Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma—An Analysis of the National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Targeted Nephrectomy Database
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Exposure
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
3.2. Primary Outcomes
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
3.4. Nephrectomy-Specific Outcomes
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, X.; Yi, M.; Dong, B.; Zheng, X.; Wu, K. The global, regional, and national burden of kidney cancer and attributable risk factor analysis from 1990 to 2017. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.P.; Campbell, S.C.; Gill, I.; Lane, B.R.; Van Poppel, H.; Smaldone, M.C.; Volpe, A.; Kutikov, A. Collaborative Review of Risk Benefit Trade-offs Between Partial and Radical Nephrectomy in the Management of Anatomically Complex Renal Masses. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingler, D.W.; Hemstreet, G.P.; Balaji, K. Feasibility of robotic radical nephrectomy—Initial results of single-institution pilot study. Urology 2005, 65, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, A.N.; Gill, I.S. Minimally invasive radical nephrectomy: A contemporary review. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Vyas, A.; Vyas, D. The History of Robotics in Surgical Specialties. Am. J. Robot. Surg. 2014, 1, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, R.; Di Maida, F.; Lane, B.R.; De Cobelli, O.; Sanguedolce, F.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Antonelli, A.; Noyes, S.; Mari, A.; Grosso, A.A.; et al. Impact of surgical approach and resection technique on the risk of Trifecta Failure after partial nephrectomy for highly complex renal masses. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2022, 48, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpiglia, F.; Mari, A.; Bertolo, R.; Antonelli, A.; Bianchi, G.; Fidanza, F.; Fiori, C.; Furlan, M.; Morgia, G.; Novara, G.; et al. Partial Nephrectomy in Clinical T1b Renal Tumors: Multicenter Comparative Study of Open, Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Approach (the RECORd Project). Urology 2016, 89, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.; Webb, C.M.; Eltahawy, E.; Faramawi, M.F.; Shera, A.L.; Davis, R.; Bissada, N.; Jadhav, S. A comparative study of open, laparoscopic and robotic partial nephrectomy in obese patients. Urol. Ann. 2015, 7, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombos, D.M.; Chughtai, B.; Trinh, Q.