Severe Fatal Mucormycosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Treated with Zanubrutinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
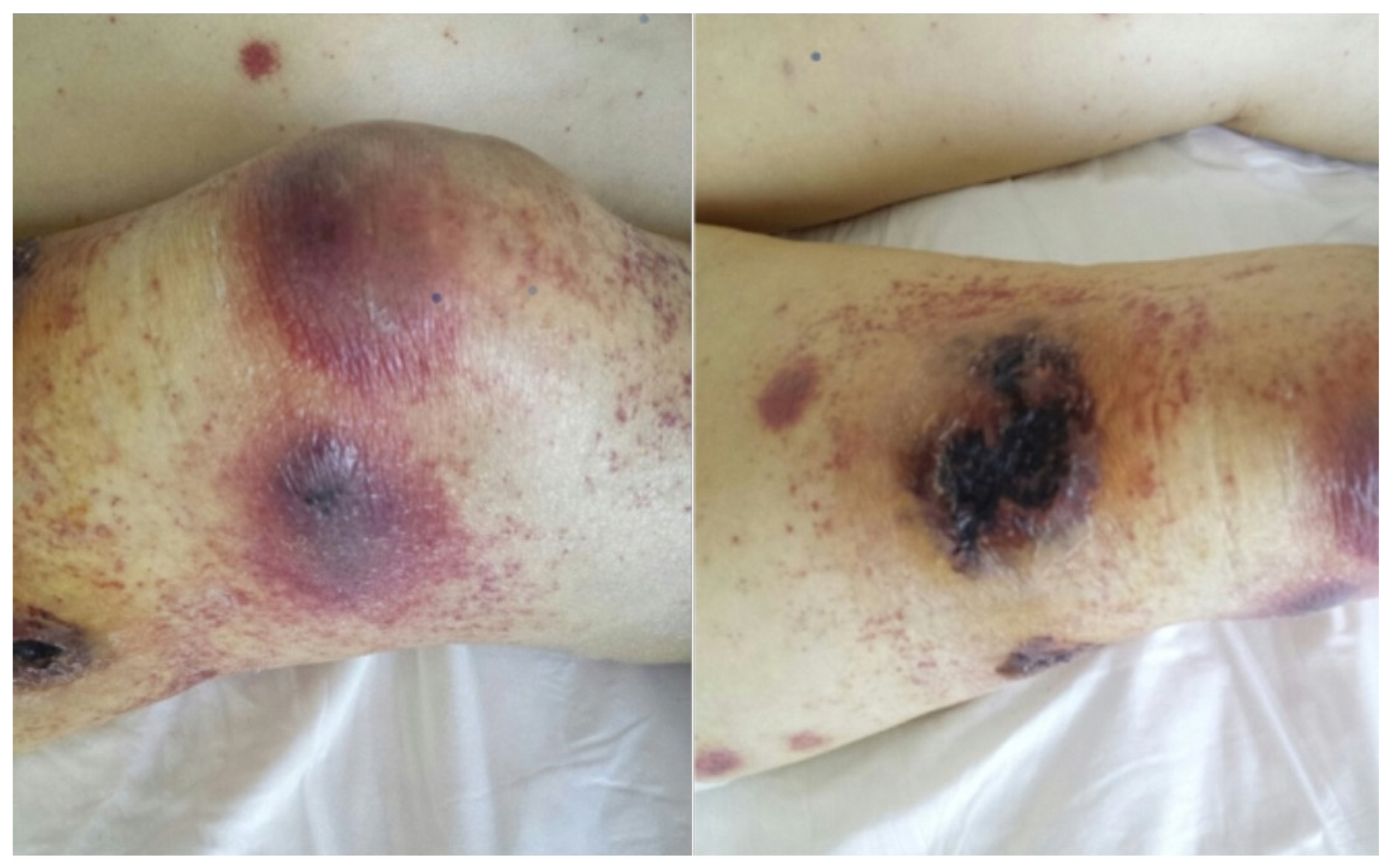
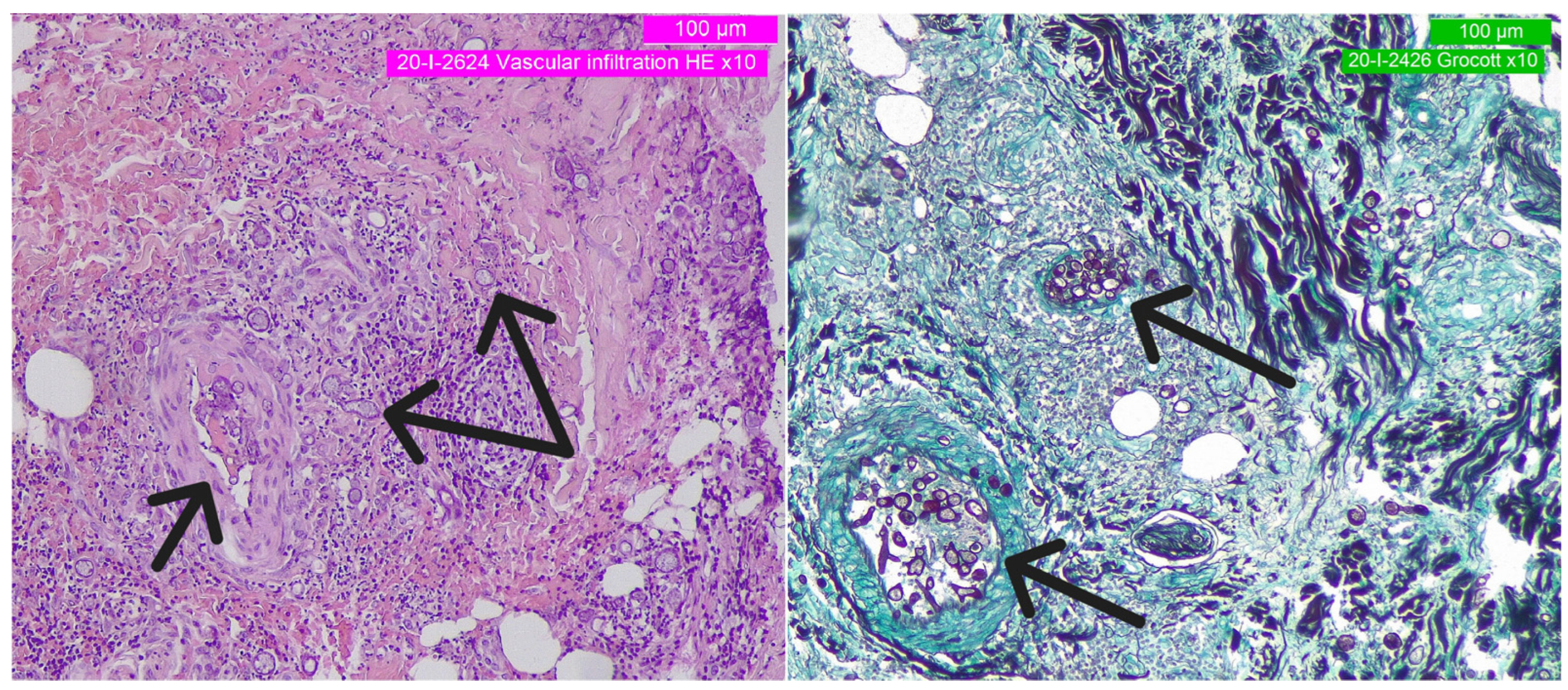
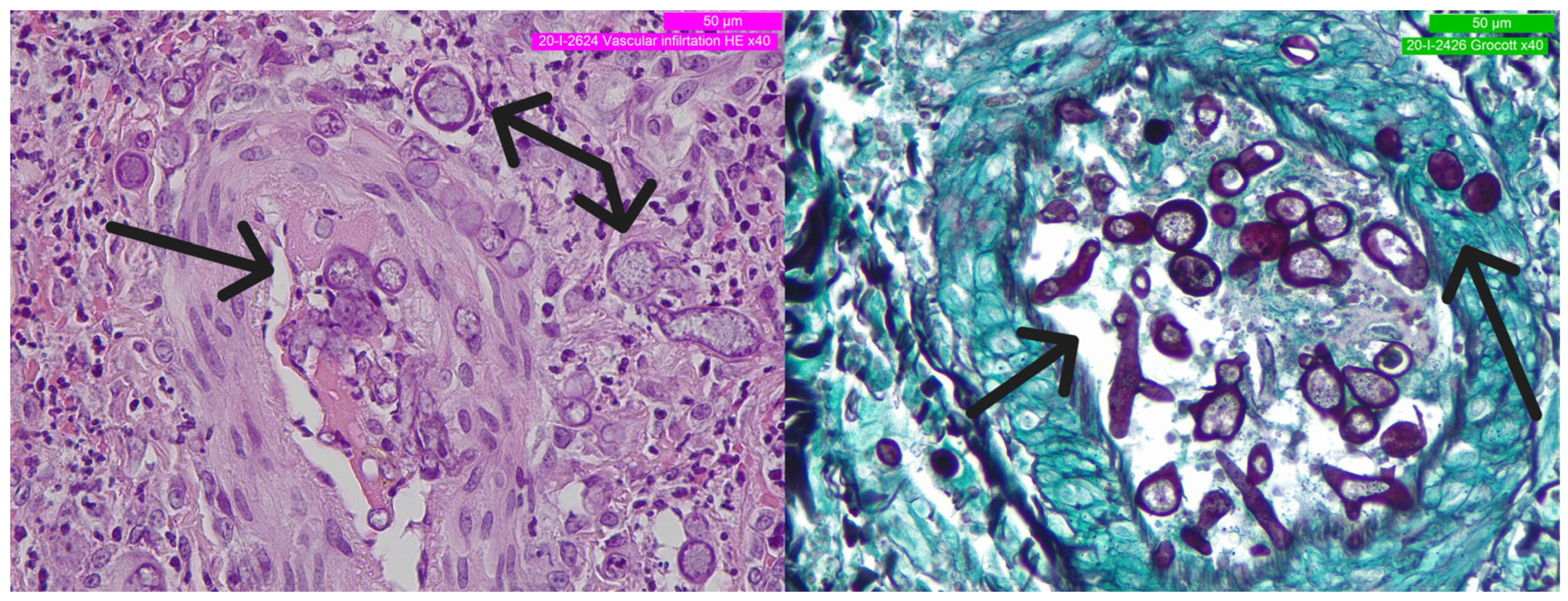
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kipps, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Wu, C.J.; Croce, C.M.; Packham, G.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Gribben, J.; Rai, K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forconi, F.; Moss, P. Perturbation of the normal immune system in patients with CLL. Blood 2015, 126, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayad, L.; Keating, M.J.; Reuben, J.M.; O’Brien, S.; Lee, B.-N.; Lerner, S.; Kurzrock, R. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood 2001, 97, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Johnson, A.J.; Lee, A.M.; Gorgün, G.; Le Dieu, R.; Blum, W.; Byrd, J.C.; Gribben, J.G. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia T cells show impaired immunological synapse formation that can be reversed with an immunomodulating drug. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, F.S.; Strefford, J.C.; Eldering, E.; Kater, A. T-cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia from an epigenetic perspective. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Molinari, M.C.; Pravato, S.; Cellini, A.; Angotzi, F.; Cavaretta, C.A.; Ruocco, V.; Imbergamo, S.; Piazza, F.; Proietti, G.; et al. A Retrospective Study on the Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin as Compared to Intravenous Formulation in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Secondary Antibody Deficiency. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalla, F.; Lucas, M.; Schuh, A.; Bhole, M.; Jain, R.; Patel, S.Y.; Misbah, S.; Chapel, H. Antibody Deficiency Secondary to Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Should Patients be Treated with Prophylactic Replacement Immunoglobulin? J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, A.; Cassin, R.; Mattiello, V.; Bortolotti, M.; Reda, G.; Barcellini, W. Should treatment of hypogammaglobulinemia with immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IgRT) become standard of care in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia? Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1062376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.J.; Yu, L.; Bäckesjö, C.-M.; Vargas, L.; Faryal, R.; Aints, A.; Christensson, B.; Berglöf, A.; Vihinen, M.; Nore, B.F.; et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk): Function, regulation, and transformation with special emphasis on the PH domain. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasso, B.; Spallarossa, A.; Russo, E.; Brullo, C. The Development of BTK Inhibitors: A Five-Year Update. Molecules 2021, 26, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, R.; Maccaferri, M.; Arletti, L.; Fiorcari, S.; Benatti, S.; Potenza, L.; Luppi, M.; Marasca, R. Immunomodulatory effect of ibrutinib: Reducing the barrier against fungal infections. Blood Rev. 2020, 40, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovsky, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Natarajan, G.; Woyach, J.