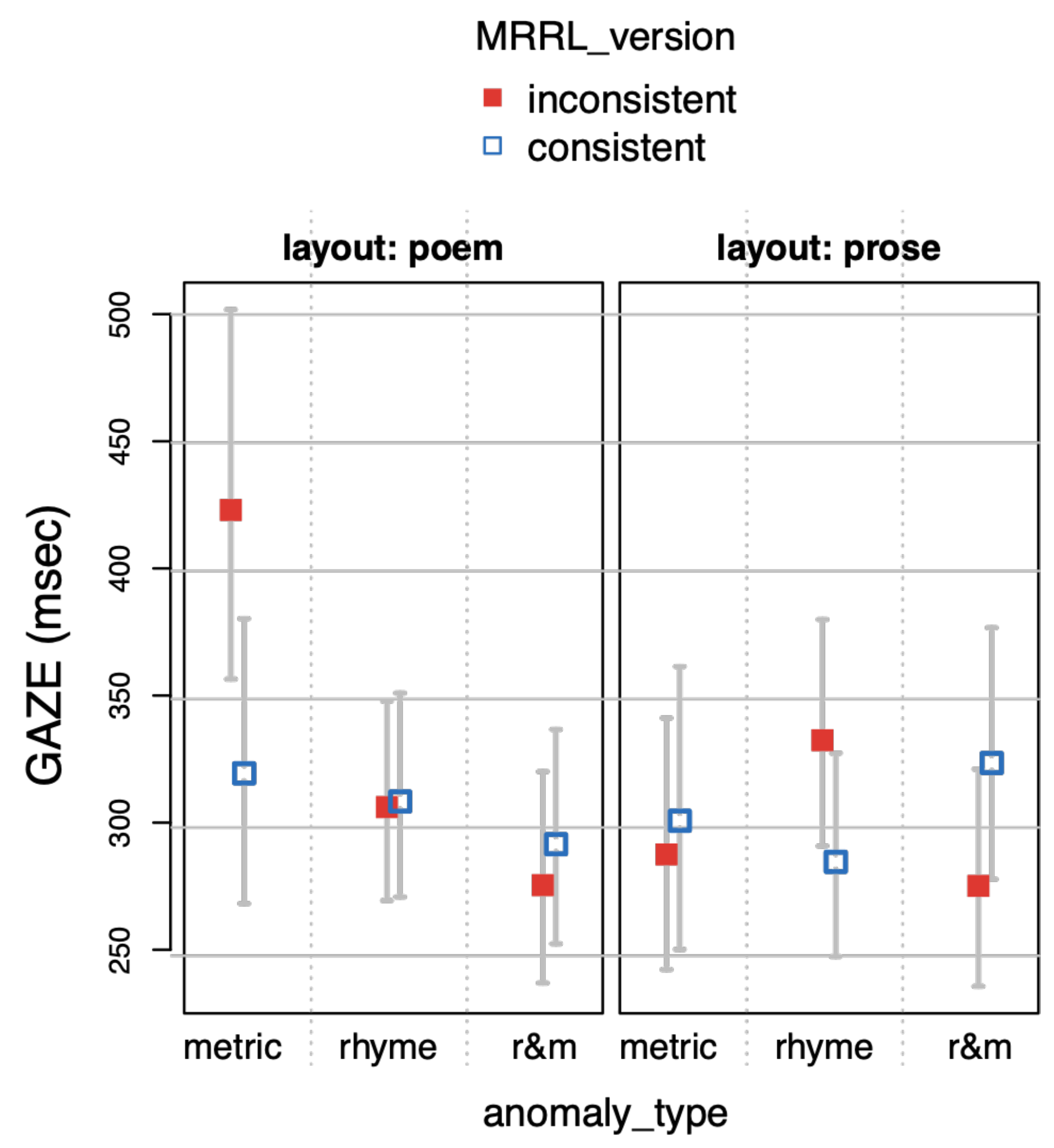
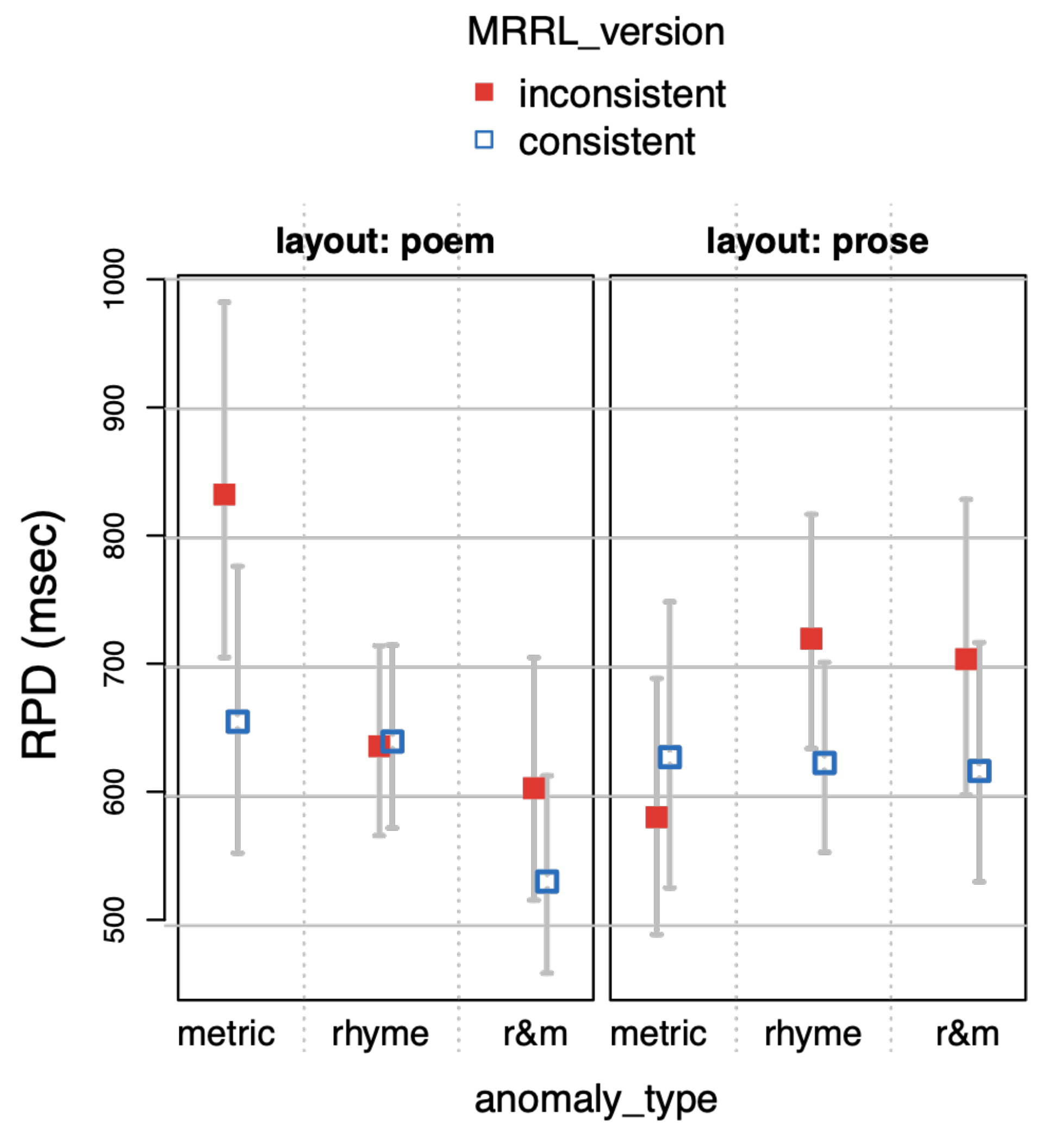
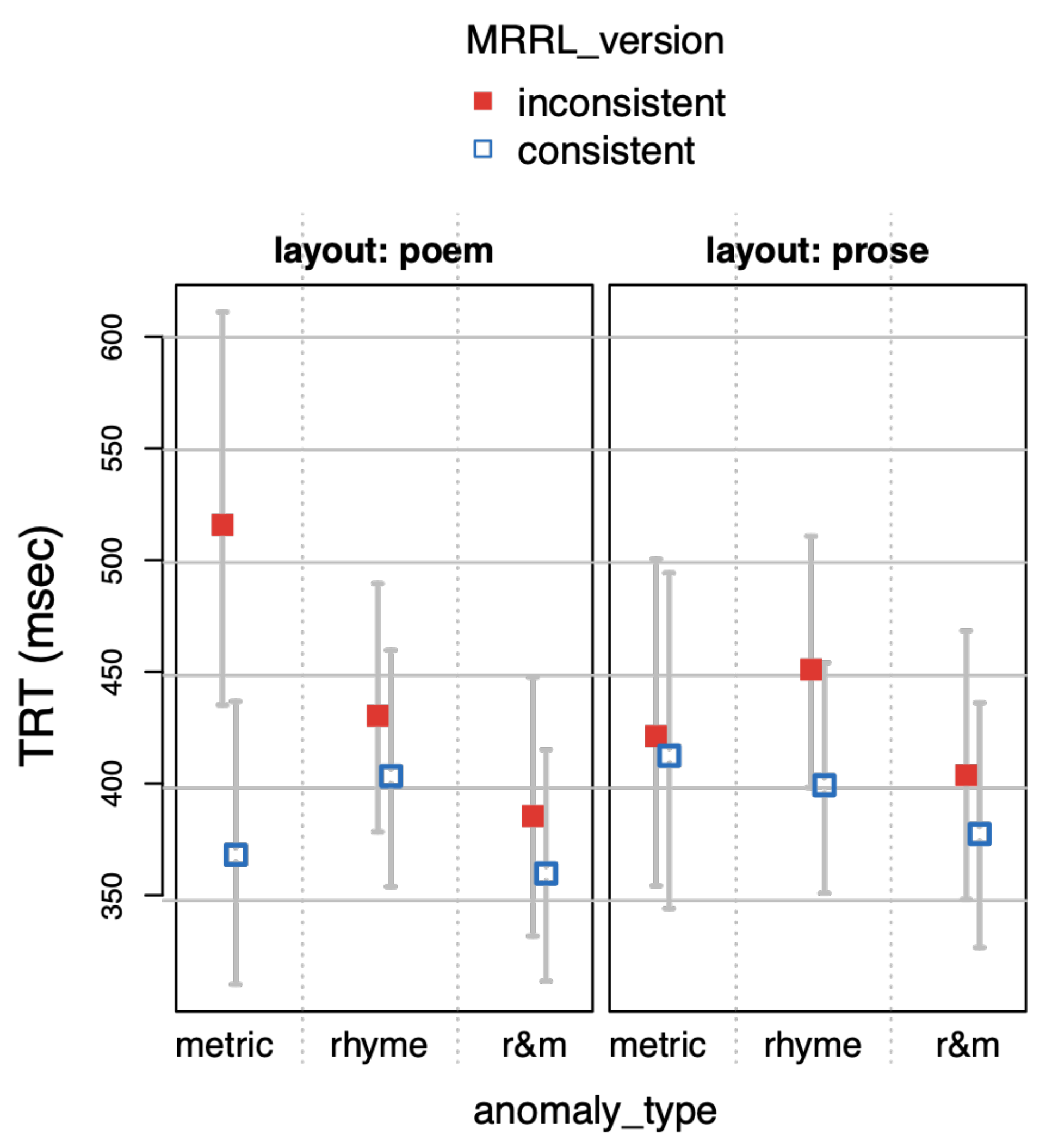
The main model of part 1 included the study design factors layout (layout with levels poem vs. prose), MRRL_version (with levels inconsistent vs. consistent), and anomaly_type (levels metric vs. rhyme vs. r&m for rhyme+metric, respectively) and all interactions between the three factors.
In both the base and the main model, intercepts for participants and items were included as random factors. The rationale for this is the different sets of IAs and predictors in both models. Some readers might react to anomalies and layout manipulations differently, resulting in estimate variance, even after general reading measures have had normalized across all IAs. Also, stimulus manipulations might have different effects in different items. Furthermore, slopes for word length and frequency were added in the base model, and the slope for MRRL_version in the main model.
Variables in the base and complete model. We included three types of variables in both the base and the complete model: lexical, structural, and oculomotor variables.
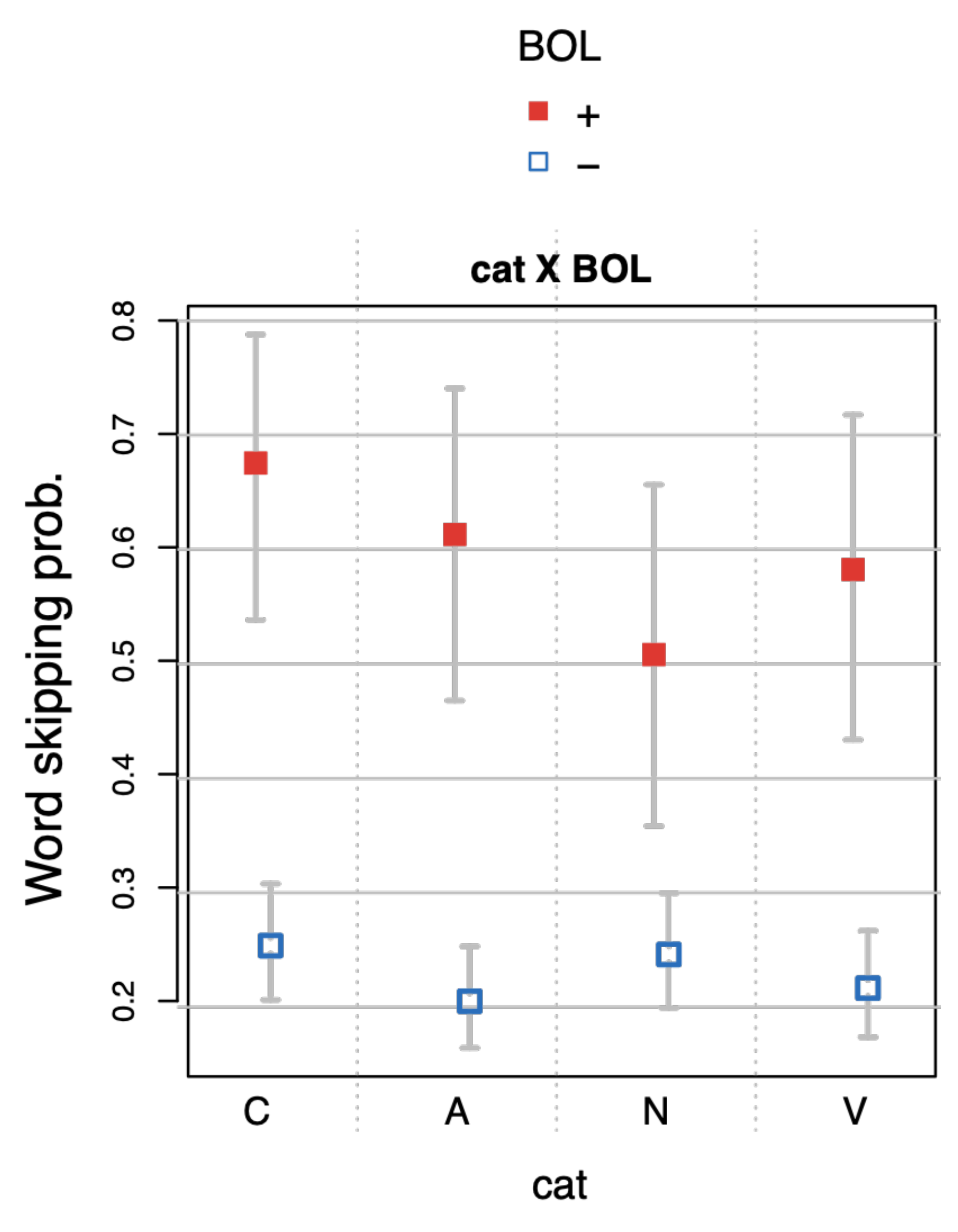
