Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Conjunction with Cranial Radiation for Older Adults with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastasis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
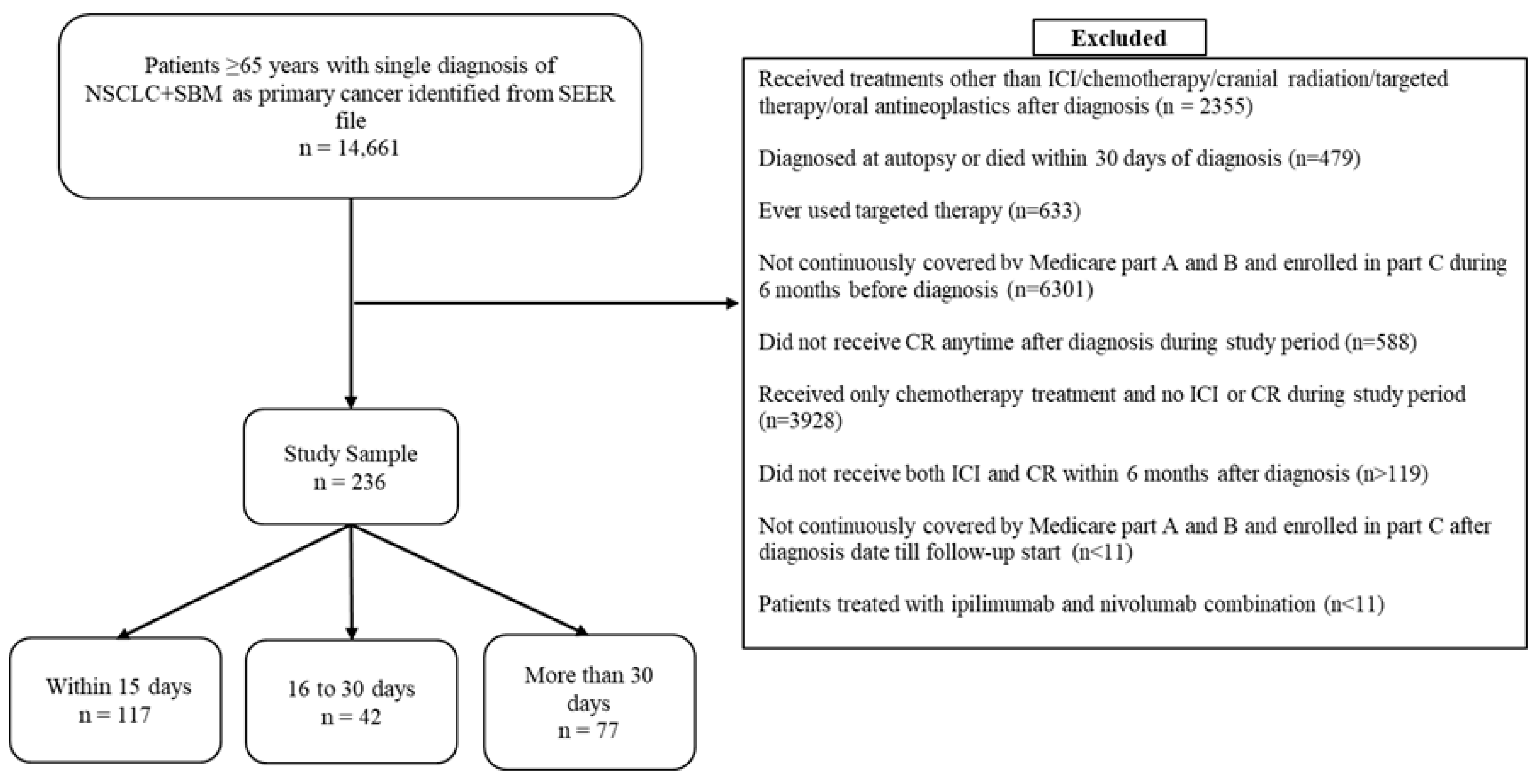
2.2. Study Sample
2.3. Treatment Groups
2.4. Survival Outcome
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Validation Study
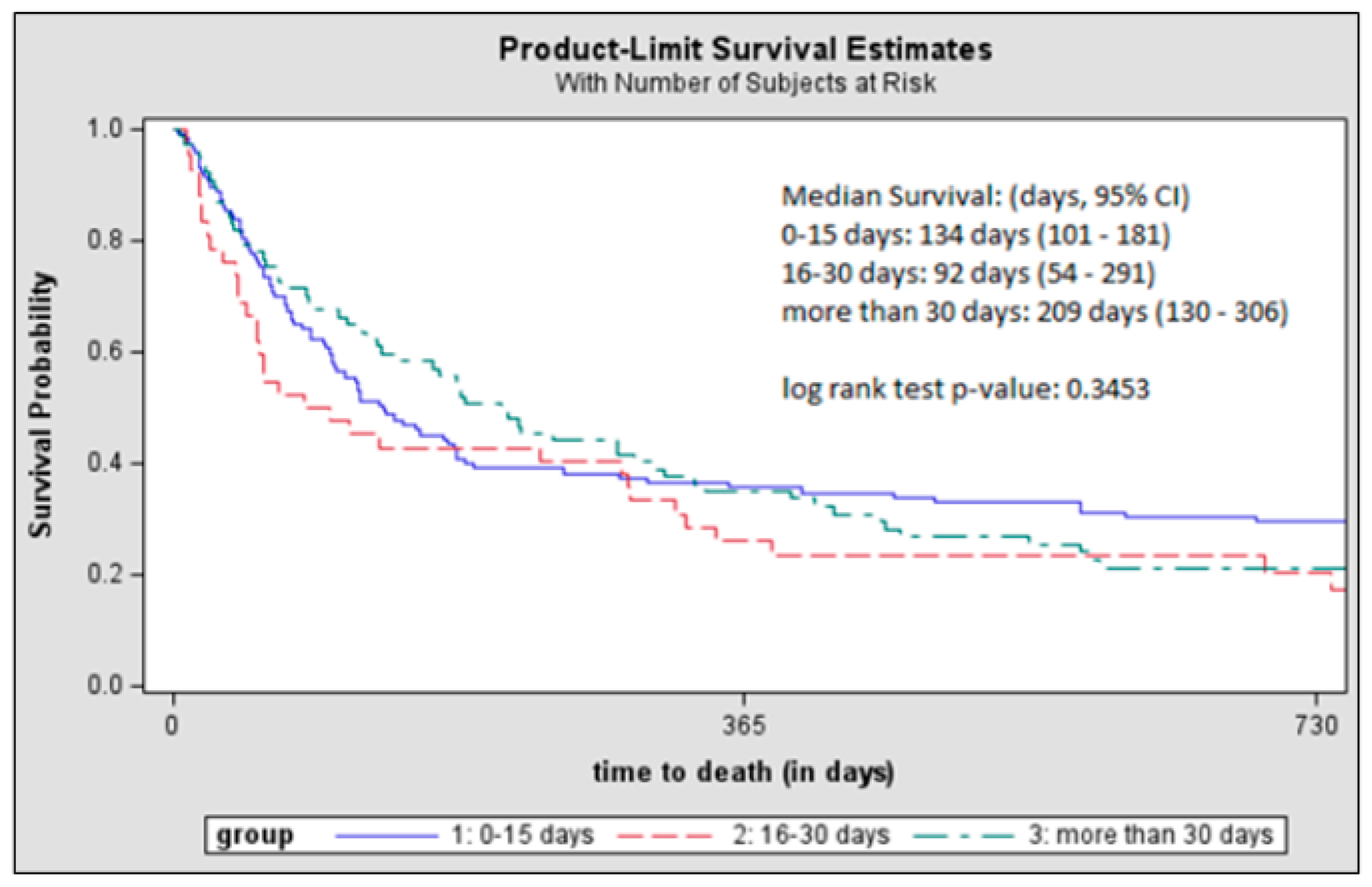
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| BM | Brain metastasis |
| CR | Cranial radiation |
| OS | Overall survival |
| SBM | Synchronous brain metastasis |
| SRS | Stereotactic radiosurgery |
| WBRT | Whole brain radiation therapy |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiotherapy |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| SEER | Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Result |
| HCPCS | Healthcare Common Procedural Coding System |
| ICD-9/10-CM | International Classification of Diseases Ninth/Tenth Revision Clinical Modification |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| KM | Kaplan–Meier |
| CPH | Cox proportional hazards |
Appendix A
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, K. Lung cancer: Understanding its molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO classification. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, W.; Inuzuka, H.; Simon, D.K.; Wei, W. Molecular Subtypes and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2025, 30, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurman, Z.; Mashiach, E.; Link, K.E.; Donahue, B.; Sulman, E.; Silverman, J.; Golfinos, J.; Oermann, E.; Kondziolka, D. Causes of Death in Patients With Brain Metastases. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y. Epidemiology of Brain Metastases. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Goffin, J.R.; Arnold, A.; Ellis, P.M. Survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after a diagnosis of brain metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2013, 20, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Soler, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Sankar, K. Emerging Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Rioth, M.J.; Horn, L. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2014, 15, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csoszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: Pembrolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non–small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score of 50% or greater. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.; Cicin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: A multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1–Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.; Powell, S.; et al. Pembrolizuchmab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Luft, A.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Gümüş, M.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Çay, Ş.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy for Squamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, H.; McCleod, M.; Hussein, M.; Morabito, A.; Rittmeyer, A.; Conter, H.J.; Kopp, H.G.; Daniel, D.; McCune, S.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Inan, C.; Ricken, G.; Widhalm, G.; Dieckmann, K.; Birner, P.; Oberndorfer, F.; Dome, B.; Bartsch, R.; Zielinski, C.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (Tils) and Pd-L1 Expression in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases (Bm) and Matched Primary Tumors (Pt). Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iv465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.J.; Yeo, N.; Gee, H.; Kong, B.Y.; Hau, E.; da Silva, I.P.; Nagrial, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors +/− Chemotherapy for Patients With NSCLC and Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2025, 16, e15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Venur, V.A.; Preusser, M.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Brain Metastases: From Biology to Treatment. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2016, 36, e116-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Duan, H.; Zhou, R. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for brain metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer: From rationale to clinical application. Immunotherapy 2021, 13, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Referenced with Permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Guideline Name V.2.2021. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2021. All Rights Reserved. To View the Most Recent and Complete Version of the Guideline, go Online to NCCN.org. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/ (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Referenced with Permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Guideline Name V.4.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All Rights Reserved. To View the Most Recent and Complete Version of the Guideline, Go Online to NCCN.org. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev-Kumar, G.; Pitroda, S.P. Synergizing radiotherapy and immunotherapy: Current challenges and strategies for optimization. Neoplasia 2023, 36, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Sinha, D.; Abdisalaam, S.; Krishnan, S.; Asaithamby, A. Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.W.; Sherer, M.V.; Zamarin, D.; Sharabi, A.B.; Dyer, B.A.; Mell, L.K.; Mayadev, J.S. Immunotherapy and radiation therapy sequencing: State of the data on timing, efficacy, and safety. Cancer 2021, 127, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.; de Wit, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Dong, W.; Liao, Z.; Gandhi, S.J.; Gay, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Chun, S.G.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Fossella, F.V.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy with or without immunotherapy for early-stage or isolated lung parenchymal recurrent node-negative non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, C.B.; Daly, M.E.; Redman, M.W.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Gray, J.E.; Hesketh, P.J.; Hu, C.; Monjazeb, A.M.; Steuer, C.E.; Ganti, A.K.; et al. SWOG/NRG S1914: Randomized phase III trial of induction/consolidation atezolizumab + SBRT versus SBRT alone in high risk, early-stage NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, S.K.; Houghton, B.; Robinson, A.G.; Quantin, X.; Wehler, T.; Kowalski, D.; Ahn, M.J.; Erman, M.; Giaccone, G.; Borghaei, H.; et al. KEYNOTE-867: Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) with or without Pembrolizumab in Patients with Unresected Stage I or II Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, e376–e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Provides Update on Phase 3 KEYNOTE-867 and KEYNOTE-630 Trials—Merck.com. Available online: https://www.merck.com/news/merck-provides-update-on-phase-3-keynote-867-and-keynote-630-trials/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Bestvina, C.M.; Pointer, K.B.; Karrison, T.; Al-Hallaq, H.; Hoffman, P.C.; Jelinek, M.J.; Juloori, A.; Melotek, J.M.; Murgu, S.; Partouche, J.; et al. A Phase 1 Trial of Concurrent or Sequential Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients With Stage IV NSCLC Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Jiang, W.