Enhancing CAR-T Efficacy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Radiation Bridging Therapy: A Real-World Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Assessments and Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Patient Characteristics by CAR-T Product
3.3. Bridging Therapy
3.4. Response to BT Prior to CAR-T Infusion
3.5. CAR-T Efficacy
3.6. Outcomes Based on BT, RBT Field and Disease Status at Infusion
3.7. Safety and Toxicity
3.8. Predictors of Efficacy and Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jager, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Locke, F.L.; Ma, L.; Asubonteng, J.; Hu, Z.H.; Siddiqi, T.; Ahmed, S.; Ghobadi, A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lin, Y.; et al. Real-World Evidence of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for the Treatment of Large B Cell Lymphoma in the United States. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 581.e1-581.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnl, A.; Roddie, C.; Kirkwood, A.A.; Tholouli, E.; Menne, T.; Patel, A.; Besley, C.; Chaganti, S.; Sanderson, R.; O’Reilly, M.; et al. A national service for delivering CD19 CAR-Tin large B-cell lymphoma—The UK real-world experience. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethge, W.A.; Martus, P.; Schmitt, M.; Holtick, U.; Subklewe, M.; von Tresckow, B.; Ayuk, F.; Wagner-Drouet, E.M.; Wulf, G.G.; Marks, R.; et al. GLA/DRST real-world outcome analysis of CAR T-cell therapies for large B-cell lymphoma in Germany. Blood 2022, 140, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachy, E.; Le Gouill, S.; Di Blasi, R.; Sesques, P.; Manson, G.; Cartron, G.; Beauvais, D.; Roulin, L.; Gros, F.X.; Rubio, M.T.; et al. A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Gutierrez, A.; Reguera, J.L.; Iacoboni, G.; Lopez-Corral, L.; Terol, M.J.; Ortiz-Maldonado, V.; Sanz, J.; Guerra-Dominguez, L.; Bailen, R.; et al. Best Treatment Option for Patients With Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma in the CAR-T Cell Era: Real-World Evidence From GELTAMO/GETH Spanish Groups. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsburg, D.J.; Frigault, M.; Heim, M.; Foley, S.R.; Hill, B.T.; Ho, C.M.; Jacobson, C.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Locke, F.L.; Ram, R.; et al. Real-World Outcomes for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (aBNHL) Treated with Commercial Tisagenlecleucel: Subgroup Analyses from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) Registry. Blood 2022, 140, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, J.R.; Oluwole, O.O.; Kersten, M.