Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
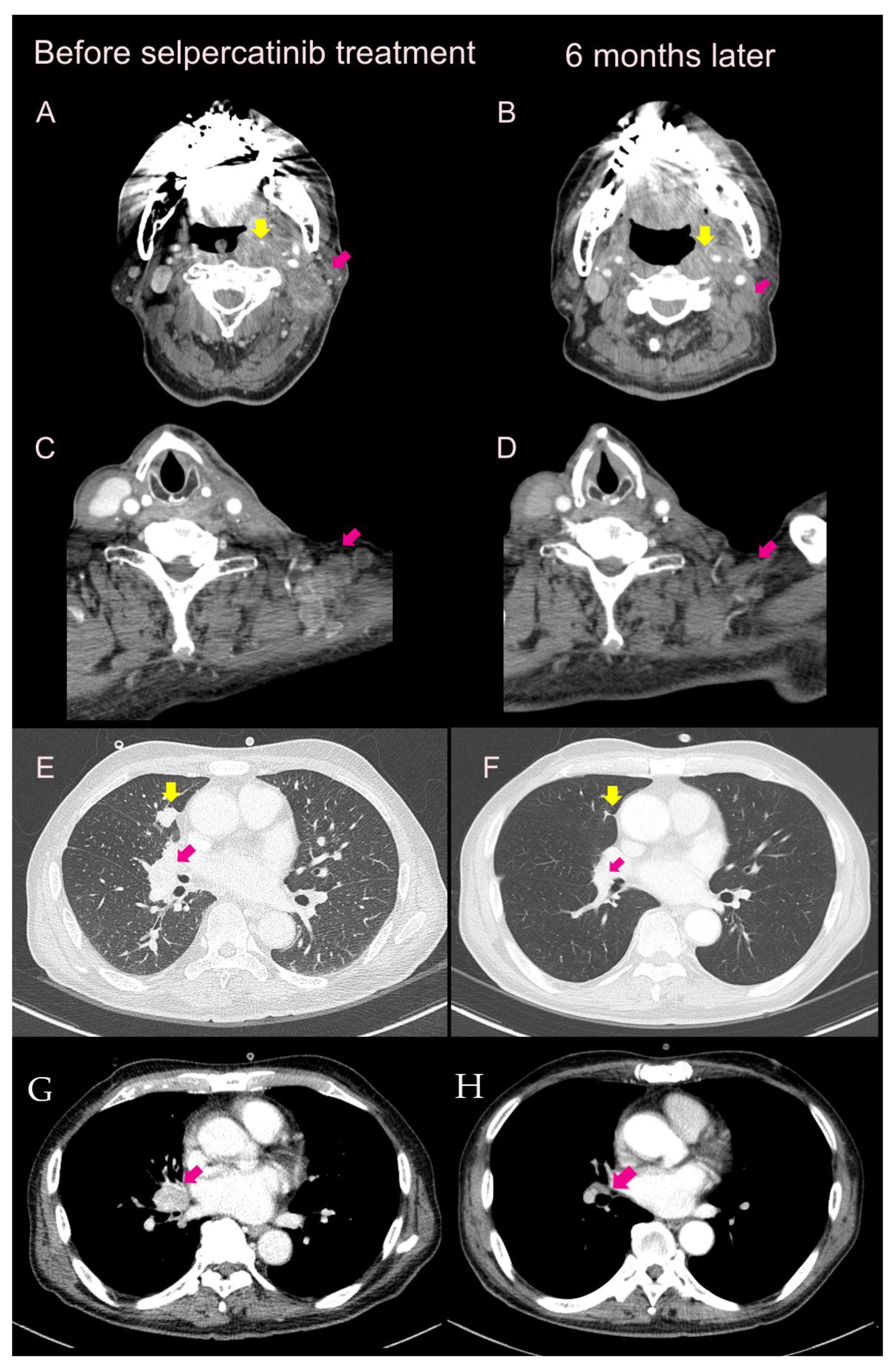
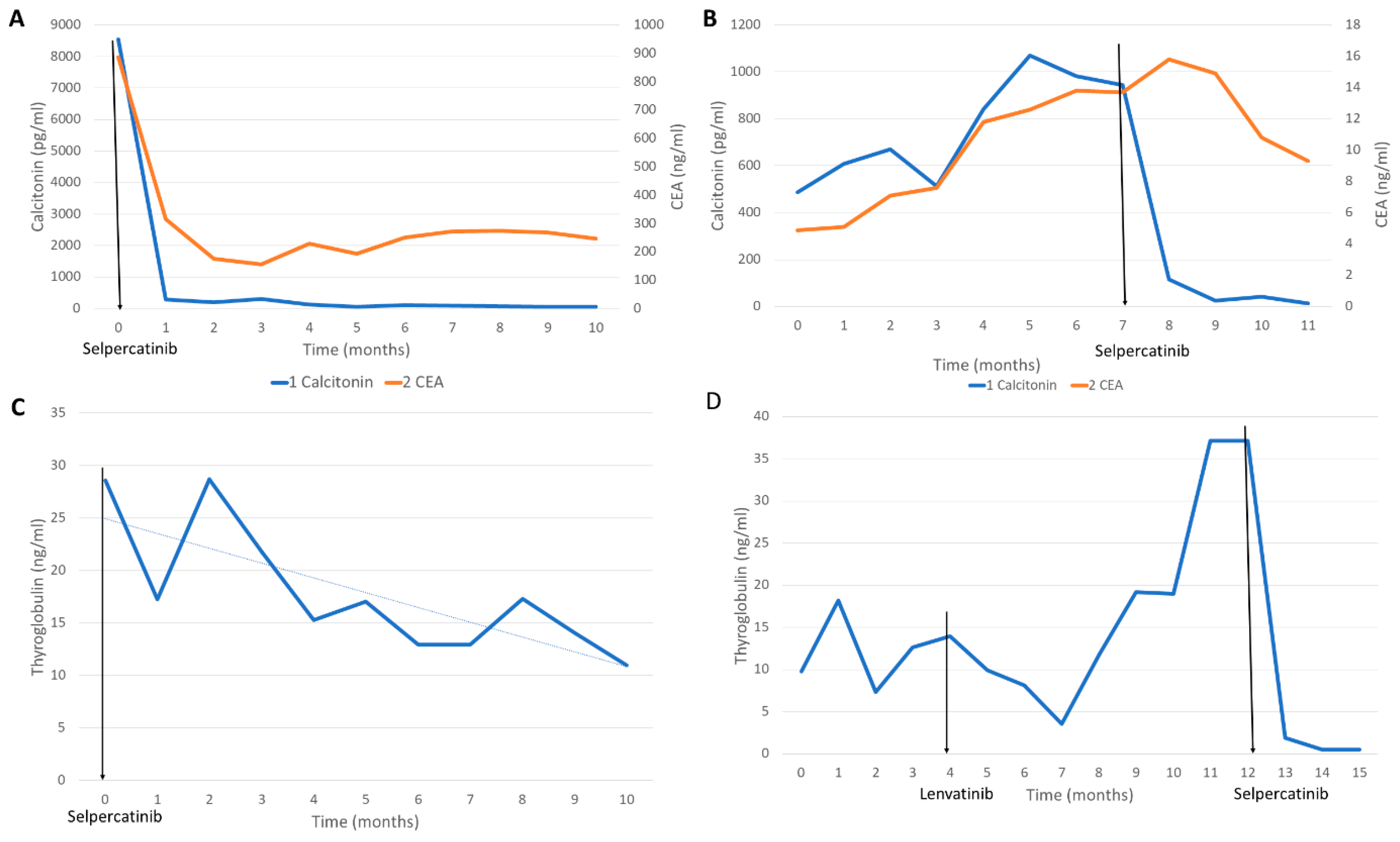
2.1. Case 1
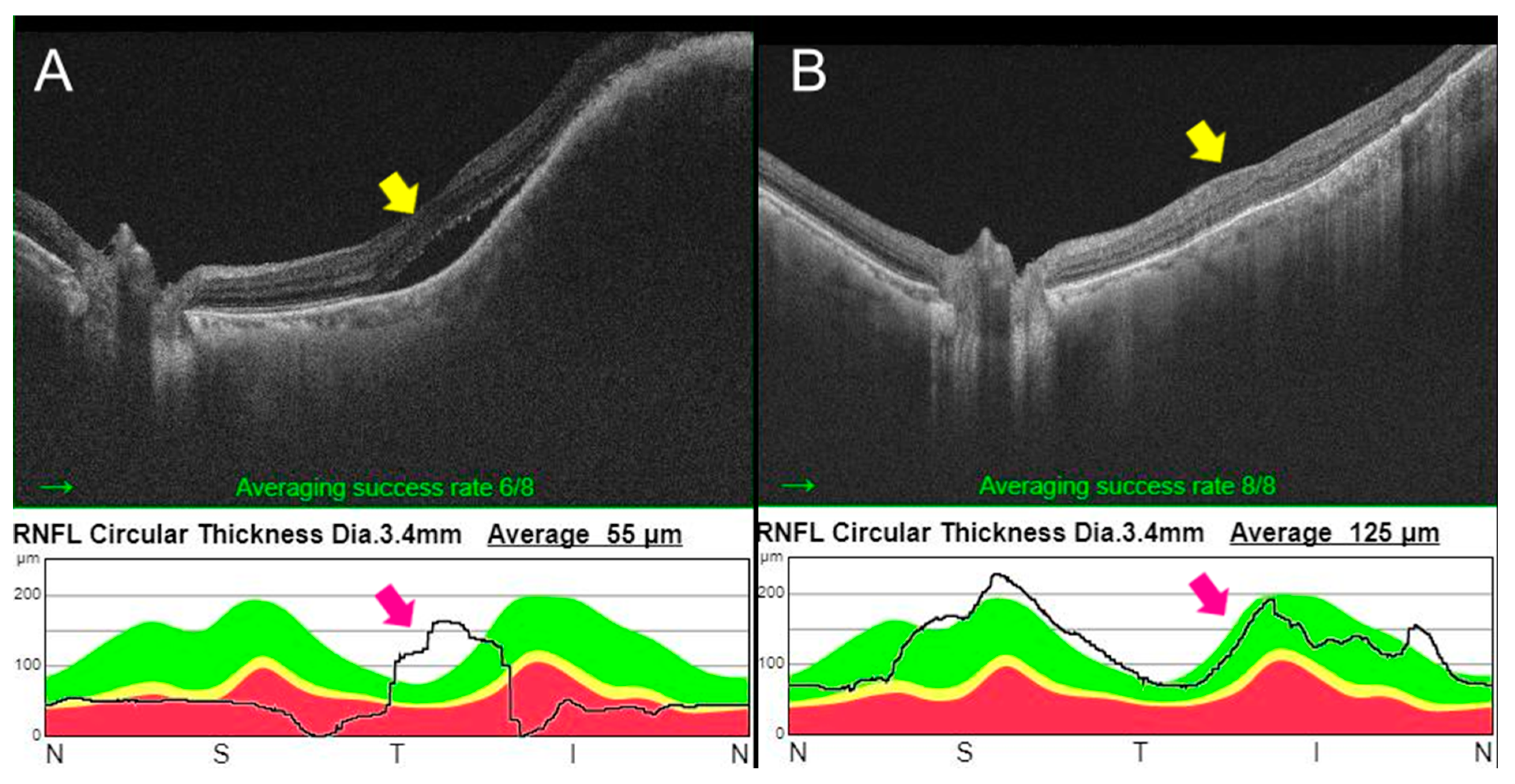
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
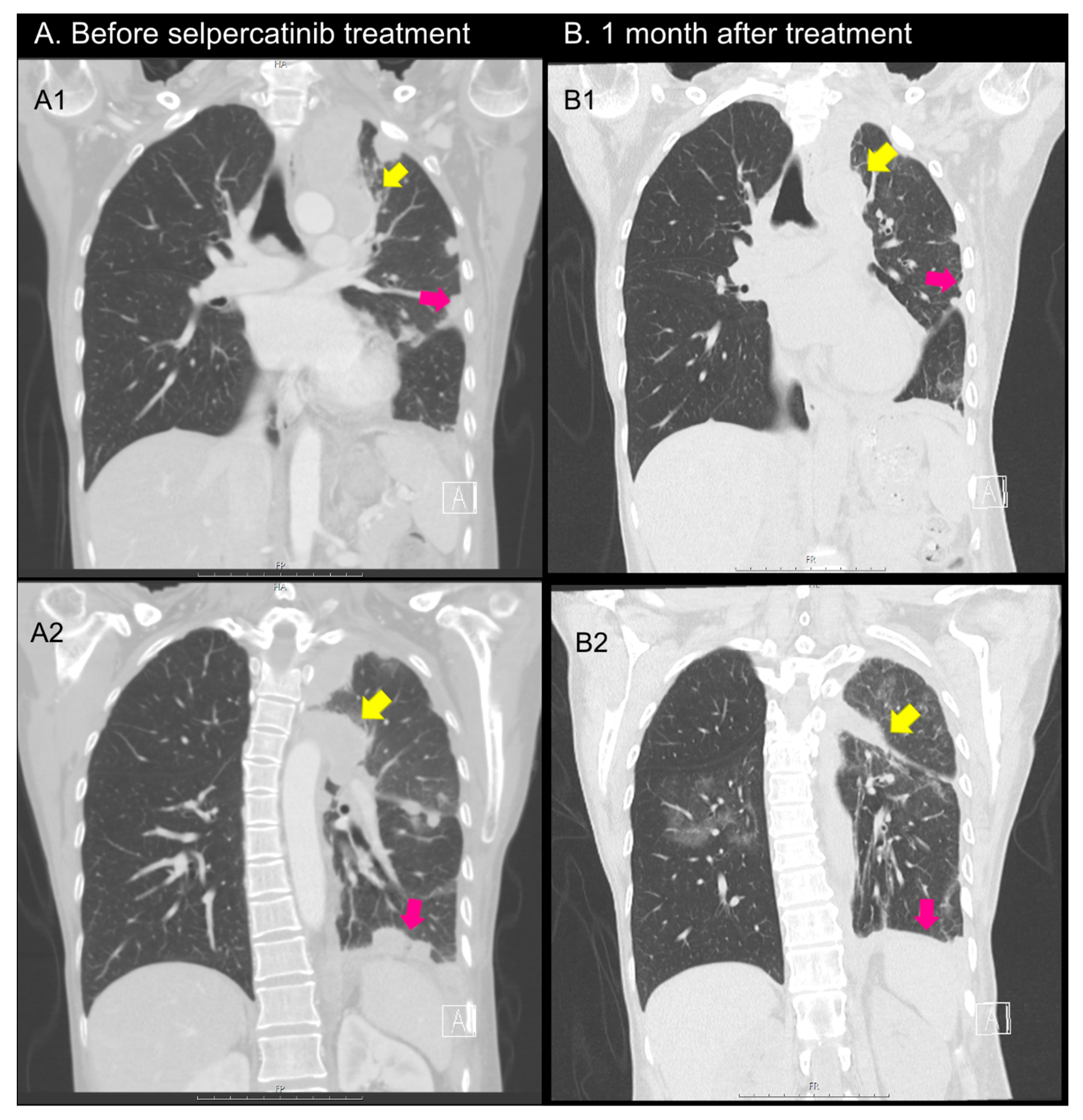
2.4. Case 4
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirth, L.J.; Sherman, E.; Robinson, B.; Solomon, B.; Kang, H.; Lorch, J.; Worden, F.; Brose, M.; Patel, J.; Leboulleux, S.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET-Altered Thyroid Cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Velcheti, V.; Tuch, B.B.; Ebata, K.; Busaidy, N.L.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Wirth, L.J.; Stock, S.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; et al. Selective RET kinase inhibition for patients with RET-altered cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, K.Z.; Velcheti, V.; Mooers, B.H.M.; Wu, J.; Subbiah, V. Precision therapy for RET-altered cancers with RET inhibitors. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.H.; Oh, Y.L.; Hong, M.; Yun, J.W.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, D.; Ji, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, W.Y.; Shin, H.T.; et al. Identification of Driving ALK Fusion Genes and Genomic Landscape of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, R.; Romei, C.; Ramone, T.; Prete, A.; Tacito, A.; Cappagli, V.; Bottici, V.; Viola, D.; Torregrossa, L.; Ugolini, C.; et al. Genetic Landscape of Somatic Mutations in a Large Cohort of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas Studied by Next-Generation Targeted Sequencing. iScience 2019, 20, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Lee, H.; Im, S.W.; Song, Y.S.; Oh, D.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Won, J.K.; Jung, K.C.; Kwon, D.; Chung, E.J.; et al. NTRK and RET fusion-directed therapy in pediatric thyroid cancer yields a tumor response and radioiodine uptake. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e144847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisei, R.; Schlumberger, M.J.; Müller, S.P.; Schöffski, P.; Brose, M.S.; Shah, M.H.; Licitra, L.; Jarzab, B.; Medvedev, V.; Kreissl, M.C.; et al. Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, S.A., Jr.; Robinson, B.G.; Gagel, R.F.; Dralle, H.; Fagin, J.A.; Santoro, M.; Baudin, E.; Elisei, R.; Jarzab, B.; Vasselli, J.R.; et al. Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: A randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, M.S.; Nutting, C.M.; Jarzab, B.; Elisei, R.; Siena, S.; Bastholt, L.; De La Fouchardiere, C.; Pacini, F.; Paschke, R.; Shong, Y.K.; et al. Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Tahara, M.; Wirth, L.J.; Robinson, B.; Brose, M.S.; Elisei, R.; Habra, M.A.; Newbold, K.; Shah, M.H.; Hoff, A.O.; et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lim, D.J.; Kang, H.C.; Kim, I.J.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Vandetanib for the Management of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Real-World Multicenter Experience. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, D.; Larkins, E.; Mushti, S.L.; Rodriguez, L.; Skinner, A.M.; Helms, W.S.; Price, L.S.L.; Zirkelbach, J.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Selpercatinib for the Treatment of Lung and Thyroid Cancers with RET Gene Mutations or Fusions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ji, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ge, M.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Lei, S.; Shi, F.; Guo, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of selpercatinib in Chinese patients with advanced RET-altered thyroid cancers: Results from the phase II LIBRETTO-321 study. Ther Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221119318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Ciampi, R.; Matrone, A.; Prete, A.; Gambale, C.; Ramone, T.; Simeakis, G.; Materazzi, G.; Torregrossa, L.; Ugolini, C.; et al. Somatic RET Indels in Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Prevalence and Response to Selpercatinib. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Seymour, L.; Litière, S.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1—Standardisation and disease-specific adaptations: Perspectives from the RECIST Working Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eli Lilly and Company USA, Ltd. Retevmo (Selpercatinib). Prescribing Information. Available online: https://pi.lilly.com/us/retevmo-uspi.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Yi, J.W.; Kang, H.I.; Kim, S.J.; Seong, C.Y.; Chai, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Seong, M.W.; Lee, K.E.; Park, S.S. A Novel RET D898Y Germline Mutation in a Patient with Pheochromocytoma. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 8657914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Yang, D.; Velcheti, V.; Drilon, A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. State-of-the-Art Strategies for Targeting RET-Dependent Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, A.; Prete, A.; Sartini, M.S.; Elisei, R. Significant response of medullary thyroid cancer choroidal metastases to highly selective RET inhibitor selpercatinib: A case report. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinetti, F.; Bordi, P.; Bini, P.; Bidin, L.; Camisa, R.; Tiseo, M. Enteral Administration of TKIs: Report of a Response to Ceritinib in an ALK-positive NSCLC Patient and Literature Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, R.C.; Sen, S.; Hobbs, B.P.; Hong, D.S. Histology-agnostic drug development—Considering issues beyond the tissue. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Subbiah, V.; Gautschi, O.; Tomasini, P.; de Braud, F.; Solomon, B.J.; Shao-Weng Tan, D.; Alonso, G.; Wolf, J.; Park, K.; et al. Selpercatinib in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Safety and Efficacy from the Registrational LIBRETTO-001 Phase I/II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.C.; Liu, W.L.; Zhu, X.L.; Yu, P.C.; Shi, X.; Han, P.Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L.Y.; Semenov, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Enhances the Diagnosis Efficiency in Thyroid Nodules. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 677892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mercier, M.; D’Haene, N.; De Nève, N.; Blanchard, O.; Degand, C.; Rorive, S.; Salmon, I. Next-generation sequencing improves the diagnosis of thyroid FNA specimens with indeterminate cytology. Histopathology 2015, 66, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.X.; Espin-Garcia, O.; Bedard, P.L.; Stockley, T.; Prince, R.; Mete, O.; Krzyzanowska, M.K. Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Advanced Thyroid Cancers. Thyroid 2022, 32, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luthra, R.; Routbort, M.J.; Patel, K.P.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Broaddus, R.R.; Williams, M.D. Molecular Profile of Advanced Thyroid Carcinomas by Next-Generation Sequencing: Characterizing Tumors Beyond Diagnosis for Targeted Therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Remon, J.; Mateo, J.; Westphalen, C.B.; Barlesi, F.; Lolkema, M.P.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; Robson, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, Y.; Kirita, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Ohe, Y.; Nishio, M.; Seto, T.; Kodani, M.; Taima, K.; Hattori, Y.; Kohno, T.; et al. 1333P—Detectability of RET fusions by amplicon-based next generation sequencing in nationwide lung cancer genomic screening project: LC-SCRUM-Japan. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, v475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illini, O.; Hochmair, M.J.; Fabikan, H.; Weinlinger, C.; Tufman, A.; Swalduz, A.; Lamberg, K.