Lexical variables. We computed five lexical features: 1. word category annotated cat (labeled catC, catA, catN, catV; which identified levels closed class, adverb/adjective, noun, verb), 2. word length, i.e., the number of characters for each word (word_length) and 3. log word frequency (log.freq) based on the DeReWo-2014 corpus-based word lists (Belica, C., Kupietz, M., Lüngen, H., & Perkuhn, R., 2012).
We computed 4. the
consonant vowel quotient (
cvq), as an indicator of pronounceability (
Kraxenberger et al., 2018;
Lee et al., 2002;
Rayner & Pollatsek, 1989;
Xue et al., 2019). The calculation was based on letters rather than sounds. For German, a high level of consonants is assumed to impede pronunciation, as can be experienced in tongue twisters (e.g. “Schlickkrebskriechgang” / ”Schlickkriechkrebs-schleichgang”). We also added the consonant vowel quotient of the succeeding word (cvq.p1) as an indicator of parafoveal processing of phonological/pronunciation information.
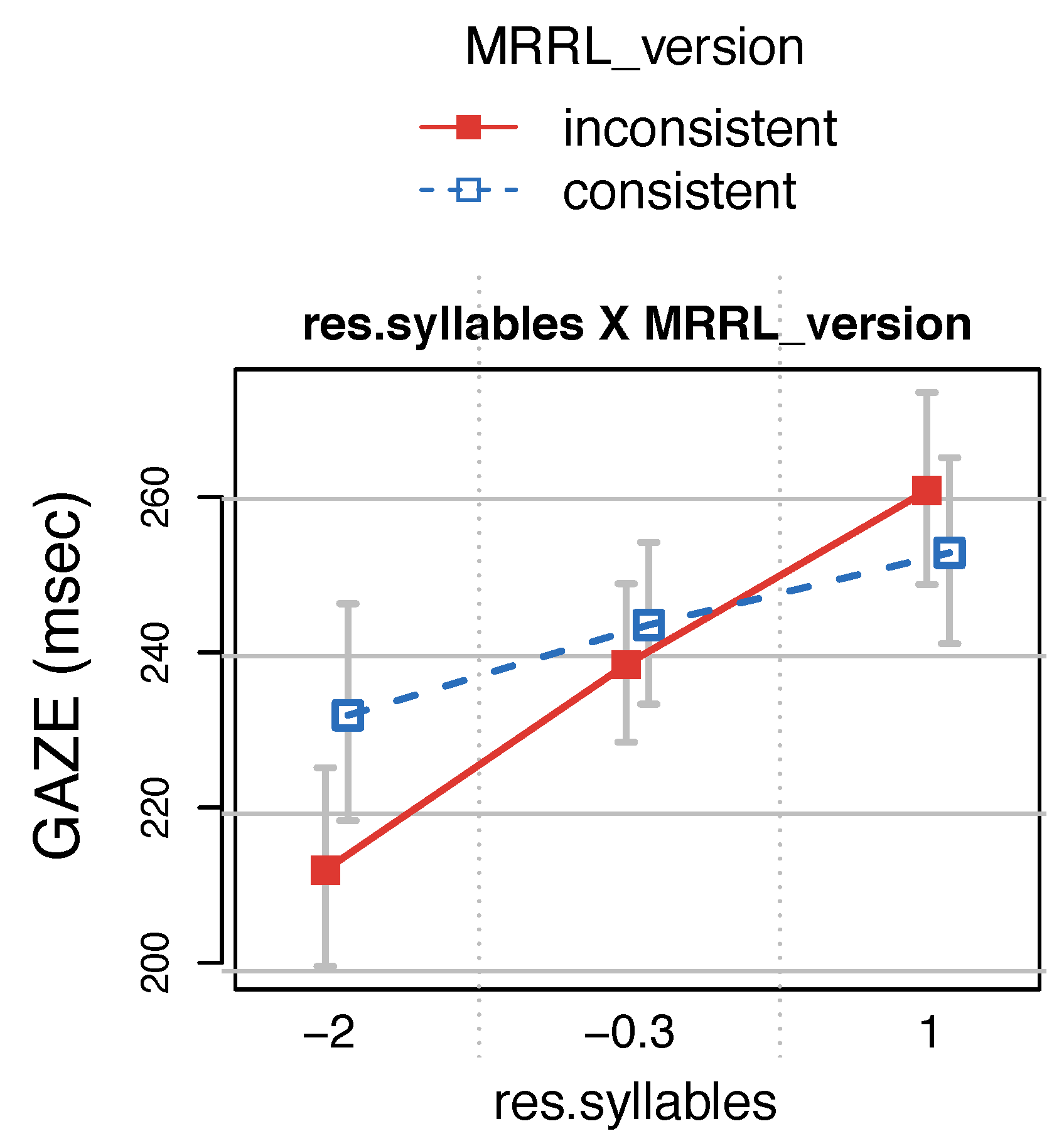
Finally, 5. the
number of syllables (
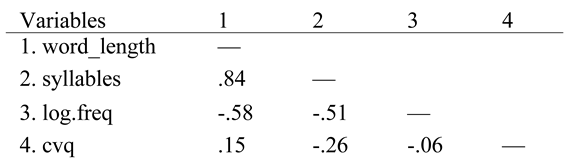
syllables) of a word were computed as an estimate of how long it would take to be spoken. Naturally, number of syllables and the number of characters (
word_length) of words are highly correlated (.84, see
