Biomarker Turnaround Times and Impact on Treatment Decisions in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma at a Large Canadian Community Hospital with an Affiliated Regional Cancer Centre
Abstract
1. Introduction
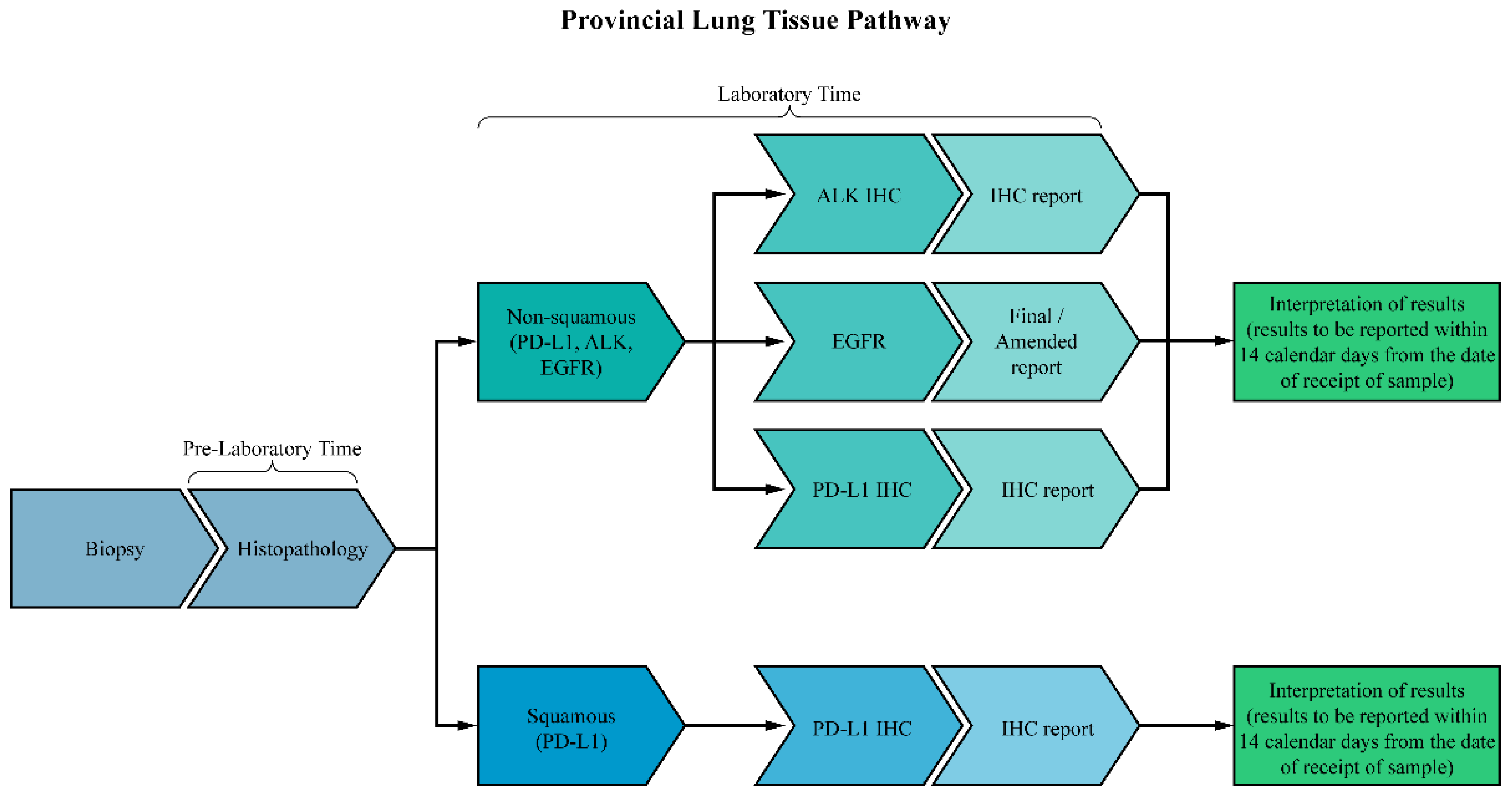
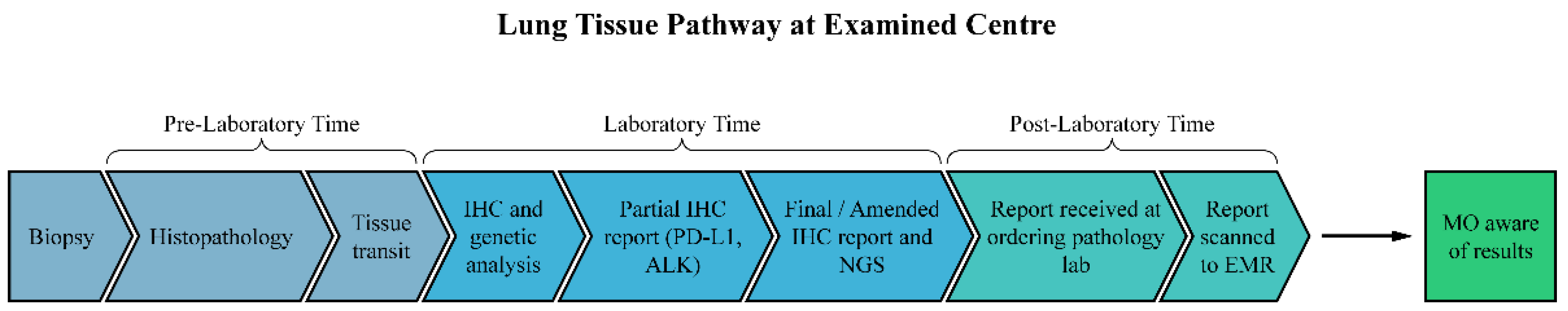
2. Materials and Methods
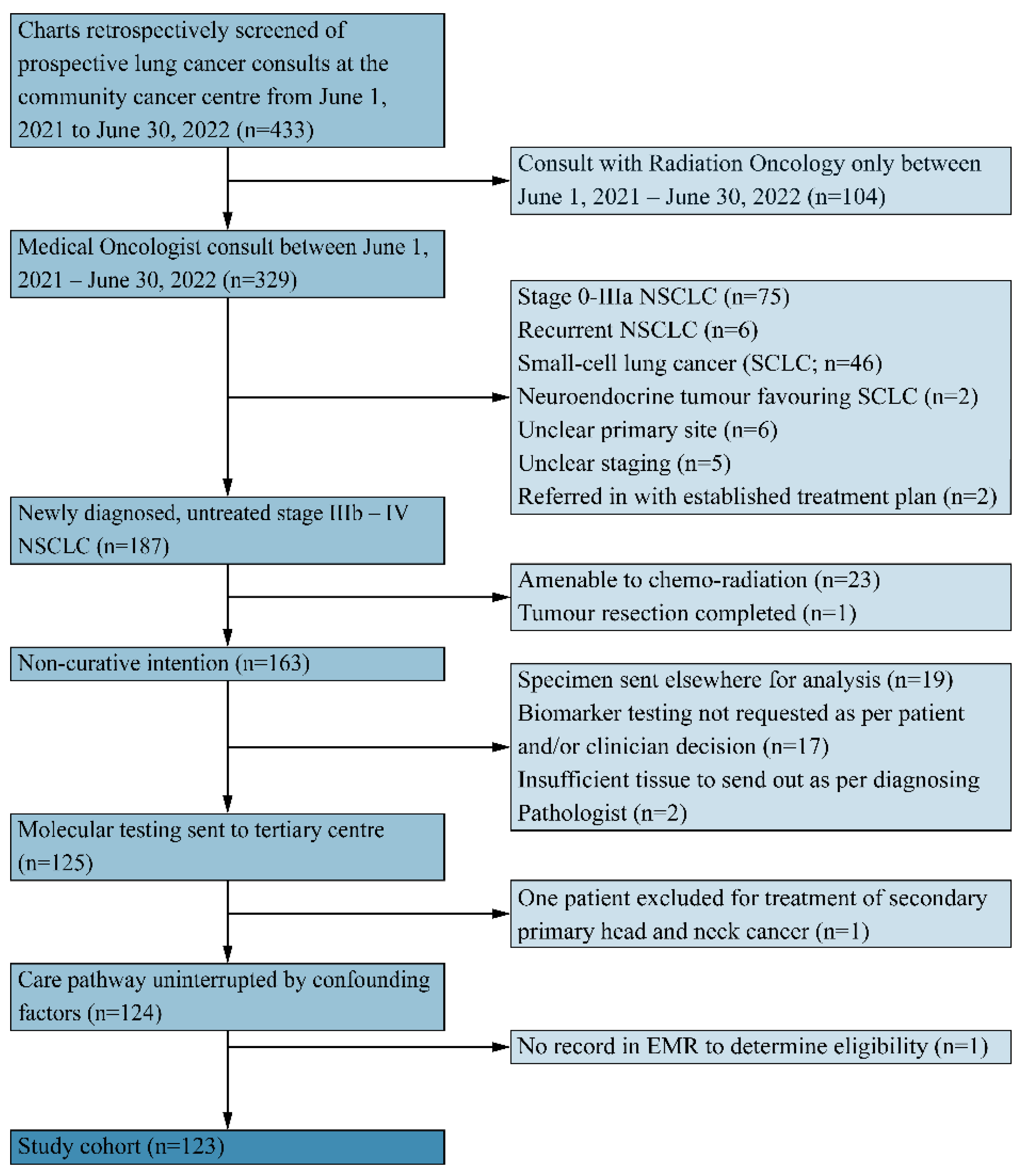
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics, Tumour Characteristics, and Details on Molecular Biomarkers
Quality of Biopsied Samples and Other Testing
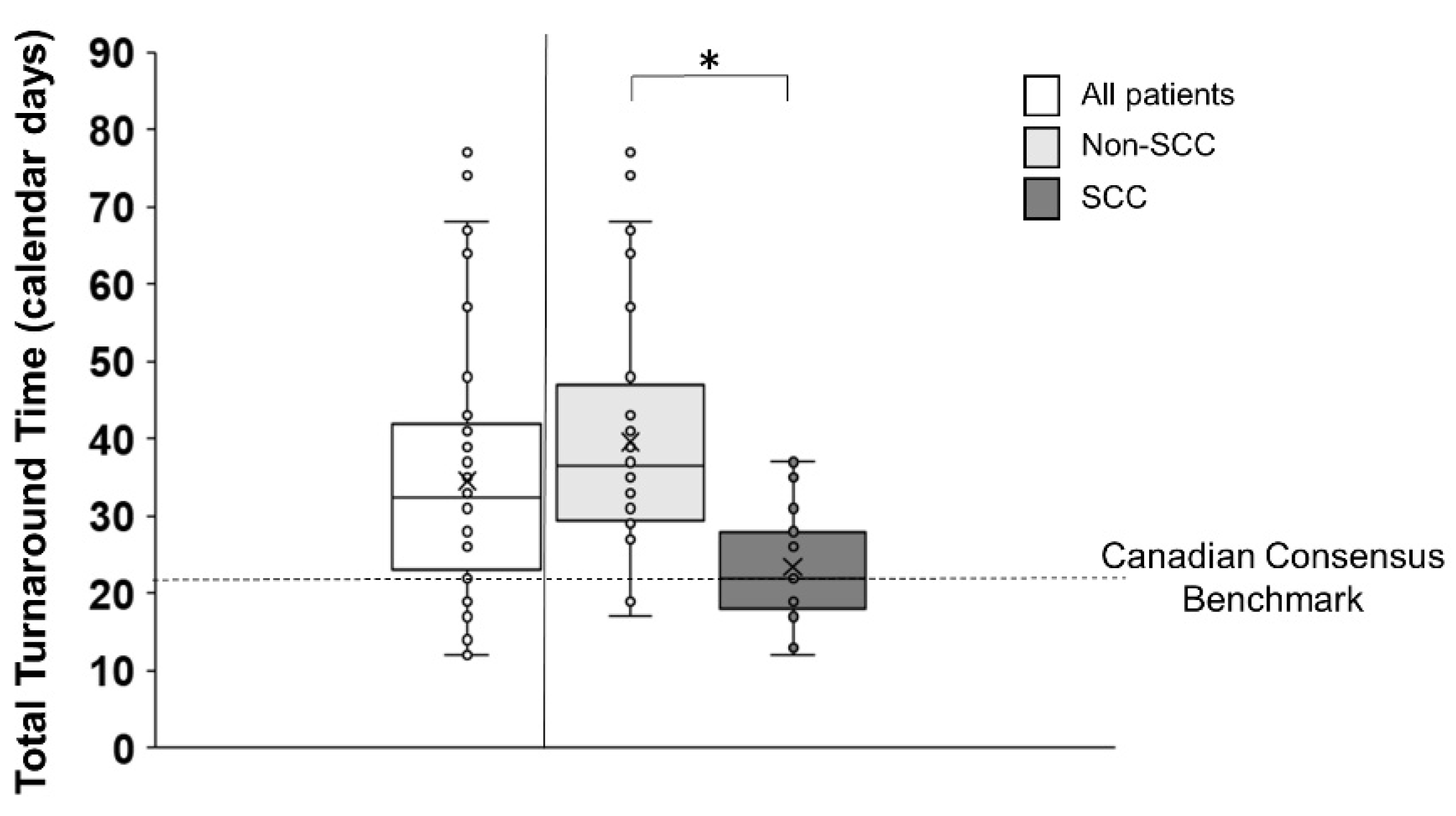
3.2. Total Turnaround Time (Total TAT)
3.3. Pre-Laboratory Time
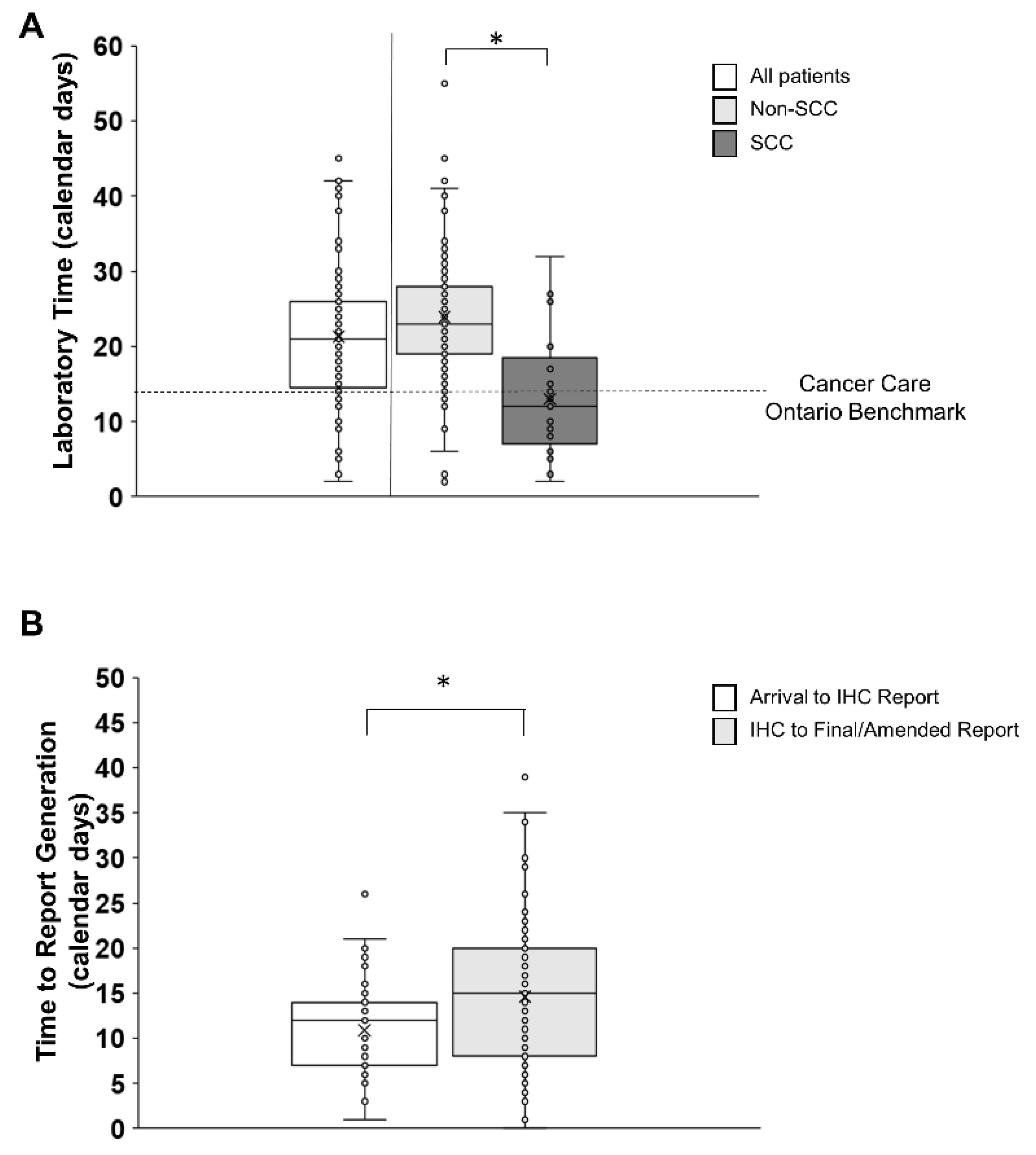
3.4. Laboratory Testing Time
3.5. Post-Laboratory Time
3.6. Treatment, Hospitalization, and Death before Optimal Treatment Prescription
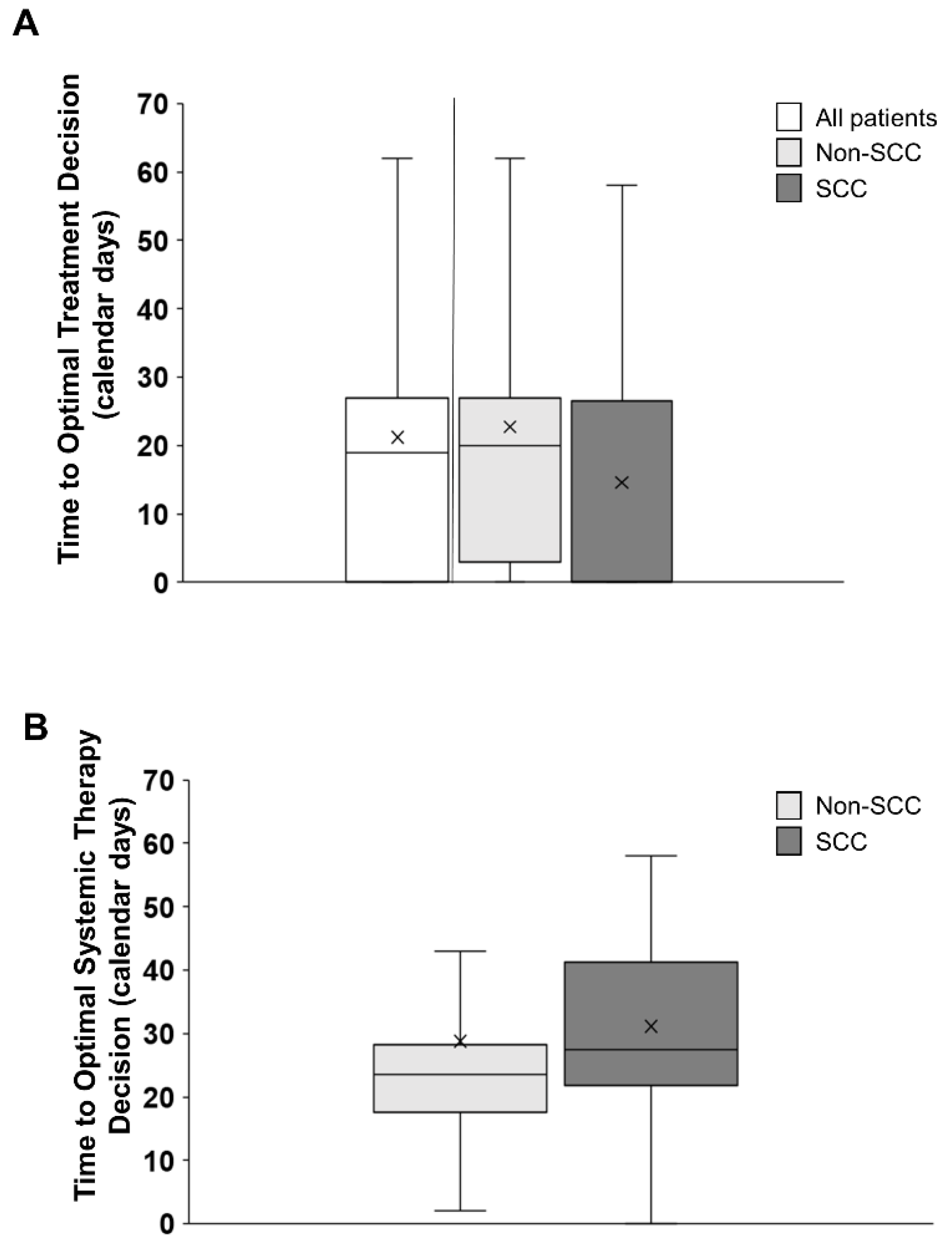
3.7. Time to Optimal Treatment Decision (TOTD and TOTSD)
4. Discussion
4.1. Delays in Pre-Laboratory, Laboratory, and Post-Laboratory Time
4.2. Delays in Optimal Treatment Decisions
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, D.R.; Poirier, A.; Woods, R.R.; Ellison, L.F.; Billette, J.-M.; Demers, A.A.; Zhang, S.X.; Yao, C.; Finley, C.; Fitzgerald, N.; et al. Projected estimates of cancer in Canada in 2022. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2022, 194, E601–E607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Phung, T.L.; Bernicker, E.G.; Cagle, P.T.; Olsen, R.J.; Thomas, J.S. Clinical Utility of Reflex Ordered Testing for Molecular Biomarkers in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, P.K.; Gomes, M.; Banerji, S.; Joubert, P.; Leighl, N.B.; Melosky, B.; Sheffield, B.S.; Stockley, T.; Ionescu, D.N. Consensus Recommendations for Optimizing Biomarker Testing to Identify and Treat Advanced EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Sekhon, H.S.; Cutz, J.C.; Hwang, D.M.