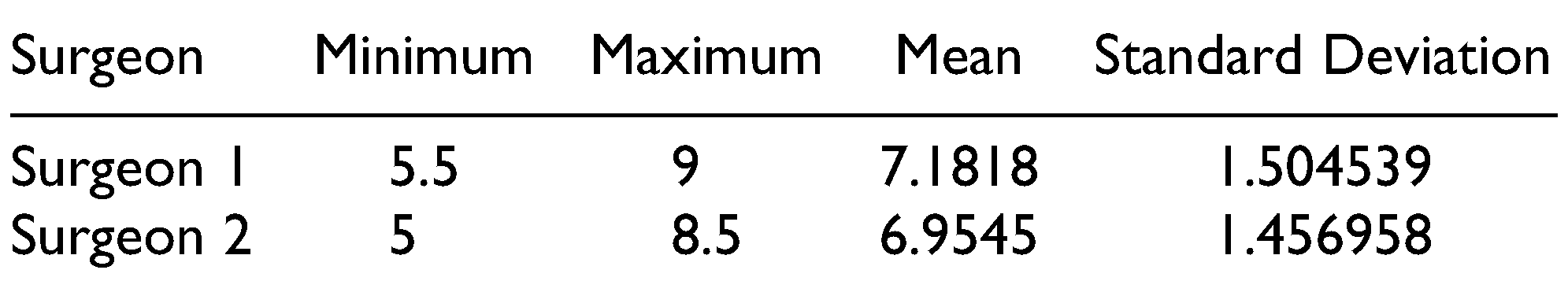Abstract
Study Design: Facial contour deformities are a very challenging issue for aesthetic and reconstructive surgeons. Free dermal fat graft is a composite graft used for the reconstruction of soft tissue defects in the maxillofacial region. The free dermal fat graft is easily adapted and contoured intraoperatively and provides a soft, natural, and favorable appearance after augmentation of the soft tissue defects. Objective: To assess the use of free dermal fat graft for reconstruction of soft tissue defects in the maxillofacial region in regard to graft success, percentage of overcorrection, any associated complications, and cone beam computed tomography scan linear measurements for defect’s depth. Methods: This is a prospective study that included a patients were grafted with free dermal fat graft for correction of facial soft tissue defects from November 2017 to July 2019. All patients possess a depression defect and facial asymmetry due to congenital facial deformities, post-traumatic deformities, and post-ablative surgical deformities. Results: Eleven patients (8 males and 3 females) with a mean age of 33.7 years were enrolled in this study. Five regions in the maxillofacial area were grafted in 11 patients. The mean of the postoperative follow-up was 6 months. The percentage of graft overcorrection was 15%. The mean for graft survival was 94.4% with no serious complications reported. Conclusions: The autologous FDFG is a versatile and less invasive method in the reconstruction of facial soft tissue defects with a very good survival rate.
Introduction
Facial contour deformities are a very challenging issue for aesthetic and reconstructive surgeons. The assessment of the facial deformities is important to develop a subsequent reconstruction plan.[1] Common causes of facial contour deformities include trauma, post-ablative defects, congenital defects, and degenerative disease.[2,3] The resection of head and neck tumors often leads to significant cervical and facial asymmetry with irregularities.[4] There are many techniques used for correction of facial soft tissue deficiency and asymmetry. These techniques utilize alloplastic materials, such as free silicon injection, or autogenous tissue transfer, such as free dermal fat graft (FDFG) and microvascular free flap.[5,6] The free vascularized flap technique is the gold standard for the correction of moderate to severe maxillofacial soft tissue defects. However, this procedure is not readily available in every maxillofacial center and is not indicated for every soft tissue defect.[3] Therefore, other techniques must be considered to correct irregularities, such as the FDFG. FDFG was firstly used in 1909 for correction of malar and chin defects. Since then, it has been widely used for corrective surgeries, including corrections of post-traumatic depression defects, hemifacial atrophy, post-ablative defects, and correction of congenital defects.[3,7] FDFG is free graft of fat with its overlying dermis connected to each other and harvested as a composite graft. FDFG tends to provide better longevity and predictability of the final outcomes than fat graft alone.[8] The FDFG can be harvested from different anatomical regions such as thigh and lower abdominal region. To reduce donor site morbidity, the graft can be harvested from a preexisting abdominal scar.[9] FDFG is easily adapted and contoured intraoperatively and provides a soft, natural, and favorable appearance after augmentation of the soft tissue defect.[7] FDFG is a non-vascularized graft that survives in a mechanism like that of a skin graft. During the first 72 hours, the graft survives and takes its nutrition by imbibition. After 72 hours, angiogenesis begins and new vessels start to occupy the graft. The dermal component of the FDFG contains vessels and proangiogenic factors that promote this vascularization process.[10] The graft is not a new technique but it has not gained popularity due to its unpredictable resorption and the difficulty in determination of defect’s depth. We present a new reliable method to determine the depth of the facial defect. We have utilized the cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). By utilizing this method, we can better determine the total graft thickness and the amount of needed overcorrection.