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Zhong, Y.; Hessler, J.D.; Liu, T.-M.; Chang, B.Y.; Larkin, K.M.; et al. Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood 2013, 122, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strijbis, K.; Tafesse, F.G.; Fairn, G.D.; Witte, M.D.; Dougan, S.K.; Watson, N.; Spooner, E.; Esteban, A.; Vyas, V.K.; Fink, G.R.; et al. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) and Vav1 Contribute to Dectin1-Dependent Phagocytosis of Candida albicans in Macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, T.; Taur, Y.; Cohen, N.; Palomba, M.L.; Seo, S.K.; Hohl, T.M.; Redelman-Sidi, G. Serious Infections in Patients Receiving Ibrutinib for Treatment of Lymphoid Cancer. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmis, B.; Kherabi, Y.; Huriez, P.; Zahar, J.-R.; Mokart, D. Infectious Complications of Targeted Therapies for Solid Cancers or Leukemias/Lymphomas. Cancers 2023, 15, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán, H.Y.; Berglöf, A.; Zain, R.; Smith, C.I.E. Comparative Analysis of BTK Inhibitors and Mechanisms Underlying Adverse Effects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.S.; Weiss, Z.F.; Hammond, S. Invasive Fungal Infections and Targeted Therapies in Hematological Malignancies. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Camps, I.; Aguilar-Company, J. Risk of infection associated with targeted therapies for solid organ and hematological malignancies. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 204993612198954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Wagner, L.; Kurzai, O. Updates on the taxonomy of mucorales with an emphasis on clinically important taxa. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J. Taxonomy of fungi causing mucormycosis and entomophthoramycosis (zygomycosis) and nomenclature of the disease: Molecular mycologic perspectives. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54 (Suppl. 1), S8–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatafora, J.W.; Chang, Y.; Benny, G.L.; Lazarus, K.; Smith, M.E.; Berbee, M.L.; Bonito, G.; Corradi, N.; Grigoriev, I.; Gryganskyi, A.; et al. A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 2016, 108, 1028–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Pawłowska, J.; Letcher, P.M.; Kirk, P.M.; Humber, R.A.; Schüßler, A.; Wrzosek, M.; Muszewska, A.; Okrasińska, A.; Istel, Ł.; et al. Notes for genera: Basal clades of Fungi (including Aphelidiomycota, Basidiobolomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Calcarisporiellomycota, Caulochytriomycota, Chytridiomycota, Entomophthoromycota, Glomeromycota, Kickxellomycota, Monoblepharomycota, Mortierellomyc. Fungal Divers. 2018, 92, 43–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.; de Hoog, S.