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Carter, R.F.; Santos, G.d.C.; Wadell, T.; Binnie, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Improving Molecular Testing and Personalized Medicine in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Ontario. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, G.; Miller, P.G.; Agarwala, V.; Li, G.; Kaushik, G.; Backenroth, D.; Gossai, A.; Frampton, G.M.; Torres, A.Z.; Lehnert, E.M.; et al. Association of Patient Characteristics and Tumour Genomics with Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using a Clinicogenomic Database. JAMA 2019, 321, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau-Stock, S.; Laurie, K.; McKinnon, M.; Zhang, T.; Wheatley-Price, P. Evolution of Systemic Treatment Uptake and Survival in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 28, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Care Ontario. Lung Cancer Tissue Pathway Map; 2019. Available online: https://www.cancercareontario.ca/sites/ccocancercare/files/assets/LungTissuePathwayMap.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Beasley, M.B.; Chitale, D.A.; Dacic, S.; Giaccone, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Saldivar, J.-S.; Squire, J.; et al. Molecular Testing Guideline for Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for EGFR and ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association of Molecular Pathology. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 823–859. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pennell, N.A.; Arcilla, M.E.; Gandara, D.R.; West, H. Biomarker Testing for Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Issues and Tough Choices. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2019, 39, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafham, G.K.; Craddock, K.J.; Huang, W.-Y.; Louie, A.V.; Zhang, L.; Hwang, D.M.; Parmar, A. Referred Molecular Testing as a Barrier to Optimal Treatment Decision Making in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Experience at a Tertiary Academic Institution in Ontario, Canada [Preprint]. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2503084/v1 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Sheffield, B.S.; Beharry, A.; Diep, J.; Perdrizet, K.; Iafolla, M.A.J.; Raskin, W.; Dudani, S.; Brett, M.A.; Starova, B.; Olsen, B.; et al. Point of Care Molecular Testing: Community-Based Rapid Next-Generation Sequencing to Support Cancer Care. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, P.K.; Menjak, I.B.; Winterton-Perks, Z.; Raphael, S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Verma, S.; Muinuddin, A.; Freedman, R.; Toor, N.; Perera, J.; et al. Impact of Reflex EGFR/ALK Testing on Time to Treatment of Patients With Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Oncol. Pract. 2017, 13, e130–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, P.M.; Verma, S.; Sehdev, S.; Younus, J.; Leighl, N.B. Challenges to Implementation of an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Testing Strategy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in a Publicly Funded Health Care System. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, D.N.; Stockley, T.L.; Banerji, S.; Couture, C.; Mather, C.A.; Xu, Z.; Blais, N.; Cheema, P.K.; Chu, Q.S.