Abstract
Background: Annually, approximately 200 new ovarian cancer cases are diagnosed in Armenia, which is considered an upper-middle-income country. This study aimed to summarize the survival outcomes of patients with relapsed ovarian cancer in Armenia based on the type of recurrence, risk factors, and choice of systemic treatment. Methods: This retrospective case-control study included 228 patients with relapsed ovarian cancer from three different institutions. Results: The median age of the patients was 55. The median follow-up times from relapse and primary diagnosis were 21 and 48 months, respectively. The incidence of platinum-sensitive relapse was 81.6% (186), while platinum-resistant relapse was observed in only 18.4% (42) of patients. The median post-progression survival of the platinum-sensitive group compared to the platinum-resistant group was 54 vs. 25 months (p < 0.001), respectively, while the median survival after relapse was 25 vs. 13 months, respectively; three- and five-year post-progression survival rates in these groups were 31.2% vs. 23.8%, and 15.1% vs. 9.5%, respectively (p = 0.113). Conclusions: Overall, despite new therapeutic approaches, ovarian cancer continues to be one of the deadly malignant diseases affecting women, especially in developing countries with a lack of resources, where chemotherapy remains the primary available systemic treatment for the majority of patients. Low survival rates demonstrate the urgent need for more research focused on this group of patients with poor outcomes.
1. Introduction
Ovarian cancer ranks third in frequency and has the highest mortality rate among gynecological cancers. In 2020, 313,959 cases of ovarian cancer were identified by Globocan (Global Cancer Observatory), and 207,252 deaths were registered [1,2]. A woman’s lifetime risk of ovarian cancer is 1 in 87 [3].
According to data from the Statistical Group in the National Center of Oncology of Armenia, 197 women were diagnosed with ovarian cancer in Armenia in 2022. The morbidity and mortality rates per 100,000 of the female population were 6.6 and 2.6, respectively [4]. The first-line therapy includes debulking surgery followed by adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy, while for patients with adverse performance status and advanced disease, treatment may start with chemotherapy and be followed by surgery [5,6,7]. Poor treatment outcomes are mainly explained by the high incidence of recurrence after the completion of primary treatment, which is observed in 25% of cases with early-stage diseases and in approximately 80% of cases with more advanced stages [8,9], as well as the lack of effective screening [10,11] and limited opportunities for radical surgery and systemic treatment [12].
When planning a treatment strategy for ovarian cancer relapse, accurate classification based on the interval from the end of platinum-containing chemotherapy to the first signs of the disease as either platinum-sensitive (more than 6 months) or platinum-resistant (less than 6 months) is key. [13,14,15]. The relapse therapy choice depends on tumor biology, the patient’s ECOG status, and toxicity from previous treatment [16]. Platinum-based chemotherapy remains the backbone of the treatment; meanwhile, the use of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors and anti-angiogenic (anti-VEGF) agents as maintenance therapy results in significant improvements in both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) [17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
Platinum-resistant ovarian cancer recurrences have the most unfavorable prognosis, as combined therapy with platinum-containing agents no longer leads to long-term outcomes [24,25,26,27].
There is no evidence to support the order of sequencing platinum combinations. Recommendations are limited to listing medications and their combinations, without specifying criteria for their use.
The primary endpoint of our study aimed to determine the OS and post-progression survival (PPS) of patients with relapsed ovarian cancer depending on the type of relapse, stage of the disease, and age of the patient. The secondary endpoint was to determine OS, PPS, and PFS based on the treatment regimen.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
The clinical material for this study were data from patients with relapsed ovarian cancer who were treated in the oncology and chemotherapy departments of the National Center of Oncology named after Fanarjyan, the Oncology Clinic of the Mikaelyan Institute of Surgery, and the Chemotherapy Clinic of Muratsan University Hospital in Armenia. Patient information was collected from medical records and outpatient cards, which were coded based on a pre-compiled coder using the scoring system displayed within it. Data regarding the current condition of patients (dead or alive) were obtained from the United Information System of Electronic Healthcare of Armenia (ArMed). A retrospective analysis of primary records of patients receiving chemotherapy for platinum-sensitive and platinum-resistant relapsed ovarian cancer was performed. This study included patients with relapsed ovarian cancer that was confirmed between 2009 and 2019, with at least a three-year follow-up after recurrence.