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Voigt, K.; Kurzai, O.; Walther, G. A revised species concept for opportunistic Mucor species reveals species-specific antifungal susceptibility profiles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.; Keighley, C.; Wolfe, R.; Lee, W.L.; Slavin, M.A.; Kong, D.C.M.; Chen, S.C.-A. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolás, F.E.; Murcia, L.; Navarro, E.; Navarro-Mendoza, M.I.; Pérez-Arques, C.; Garre, V. Mucorales species and macrophages. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrikkos, G.; Skiada, A.; Lortholary, O.; Roilides, E.; Walsh, T.J.; Kontoyiannis, D. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Mucormycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54 (Suppl. 1), S23–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaing, K.M.; Monday, L.M.; Nucci, M.; Nouér, S.A.; Revankar, S.G. Invasive Fungal Infections Associated with COVID-19. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Nonzom, S. Mucormycosis and Its Upsurge during COVID-19 Epidemic: An Updated Review. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Wagner, L.; Kurzai, O. Outbreaks of Mucorales and the Species Involved. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, M.M.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Buchanan, W.L.; Knudsen, T.A.; Sarkisova, T.A.; Schaufele, R.L.; Sein, M.; Sein, T.; Chiou, C.C.; Chu, J.H.; et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: A review of 929 reported cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 634–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chayakulkeeree, M.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Perfect, J.R. Zygomycosis: The re-emerging fungal infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 25, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Das, A.; Panda, N.; Shivaprakash, M.R.; Kaur, A.; Varma, S.C.; Singhi, S.; Bhansali, A.; Sakhuja, V. Invasive zygomycosis in India: Experience in a tertiary care hospital. Postgrad. Med. J. 2009, 85, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roilides, E.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Katragkou, A.; Benjamin, D.K.; Walsh, T.J. Zygomycosis in neonates: An uncommon but life-threatening infection. Am. J. Perinatol. 2009, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, J.F.; Chakrabarti, A. Changing epidemiology of an emerging infection: Zygomycosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 5), 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecointe, K.; Cornu, M.; Leroy, J.; Coulon, P.; Sendid, B. Polysaccharides cell wall architecture of mucorales. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.; Al-Ramadi, B.; Finkelman, M.; Hedstrom, U.; Kristensen, J.; Ali-Zadeh, H.; Klingspor, L. Assessment of the clinical utility of serial β-d-glucan concentrations in patients with persistent neutropenic fever. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, Z.; Mattiuzzi, G.; Estey, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Saeki, F.; Ridge, R.J.; Ketchum, P.A.; Finkelman, M.A.; Rex, J.H.