Patients and Methods
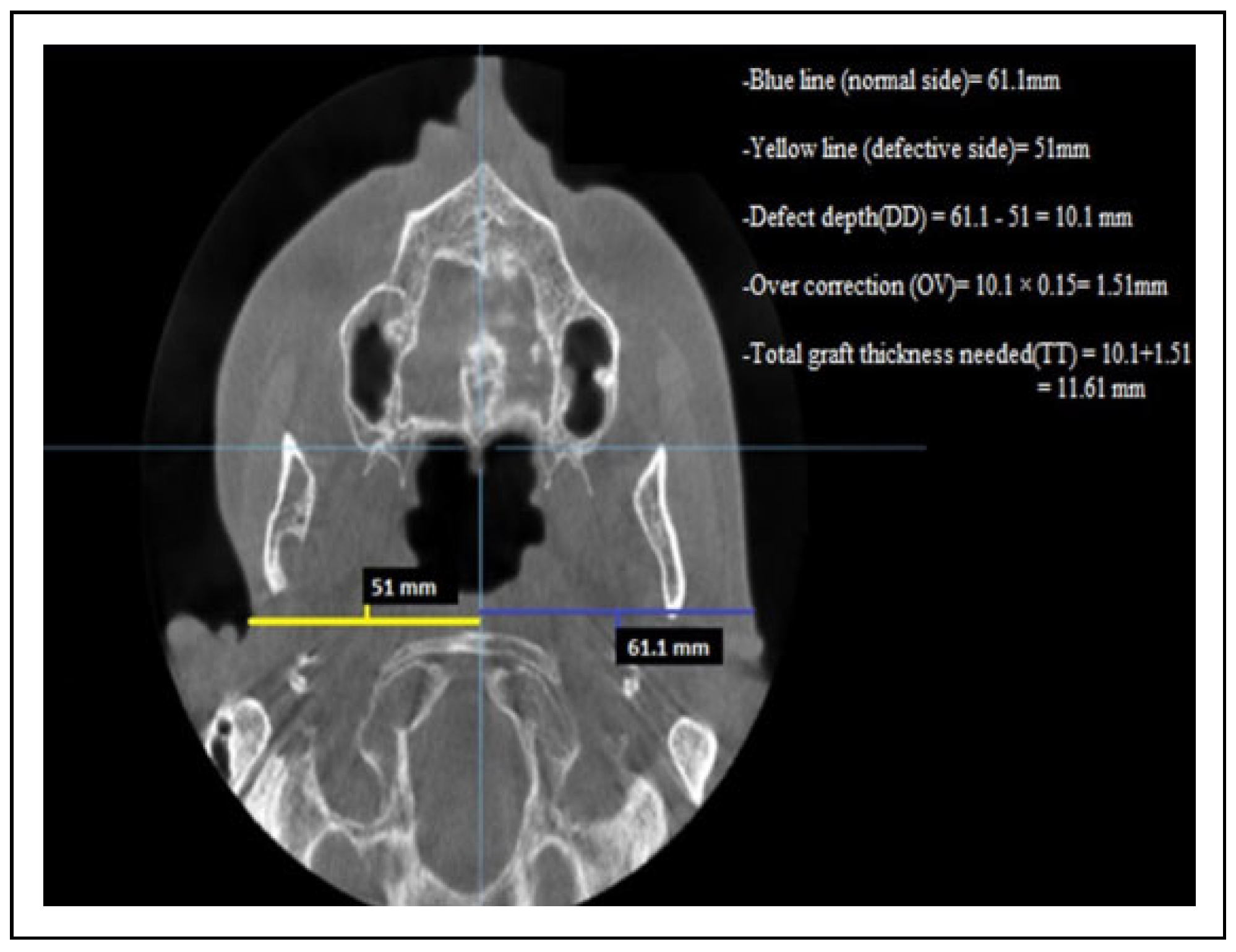
Between November 2017 and July 2019, 11 patients (8 males and 3 females) underwent reconstructive procedures using FDFG for correction of soft tissue defects in the maxillofacial region. Our inclusion criteria were patients with post-ablative, post-traumatic, and congenital facial soft tissue defects. Our exclusion criteria were those patients with aggressive malignant tumors with a high possibility of recurrence with local or distant metastasis. All patients included in the study underwent a clinical and radiograph evaluation. The size of defects was determined clinically with a ruler and the defect’s depth was determined by CBCT scan linear measurements in On-Demand 3D software. The preoperative CBCT scan evaluation was done in 3 steps (Figure 1):
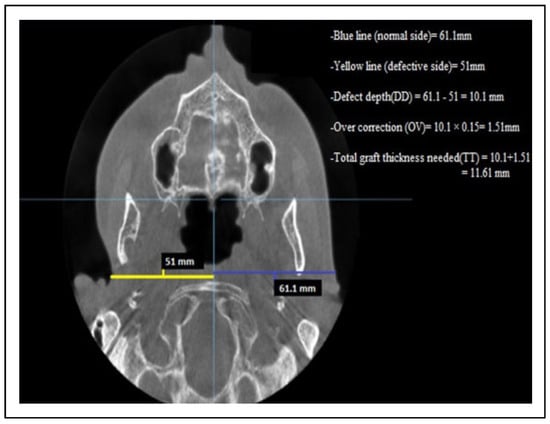
Figure 1.
Axial CBCT linear measurements for a patient with depression defect in the right preauricular region. CBCT indicates cone beam computed tomography.
- (1)
- The measurement of the defect’s depth (DD)Through axial section, a reference point was determined and each half of patient’s face was measured with a linear measurement. The measurements started in the defect side from the deepest point of the soft tissue defect into the midline.The unaffected or normal side was measured at the same horizontal plane with the opposite side from the most lateral soft tissue point into the midline. The difference between these 2 sides represents the defect’s depth (DD).
- (2)
- Determination of overcorrection in a numeric value (OV)In our study, the overcorrection percentage is 10%-15% from defect’s depth. The defect’s depth (DD) was multiplied by 0.15 to convert the percentage of overcorrection into a numeric value.
- (3)
- Determination of total graft thickness (TT).The total graft thickness that was needed for each patient was determined by the following formula:Total graft thickness(TT) = defect’s depth(DD) + overcorrection numeric value(OV).The evaluation of patient’s improvements was done through 2 methods:
- (a)
- Subjective evaluation with visual analog scale with 1 = least satisfied and 10 = most satisfied result. Patient’s and 2 surgeons’ satisfactions regarding depression filling, facial symmetry, and the overall aesthetic improvements 6 months postoperatively were evaluated.
