Neurologic Complications of Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neurotoxicities Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
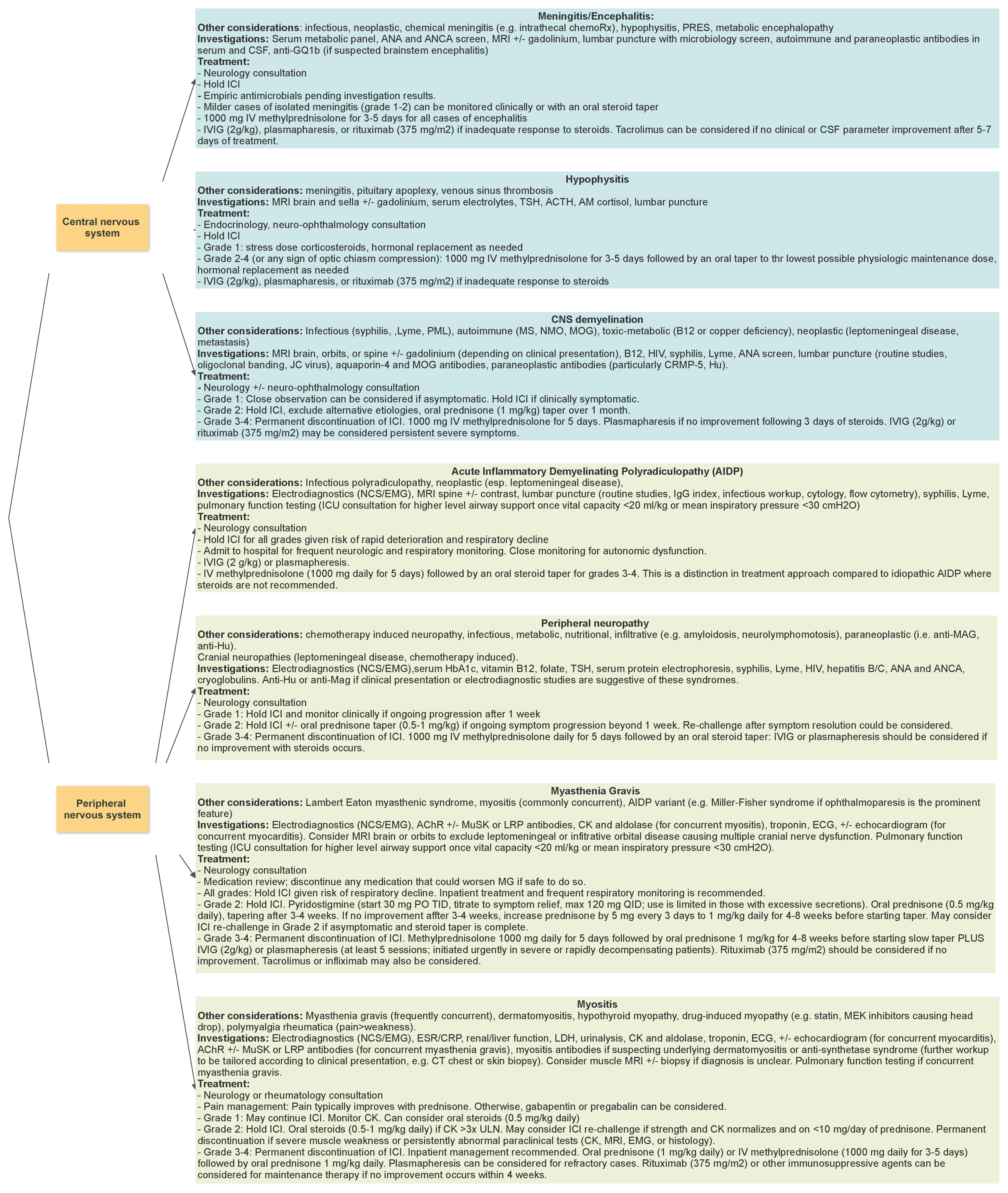
2.1. Central Nervous System Complications
2.1.1. Encephalitis
2.1.2. Meningitis
2.1.3. Hypophysitis
2.1.4. CNS Demyelination
2.1.5. Vasculitis
2.2. Peripheral Nervous System Complications
2.2.1. Radiculopathies and Neuropathies
2.2.2. Myasthenia Gravis
2.2.3. Myositis
3. Clinical Approach to Suspected ICI-Related Neurotoxicity
3.1. Approach
3.2. Unanswered Questions
3.2.1. ICIs in the Context of Pre-Existing Autoimmune Disease
3.2.2. ICIs and Paraneoplastic Syndromes
3.2.3. Rechallenging ICI
4. Immune Effector Cell Therapies
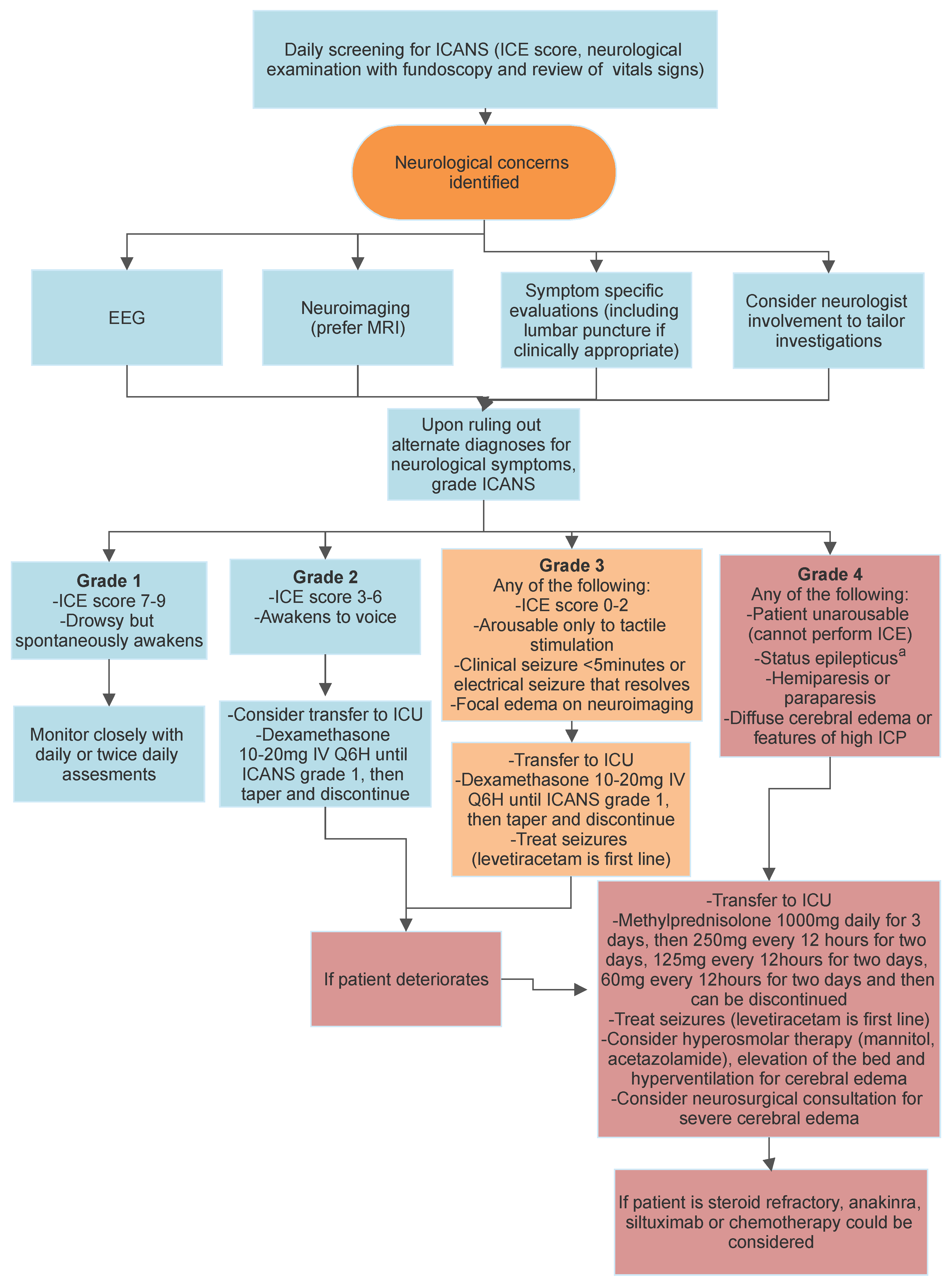
4.1. Immune Effector Cell Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS)
4.1.1. Epidemiology
4.1.2. Risk Factors for ICANS
4.1.3. Suspected Pathophysiology
4.1.4. Clinical Presentation
4.1.5. ICANS Timing and Relationship to Cytokine Release Syndrome
4.1.6. Paraclinical Testing
4.1.7. Grading
4.1.8. Clinical Screening for the Presence of ICANS
4.1.9. Management
4.1.10. Prognosis
4.1.11. A New Avenue: Emerging Off-Tumor On-Target Effects
4.2. Bispecific T-Cell Engagers (BiTEs)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Tagami, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Uede, T.; Shimizu, J.; Sakaguchi, N.; Mak, T.W.; Sakaguchi, S. Immunologic Self-Tolerance Maintained by Cd25+Cd4+Regulatory T Cells Constitutively Expressing Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte–Associated Antigen 4. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. The PD-1–PD-L Pathway in Immunological Tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The Blockade of Immune Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadelain, M.; Rivière, I.; Riddell, S. Therapeutic T Cell Engineering. Nature 2017, 545, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Riethmüller, G.; Kufer, P. A Small Bispecific Antibody Construct Expressed as a Functional Single-Chain Molecule with High Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7021–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargou, R.; Leo, E.; Zugmaier, G.; Klinger, M.; Goebeler, M.; Knop, S.; Noppeney, R.; Viardot, A.; Hess, G.; Schuler, M.; et al. Tumor Regression in Cancer Patients by Very Low Doses of a T Cell–Engaging Antibody. Science 2008, 321, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagorsen, D.; Kufer, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Bargou, R. Blinatumomab: A Historical Perspective. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, T.; Liaw, B.; Asada, M.; Niimura, T.; Zamami, Y.; Green-LaRoche, D.; Pai, L.; Levy, M.; Jeyapalan, S. Neuroimmunological Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor: A Retrospective, Pharmacovigilance Study Using FAERS Database. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 152, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, A.; Bernardini, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Honnorat, J.; Vogrig, A. Neurologic Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Neurology 2021, 96, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, R.; Villagrán, M.; Jové, M.; Simó, M.; Vilariño, N.; Alemany, M.; Palmero, R.; Martínez-Villacampa, M.M.; Nadal, E.; Bruna, J. Encephalitis Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Borja, M.; Ricordel, C.; Chiappa, A.M.; Hureaux, J.; Odier, L.; Jeannin, G.; Descourt, R.; Gervais, R.; Monnet, I.; Auliac, J.-B.; et al. Encephalitis Related to Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer: Analysis of a Multicenter Cohort. Lung Cancer 2020, 143, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Jensen, L.; Zierold, S.; Versluis, J.M.; Boehmerle, W.; Huehnchen, P.; Endres, M.; Mohr, R.; Compter, A.; Blank, C.U.; Hagenacker, T.; et al. Characteristics of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Encephalitis and Comparison with HSV-1 and Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis: A Retrospective Multicentre Cohort Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 175, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Marchal, C.; Chiappa, A.M.; Chanson, E.; Skowron, F.; Leblanc, A.; et al. Central Nervous System Complications Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuby, J.; Herren, T.; Schwegler Naumburger, G.; Papet, C.; Rudiger, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy-Associated Encephalitis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzubbo, S.; Javeri, F.; Tissier, M.; Roumi, A.; Barlog, C.; Doridam, J.; Lebbe, C.; Belin, C.; Ursu, R.; Carpentier, A.F. Neurological Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouvenin, L.; Olivier, T.; Banna, G.; Addeo, A.; Friedlaender, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Aseptic Meningitis and Encephalitis: A Case-Series and Narrative Review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2021, 12, 204209862110047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannini, S.; Koshenkova, L.; Baloglu, S.; Chaussemy, D.; Noël, G.; Schott, R. Immune-Related Aseptic Meningitis and Strategies to Manage Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: A Systematic Review. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 157, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, A.; Rouleau, S.G.; Dasari, S.; Kottschade, L.; Ryder, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; Markovic, S.; Erickson, D. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Hypophysitis: Lessons Learnt from a Large Cancer Cohort. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deligiorgi, M.V.; Liapi, C.; Trafalis, D.T. Hypophysitis Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: An Intriguing Adverse Event with Many Faces. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 1097–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.J.; Powers, A.C.; Johnson, D.B. Endocrine Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.A.; Schneider, B.J.; Brahmer, J.; Andrews, S.; Armand, P.; Bhatia, S.; Budde, L.E.; Costa, L.; Davies, M.; Dunnington, D.; et al. Management of Immunotherapy-Related Toxicities, Version 1.2019. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, H.; Johnson, J.; Jakubecz, C.; Serra, A.; Abboud, H. Prevalence of Iatrogenic CNS Inflammation at a Tertiary Neuroimmunology Clinic. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 370, 577928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.C.B.; de Brito, M.H.; Simabukuro, M.M. Central Nervous System Demyelination Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 538695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.; Vogler, C.; Hudali, T.; Bhattarai, M. Nivolumab-Associated Acute Demyelinating Encephalitis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 17, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, L.; Xu, P.; Liu, A. Meningoencephalitis without Respiratory Failure in a Young Female Patient with COVID-19 Infection in Downtown Los Angeles, Early April 2020. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, C.; Schneider, R.; Kiehl, T.-R.; Bavi, P.; Roehrl, M.H.A.; Mason, W.P.; Hogg, D. Subacute CNS Demyelination after Treatment with Nivolumab for Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Nylander, A.; Ramanan, S.; Goods, B.A.; Ponath, G.; Zabad, R.; Chiang, V.L.S.; Vortmeyer, A.O.; Hafler, D.A.; Pitt, D. CNS Demyelination and Enhanced Myelin-Reactive Responses after Ipilimumab Treatment. Neurology 2016, 86, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.R.; Jayswal, R.; Adams, V.; Anthony, L.B.; Villano, J.L. Multiple Sclerosis Outcomes after Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.; Shroff, S.; Kamiya-Matsuoka, C.; Tummala, S. Atypical Neurological Complications of Ipilimumab Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunchok, A.; Zekeridou, A.; Pittock, S. CRMP5-IgG–Associated Paraneoplastic Myelopathy with PD-L1 Inhibitor Therapy. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lou, H.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.-M. Paraneoplastic Myelitis Associated with Durvalumab Treatment for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti, L.; Picca, A.; Bini, P.; Gastaldi, M.; Alfonsi, E.; Pichiecchio, A.; Rota, E.; Rudà, R.; Bruno, F.; Villani, V.; et al. Characterization and Management of Neurological Adverse Events during Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment: An Italian Multicentric Experience. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charabi, S.; Engell-Noerregaard, L.; Nilsson, A.C.; Stenör, C. Case Report: Longitudinal Extensive Transverse Myelitis with Novel Autoantibodies Following Two Rounds of Pembrolizumab. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 655283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Minami, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeguchi, S.; Kano, K.; Takahashi, K.; Saito, T.; Sawada, J.; Terui, H.; et al. Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Secondary to Treatment with Anti-PD-1 Antibody Nivolumab: The First Report. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Tsunemi, T.; Hattori, A.; Nakagawa, E.; Yokoyama, K.; Hattori, N. Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder after Treatment with Pembrolizumab. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Menassa, D.A.; Davies, A.J.; Michael, S.; Hester, J.; Kuker, W.; Collins, G.P.; Cossins, J.; Beeson, D.; Steven, N.; et al. Seronegative Antibody-Mediated Neurology after Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.A.; Simpson, D.R.; Daniels, G.A.; Piccioni, D.E. Infliximab for Treatment-Refractory Transverse Myelitis Following Immune Therapy and Radiation. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.; Seleme, N.; Chen, J.J.; Zekeridou, A.; Sechi, E.; Walsh, R.D.; Beebe, J.D.; Sabbagh, O.; Mejico, L.J.; Gratton, S.; et al. Neuro-Ophthalmic Complications in Patients Treated with CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Blockade. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2021, 41, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.W.; Yau, M.; Mezey, N.; Joarder, I.; Micieli, J.A. Neuro-Ophthalmic Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Eye Brain 2020, 12, 139–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khimani, K.; Patel, S.P.; Whyte, A.; Al-Zubidi, N. Case Report: Neuromyelitis Optica after Treatment of Uveal Melanoma with Nivolumab and Ipilimumab. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 806501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daxini, A.; Cronin, K.; Sreih, A.G. Vasculitis Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A Systematic Review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoja, L.; Maurice, C.; Chappell, M.; MacMillan, L.; Al-Habeeb, A.S.; Al-Faraidy, N.; Butler, M.O.; Rogalla, P.; Mason, W.; Joshua, A.M.; et al. Eosinophilic Fasciitis and Acute Encephalopathy Toxicity from Pembrolizumab Treatment of a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ross, L.; Ontaneda, D. Pembrolizumab-Induced CNS Vasculitis: Neurologic Adverse Events Due to Checkpoint Inhibitors. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, e30–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, H.; Hench, J.; Stanczak, M.; Heijnen, I.; Papachristofilou, A.; Frank, S.; Zippelius, A.; Stenner-Liewen, F. Cerebral Vasculitis Mimicking Intracranial Metastatic Progression of Lung Cancer during PD-1 Blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuker, C.; Strunk, D.; Rawal, R.; Schmidt-Pogoda, A.; Werring, N.; Milles, L.; Ruck, T.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.; Minnerup, H.; et al. Primary Angiitis of the CNS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, T.; Hu, J.; Chu, Q.; Yang, X.; Chu, L.; Chu, X.; Li, Y.; et al. A Brief Report on Incidence, Radiographic Feature and Prognostic Significance of Brain MRI Changes after Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Gelsomino, F.; Rinaldi, R.; Muccioli, L.; Comito, F.; Di Federico, A.; De Giglio, A.; Lamberti, G.; Andrini, E.; Mollica, V.; et al. Peripheral Nervous System Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; David, W.S.; Amato, A.A.; Reynolds, K.L.; Clement, N.F.; Chute, D.F.; Cohen, J.V.; Lawrence, D.P.; Mooradian, M.J.; Sullivan, R.J.; et al. Varied Phenotypes and Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Neuropathies. Neurology 2019, 