-D.; Mao, J.; Te, A.; O’Malley, P.; Scherr, D.S.; Del Pizzo, J.; Hu, J.C.; Sedrakyan, A. Adoption of Technology and Its Impact on Nephrectomy Outcomes, a U.S. Population-Based Analysis (2008–2012). J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmers, M.R.; Ball, M.W.; Gorin, M.A.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Allaf, M.E. Robotic versus laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: Comparative analysis and cost considerations. Can. J. Urol. 2016, 23, 8435–8440. [Google Scholar]
- Marchioni, M.; Berardinelli, F.; Zhang, C.; Simone, G.; Uzzo, R.G.; Capitanio, U.; Minervini, A.; Lau, C.; Kaouk, J.; Langenstroer, P.; et al. Effect of Obesity and Overweight Status on Complications and Survival After Minimally Invasive Kidney Surgery in Patients with Clinical T2-4 Renal Masses. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierorazio, P.M.; Johnson, M.H.; Patel, H.D.; Sozio, S.M.; Sharma, R.; Iyoha, E.; Bass, E.B.; Allaf, M.E. Management of Renal Masses and Localized Renal Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.C.; Clark, P.E.; Chang, S.S.; Karam, J.A.; Souter, L.; Uzzo, R.G. Renal Mass and Localized Renal Cancer: Evaluation, Management, and Follow-Up: AUA Guideline: Part I. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.C.; Derweesh, I.; Porpiglia, F.; Zargar, H.; Mottrie, A.; Autorino, R. Partial Nephrectomy Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Clinical T1b and T2 Renal Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.G.; Khandwala, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Han, D.H.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Chang, S.L.; Chung, B.I. Association of Robotic-Assisted vs Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy with Perioperative Outcomes and Health Care Costs, 2003 to 2015. JAMA 2017, 318, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, E.B.; Harris, A.H.; Giori, N.J. Large Surgical Databases with Direct Data Abstraction: VASQIP and ACS-NSQIP. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 104 (Suppl. S3), 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocerossa, F.; Carbonara, U.; Cantiello, F.; Marchioni, M.; Ditonno, P.; Mir, M.C.; Porpiglia, F.; Derweesh, I.; Hampton, L.J.; Damiano, R.; et al. Robot-assisted Radical Nephrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershman, B.; Bukavina, L.; Chen, Z.; Konety, B.; Schumache, F.; Li, L.; Kutikov, A.; Smaldone, M.; Abouassaly, R.; Kim, S.P. The Association of Robot-assisted Versus Pure Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy with Perioperative Outcomes and Hospital Costs. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, A.D.; Miano, R.; Annino, F.; Micali, S.; Spera, E.; Iorio, B.; Vespasiani, G.; Gaston, R. Robotic radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review. BMC Urol. 2014, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; Autorino, R.; Spana, G.; Laydner, H.; Hillyer, S.P.; Khanna, R.; Yang, B.; Altunrende, F.; Isac, W.; Stein, R.J.; et al. Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical nephrectomy: Surgical technique and comparative outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Monn, M.F.; Bahler, C.D.; Sundaram, C.P. Does Robotic Assistance Confer an Economic Benefit during Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy? J. Urol. 2014, 192, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anele, U.A.; Marchioni, M.; Yang, B.; Simone, G.; Uzzo, R.G.; Lau, C.; Mir, M.C.; Capitanio, U.; Porter, J.; Jacobsohn, K.; et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: A large multi-institutional analysis (ROSULA Collaborative Group). World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, T.; Galich, A.; Sterrett, S.; Klingler, D.; Smith, L.; Balaji, K. Radical nephrectomy performed by open, laparoscopy with or without hand-assistance or robotic methods by the same surgeon produces comparable perioperative results. Int. Braz. J. 2006, 32, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemal, A.K.; Kumar, A. A prospective comparison of laparoscopic and robotic radical nephrectomy for T1-2N0M0 renal cell carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2009, 27, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozminski, D.J.; Cerf, M.J.; Feustel, P.J.; Kogan, B.A. Robot set-up time in urologic surgery: An opportunity for quality improvement. J. Robot. Surg. 2020, 14, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Hevelone, N.D.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Kowalczyk, K.J.; Hu, J.C. Use, costs and comparative effectiveness of robotic assisted, laparoscopic and open urological surgery. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