- (b)
- Objective evaluation by the clinical examination 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months postoperatively. The patients were examined for any sign of infection, liquefaction, rate of graft resorption, and facial symmetry. CBCT scans were used to evaluate linear measurements of augmented region 6 months postoperatively and compare it with the preoperative defect side linear measurements.
Surgical Technique
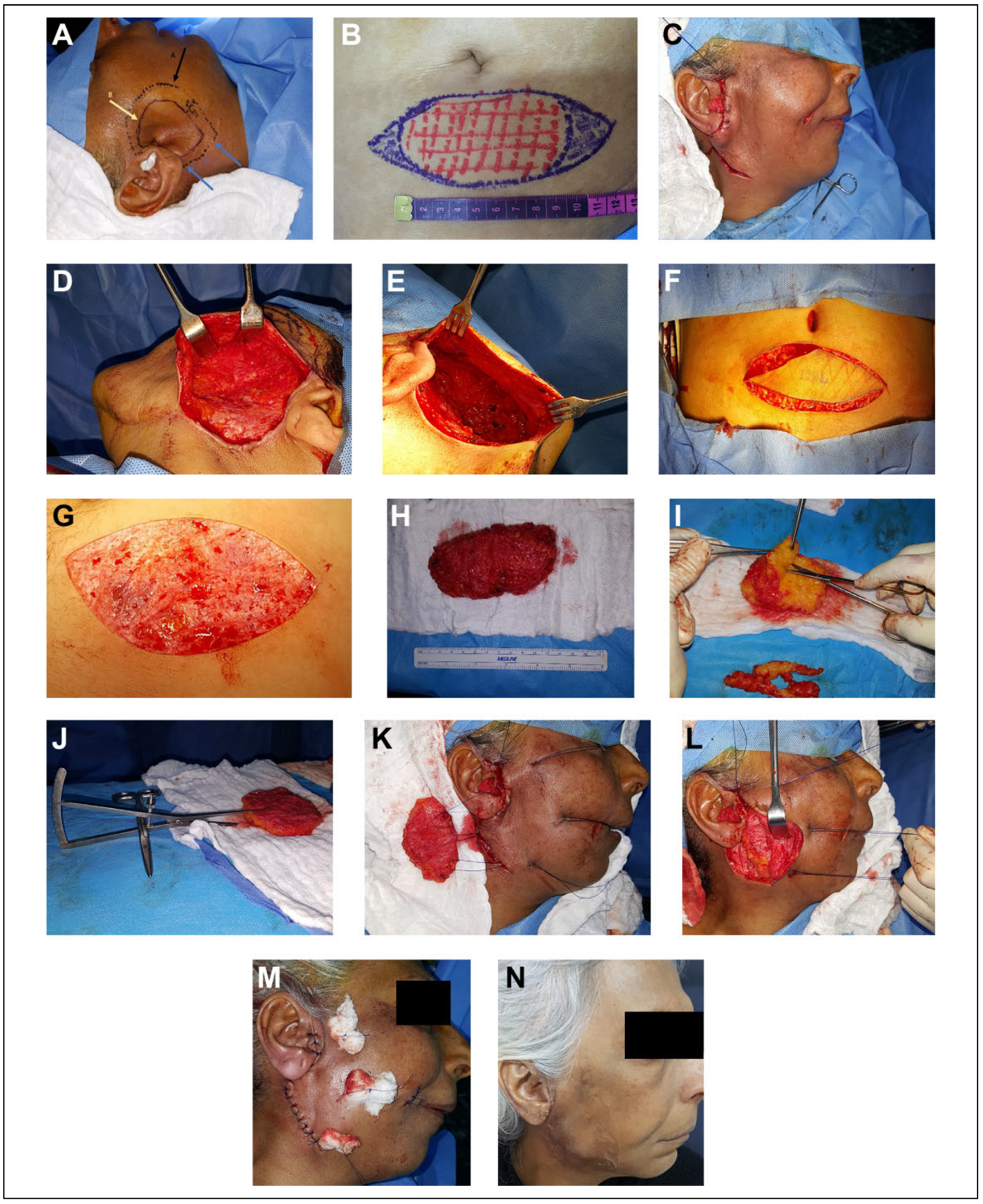
Consent was obtained from the patients prior to surgery. The recipient and the donor sites were marked and the outline of the defect was measured with a ruler (Figure 2A and B). The defects were approached through a preexisting scar if present. Face-lift incision, infraorbital incision, and submandibular incision were used and this depends on the defect’s site. With a blunt end dissector scissor, superficial dissection in a subdermal plane was done to allow intimate contact between graft and subdermal plexus. The dissection of the subdermal pocket was continued 1 centimeter beyond the defect to allow the surrounding skin to be redraped (Figure 2C to E). The graft was harvested from lower abdominal region through an elliptical incision with a 3:1 length to width ratio for tensionless wound closure. De-epithelization in situ using a number 21 blade was conducted and all epidermal component was excised gently and in a uniform fashion (Figure 2F and G). The resultant composite FDFG was transported into the surgical trolley for final graft trimming and adjustment in corresponding to the predetermined measurements (Figure 2H to J). The graft was gently beveled by the dissector scissors at the point of junction of the dermis into fat so the dermal component of the graft is larger than fat component. The graft was introduced into the prepared pocket in the recipient site with the dermal component in contact with the subdermal plexus. The augmented region was checked for the accuracy of defect augmentation in all directions. Three to four pull-through 0.3 nylon sutures were introduced into skin flap then into corresponding graft corners and the graft was introduced into the prepared pocket by pulling the pull-through sutures. Pull-through sutures were tied over a small piece of gauze (tie overdressing). The skin was closed by simple interrupted sutures using a 0.4 nylon suture (Figure 2K to M). Antibiotics and analgesia were continued for 5 days postoperatively.