93, e1093–e1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasocki, A.; Smith, K. Autoimmune Polyradiculitis Due to Combination Immunotherapy with Ipilimumab and Nivolumab for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Seki, M.; Yaguchi, H.; Sakuta, K.; Mukai, T.; Yamada, S.; Oki, K.; Nakahara, J.; Suzuki, S. Polyradiculoneuropathy Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, E.; Shrestha, A.K.; Elkhooly, M.; Wilson, H.; Ebbert, M.; Srivastava, S.; Wen, S.; Rollins, S.; Sriwastava, S. CNS and PNS Manifestation in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 432, 120089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Haggiagi, A.; Tzatha, E.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Santomasso, B. Electrophysiological Findings in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Peripheral Neuropathy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.J.; Naidoo, J.; Santomasso, B.D.; Lacchetti, C.; Adkins, S.; Anadkat, M.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4073–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Palmiero, R.A.; Ferrero, B.; Franchino, F.; Pellerino, A.; Milanesi, E.; Soffietti, R.; Rudà, R. Pembrolizumab-Induced Isolated Cranial Neuropathy: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 669493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, H.; Johnson, D.H.; Trinh, V.A.; Rodgers, T.E.; Lin, H.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E.; Fa’ak, F.; Saberian, C.; Yee, C.; Davies, M.A.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Related Myasthenia Gravis: Single Center Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Ishikawa, N.; Konoeda, F.; Seki, N.; Fukushima, S.; Takahashi, K.; Uhara, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Inomata, S.; Otani, Y.; et al. Nivolumab-Related Myasthenia Gravis with Myositis and Myocarditis in Japan. Neurology 2017, 89, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-P.; Lin, W.-C.; Su, W.-C.; Sun, Y.-T. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Myasthenia Gravis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Velasco, R.; Dols-Icardo, O.; El Bounasri, S.; López-Vilaró, L.; Trujillo, J.C.; Reyes-Leiva, D.; Suárez-Calvet, X.; Cortés-Vicente, E.; Illa, I.; Gallardo, E. Reduced Number of Thymoma CTLA4-Positive Cells Is Associated with a Higher Probability of Developing Myasthenia Gravis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Sugisaka, J.; Ono, H.; Kawashima, Y.; Aiba, T.; Kawana, S.; Saito, R.; Aso, M.; Tsurumi, K.; et al. Profiling Preexisting Antibodies in Patients Treated with Anti–PD-1 Therapy for Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruwatari, K.; Sato, R.; Nakane, S.; Sakata, S.; Takamatsu, K.; Jodai, T.; Mito, R.; Horio, Y.; Saeki, S.; Tomita, Y.; et al. The Risks and Benefits of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Anti-AChR Antibody-Seropositive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, O.; Yokota, K.; Atsuta, N.; Katsuno, M.; Akiyama, M.; Ando, Y. Nivolumab for the Treatment of Malignant Melanoma in a Patient with Pre-Existing Myasthenia Gravis. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.; Loquai, C.; Pföhler, C.; Kähler, K.C.; Knauss, S.; Heppt, M.V.; Gutzmer, R.; Dimitriou, F.; Meier, F.; Mitzel-Rink, H.; et al. Myositis and Neuromuscular Side-Effects Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 106, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, N.; Maeda, A.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Kirino, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Namkoong, H.; Horita, N.; Yoshimi, R.; Nakajima, H. YCU irAE Working Group Incidence and Distinct Features of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myositis from Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis: A Single-Center Experience with Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 803410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, H.; Hatano, T.; Kanai, K.; Aoki, N.; Kamiyama, D.; Yokoyama, K.; Takanashi, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Shimo, Y.; Hattori, N. Pembrolizumab-Related Systemic Myositis Involving Ocular and Hindneck Muscles Resembling Myasthenic Gravis: A Case Report. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touat, M.; Maisonobe, T.; Knauss, S.; Ben Hadj Salem, O.; Hervier, B.; Auré, K.; Szwebel, T.-A.; Kramkimel, N.; Lethrosne, C.; Bruch, J.-F.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myositis and Myocarditis in Patients with Cancer. Neurology 2018, 91, e985–e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, E.; Markovic, S.N.; McKeon, A.; Dubey, D.; Liewluck, T.; Lennon, V.A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Klein, C.J.; Mauermann, M.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. Neurologic Autoimmunity and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Autoantibody Profiles and Outcomes. Neurology 2020, 95, e2442–e2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B.; Benesova, K.; Hassel, J.C.; Wick, W.; Jordan, K. How We Identify and Treat Neuromuscular Toxicity Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Farina, A.; Honnorat, J.; Joubert, B. How to Diagnose and Manage Neurological Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: An Update. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Ascierto, P.A.; Brufsky, J.; Cappelli, L.C.; Cortazar, F.B.; Gerber, D.E.; Hamad, L.; Hansen, E.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Clinical Practice Guideline on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Adverse Events. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tison, A.; Garaud, S.; Chiche, L.; Cornec, D.; Kostine, M. Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Use in Patients with Cancer and Pre-Existing Autoimmune Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes in the Era of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.; Villagrán-García, M.; Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Taillandier, L.; Michaud, M.; Lefilliatre, M.; Wang, A.; Lepine, Z.; et al. Anti-Hu Antibodies in Patients with Neurologic Side Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Fouret, M.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Pinto, A.-L.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Roger, M.; Raimbourg, J.; Dayen, C.; et al. Increased Frequency of Anti-Ma2 Encephalitis Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, A.J.; Perez, M.A.; Perrone, C.M.; Bae, C.J.; Pruitt, A.A.; Lancaster, E. A Case Series of PD-1 Inhibitor-Associated Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 334, 576980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongay-Ochoa, N.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Honnorat, J. Anti-Hu-Associated Paraneoplastic Syndromes Triggered by Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.; Joyce, R.; Moynagh, P.; O’Donnell, L.; Blazkova, S.; Counihan, T.J. Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated with Ma2 Antibodies and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Pract. Neurol. 2020, 20, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitter, D.; Mejico, L.; Latorre, J.G.; Cuello-Oderiz, C. New-Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus (NORSE) as a Recurrence of Anti-Neuronal Nuclear Antibody 2 (ANNA-2) Encephalitis after Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Therapy. Cureus 2021, 13, e16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, S.; Uryu, K.; Iwasaki, S.; Harada, H. A Case of Anti-CRMP5 Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome Induced by Atezolizumab for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Intern. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonaggio, A.; Michot, J.M.; Voisin, A.L.; Le Pavec, J.; Collins, M.; Lallart, A.; Cengizalp, G.; Vozy, A.; Laparra, A.; Varga, A.; et al. Evaluation of Readministration of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors after Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allouchery, M.; Lombard, T.; Martin, M.; Rouby, F.; Sassier, M.; Bertin, C.; Atzenhoffer, M.; Miremont-Salame, G.; Perault-Pochat, M.-C.; Puyade, M. Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge after Discontinuation for Grade ≥2 Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolladille, C.; Ederhy, S.; Sassier, M.; Cautela, J.; Thuny, F.; Cohen, A.A.; Fedrizzi, S.; Chrétien, B.; Da-Silva, A.; Plane, A.