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Perales, M.A.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; Sureda, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Farooq, U.; et al. Survival with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Solomon, S.R.; Arnason, J.; Johnston, P.B.; Glass, B.; Bachanova, V.; Ibrahimi, S.; Mielke, S.; Mutsaers, P.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: Primary analysis of the phase 3 TRANSFORM study. Blood 2023, 141, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Dickinson, M.; Munoz, J.; Ulrickson, M.L.; Thieblemont, C.; Oluwole, O.O.; Herrera, A.F.; Ujjani, C.S.; Lin, Y.; Riedell, P.A.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as first-line therapy in high-risk large B-cell lymphoma: The phase 2 ZUMA-12 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnix, C.C.; Gunther, J.R.; Dabaja, B.S.; Strati, P.; Fang, P.; Hawkins, M.C.; Adkins, S.; Westin, J.; Ahmed, S.; Fayad, L.; et al. Bridging therapy prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddie, C.; Neill, L.; Osborne, W.; Iyengar, S.; Tholouli, E.; Irvine, D.; Chaganti, S.; Besley, C.; Bloor, A.; Jones, C.; et al. Effective bridging therapy can improve CD19 CAR-T outcomes while maintaining safety in patients with large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2872–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, S.T.; Dholaria, B.R.; Sengsayadeth, S.M.; Savani, B.N.; Oluwole, O.O. Role of bridging therapy during chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. EJHaem 2022, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, O.; Breen, W.G.; Lester, S.C.; Rule, W.G.; Stish, B.J.; Rosenthal, A.; Munoz, J.; Lin, Y.; Bansal, R.; Hathcock, M.A.; et al. Don’t Put the CART Before the Horse: The Role of Radiation Therapy in Peri-CAR T-cell Therapy for Aggressive B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 116, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladbury, C.; Dandapani, S.; Hao, C.; Fabros, M.; Amini, A.; Sampath, S.; Glaser, S.; Sokolov, K.; Yeh, J.; Baird, J.H.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Bridging Therapies Prior to CAR T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbeling, H.; Silverman, E.A.; Michaud, L.; Tomas, A.A.; Shouval, R.; Flynn, J.; Devlin, S.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Tringale, K.R.; Batlevi, C.; et al. Bridging Radiation Rapidly and Effectively Cytoreduces High-Risk Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas Prior to Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 259.1-259.