First-Line (1L) Treatment Decision Patterns and Survival of Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC) Patients in a Latin American (LATAM) Public Institution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Survival Outcomes
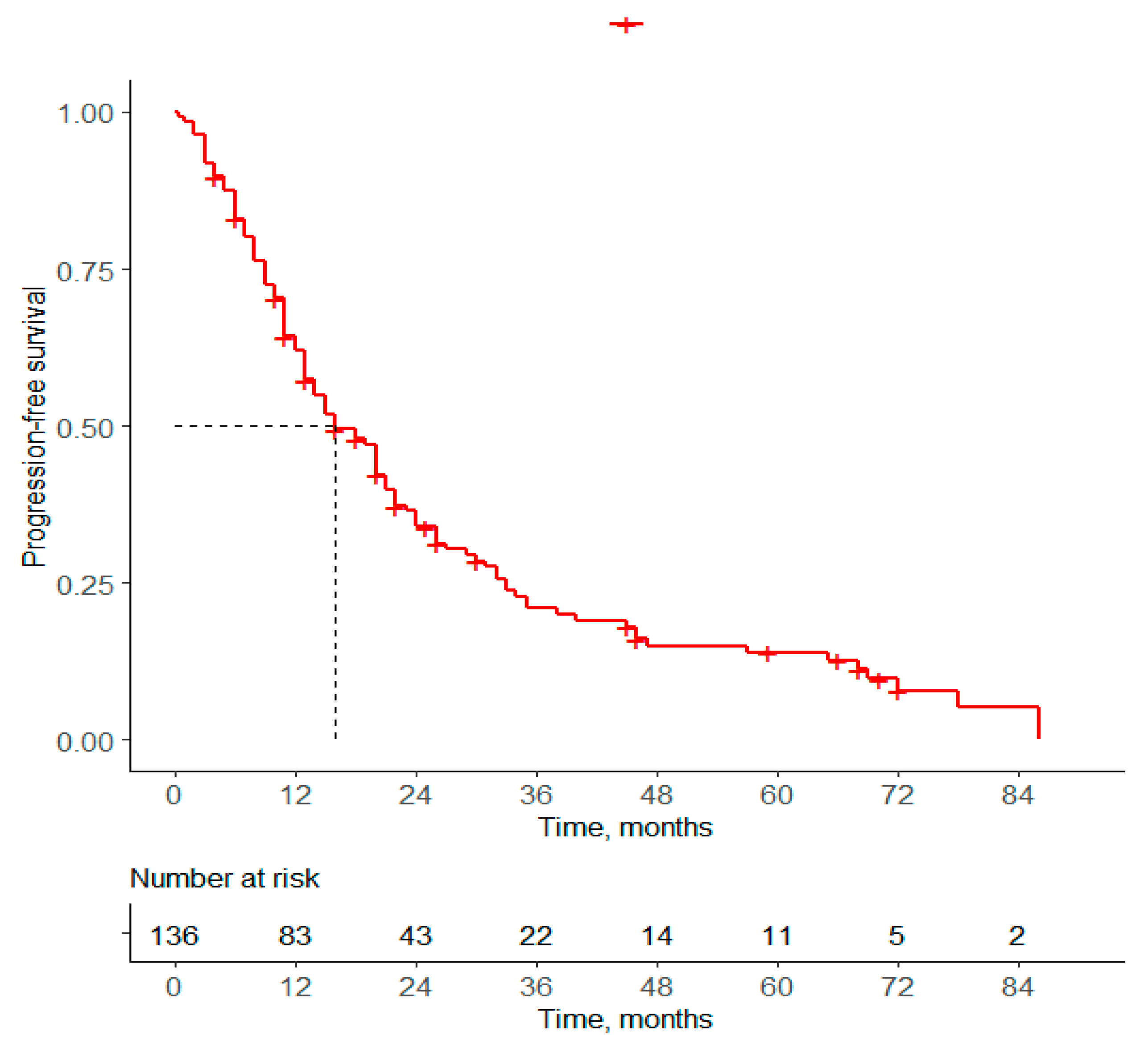
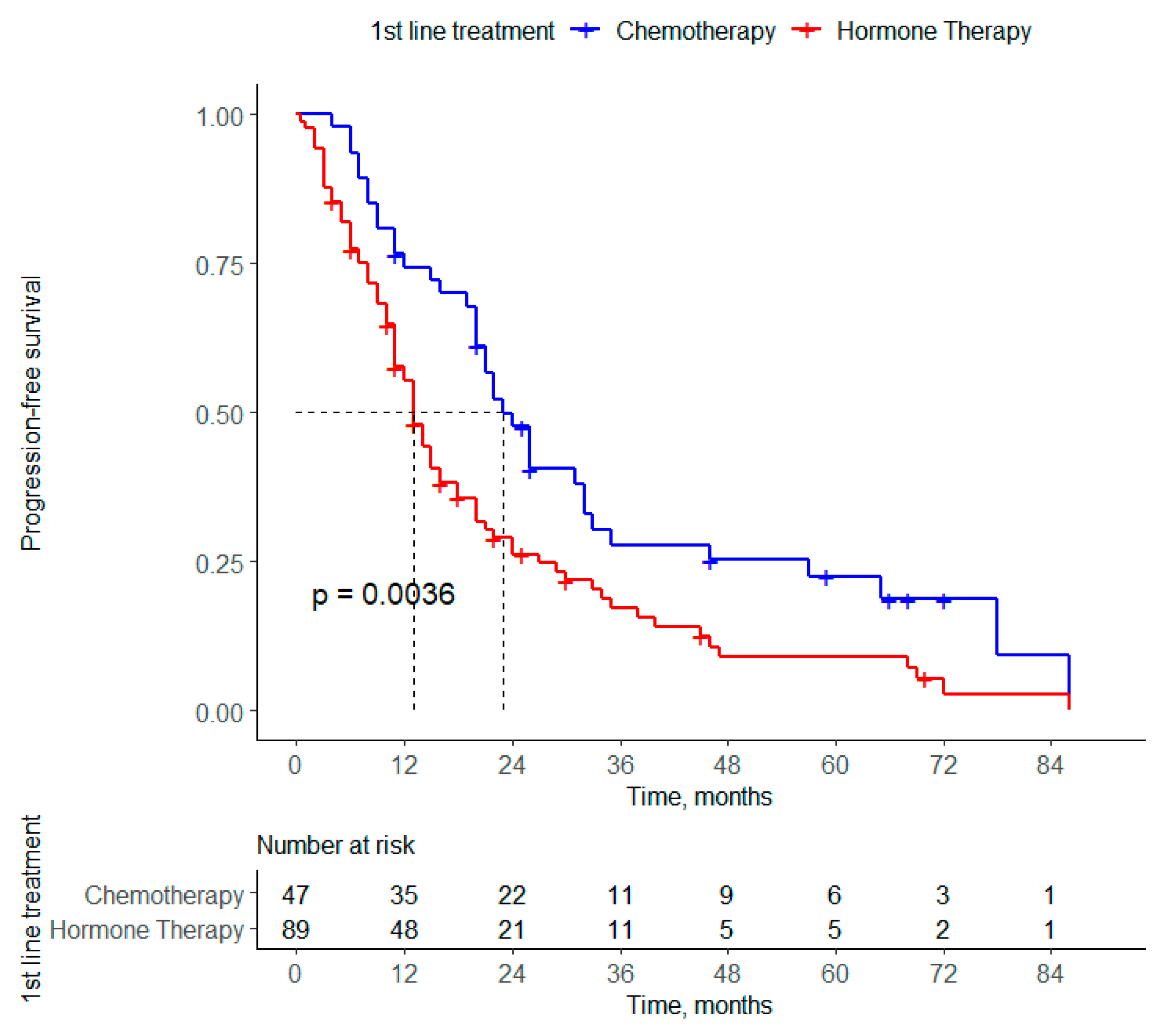
3.2.1. Progression-Free Survival
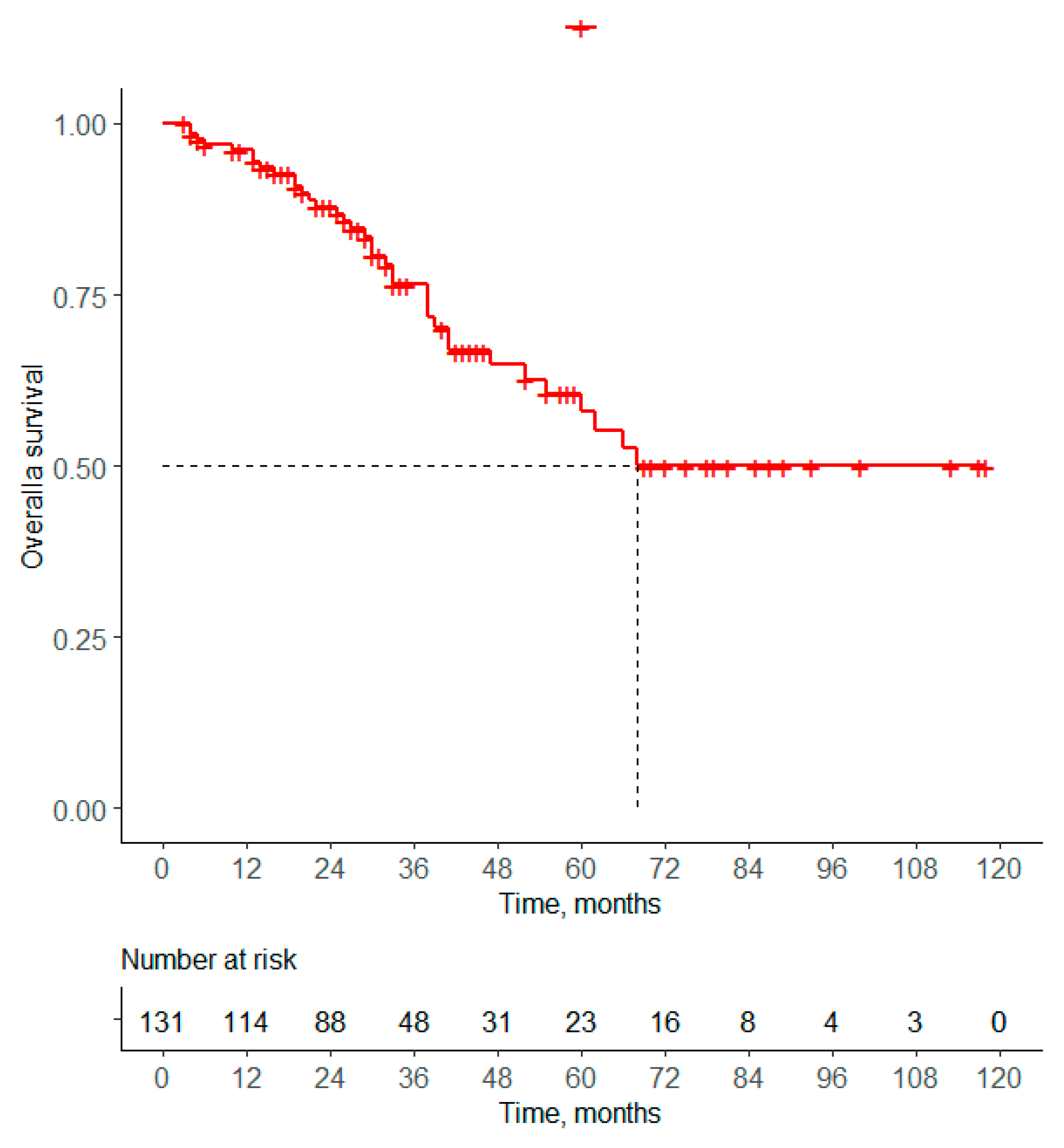
3.2.2. Overall Survival
3.2.3. Patients with “Aggressive Disease”
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeros, M.; Laversanne, M.; Barrios, E.; Cancela, M.C.; de Vries, E.; Pardo, C.; Bray, F. An updated profile of the cancer burden, patterns and trends in Latin America and the Caribbean. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2022, 13, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer News Cases 2000–2020. Cancer Epidemiology Unit—Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplásicas (INEN). Available online: https://portal.inen.sld.pe/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Payet, E. Registro de Cáncer de Lima Metropolitana: Incidencia y Mortalidad 2013–2015; Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplásicas: Lima, Peru, 2021; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Sala Situacional de Cáncer en el Perú. I Trimestre 2024. UT ENT CDC Perú. Vigilancia Epidemiológica del Cáncer Ministerio de Salud; Ministerio de Salud (MINSA): Lima, Peru, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ley N° 31336. Ley Nacional del Cáncer. Diario Nacional El Peruano. 10 August 2021. Available online: https://busquedas.elperuano.pe/dispositivo/NL/1980284-2 (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Cardoso, F.; Spence, D.; Merts, S.; Corneliussen-James, D.; Sabelko, K.; Gralow, J.; Cardoso, M.J.; Peccatori, F.; Paonessa, D.; Benares, A.; et al. Global analysis of advanced/metastatic breast cancer: Decade report (2005–2015). Breast 2018, 39, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Diéras, V.; Rugo, H.S.; Harbeck, N.; Im, S.A.; Gelmon, K.A.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Martin, M.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; et al. Overall survival with palbociclib plus letrozole in advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Hart, L.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Winer, E.P.; Janni, W.; et al. Overall survival with ribociclib plus letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, M.P.; Toi, M.; Huober, J.; Sohn, J.H.; Trédan, O.; Park, I.; Campone, M.; Chen, S.C.; Manso, L.M.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; et al. MONARCH 3: Final overall survival results of abemaciclib plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor as first-line therapy for HR+, HER2- advanced breast cancer. Abstract GS01-12. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, GS01–GS12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.F.R.; Bondarenko, I.M.; Trishkina, E.; Dvorkin, M.; Panasci, L.; Manikhas, A.; Shparyk, Y.; Cardona-Huerta, S.; Cheung, K.L.; Philco-Salas, M.J.; et al. Fulvestrant 500 mg versus anastrozole 1 mg for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer (FALCON): An international, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Im, S.A.; Slamon, D.J.; Harbeck, N.; Bondarenko, I.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; et al. Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2- ABC: Updated exploratory analyses of PALOMA-3, a double-blind, phase III randomized study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neven, P.; Fasching, P.A.; Chia, S.; Jerusalem, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Martin, M.; Nusch, A.; et al. Updated overall survival from the MONALEESA-3 trial in postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer receiving first-line ribociclib plus fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart-Cussac, A.; Sledge, G.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.H.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. Final overall survival analysis of MONARCH 2: A phase 3 trial of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in patients with hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Poster presentation. In Proceedings of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 6–10 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Juric, D.; Loibl, S.; Campone, M.; Mayer, I.A.; Rubovszky, G.; Yamashita, T.; Kaufman, B.; Lu, Y.S.; et al. Overall survival results from SOLAR-1, a phase III study of alpelisib + fulvestrant for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. In Proceedings of the ESMO Virtual Congress, Virtual, 9–12 December 2020. Abstract LBA18 Presented 19 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Howell, S.J.; Dalenc, F.; Cortes, J.; Gomez Moreno, H.L.; Jhaveri, K.; Krivorotko, P.; Loibl, S.; Morales Murillo, S.; et al. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.C.; Kaklamani, V.G.; Neven, P.; Streich, G.; Montero, A.J.; Forget, F.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Sohn, J.H.; Taylor, D.; Harnden, K.K.; et al. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) Versus Standard Endocrine Therapy for Estrogen Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III EMERALD Trial. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3246–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baselga, J.; Campone, M.; Piccart, M.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Rugo, H.S.; Sahmoud, T.; Noguchi, S.; Gnant, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Lebrun, F.; et al. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.; Gradishar, W.; Mauriac, L.; Bines, J.; Amant, F.; Federico, M.; Fein, L.; Romieu, G.; Buzdar, A.; Robertson, J.F.R.; et al. Double-blind, randomized placebo controlled trial of fulvestrant compared with exemestane after prior nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer: Results from EFECT. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, H.J.; Somerfield, M.R.; Barton, D.L.; Dorris, A.; Fallowfield, J.; Jain, D.; Johnston, S.R.D.; Korde, L.A.; Litton, J.K.; Macrae, E.R.; et al. Endocrine Treatment and Targeted Therapy for Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3959–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Senkus, E.; Curigliano, G.; Aapro, M.S.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Bhattacharyya, G.S.; Biganzoli, L.; et al. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1623–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Senkus, E.; Costa, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Aapro, M.; André, F.; Harbeck, N.; Aguilar Lopez, B.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; et al. 4th ESO-ESMO International Consensus Guidelines for Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC 4). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 8, 1634–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, J.; Miles, D.; Vukelja, S.; Moiseyenko, V.; Ayoub, J.P.; Cervantes, G.; Fumoleau, P.; Jones, S.; Lui, W.Y.; Mauriac, L.; et al. Superior survival with capecitabine plus docetaxel combination therapy in anthracycline pretreated patients with advanced breast cancer: Phase III trial results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2812–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.; Stockler, M.; Puntoni, M.; Sormani, M.; Nanni, O.; Amadori, D.; Wilcken, N.; D’Amico, M.; DeCensi, A.; Bruzzi, P. Duration of chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, S.; Parker, S.; Thornton, C.E.; Ghersi, D.; Simes, J.; Wilcken, N. Single agent versus combination chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 2, CD003372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albain, K.S.; Calderillo-Ruiz, G.; Jordaan, J.P.; Llombart, A.; Pluzanska, A.; Pawlicki, M.; Melemed, A.S.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Reyes, J.M. Global phase III study of gemcitabine plus paclitaxel (GT) vs. paclitaxel (T) as frontline therapy for metastatic breast cancer (MBC): First report of overall survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Colleoni, M.; Di Leo, A.; Francia, G.; Gennari, A.; Gligorov, J.; Llombart, A. Oral chemotherapy in advanced breast cancer: Expert perspectives on its role in clinical practice. Cancer Treat. Commun. 