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Qian, J.M.; Tang, C.; Fang, P.; Logan, J.; D’Souza, N.M.; Haydu, L.E.; Wang, X.A.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery of early melanoma brain metastases after initiation of anti-CTLA-4 treatment is associated with improved intracranial control. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 125, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Shih, H.H.; Xu, Z.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P. The effect of timing of stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of melanoma brain metastases treated with ipilimumab. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Shoukat, S.; Oliver, D.E.; Chowdhary, M.; Rizzo, M.; Lawson, D.H.; Khosa, F.; Liu, Y.; Khan, M.K. Ipilimumab and Stereotactic Radiosurgery Versus Stereotactic Radiosurgery Alone for Newly Diagnosed Melanoma Brain Metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiess, A.P.; Wolchok, J.D.; Barker, C.A.; Postow, M.A.; Tabar, V.; Huse, J.T.; Chan, T.A.; Yamada, Y.; Beal, K. Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in patients receiving ipilimumab: Safety profile and efficacy of combined treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Kim, S.; Arrington, J.; Naghavi, A.O.; Dilling, T.J.; Creelan, B.C.; Antonia, S.J.; Caudell, J.J.; Harrison, L.B.; Sahebjam, S.; et al. Outcomes targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in conjunction with stereotactic radiation for patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, T.L.; Witt, J.S.; Burr, A.R.; Yadav, P.; Leal, T.; Baschnagel, A.M. Combined Immunotherapy and Stereotactic Radiotherapy Improves Neurologic Outcomes in Patients with Non–small-cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.L.; Shi, S.; Sborov, K.; Gensheimer, M.F.; Li, G.; Nagpal, S.; Chang, S.D.; Gibbs, I.C.; Soltys, S.G.; Pollom, E.L. Adverse Radiation Effect and Disease Control in Patients Undergoing Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy for Brain Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e1399–e1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Cho, K.R.; Choi, J.W.; Kong, D.S.; Seol, H.J.; Nam, D.H.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastasis: The role of gamma knife radiosurgery. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2021, 64, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.M.; Martin, A.M.; Martin, K.; Hammoudeh, L.; Catalano, P.J.; Hodi, F.S.; Cagney, D.N.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Response rate and local recurrence after concurrent immune checkpoint therapy and radiotherapy for non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma brain metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 5274–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, E.; Hubbeling, H.; Yeap, B.; Mehan, W.A.; Shaw, A.T.; Oh, K.S.; Gainor, J.; Shih, H.A. Improved Overall Survival and Locoregional Disease Control With Concurrent PD-1 Pathway Inhibitors and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Lung Cancer Patients With Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 101, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, M.J.; Xu, Z.; Donahue, J.; Eluvathingal Muttikkal, T.J.; Cordeiro, D.; Hansen, L.; Mohammed, N.; Gentzler, R.D.; Larner, J.; Fadul, C.E.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with and without checkpoint inhibition for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer to the brain: A matched cohort study. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Qian, J.M.; Yu, J.B.; Chiang, V.L. Local tumor response and survival outcomes after combined stereotactic radiosurgery and immunotherapy in non–small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomo, S.; Oda, K.; Oguchi, K. Synergistic effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors in combination with stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: A propensity score–matched analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 139, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Liao, G. Anti-pd1 therapy plus whole-brain radiation therapy may prolong pfs in selected non–small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A retrospective study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 8903–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Douglass, J.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.; Sharfman, W.; Hammers, H.; et al. Concurrent Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Melanoma, and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, R.; Kim, J.M.; Miller, J.A.; Juloori, A.; Chao, S.T.; Murphy, E.S.; Peereboom, D.M.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. The impact of sequencing PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastasis. Neuro. Oncol. 2019, 21, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, P.H.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors with or without Radiotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrigilan, S.; Meola, A.; Chang, S.D.; Rezaeian, S.; Nemati, H.; Almasi, T.; Rostampour, N. Stereotactic radiosurgery with immune checkpoint inhibitors for brain metastases: A meta-analysis study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 37, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.M.; Goyal, A.; Rovin, R.A.; Lee, A.; Mcdonald, K.L. Concurrent versus non-concurrent immune checkpoint inhibition with stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic brain disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritaz, C.; Broutin, S.; Chaput, N.; Marabelle, A.; Paci, A. Immune checkpoint-targeted antibodies: A room for dose and schedule optimization? J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung and Bronchus Cancer—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Montrone, M.; Rosati, G.; Longo, V.; Catino, A.; Massafra, R.; Nardone, A.; Pesola, F.; Montagna, E.S.; Marech, I.; Pizzutilo, P.; et al. Immunotherapy in Elderly Patients Affected by Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambs, A.; Warren, J.L.; Bellizzi, K.M.; Topor, M.; Haffer, S.C.; Clauser, S.B. Overview of the SEER—Medicare Health Outcomes Survey Linked Dataset. Health Care Financ. Rev. 2008, 29, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.L.; Klabunde, C.N.; Schrag, D.; Bach, P.B.; Riley, G.F. Overview of the SEER-Medicare data: Content, research applications, and generalizability to the United States elderly population. Med. Care 2002, 40, IV-3–IV-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview of the SEER Program. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/about/overview.html (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Mahashabde, R.; Bhatti, S.A.; Martin, B.C.; Painter, J.T.; Rodriguez, A.; Ying, J.; Li, C. Real-World Survival of First-Line Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Versus Chemotherapy in Older Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastases. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, J.; Bai, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, L. Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Patients With Different Metastatic Sites: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar]