Table 1). We therefore computed residualized number syllables (
res.syllables) in a simple regression over word-types, where syllables were predicted from word length.
Res.syllables is thus independent of word length and reflects pronunciation more purely. In earlier research, syllable number has been shown to influence skipping, but no effect on reading time measures beyond word length was found in normal reading (
Fitzsimmons & Drieghe, 2011). Hence, we would consider any such effect in our results a strong indicator for an eye-voice-span synchronization induced by MRRL-language.
Also, since the cvq turned out to be highly negatively correlated with res.syllables, we computed the residual cvq (res.cvq) by predicting the cvq from both res.syllables and word_length in a linear regression model over word types.
Structural variables. In addition, we computed variables related to particular IA-positions that are known to influence reading, such as the beginning (BOL) or end of a line (EOL).
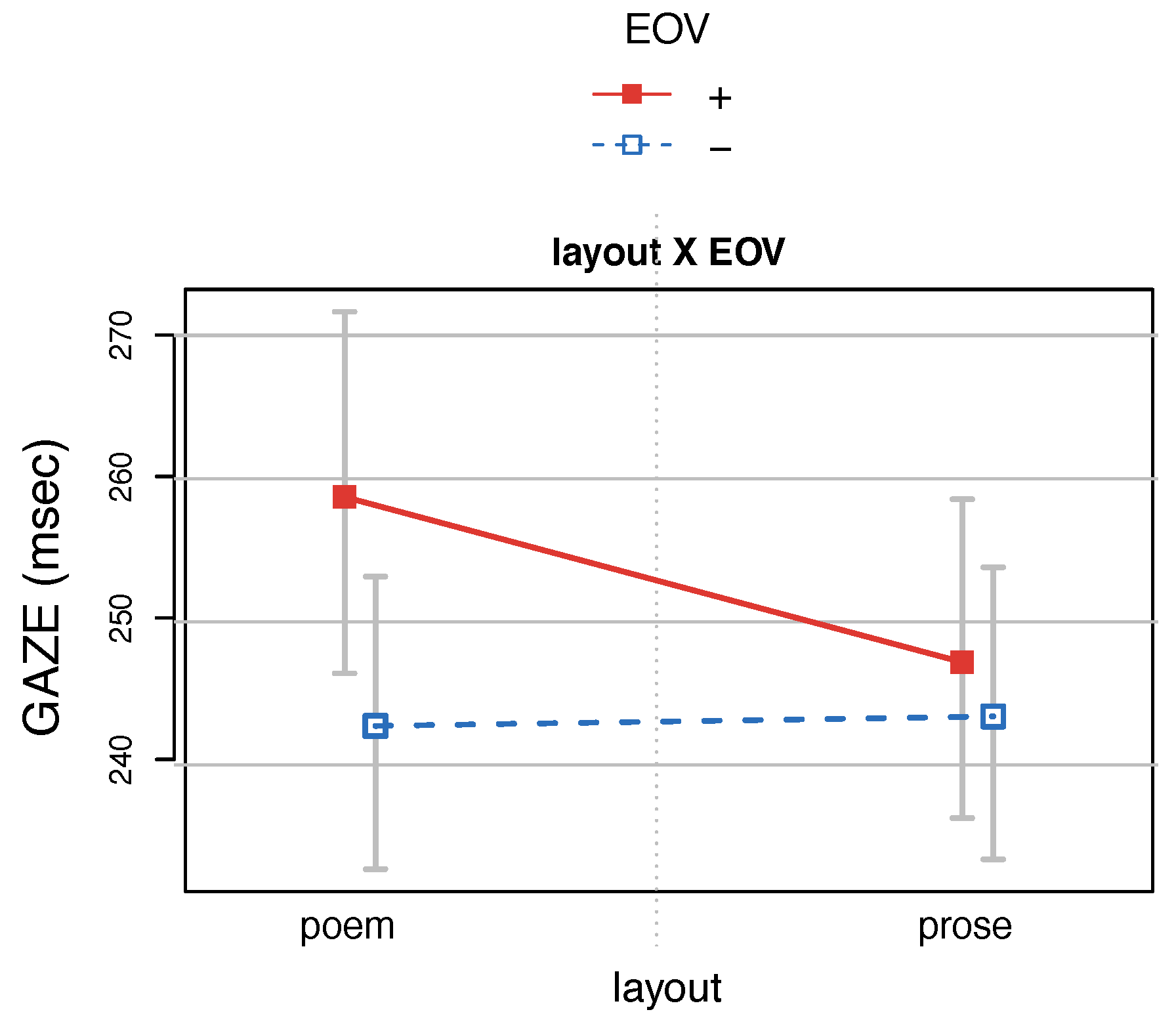
Furthermore, we included the variables beginning of verse (BOV) and end of verse (EOV). Although EOVs coincide with EOLs in poem layout, they do not necessarily do so in prose layout. The ending of a verse signals an end point of an important (rhythmic) unit and could thus influence subvocalization, e.g. by triggering a pause, independent of a visual line break.