2.2. Stratification According to Remission Type
Within the framework of this study, data were examined for patients who met the following criteria: the presence of morphologically-confirmed (by the Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO)) stage I–IV epithelial ovarian cancer (including primary peritoneal and fallopian tube cancer), recurrence after surgery, and single or combination chemotherapy based on cisplatin or carboplatin treatment agents, either within 6 months after completing treatment (platinum-resistant) or more than 6 months after treatment (platinum-sensitive).
The remission duration and confirmation of remission status were evaluated in accordance with the accepted standards.
In line with general recommendations, we defined a complete response as the disappearance of all pathological lesions (both clinical and radiological) with the regulation of the CA-125 serum tumor marker level (≤35 U/mL). A partial response was defined as partial clinical improvement with a greater than 25% (but not complete) reduction in CA-125 serum tumor marker levels and radiological regress of the tumor mass. The disease was assessed as progressive when the patient’s clinical condition worsened, or the level of the tumor marker CA-125 increased by more than 25%, or radiological progression was confirmed. All other conditions were considered stable diseases. Staging was conducted according to the FIGO international staging system, which is accepted as a standard in gynecological oncology [28].
OS was measured from the time of diagnosis to death, regardless of the cause. PPS was defined as the time from the first relapse to death (any cause), and finally, PFS was calculated from the time of the first relapse to the occurrence of disease progression.
2.3. Features and Data Analysis
Statistical analysis of obtained data was conducted using the SPSS Statistics 23 computer program. For data analysis, depending on the type of relapse, three-year and five-year survival rates were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier nonparametric statistical method, during which the log rank (Mantel–Cox) statistical test was performed. A p-value < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant. Categorical variables were compared by the chi-square test.
X2 Pearson’s test/Pearson’s chi-squared test with Fisher’s exact test was used to evaluate differences in three- and five-year survival by June 2023.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.1.1. Histologic Subtypes
Our study was conducted to analyze data from patients with epithelial malignant tumors. We did not include tumors such as granulosa cell tumors, Brenner tumors, dysgerminomas, and sarcomas, as their treatment approaches, regimens, treatment outcomes, and prognosis vary from those of epithelial tumors. Our findings showed that the vast majority of patients were diagnosed with serous adenocarcinoma (95.2%). A less common histological subtype was undifferentiated carcinoma (4% of cases), which is known to have a high recurrence rate (Table 1). Mucinous carcinoma was confirmed in 3% of patients, while endometrioid cancer was confirmed in 2%. Other histological variants, like clear cell and squamous cell cancer, were each documented in only 1% of cases.

Table 1.
Patients’ categorization according to histological subtype.
3.1.2. Stratification According to the Primary Treatment
When analyzing the modality of the primary treatment performed in patients with relapsed ovarian cancer, the following data was obtained. The largest number of patients, 128 (56.1%), received a combination of surgery + adjuvant chemotherapy as primary treatment. For 34 (14.9%) patients, primary treatment was carried out with neoadjuvant chemotherapy + surgery, while diagnostic laparoscopy before initiation of primary treatment was performed for 66 patients, 30 (13.1%) of whom were treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy + surgery after laparoscopy, and 36 (15.8%) of whom were treated with surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy.
3.1.3. Stratification According to Patient Age
This study involved 228 females who had a median patient age of 55.5 years. The majority of patients (151 (66.2%)) who experienced a disease recurrence were aged 40–59 years. The number of participants over 60 y/o was 63 (27.6%). Only 14 (6.2%) patients in this study were younger, aged 20–39 y/o (Figure 1). The median follow-up time starting from the relapse was 21 (0–137) months. The median follow-up time starting from the primary diagnosis was 48 (6–347) months. According to the dataset, in the platinum-sensitive group’s young age group (20–39), median OS and median PPS were 119 and 66 months, respectively; in the 40–59 age group median OS and median PPS were 54 and 24 months, respectively; and they were 51 and 19 months, respectively, in the elderly group aged >60 years old. Meanwhile, in the platinum-resistant group, the median OS and median PPS were 17 and 9 months, respectively, in the 20–39 age group, 29 and 19 months, respectively, in the 40–59 age group, and 21 and 12 months, respectively, in the age group over 60 (Table 2). A significant difference was observed between various age groups when comparing median PPSs and OSs (p-value = 0.01). A younger age at the time of diagnosis was associated with higher PPS. Likewise, a similar tendency was observed in terms of OS (p-value = 0.006) (Table 2 and Figure 2). The overall cumulative five-year survival rate for all patients in this study regardless of relapse type was 35.5%.
