Efficacy of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab–Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
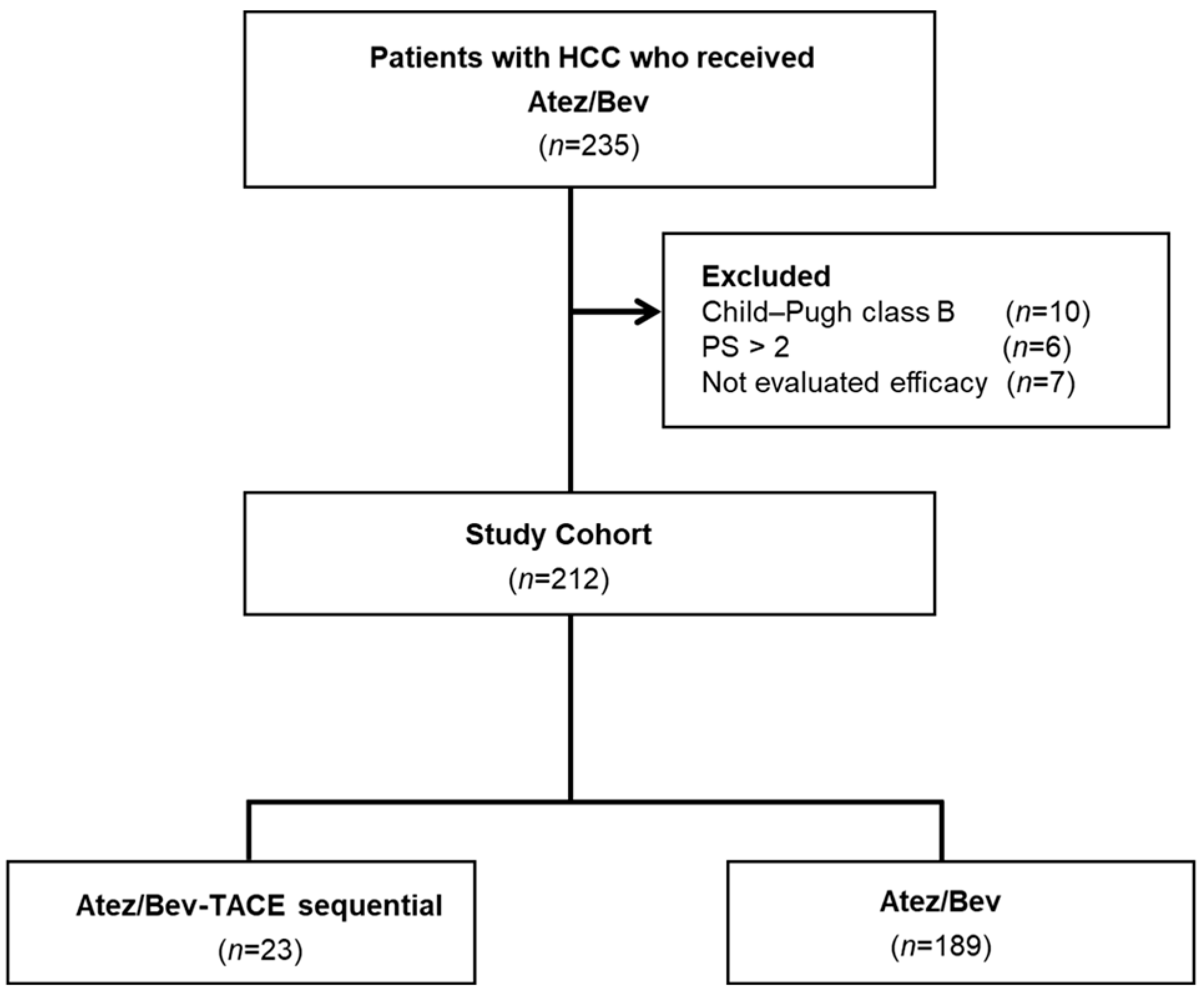
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Assessment of Hepatic Reserve Function
2.3. Atez/Bev Treatment Protocol
2.4. Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Atez/Bev Treatment
2.5. Atez/Bev-TACE Sequential Therapy
2.6. TACE Treatment Protocol
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
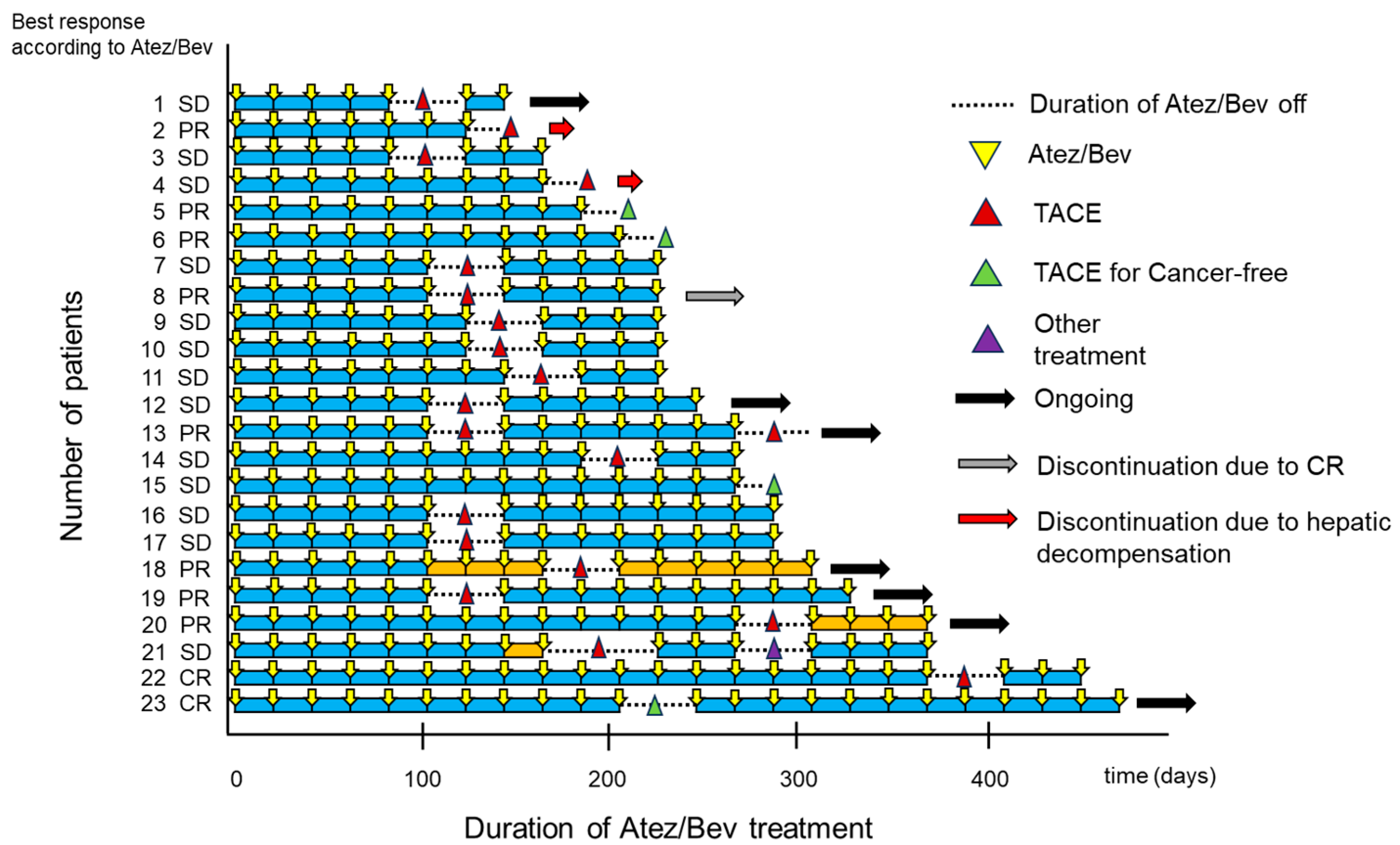
3.2. Swimmer Plot Analysis Assessment by Investigator Assessment
3.3. Best Therapeutic Response of Atez/Bev-TACE Sequential Therapy According to mRECIST Criteria
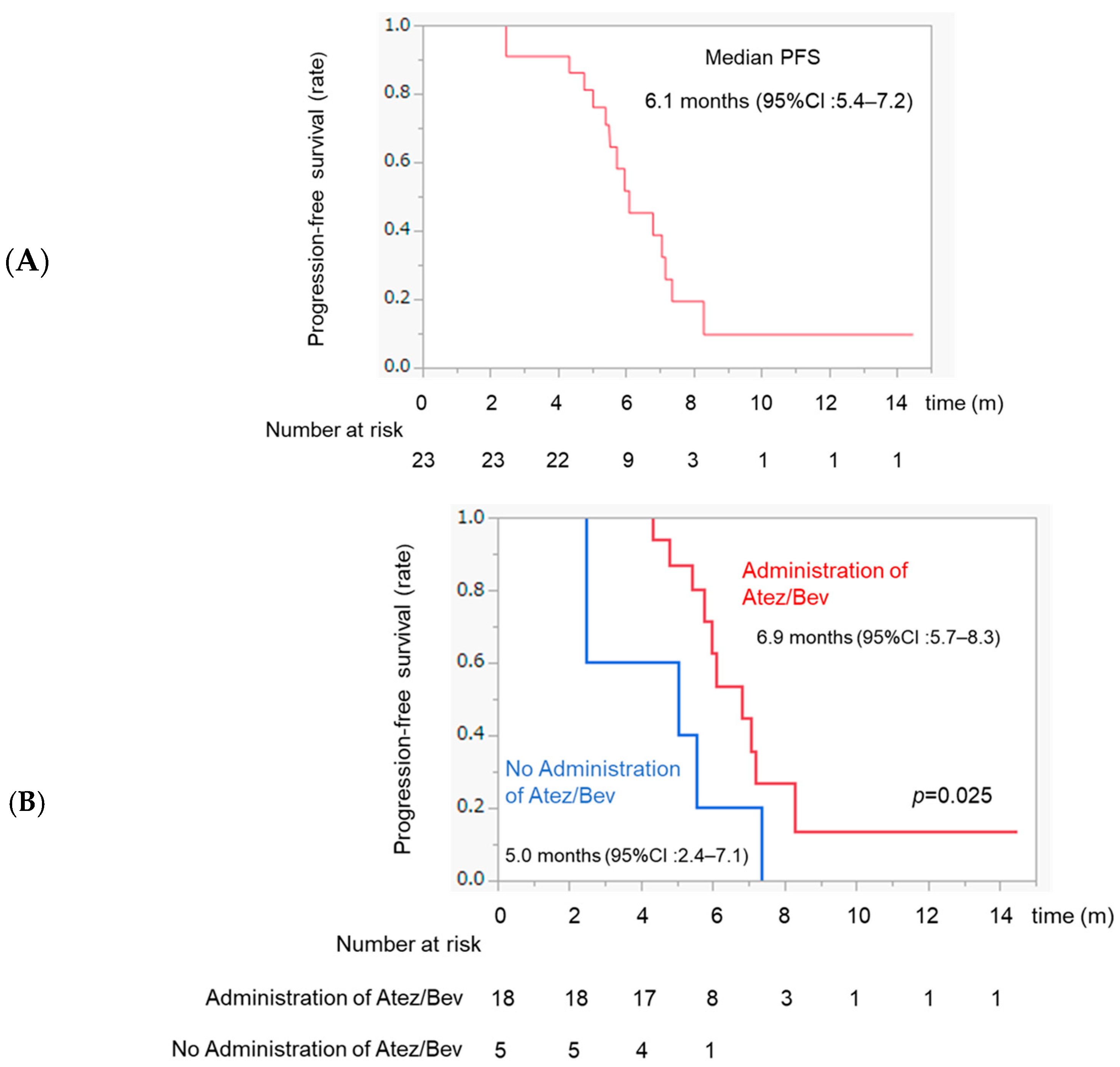
3.4. PFS after TACE and Comparison of PFS between Patients with and without Atez/Bev Administration after TACE
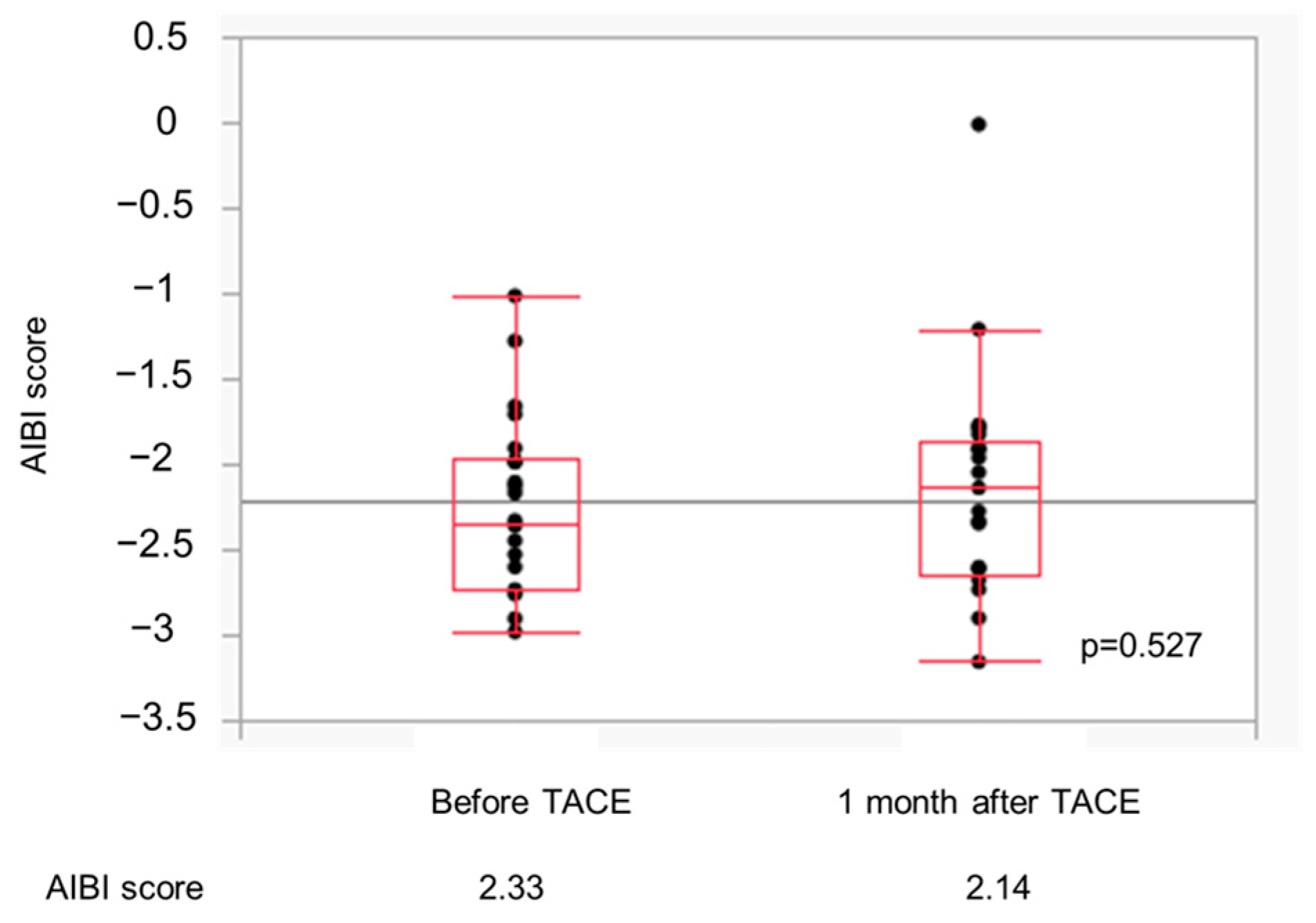
3.5. Changes in the ALBI Score in the Atez/Bev-TACE Sequential Treatment Group
3.6. Patient Characteristics in Patients with Intermediate-Stage HCC
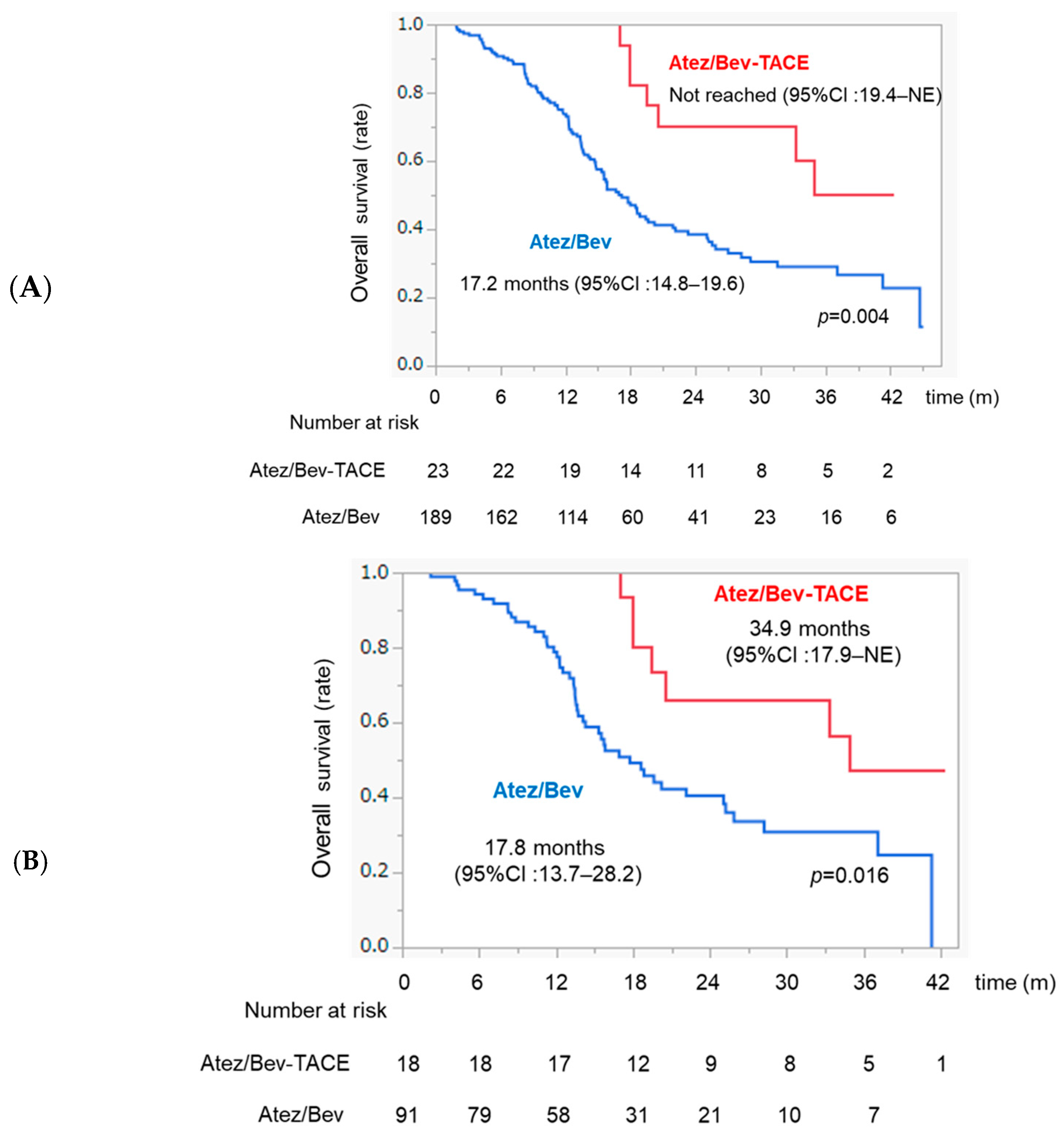
3.7. Comparison of OS between Atez/Bev and Atez/Bev-TACE Sequential Therapy in the Whole Sample and in Patients with Intermediate-Stage HCC
3.8. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Factors Associated with OS in Patients with Intermediate-Stage HCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Response Category | m-RECIST |
|---|---|
| CR | 6 (26.1%) |
| PR | 11 (47.8%) |
| SD | 2 (8.7%) |
| PD | 4 (17.3%) |
| ORR | 17 (73.9%) |
| DCR | 19 (82.6%) |
References
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global Burden of Primary Liver Cancer in 2020 and Predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, K.; Ding, N.