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L. -D-Glucan as a Diagnostic Adjunct for Invasive Fungal Infections: Validation, Cutoff Development, and Performance in Patients with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, J.A.; Klont, R.; Masson, C.; Theunissen, K.; Meersseman, W.; Lagrou, K.; Heinen, C.; Crepin, B.; Eldere, J.V.; Tabouret, M.; et al. Optimization of the cutoff value for the Aspergillus double-sandwich enzyme immunoassay. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, M.H.; Kauffman, C.A. Aspergillus Galactomannan for Diagnosing Invasive Aspergillosis. JAMA 2017, 318, 1175–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, L.; Herbrecht, R.; Grenouillet, F.; Morio, F.; Alanio, A.; Letscher-Bru, V.; Cassaing, S.; Chouaki, T.; Kauffmann-Lacroix, C.; Poirier, P.; et al. Early diagnosis and monitoring of mucormycosis by detection of circulating DNA in serum: Retrospective analysis of 44 cases collected through the French Surveillance Network of Invasive Fungal Infections (RESSIF). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 810.e1–810.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, D.; Van Cauteren, D.; Lanternier, F.; Dannaoui, E.; Che, D.; Dromer, F.; Desenclos, J.-C.; Lortholary, O. Increasing incidence of zygomycosis (mucormycosis), France 1997–2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.; Lutynski, A.; Minden, M.; Rotstein, C. Successful Treatment of Gastrointestinal Mucormycosis in an Adult with Acute Leukemia: Case Report and Literature Review. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prakash, H.; Chakrabarti, A. Global epidemiology of mucormycosis. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiada, A.; Pagano, L.; Groll, A.; Zimmerli, S.; Dupont, B.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Florl, C.; Bouza, E.; Klimko, N.; Gaustad, P.; et al. Zygomycosis in Europe: Analysis of 230 cases accrued by the registry of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Working Group on Zygomycosis between 2005 and 2007. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilak, R.; Raina, P.; Gupta, S.; Tilak, V.; Prakash, P.; Gulati, A. Cutaneous zygomycosis: A possible postoperative complication in immunocompetent individuals. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2009, 75, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhara, S.R.; Paragache, G.; Panda, N.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Mucormycosis in immunocompetent individuals: An increasing trend. J. Otolaryngol. 2005, 34, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimann, S.; Vehreschild, M.; Cornely, O.; Heinz, W.; Grüner, B.; Silling, G.; Kessel, J.; Seidel, D.; Vehreschild, J. Healthcare burden of probable and proven invasive mucormycosis: A multi-centre cost-of-illness analysis of patients treated in tertiary care hospitals between 2003 and 2016. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 101, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Yang, H.; Song, J.; Kelkar, S.S.; Yang, X.; Azie, N.; Harrington, R.; Fan, A.; Lee, E.; Spalding, J.R. Prevalence, clinical and economic burden of mucormycosis-related hospitalizations in the United States: A retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, A.; Facco, M.; Gurrieri, C.; Pagnin, E.; Martini, V.; Imbergamo, S.; Frezzato, F.; Trimarco, V.; Severin, F.; Raggi, F.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Effect of IGHV Mutational Status and Load in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Focus on FCR and BR Treatments. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 678–685.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Bonaldi, L.; Rigolin, G.M.; Mauro, F.R.; Martines, A.; Frezzato, F.; Pravato, S.; Gargarella, L.R.; Bardi, M.A.; Cavallari, M.; et al. The complex karyotype landscape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia allows the refinement of the risk of Richter syndrome transformation. Haematologica 2021, 107, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A. Cutaneous zygomycosis: Major concerns. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 131, 739–741. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, T.J.; Gamaletsou, M.N.; McGinnis, M.R.; Hayden, R.T.; Kontoyiannis, D. Early clinical and laboratory diagnosis of invasive pulmonary, extrapulmonary, and disseminated mucormycosis (zygomycosis). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54 (Suppl. 1), 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Nadali, G.; Facchinelli, D.; Candoni, A.; Cattaneo, C.; Laurenti, L.; Fanci, R.; Farina, F.; Lessi, F.; Visentin, A.; et al. Infections in patients with lymphoproliferative diseases treated with targeted agents: SEIFEM multicentric retrospective study. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.C.; Hohaus, S.; Cuccaro, A.; Innocenti, I.; De Carolis, E.; Za, T.; D’alò, F.; Laurenti, L.; Fianchi, L.; Sica, S.; et al. Invasive fungal infections in chronic lymphoproliferative disorders: A monocentric retrospective study. Haematologica 2017, 102, e108–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, A.; Gurrieri, C.; Imbergamo, S.; Lessi, F.; Di Maggio, S.A.; Frezzato, F.; Adami, F.; Zambello, R.; Piazza, F.; Semenzato, G.; et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of invasive fungal infections in a large cohort of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Mauro, F.R.; Cibien, F.; Vitale, C.; Reda, G.; Fresa, A.; Ciolli, S.; Pietrasanta, D.; Marchetti, M.; Murru, R.; et al. Continuous treatment with Ibrutinib in 100 untreated patients with TP 53 disrupted chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A real-life campus CLL study. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E95–E99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, F.R.; Giannarelli, D.; Visentin, A.; Reda, G.; Sportoletti, P.; Frustaci, A.M.; Chiarenza, A.; Ciolli, S.; Vitale, C.