Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
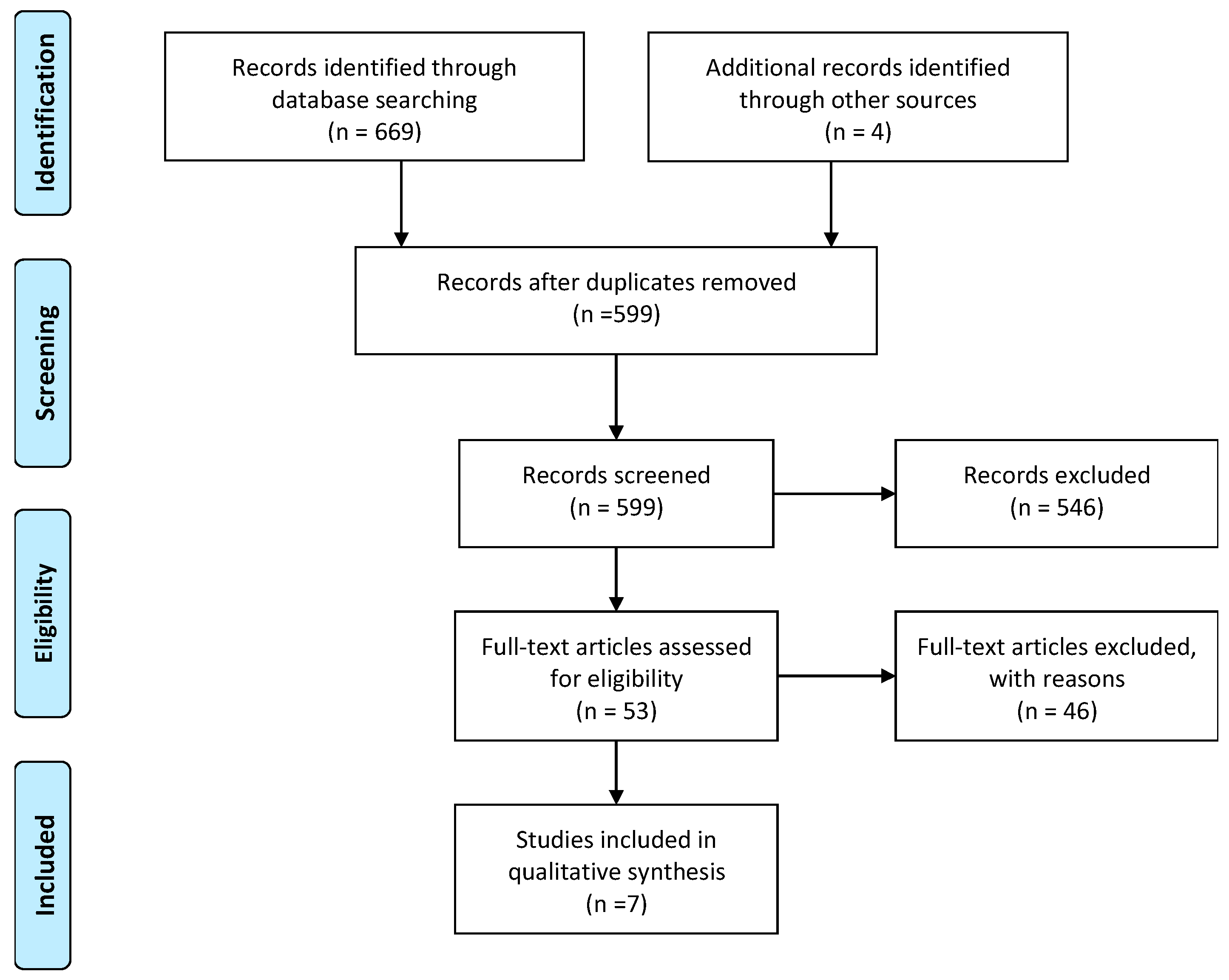
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Strategy
2.2. Study Identification
3. Mesothelioma
3.1. Predictive Factors and Prognosis
3.2. Therapeutic Interventions
3.3. Main Disabling Sequelae
4. Quality of Life and Rehabilitative Interventions
4.1. Quality of Life, Functioning, and Disability in MPM Patients
4.2. Respiratory Interventions
4.3. Physical Exercise Interventions
4.4. Psychological Interventions
4.5. Pain Management
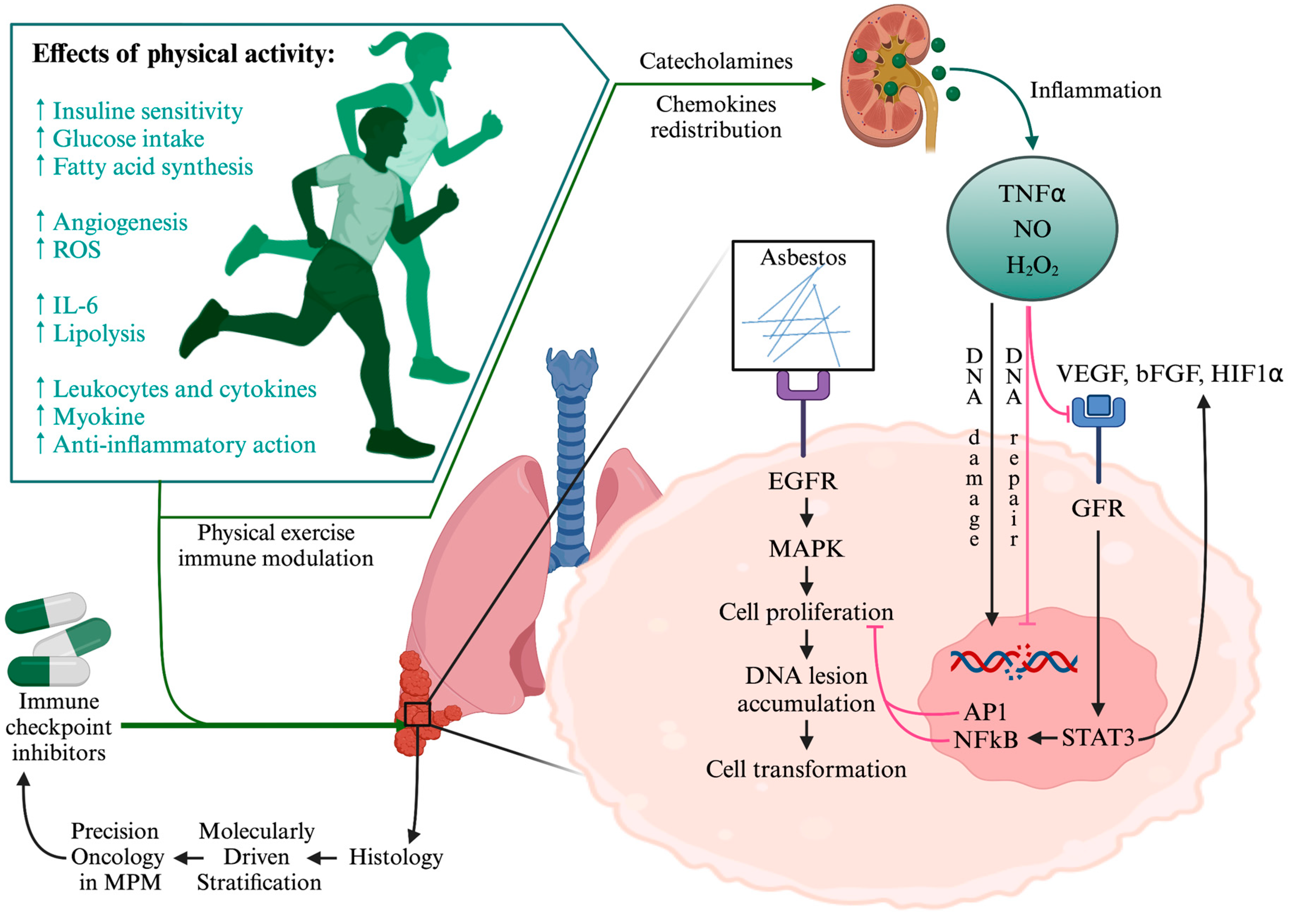
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. Tailored Multidisciplinary Rehabilitative Interventions
5.2. Possible Synergism between Physical Exercise, Immune System, and Immunotherapy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibby, A.C.; Tsim, S.; Kanellakis, N.; Ball, H.; Talbot, D.C.; Blyth, K.G.; Maskell, N.A.; Psallidas, I. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: An update on investigation, diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, M.; Rizzo, P.; Bononi, I.; Clementz, A.; Ferrari, R.; Martini, F.; Tognon, M.G. New Perspectives on Diagnosis and Therapy of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, I. Management of malignant pleural mesothelioma-The European experience. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6 (Suppl. S2), S238–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bille, A.; Okiror, L.; Harling, L.; Pernazza, F.; Muzio, A.; Roveta, A.; Grosso, F. Analysis of survival of patients with metastatic malignant pleural mesothelioma. Tumori J. 2021, 107, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solli, P.; Brandolini, J.; Pardolesi, A.; Nardini, M.; Lacava, N.; Parri, S.F.; Kawamukai, K.; Bonfanti, B.; Bertolaccini, L. Diaphragmatic and pericardial reconstruction after surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S298–S303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, F.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Zucchetti, M.; Ibrahim, T.; Tamberi, S.; Matteo, C.; Rulli, E.; Comandini, D.; Palmerini, E.; Baldi, G.G.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and activity of trabectedin as first-line treatment in elderly patients who are affected by advanced sarcoma and are unfit to receive standard chemotherapy: A phase 2 study (TR1US study) from the Italian Sarcoma Group. Cancer 2020, 126, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxas, Y.; Fruh, M.; Eboulet, E.I.; Grosso, F.; Pless, M.; Zucali, P.A.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Mark, M.; Schneider, M.; Maconi, A.; et al. Lurbinectedin as second- or third-line palliative therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: An international, multi-centre, single-arm, phase II trial (SAKK 17/16). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoglio, P.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Chella, A.; Aprile, V.; Dini, P.; Korasidis, S.; Fanucchi, O.; Mussi, A. Is less also better? A single-institution experience on treatment of early stage Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, F.; Roveta, A.; Gallizzi, G.; Belletti, M. Management of recurrent pleural mesothelioma: Successful rechallenge with nintedanib in combination with chemotherapy. Clin. Case Rep. 2018, 6, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, V.; Lenzini, A.; Lococo, F.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Mastromarino, M.G.; Guglielmi, G.; Palmiero, G.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: The Forefront of Surgery-Based Multimodality Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Zucali, P.A.; Favaretto, A.G.; Grossi, F.; Bidoli, P.; Del Conte, G.; Ceribelli, A.; Bearz, A.; Morenghi, E.; Cavina, R.; et al. Phase II study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; O’Brien, M.E.; Stahel, R.A.; Nackaerts, K.; Baas, P.; Karthaus, M.; Eberhardt, W.; Paz-Ares, L.; Sundstrom, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Pemetrexed plus cisplatin or pemetrexed plus carboplatin for chemonaïve patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results of the International Expanded Access Program. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.A.; Aerts, J.G.; Popat, S.; Fennell, D.A. Novel insights into mesothelioma biology and implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintoul, R.C.; Ritchie, A.J.; Edwards, J.G.; Waller, D.A.; Coonar, A.S.; Bennett, M.; Lovato, E.; Hughes, V.; Fox-Rushby, J.A.; Sharples, L.D.; et al. Efficacy and cost of video-assisted thoracoscopic partial pleurectomy versus talc pleurodesis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MesoVATS): An open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, T.; Lang-Lazdunski, L.; Waller, D.; Bliss, J.M.; Tan, C.; Entwisle, J.; Snee, M.; O’Brien, M.; Thomas, G.; Senan, S.; et al. Extra-pleural pneumonectomy versus no extra-pleural pneumonectomy for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Clinical outcomes of the Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery (MARS) randomised feasibility study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.G. Surgical resection of mesothelioma: An evidence-free practice. Lancet 2014, 384, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherpereel, A.; Astoul, P.; Baas, P.; Berghmans, T.; Clayson, H.; de Vuyst, P.; Dienemann, H.