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Huemer, F.; Vikström, A.; et al. Selpercatinib in RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (SIREN): A retrospective analysis of patients treated through an access program. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211019675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivieri, A.; Lavra, L.; Magi, F.; Morgante, A.; Calò, L.; Polisca, P.; Salehi, L.B.; Sciacchitano, S. Thyroid hormones regulate cardiac repolarization and QT-interval related gene expression in hiPSC cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, L.J.; Tahara, M.; Robinson, B.; Francis, S.; Brose, M.S.; Habra, M.A.; Newbold, K.; Kiyota, N.; Dutcus, C.E.; Mathias, E.; et al. Treatment-emergent hypertension and efficacy in the phase 3 Study of (E7080) lenvatinib in differentiated cancer of the thyroid (SELECT). Cancer 2018, 124, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellekens, A.F.A.; Mulder, S.F.; van Eijndhoven, P.F.P.; Smilde, T.J.; van Herpen, C.M.L. Psychotic symptoms in the course of sunitinib treatment for advanced renal cell cancer. Two cases. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2011, 33, 83.e1–83.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veldt, A.A.M.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.M.; Hoekman, K.; Barkhof, F.; Boven, E. Reversible cognitive disorders after sunitinib for advanced renal cell cancer in patients with preexisting arteriosclerotic leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalchiem-Dekel, O.; Falcon, C.J.; Bestvina, C.M.; Liu, D.; Kaplanis, L.A.; Wilhelm, C.; Eichholz, J.; Harada, G.; Wirth, L.J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; et al. Brief Report: Chylothorax and Chylous Ascites during RET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prete, A.; Gambale, C.; Cappagli, V.; Bottici, V.; Rossi, P.; Caciagli, M.; Papini, P.; Taddei, D.; Ortori, S.; Gabbrielli, L.; et al. Chylous effusions in advanced medullary thyroid cancer patients treated with selpercatinib. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 187, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at selpercatinib treatment | 62 | 67 | 32 | 59 |