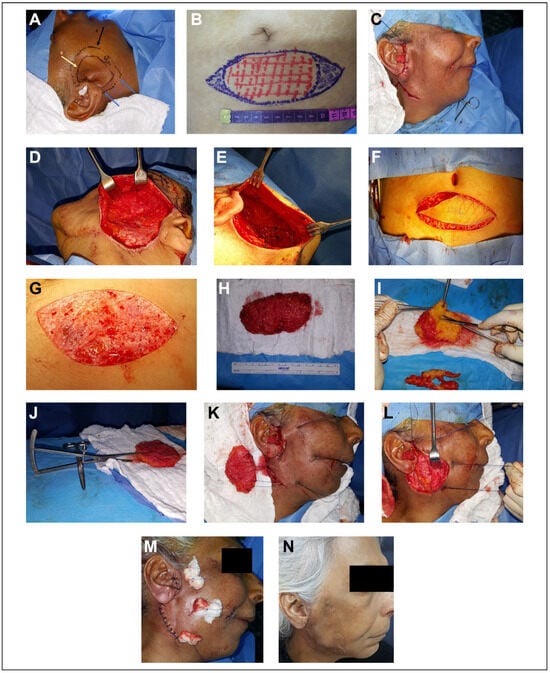
Figure 2.
A, Marking of the recipient site. The black arrow represents the limits of the subdermal dissection. The yellow arrow represents the outline of the defect. The blue arrow represents the site of the incision. B, Marking of the donor site. C, Face-lift approach in a patient with parotid region defect. D, The limit of the dissection is 1 centimeter beyond the boundaries of the defect. E, Subdermal pocketing preparation with dissector scissors. F, Graft harvested through a lower abdominal elliptical incision. G, De-epithelization in situ with number 21 blade. H, Complete graft harvested with a depth less than 2 centimeters. I, The excess fat trimmed and adjusted with dissector scissors. J, Checking the depth of the harvested graft with a caliper. K, Three pull-through sutures introduced through the graft to introduce and secure the graft in position. L, The graft in position. M, The graft secured with nylon sutures and tied over a piece of gauze (tie overdressing) and the skin closed by a simple interrupted suture. N, One week later at the time of suture removal.
Results
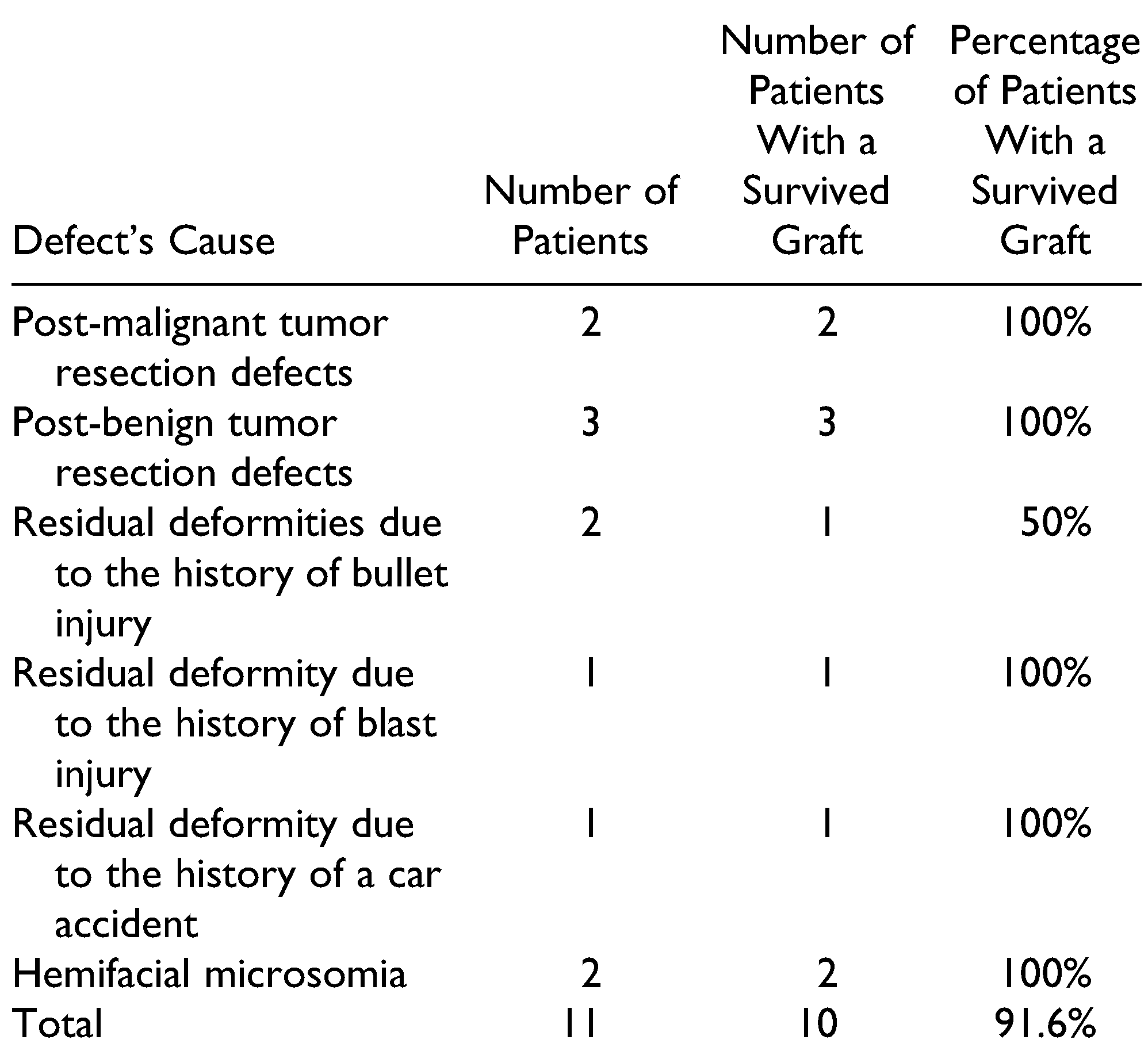
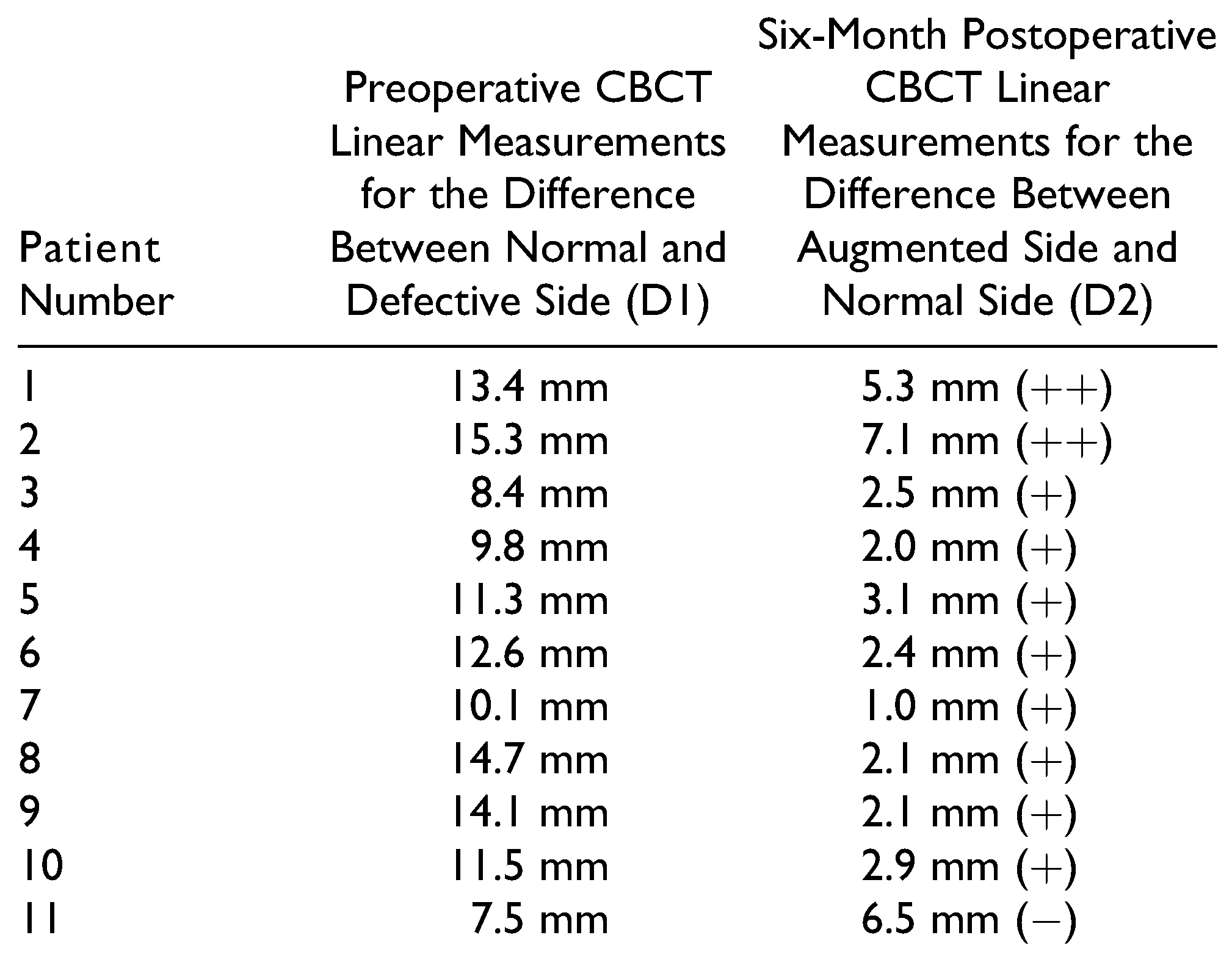
The defects in 4 patients were due to previous history of trauma (residual deformities), 5 patients with post-ablative defects, and 2 patients with congenital defect (hemifacial macrosomia). The augmented regions were parotid, submandibular, cheek, zygoma, and preauricular with cheek regions. The FDFG has 2 components, fat component and dermal component, which is the key for graft survival. The graft survival was evaluated clinically 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months postoperatively. The survival rate was 91.6%, only 1 case showed a high resorption rate. This was in a