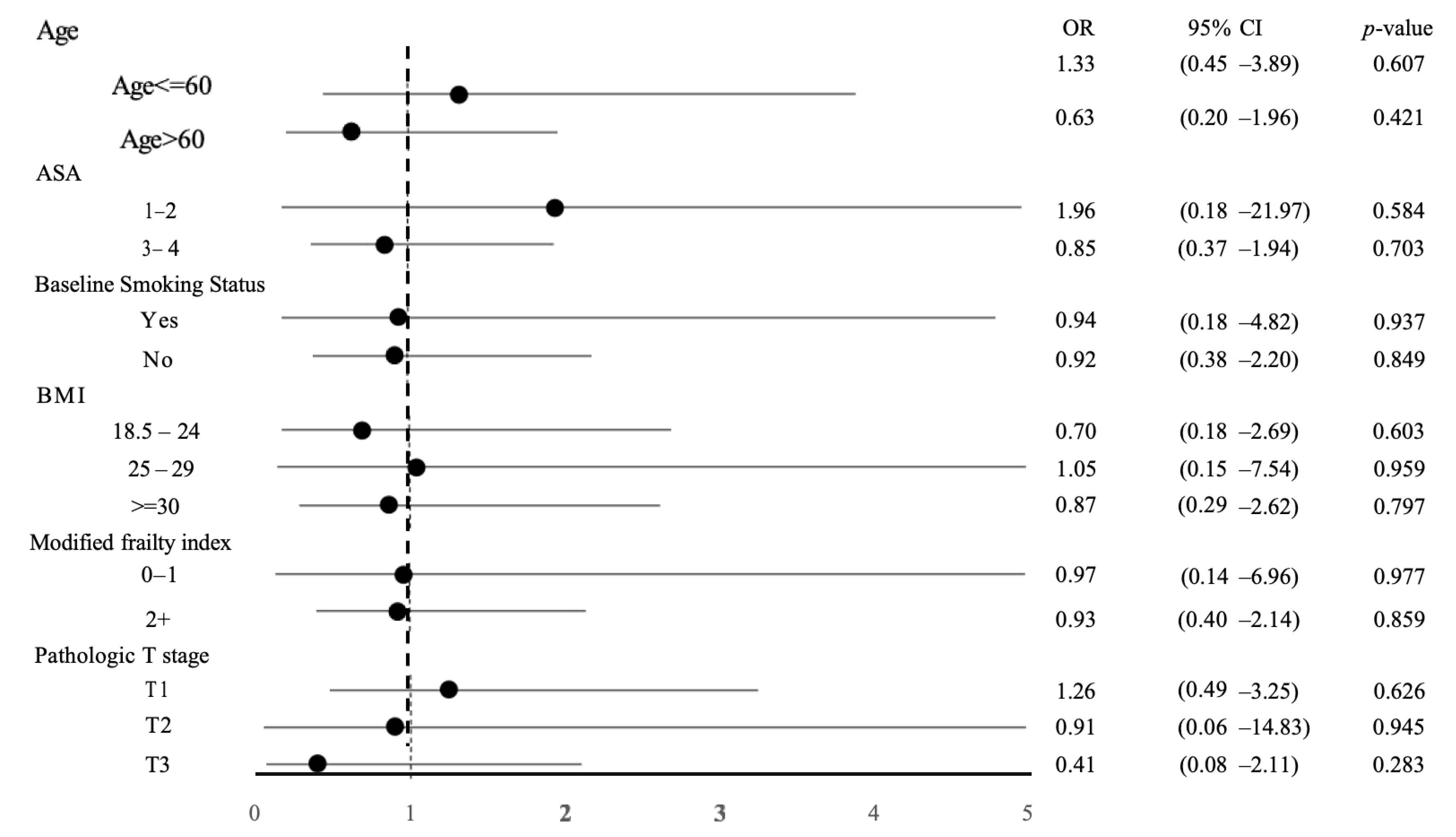
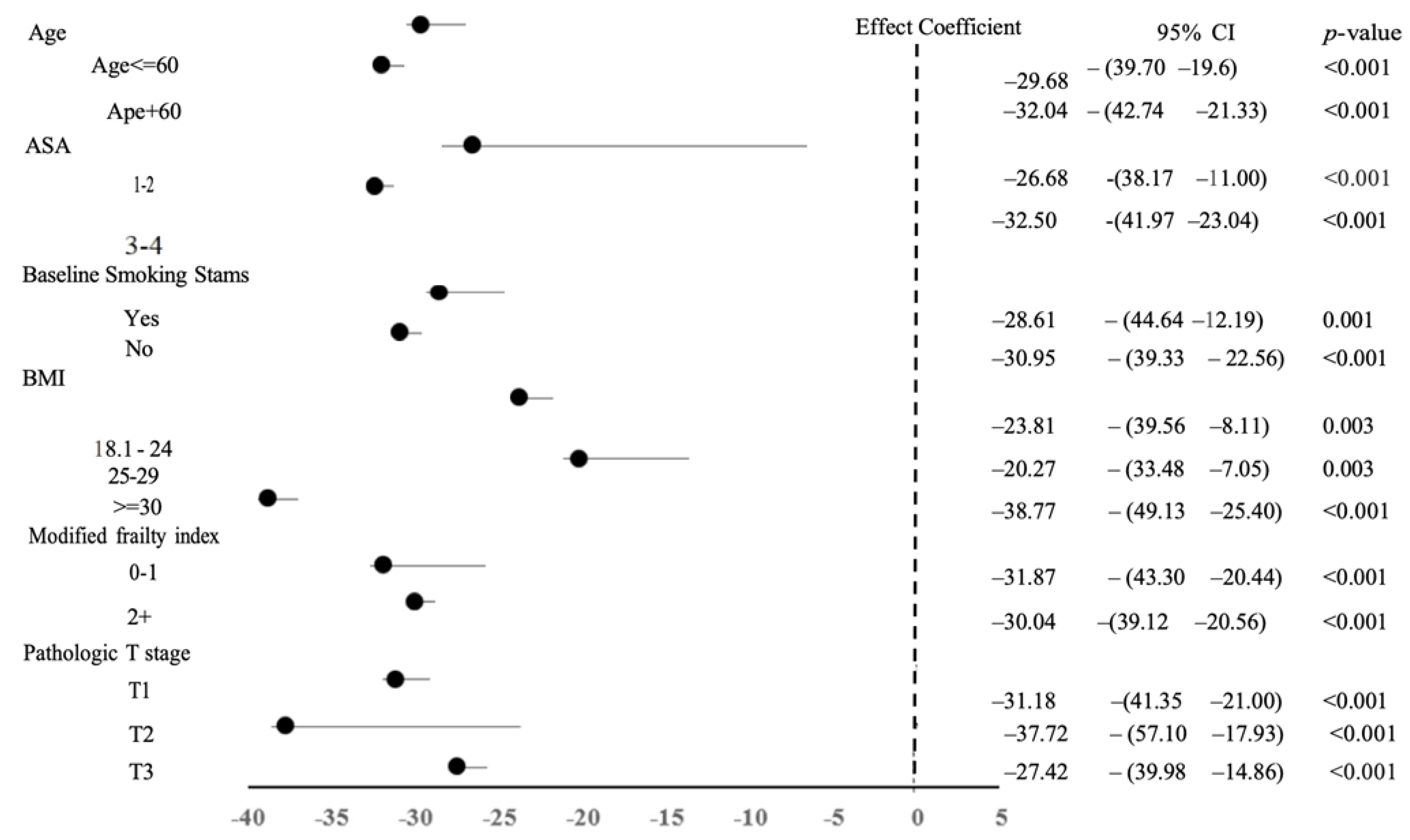
| Variables | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | RARN | LRN | SMD | Total | RARN | LRN | SMD | |
| n = 1545 | n = 722 | n = 823 | n = 1344 | n = 672 | n = 672 | |||
| Age | 62.97 ± 11.97 | 62.47 ± 11.97 | 63.41 ± 11.96 | −0.079 | 62.93 ± 11.82 | 62.98 ± 11.70 | 62.89 ± 11.95 | 0.007 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 519 (33.59) | 233 (32.27) | 286 (34.75) | 0.053 | 455 (33.85) | 225 (33.48) | 230 (34.23) | 0.016 |
| Male | 1026 (66.41) | 489 (67.73) | 537 (65.25) | 889 (66.15) | 447 (66.52) | 442 (65.77) | ||
| BMI | 30.90 ± 7.03 | 30.75 ± 6.80 | 31.03 ± 7.23 | −0.039 | 30.96 ± 6.99 | 30.96 ± 6.90 | 30.95 ± 7.09 | 0.001 |
| Current smoking status | ||||||||
| No | 1294 (83.75) | 605 (83.80) | 689 (83.72) | 0.002 | 1127 (83.85) | 567 (84.38) | 560 (83.33) | 0.028 |
| Yes | 251 (16.25) | 117 (16.20) | 134 (16.28) | 217 (16.15) | 105 (15.63) | 112 (16.67) | ||
| ASA | ||||||||
| 1–2 | 498 (32.23) | 255 (35.32) | 243 (29.53) | 0.124 | 447 (33.26) | 221 (32.89) | 226 (33.63) | 0.016 |
| 3–4 | 1047 (67.77) | 467 (64.68) | 580 (70.47) | 897 (66.74) | 451 (67.11) | 446 (66.37) | ||
| Baseline dialysis status | ||||||||
| No | 1456 (94.24) | 674 (93.35) | 782 (95.02) | 0.71 | 1267 (94.27) | 634 (94.35) | 633 (94.20) | 0.006 |
| Yes | 89 (5.76) | 48 (6.65) | 41 (4.98) | 77 (5.73) | 38 (5.65) | 39 (5.80) | ||
| Chronic steroid use | ||||||||
| No | 1467 (94.95) | 684 (94.74) | 783 (95.14) | 0.018 | 1276 (94.94) | 638 (94.94) | 638 (94.94) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 78 (5.05) | 38 (5.26) | 40 (4.86) | 68 (5.06) | 34 (5.06) | 34 (5.06) | ||
| Modified frailty index | ||||||||
| Score 0–1 | 479 (31.00) | 226 (31.30) | 253 (30.74) | 0.012 | 424 (31.55) | 209 (31.10) | 215 (31.99) | 0.019 |
| Score 2+ | 1066 (69.00) | 496 (68.70) | 570 (69.26) | 920 (68.45) | 463 (68.90) | 457 (68.01) | ||
| Lymph node dissection status | ||||||||
| No | 1318 (85.31) | 609 (84.35) | 709 (86.15) | 0.051 | 1152 (85.71) | 574 (85.42) | 578 (86.01) | 0.017 |
| Yes | 227 (14.69) | 113 (15.65) | 114 (13.85) | 192 (14.29) | 98 (14.58) | 94 (13.99) | ||