| Sex | M | F | F | F |
| Tumor type | MTC | MTC | PTC | PTC |
| Mutation | RET mutation D898Y Germline | RET mutation M918T Somatic | CCDC6-RET gene fusion | CCDC6-RET gene fusion |
| Previous TKI treatment | Vandetanib | Vandetanib | None | Lenvatinib |
| Detection methods for RET alteration | Germline mutation study on blood sample | NGS on hepatic metastatic tissue | NGS on neck LN metastatic tissue | NGS on lung metastatic tissue |
| Metastasis site | LN, lung, bone | LN, lung, liver, choroidal | LN, lung | LN, lung, pleura, bone |
| Adverse events with selpercatinib treatment a | HTN (G3), QTc prolongation (G1), headache (G1~2) | QTc prolongation (G3) | HTN (G2), Dry mouth (G2), photosensitivity (G1), diarrhea (G1), | Dry mouth (G1) Diarrhea (G1) VPC (G1) |
| Key points of case | PEG administration History of ICH | Hepatic, choroidal metastasis | First-line use | Panic disorder Pleural effusion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, H.-S.; Ha, J.; Ha, S.; Bae, J.S.; Jung, C.K.; Lim, D.-J. Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3020-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030229
Baek H-S, Ha J, Ha S, Bae JS, Jung CK, Lim D-J. Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):3020-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030229
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Han-Sang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seunggyun Ha, Ja Seong Bae, Chan Kwon Jung, and Dong-Jun Lim. 2023. "Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 3020-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030229
APA StyleBaek, H.-S., Ha, J., Ha, S., Bae, J. S., Jung, C. K., & Lim, D.-J. (2023). Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea. Current Oncology, 30(3), 3020-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030229