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Hennequin, C.; Hillerdal, G.; et al. Guidelines of the European Respiratory Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Lenzini, A.; Aprile, V.; Alì, G.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. New Insights in Pleural Mesothelioma Classification Update: Diagnostic Traps and Prognostic Implications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Kanodia, S.; Chao, A.; Miller, A.; Wali, A.; Weissman, D.; Adjei, A.; Baumann, F.; Boffetta, P.; Buck, B.; et al. Consensus Report of the 2015 Weinman International Conference on Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1246–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruti, P.; Lonni, S.; Baglivo, F.; Marchetti, G. Endoscopic diagnosis and management of pleural effusion in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S269–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brims, F.J.; Davies, H.E.; Lee, Y.C. Respiratory chest pain: Diagnosis and treatment. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 94, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.; Darlison, L.; Tod, A.M. Living with mesothelioma. A literature review. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2010, 19, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, M.; Kim, J.; Fusco, N. Editorial: Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients and Survivors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 620574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, M.; de Sire, A.; Lippi, L.; Venetis, K.; Sajjadi, E.; Gimigliano, F.; Gennari, A.; Criscitiello, C.; Cisari, C.; Fusco, N. Impact of Rehabilitation on Breast Cancer Related Fatigue: A Pilot Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 556718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, M.; Staerkind, M.; Christensen, J.; Vibe-Petersen, J.; Larsen, K.; Pedersen, J.; Langberg, H. Effect of postsurgical rehabilitation programmes in patients operated for lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, D.; Beckenkamp, P.R.; Hancock, M.; Solomon, M.; Young, J. Preoperative exercise halves the postoperative complication rate in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review of the effect of exercise on complications, length of stay and quality of life in patients with cancer. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Grosso, F.; Zucali, P.A.; Mencoboni, M.; Pasello, G.; Ripa, C.; Degiovanni, D.; Simonelli, M.; Bruzzone, A.; Dipietrantonj, C.; et al. Prognostic factors in elderly patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results of a multicenter survey. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadota, K.; Suzuki, K.; Colovos, C.; Sima, C.S.; Rusch, V.W.; Travis, W.D.; Adusumilli, P.S. A nuclear grading system is a strong predictor of survival in epitheloid diffuse malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D.; Sahmoud, T.; Therasse, P.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Postmus, P.E.; Giaccone, G. Prognostic factors in patients with pleural mesothelioma: The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, J.E.; Green, M.R.; Chahinian, A.P.; Corson, J.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Vogelzang, N.J. Factors predictive of survival among 337 patients with mesothelioma treated between 1984 and 1994 by the Cancer and Leukemia Group, B. Chest 1998, 113, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brims, F.J.; Meniawy, T.M.; Duffus, I.; de Fonseka, D.; Segal, A.; Creaney, J.; Maskell, N.; Lake, R.A.; de Klerk, N.; Nowak, A.K. A Novel Clinical Prediction Model for Prognosis in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Using Decision Tree Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.P. Prognostic factors in mesothelioma. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.G.; Faux, S.P.; Plummer, S.M.; Abrams, K.R.; Walker, R.A.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a novel prognostic factor in malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brosseau, S.; Danel, C.; Scherpereel, A.; Mazières, J.; Lantuejoul, S.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Gounant, V.; Antoine, M.; et al. Shorter Survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Patients with High PD-L1 Expression Associated with Sarcomatoid or Biphasic Histology Subtype: A Series of 214 Cases from the Bio-MAPS Cohort. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e564–e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levallet, G.; Vaisse-Lesteven, M.; Le Stang, N.; Ilg, A.G.; Brochard, P.; Astoul, P.; Pairon, J.C.; Bergot, E.; Zalcman, G.; Galateau-Sallé, F. Plasma cell membrane localization of c-MET predicts longer survival in patients with malignant mesothelioma: A series of 157 cases from the MESOPATH Group. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucali, P.A.; Giovannetti, E.; Destro, A.; Mencoboni, M.