We also included page number, the running word number on a single page (wpos), and the interaction between the two in order to capture adaptation effects throughout reading a complete item. To account for potential practice or fatigue effects we included the variable trial (values 1 to 8), encoding the presentation order of trials throughout the experiment, i.e., the position number of each trial in the experiment.
Oculomotor variables. To account for potential preview and spill-over effects we included the gaze durations of the predecessor word (gaze_pre.word) as a linear predictor. Because first pass duration measures can vary considerably depending on whether first pass reading is followed by a regressive saccade, we also added the binary predictor first_pass_regression.
Eye tracking parameters. Before we computed eye-tracking measures from the fixation reports, all single fixations on an IA shorter than 40 milliseconds were treated as overshoots and assigned to the previously fixated IA. Data cleaning, including outlier elimination, was done completely automatically. For each IA, we computed
first fixation durations (
FFD),
single fixation durations (
SFD; equaling
FFDs, but excluding all cases with more than one fixation during first pass),
gaze duration (
GAZE, the sum of all fixations on the target IA during first pass),
regression path duration (
RPD), the sum of all fixation durations during first pass plus if the first pass is followed by a regressive saccade all fixation durations on predecessor IAs, until a saccade goes past the target IA (
Konieczny et al., 1997), right bounded reading time (
RBRT, the sum of all fixation durations on the target IA until a saccade goes past the IA),
total reading times (
TRT, the sum of all fixations on an IA), and
second pass reading time (
SPRT, computed as
TRT minus
GAZE). All first pass measures (
SFD,
FFD,
RD, and
RBRT) required the first fixation resulting from a progressive saccade. Also, we analyzed conditionalized times, meaning that zero values were treated as missing values. For data analysis, all time-based parameters were logarithmized.
In addition to these reading time measures, we computed variables coding whether or not a word has been skipped (SKIP).
Before model fitting, we calculated overlaps and correlations between the eye tracking parameters (see
Table 2). Because single fixation durations (
SFD) are a subset of first fixation durations and first pass reading times, their correlation must equal 1. All other measures – with the exception of
SPRT (second pass reading times) and both
SFD and
GAZE – are significantly correlated with each other (p<.001), albeit to a varying degree.
Single and first fixations are a subset of fixations that constitute gaze durations, and therefore their correlation is 1. However, since single fixation durations (SFD) and GAZE share only 74.7% of the data points, we will report results from both model fits. First fixation durations (FFD), on the other hand, will be ignored. Right bound reading times (RBRTs) are highly correlated with regression path durations (RPD), so they will be ignored, too. We also ignored second pass reading times (SPRTs), because they are highly correlated with total reading times (TRT, .87). The remaining measures should suffice to tap into early and later processing stages.
Total reading times are a combined measure of first pass and later processing. Therefore, there will be an overlap with GAZE and single fixation durations (SFD), but any deviations would suggest later stage processes. Total reading times (TRT) are thus considered a measure of overall processing difficulty.