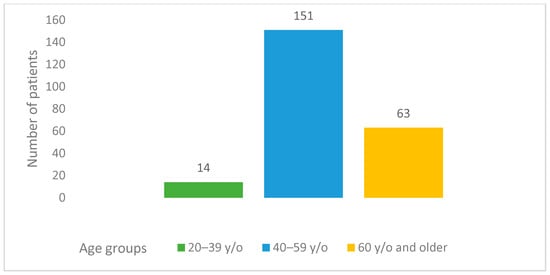
Figure 1.
Age groups of patients with relapsed ovarian cancer.

Table 2.
Survival rates according to patients’ ages at the time of diagnosis.
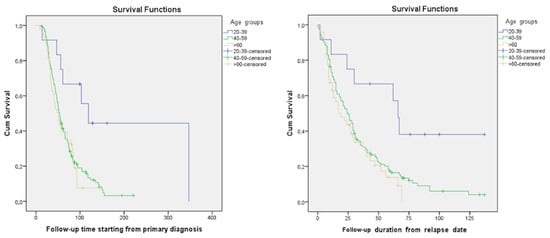
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Maier curves based on patients’ ages at the time of diagnosis in the platinum-sensitive group.
3.1.4. Stratification According to the Stage of the Disease
Data showed that 87.3% of patients with relapsed ovarian cancer were diagnosed with late stages (III and IV) of the disease at their primary treatment, while the proportion of early stages among patients with recurrent ovarian cancer was only 12.7%. The median OS in the platinum-sensitive relapsed group was 40 months for patients who initially had stage I disease, as shown in Table 3. In comparison, all other stage groups had a similar median OS (20–26 months) (p-value = 0.275).

Table 3.
Survival rates according to the disease stage at the time of diagnosis.
Our findings indicated that the incidence of platinum-sensitive relapses in the study group was 81.6% (186 of 228), and only 18.4% (42 of 228) were diagnosed with platinum-resistant relapse. From provided data it became clear that the group of patients whose data was analyzed in our study was homogeneous according to key characteristics, including the stage of the disease, age, and primary treatment of relapses. This allowed us to perform statistical analysis and obtain reliable results.
Using the Kaplan–Meier method, we calculated the median survival of patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, as well as their maximum and minimum survival times. According to our data, the median OS of patients in the platinum-sensitive group compared to the platinum-resistant group was 54 months (95% CI 48.4; 59.6) vs. 25 months (95% CI 20; 30.0) (p-value = 0.000). Meanwhile, the median PPSs in the platinum-sensitive group compared to the platinum-resistant group were 25 months (95% CI 19.8; 30.2) and 13 months (95% CI 9.3; 16.7), respectively (p-value = 0.1113); three-year and five-year survival rates were 31.2% vs. 23.8% and 15.1% vs. 9.5%, respectively (Figure 3).
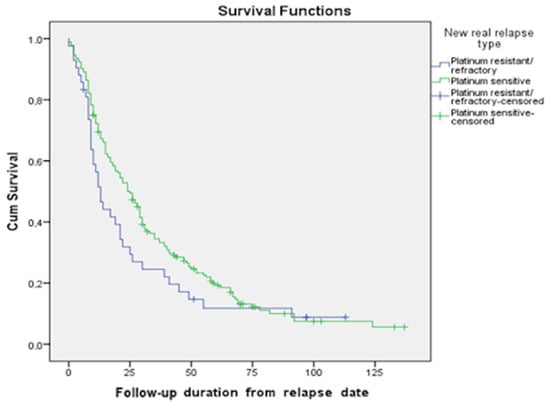
Figure 3.
Survival functions based on the type of relapse (PPS).
3.2. Survival after Relapse Based on the Choice of Systemic Treatment
3.2.1. Platinum-Sensitive Relapse
We possess data regarding survival rates for the most frequently used regimens. These statistics showed that, for platinum-sensitive relapse, the most effective regimens were found to be paclitaxel/carboplatin/bevacizumab (mPFS 28.0 months), paclitaxel/carboplatin (mPFS 26.4 months), gemcitabine/cisplatin (mPFS 19.3 months), gemcitabine/carboplatin (mPFS 17.3 months), and gemcitabine/carboplatin/bevacizumab (mPFS 14.0 months) (Figure 4).