-C.; Melosky, B.; et al. Consensus Recommendations to Optimize Testing for New Targetable Alterations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4981–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Tsao, M.S.; Le, L.W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Feld, R.; Burkes, R.L.; Liu, G.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Hwang, D.; Tanguay, J.; et al. Biomarker testing and time to treatment decision in patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melosky, B.; Blais, N.; Cheema, P.; Couture, C.; Juergens, R.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Tsao, M.-S.; Wheatley-Price, P.; Xu, Z.; Ionescu, D.N. Standardizing Biomarker Testing for Canadian Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, M.R.; Ellis, P.M.; Verma, S.; Duncan, E.; Leighl, N.B. Approach to Biomarker Testing: Perspectives from Various Specialties. Curr. Oncol. 2016, 23, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DiStasio, M.; Chen, Y.; Rangachari, R.; Costa, D.B.; Heher, Y.K.; VanderLaan, P.A. Molecular Testing Turnaround Time for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Routine Clinical Practice Confirms Feasibility of CAP/IASLC/AMP Guideline Recommendations: A Single-center Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e349–e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heher, Y.K.; Chen, Y.; VanderLaan, P.A. Pre-analytic error: A significant patient safety risk. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Robinson, H.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Farago, A.F.; Kamesan, V.; Iafrate, A.J.; Shaw, A.T.; Lennerz, J.K. Expediting Comprehensive Molecular Analysis to Optimize Initial Treatment of Lung Cancer Patients With Minimal Smoking History. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, G.A.; Temin, S.; Azzoli, C.G.; Giaccone, G.; Baker, S., Jr.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ellis, P.M.; Gajra, A.; Rackear, N.; Schiller, J.H.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3488–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, J.W.; Weisman, A.D. Psychosocial components of lagtime in cancer diagnosis. J. Psychosom. Res. 1975, 19, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, A.; Suleman, S.; Hyde, N.; Hodgkiss, A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ 2018, 25, k1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggondowati, T.; Ganti, A.K.; Watanabe-Galloway, S.; Haynatzki, G.; Islam, K.M. Effect of time to treatment on survival in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, B.S.; Eaton, K.; Emond, B.; Lafeuille, M.-H.; Hilts, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Morrison, L.; Stevens, A.L.; Ewara, E.M.; Cheema, P. Cost Savings of Expedited Care with Upfront Next-Generation Sequencing Testing versus Single-Gene Testing among Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Based on Current Canadian Practices. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2348–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Care Ontario. Comprehensive Cancer Biomarker Testing Program; 2023. Available online: https://www.cancercareontario.ca/sites/ccocancercare/files/assets/ComprehensiveCancerTestingIndications.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
| Age at Consult (Years), Mean (SD) | 70.7 (9.6) |