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, J.; Qu, Z. Lenvatinib in Combination with Transarterial Chemoembolization for Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Uhcc): A Retrospective Controlled Study. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Villanueva, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Schwartz, M.; Meyer, T.; Galle, P.R.; Lencioni, R.; Greten, T.F.; Kudo, M.; Mandrekar, S.J.; et al. Trial Design and Endpoints in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Aasld Consensus Conference. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 158–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib Versus Sorafenib in First-Line Treatment of Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomised Phase 3 Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Japan: Current Trends. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. Updated Efficacy and Safety Data from Imbrave150: Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Vs. Sorafenib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A 2017 Update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolondi, L.; Burroughs, A.; Dufour, J.F.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Sangro, B. Heterogeneity of Patients with Intermediate (Bclc B) Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Proposal for a Subclassification to Facilitate Treatment Decisions. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. Bclc Strategy for Prognosis Prediction and Treatment Recommendation: The 2022 Update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimose, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Tanaka, M.; Niizeki, T.; Shirono, T.; Noda, Y.; Kamachi, N.; Okamura, S.; Nakano, M.; Suga, H.; et al. Alternating Lenvatinib and Trans-Arterial Therapy Prolongs Overall Survival in Patients with Inter-Mediate Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Ikeda, M.; Torimura, T.; Tanabe, N.; Aikata, H.; Izumi, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Nojiri, S.; Hino, K.; et al. Randomised, Multicentre Prospective Trial of Transarterial Chemoembolisation (Tace) Plus Sorafenib as Compared with Tace Alone in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Tactics Trial. Gut 2020, 69, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Saeki, I.; Ishikawa, T.; Inaba, Y.; Morimoto, N.; Aikata, H.; Tanabe, N.; Wada, Y.; Kondo, Y.; et al. A Phase 2, Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Arm Trial of Transarterial Chemoembolization Therapy in Combination Strategy with Lenvatinib in Patients with Unresectable Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Tactics-L Trial. Liver Cancer 2024, 13, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in Cancer and Other Diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischfield, D.J.; Gurevich, A.; Johnson, O.; Gatmaytan, I.; Nadolski, G.J.; Soulen, M.C.; Kaplan, D.E.; Furth, E.; Hunt, S.J.; Gade, T.P.F. Transarterial Embolization Modulates the Immune Response within Target and Nontarget Hepatocellular Carcinomas in a Rat Model. Radiology 2022, 303, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholongitas, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Vangeli, M.; Terreni, N.; Patch, D.; Burroughs, A.K. Systematic Review: The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease--Should It Replace Child-Pugh’s Classification for Assessing Prognosis in Cirrhosis? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Kokudo, N.; Kubo, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Validation and Potential of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Prognostication in a Nationwide Survey of 46,681 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan: The Need for a More Detailed Evaluation of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freites-Martinez, A.; Santana, N.