Alkylated Polyphenyl Ethers as High-Performance Synthetic Lubricants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
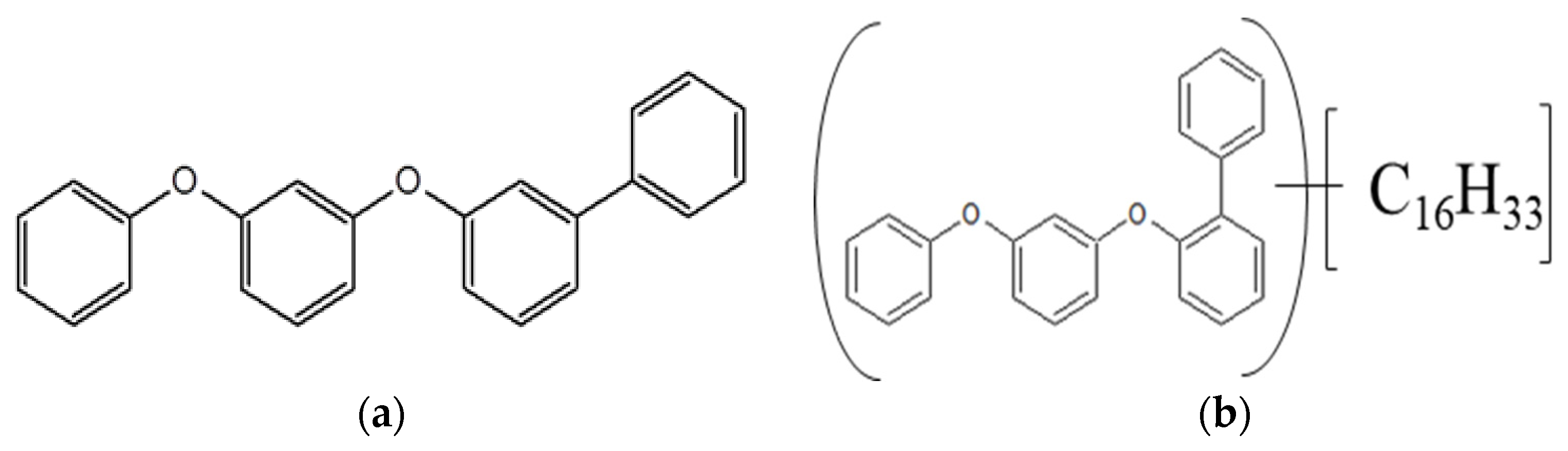
2.1. Lubricants
2.2. Tribological Tests
2.3. Measurement of Gaseous Products Generated by Lubricant Decomposition
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tribological Properties of Polyphenyl Ethers
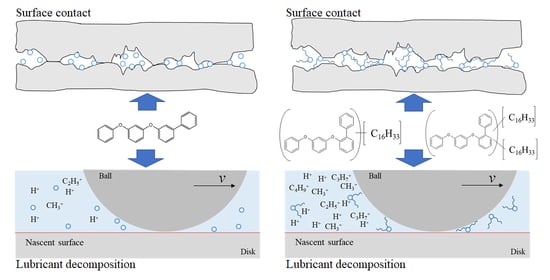
3.2. Tribochemical Decomposition of Polyphenyl Ethers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stopher, M.A.; Rivera-Diaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Hydrogen embrittlement in bearing steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Minami, I.; Nanao, H.; Mori, S. Investigation of decomposition of hydrocarbon oil on the nascent surface of steel. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimotomai, N.; Nanao, H.; Mori, S. Tribochemical reaction of benzene on nascent steel surface and effect of temperature. Tribol. Online 2012, 7, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esfahani, E.A.; Soltanahmadi, S.; Morina, A.; Han, B.; Nedelcu, I.; van Eijk, M.C.P.; Neville, A. The multiple roles of a chemical tribofilm in hydrogen uptake from lubricated rubbing contacts. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurten, D.; Khader, I.; Kailer, A. Tribochemical degradation of vacuum-stable lubricants: A comparative study between multialkylated cyclopentane and perfluoropolyether in a vacuum ball-on-disc and full-bearing tests. Lubri. Sci. 2020, 32, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, H.; Tanaka, H.; Sugimura, J. Observation of hydrogen permeation into fresh bearing steel surface by thermal desorption spectroscopy. Tribol. Online 2011, 6, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagumo, M. Hydrogen related failure of steels—A new aspect. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurten, D.; Khader, I.; Raga, R.; Casajus, P.; Winzer, N.; Kailer, A.; Spallek, R.; Scherge, M. Hydrogen assisted rolling contact fatigue due to lubricant degradation and formation of white etching areas. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 99, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Ratoi, M.; Sugimura, J. The role of synthetic oils in controlling hydrogen permeation of rolling/sliding contacts. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Nanao, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Kubo, T.; Mori, S. Effect of lubricant additives on tribochemical decomposition of hydrocarbon oil on nascent steel surfaces. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2010, 53, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Evans, M.H.; Wang, L.; Ingram, M.; Rowland, Z.; Llanos, G.; Wood, R.J.K. The effect of over-based calcium sulfonate detergent additives on white etching crack (WEC) formation in rolling contact fatigue tested 100Cr6 steel. Tribol. Int. 2019, 133, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.L.; Harris, J.W. Long-term trends in industrial lubricant additives. In Lubricant Additives Chemistry and Applications; Rudnick, L.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 615–616. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, F.; Improta, G.; Triassi, M.; Cicatelli, A.; Castiglione, S. Effects of zinc pollution and compost amendment on the root microbiome of a metal tolerant polar clone. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Mori, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nanao, H. Study of tribochemical decomposition of ionic liquids on a nascent steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8965–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Nanao, H.; Takiwatari, K.; Mori, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Ikejima, S.; Konno, T. The Effect of the chemical structures of synthetic hydrocarbon oils on their tribochemical decomposition. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, S.; Okasaka, M.; Kubota, Y.; Akabe, S. Trends in automotive instrument and auxiliary bearing technology. NTN Tech. Rev. 1996, 65, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bair, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.J. The pressure-viscosity of coefficient for Newtonian EHL film thickness with general pezociscous response. J. Tribol. 