|---|---|
| Sex (Male), N (%) | 60 (48.8%) |
| Pathology subtype, N (%) | |
| Non-SCC | 90 (73.1%) |
| SCC | 27 (22%) |
| Other (neuroendocrine; spindle cell) | 2 (1.6%) |
| Unknown | 4 (3.3%) |
| Stage, N (%) | |
| Stage IIIB | 12 (9.8%) |
| Stage IIIC | 3 (2.4%) |
| Stage IV | 108 (87.8%) |
| Comorbidities, N (%) | |
| No Comorbidity | 55 (44.7%) |
| 1 Comorbidity | 39 (31.7%) |
| 2 Comorbidities | 21 (17.0%) |
| ≥3 Comorbidities | 8 (6.5%) |
| Smoking History, N (%) | |
| Smoker | 99 (80.5%) |
| Never Smoker | 24 (19.5%) |
| Performance Status (ECOG), N (%) | |
| Zero | 1 (0.8%) |
| 1–2 | 41 (33.3%) |
| 3 | 16 (13.0%) |
| 4–5 | 4 (3.3%) |
| Not stated | 52 (42.3%) |
| Described qualitatively (“excellent”; “too poor for systemic treatment”; “bedridden”; “poor”; “borderline”; | 9 (7.3%) |
| Outcome Measure | N (percentage) |
|---|---|
| Liquid Biopsy Performed | 20 (16.2) (18 non-SCC, 1 other, 1 undefined) |
| Insufficient tissue, repeat biopsy | 21 (17), 7 |
| Biomarker Results Available at Referral (all patients) | 15 (12.2) |
| Non-SCC | 10 (11.1) |
| SCC | 5 (18.5) |
| Biomarker Results Available at Consult (all patients) | 25 (20.3) |
| Non-SCC | 13 (14.4) |
| SCC | 11 (40.7) |
| Other histology | 1 (0.8) |
| EGFR | All (%) | Non-SCC (%) | SCC (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 13 (10.6%) | 12 (13.3%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (16.6%) |
| Negative | 71 (57.7%) | 65 (72.2%) | 3 (11.1%) | 3 (50%) |
| Not tested | 25 (20.3%) | 3 (3.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Insufficient Tissue | 14 (11.4%) | 10 (11.1%) | 2 (7.4%) | 2 (33.3%) |
| ALK | ||||
| Positive | 1 (0.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Negative | 92 (74.8%) | 83 (92.2%) | 4 (14.8%) | 5 (83.3%) |