2016, 6, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.S.; Mahidin, E.I.B.M.; Azim, H.; Eralp, Y.; Yap, Y.S.; Im, S.A.; Rihani, J.; Bowles, J.; Alfaro, T.D.; Wu, J.; et al. Primary results from the randomized Phase II RIGHT Choice trial of premenopausal patients with aggressive HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer treated with ribociclib + endocrine therapy vs. physician’s choice combination chemotherapy. Abstract GS1-10. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, GS1-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nuñez, P.; Acuña-Aguilar, L.E.; Gómez-Valles, F.O.; Ramírez-Valdespino, C.A.; Mayrovitz, H.N. Subtypes of breast cancer. In Breast Cancer; Exon Publications: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2022; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Clinical Practice Guidelines. Breast Cancer; Version 6; NCCN: Fort Washington, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, F.; Paluch Shimon, S.; Schumacher-Wulf, E.; Matos, L.; Gelmon, K.; Aapro, M.S.; Bajpai, J.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Bergstaen-Nordstrom, E.; et al. 6th and 7th International consensus guidelines for the management of advanced breast cancer (ABC guidelines 6 and 7). Breast 2024, 76, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Cortes, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Glogorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, L.A.; Gumusay, O.; Idossa, D.; Rugo, H.S. Systemic therapy for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early stage and metastatic breast cancer. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 480–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufsky, A.M. Delaying Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2015, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Xie, Y.F.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, G. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes of breast cancer patients with disease progression during neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Breast 2023, 70, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrew, N.P.; Finn, R.S. Clinical Review on the Management of Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2021, 18, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.H.; Sampaio, C.; Vinholes, J.; Caponero, R. What is the role of chemotherapy in estrogen receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer? Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, C.H. The role of chemotherapy in hormone receptor positive advanced breast cancer. Gac. Mex. Oncol. GAMO 2010, 9, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.S.; Mahidin, E.I.B.M.; Azim, H.; Eralp, Y.; Yap, Y.S.; Im, S.A.; Rihani, J.; Gokmen, E.; El Bastawisy, A.; Karadurmus, N.; et al. Final results of RIGHT Choice: Ribociclib plus endocrine therapy versus combination chemotherapy in premenopausal women with clinically aggressive hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2812–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinillos, L.; Pinto, J.A.; Sarria, G. History of the development of radiotherapy in Latin America. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria, G.R.; Martinez, D.A.; Li, B.; Del Castillo, R.; Salgado, A.; Pinillos, L.; Felix, A.; Bobadilla, I.; Ferraris, G.; Castilho, M.; et al. Radiotherapy and cancer status in Latin America: Economic analysis of investment opportunities up to 2030. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 116, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.M.; Gómez, A.C.; Zingg-De Jongh, W.; Ausejo, J.; Córdova, I.; Schwarz Luis, J.; Bretel, D.; Fajardo, W.; Saravia-Huarca, L.G.; Barboza-Meca, J.; et al. A nationwide pilot study on breast cancer screening in Peru. Ecancermedicalscience 2023, 17, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, N.; Barchuk, S.; Inurrigarro, G.; Celano, C.; Soriano-García, J.L.; Bolaños, P.; Mohs-Alfaro, M.; Tapia-González, H.; Perez-Martinez, R.; Samtani, S.; et al. Status of breast cancer in Latin American: Results of the breast cancer revealed initiative. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2023, 181, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Mesías, G.; Rioja-Viera, P.; Morante-Cruz, Z.; Toledo-Morote, Y.; Neciosup-Delgado, S.; Gómez-Moreno, H. The current situation regarding the availability and accessibility of anticancer drugs for breast cancer in the Peruvian public health systems. Ecancermedicalscience 2021, 15, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Documento Técnico: “Tratamiento Multidisciplinario del Cáncer de Mama Metastásico” Resolución Jefatural N°, 1.6.6.-2.0.2.1.-J-INEN. Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplásicas. 28 May 2021. Available online: https://portal.inen.sld.pe/guias-tecnicas/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Instituto Nacional de Salud. RENETSA. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/ins/colecciones/11902-renetsa (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Yu, P.; Ouyang, Q.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Tong, Z.; et al. Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: A nation-wide multicenter epidemiological study in China. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 599604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonotto, M.; Gerratana, L.; Arpino, G.; Di Maio, M.; De Angelis, C.; Iacono, D.; Cinausero, M.; Milano, M.; Gargiulo, P.; Fontanella, C.; et al. First line treatment in patients with luminal-like metastatic breast cancer: A propensity score-matched analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, vi8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as