patient with previous trauma in the zygomatic region. The patient had undergone multiple surgical interventions and the recipient bed was poorly vascularized and the harvested graft also had a small dermal component. These factors likely contributed to resorption. The graft survival results are shown in Table 1. No serious complications were reported in the current study. Considering the donor site selection is very important for decreasing the risk of an epithelial cyst, the preferred donor site is the suprapubic region in females and the left or right lower abdominal quadrants in males. At 6 months, the patient’s improvement was evaluated by 2 outcomes. The first outcome was the patient’s and surgeon’s satisfaction. This was measured using the visual analog scale, which has been previously used for evaluation of facial symmetry.[11] On a 10-point scale with “10” being “most satisfied,” patients reported satisfaction ratings of 5-10, with a mean of 7.68. These results indicate that FDFG is highly successful in terms of patient experience, clinical effectiveness, and safety of the intervention (Table 2). The 2 independent surgeons gave a score from 1 to 10 to describe their satisfaction. The mean of first surgeon is 7.18 and for the second surgeon is 6.95 (Table 3). The second method used CBCT scan linear measurements for the normal and the augmented side. These measurements were compared with the preoperative measurements (Table 4 and Figure 3). In the current study, 2 patients were overcorrected by 30%. During the 6-month follow-up period, the 2 patients showed minimal graft resorption and the final results were considered to be overcorrected with slight facial asymmetry. The other cases were overcorrected by 10-15%, and the final result at 6 months demonstrated good facial symmetry.