- FDA Approves Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab and Chemotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab-and-chemotherapy-first-line-treatment-metastatic-nsclc (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Lamba, N.; Kearney, R.B.; Catalano, P.J.; Hassett, M.J.; Wen, P.Y.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Aizer, A.A. Population-based estimates of survival among elderly patients with brain metastases. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadetsky, N.; Hernandez, A.; Wallick, C.J.; McKenna, E.F.; Surinach, A.; Colburn, D.E. Survival outcomes in an older US population with advanced melanoma and central nervous system metastases: SEER-Medicare analysis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6216–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, B.; Trikalinos, N.A.; Mor, V.; Wilson, I.B.; Dahabreh, I.J. Real-world use and survival outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitors in older adults with non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEER-Medicare: Comorbidity SAS Macros. Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/considerations/calculation.html (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Davidoff, A.J.; Gardner, L.D.; Zuckerman, I.H.; Hendrick, F.; Ke, X.; Edelman, M.J. Validation of Disability Status, a Claims-Based Measure of Functional Status for Cancer Treatment and Outcomes Studies. Med. Care 2014, 52, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidoff, A.J.; Zuckerman, I.H.; Pandya, N.; Hendrick, F.; Ke, X.; Hurria, A.; Lichtman, S.M.; Hussain, A.; Weiner, J.P.; Edelman, M.J. A Novel Approach to Improve Health Status Measurement in Observational Claims-based Studies of Cancer Treatment and Outcomes. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2013, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.-Y.; Self, G.S.; Liu, X. The Cox Proportional Hazards Model with Change Point: An Epidemiologic Application. Int. Biom. Soc. 1990, 46, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Parker, M.; Materi, J.; Azad, T.D.; Kamson, D.O.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Rincon-Torroella, J.; Bettegowda, C. Epidemiology and survival outcomes of synchronous and metachronous brain metastases: A retrospective population-based study. Neurosurg. Focus 2023, 55, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlano, M.C.; Denaro, N.; Galizia, D.; Ruatta, F.; Occelli, M.; Minei, S.; Abbona, A.; Paccagnella, M.; Ghidini, M.; Garrone, O. How Chemotherapy Affects the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.H.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Dang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.M. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with or without whole-brain radiotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117 (Suppl.), 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycan, T.W.; Norton, D.L.; Ohar, J.A. COPD and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Cancer: A Literature Review. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2024, 19, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muğlu, H.; Sünger, E.; Köylü, B.; Tunalı, D.; Erol, C.; Selcukbiricik, F.; Bilici, A.; Olmez, O.F. Late-Onset Myocarditis Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Therapy: A Case Series with Literature Review. Medicina (B Aires) 2025, 61, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measures That Are Limited or Not Available in the Data. Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/considerations/measures.html#12 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Defining Date of Diagnosis & Treatment—SEER-Medicare. Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/considerations/date.html (accessed on 1 January 2022).