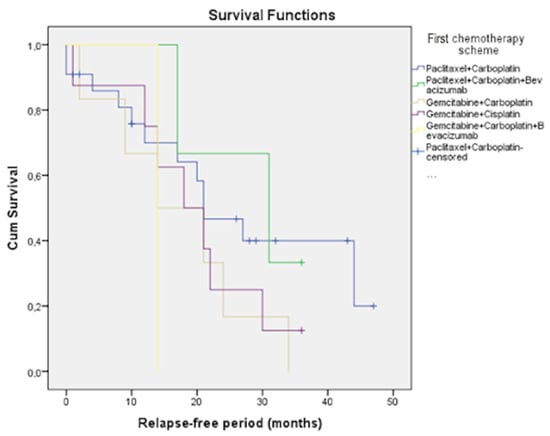
Figure 4.
PFS in the platinum-sensitive group.
Additionally, we analyzed the results for three-year and five-year PPS for each chemotherapy regimen in both patient groups. In the platinum-sensitive group, patients’ overall three-year and five-year survival rates with paclitaxel/carboplatin treatment were 29.2% and 12.5%, respectively; with paclitaxel/carboplatin/bevacizumab, 55.6% and 44.4%, respectively; gemcitabine/carboplatin, 28.6% and 0, respectively; gemcitabine/carboplatin/bevacizumab, 66.7% and 16.7%, respectively; and gemcitabine/cisplatin, 33.3% and 13.3%, respectively (Figure 5a).
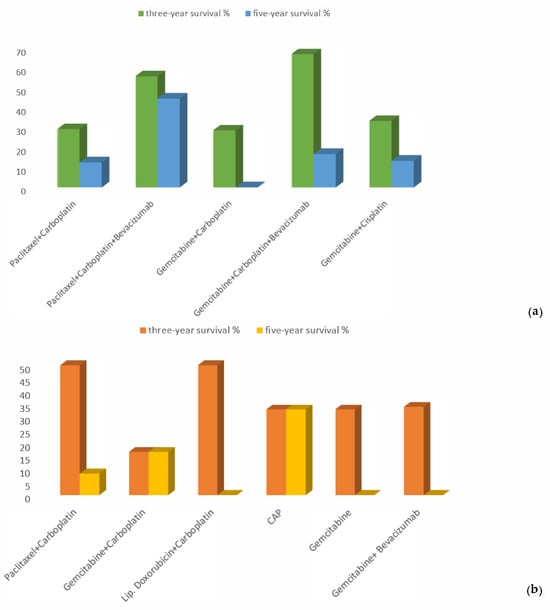
Figure 5.
Proportions of three-year and five-year PPS in the (a) platinum-sensitive and (b) platinum-resistant groups.
3.2.2. Platinum-Resistant Relapse
We conducted a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of regimens that were administered in Armenian clinics to patients who experienced a platinum-resistant relapse with a platinum-free interval (PFI) less than 6 months. Three-year PPS rates for the analyzed groups according to the treatment they received were as follows: gemcitabine, 33%; gemcitabine/bevacizumab, 34%; gemcitabine/carboplatin, 16.7%; cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/cisplatin, 33%; pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD)/carboplatin, 50%; and paclitaxel/carboplatin, 33% (p-value = 0.99).
Five-year PPS rates were calculated only for patients who received paclitaxel/carboplatin (8.3%), gemcitabine/carboplatin (16.7%), and cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/cisplatin (33%) (p-value = 0.79). In this group, the treatment response after relapse was reached by only seven patients; therefore, we did not include their mPFS results in this study, as the number of patients was too small (Figure 5b).
4. Discussion
Our study showed that the majority of patients with recurrent ovarian cancer involved in the research were from 40 to 59 years old. This was probably because the median age of patients in Armenia was 55, which is considerably younger compared to statistics from the United States, where the median age for this disease is 63 [29], and also lower than that reported in Japanese studies, where the median age of patients at relapse was reported as 59 [30]. Conversely, in India, ovarian cancer is present in a younger age group, with a median age < 55 years reported by most studies, and even <50 years in some regions of the country [31]. This phenomenon might be attributed to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of ovarian cancer among the elderly population in limited-source settings. Our data demonstrated that the best OS and PPS were detected in the younger age group of the platinum-sensitive group, which was twice as high (119 months) compared to those of other age groups. These results correlate with statistics in the literature regarding age-connected mortality in ovarian cancer: the older the patient is, the worse the survival rate [32]. However, when we assessed the platinum-resistant group, the picture was different—the middle-aged group (40–59) exhibited longer survival, while the elderly and young adult groups had relatively the same survival rates. These non-intuitive results might be attributed to the small sample size in the platinum-resistant group.