| Not tested | 21 (17.1%) | 1 (1.1%) | 20 (74.1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Insufficient Tissue | 9(7.3%) | 5 (5.5%) | 3 (11.1%) | 1 (16.6%) |
| PD-L1 | ||||
| Positive (>50%) | 59 (48%) | 46 (51.1%) | 12 (44.4%) | 2 (33.3%) |
| Low Positive (1–49%) | 24 (19.5%) | 17 (18.8%) | 6 (22.2%) | 1 (16.6%) |
| Negative (<1%) | 29 (23.6%) | 20 (22.2%) | 7 (25.9%) | 2 (33.3%) |
| Unknown | 1 (0.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Insufficient Tissue | 10 (8.1%) | 6 (6.6%) | 3 (11.1%) | 1 (16.6%) |
| ROS-1 | ||||
| Positive | 3 (2.4%) | 3 (3.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Negative | 22 (17.9%) | 20 (22.2%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (50%) |
| Not tested | 91 (74%) | 61 (67.8%) | 27 (100%) | 3 (50%) |
| Insufficient tissue | 6 (4.9%) | 5 (5.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Equivocal | 1 (0.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Outcome Measure | All Patients (Median and IQR; Calendar Days) | Non-SCC (Median and IQR; Calendar Days) | SCC (Median and IQR; Calendar Days) | Consensus or Guideline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-laboratory Testing | 5 (3, 8.75) | - | - | |
| Histopathology to Tissue Arrival | 5 (3, 8.75) | ≤3 business days | ||
| Laboratory Testing | 21 (14, 27) | 23 (19, 28) | 12 (7, 18.5) | ≤10 business days ≤14 calendar days |
| Time to Partial IHC Report (ALK, PD-L1) | - | 12 (7, 14) | 12 (7, 18.5) | |
| Time from Partial IHC Report to Amended/ Final Report (EGFR, etc.) | - | 15 (8, 20) | N/A | |
| Post-laboratory Testing | ≤24 h | |||
| Time to Partial IHC Report scanned in EMR | - | 2 (1, 6) | 3 (1, 3) | |