-F.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge after Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.J.; Grimshaw, A.A.; Silberstein, J.; Murdaugh, D.; Wildes, T.M.; Rosko, A.E.; Giri, S. Clinical Presentation, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: A Systematic Review. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, M.R.; Dickinson, M.; Purtill, D.; Barba, P.; Santoro, A.; Hamad, N.; Kato, K.; Sureda, A.; Greil, R.; Thieblemont, C.; et al. Second-Line Tisagenlecleucel or Standard Care in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Taraseviciute, A.; Turtle, C.J. Neurotoxicity Associated with CD19-Targeted CAR-T Cell Therapies. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Perales, M.-A.; Kersten, M.-J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; McGuirk, J.; Pagel, J.M.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.B.; Danish, H.H.; Ali, A.B.; Li, K.; LaRose, S.; Monk, A.D.; Cote, D.J.; Spendley, L.; Kim, A.H.; Robertson, M.S.; et al. Neurological Toxicities Associated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Brain 2019, 142, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, C.; Devic, P.; Ayrignac, X.; Dos Santos, A.; Paix, A.; Sirven-Villaros, L.; Simard, C.; Lamure, S.; Gastinne, T.; Ursu, R.; et al. Description of Neurotoxicity in a Series of Patients Treated with CAR T-Cell Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidi, Y.; Eckhardt, C.A.; Quadri, S.A.; Malik, P.; Firme, M.S.; Jones, D.K.; Jain, A.; Danish, H.H.; Rubin, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; et al. Forecasting Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome after Chimeric Antigen Receptor t-Cell Therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.C.; Neelapu, S.S.; Giavridis, T.; Sadelain, M. Cytokine Release Syndrome and Associated Neurotoxicity in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Rasche, L.; Kortüm, K.M.; Danhof, S.; Hudecek, M.; Einsele, H. Toxicities of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Multiple Myeloma: An Overview of Experience from Clinical Trials, Pathophysiology, and Management Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 620312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Ailawadhi, S.; Arnulf, B.; Patel, K.; Cavo, M.; Nooka, A.K.; Manier, S.; Callander, N.; Costa, L.J.; Vij, R.; et al. Ide-Cel or Standard Regimens in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavridis, T.; van der Stegen, S.J.C.; Eyquem, J.; Hamieh, M.; Piersigilli, A.; Sadelain, M. CAR T Cell–Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome Is Mediated by Macrophages and Abated by IL-1 Blockade. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norelli, M.; Camisa, B.; Barbiera, G.; Falcone, L.; Purevdorj, A.; Genua, M.; Sanvito, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Doglioni, C.; Cristofori, P.; et al. Monocyte-Derived IL-1 and IL-6 Are Differentially Required for Cytokine-Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity Due to CAR T Cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Finney, O.C.; Li, D.; Brakke, H.M.; Hicks, R.M.; Futrell, R.B.; Gamble, D.N.; Rawlings-Rhea, S.D.; Khalatbari, H.K.; Ishak, G.E.; et al. Glial Injury in Neurotoxicity after Pediatric CD19-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Hay, K.A.; Hanafi, L.-A.; Li, D.; Myerson, D.; Gonzalez-Cuyar, L.F.; Yeung, C.; Liles, W.C.; Wurfel, M.; Lopez, J.A.; et al. Endothelial Activation and Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Neurotoxicity after Adoptive Immunotherapy with CD19 CAR-T Cells. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1404–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, M.; Solomon, I.H.; Sutherland, C.L.; Nikiforow, S.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stone, R.M.; Vaitkevicius, H.; Galinsky, I.A.; Padera, R.F.; Trede, N.; et al. Neuropathology of a Case with Fatal CAR T-Cell-Associated Cerebral Edema. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Xie, M.