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A.; Alliance, A.L.; Lymphoma, G.; Eastern Cooperative Oncology, G.; et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Jain, T.; Santomasso, B.D.; Mead, E.; Wudhikarn, K.; Silverberg, M.L.; Batlevi, Y.; Shouval, R.; Devlin, S.M.; Batlevi, C.; et al. Comparing CAR T-cell toxicity grading systems: Application of the ASTCT grading system and implications for management. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Jacobson, C.A.; Ghobadi, A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Five-year follow-up of ZUMA-1 supports the curative potential of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2023, 141, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Tam, C.S.; Borchmann, P.; Worel, N.; McGuirk, J.P.; Holte, H.; Waller, E.K.; Jaglowski, S.; Bishop, M.R.; Damon, L.E.; et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.R.; Berger, T.R.; Graham, C.; Larson, R.C.; Maus, M.V. Four challenges to CAR T cells breaking the glass ceiling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieblemont, C.; Chartier, L.; Duhrsen, U.; Vitolo, U.; Barrington, S.F.; Zaucha, J.M.; Vercellino, L.; Gomes Silva, M.; Patrocinio-Carvalho, I.; Decazes, P.; et al. A tumor volume and performance status model to predict outcome before treatment in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 5995–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijzer, K.; de Boer, J.W.; van Doesum, J.A.; Noordzij, W.; Huls, G.A.; van Dijk, L.V.; van Meerten, T.; Niezink, A.G.H. Reducing and controlling metabolic active tumor volume prior to CAR T-cell infusion can improve survival outcomes in patients with large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Iacoboni, G.; Reguera, J.L.; Corral, L.L.; Morales, R.H.; Ortiz-Maldonado, V.; Guerreiro, M.; Caballero, A.C.; Dominguez, M.L.G.; Pina, J.M.S.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to tisagenlecleucel for the treatment of aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2023, 108, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellino, L.; Di Blasi, R.; Kanoun, S.; Tessoulin, B.; Rossi, C.; D’Aveni-Piney, M.; Oberic, L.; Bodet-Milin, C.; Bories, P.; Olivier, P.; et al. Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5607–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, L.; Riether, C.; Aebersold, D.M.; Medova, M.; Zimmer, Y. CAR T cell-based immunotherapy and radiation therapy: Potential, promises and risks. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegya-Raman, N.; Wright, C.M.; Ladbury, C.J.; Chew, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.Y.; Burke, S.; Baron, J.; Sim, A.J.; LaRiviere, M.J.; et al. Bridging Radiotherapy Prior to Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for B-Cell Lymphomas: An ILROG Multi-Institutional Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, S50–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, O.; Lester, S.C.; Breen, W.G.; Rule, W.G.; Lin, Y.; Bennani, N.N.; Rosenthal, A.; Munoz, J.; Murthy, H.S.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; et al. Incorporating radiation with anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A multicenter consensus approach. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 99, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.M.; LaRiviere, M.J.; Baron, J.A.; Uche, C.; Xiao, Y.; Arscott, W.T.; Anstadt, E.J.; Barsky, A.R.; Miller, D.; LaRose, M.I.; et al. Bridging Radiation Therapy Before Commercial Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.J.; Jain, M.D.; Figura, N.B.; Chavez, J.C.; Shah, B.D.; Khimani, F.; Lazaryan, A.; Krivenko, G.; Davila, M.L.; Liu, H.D.; et al. Radiation Therapy as a Bridging Strategy for CAR T Cell Therapy With Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, B.; Khaouam, N.; Filion, E.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Bujold, A.; Lambert, L. Palliative Radiation Therapy for Advanced Head and Neck Carcinomas: A Phase 2 Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahalom, J.; Dabaja, B.S.; Ricardi, U.; Ng, A.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Vogelius, I.R.; Illidge, T.; Qi, S.; Wirth, A.; Specht, L. ILROG emergency guidelines for radiation therapy of hematological malignancies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Blood 2020, 135, 1829–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzar, G.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Dudzinski, S.O.; Jallouk, A.; Yoder, A.K.; Nasr, L.F.; Corrigan, K.L.; Gunther, J.R.; Ahmed, S.; Fayad, L.; et al. Outcomes with Bridging Radiation Therapy Prior to CAR-T Cell Therapy in Pts with Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, e483–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, O.; Breen, W.G.; Rule, W.G.; Lin, Y.; Munoz, J.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Peterson, J.L. Comprehensive Bridging Radiotherapy for Limited Pre-CART Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallington, D.G.; Imber, B.S.; Scordo, M.; Robinson, T.J. The Role of Radiotherapy in Lymphoma Patients Undergoing CAR T Therapy: Past, Present, and Future. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 35, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Patients N = 100 | No BT N = 20 | RBT N = 48 | SBT N = 32 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 59 (20–81) | 61 (20–78) | 59 (30–81) | 62 (21–78) | 0.62 |