| Time to Amended/Final Report scanned in EMR | - | 3 (1, 8) | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fleming, K.E.; Hupel, A.; Mithoowani, H.; Lulic-Kuryllo, T.; Valdes, M. Biomarker Turnaround Times and Impact on Treatment Decisions in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma at a Large Canadian Community Hospital with an Affiliated Regional Cancer Centre. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 1515-1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030115
Fleming KE, Hupel A, Mithoowani H, Lulic-Kuryllo T, Valdes M. Biomarker Turnaround Times and Impact on Treatment Decisions in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma at a Large Canadian Community Hospital with an Affiliated Regional Cancer Centre. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(3):1515-1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030115
Chicago/Turabian StyleFleming, Katelyn E., Ava Hupel, Hamid Mithoowani, Tea Lulic-Kuryllo, and Mario Valdes. 2024. "Biomarker Turnaround Times and Impact on Treatment Decisions in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma at a Large Canadian Community Hospital with an Affiliated Regional Cancer Centre" Current Oncology 31, no. 3: 1515-1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030115
APA StyleFleming, K. E., Hupel, A., Mithoowani, H., Lulic-Kuryllo, T., & Valdes, M. (2024). Biomarker Turnaround Times and Impact on Treatment Decisions in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma at a Large Canadian Community Hospital with an Affiliated Regional Cancer Centre. Current Oncology, 31(3), 1515-1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31030115