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Viera, A. Using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (Ctcae—Version 5.0) to Evaluate the Severity of Adverse Events of Anticancer Therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021, 112, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified Recist (Mrecist) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. A Changing Role of Transarterial Chemoembolization in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Plus Anti-Vegf/Tki Plus Transarterial Chemoembolization: From Total Embolization to Partial Embolization (Immune Boost Transarterial Chemoembolization). Liver Cancer 2024, 13, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimose, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Niizeki, T.; Shirono, T.; Tanaka, M.; Koga, H.; Torimura, T. Indication of Suitable Transarterial Chemoembolization and Multikinase Inhibitors for Intermediate Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, H.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, J. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone in Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimose, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Niizeki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Shirono, T.; Moriyama, E.; Noda, Y.; Nakano, M.; Suga, H.; Kuromatsu, R.; et al. Efficacy of Lenvatinib Combined with Transcatheter Intra-Arterial Therapies for Patients with Advanced-Stage of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchino, K.; Tateishi, R.; Shiina, S.; Kanda, M.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y.; Goto, T.; Omata, M.; Yoshida, H.; Koike, K. Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Extrahepatic Metastasis: Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors. Cancer 2011, 117, 4475–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, H.; Shimose, S.; Niizeki, T.; Koga, H.; Torimura, T. Clinical Significance of the Discrepancy between Radiological Findings and Biochemical Responses in Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Yamashita, T.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.; Ducreux, M.; Cheng, A.-L.; Tsuchiya, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Hige, S.; Take, R.; et al. IMbrave150: Exploratory analyses for investigating associations between overall survival (OS) and depth of response (DpR) or duration of response (DoR) in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1520–S1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, A.; Cristofori, C.; Cardin, R.; Pivetta, G.; Ragazzi, R.; Baldan, A.; Girardi, L.; Cillo, U.; Burra, P.; Giacomin, A.; et al. Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (Tace) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Hcc): The Role of Angiogenesis and Invasiveness. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Plus Anti-Vegf/Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Combined with Tace (Triple Therapy) in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2024, 13, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Michitaka, K.; Kudo, M. Newly Proposed Albi Grade and Albi-T Score as Tools for Assessment of Hepatic Function and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Gan, L.; Zeng, D.; Lin, L.; Xiong, Z.; Liao, F.; Wang, A. Clinical Efficacy of Lenvatinib, Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization, and Pd-1/L1 Inhibitors in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Kudo, M.; Erinjeri, J.; Qin, S.; Ren, Z.; Chan, S.; Sangro, B. EMERALD-1: A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled study of transarterial chemoembolization combined with durvalumab with or without bevacizumab in participants with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for embolization. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S3), LBA432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Finn, R.S.; Ren, Z.; Guo, Y.; Han, G.; Lin, H.; Kudo, M. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with or without lenvatinib (len) + pembrolizumab (pembro) for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Phase III LEAP-012 study. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Inaba, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Sone, M.; Yamakado, K.; Nishiofuku, H.; Kudo, M. IMPACT: Randomized, multicenter, phase III study evaluating the efficacy of immunotherapy (atezolizumab) plus anti-VEGF therapy (bevacizumab) in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1520–S1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | All Patients | Atez/ Bev-TACE | Atez/Bev | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 212 | 23 | 189 | |
| Age (years old) | 73 (37–93) | 69 (50–84) | 73 (37–93) | 0.255 |
| Sex (female/male) | 45/167 | 5/18 | 40/149 | 0.893 |
| PS (0/1/) | 182/30 | 19/4 | 163/26 | 0.636 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 23.0 (15.9–35.3) | 23.9 (15.4–35.3) | 23.1 (15.9–35.2) | 0.091 |
| Etiology (viral/non-viral) | 126/86 | 12/11 | 114/75 | 0.452 |
| ALBI score (Median (range)) | −2.44 (−3.50–−1.55) | −2.45 (−2.96–−1.71) | −2.44 (−3.50–−1.55) | 0.964 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b) | 71/76/65 | 10/6/7 | 61/70/58 | 0.483 |
| BCLC stage (A/B/C) | 2/109/101 | 1/18/4 | 1/91/97 | 0.003 |
| tumor size (mm) | 32 (10–136) | 26 (11–132) | 32.0 (10–136) | 0.255 |
