Modeling 5-FU-Induced Chemotherapy Selection of a Drug-Resistant Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culturing and Chemotherapy Treatment
2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Machine Learning Model (ML)–Genetic Algorithm (GA)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
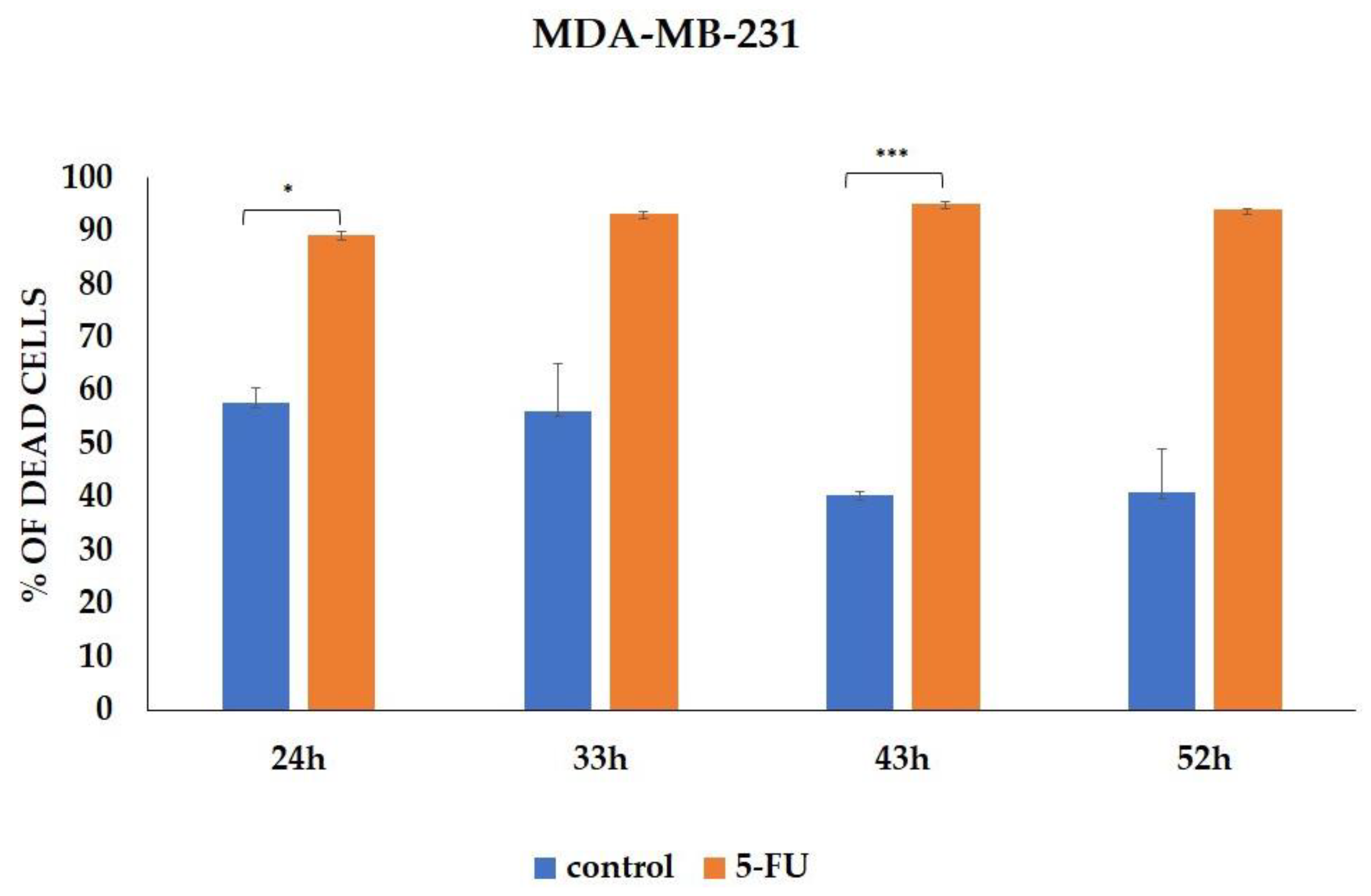
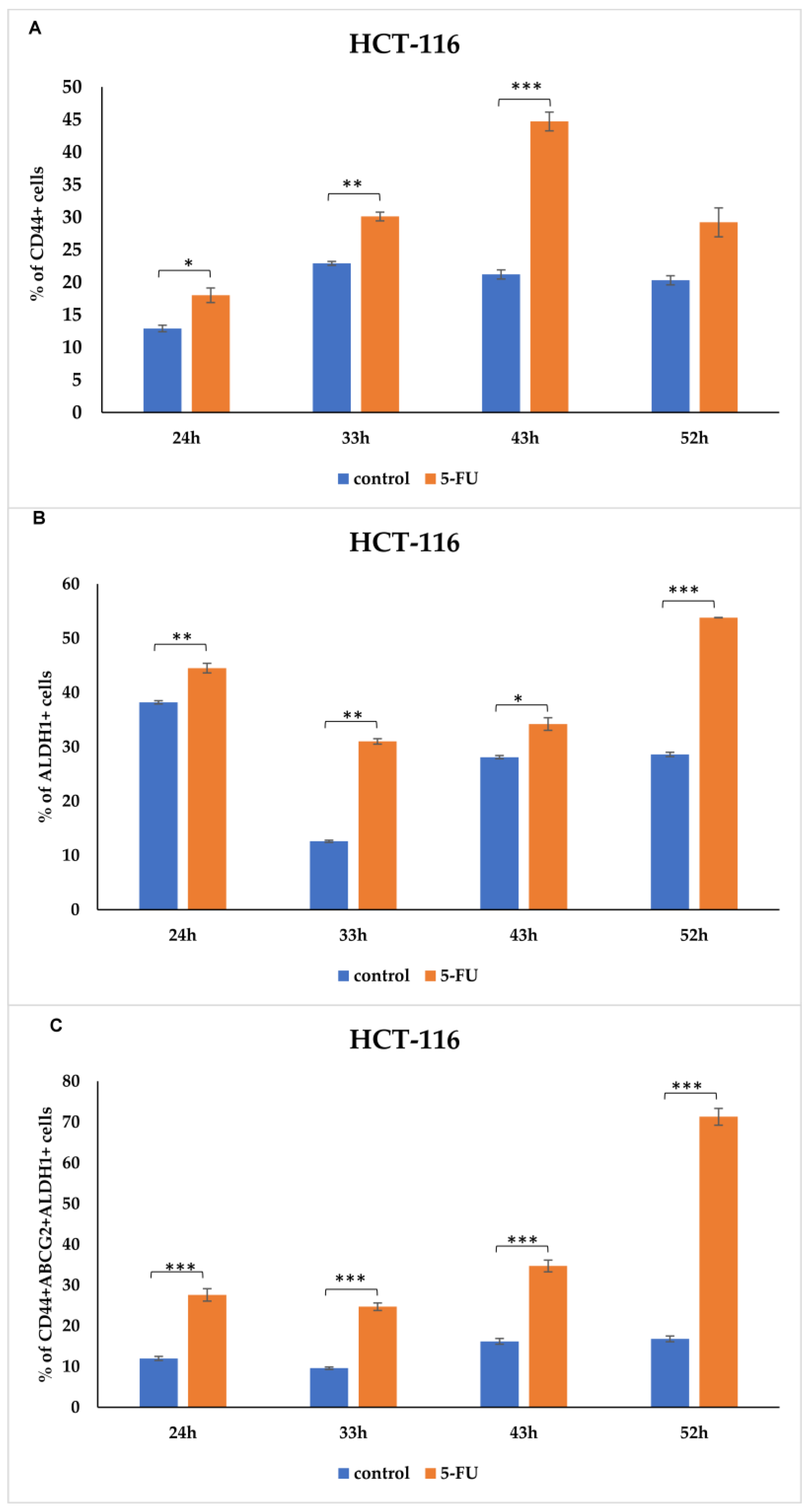
3.1. CSCs Markers Analyzed by Flow Cytometry
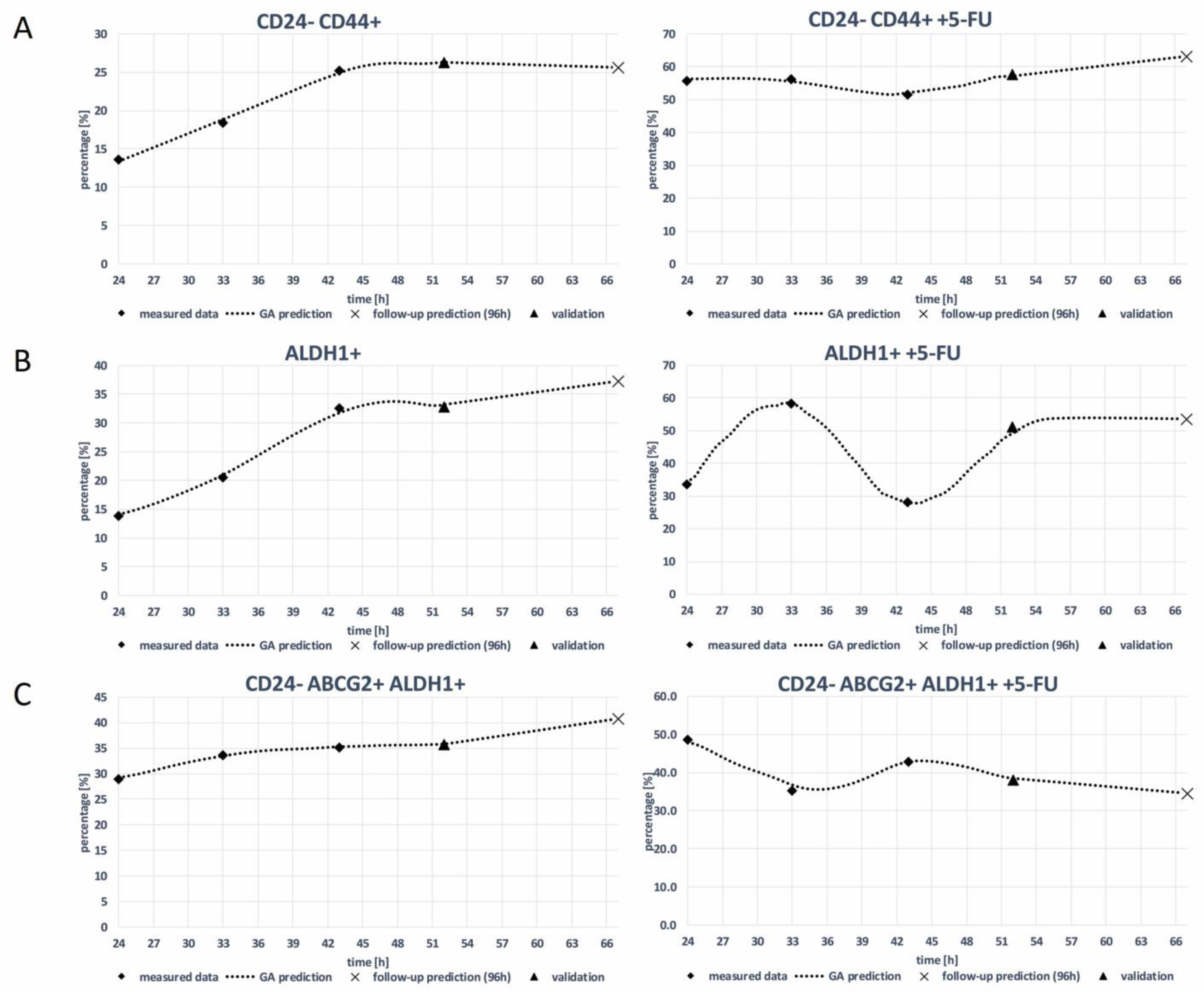
3.2. Genetic Algorithm (GA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enciso-Benavides, J.; Alfaro, L.; Castañeda-Altamirano, C.; Rojas, N.; González-Cabeza, J.; Enciso, N.; Riesco, F.; Castillo, M.; Enciso, J. Biological characteristics of a sub-population of cancer stem cells from two triple-negative breast tumour cell lines. Heliyon 2021, 10, e07273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 69, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Bai, Y.; Ngo, H.X.; Okui, T.; Kanno, T. Overview of Evidence-Based Chemotherapy for Oral Cancer: Focus on Drug Resistance Related to the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Biomolecules 2021, 16, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayatmand, H.; Razmkhah, M.; Razeghian-Jahromi, I. Drug resistance in cancer therapy: The Pandora’s Box of cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Hu, B. Mathematical modeling, and computational prediction of cancer drug resistance. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ajani, J.A.; Song, S. Drug resistance and Cancer stem cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.B.; Wei, W.Q.; Weeraratne, D.; Frisse, M.E.; Misulis, K.; Rhee, K.; Zhao, J.; Snowdon, J.L. Precision Medicine, AI, and the Future of Personalized Health Care. CTS-Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 14, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyanti, P.R.; Medema, J.P. Intra-tumor heterogeneity from a cancer stem cell perspective. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, C.J.; Chen, T.; González, I.; Cao, D.; Peng, Y. Cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer: A potential target and prognostic marker. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-Y.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.-G.; Liu, S.-L. Role of CD44(high)/CD133(high) HCT-116 cells in the tumorigenesis of colon cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7657–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.; Chen, M.; Baskaran, R.; Lin, Y.; Day, C.H.; Lin, Y.; Tu, C.; Padma, V.V.; Kuo, W.; Huang, C. Oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells is mediated via activation of ABCG2 to alleviate ER stress induced apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5458–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Song, X.; Xu, D.; Tiek, D.; Goenka, A.; Wu, B.; Sastry, N.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.-Y. Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics 2020, 9, 8721–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashzar, M.R.; Baharlou, R.; Karami, J.; Abdollahi, H.; Rezaei, R.; Pourramezan, F.; Moghaddam, S.H.Z. Cancer stem cells: A review from origin to therapeutic implications. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Srivastava, D.; Sahu, M.; Tiwari, S.; Ambasta, R.K.; Kumar, P. Artificial intelligence to deep learning: Machine intelligence approach for drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1315–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, R.; Islam, S.R.; Kazi, J.U. Machine learning in the prediction of cancer therapy. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4003–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Malviya, R.; Singh, A.K. Prediction of Cancer Treatment Using Advancements in Machine Learning. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.R. Riccardo Poli, William B. Langdon, Nicholas F. McPhee: A Field Guide to Genetic Programming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The different mechanisms of cancer drug resistance: A brief review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, L.; Kistenmacher, A.-K.; Suo, H.; Kitte, R.; Dluczek, S.; Strauß, A.; Blaudszun, A.-R.; Yevsa, T.; Fricke, S.; Kossatz-Boehlert, U. Cancer Stem Cells-Origins and Biomarkers: Perspectives for Targeted Personalized Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Model | R2—Score of the Prediction |
|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 CD24- CD44+ | 0.97 |
| MDA-MB-231 CD24- CD44+ + 5-FU | 0.98 |
| MDA-MB-231 ALDH1+ | 0.96 |
| MDA-MB-231 ALDH1+ + 5-FU | 0.98 |
| MDA-MB-231 CD24- ABCG2+ ALDH1+ | 0.95 |
| MDA-MB-231 CD24- ABCG2+ ALDH1+ + 5-FU | 0.96 |
| HCT-116 CD44+ | 0.97 |
| HCT-116 CD44+ + 5-FU | 0.97 |
| HCT-116 ALDH1+ | 0.98 |
| HCT-116 ALDH1+ + 5-FU | 0.93 |
| HCT-116 CD44+ ABCG2+ ALDH1+ | 0.96 |