first-line for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabholtz, J.M.; Buzdar, A.; Pollak, M.; Harwin, W.; Burton, G.; Mangalik, A.; Steinberg, M.; Webster, A.; von Euler, M. Anastrozole Is Superior to Tamoxifen as First-Line Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women: Results of a North American Multicenter Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3758–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, A.K.M.; Ibragimova, K.I.E.; Geurts, S.M.E.; Bos, M.E.M.M.; Erdkamp, F.L.G.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G. The role of chemotherapy in treatment of advanced breast cancer: An overview for clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 153, 102988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruti, A.; Zola, P.; Buniva, T.; Bau, M.G.; Farris, A.; Sarobba, M.G.; Bottini, A.; Tampellini, M.; Durando, A.; Destefanis, M.; et al. Prognostic factors in metastatic breast cancer patients obtaining objective response or disease stabilization after first-line chemotherapy with epirubicin. Evidence for a positive effect of maintenance hormonal therapy on overall survival. Anticancer. Res. 1997, 17, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macalalad, A.R.; Hao, Y.; Lin, P.L.; Signorovitch, J.E.; Wu, E.Q.; Ohashi, E.; Zhou, Z.; Kelley, C. Treatment patterns and duration in post-menopausal women with HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer in the US: A retrospective chart review in community oncology practices 2004–2010. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015, 31, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, R.K.; Roy, J.; Allu, S.R. Therapies for the Treatment of Advanced/Metastatic Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: Current Situation and Future Directions. Cancers 2024, 16, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, F.; Gómez, H.L.; Neciosup, S.P.; Limón, R.; Torrico, M.; Morillas, L.; Torres, R.; Sánchez, C.; Araya, I.; Gómez, R.; et al. Advanced Breast Cancer guidelines in Latin America: Assessment, adaptation, and implementation of Fifth Advanced Breast Cancer consensus guidelines. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2024, 10, e2200067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sukhun, S.; Temin, S.; Barrios, C.H.; Antone, N.Z.; Guerra, Y.C.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Chopra, R.; Danso, M.A.; Gomez, H.L.; Homian, N.M.; et al. Systemic treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer: ASCO Resource-Stratified Guideline. JCO Global Oncol. 2024, 10, e2300285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llera, A.S. A fresh perspective on Latin America cancer care: Uncovering hidden messages in unconventional data sources. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 24, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1L Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Patients n = 143 | Endocrine Therapy (ET) n = 95 | Chemotherapy (CT) n = 48 | p-Value | |