| CAR-T, n (%) | 0.23 | ||||
| Axi-cel | 50 (50) | 9 (45) | 21 (44) | 20 (63) | |
| Tisa-cel | 50 (50) | 11 (55) | 27 (56) | 12 (38) | |
| Histology, n (%) | 0.05 | ||||
| DLBCL | 59 (59) | 12 (60) | 23 (48) | 24 (75) | |
| tFL | 22 (22) | 5 (25) | 11 (23) | 6 (19) | |
| PMBCL | 7 (7) | 2 (10) | 3 (6) | 2 (6) | |
| HGBCL | 12 (12) | 1 (5) | 11 (23) | 0 (0) | |
| Primary refractory, n (%) | 70 (70) | 12 (60) | 36 (75) | 22 (69) | 0.46 |
| Ineligibility to pivotal trial, n (%) | 57 (57) | 4 (20) | 27 (56) | 26 (81) | <0.01 |
| At apheresis, n (%) | |||||
| Stage III or IV | 66 (66) | 11 (55) | 26 (54) | 29 (91) | <0.01 |
| Bulky disease | 18 (18) | 0 (0) | 9 (19) | 9 (28) | 0.04 |
| Elevated LDH | 62 (62) | 7 (35) | 28 (58) | 27 (84) | <0.01 |
| ≥2 extranodal sites | 23 (23) | 3 (15) | 7 (15) | 13 (41) | 0.06 |
| At lymphodepletion, n (%) | |||||
| Stage III or IV | 61 (61) | 14 (70) | 23 (48) | 24 (75) | 0.03 |
| Bulky disease | 14 (14) | 1 (5) | 7 (15) | 6 (19) | 0.38 |
| Elevated LDH | 55 (55) | 9 (45) | 23 (48) | 23 (72) | 0.07 |
| ≥2 extranodal sites | 27 (27) | 2 (10) | 11 (23) | 14 (44) | <0.01 |
| Status at infusion, n (%) | |||||
| PD | 57 (57) | 16 (80) | 22 (46) | 19 (59) | |
| SD | 13 (13) | 4 (20) | 7 (15) | 2 (6) | 0.03 |
| PR | 19 (19) | 0 (0) | 13 (27) | 6 (19) | |
| CR | 11 (11) | 0 (0) | 6 (13) | 5 (16) |
| All Patients N = 100 | Axi-cel N = 50 | Tisa-cel N = 50 | No BT N = 20 | RBT N = 48 | SBT N = 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best response (%) | ||||||
| ORR | 72 | 84 * | 60 * | 70 | 79 | 63 |
| CR | 60 | 78 * | 42 * | 60 | 67 | 50 |
| Median PFS, mo | NR | NR * | 2.0 (1.0–9.7) * | NR | NR | 2.3 (1.0-NE) |
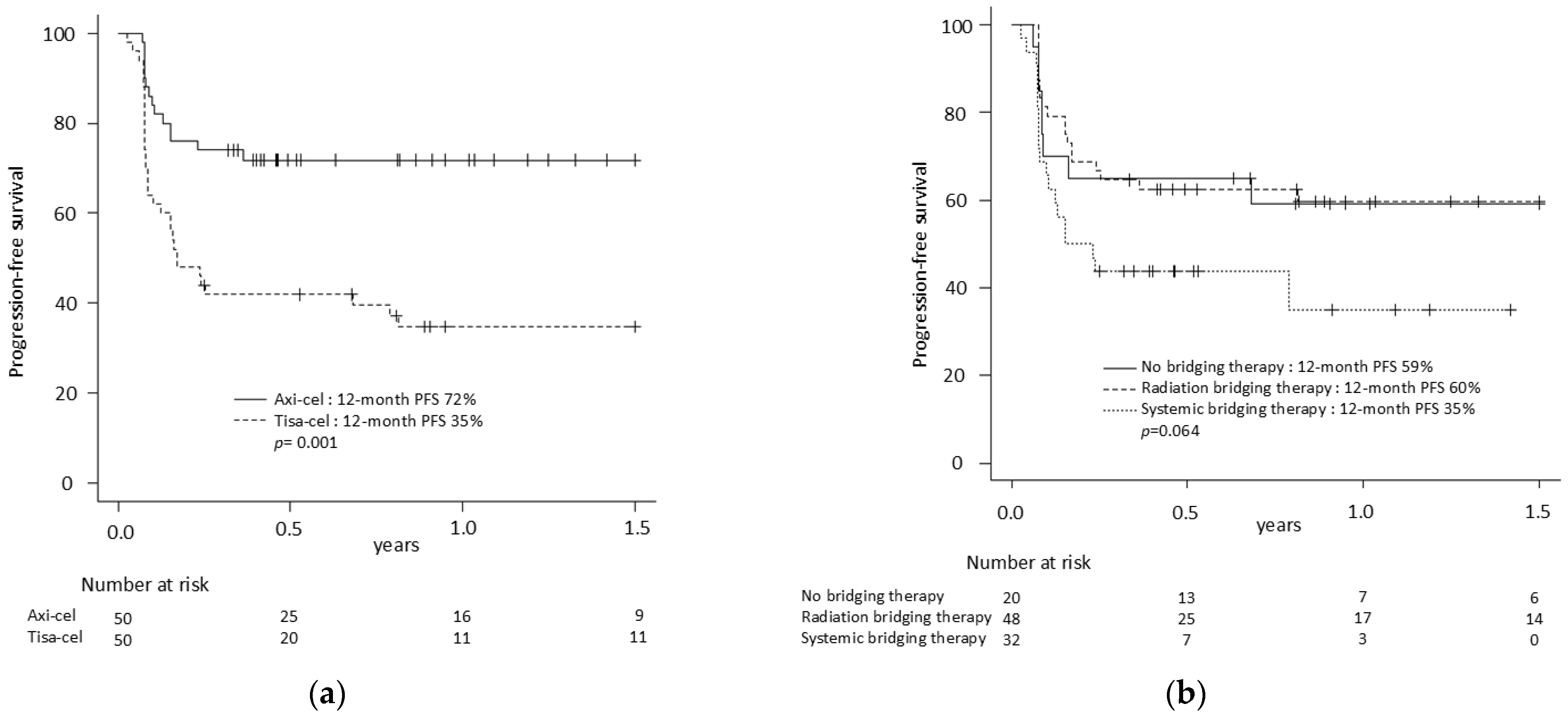
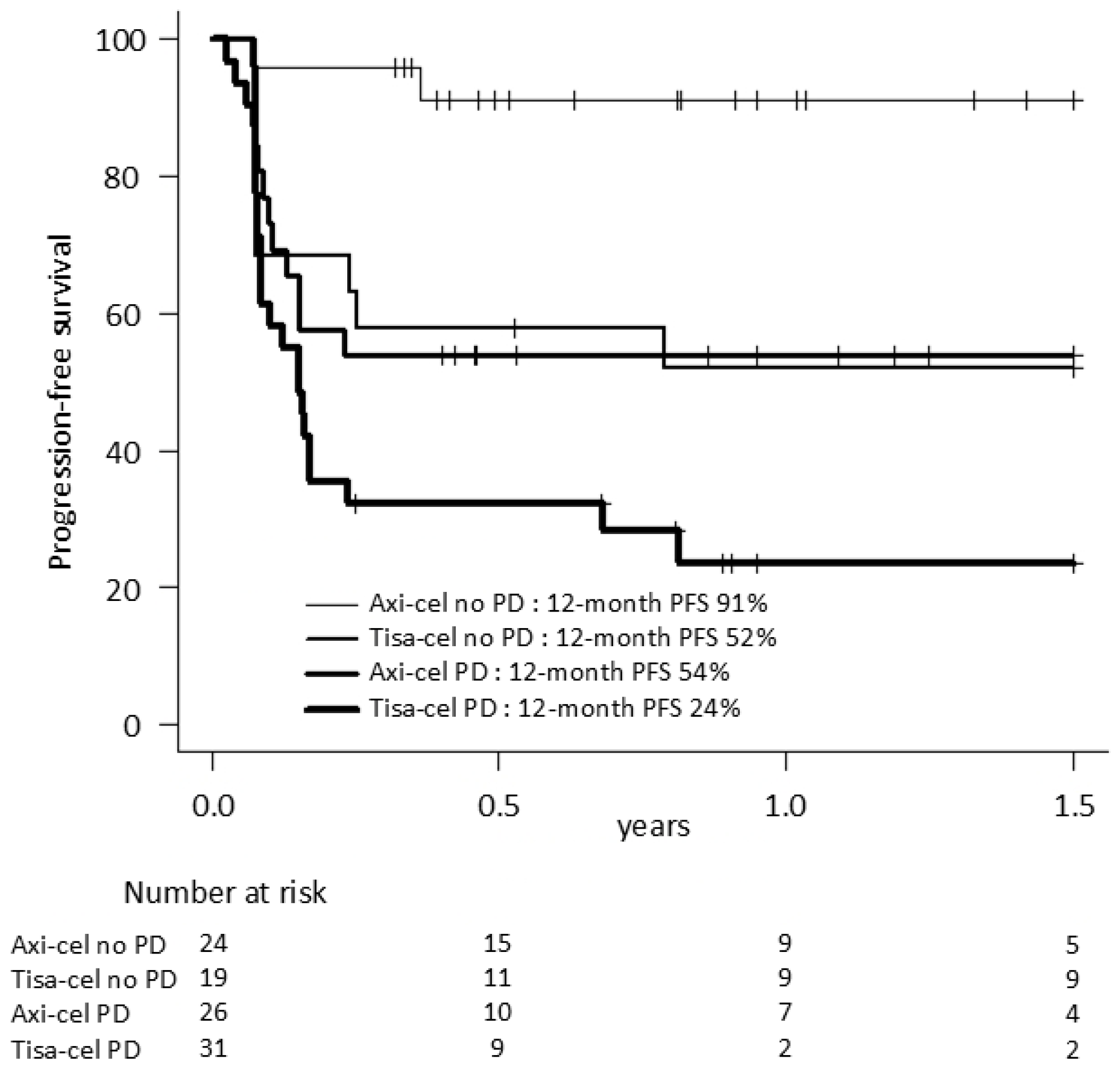
| 12-month PFS (95% CI) | 53% (42–61) | 72% (57–82) * | 35% (22–48) * | 59% (34–77) | 60% (44–72) | 35% (16–55) |
| Median OS, mo | 26.0 (17.3-NR) | NR | 22.2 (7.0-NE) | 37.2 (8.2-NE) † | NR † | 12.5 (3.4–26.0) † |
| 12-month OS (95% CI) | 69% (58–77) | 82% (68–91) | 57% (42–70) | 74% (48–88) † | 79% (63–88) † | 52% (31–69) † |
| Safety Outcome | All Patients N = 100 | Axi-cel N = 50 | Tisa-cel N = 50 | No BT N = 20 | RBT N = 48 | SBT N = 32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRS, % | ||||||
| Any grade | 79 | 92 * | 66 * | 85 | 77 | 78 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 13 |
| ICANS, % | ||||||
| Any grade | 33 | 56 * | 10 * | 15 † | 27 † | 53 † |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 16 | 28 * | 4 * | 5 | 15 | 25 |