Table 1.
The Survival Rate of FDFG Based on Causes of Deformity.

Table 2.
Questions for the Patients to Verify Their Satisfaction and Descriptive Statistics for Patient’s Satisfaction.

Table 3.
The Degree of Improvement for Each Patient was Evaluated by 2 Independent Surgeons Using the Visual Analog Scale Ranging From Score 1 (Least Satisfied) to Score 10 (More Satisfied).

Table 4.
Axial CBCT Scan Linear Measurements for the Differences Between the Normal and the Defective Side Preoperatively and 6 Months Postoperatively.a
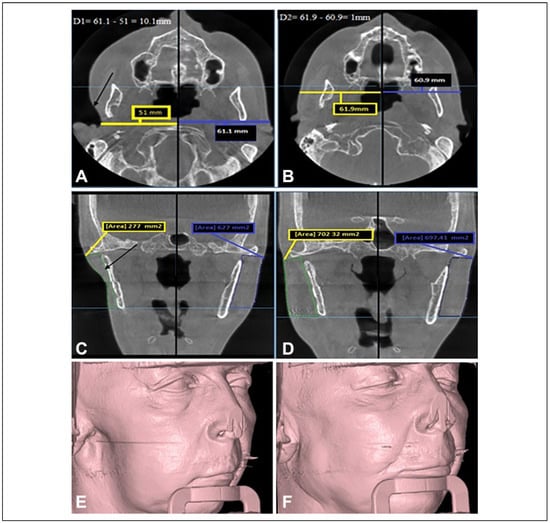
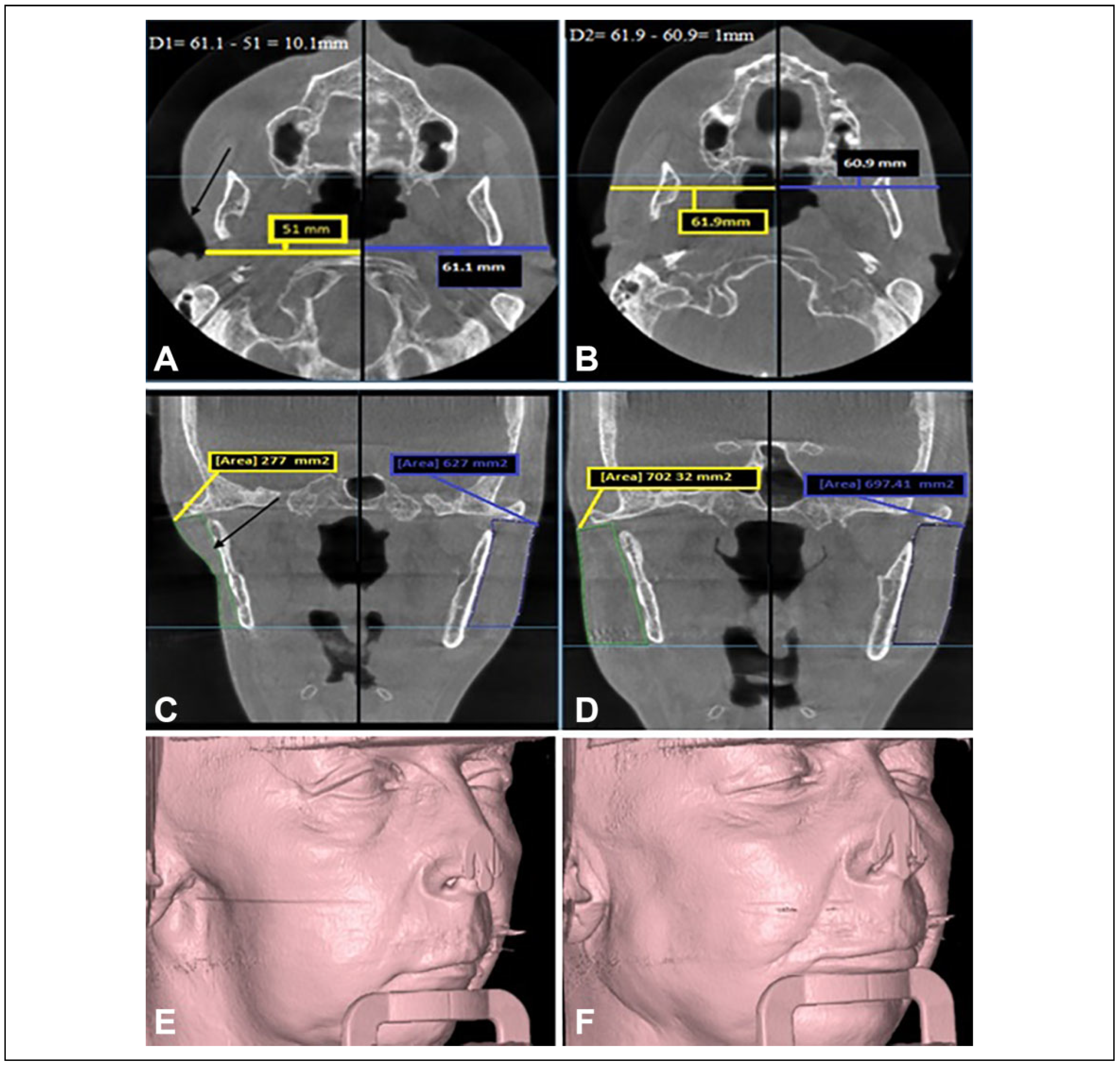
Figure 3.