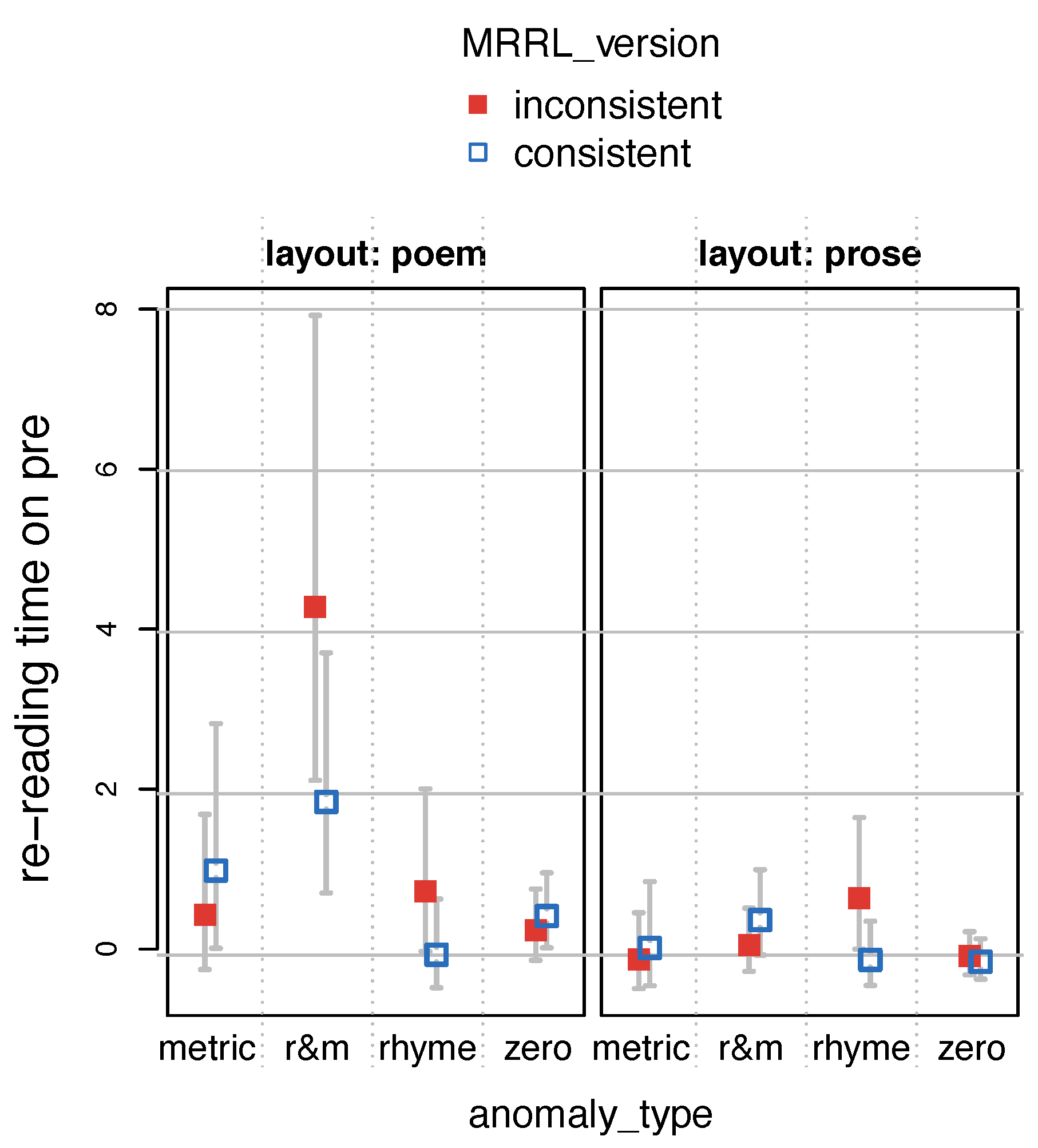
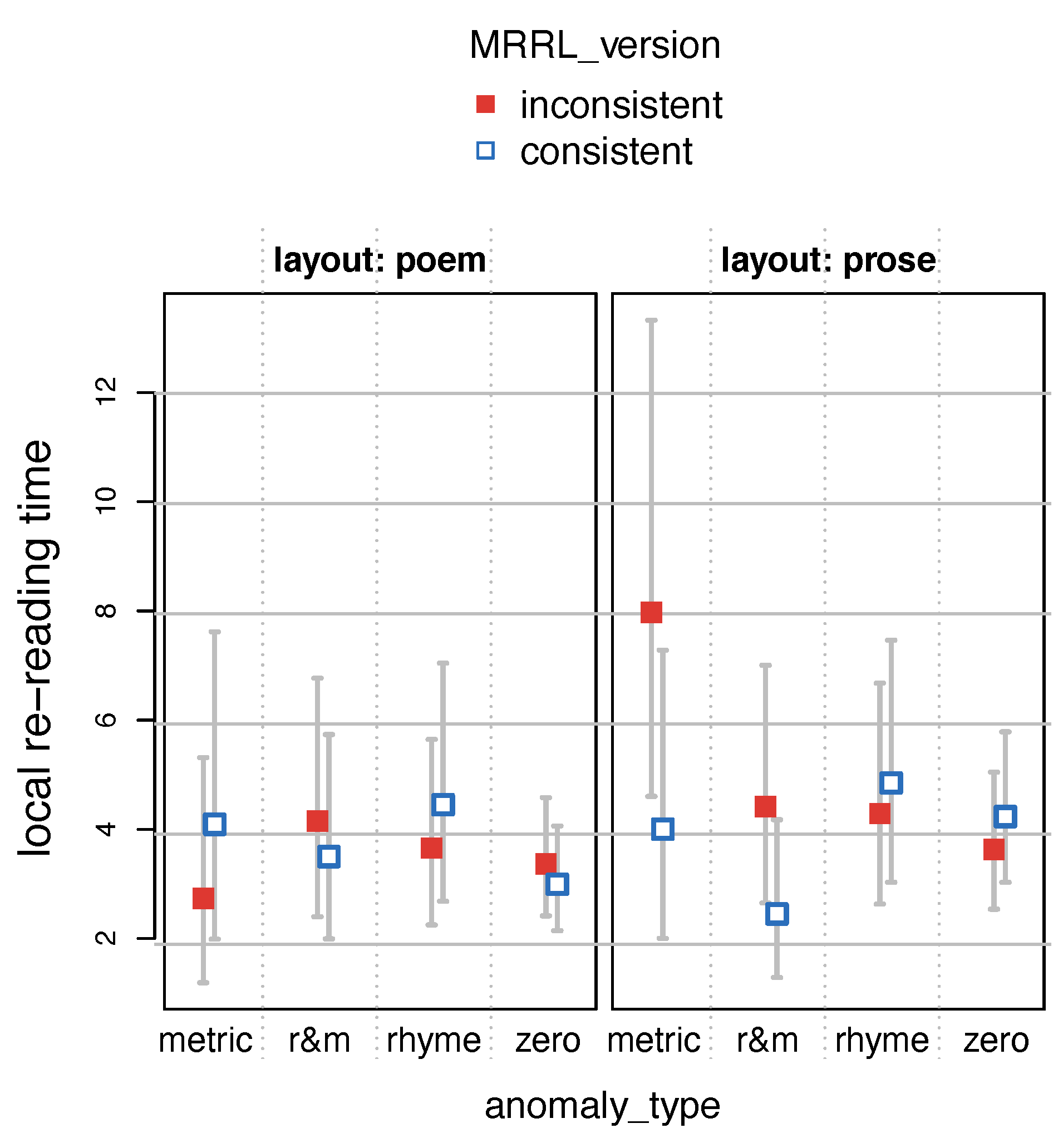
Finally, we computed
Load Contributions (
Konieczny et al., 2000) as a measure of selective re-reading.
Load contributions (
LC) measures the time spent rereading (sum of all fixations on) a previous region in the regression path of a later region. This measure is of particular relevance, because we are interested in whether the eyes re-fixate the pre-rhymes in cases of meter and rhyme anomalies.
Before each stage, and for each response duration variable, extreme values were eliminated. We first identified extreme values by using the function boxplot() with range 3. Hence, outliers were defined as values beyond the most extreme data point which is no more than three times the inter-quartile range from the box.
Then we fit the base model (stage 1), and again in the same way identified and eliminated extremes in the residuals. The base model was fit a second time and the resulting residuals were finally merged back into the dataset. From here on, only the critical interest areas were used to fit the main model.
For duration variables, we fit linear mixed effects regression models, using the function
lmer() from the
lme4 R-package (version 1.1-21;
Bates et al., 2015, p. 4). The binary variable skip was analyzed with
logistic mixed effects regression, using the function
glmer().
For all model fits, we used
sum contrast coding, creating predictors for all but the last level of any categorial variable and assigning 1 to the corresponding level for each comparison as well as -1 to the last level for all comparisons. Remaining levels were coded 0 (
Table 3).