2006, 128, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.R.; Johnson, K.L. Regimes of traction in elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C 1986, 200, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, R.; Nonaka, T.; Kubo, A.; Matsuo, K. Thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication of rolling/sliding line contacts. J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Zenoni, A.; Lee, Y.; Hayashi, Y. Characterization of a polyphenyl ether oil irradiated at high doses in a TRIGA Mark II nuclear reacor. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2021, 497, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiche, B.; Ponjavic, A.; Wong, J.S.S. Flow measurements of a polyphenyl ether oil in an elastohydrodynamic contact. J. Phys. Condens. Matt. 2016, 28, 134005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herber, J.F.; Joaquim, M.E.; Adams, T. Polyphenyl ethers: Lubrication in extreme environments. Lubr. Eng. 2001, 57, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, H.K.; Klenke, C.J.; Saba, C.S. Effect of formulation and temperature on boundary lubrication performance of polyphenylethers (5P4E). Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, T.; Imado, K. Study on changes in the rheologic properties of EHL film using fluorescence measurements. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Vergne, P. A quantitative determination of minimum film thickness in elastohydrodynamic circular contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2021, 69, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoga, M.; Aoki, S.; Suzuki, A.; Yohsida, Y.; Fujinami, Y.; Masuko, M. Toward resolving anxiety about the accelerated corrosive wear of steel lubricated with the fluorine-containing ionic liquids. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourani, M.J.; Hessell, E.T.; Abramshe, R.A.; Liang, J. Alkylated naphthalenes as hyigh-perfotmance synthetic lubricating fluids. Tribol. Trans. 2007, 50, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Morimoto, M.; Tani, H.; Tgawa, N.; Koganezawa, S. Tribological properties of alkyldiphenlethers in boundary lubrication. Lubricants 2019, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2004, 362, 2477–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered, amorphous, and diamondlike carbon. Phys. Rev. B Condes. Matter Mater. Phys. 2001, 64, 075414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.K.; Li, L. Characterization of amorphous and nanocrystalline carbon films. Matt. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Xiong, W.; Zheng, S.; Chen, C.; He, S.; Cheng, Q. Evaluation of the sp3/sp2 ratio of DLC films by RFPECVD and its quantitative relationship with optical band gap. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akemann, W.; Otto, A. Vibrational frequencies of C2H4 and C2H6 adsorbed on potassium, indium, and noble metal films. Langmuir 1995, 11, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammage, M.D.; Stauffer, S.; Henkelman, G.; Becker, M.F.; Keto, J.W.; Kovar, D. Ethylene binding to Au/Cu alloy nanoparticles. Surf. Sci. 2016, 653, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameoka, H.; Sonoda, N. Organic Chemistry; Kagakudojin: Kyoto, Japan, 1995; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]















| Physical Properties | 4P2E | R1-4P2E | R2-4P2E | ADE (C18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (15 °C g·cm−3) | 1.167 | 1.014 | 0.952 | 0.928 |
| 40 °C viscosity (mm2·s−1) | 125 | 240 | 410 | 26.1 |
| Viscosity index | −103 | 32 | 90 | 110 |
| Flash point (°C) | 260 | 308 | 334 | 250 |
| Pour point (°C) | 2.5 | −15 | −20 | −50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, R.; Tani, H.; Koganezawa, S.; Hata, M. Alkylated Polyphenyl Ethers as High-Performance Synthetic Lubricants. Lubricants 2022, 10, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10100275
Lu R, Tani H, Koganezawa S, Hata M. Alkylated Polyphenyl Ethers as High-Performance Synthetic Lubricants. Lubricants. 2022; 10(10):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10100275
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Renguo, Hiroshi Tani, Shinji Koganezawa, and Masayuki Hata. 2022. "Alkylated Polyphenyl Ethers as High-Performance Synthetic Lubricants" Lubricants 10, no. 10: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10100275
APA StyleLu, R., Tani, H., Koganezawa, S., & Hata, M. (2022). Alkylated Polyphenyl Ethers as High-Performance Synthetic Lubricants. Lubricants, 10(10), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10100275