The preoperative and 6-month postoperative CBCT scan for the patient in Figure 4: (A) an axial CBCT scan shows the preoperative linear measurement, the difference between the 2 sides was 10.1 mm; (B) an axial CBCT for the same patient 6 months postoperatively, the difference between the 2 sides was reduced to only 1 mm; (C) a coronal CBCT scan shows the area measurement of the normal and the defective side preoperatively; (D) coronal CBCT scan 6 months postoperatively; (E and F) preoperative and 6-month postoperative 3-D CBCT imaging. Preoperative defect’s depth (D1) = normal side measurement — defective side measurement. Postoperative measurement (D2) = augmented side measurement — normal side measurement. CBCT indicates cone beam computed tomography.
Discussion
Use of fat graft for reconstruction of facial soft tissue defects was firstly reported in 1893. However, this technique has been slow to gain popularity because of unpredictable graft resorption rates and risks of epithelial cysts.[3] With recent refinements in the FDFG technique and reduced complications, the technique has gained popularity for soft tissue reconstruction in the maxillofacial region. FDFG uses biocompatible tissue, is infection-resistant, has minimal donor site morbidity, and has good longevity over time.[3] Multiple factors need to be considered to avoid graft resorption. The grafts are not thicker than 2 centimeters, gentle graft handling, good vascular bed, adequate graft immobilization, hematoma and subsequent infection avoidance.[9] For aesthetic reasons, the graft should be harvested from a hidden area from the lower abdomen or suprapubic region. For functional reasons, the graft should be harvested from areas that are hairless or from skin with thin hairs to reduce the possibility of epithelial cyst formation.[2] The complications can occur early within days postoperatively or months later. Early complications include seroma, hematoma, liquefaction, infection, and ecchymosis within the donor or recipient site. Late complications include cyst formation, undercorrection, overcorrection, and graft resorption.[2,12] The current study is in agreement with Little, who avoid overcorrection of FDFG in his study.[13] When properly performed, FDFG is a suitable option for soft tissue reconstruction, even in irradiate patients. Tissues that are exposed to radiation therapy are damaged and are not ideal for grafting procedure due to compromised blood supply of the receiving bed. This is due to the excessive release of cytokines that cause fibrosis and aberrant vascular tissue.[14] Despite these factors, studies have shown good results with FDFG in patients who have previously undergone radiation therapy.[14] In the current study, 2 patients with preauricular depression defects who underwent previous radiation therapy were treated with FDFG to reconstruct the soft tissue defects (Figure 4). Their grafts were survived with very good final cosmetic results. The current study is in agreement with the previous study done by Inchingolo et al.[14] We thought that the graft survived even in the irradiate patients due to the dermal component of the graft and its proangiogenic properties with high ability of graft perfusion reestablishment.
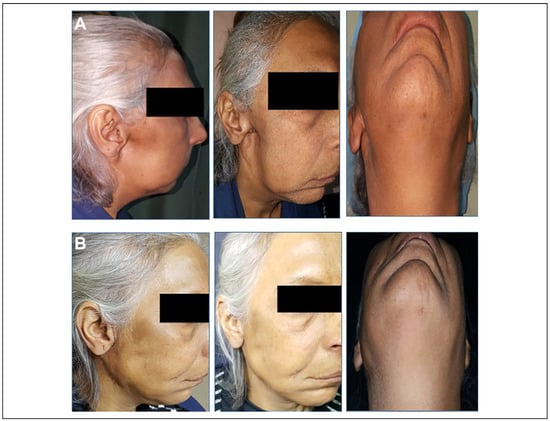
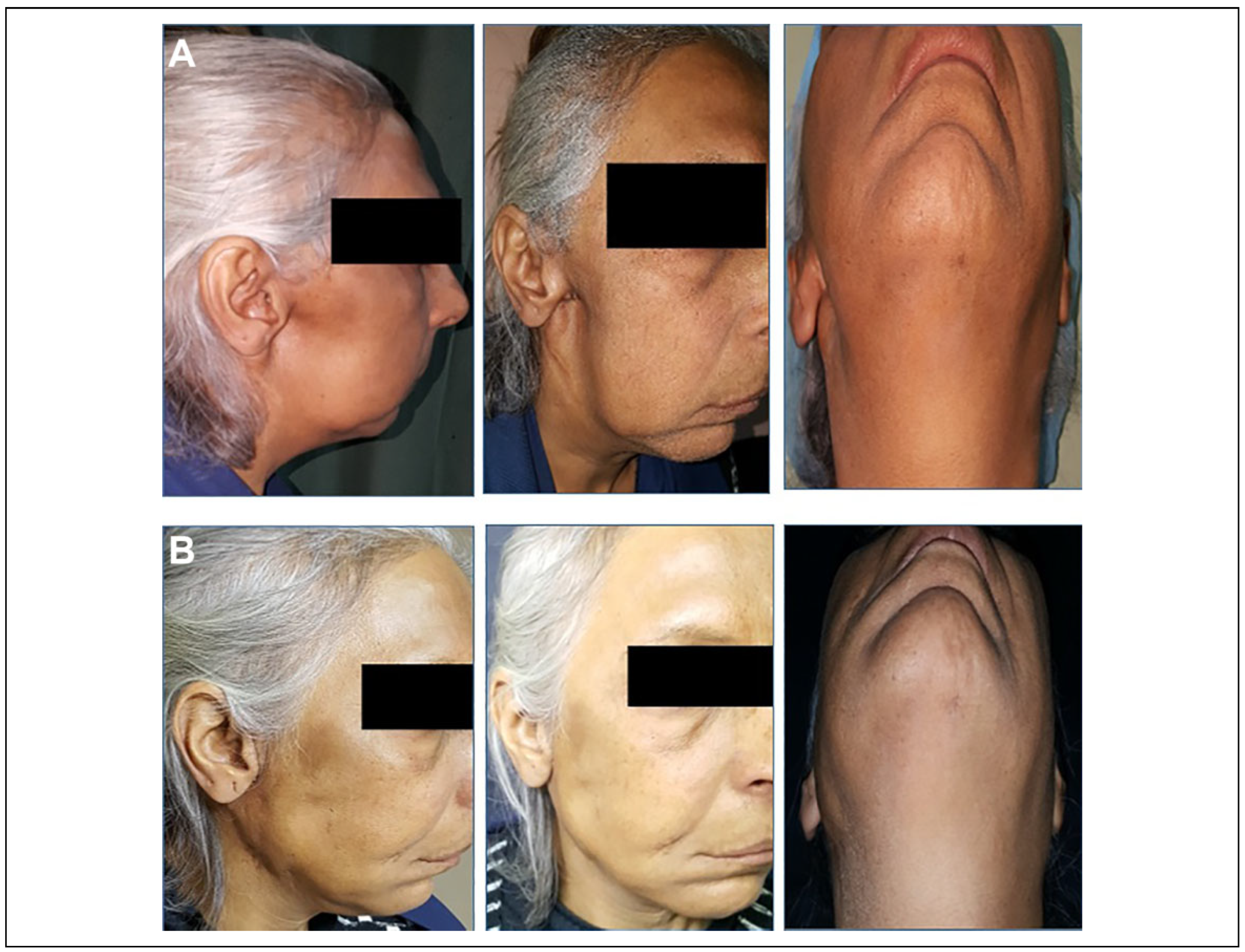
Figure 4.
A, The lateral, 3-quarter, and worm view for a 55-year-old patient with a history of resected malignant parotid tumor 2 years prior to her presentation. Depression defect and facial asymmetry was the chief complaint of her. B, The same views for the same patient 6 months postoperatively after FDFG augmentation. FDFG indicates free dermal fat graft.
Conclusion