| Age at diagnosis, years | ||||
| Average/range | 54.2 (24–85) | 54.5 (29–85) | 53.6 (24–84) | 0.707 |
| Age groups, years | ||||
| <50 | 51 (35.7%) | 33 (34.7%) | 18 (37.5%) | |
| ≥50 | 92 (64.3%) | 62 (65.3%) | 30 (62.5%) | 0.745 |
| ECOG at diagnosis | ||||
| 0–1 | 133 (93.0%) | 89 (93.7%) | 44 (91.7%) | |
| 2 | 10 (7.0%) | 6 (6.3%) | 4 (8.3%) | 0.921 |
| De novo disease | ||||
| Yes | 41 (28.7%) | 19 (20.0%) | 22 (45.8%) | |
| No | 102 (71.3%) | 76 (80.0%) | 26 (54.2%) | <0.001 |
| Metastatic sites | ||||
| Bone | 85 (59.4%) | 52 (54.7%) | 33 (68.8%) | 0.107 |
| Lung | 39 (27.3%) | 22 (23.2%) | 18 (37.5%) | 0.071 |
| Lymph node | 29 (20.3%) | 24 (25.3%) | 6 (12.5%) | 0.077 |
| Locoregional | 15 (10.5%) | 13 (13.6%) | 3 (6.3%) | 0.183 |
| Liver | 13 (9.1%) | 11 (11.6%) | 3 (6.3%) | 0.475 |
| Contralateral | 5 (3.5%) | 3 (3.2%) | 2 (4.2%) | 1 |
| Dermis | 4 (2.8%) | 2 (2.1%) | 2 (4.2%) | 0.866 |
| Soft tissue | 3 (2.1%) | 2 (2.1%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 |
| Peritoneal | 2 (1.4%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 |
| Mediastinum | 2 (1.4%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 |
| Cutaneous | 2 (1.4%) | 2 (2.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.796 |
| Suprarenal | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 |
| Ovary | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.727 |
| Pancreas | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.727 |
| Number of metastases | ||||
| 1 | 99 (69.2%) | 66 (69.5%) | 33 (68.8%) | |
| 2 | 32 (22.4%) | 23 (24.2%) | 9 (18.8%) | |
| 3 | 9 (6.3%) | 5 (5.3%) | 4 (8.3%) | |
| ≥4 | 3 (2.1%) | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (4.2%) | NE |
| Luminal subtype | ||||
| A | 40 (31.0%) | 24 (28.6%) | 16 (35.6%) | |
| B | 89 (69.0%) | 60 (71.4%) | 29 (64.4%) | 0.414 |
| NR | 14 | 11 | 3 | |
| Intensity of HER2 expression | ||||
| 0 | 81 (60.4%) | 56 (62.2%) | 25 (56.8%) | |
| 1+/2+ | 53 (39.6%) | 34 (37.8%) | 19 (43.2%) | 0.548 |
| NR | 9 | 5 | 4 | |
| Ki-67 | ||||
| <20% | 27 (20.9%) | 17 (20.2%) | 10 (22.2%) | |
| ≥20% | 63 (48.8%) | 32 (45.2%) | 25 (55.6%) | 0.339 |
| NR | 14 | 11 | 3 | |
| Univariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Clinical stage IV | |||
| Recurrent | Ref. | ||
| Progressive | 3.78 | 1.23–11.68 | 0.019 |
| De novo | 4.37 | 1.98–9.94 | <0.001 |
| OS (months) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 36 | 60 | p-Value | |
| All patients | 96.1% | 76.4% | 57.8% | - |
| 1L treatment | ||||
| Endocrine therapy (ET) | 94.0% | 82.4% | 66.2% | |