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Gianoncelli, L.; Lorenzi, E.; De Vincenzo, F.; Simonelli, M.; Perrino, M.; et al. Thymidylate synthase and excision repair cross-complementing group-1 as predictors of responsiveness in mesothelioma patients treated with pemetrexed/carboplatin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.W.; Creaney, J.; Lake, R.; Nowak, A.; Musk, A.W.; de Klerk, N.; Winzell, P.; Hellstrom, K.E.; Hellstrom, I. Mesothelin-family proteins and diagnosis of mesothelioma. Lancet 2003, 362, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Laszik, Z.G.; Lerner, M.; Raffeld, M.; Postier, R.; Brackett, D. Mesothelin is overexpressed in pancreaticobiliary adenocarcinomas but not in normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Bera, T.K.; Willingham, M.C.; Onda, M.; Hassan, R.; FitzGerald, D.; Pastan, I. Mesothelin expression in human lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, F.; Flores, E.; Napolitano, A.; Kanodia, S.; Taioli, E.; Pass, H.; Yang, H.; Carbone, M. Mesothelioma patients with germline BAP1 mutations have 7-fold improved long-term survival. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounant, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauderer, M.G.; Kass, S.L.; Woo, K.; Sima, C.S.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Krug, L.M. Vinorelbine and gemcitabine as second- or third-line therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.; Zucali, P.A.; Pagano, M.; Grosso, F.; Pasello, G.; Garassino, M.C.; Tiseo, M.; Parra, H.S.; Grossi, F.; Cappuzzo, F.; et al. Randomized phase II study on gemcitabine with or without ramucirumab as second-line treatment for advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM): Results of Italian Rames Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 22, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.; Fennell, D.A.; Ewings, S.; Ottensmeier, C.; Califano, R.; Hanna, G.G.; Hill, K.; Danson, S.; Steele, N.; Nye, M.; et al. Nivolumab versus placebo in patients with relapsed malignant mesothelioma (CONFIRM): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, I.; Bishop, L.; Darlison, L.; De Fonseka, D.; Edey, A.; Edwards, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Fennell, D.A.; Holmes, S.; Kerr, K.M.; et al. British Thoracic Society Guideline for the investigation and management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorax 2018, 73, i1–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, R.J.; Whiting, C.; Cowan, K.; James Lind Alliance Mesothelioma Priority Setting Partnership Steering Committee. Research priorities in mesothelioma: A James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnership. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Okada, M.; Tanaka, F.; Yamanaka, T.; Soejima, T.; Kamikonya, N.; Tsujimura, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Yokoi, K.; Nakano, T. Trimodality strategy for treating malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results of a feasibility study of induction pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and postoperative hemithoracic radiation (Japan Mesothelioma Interest Group 0601 Trial). Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 21, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, R.A.; Riesterer, O.; Xyrafas, A.; Opitz, I.; Beyeler, M.; Ochsenbein, A.; Früh, M.; Cathomas, R.; Nackaerts, K.; Peters, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and extrapleural pneumonectomy of malignant pleural mesothelioma with or without hemithoracic radiotherapy (SAKK 17/04): A randomised, international, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asciak, R.; George, V.; Rahman, N.M. Update on biology and management of mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.M.; Pepperell, J.; Rehal, S.; Saba, T.; Tang, A.; Ali, N.; West, A.; Hettiarachchi, G.; Mukherjee, D.; Samuel, J.; et al. Effect of Opioids vs NSAIDs and Larger vs Smaller Chest Tube Size on Pain Control and Pleurodesis Efficacy among Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion: The TIME1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.E.; Mishra, E.K.; Kahan, B.C.; Wrightson, J.M.; Stanton, A.E.; Guhan, A.; Davies, C.W.; Grayez, J.; Harrison, R.; Prasad, A.; et al. Effect of an indwelling pleural catheter vs chest tube and talc pleurodesis for relieving dyspnea in patients with malignant pleural effusion: The TIME2 randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 307, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Fysh, E.T.H.; Smith, N.A.; Lee, P.; Kwan, B.C.H.; Yap, E.; Horwood, F.C.; Piccolo, F.; Lam, D.C.L.; Garske, L.A.; et al. Effect of an Indwelling Pleural Catheter vs Talc Pleurodesis on Hospitalization Days in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion: The AMPLE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmy, T.L.; Gu, L.; Burkhalter, J.E.; Toloza, E.M.; D’Amico, T.A.; Sutherland, S.; Wang, X.; Archer, L.; Veit, L.J.; Kohman, L.; et al. Optimal management of malignant pleural effusions (results of CALGB 30102). J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2012, 10, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.; Rusch, V.; Pass, H.; Asamura, H.; Nakano, T.; Edwards, J.; Giroux, D.J.; Hasegawa, S.; Kernstine, K.H.; Waller, D.; et al. Recommendations for uniform definitions of surgical techniques for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A consensus report of the international association for the study of lung cancer international staging committee and the international mesothelioma interest group. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Darlison, L.; Edwards, J.; Elliott, D.; Fennell, D.A.; Popat, S.; Rintoul, R.C.; Waller, D.; Ali, C.; Bille, A.; et al. Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery 2 (MARS 2): Protocol for a multicentre randomised trial comparing (extended) pleurectomy decortication versus no (extended) pleurectomy decortication for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, S.; Can, G.; Aydiner, A.; Ozdilli, K.; Durna, Z. Quality of life, symptom experience and distress of lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2010, 14, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, C.L.; McDonald, C.F.; Irving, L.; Clark, R.A.; Gough, K.; Murnane, A.; Mileshkin, L.; Krishnasamy, M.; Denehy, L. Low physical activity levels and functional decline in individuals with lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasymjanova, G.; Correa, J.A.; Kreisman, H.; Dajczman, E.; Pepe, C.; Dobson, S.; Lajeunesse, L.; Sharma, R.; Small, D. Prognostic value of the six-minute walk in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmucci, F.; Franzoi, I.G.; Bonafede, M.; Borgogno, F.V.; Grosso, F.; Granieri, A. “The Less I Think About It, the Better I Feel”: A Thematic Analysis of the Subjective Experience of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients and Their Caregivers. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, R.; Connaghan, J.; Arber, A.; Klepacz, N.; Blyth, K.G.; McPhelim, J.; Murray, P.; Rupani, H.; Chauhan, A.; Williams, P.; et al. Advanced Symptom Management System for Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (ASyMSmeso): Mixed Methods Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.M.; Lieberman-Cribbin, W.; Wolf, A.; Flores, R.M.; Taioli, E. Systematic review of quality of life following pleurectomy decortication and extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamichi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakamura, A.; Kuroda, A.; Tanaka, T.; Takeuchi, J.; Matsumoto, S.; Morimoto, T.; Kondo, N.; Domen, K.; et al. Quality of life and lung function after pleurectomy/decortication for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Interact. CardioVasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 33, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollen, P.J.; Gralla, R.J.; Liepa, A.M.; Symanowski, J.T.; Rusthoven, J.J. Adapting the Lung Cancer Symptom Scale (LCSS) to mesothelioma: Using the LCSS-Meso conceptual model for validation. Cancer 2004, 101, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoon, S.N.; Lawrie, I.; Qi, C.; Rahman, N.; Maskell, N.; Forbes, K.; Gerry, S.; Monterosso, L.; Chauhan, A.; Brims, F.J.H. Symptom Burden and Unmet Needs in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Exploratory Analyses from the RESPECT-Meso Study. J. Palliat. Care 2021, 36, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruit, M.A.; Singh, S.J.; Garvey, C.; ZuWallack, R.; Nici, L.; Rochester, C.; Hill, K.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Man, W.D.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Key concepts and advances in pulmonary rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, e13–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, C.; Grosbois, J.M.; Cortot, A.B.; Peres, S.; Heron, C.; Delourme, J.; Gierczynski, M.; Hoorelbeke, A.; Scherpereel, A.; Le Rouzic, O. Real-life feasibility of home-based pulmonary rehabilitation in chemotherapy-treated patients with thoracic cancers: A pilot study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, E.; Lee, Y.C.G.; Newton, R.U.; Lyons-Wall, P.; McVeigh, J.; Nowak, A.K.; Cheah, H.M.; Nguyen, B.; Fitzgerald, D.B.; Creaney, J.; et al. Body composition and nutritional status in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Implications for activity levels and quality of life. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.W.S.; Musk, A.W.; Lake, R.A. Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet 2005, 366, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Vardy, J.; Harvie, R.; Chatfield, M.; van Zandwijk, N.; Clarke, S.; Pavlakis, N. Health-related quality of life and inflammatory markers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, M.; Lippi, L.; Folli, A.; Turco, A.; Zattoni, L.; Maconi, A.; de Sire, A.; Fusco, N. Integrating molecular biomarkers in breast cancer rehabilitation. What is the current evidence? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 930361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrillo, M.; Migliario, M.; Marotta, N.; Lippi, L.; Antonelli, A.; Calafiore, D.; Ammendolia, V.; Fortunato, L.; Renò, F.; Giudice, A.; et al. Oral Health in Breast Cancer Women with Vitamin D Deficiency: A Machine Learning Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uster, A.; Ruehlin, M.; Mey, S.; Gisi, D.; Knols, R.; Imoberdorf, R.; Pless, M.; Ballmer, P.E. Effects of nutrition and physical exercise intervention in palliative cancer patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, L.; de Sire, A.; Mezian, K.; Curci, C.; Perrero, L.; Turco, A.; Andaloro, S.; Ammendolia, A.; Fusco, N.; Invernizzi, M. Impact of exercise training on muscle mitochondria modifications in older adults: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 1495–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, L.; de Sire, A.; Folli, A.; Turco, A.; Moalli, S.; Marcasciano, M.; Ammendolia, A.; Invernizzi, M. Obesity and Cancer Rehabilitation for Functional Recovery and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilonen, I.K.; Rasanen, J.V.; Sihvo, E.I.; Knuuttila, A.; Sovijarvi, A.R.; Sintonen, H.; Salo, J.A. Pneumonectomy: Post-operative quality of life and lung function. Lung Cancer 2007, 58, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.N.; da Silva, R.A.; Gross, J.L.; Deheinzelin, D.; Negri, E.M. Assessment of pulmonary function and quality of life in patients submitted to pulmonary resection for cancer. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marulli, G.; Rea, F.; Nicotra, S.; Favaretto, A.G.; Perissinotto, E.; Chizzolini, M.; Vianello, A.; Braccioni, F. Effect of induction chemotherapy on lung function and exercise capacity in patients affected by malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2010, 37, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Baldi, A.; Schillaci, O.; Mineo, T.C. Clinical impact of extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, J.; Fukushima, T.; Tanaka, T.; Fu, J.B.; Morishita, S. Physical function predicts mortality in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 5623–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Fusco, N.; Sajjadi, E.; Lippi, L.; Cisari, C.; Invernizzi, M. Lymphedema Rehabilitation Using Self-Adaptive Inelastic Compression in Breast Cancer: A Proof-of-Principle Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sire, A.; Invernizzi, M.; Lippi, L.; Cisari, C.; Ozcakar, L.; Franchignoni, F. Blurred lines between axillary web syndrome and Mondor’s disease after breast cancer surgery: A case report. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Losco, L.; Cisari, C.; Gennari, A.; Boldorini, R.; Fusco, N.; Cigna, E.; Invernizzi, M. Axillary web syndrome in women after breast cancer surgery referred to an Oncological Rehabilitation Unit: Which are the main risk factors? A retrospective case-control study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8028–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Losco, L.; Cigna, E.; Lippi, L.; Gimigliano, F.; Gennari, A.; Cisari, C.; Chen, H.; Fusco, N.; Invernizzi, M. Three-dimensional laser scanning as a reliable and reproducible diagnostic tool in breast cancer related lymphedema rehabilitation: A proof-of-principle study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 4476–4485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muruganandan, S.; Jeffery, E.; McIntyre, C.; Lee, Y.C. Nutrition, exercise, and complementary medicine: Potential role in mesothelioma? Curr. Pulmonol. Rep. 2016, 5, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Morishita, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakamichi, T.; Uchiyama, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Domen, K. Physical function and health-related quality of life in the convalescent phase in surgically treated patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 4107–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Morishita, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Itani, Y.; Mabuchi, S.; Kodama, N.; Hasegawa, S.; Domen, K. Physical function and health-related quality of life in patients undergoing surgical treatment for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Support. Care Cancer 2017, 25, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Rice, S.J.; Belani, C.P. Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Lung Cancer. PM&R 2016, 8, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, M.; Corner, J.; Krishnasamy, M.; Plant, H.; Bailey, C.; A’Hern, R. Multicentre randomised controlled trial of nursing intervention for breathlessness in patients with lung cancer. BMJ 1999, 318, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hately, J.; Laurence, V.; Scott, A.; Baker, R.; Thomas, P. Breathlessness clinics within specialist palliative care settings can improve the quality of life and functional capacity of patients with lung cancer. Palliat. Med. 2003, 17, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, R.; English, A.; Nabb, S.; Rigby, A.S.; Johnson, M.J. A randomised trial of high vs low intensity training in breathing techniques for breathless patients with malignant lung disease: A feasibility study. Lung Cancer 2010, 70, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.J.; Kanaan, M.; Richardson, G.; Nabb, S.; Torgerson, D.; English, A.; Barton, R.; Booth, S. A randomised controlled trial of three or one breathing technique training sessions for breathlessness in people with malignant lung disease. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molassiotis, A.; Charalambous, A.; Taylor, P.; Stamataki, Z.; Summers, Y. The effect of resistance inspiratory muscle training in the management of breathlessness in patients with thoracic malignancies: A feasibility randomised trial. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 23, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzorno, M.; Desilvestri, M.; Lippi, L.; Marchioni, M.; Audo, A.; de Sire, A.; Invernizzi, M.; Perrero, L. Early cardiac rehabilitation: Could it improve functional outcomes and reduce length of stay and sanitary costs in patients aged 75 years or older? A retrospective case-control study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 33, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Lippi, L.; Aprile, V.; Calafiore, D.; Folli, A.; D’Abrosca, F.; Moalli, S.; Lucchi, M.; Ammendolia, A.; Invernizzi, M. Pharmacological, nutritional, and rehabilitative interventions to improve the complex management of osteoporosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A narrative review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, E.L.; Reid, W.D.; Crowe, J.; O’Brien, K.; Brooks, D. Inspiratory muscle training in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 1440–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, M.; de Sire, A.; D’Andrea, F.; Carrera, D.; Reno, F.; Migliaccio, S.; Iolascon, G.; Cisari, C. Effects of essential amino acid supplementation and rehabilitation on functioning in hip fracture patients: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Baricich, A.; Reno, F.; Cisari, C.; Fusco, N.; Invernizzi, M. Myostatin as a potential biomarker to monitor sarcopenia in hip fracture patients undergoing a multidisciplinary rehabilitation and nutritional treatment: A preliminary study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, P.B.; Phillips, K.M.; Jim, H.S.L.; Small, B.J.; Faul, L.A.; Meade, C.D.; Thompson, L.; Williams, C.C.; Loftus, L.S.; Fishman, M.; et al. Effects of self-directed stress management training and home-based exercise on quality of life in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: A randomized controlled trial. Psycho Oncol. 2013, 22, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.; Hussain, A.; Maddocks, M.; Wilcock, A. Occupational therapy needs of patients with thoracic cancer at the time of diagnosis: Findings of a dedicated rehabilitation service. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 21, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayly, J.; Fettes, L.; Douglas, E.; Teixiera, M.J.; Peat, N.; Tunnard, I.; Patel, V.; Gao, W.; Wilcock, A.; Higginson, I.J.; et al. Short-term integrated rehabilitation for people with newly diagnosed thoracic cancer: A multi-centre randomized controlled feasibility trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonafede, M.; Granieri, A.; Binazzi, A.; Mensi, C.; Grosso, F.; Santoro, G.; Franzoi, I.G.; Marinaccio, A.; Guglielmucci, F. Psychological Distress after a Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma in a Group of Patients and Caregivers at the National Priority Contaminated Site of Casale Monferrato. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherborne, V.; Seymour, J.; Taylor, B.; Tod, A. What are the psychological effects of mesothelioma on patients and their carers? A scoping review. Psychooncology 2020, 29, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventafridda, V.; Tamburini, M.; Caraceni, A.; De Conno, F.; Naldi, F. A validation study of the WHO method for cancer pain relief. Cancer. 1987, 59, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiffen, P.J.; Wee, B.; Derry, S.; Bell, R.F.; Moore, R.A. Opioids for cancer pain—An overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD012592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinkler, M.; Royston, R.; Kendall, C. Palliative care for patients with mesothelioma. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 78, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, A.; Hanks, G.; Kaasa, S.; Bennett, M.I.; Brunelli, C.; Cherny, N.; Dale, O.; De Conno, F.; Fallon, M.; Hanna, M.; et al. Use of opioid analgesics in the treatment of cancer pain: Evidence-based recommendations from the EAPC. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e58–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, L.E.; Wiffen, P.J.; Moore, R.A.; Gilron, I. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 7, CD008943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.R.; Tan, L.; Ball, D.L. Radiotherapy in the treatment of malignant mesothelioma of the pleura, with special reference to its use in palliation. Australas. Radiol. 1994, 38, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, D.; Macbeth, F.R.; Cram, I. The role of palliative radiotherapy in malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 3, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clive, A.O.; Taylor, H.; Dobson, L.; Wilson, P.; de Winton, E.; Panakis, N.; Pepperell, J.; Howell, T.; Stewart, S.A.; Penz, E.; et al. Prophylactic radiotherapy for the prevention of procedure-tract metastases after surgical and large-bore pleural procedures in malignant pleural mesothelioma (SMART): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Perrot, M.; Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Cho, B.C.J. Radiotherapy for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e532–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Neville, E. Lung cancer * 8: Management of malignant mesothelioma. Thorax 2003, 58, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- France, B.D.; Lewis, R.A.; Sharma, M.L.; Poolman, M. Cordotomy in mesothelioma-related pain: A systematic review. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2014, 4, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernetti, A.; Agostini, F.; de Sire, A.; Mangone, M.; Tognolo, L.; Di Cesare, A.; Ruiu, P.; Paolucci, T.; Invernizzi, M.; Paoloni, M. Neuropathic Pain and Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review of International Guidelines. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudre, D.; Chen, Z.; Richard, A.; Cabaset, S.; Dehler, A.; Schmid, M.; Rohrmann, S. Multidisciplinary Outpatient Cancer Rehabilitation Can Improve Cancer Patients Physical and Psychosocial Status-a Systematic Review. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.E.; Watkins, D.; Ryan, C.; Priest, K.; Corbishley, C.; Norton, A.; Ashley, S.; Rowell, N.; Sayer, R. A randomised trial in malignant mesothelioma (M) of early (E) versus delayed (D) chemotherapy in symptomatically stable patients: The MED trial. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muers, M.F.; Stephens, R.J.; Fisher, P.; Darlison, L.; Higgs, C.M.B.; Lowry, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; O’Brien, M.; Peake, M.; Rudd, R.; et al. Active symptom control with or without chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MS01): A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Amatya, B.; Ng, L.; Demetrios, M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Turner-Stokes, L. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for follow-up of women treated for breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12, CD009553. [Google Scholar]
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 16, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.; Koga, K.; Chen, T.; Zhuo, M. Neuronal and microglial mechanisms for neuropathic pain in the spinal dorsal horn and anterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, M.C.; Prevost, A.T.; McCrone, P.; Brafman-Price, B.; Bentley, A.; Higginson, I.J.; Todd, C.; Booth, S. Is a specialist breathlessness service more effective and cost-effective for patients with advanced cancer and their carers than standard care? Findings of a mixed-method randomised controlled trial. BMC Med. 2014, 31, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Cancer and inflammation: An old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 677–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabutis, N.; Schally, A.V.; Siejka, A. P53, GHRH, inflammation and cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Pietrocola, F.; Kroemer, G. Nutrition, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.W. Biomarker-guided targeted and immunotherapies in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920971421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Kuribayashi, K.; Minami, T.; Ohmuraya, M.; Kijima, T. Epigenetic Alterations and Biomarkers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Current Standards and Future Perspectives in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 554570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetis, K.; Invernizzi, M.; Sajjadi, E.; Curigliano, G.; Fusco, N. Cellular immunotherapy in breast cancer: The quest for consistent biomarkers. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 90, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Dafni, U.; Shah, R.; O’Brien, M.; Pope, A.; Fisher, P.; Spicer, J.; Roy, A.; Gilligan, D.; et al. A multicentre randomised phase III trial comparing pembrolizumab versus single-agent chemotherapy for advanced pre-treated malignant pleural mesothelioma: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 9-15) PROMISE-meso trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1734–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Lesterhuis, W.J.; Kok, P.-S.; Brown, C.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Karikios, D.J.; John, T.; Kao, S.C.H.; Leslie, C.; Cook, A.M.; et al. Durvalumab with first-line chemotherapy in previously untreated malignant pleural mesothelioma (DREAM): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial with a safety run-in. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disselhorst, M.J.; Quispel-Janssen, J.; Lalezari, F.; Monkhorst, K.; de Vries, J.F.; van der Noort, V.; Harms, E.; Burgers, S.; Baas, P. Ipilimumab and nivolumab in the treatment of recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma (INITIATE): Results of a prospective, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmen Olofsson, G.; Jensen, A.W.P.; Idorn, M.; Thor Straten, P. Exercise Oncology and Immuno-Oncology; A (Future) Dynamic Duo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard-Barbash, R.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Siddiqi, S.M.; McTiernan, A.; Alfano, C.M. Physical activity, biomarkers, and disease outcomes in cancer survivors: A systematic review. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 815–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betof, A.S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Jones, L.W. Effects and potential mechanisms of exercise training on cancer progression: A translational perspective. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, S75–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; de Sire, A.; Arienti, C.; Patrini, M.; Negrini, S.; Ceravolo, M.G.; International Multiprofessional Steering Committee of Cochrane Rehabilitation REH-COVER action. Systematic rapid living review on rehabilitation needs due to COVID-19: Update to May 31st, 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, A.