| ICU transfer within 30 days, % | 26 | 32 | 20 | 5 | 27 | 38 |
| Grade ≥ 3 at 1 month, % Neutropenia Anemia Thrombopenia | 42 20 31 | 65 * 27 45 * | 18 * 14 16 * | 25 † 0 † 15 † | 33 † 15 † 19 † | 67 † 43 † 60 † |
| Grade ≥ 3 at 3 months, % Neutropenia Anemia Thrombopenia | 17 4 10 | 29 * 7 11 | 3 * 0 8 | 29 0 0 † | 12 2 7 † | 18 9 23 † |
| NRM at 3 months | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 † | 0 † | 13 † |
| Clinical Variable | Progression Free Survival | Overall Survival | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | 95% CI | |
| Tisa-cel (vs. axi-cel) | 4.10 | 1.95–8.62 | <0.01 | 1.98 | 0.89–4.41 | 0.10 |
| Elevated LDH at apheresis | 5.69 | 1.72–18.82 | <0.01 | 6.17 | 1.40–27.18 | 0.02 |
| Stage III-IV at apheresis | 1.33 | 0.54–3.26 | 0.54 | 2.22 | 0.88–5.62 | 0.09 |
| RBT | 0.46 | 0.22–0.96 | 0.04 | 0.51 | 0.24–1.09 | 0.08 |
| PD at infusion | 2.13 | 1.04–4.35 | 0.04 | 2.07 | 0.96–4.45 | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laverdure, E.; Mollica, L.; Ahmad, I.; Cohen, S.; Lachance, S.; Veilleux, O.; Bernard, M.; Marchand, E.-L.; Delisle, J.-S.; Bernard, L.; et al. Enhancing CAR-T Efficacy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Radiation Bridging Therapy: A Real-World Single-Center Experience. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030173
Laverdure E, Mollica L, Ahmad I, Cohen S, Lachance S, Veilleux O, Bernard M, Marchand E-L, Delisle J-S, Bernard L, et al. Enhancing CAR-T Efficacy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Radiation Bridging Therapy: A Real-World Single-Center Experience. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030173
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaverdure, Eva, Luigina Mollica, Imran Ahmad, Sandra Cohen, Silvy Lachance, Olivier Veilleux, Maryse Bernard, Eve-Lyne Marchand, Jean-Sébastien Delisle, Lea Bernard, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing CAR-T Efficacy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Radiation Bridging Therapy: A Real-World Single-Center Experience" Current Oncology 32, no. 3: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030173
APA StyleLaverdure, E., Mollica, L., Ahmad, I., Cohen, S., Lachance, S., Veilleux, O., Bernard, M., Marchand, E.-L., Delisle, J.-S., Bernard, L., Boileau, M., Petrella, T., Pilon, S.-J., Bouchard, P., Roy, D.-C., Busque, L., & Fleury, I. (2025). Enhancing CAR-T Efficacy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Radiation Bridging Therapy: A Real-World Single-Center Experience. Current Oncology, 32(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030173