| Subsequent ICI-CR Treatment Received | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within 15 Days | 16 to 30 Days | More than 30 Days | |||||
| n = 117 | n = 42 | n = 77 | |||||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-value | ||||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 73.6 (5.8) | 73.3 (5.7) | 72.1 (5.7) | 0.2914 | |||
| Time from diagnosis to first ICI (days) | 64.6 (33.1) | 84.9 (29.4) | 123.7 (31.7) | <0.0001 | |||
| Time from diagnosis to first radiation (days) | 52.8 (32.5) | 64.3 (35.0) | 41.0 (21.3) | 0.0100 | |||
| Time from diagnosis to start of follow-up (days) | 68.6 (35.1) | 90.7 (30.5) | 123.7 (31.7) | <0.0001 | |||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 60 | 51.3 | 17 | 40.5 | 33 | 42.9 | 0.3505 |
| Female | 57 | 48.7 | 25 | 59.5 | 44 | 57.1 | |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 89 | 76.1 | >31 | _a | >66 | _a | 0.0944 |
| Other | 28 | 23.9 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | |
| Marital status at diagnosis | |||||||
| Non-married | 46 | 39.3 | 20 | 47.6 | 28 | 36.4 | 0.4814 |
| Married | 71 | 60.7 | 22 | 52.4 | 49 | 63.6 | |
| Census Tract Poverty Indicator | |||||||
| 0–<5% poverty | 26 | 22.2 | >11 | _a | >20 | _a | 0.4676 |
| 5–<10% | 33 | 28.2 | <11 | _a | >19 | _a | |
| 10–<20% | 33 | 28.2 | <11 | _a | >20 | _a | |
| 20–100% or unknown | 25 | 21.4 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | |
| Rurality of patient’s county of residence | |||||||
| Metropolitan | 102 | 87.2 | >31 | _a | >66 | _a | 0.9196 |
| Non-metropolitan | 15 | 12.8 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | |
| Lung metastases at diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 93 | 79.5 | >31 | _a | <66 | _a | 0.6670 |
| Yes | 24 | 20.5 | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| Bone metastases at diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 79 | 67.5 | 26 | 61.9 | 55 | 71.4 | 0.5664 |
| Yes | 38 | 32.5 | 16 | 38.1 | 22 | 28.6 | |
| Liver metastases at diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 98 | 83.8 | >31 | _a | <66 | _a | 0.7481 |
| Yes | 19 | 16.2 | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| Baseline Charlson Comorbidity | |||||||
| 0 | 59 | 50.4 | <18 | _a | <48 | _a | 0.1690 |
| 1 | 31 | 26.5 | >14 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| ≥2 | 27 | 23.1 | <11 | _a | <18 | _a | |
| Baseline ECOG performance status proxy | |||||||
| ECOG 0–2 | >106 | _a | >31 | _a | >66 | _a | 0.2423 |
| ECOG 3–4 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | |
| First treatment after diagnosis | |||||||
| ICI | 28 | 23.9 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | <0.0001 |
| Radiation | 89 | 76.1 | >31 | _a | >66 | _a | |
| SRS within 6 months after diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 54 | 46.1 | 25 | 59.5 | 41 | 53.3 | 0.2903 |
| Yes | 63 | 53.9 | 17 | 40.5 | 36 | 46.7 | |
| Neurosurgical resection within 6 months after diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 94 | 80.3 | >31 | _a | <66 | _a | 0.7259 |
| Yes | 23 | 19.7 | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| Type of treatment | |||||||
| First-line ICI | 105 | 89.7 | >31 | _a | <66 | _a | <0.0001 |
| Second or greater line ICI | 12 | 10.3 | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| Chemotherapy within 6 months after diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 86 | 73.5 | 29 | 69.1 | 15 | 19.5 | <0.0001 |
| Yes | 31 | 26.5 | 13 | 30.9 | 62 | 80.5 | |
| Year of diagnosis | |||||||
| 2015 | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | NA |
| 2016 | >25 | _a | <18 | _a | >18 | _a | |
| 2017 | >18 | _a | >14 | _a | <48 | _a | |
| NSCLC histology | |||||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 83 | 70.9 | >14 | _a | <48 | _a | 0.0528 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 16 | 13.7 | <11 | _a | >11 | _a | |
| Other | 18 | 15.4 | <18 | _a | <18 | _a | |
| Primary tumor grade | |||||||