FDFG is an autogenous tissue transfer and is a suitable reconstructive option that is used for the correction of facial soft tissue depression defects and facial asymmetry. FDFG can be used for the correction of mild to moderate soft tissue defects with depths of less than 2 centimeters. Although an additional surgical site is needed for graft harvesting, the morbidity of the donor site can be reduced by placing the incision in a preexisting abdominal scar or a hidden suprapubic region. The overcorrection of FDFG is 10%-15% to provide a reliable and satisfactory final cosmetic result. FDFG has a very good survival rate with no reported serious complications.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Kadam, D.; Pillai, V.; Bhandary, S.; Hukkeri, R.Y.; Kadam, M. Facial contour deformity correction with microvascular flaps based on the 3-dimentional template and facial moulage. Indian J Plast Surg. 2013, 46, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, S.H.; Pförtner, R.; Ladwein, F.; Schmeling, C.; Rieger, G.; Mohr, C. Use of dermis-fat grafts in the prevention of Frey’s syndrome after parotidectomy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016, 44, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.G.; Thapliyal, G.K. Free dermal fat graft for restoration of soft tissue defects in maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012, 11, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Honeybrook, A.; Athavale, S.M.; Rangarajan, S.V.; Rohde, S.L.; Netterville, J.L. Free dermal fat graft reconstruction of the head and neck: an alternate reconstructive option. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2017, 38, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larossa, D.; Whitaker, L.; Mordick, T. Soft-tissue reconstruction of the face: a comparison of dermal-fat grafting and vascularized tissue transfer. Ann Plast Surg. 1992, 29, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Elbarbary, A.S.; Nasser, S. Implementing fat grafting in the management of complex facial reconstructive patients. Egypt J Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011, 35, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kempf, K.K.; Seyfer, A.E. Facial defect augmentation with a dermal-fat graft. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985, 59, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papel, I.D.; Frodel, J.; Holt, G.; Larrabee, W.; Nachlas, N.; Park, S. Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 4th ed.; Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.: New York/Stuttgart/Delhi/Rio de Janeiro, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.E.; Guida, R.A.; Cook, T.A. Autologous free dermal fat graft: reconstruction of facial contour defects. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995, 121, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muresan, C.; Brownstein, G.M.; Shureih, S.F. Abdominoplastyderived dermal-fat graft augmentation gluteoplasty. Aesthetic Surg J. 2014, 34, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Chung, D.H.; Lee, J.W.; Cha, K.S. Assessing soft-tissue characteristics of facial asymmetry with photographs. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2010, 138, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolis, M.; Zavattero, E.; Iaquinta, C.; Berrone, S. Dermofat graft after superficial parotidectomy to prevent Frey syndrome and depressed deformity. J Craniofac Surg. 2013, 24, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, J.W. Applications of the classic dermal fat graft in primary and secondary facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002, 109, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Tatullo, M.; Pacifici, A.; et al. Use of dermal-fat grafts in the post-oncological reconstructive surgery of atrophies in the zygomatic region: clinical evaluations in the patients undergone to previous radiation therapy. Head Face Med. 2012, 8, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. The Author(s) 2020.