In sum coding, the intercept represents the grand mean, and each contrast represents a comparison of a factor level mean to the grand mean. Therefore, all effects are independent of each other. Hence, simple contrasts can be interpreted similar to main effects in ANOVAs – even when the predictor also occurs in interaction terms in the model.
P-values for linear mixed models were estimated with Satterthwaite's approximation of degrees of freedom, using the
lmerTest R-package (version 3.1-0, (
Kuznetsova et al., 2017).
We will first present reading time results, starting with the main model and continuing with the complete model. Skipping results will be presented next, and lastly, we will present Load Contribution results.
Extreme values. For single fixation durations, seven extreme values were filtered from raw data (0.02%). Additional 32 data points (0.08%) were eliminated as outliers from the complete model, and 35 (0.09%) from the base model. No extreme values were excluded after fitting the main model.
For gaze durations (first pass reading times), seven extreme values were filtered from raw data (0.02%). No extreme values were excluded from the data set for the base, the complete and the main model.
For regression path durations, 32 extreme values were filtered from raw data (0.08%), 10 data points (0.03%) were eliminated as outliers from the complete model, 13 data points (0.03%) from the base model. No extreme values were excluded from the dataset for the main model.
For total reading times, 2 extreme values were filtered from raw data (0%). One additional data point (0%) was eliminated as outlier from the complete model, and 2 data points (0%) were as outliers eliminated for the base model. No extreme values were excluded from the dataset for the main model.