| Number of tumors <5/≥5 | 74/138 | 9/14 | 65/124 | 0.652 |
| Macrovascular invasion (No/Yes) | 173/39 | 21/2 | 152/37 | 0.203 |
| Extrahepatic spread (No/Yes) | 140/72 | 20/3 | 120/69 | 0.016 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 32.1 (1.2–284, 543) | 6.4 (1.4–1167) | 36.5 (1.2–209, 295) | 0.082 |
| Number of Atez/Bev cycles before TACE | 7 (5–19) | n.s | ||
| Treatment line (first-line/later-lines) | 143/69 | 13/10 | 130/59 | 0.236 |
| Characteristic | All Patients | Atez/Bev-TACE | Atez/Bev | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 109 | 18 | 91 | |
| Age (years old) | 74 (50–93) | 71 (50–84) | 75 (51–93) | 0.219 |
| Sex (female/male) | 24/85 | 5/13 | 19/72 | 0.518 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 23.0 (16.6–35.3) | 23.2 (19.5–29.6) | 23.0 (16.6–35.2) | 0.641 |
| Etiology (viral/non-viral) | 62/47 | 11/7 | 51/40 | 0.691 |
| ALBI score (Median (range)) | −2.46 (−3.50–−1.59) | −2.47 (−2.92–−1.70) | −2.44 (−3.50–−1.59) | 0.873 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b) | 38/35/36 | 8/4/6 | 30/31/30 | 0.542 |
| Up-to-seven (in/out) | 23/86 | 4/14 | 19/72 | 0.895 |
| tumor size (mm) | 32 (10–136) | 25.0 (11–132) | 30.0 (10–136) | 0.285 |
| Number of tumors <5/≥5 | 36/73 | 7/11 | 29/62 | 0.562 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 11.4 (1.2–129, 743) | 10.7 (1.4–1167) | 11.4 (1.2–129, 743) | 0.725 |
| Number of Atez/Bev cycles before TACE | 10 (6–19) | |||
| Treatment line (first-line/later-lines) | 74/35 | 11/7 | 63/28 | 0.500 |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age, <70 vs. ≥70 | 0.615 | |||
| Sex, female vs. male | 0.800 | |||
| Etiology, viral vs. non-viral | 0.355 | |||
| mALBI grade, 1 or 2a vs. 2b | <0.001 | 0.311 | 0.175–0.553 | <0.001 |
| Up-to-seven (in/out) | 0.048 | 0.729 | 0.353–1.502 | 0.391 |
