Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
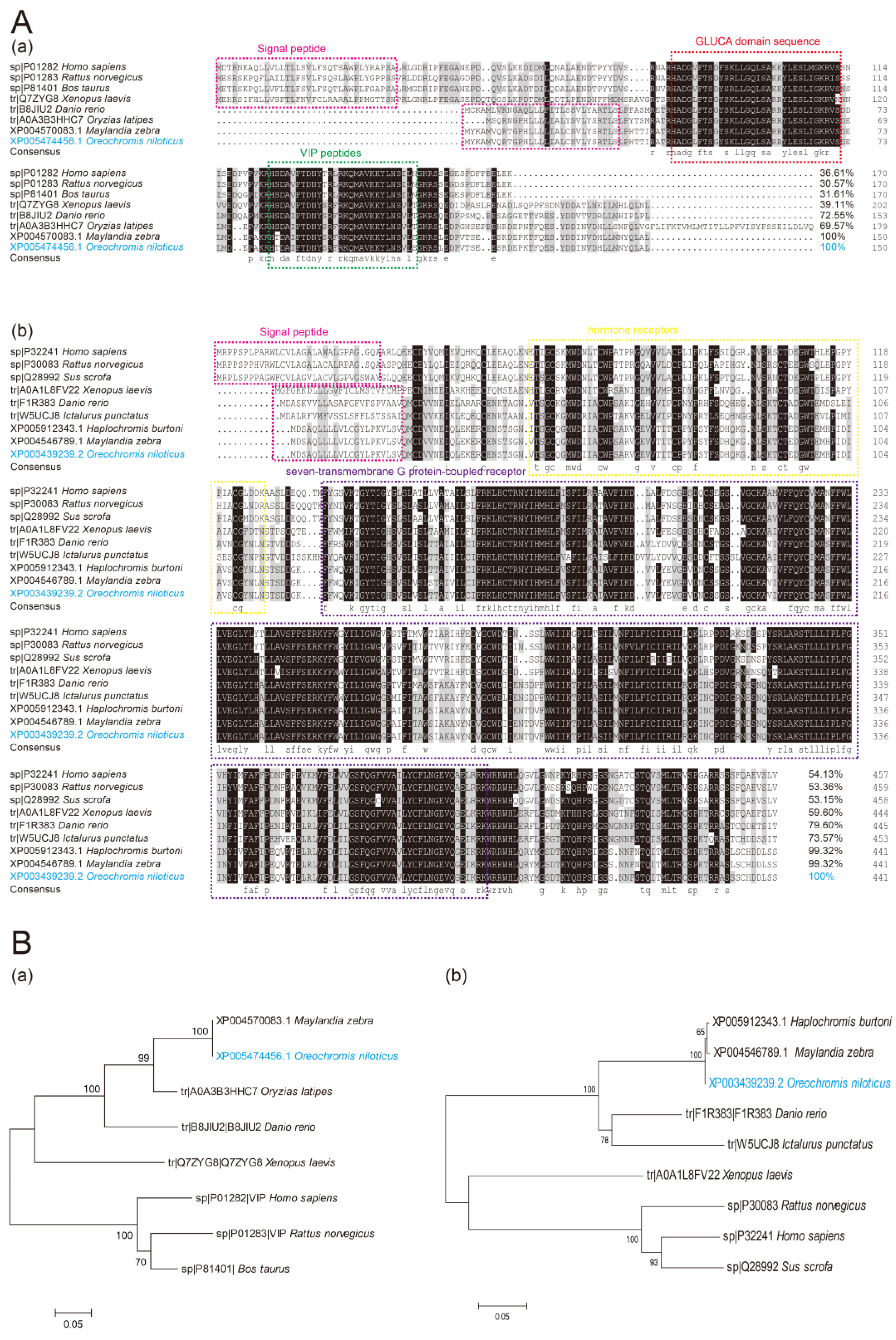
2.1. Sequence Analyses of On-VIP and On-VIPR1
2.2. Expression Pattern Analyses of On-VIP and On-VIPR1 Amongst Different Tissues
2.3. Expression Pattern Analyses of On-VIP and On-VIPR1 during Bacterial Challenge
2.4. Effects of On-VIP on Inflammatory Factors in Tilapia MO/MΦ
2.5. Effects of On-VIP on Immune-Related Pathways in Tilapia MO/MΦ
2.6. Effects of On-VIP on cAMP-PKA Pathway in Tilapia MO/MΦ
2.7. Effects of On-VIP on the Survival Rate and Bacterial Number of Tilapia under Bacterial Infection
2.8. Effects of On-VIP on Inflammatory Factors of Tilapia under Bacterial Infection
2.9. Effects of On-VIP on Immune-Related Pathways of Tilapia under Bacterial Infection
2.10. Effects of On-VIP on cAMP-PKA Pathway of Tilapia under Bacterial Infection
2.11. Effects of On-VIP on Apoptosis and Pyroptosis Factors of Tilapia under Bacterial Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish Preparation
4.2. On-VIP Preparation
4.3. S. Agalatiae Infection and Sample Collection
4.4. Monocytes/Macrophages (MO/MΦ) Isolation and On-VIP Functions Assay In Vitro
4.5. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.6. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of On-VIP and On-VIPR1
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry
4.10. On-VIP Function and Molecular Mechanism Assay In Vivo
4.11. Animal Ethics
4.12. Drawings and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Said, S.I.; Mutt, V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: Isolation from small intestine. Science 1970, 169, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L.; Tajti, J.; Szalárdy, L.; Vécsei, L. PACAP and its role in primary headaches. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Said, S.I.; Rosenberg, R.N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: Abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science 1976, 192, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenkrug, J. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: Measurement, distribution and putative neurotransmitter function. Digestion 1979, 19, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Akiba, Y.; Kaunitz, J.D. Recent advances in vasoactive intestinal peptide physiology and pathophysiology: Focus on the gastrointestinal system. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Chorny, A.; Delgado, M. Regulation of immune tolerance by anti-inflammatory neuropeptides. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, I. Conformational switches in the VPAC1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmar, A.J.; Arimura, A.; Gozes, I.; Journot, L.; Laburthe, M.; Pisegna, J.R.; Rawlings, S.R.; Robberecht, P.; Said, S.I.; Sreedharan, S.P.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XVIII. Nomenclature of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Shigemoto, R.; Mori, K.; Takahashi, K.; Nagata, S. Functional expression and tissue distribution of a novel receptor for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Neuron 1992, 8, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Pozo, D.; Ganea, D. The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 249–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Röcken, C.; Mawrin, C.; Weise, W.; Höllt, V.; Schulz, S. Immunocytochemical identification of VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptors in normal and neoplastic human tissues with subtype-specific antibodies. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2004, 10, 8235–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fizanne, L.; Sigaudo-Roussel, D.; Saumet, J.L.; Fromy, B. Evidence for the involvement of VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors in pressure-induced vasodilatation in rodents. J. Physiol. 2004, 554, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Dorsam, G.P. Stimulatory and suppressive signal transduction regulates vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) in primary mouse CD4 T cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Voice, J.K.; Shen, S.; Dorsam, G.; Kong, Y.; West, K.M.; Morrison, C.F.; Harmar, A.J. Enhanced delayed-type hypersensitivity and diminished immediate-type hypersensitivity in mice lacking the inducible VPAC2 receptor for vasoactive intestinal peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13854–13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, J.; Hahn, P.; Kroehling, L.; Nguyen, H.; Li, D.; Littman, D.R. Feeding-dependent VIP neuron-ILC3 circuit regulates the intestinal barrier. Nature 2020, 579, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.M.; Nishioka, R.S.; Bern, H.A. Novel effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and peptide histidine isoleucine: Inhibition of in vitro secretion of prolactin in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1988, 72, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, M.S.; Pena, J.T.; Plesch, F.N.; Decker, S.E.; Weber, G.J.; Forrest, J.N., Jr. Shark rectal gland vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor: Cloning, functional expression, and regulation of CFTR chloride channels. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 291, R1157–R1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Zmora, N.; Levavi-Sivan, B.; Zohar, Y. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Indirectly Elicits Pituitary LH Secretion Independent of GnRH in Female Zebrafish. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqab264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifa, L.; Chenhong, L.; Dey, M.; Gagalac, F.; Dunham, R. Cold tolerance of three strains of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in China. Aquaculture 2002, 213, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulu, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Mphande, J.; Munang’andu, H.M. Prevention and Control of Streptococcosis in Tilapia Culture: A Systematic Review. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2021, 33, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N.; Obata, K.; Yanaihara, N.; Okamoto, H. Human preprovasoactive intestinal polypeptide contains a novel PHI-27-like peptide, PHM-27. Nature 1983, 304, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenkrug, J.; de Muckadell, O.B.S. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the porcine central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 1978, 31, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, R.; Delgado-Maroto, V.; Caro, M.; Forte-Lago, I.; Duran-Prado, M.; O’Valle, F.; Lichtman, A.H.; Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Delgado, M. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Ameliorates Acute Myocarditis and Atherosclerosis by Regulating Inflammatory and Autoimmune Responses. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leceta, J.; Garin, M.I.; Conde, C. Mechanism of Immunoregulatory Properties of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide in the K/BxN Mice Model of Autoimmune Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 701862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnett, N.W.; Reeve, J.R., Jr.; Dimaline, R.; Shively, J.E.; Hawke, D.; Walsh, J.H. The isolation and sequence analysis of vasoactive intestinal peptide from a ganglioneuroblastoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 59, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giammarressi, M.; Vanegas, O.; Febres, A.; Silva-López, A.; López, E.D.; Ponte-Sucre, A. Chemotactic activities of vasoactive intestinal peptide, neuropeptide Y and substance P in Leishmania braziliensis. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 219, 108009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudry, D.; Gonzalez, B.J.; Basille, M.; Yon, L.; Fournier, A.; Vaudry, H. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: From structure to functions. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 269–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nam, B.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Kong, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, T.J. Identification and characterization of the prepro-vasoactive intestinal peptide gene from the teleost Paralichthys olivaceus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamachi, T.; Tanigawa, A.; Konno, N.; Shioda, S.; Matsuda, K. Expression Patterns of PACAP and PAC1R Genes and Anorexigenic Action of PACAP1 and PACAP2 in Zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaniakou, A.; Brothers, S.; Gould, G.; Zahiremani, M.; Paton, J.; Chappe, F.; Li, A.; Anini, Y.; Croll, R.P.; Chappe, V. Disrupted local innervation results in less VIP expression in CF mice tissues. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Anderson, P.; Delgado, M. Emerging roles of vasoactive intestinal peptide: A new approach for autoimmune therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, iii70–iii76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. SP protects Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against acute Streptococcus agalatiae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Niu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. HMG20A from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) involved in the immune response to bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Huang, Y.; Niu, J.; Luo, G.