| Chemotherapy (CT) | 100% | 71.2% | 52.2% | 0.36 |
| Treatment sequencing | ||||
| ET-ET | 100% | 83.9% | 65.4% | |
| ET-CT | 88.0% | 80.3% | 64.3% | |
| CT-ET | 100% | 65.4% | 52.5% | |
| CT-CT | 100% | 87.5% | 58.3% | 0.42 |
| Patients (pts) Received 1L CT | Peruvian pts | MONALEESA (ML) Trials | RIGHT Choice Trial | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age | 52 (24–80) year | 55 year | Premenopausal | |
| Postmenopausal | 62% | 80% | 0% | |
| Premenopausal | 38% | 20% ML-2 20% ML-3 100% ML-7 | 100% | |
| De novo (diagnosis) | 46% | 35% | NR | |
| ECOG 0–1 | 92% | 99% | 99% | |
| Luminal B subtype | 66% | NR | NR | |
| Visceral metastases | 46% | 60% | 50% | |
| Visceral crisis | 6% | 0% | 50% | |
| Met aggressive disease (RIGHT Choice) definition | 54% | ND | 100% | |
| “Aggressive disease” criteria | Symptomatic visceral metastases | 23% | ND | 67.6% |
| Rapid disease progression | 96% | ND | 18.5% | |
| Markedly symptomatic non-visceral metastases | 54% | ND | 14% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valencia, G.; Rioja, P.; Chirito, M.; Peralta, O.; Sánchez, J.; Rabanal, C.; Mantilla, R.; Morante, Z.; Fuentes, H.; Castaneda, C.; et al. First-Line (1L) Treatment Decision Patterns and Survival of Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC) Patients in a Latin American (LATAM) Public Institution. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 7890-7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31120581
Valencia G, Rioja P, Chirito M, Peralta O, Sánchez J, Rabanal C, Mantilla R, Morante Z, Fuentes H, Castaneda C, et al. First-Line (1L) Treatment Decision Patterns and Survival of Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC) Patients in a Latin American (LATAM) Public Institution. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(12):7890-7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31120581
Chicago/Turabian StyleValencia, Guillermo, Patricia Rioja, Miguel Chirito, Olenka Peralta, Jorge Sánchez, Connie Rabanal, Raúl Mantilla, Zaida Morante, Hugo Fuentes, Carlos Castaneda, and et al. 2024. "First-Line (1L) Treatment Decision Patterns and Survival of Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC) Patients in a Latin American (LATAM) Public Institution" Current Oncology 31, no. 12: 7890-7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31120581
APA StyleValencia, G., Rioja, P., Chirito, M., Peralta, O., Sánchez, J., Rabanal, C., Mantilla, R., Morante, Z., Fuentes, H., Castaneda, C., Vidaurre, T., Pacheco, C., Neciosup, S., & Gomez, H. L. (2024). First-Line (1L) Treatment Decision Patterns and Survival of Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC) Patients in a Latin American (LATAM) Public Institution. Current Oncology, 31(12), 7890-7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31120581