| HCT-116 CD44+ ABCG2+ ALDH1+ + 5-FU | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramović Hamzagić, A.; Cvetković, D.; Gazdić Janković, M.; Milivojević Dimitrijević, N.; Nikolić, D.; Živanović, M.; Kastratović, N.; Petrović, I.; Nikolić, S.; Jovanović, M.; et al. Modeling 5-FU-Induced Chemotherapy Selection of a Drug-Resistant Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 1221-1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030091
Ramović Hamzagić A, Cvetković D, Gazdić Janković M, Milivojević Dimitrijević N, Nikolić D, Živanović M, Kastratović N, Petrović I, Nikolić S, Jovanović M, et al. Modeling 5-FU-Induced Chemotherapy Selection of a Drug-Resistant Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(3):1221-1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030091
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamović Hamzagić, Amra, Danijela Cvetković, Marina Gazdić Janković, Nevena Milivojević Dimitrijević, Dalibor Nikolić, Marko Živanović, Nikolina Kastratović, Ivica Petrović, Sandra Nikolić, Milena Jovanović, and et al. 2024. "Modeling 5-FU-Induced Chemotherapy Selection of a Drug-Resistant Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation" Current Oncology 31, no. 3: 1221-1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030091
APA StyleRamović Hamzagić, A., Cvetković, D., Gazdić Janković, M., Milivojević Dimitrijević, N., Nikolić, D., Živanović, M., Kastratović, N., Petrović, I., Nikolić, S., Jovanović, M., Šeklić, D., Filipović, N., & Ljujić, B. (2024). Modeling 5-FU-Induced Chemotherapy Selection of a Drug-Resistant Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation. Current Oncology, 31(3), 1221-1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030091