| Number of tumors, <5 vs. ≥5 | 0.881 | |||
| Tumor size, <30 vs. ≥30 | 0.017 | 0.696 | 0.385–1.256 | 0.228 |
| AFP, <400 vs. ≥400 ng/mL | 0.001 | 0.228 | 0.116–0.449 | <0.001 |
| Treatment line, (first-line vs. later-lines) | 0.094 | |||
| Atez/Bev-TACE sequential, (+/−) | 0.015 | 0.311 | 0.138–0.702 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moriyama, E.; Shimose, S.; Niizeki, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Tanaka, M.; Shirono, T.; Noda, Y.; Nakano, M.; Kuromatsu, R.; Koga, H.; et al. Efficacy of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab–Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 5821-5831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31100432
Moriyama E, Shimose S, Niizeki T, Iwamoto H, Tanaka M, Shirono T, Noda Y, Nakano M, Kuromatsu R, Koga H, et al. Efficacy of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab–Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(10):5821-5831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31100432
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoriyama, Etsuko, Shigeo Shimose, Takashi Niizeki, Hideki Iwamoto, Masatoshi Tanaka, Tomotake Shirono, Yu Noda, Masahito Nakano, Ryoko Kuromatsu, Hironori Koga, and et al. 2024. "Efficacy of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab–Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Current Oncology 31, no. 10: 5821-5831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31100432
APA StyleMoriyama, E., Shimose, S., Niizeki, T., Iwamoto, H., Tanaka, M., Shirono, T., Noda, Y., Nakano, M., Kuromatsu, R., Koga, H., & Kawaguchi, T. (2024). Efficacy of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab–Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Current Oncology, 31(10), 5821-5831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31100432