As the results revealed, the majority of patients with ovarian cancer had serous adenocarcinoma (95.5%), which is a much higher rate than in Eastern European countries like Poland, where the incidence of high-grade serous adenocarcinoma is approximately 74% [33]. One of the possible explanations for this difference could be the fact that our study included only patients with recurrence, which may be more frequent in the serous adenocarcinoma subtype.
According to our study results, the vast majority of patients with relapsed ovarian cancer initially had advanced FIGO stages III and IV, and the proportion of early stages among patients with recurrent ovarian cancer was approximately 13%. These data once again confirm the fact that disease stage is the most unfavorable prognostic factor in ovarian cancer, emphasizing the importance of early detection [34]. Interestingly, the median survival after relapse in the platinum-sensitive relapsed group was twice as good (40 months) for patients who initially had stage I disease. In comparison, all other stage groups had similar survival rates (20–26 months). These data differ from the results of the article published by Rajendra Kumar Meena in 2022 in JCO Global Oncology, according to which stage I and II patients have better survival than more advanced-stage groups do [31]. An Italian study that was carried out by Gadducci et al. also showed statistical significance between survival after recurrence and initial clinical stage (I, IIA vs. IIB–IV) [35].
According to our study results, regardless of the type of relapse, the cumulative five-year OS for Armenian patients was 35.5%, which was lower compared to that of Sudan (38%), which is classified as a low-middle-income country [36]. Our data showed that more than 80% of patients with ovarian cancer relapse had platinum-sensitive disease, so the majority of them had a chance to be treated with a platinum combination again, in the absence of comorbidities [5,8,13,14]. As a result, three- and five-year PPS rates of platinum-sensitive relapse were almost twice as high as those of the platinum-resistant type were. These results are similar to those of the study conducted by Ai Miyoshi et al., which showed that the patients who had a relapse with a treatment-free interval (TFI) of less than 6 months had notably worse outcomes than those with a TFI exceeding 6 months [30].
Platinum-sensitive relapse is considered a chemo-sensitive disease in more than half of patients [37]. As demonstrated in our study results, paclitaxel/carboplatin was one of the most effective regimens for platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. This was also the main regimen patients received during their primary treatment. One of the biggest advantages of this regimen is its affordability and availability. Our results are in line with the generally accepted guidelines, showing that rechallenging the “backbone’’ regimen remains one of the most effective treatments in cases of recurrence [13,14,15,16,17,18]. A generally accepted standard of care is readministration of a platinum agent combined with one of the following medications: PLD, paclitaxel, or gemcitabine, with or without a VEGF inhibitor like bevacizumab [38,39].
Based on our analysis, adding bevacizumab to the chemotherapy regimen resulted in higher three-year and five-year PPS, which was also shown in the AURELIA trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO) by Pujade-Lauraine et al. [40]. The shortest survival rates were observed in patient groups that did not receive platinum compound therapy without having a chance to reach three- and five-year OS.
One of the goals of our study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a range of regimens in the treatment of platinum-resistant relapses and their impact on three- and five-year PPS rates. The generally accepted standard of care for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer is single-agent chemotherapy with non-platinum agents like gemcitabine, docetaxel, paclitaxel, topotecan, PLD, etc. [41,42,43].
As we have already demonstrated, the three-year PPS for patients with platinum-resistant relapses was 23.8%, while their five-year PPS was only 9.5%. The primary monotherapy regimen that exhibited better survival rates was gemcitabine. Our study did not show a survival benefit with bevacizumab in this group of patients. Interestingly, some patients received platinum compounds during their relapse treatment even though their platinum-free intervals were less than 6 months, which is not accepted as a standardized approach. Nevertheless, only these particular groups of patients (treated using paclitaxel/carboplatin, gemcitabine/carboplatin, or cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/cisplatin) reached five-year survival after relapse. This can be explained by the retrospective analysis conducted by the Australian Ovarian Cancer Study. According to the latter, PPS improved after platinum-based chemotherapy, even for patients with a platinum-free interval of less than 6 months (the median PPS was 17.7 months after platinum-based chemotherapy vs. 10.6 months after a non-platinum regimen). However, a platinum-free interval of more than 6 months does not necessarily guarantee a response to future platinum-based chemotherapy [18,44].