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. LECT2 Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 667781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmar, A.J.; Fahrenkrug, J.; Gozes, I.; Laburthe, M.; May, V.; Pisegna, J.R.; Vaudry, D.; Vaudry, H.; Waschek, J.A.; Said, S.I. Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: IUPHAR review 1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couvineau, A.; Laburthe, M. VPAC receptors: Structure, molecular pharmacology and interaction with accessory proteins. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent gene activation at multiple levels in the human monocytic cell line THP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, M.; Ganea, D. Inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced janus kinase-1-STAT1 activation in macrophages by vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit the MEKK1/MEK4/JNK signaling pathway in endotoxin-activated microglia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cañas, I.; Juarranz, Y.; Santiago, B.; Arranz, A.; Martinez, C.; Galindo, M.; Payá, M.; Gomariz, R.P.; Pablos, J.L. VIP down-regulates TLR4 expression and TLR4-mediated chemokine production in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, M.; Munoz-Elias, E.J.; Kan, Y.; Gozes, I.; Fridkin, M.; Brenneman, D.E.; Gomariz, R.P.; Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit tumor necrosis factor alpha transcriptional activation by regulating nuclear factor-kB and cAMP response element-binding protein/c-Jun. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31427–31436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsa, J.A.; Cacicedo, L.; Lara, J.I.; Lorenzo, M.J.; Pazos, F.; Sanchez-Franco, F. Autocrine and/or paracrine action of vasoactive intestinal peptide on thyrotropin-releasing hormone induced prolactin release. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, E.B. Special topic: Apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, I.; Golden, J. Apoptosis-targeting therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Takeba, Y.; Iiri, T.; Ohta, Y.; Ootaki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, D.; Koizumi, S.; Otsubo, T.; Matsumoto, N. Vasoactive intestinal peptide increases apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the cAMP/Bcl-xL pathway. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Tian, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yu, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, Y.; Ma, P.; et al. Pyroptosis: A new frontier in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.; Ganesan, R.; Hegedűs, C.; Kovács, K.; Kufer, T.A.; Virág, L. Programmed necrotic cell death of macrophages: Focus on pyroptosis, necroptosis, and parthanatos. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shao, T.; Fan, D.D.; Lin, A.F.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. The zebrafish NLRP3 inflammasome has functional roles in ASC-dependent interleukin-1β maturation and gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1120–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Hovingh, E.S.; Foerster, E.G.; Abdel-Nour, M.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. NOD1 and NOD2 in inflammation, immunity and disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 670, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Ding, J.; Li, P.; Hu, L.; Shao, F. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature 2014, 514, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Gong, Y.N.; Lu, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Shao, F. The NLRC4 inflammasome receptors for bacterial flagellin and type III secretion apparatus. Nature 2011, 477, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorny, A.; Delgado, M. Neuropeptides rescue mice from lethal sepsis by down-regulating secretion of the late-acting inflammatory mediator high mobility group box 1. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Jian, J.; Lu, Y.; Cai, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wu, Z. Complete genome sequence of Streptococcus agalactiae ZQ0910, a pathogen causing meningoencephalitis in the GIFT strain of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5132–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314895
Zhang Z, Li Q, Huang Y, Xu Z, Chen X, Jiang B, Huang Y, Jian J. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314895
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiqiang, Qi Li, Yongxiong Huang, Zhou Xu, Xinjin Chen, Baijian Jiang, Yu Huang, and Jichang Jian. 2022. "Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314895
APA StyleZhang, Z., Li, Q., Huang, Y., Xu, Z., Chen, X., Jiang, B., Huang, Y., & Jian, J. (2022). Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) Protects Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalatiae Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314895