| Pathologic T stage | ||||||||
| T1 | 799 (52.46) | 371 (52.40) | 428 (52.52) | 0.066 | 712 (52.98) | 357 (53.13) | 355 (52.83) | 0.037 |
| T2 | 188 (12.34) | 80 (11.30) | 108 (13.25) | 166 (12.35) | 79 (11.76) | 87 (12.95) | ||
| T3 | 536 (35.19) | 257 (36.30) | 279 (34.23) | 466 (34.67) | 236 (35.12) | 230 (34.23) | ||
| Variables | Total | RARN | LRN | LRN vs. RARN | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1344 | n = 672 | n = 672 | OR (95% CI) | ||
| Major Complications | 27 (2.01) | 14 (2.08) | 13 (1.93) | 0.93 (0.43, 2.00) | 0.848 |
| 30-day Mortality | 4 (0.30) | 3 (0.45) | 1 (0.15) | 0.33 (0.03, 3.22) | 0.342 |
| Return to Operation Room | 18 (1.34) | 10 (1.49) | 8 (1.19) | 0.80 (0.31, 2.05) | 0.638 |
| Cardiac Arrest | 3 (0.22) | 2 (0.30) | 1 (0.15) | 0.50 (0.04, 5.54) | 0.572 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 9 (0.67) | 3 (0.45) | 6 (0.89) | 2.01 (0.50, 8.11) | 0.327 |
| Stroke/Cerebrovascular Accident | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | NA | - |
| Secondary Outcomes | |||||
| Unplanned Intubation | 5 (0.37) | 1 (0.15) | 4 (0.60) | 4.02 (0.45, 36.20) | 0.215 |
| Ventilator > 48 h | 4 (0.30) | 1 (0.15) | 3 (0.45) | 3.01 (0.31, 29.12) | 0.342 |
| Sepsis | 5 (0.37) | 2 (0.30) | 3 (0.45) | 1.50 (0.25, 9.06) | 0.657 |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 12 (0.89) | 5 (0.74) | 7 (1.04) | 1.40 (0.44, 4.47) | 0.566 |
| Surgical Site Infection | 26 (1.93) | 8 (1.19) | 18 (2.68) | 2.28 (1.01, 5.16) | 0.047 |
| Superficial Surgical Site Infection | 19 (1.41) | 8 (1.19) | 11 (1.64) | 1.38 (0.58, 3.31) | 0.469 |
| Deep Surgical Site Infection | 3 (0.22) | 0 (0.00) | 3 (0.45) | NA | - |
| Organ Site Surgical Site Infection | 4 (0.30) | 0 (0.00) | 4 (0.60) | NA | - |
| Pulmonary Embolism | 5 (0.37) | 2 (0.30) | 3 (0.45) | 1.50 (0.25, 9.06) | 0.657 |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | 6 (0.45) | 1 (0.15) | 5 (0.74) | 5.03 (0.58, 43.35) | 0.142 |
| Prolonged Length of Stay | 212 (15.77) | 87 (12.95) | 125 (18.60) | 1.54 (1.15, 2.06) | 0.004 |
| Transfusion within 72 h of Surgery | 44 (3.27) | 20 (2.98) | 24 (3.57) | 1.21 (0.65, 2.23) | 0.547 |
| Hospitalized > 30 days | 14 (1.04) | 6 (0.89) | 8 (1.19) | 1.34 (0.46, 3.90) | 0.594 |
| Wound Disruption | 6 (0.45) | 4 (0.60) | 2 (0.30) | 0.50 (0.09, 2.74) | 0.424 |
| Unplanned Readmission | 47 (3.50) | 19 (2.83) | 28 (4.17) | 1.49 (0.84, 2.66) | 0.173 |