| Grade I/Grade II (well differentiated/moderately differentiated) | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | 0.7529 |
| Grade III/Grade IV (poorly differentiated/undifferentiated; anaplastic) | >25 | _a | <18 | _a | >18 | _a | |
| cell type not determined | >18 | _a | >14 | _a | <48 | _a | |
| Primary tumor laterality | |||||||
| Bilateral involvement/midline/one side/lateral origin unknown | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | <11 | _a | 0.2750 |
| Right: origin of primary | >25 | _a | <18 | _a | >18 | _a | |
| Left: origin of primary | >18 | _a | >14 | _a | <48 | _a | |
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Timing of ICI-CR treatment | ||
| ≤15 vs. >30 days | 1.09 (0.71–1.66) | 0.6724 |
| 16–30 vs. >30 days | 1.51 (0.90–2.53) | 0.1145 |
| ≤15 vs. 16–30 days | 0.72 (0.45–1.14) | 0.1629 |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 0.0128 |
| Marital status at diagnosis | ||
| Not married | 1 | - |
| Married | 1.07 (0.77–1.49) | 0.6510 |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 1 | - |
| Male | 0.73 (0.53–1.01) | 0.0644 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||
| Non-Hispanic White | 1 | - |
| Other | 0.81 (0.50–1.32) | 0.4153 |
| Census tract poverty indicator | ||
| 0–<5% | 1 | - |
| 5–<10 | 1.08 (0.69–1.68) | 0.7156 |
| 10–<20 | 0.82 (0.53–1.28) | 0.3981 |
| 20–100 | 1.63 (0.95–2.80) | 0.0757 |
| unknown | 1.14 (0.55–2.34) | 0.7146 |
| Rurality of patient’s county of residence | ||
| Metropolitan area | 1 | - |
| Non-metropolitan area | 0.82 (0.50–1.34) | 0.4333 |
| Metastases at diagnosis | ||
| Bone metastasis | 1.45 (1.04–2.02) | 0.0270 |
| Liver metastasis | 0.96 (0.64–1.44) | 0.8616 |
| Lung metastasis | 1.43 (0.99–2.07) | 0.0542 |
| Charlson comorbidity index score | ||
| 0 | 1 | - |
| 1 | 0.89 (0.60–1.32) | 0.5887 |
| ≥2 | 0.87 (0.58–1.32) | 0.5361 |
| Baseline ECOG performance status proxy | ||
| 0–2 | 1 | - |
| 3–4 | 0.83 (0.30–2.28) | 0.7309 |
| Histology | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 1 | - |
| Squamous cell | 0.81 (0.53–1.24) | 0.0092 |
| Other type | 1.81 (1.15–2.83) | 0.3408 |
| Tumor grade | ||
| 1–2 | 1 | - |
| 3–4 | 0.90 (0.49–1.63) | 0.7323 |
| undetermined | 1.24 (0.70–2.21) | 0.4516 |
| Treatments within 6 months from diagnosis | ||
| SRS | 0.67 (0.49–0.93) | 0.0170 |
| Chemotherapy | 1.32 (0.89–1.95) | 0.1578 |
| Neurosurgical resection | 0.58 (0.37–0.91) | 0.0180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahashabde, R.V.; Bhatti, S.A.; Martin, B.C.; Painter, J.T.; Patel, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Ying, J.; Li, C. Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Conjunction with Cranial Radiation for Older Adults with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastasis. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32090499
Mahashabde RV, Bhatti SA, Martin BC, Painter JT, Patel M, Rodriguez A, Ying J, Li C. Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Conjunction with Cranial Radiation for Older Adults with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastasis. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(9):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32090499
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahashabde, Ruchira V., Sajjad A. Bhatti, Bradley C. Martin, Jacob T. Painter, Mausam Patel, Analiz Rodriguez, Jun Ying, and Chenghui Li. 2025. "Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Conjunction with Cranial Radiation for Older Adults with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastasis" Current Oncology 32, no. 9: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32090499
APA StyleMahashabde, R. V., Bhatti, S. A., Martin, B. C., Painter, J. T., Patel, M., Rodriguez, A., Ying, J., & Li, C. (2025). Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Conjunction with Cranial Radiation for Older Adults with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Synchronous Brain Metastasis. Current Oncology, 32(9), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32090499