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, N.; Li, P.; Liang, A.; Young, K.H.; Qian, W. Treatment-Related Adverse Events of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR T) in Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, M.V.; Alexander, S.; Bishop, M.R.; Brudno, J.N.; Callahan, C.; Davila, M.L.; Diamonte, C.; Dietrich, J.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; Frigault, M.J.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Clinical Practice Guideline on Immune Effector Cell-Related Adverse Events. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidus, A.H.; Anderson, M.A.; Harrison, S.J.; Dickinson, M.; Kalincik, T.; Lasocki, A. Neuroimaging Findings in Immune Effector Cell Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchat, I.; Danish, H.H.; Rubin, D.B.; Jacobson, C.; Robertson, M.; Vaitkevicius, H.; Lee, J.W. EEG Findings in CAR T-Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity: Clinical and Radiological Correlations. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Ponce, R.; Liles, W.C.; Garden, G.A.; Turtle, C.J. Cytokines in CAR T Cell–Associated Neurotoxicity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 577027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomasso, B.D.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Adkins, S.; Lacchetti, C.; Schneider, B.J.; Anadkat, M.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3978–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.H. Management of Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS). In The EBMT/EHA CAR-T Cell Handbook; Kröger, N., Gribben, J., Chabannon, C., Yakoub-Agha, I., Einsele, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 141–145. ISBN 978-3-030-94352-3. [Google Scholar]
- Neelapu, S.S. Managing the Toxicities of CAR T-cell Therapy. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Tummala, S.; Kebriaei, P.; Wierda, W.; Locke, F.L.; Lin, Y.; Jain, N.; Daver, N.; Gulbis, A.M.; Adkins, S.; et al. Toxicity Management after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: One Size Does Not Fit “ALL”. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, L.; Rees, J.; Roddie, C. Neurotoxicity—CAR T-Cell Therapy: What the Neurologist Needs to Know. Pract. Neurol. 2020, 20, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karschnia, P.; Jordan, J.T.; Forst, D.A.; Arrillaga-Romany, I.C.; Batchelor, T.T.; Baehring, J.M.; Clement, N.F.; Gonzalez Castro, L.N.; Herlopian, A.; Maus, M.V.; et al. Clinical Presentation, Management, and Biomarkers of Neurotoxicity after Adoptive Immunotherapy with CAR T Cells. Blood 2019, 133, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, D.; Belin, C.; Moroni, C.; Cuzzubbo, S.; Ursu, R.; Sirven-Villaros, L.; Di Blasi, R.; Thieblemont, C.; Carpentier, A.F. Evaluation of Mid-Term (6–12 Months) Neurotoxicity in B-Cell Lymphoma Patients Treated with CAR T Cells: A Prospective Cohort Study. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruark, J.; Mullane, E.; Cleary, N.; Cordeiro, A.; Bezerra, E.D.; Wu, V.; Voutsinas, J.; Shaw, B.E.; Flynn, K.E.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Patient-Reported Neuropsychiatric Outcomes of Long-Term Survivors after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barata, A.; Hoogland, A.I.; Small, B.J.; Locke, F.L.; Jim, H.S.L. Response to: Perceived Cognitive Changes Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Lymphoma: Perceptual Anticipation? Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2023, 29, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Xu, S.; Han, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, J.; Hu, T.; Li, H.; Wei, J.; Dou, X.; Zhou, F.; et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms among Patients Hospitalized with Hematological Malignancies after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapy: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 286, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.D.; Parekh, S.; Santomasso, B.D.; Gállego Pérez-Larraya, J.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Arnulf, B.; Mateos, M.-V.; Lendvai, N.; Jackson, C.C.; De Braganca, K.C.; et al. Incidence and Management of CAR-T Neurotoxicity in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel in CARTITUDE Studies. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oekelen, O.; Aleman, A.; Upadhyaya, B.; Schnakenberg, S.; Madduri, D.; Gavane, S.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Crary, J.F.; Fowkes, M.E.; Stacy, C.B.; et al. Neurocognitive and Hypokinetic Movement Disorder with Features of Parkinsonism after BCMA-Targeting CAR-T Cell Therapy. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailankody, S.; Devlin, S.M.; Landa, J.; Nath, K.; Diamonte, C.; Carstens, E.J.; Russo, D.; Auclair, R.; Fitzgerald, L.; Cadzin, B.; et al. GPRC5D-Targeted CAR T Cells for Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xi, R.; Mao, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, T. Efficacy and Safety of Blinatumomab for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023, 23, e139–e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrapodi, M.M.; Mascolo, A.; di Mauro, G.; Mondillo, G.; Pota, E.; Rossi, F. The Safety of Blinatumomab in Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 929122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.S.; Schiller, G.; Benjamin, R.; Jia, C.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, M.; Zimmerman, Z.; Topp, M.S. Neurologic Adverse Events in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Blinatumomab: Management and Mitigating Factors. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, S.; Kuo, E.; Lau, K.M. Neurotoxicity with Blinatumomab in Combination with Intrathecal Methotrexate Therapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2023, 64, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Litzow, M.R. Management of Toxicities Associated with Novel Immunotherapy Agents in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2020, 11, 204062071989989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Royo, D.; Juárez-Salcedo, L.M.; Dalia, S. Management of Adverse Effects of New Monoclonal Antibody Treatments in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Drugs Context 2020, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeberl, F.; Tiedt, S.; Schmitt, A.; Blumenberg, V.; Karschnia, P.; Burbano, V.G.; Bücklein, V.L.; Rejeski, K.; Schmidt, C.; Busch, G.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain Serum Levels Correlate with the Severity of Neurotoxicity after CAR T-Cell Treatment. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3022–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, O.H.; Zhou, A.Y.; Caimi, P.F.; Luckett, P.H.; Wisch, J.K.; Derenoncourt, P.-R.; Lee, K.; Wu, G.F.; de Lima, M.J.G.; Campian, J.L.; et al. Assessment of Pretreatment and Posttreatment Evolution of Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in Patients Who Develop Immune Effector Cell–Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domain | Allocated Points |
|---|---|
| Orientation to year, month, city, hospital | 4 |
| Naming of three objects | 3 |
| Following a command | 1 |
| Writing a standard sentence | 1 |
| Attention (counting backwards from 100 by 10) | 1 |
| Total number of points | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsalem, A.N.; Scarffe, L.A.; Briemberg, H.R.; Aaroe, A.E.; Harrison, R.A. Neurologic Complications of Cancer Immunotherapy. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5876-5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060440
Alsalem AN, Scarffe LA, Briemberg HR, Aaroe AE, Harrison RA. Neurologic Complications of Cancer Immunotherapy. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(6):5876-5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060440
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsalem, Aseel N., Leslie A. Scarffe, Hannah R. Briemberg, Ashley E. Aaroe, and Rebecca A. Harrison. 2023. "Neurologic Complications of Cancer Immunotherapy" Current Oncology 30, no. 6: 5876-5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060440
APA StyleAlsalem, A. N., Scarffe, L. A., Briemberg, H. R., Aaroe, A. E., & Harrison, R. A. (2023). Neurologic Complications of Cancer Immunotherapy. Current Oncology, 30(6), 5876-5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060440