| Acute Renal Failure | 3 (0.22) | 2 (0.30) | 1 (0.15) | 0.50 (0.04, 5.54) | 0.572 |
| Clostridium Difficile | 3 (0.22) | 2 (0.30) | 1 (0.15) | 0.50 (0.04, 5.54) | 0.572 |
| Nephrectomy-Specific Outcomes | |||||
| Lymphocele or Other Lymphatic Leaks | 14 (1.04) | 8 (1.19) | 6 (0.89) | 0.75 (0.26, 2.18) | 0.594 |
| Prolonged Postop NPO or NGT use | 20 (1.49) | 8 (1.19) | 12 (1.79) | 1.51 (0.61, 3.74) | 0.375 |
| Total Operation Time | 162 ± 69 | 177 ± 72 | 146 ± 63 | −30.67 (−38.18, −23.15) * | <0.001 |
| Unplanned Conversion Rate to Open Approach | 37(2.75) | 8 (1.16) | 29 (4.30) | 3.70 (3.25, 4.15) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mundra, V.; Hu, S.; Titus, R.S.; Luna-Velazquez, E.; Melchiode, Z.; Xu, J.; Riveros, C.; Ranganathan, S.; Huang, E.; Miles, B.J.; et al. Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma—An Analysis of the National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Targeted Nephrectomy Database. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060358
Mundra V, Hu S, Titus RS, Luna-Velazquez E, Melchiode Z, Xu J, Riveros C, Ranganathan S, Huang E, Miles BJ, et al. Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma—An Analysis of the National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Targeted Nephrectomy Database. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(6):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060358
Chicago/Turabian StyleMundra, Vatsala, Siqi Hu, Renil Sinu Titus, Eusebio Luna-Velazquez, Zachary Melchiode, Jiaqiong Xu, Carlos Riveros, Sanjana Ranganathan, Emily Huang, Brian J. Miles, and et al. 2025. "Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma—An Analysis of the National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Targeted Nephrectomy Database" Current Oncology 32, no. 6: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060358
APA StyleMundra, V., Hu, S., Titus, R. S., Luna-Velazquez, E., Melchiode, Z., Xu, J., Riveros, C., Ranganathan, S., Huang, E., Miles, B. J., Kaushik, D., Wallis, C. J. D., & Satkunasivam, R. (2025). Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma—An Analysis of the National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) Targeted Nephrectomy Database. Current Oncology, 32(6), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060358