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Ferrillo, M.; Cobo-Vázquez, C.; Sanchez-Labrador, L.; Ammendolia, A.; Migliario, M.; de Sire, A. Type I Collagen-Based Devices to Treat Nerve Injuries after Oral Surgery Procedures. A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sire, A.; Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Patrini, M.; Ceravolo, M.G.; International Multiprofessional Steering Committee of Cochrane Rehabilitation REH-COVER Action. Rehabilitation and COVID-19: The Cochrane Rehabilitation 2020 rapid living systematic review. Update as of August 31st, 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sire, A.; Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; Patrini, M.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Ceravolo, M.G.; International Multiprofessional Steering Committee of Cochrane Rehabilitation REH-COVER Action. Rehabilitation and COVID-19: A rapid living systematic review by Cochrane Rehabilitation Field updated as of December 31st, 2020 and synthesis of the scientific literature of 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelwyn, G.J.; Wenneer, E.; Demaria, S.; Jones, L.W. Exercise in Regulation of Inflammation-Immune Axis Function in Cancer Initiation and Progression. Oncology 2015, 29, 908–920. [Google Scholar]

| Clinical Characteristics | Blood Test | Molecular Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Albumin | BAP1 |
| Cancer-Directed Surgery | Hemoglobin | COX-2 |
| Chemotherapy | LDH | EZH2 |
| Chest Pain | NLR | FGF-binders |
| Gender | PLT | MET |
| Histologic Diagnosis | WBC | PD-L1 |
| Histologic Type | SMRP | |
| Pleural Involvement | TSP-1 | |
| PS | VEGF | |
| Race | ||
| Stage | ||
| Weight Loss |
| Systemic Therapy | Radiotherapy | Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin and pemetrexed | Adjuvant | Talc pleurodesis |
| Carboplatin and pemetrexed | Palliative | EPP |
| Nivolumab and ipilimumab | PD | |
| Additional bevacizumab | EPD | |
| TTF | ||
| Ramucirumab and gemcitabine | ||
| Nivolumab |
| Fatigue | Early and Severe Symptom Burden |
|---|---|
| Significantly reduces HRQoL | |
| Cough | Impacts physical and social functioning |
| Dyspnea | Associated with worse overall HRQoL |
| Chest Pain | Negatively affects physical and emotional functioning |
| Lethargy | Leads to reduced activity levels |
| Contributes to poor HRQoL | |
| Weight Loss | Impairs physical health and HRQoL |
| Quality of Life, Functioning, and Disability in MPM Patients |
|---|
| 38% malnourished and 54% pre-sarcopenic |
| Malnutrition decreases HRQoL |
| Malnutrition increases mortality risk |
| Fatigue correlated with inflammatory markers; affects HRQoL and overall survival |
| Induction chemotherapy improves FEV1 and VO2 peak |
| Surgery (EPP) with adjuvant therapies shows mixed results on functional tests |
| Physical function metrics correlate with mortality |
| Respiratory interventions |
| Comprehensive intervention improves breathlessness, PS, physical/emotional states |
| Significant improvements in breathlessness, functional capacity, activity levels, distress, fatigue, emotional function, and depression |
| Three-session group showed potential benefits for breathlessness severity and distress |
| One session per week may be cost-effective in symptom management |
| Physical exercise interventions |
| Exercise and stress management improve anxiety and depression in chemotherapy patients |
| Home-based exercise improves 6MWT in the MPM subgroup |
| Early rehabilitative approach feasible and safe, potential HRQoL benefits |
| Early mobilization post-surgery shows potential benefits but lacks home-based intervention data |
| Psychological interventions |
| Significant burden of anxiety (19%) and depression (12.9%) in MPM patients |
| Supportive counseling/psychological support included in interventions |
| Pain management |
| WHO Analgesic Ladder is an effective framework; 95% of cancer patients find pain relief with opioids within 14 days |
| Radiotherapy is effective in pain management, especially with bone erosion/cutaneous involvement |
| Cordotomy is promising for pain relief, medication reduction, and sleep disturbances |
| Multidisciplinary approach needed, including psychoeducational and mind–body therapies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lippi, L.; de Sire, A.; Aprile, V.; Calafiore, D.; Folli, A.; Refati, F.; Balduit, A.; Mangogna, A.; Ivanova, M.; Venetis, K.; et al. Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 4318-4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080322
Lippi L, de Sire A, Aprile V, Calafiore D, Folli A, Refati F, Balduit A, Mangogna A, Ivanova M, Venetis K, et al. Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(8):4318-4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080322
Chicago/Turabian StyleLippi, Lorenzo, Alessandro de Sire, Vittorio Aprile, Dario Calafiore, Arianna Folli, Fjorelo Refati, Andrea Balduit, Alessandro Mangogna, Mariia Ivanova, Konstantinos Venetis, and et al. 2024. "Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review" Current Oncology 31, no. 8: 4318-4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080322
APA StyleLippi, L., de Sire, A., Aprile, V., Calafiore, D., Folli, A., Refati, F., Balduit, A., Mangogna, A., Ivanova, M., Venetis, K., Fusco, N., & Invernizzi, M. (2024). Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review. Current Oncology, 31(8), 4318-4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080322