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Prognostic Impact and Risk Factors of Infections in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with Ibrutinib. Cancers 2021, 13, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorcari, S.; Maffei, R.; Vallerini, D.; Scarfò, L.; Barozzi, P.; Maccaferri, M.; Potenza, L.; Ghia, P.; Luppi, M.; Marasca, R. BTK Inhibition Impairs the Innate Response against Fungal Infection in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunic, A.L.; Medenica, M.; Busbey, S. Solitary embolic cutaneous aspergillosis in the immunocompromised patient with acute myelogenous leukemia—A propos another case caused by Aspergillus flavus. Int. J. Dermatol. 2003, 42, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiada, A.; Pavleas, I.; Drogari-Apiranthitou, M. Epidemiology and Diagnosis of Mucormycosis: An Update. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham-Marusich, A.R.; Hubbard, B.; Kvam, A.J.; Gates-Hollingsworth, M.; Green, H.R.; Soukup, E.; Limper, A.H.; Kozel, T.R. Conservation of Mannan Synthesis in Fungi of the Zygomycota and Ascomycota Reveals a Broad Diagnostic Target. mSphere 2018, 3, e00094-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, P.; Cornely, O.A.; Dannaoui, E. Antifungal combinations in Mucorales: A microbiological perspective. Mycoses 2019, 62, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannaoui, E. Antifungal resistance in mucorales. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Fu, Y.; Edwards, J.E.; Ibrahim, A.S. Combination therapy with amphotericin B lipid complex and caspofungin acetate of disseminated zygomycosis in diabetic ketoacidotic mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.; Bryant, R.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Edwards, J.J.; Filler, S.G.; Goldberg, R.; Spellberg, B. Combination polyene-caspofungin treatment of rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, E.; Aslan, E.; Akalın, H.; Saraydaroğlu, Ö.; Hakyemez, B.; Erişen, L.; Yazıcı, B.; Gürcüoğlu, E.; Yılmaz, E.; Ener, B.; et al. A mucormycosis case treated with a combination of caspofungin and amphotericin B. J. Mycol. Med. 2013, 23, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargouri, M.; Marrakchi, C.; Feki, W.; Charfi, S.; Maaloul, I.; Lahiani, D.; Elleuch, E.; Koubaa, M.; Mnif, Z.; Ayadi, A.; et al. Combination of amphotericin B and caspofungin in the treatment of mucormycosis. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2019, 26, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyvernitakis, A.; Torres, H.A.; Jiang, Y.; Chamilos, G.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D. Initial use of combination treatment does not impact survival of 106 patients with haematologic malignancies and mucormycosis: A propensity score analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 811.e1–811.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornely, O.A.