It should be recognized and emphasized that, especially in a developing country like Armenia, the availability of and accessibility to medications often have a significant impact on the choice of anti-relapse treatment. There is a lack of treatment accessibility due to insufficient government coverage and limited availability of essential medications [45].
This study had certain limitations, including the following.
- Due to its retrospective design, there was a notably inadequate documentation of important details in medical records, particularly regarding treatment-related toxicity.
- Most patients who relapsed received only chemotherapy due to a lack of access to the targeted therapy. A number of targeted agents, like bevacizumab, PARP inhibitors (olaparib, rucaparib, and niraparib), immunotherapy (pembrolizumab and dostarlimab), and folate receptor alfa inhibitor marvetuximab soravtansine-gynx, are not affordable for Armenian patients. Except for bevacizumab, which was available for a few patients, all other abovementioned agents are not even registered in Armenia.
- There was a small cohort of patients in the platinum-resistant group.
- In our study, we did not take into consideration the impact of “second look” surgeries during the treatment of recurrences.
5. Conclusions
The present analysis will contribute to the improvement of treatment outcomes for patients with relapsed ovarian cancer. Overall, despite new therapeutic approaches, ovarian cancer continues to be one of the deadly malignant diseases affecting women, especially in developing countries with a lack of resources, where chemotherapy is still the primary available systemic treatment for the majority of these patients. Persistently low survival rates highlight the urgent need for more research regarding this group of patients with poor outcomes.
Author Contributions
L.H.—project administration, data curation, supervision, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and investigation. E.M.—visualization, conceptualization, and writing—review and editing. S.B.—visualization, conceptualization, and writing—review and editing. N.K.—visualization, conceptualization, and writing—review and editing. A.J.—data curation and writing—review and editing. G.T.—visualization and writing—review and editing. A.A. (Armen Avagyan)—writing—review and editing. L.S.—writing—review and editing. D.Z.—writing—review and editing. N.M.—writing—review and editing. A.A. (Anna Avinyan)—writing—review and editing. A.G. (Arevik Galoyan)—writing—review and editing. M.S.—writing—review and editing. M.H.—writing—review and editing. H.N.—data curation and investigation. A.S.—data curation and investigation. A.G. (Armenuhi Galstyan)—writing—review and editing. S.D.—conceptualization and writing—review and editing. A.M.—conceptualization, project administration, supervision, and visualization. G.J.—conceptualization, project administration, supervision, visualization, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yerevan State Medical University (Code N 5-4/21, date 16 December 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was waived, as this study was a retrospective audit of medical records.
Data Availability Statement
Data that support the findings will be available in the repository at URL [https://figshare.com/s/b9c0f3ab18b666fa523c] (accessed on 9 February 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
L.H. reports lecture fees and travel support from Roche and Novartis Pharmaceuticals outside of the submitted work.
References
- Cabasag, C.J.; Fagan, P.J.; Ferlay, J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Liu, L.; van der Aa, M.A.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. Ovarian Cancer Today and Tomorrow: A Global Assessment by World Region and Human Development Index Using GLOBOCAN 2020. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovarian Cancer By The Numbers|OCRA. Available online: https://ocrahope.org/get-the-facts/statistics/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Ovarian Cancer Statistics|How Common is Ovarian Cancer|American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/ovarian-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Statistical Committee of the Republic of Armenia Statistical Yearbook of Armenia 2023: Health and Healthcare. Available online: https://nih.am/assets/pdf/atvk/2d5537b6227666a32f97571d7dd15420.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- NCCN. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Ovarian Cancer/Fallopian Tube Cancer/Primary Peritoneal Cancer, Version 1.2024. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/ovarian.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Jiang, R.; Zhu, J.; Kim, J.-W.; Liu, J.; Kato, K.; Kim, H.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, T.; Aoki, D.; et al. Study of Upfront Surgery versus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by Interval Debulking Surgery for Patients with Stage IIIC and IV Ovarian Cancer, SGOG SUNNY (SOC-2) Trial Concept. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 31, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsonis, O.; Gkrozou, F.; Vlachos, K.; Paschopoulos, M.; Mitsis, M.C.; Zakynthinakis-Kyriakou, N.; Boussios, S.; Pappas-Gogos, G. Upfront Debulking Surgery for High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: Current Evidence. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, S.; Laganà, A.S.; Casarin, J.; Raffaelli, R.; Cromi, A.; Franchi, M.; Barra, F.; Alkatout, I.; Ferrero, S.; Ghezzi, F. Secondary and Tertiary Ovarian Cancer Recurrence: What Is the Best Management? Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salani, R.; Backes, F.J.; Fung, M.F.K.; Holschneider, C.H.; Parker, L.P.; Bristow, R.E.; Goff, B.A. Posttreatment Surveillance and Diagnosis of Recurrence in Women with Gynecologic Malignancies: Society of Gynecologic Oncologists Recommendations. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patni, R. Screening for Ovarian Cancer: An Update. J. Life Health 2019, 10, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommendation: Ovarian Cancer: Screening|United States Preventive Services Taskforce. Available online: https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/ovarian-cancer-screening (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Song, Y.J. Prediction of Optimal Debulking Surgery in Ovarian Cancer. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung-Kee-Fung, M.; Oliver, T.; Elit, L.; Oza, A.; Hirte, H.W.; Bryson, P. Optimal Chemotherapy Treatment for Women with Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Tor. Ont 2007, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignata, S.; Pisano, C.; Di Napoli, M.; Cecere, S.C.; Tambaro, R.; Attademo, L. Treatment of Recurrent Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer 2019, 125 (Suppl. 24), 4609–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newly Diagnosed and Relapsed Epithelial Ovarian Cancer|ESMO. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/guidelines-by-topic/esmo-clinical-practice-guidelines-gynaecological-cancers/newly-diagnosed-and-relapsed-epithelial-ovarian-cancer/eupdate-newly-diagnosed-epithelial-ovarian-carcinoma-treatment-recommendations (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Claussen, C.; Rody, A.; Hanker, L. Treatment of Recurrent Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2020, 80, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, S.; Sood, N.; Nicum, S. The Challenges and Opportunities in Ovarian Cancer Relapse—The Role of Second and Third-Line Chemotherapy: Literature Review. Gynecol. Pelvic Med. 2022, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, T.; Ferrero, A.; Sehouli, J.; O’Donnell, D.M.; González-Martín, A.; Joly, F.; van der Velden, J.; Blecharz, P.; Tan, D.S.P.; Querleu, D.; et al. The Systemic Treatment of Recurrent Ovarian Cancer Revisited. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2021, 32, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, J.; Ledermann, J.A. Management of Platinum-Sensitive Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33 (2 Suppl 6), S12–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, A.; Floquet, A.; Ledermann, J.A.; Asher, R.; Penson, R.T.; Oza, A.M.; Korach, J.; Huzarski, T.; Pignata, S.; Friedlander, M.; et al. Final Overall Survival (OS) Results from SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21: A Phase III Trial Assessing Maintenance Olaparib in Patients (Pts) with Platinum-Sensitive, Relapsed Ovarian Cancer and a BRCA Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Monk, B.J.; Herrstedt, J.; Oza, A.M.; Mahner, S.; Redondo, A.; Fabbro, M.; Ledermann, J.A.; Lorusso, D.; Vergote, I.; et al. ENGOT-OV16/NOVA Investigators. Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive, Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Harter, P.; Gourley, C.; Friedlander, M.; Vergote, I.; Rustin, G.; Scott, C.; Meier, W.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Safra, T.; et al. Overall Survival in Patients with Platinum-Sensitive Recurrent Serous Ovarian Cancer Receiving Olaparib Maintenance Monotherapy: An Updated Analysis from a Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Ledermann, J.A.; Selle, F.; Gebski, V.; Penson, R.T.; Oza, A.M.; Korach, J.; Huzarski, T.; Poveda, A.; Pignata, S.; et al. SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21 investigators. Olaparib Tablets as Maintenance Therapy in Patients with Platinum-Sensitive, Relapsed Ovarian Cancer and a BRCA1/2 Mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.; Tinker, A.V.; Friedlander, M. “Platinum-Resistant” Ovarian Cancer: What Is It, Who to Treat and How to Measure Benefit? Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 133, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, U.; Marth, C.; Largillier, R.; Kaern, J.; Brown, C.; Heywood, M.; Bonaventura, T.; Vergote, I.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Fossati, R.; et al. Final Overall Survival Results of Phase III GCIG CALYPSO Trial of Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin and Carboplatin vs. Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer Patients. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, B.; Tang, D.; Bowden, N.A. Biomarkers of Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer: What Can We Use to Improve Treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, R303–R318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havasi, A.; Cainap, S.S.; Havasi, A.T.; Cainap, C. Ovarian Cancer—Insights into Platinum Resistance and Overcoming It. Medicina 2023, 59, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, H.; Shimada, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Yaegashi, N. TNM Classification of Gynaecological Malignant Tumours, Eighth Edition: Changes between the Seventh and Eighth Editions. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors|Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer. American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/ovarian-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Miyoshi, A.; Kanao, S.; Naoi, H.; Otsuka, H.; Yokoi, T. Ovarian Cancer: Post-Relapse Survival and Prognostic Factors. J. Clin. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 7, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.K.; Syed, N.A.; Sheikh, Z.A.; Guru, F.R.; Mir, M.H.; Banday, S.Z.; MP, A.K.; Parveen, S.; Dar, N.A.; Bhat, G.M. Patterns of Treatment and Outcomes in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Retrospective North Indian Single-Institution Experience. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2022, 8, e2200032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, L.A. Ovarian Cancer. Survival and Treatment Differences by Age. Cancer 1993, 71 (S2), 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millert-Kalińska, S.; Przybylski, M.; Pruski, D.; Stawicka-Niełacna, M.; Mądry, R. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer—Varied Treatment Results. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, F. Research Progress in Prognostic Factors and Biomarkers of Ovarian Cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3976–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadducci, A.; Fuso, L.; Cosio, S.; Landoni, F.; Maggino, T.; Perotto, S.; Sartori, E.; Testa, A.; Galletto, L.; Zola, P. Are Surveillance Procedures of Clinical Benefit for Patients Treated for Ovarian Cancer? A Retrospective Italian Multicentric Study. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2009, 19, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuidris, D.O.; Weng, H.-Y.; Elhaj, A.M.; Eltayeb, E.A.; Elsanousi, M.; Ibnoof, R.S.; Mohammed, S.I. Incidence and Survival Rates of Ovarian Cancer in Low-Income Women in Sudan. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronlund, B.; Høgdall, C.; Hansen, H.H.; Engelholm, S.A. Results of Reinduction Therapy with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Recurrent Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2001, 83, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehouli, J.; Chekerov, R.; Reinthaller, A.; Richter, R.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Harter, P.; Woopen, H.; Petru, E.; Hanker, L.C.; Keil, E.; et al. Topotecan plus Carboplatin versus Standard Therapy with Paclitaxel plus Carboplatin (PC) or Gemcitabine plus Carboplatin (GC) or Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin plus Carboplatin (PLDC): A Randomized Phase III Trial of the NOGGO-AGO-Study Group-AGO Austria and GEICO-ENGOT-GCIG Intergroup Study (HECTOR). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2236–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.K.B.; Ledermann, J.A.; Colombo, N.; du Bois, A.; Delaloye, J.-F.; Kristensen, G.B.; Wheeler, S.; Swart, A.M.; Qian, W.; Torri, V.; et al. ICON and AGO Collaborators. Paclitaxel plus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy versus Conventional Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Women with Relapsed Ovarian Cancer: The ICON4/AGO-OVAR-2.2 Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2003, 361, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Hilpert, F.; Weber, B.; Reuss, A.; Poveda, A.; Kristensen, G.; Sorio, R.; Vergote, I.; Witteveen, P.; Bamias, A.; et al. Bevacizumab Combined With Chemotherapy for Platinum-Resistant Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: The AURELIA Open-Label Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 69, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudou, M.; Zhong, D.; Wu, T.; Wu, X. Topotecan for Ovarian Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2008, CD005589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D.; Shen, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wu, X.; Cui, M.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, W.; et al. Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2021, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Nøttrup, T.J.; Roed, H. Gemcitabine for Recurrent Ovarian Cancer-a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 155, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, K.; Gao, B.; Mapagu, C.; Fereday, S.; Emmanuel, C.; Alsop, K.; Traficante, N.; Harnett, P.R.; Bowtell, D.D.L.; deFazio, A. Response Rates to Second-Line Platinum-Based Therapy in Ovarian Cancer Patients Challenge the Clinical Definition of Platinum Resistance. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedirian, K.; Aghabekyan, T.; Mesrobian, A.; Shekherdimian, S.; Zohrabyan, D.; Safaryan, L.; Sargsyan, L.; Avagyan, A.; Harutyunyan, L.; Voskanyan, A.; et al. Overview of Cancer Control in Armenia and Policy Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).