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Arenz, D.; Chen, S.C.A.; Dannaoui, E.; Hochhegger, B.; Hoenigl, M.; Jensen, H.E.; Lagrou, K.; Lewis, R.E.; et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of mucormycosis: An initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in cooperation with the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e405–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, C.; Jarque, I.; Fortun, J.; Casado, A.; Peman, J. IFISTRATEGY: Spanish National Survey of Invasive Fungal Infection in Hemato-Oncologic Patients. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, J.; Teh, B.W.; Micklethwaite, K.; Slavin, M. Azole antifungals and new targeted therapies for hematological malignancy. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Non-Immunological Risk Factors | Immunological Risk Factors | Special and Novel Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Decompensated diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis [31,32,33] | Immunodepression Primitive: solid and/or hematologic malignancies; autoimmunity | Premature neonates [34] |
| Iron overload | ||
| Major trauma | ||
| Prolonged use of corticosteroids | ||
| Intravenous drug abuse [27] | ||
| Iatrogenic/secondary: hematopoietic stem cell (HSCT); solid organ transplant | Preventive or therapeutic antimycotic drugs (voriconazole, itraconazole, or caspofungin) [35] | |
| BTK inhibitor [12,15,16,17,18,19] | ||
| SARS-CoV-2 infecion and treatment [28,29] |
| 2006 | FCR protocol (Fludarabine-Cyclophosphamide-Rituximab) |
| 2010 | FCR |
| 2012 | Rituximab |
| 2013 | Bendamustine |
| 2014–2016 | Ibrutinib (discontinued due to infections) |
| 2017–2020 | Venetoclax |
| 2020 | Idelalisib-Rituximab |
| May 2020 | Zanubrutinib |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maggioni, G.; Fedrigo, M.; Visentin, A.; Carturan, E.; Ruocco, V.; Trentin, L.; Alaibac, M.; Angelini, A. Severe Fatal Mucormycosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Treated with Zanubrutinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8255-8265. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090599
Maggioni G, Fedrigo M, Visentin A, Carturan E, Ruocco V, Trentin L, Alaibac M, Angelini A. Severe Fatal Mucormycosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Treated with Zanubrutinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(9):8255-8265. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaggioni, Giuseppe, Marny Fedrigo, Andrea Visentin, Elisa Carturan, Valeria Ruocco, Livio Trentin, Mauro Alaibac, and Annalisa Angelini. 2023. "Severe Fatal Mucormycosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Treated with Zanubrutinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" Current Oncology 30, no. 9: 8255-8265. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090599
APA StyleMaggioni, G., Fedrigo, M., Visentin, A., Carturan, E., Ruocco, V., Trentin, L., Alaibac, M., & Angelini, A. (2023). Severe Fatal Mucormycosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Treated with Zanubrutinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Current Oncology, 30(9), 8255-8265. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090599








