Hemoglobin and Neutrophil Count as Prognostic Factors in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients in 2nd Line Treatment Setting: Results from a Small Monocentric Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
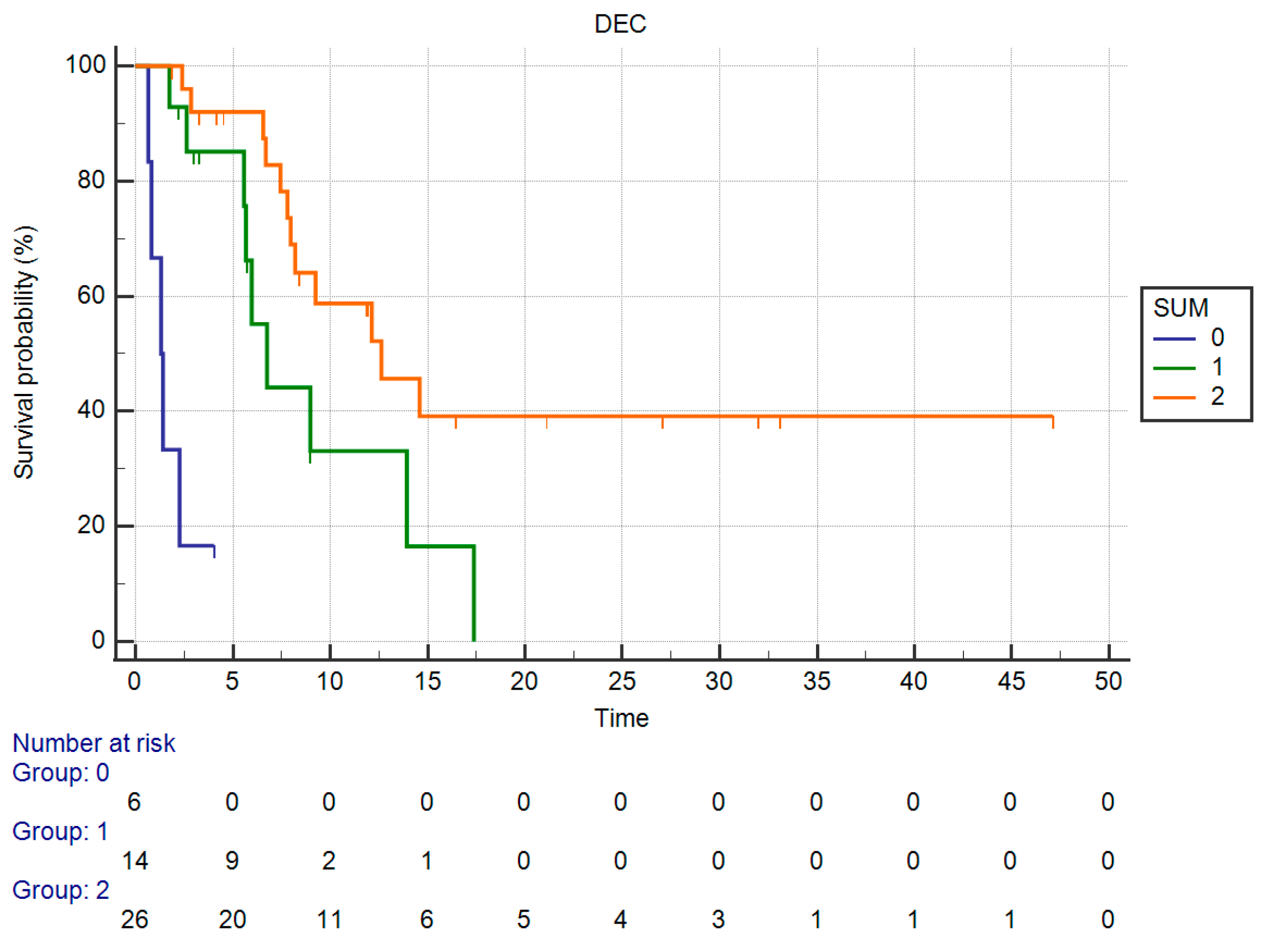
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Laboratory Tests Results
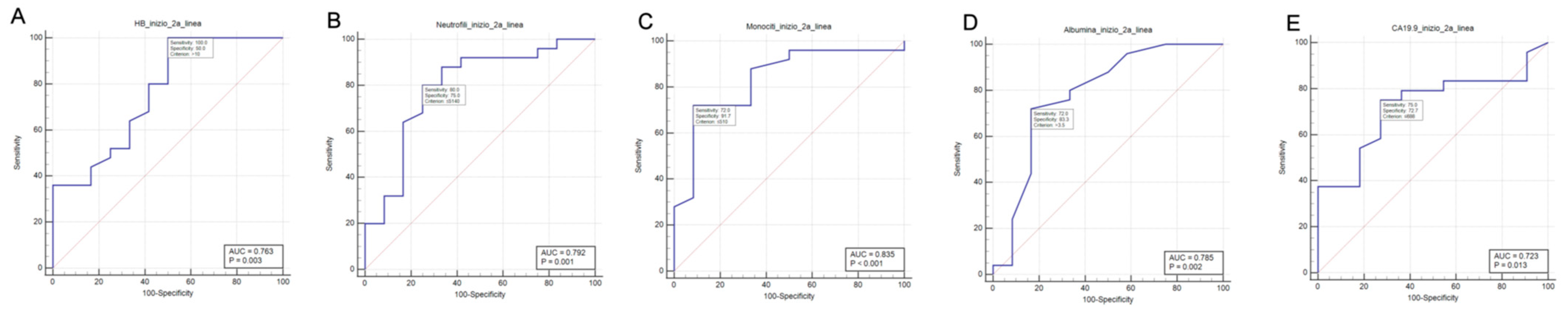
3.2. ROC Curve Analysis Results
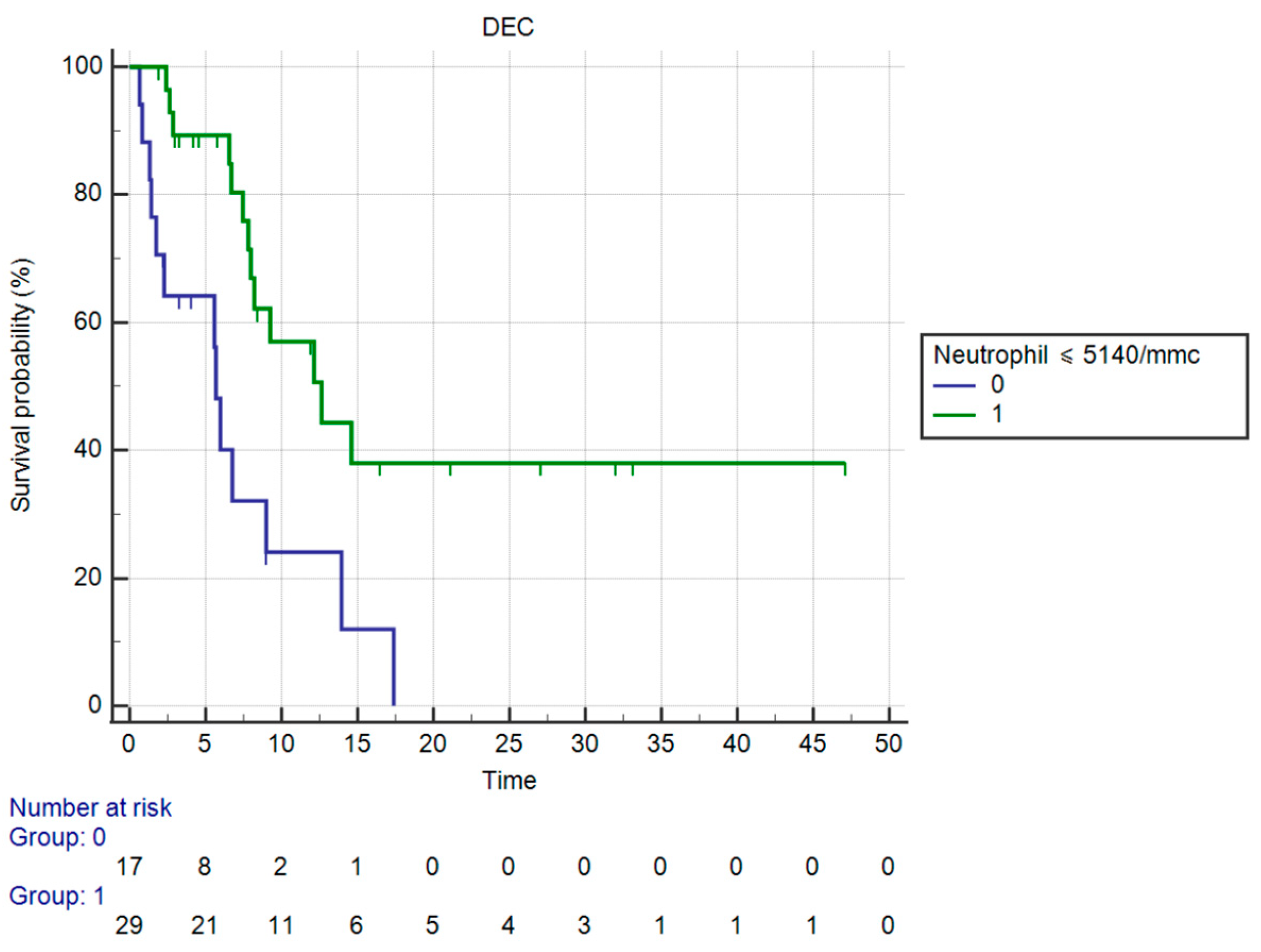
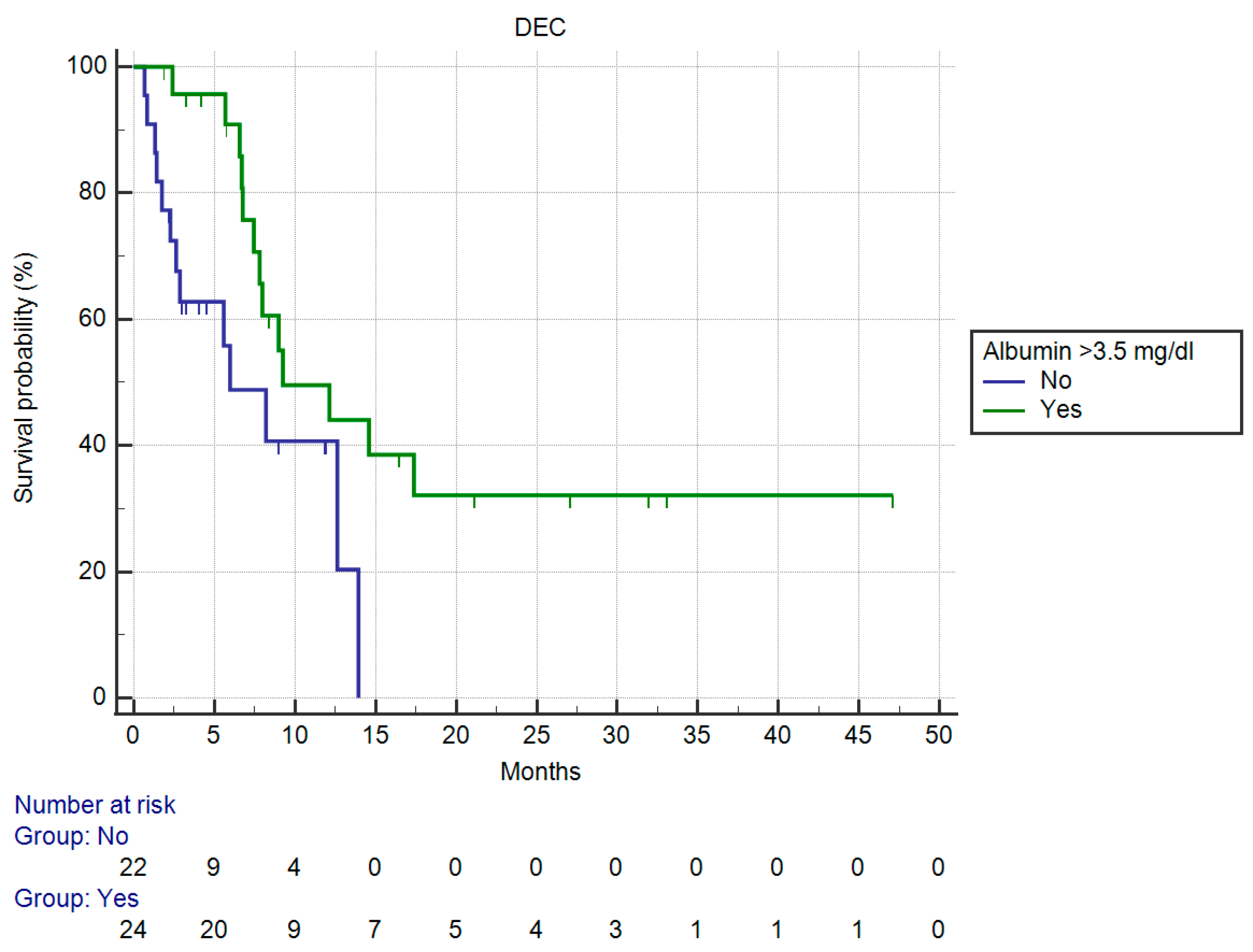
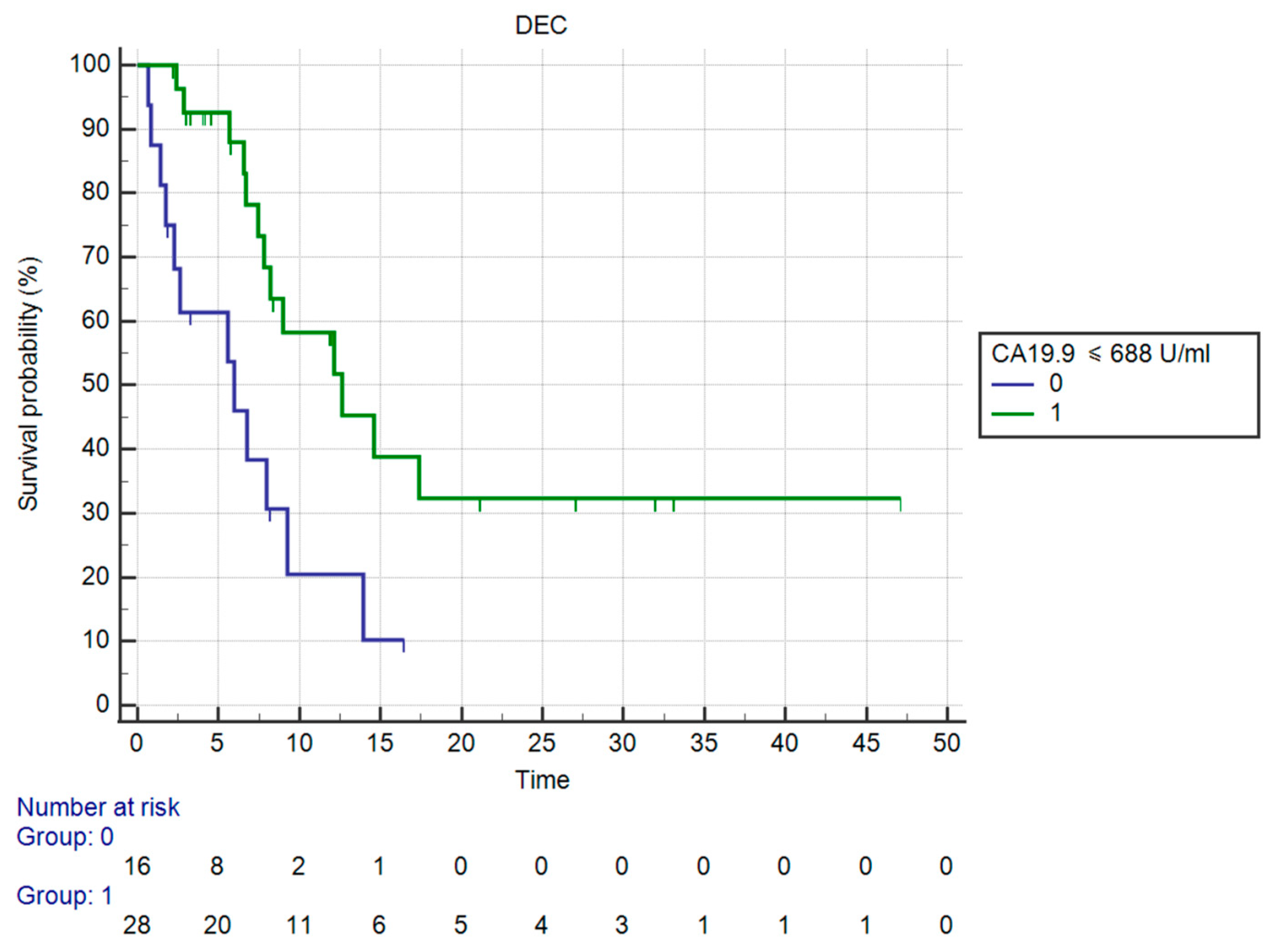
3.3. Results of Univariate Analysis for OS
3.4. Results of Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valle, J.W.; Borbath, I.; Khan, S.A.; Huguet, F.; Gruenberger, T.; Arnold, D. Biliary cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v28–v37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.; Wasan, H.; Palmer, D.H.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Iveson, T.; Hughes, S.; Pereira, S.P.; et al. Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine versus Gemcitabine for Biliary Tract Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Ricci, A.D.; Tober, N.; Nigro, M.C.; Mosca, M.; Palloni, A.; Abbati, F.; Frega, G.; De Lorenzo, S.; Tavolari, S.; et al. Second-line Treatment in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer: Today and Tomorrow. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 3013–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarca, A.; Palmer, D.H.; Wasan, H.S.; Ross, P.J.; Ma, Y.T.; Arora, A.; Falk, S.; Gillmore, R.; Wadsley, J.; Patel, K.; et al. Second-line FOLFOX chemotherapy versus active symptom control for advanced biliary tract cancer (ABC-06): A phase 3, open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Gunchick, V.; Mody, K.; Xiao, L.; Surapaneni, P.; Shroff, R.T.; Sahai, V. Multi-institutional Retrospective Analysis of FOLFIRI In Patients with Advanced Biliary Tract Cancers. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, L.; Cereda, S.; Aprile, G.; Di Girolamo, S.; Santini, D.; Silvestris, N.; Lonardi, S.; Leone, F.; Milella, M.; Vivaldi, C.; et al. Multivariate prognostic factors analysis for second-line chemotherapy in advanced biliary tract cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzillet, C.; Gardini, A.C.; Brieau, B.; Vivaldi, C.; Smolenschi, C.; Brandi, G.; Tougeron, D.; Filippi, R.; Vienot, A.; Silvestris, N.; et al. Prediction of survival with second-line therapy in biliary tract cancer: Actualisation of the AGEO CT2BIL cohort and European multicentre validations. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 111, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Greten, F.; Karin, M. Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, P.L.; Goodchild, G.; Pereira, S.P. Molecular Pathogenesis of Cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeppert, B.; Frauenschuh, L.; Zucknick, M.; Roessler, S.; Mehrabi, A.; Hafezi, M.; Stenzinger, A.; Warth, A.; Pathil, A.; Renner, M.; et al. Major histocompatibility complex class I expression impacts on patient survival and type and density of immune cells in biliary tract cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils in Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 983698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Saxena, S.; Awaji, M.; Singh, R.K. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Cancer: Going Pro. Cancers 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Cropet, C.; Van Glabbeke, M.; Sebban, C.; Le Cesne, A.; Judson, I.; Tredan, O.; Verweij, J.; Biron, P.; Labidi, I.; et al. Lymphopenia as a Prognostic Factor for Overall Survival in Advanced Carcinomas, Sarcomas, and Lymphomas. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 5383–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Cabiddu, M.; Coinu, A.; Borgonovo, K.; Ghilardi, M.; Lonati, V.; Barni, S. Prognostic role of lactate dehydrogenase in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 76 studies. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenci, E.; Cantini, L.; Pecci, F.; Cognigni, V.; Agostinelli, V.; Mentrasti, G.; Lupi, A.; Ranallo, N.; Paoloni, F.; Rinaldi, S.; et al. The Gustave Roussy Immune (GRIm)-Score Variation Is an Early-on-Treatment Biomarker of Outcome in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients Treated with First-Line Pembrolizumab. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittoni, A.; Pecci, F.; Mentrasti, G.; Crocetti, S.; Lupi, A.; Lanese, A.; Pellei, C.; Ciotti, C.; Cantini, L.; Giampieri, R.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index: A prognostic tiebreaker among all in advanced pancreatic cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, J.L. The anemia of cancer: Death by a thousand cuts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, J.W. The Anemia of Inflammation/Malignancy: Mechanisms and Management. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2008, 2008, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, H.L. Benefits of Early Intervention with Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Proteins in Chemotherapy-Induced Anemia. Oncology 2006, 20, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Macciò, A.; Madeddu, C.; Gramignano, G.; Mulas, C.; Tanca, L.; Cherchi, M.C.; Floris, C.; Omoto, I.; Barracca, A.; Ganz, T. The role of inflammation, iron, and nutritional status in cancer-related anemia: Results of a large, prospective, observational study. Haematologica 2015, 100, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, M. Intravenous iron in chemotherapy-induced anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszewski, H. Hematological paraneoplastic syndromes. Semin. Oncol. 1997, 24, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Arias, A.; Cetina, L.; Candelaria, M.; Robles, E.; Dueñas-González, A. The prognostic significance of leukocytosis in cervical cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2007, 17, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilova, A.B.; Baldueva, I.A. Neutrophils as tumor microenviroment member. Vopr. Onkol. 2016, 62, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fridlender, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Kim, S.; Kapoor, V.; Cheng, G.; Ling, L.; Worthen, G.S.; Albelda, S.M. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer Immunoediting: Integrating Immunity’s Roles in Cancer Suppression and Promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumanto, Y.H.; Dam, W.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Meijer, C.; Mulder, N.H. Platelets and Granulocytes, in Particular the Neutrophils, Form Important Compartments for Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana, A.; Nieto-Jiménez, C.; Pandiella, A.; Templeton, A.J. Neutrophils in cancer: Prognostic role and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, K.; Ito, Z.; Suka, M.; Kanai, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Odahara, S.; Matsudaira, H.; Haruki, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Saito, R.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of the prognosis of pancreatic cancer: Peripheral blood neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and immunohistochemical analyses of the tumour site. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Culakova, E.; Lyman, G.H.; Francis, C.W. Development and validation of a predictive model for chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Blood 2008, 111, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langiu, M.; Palacios-Acedo, A.-L.; Crescence, L.; Mege, D.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Neutrophils, Cancer and Thrombosis: The New Bermuda Triangle in Cancer Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laridan, E.; Martinod, K.; De Meyer, S.F. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Arterial and Venous Thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Xiong, M.; Ren, L.; Bai, L. Prognostic value of neutrophil distribution in cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Hu, P.; Donskov, F.; Wang, G.; Liu, Q.; Du, J. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils as a New Prognostic Factor in Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.-W.; Fu, Y.; Su, Q.; Guan, M.-J.; Kong, P.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wang, H.-L. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Oncologic Outcomes of Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merav, E.S.; Zvi, G.F. Cancer-related circulating and tumor-associated neutrophils—Subtypes, sources and function. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 4316–4342. [Google Scholar]



| Characteristics, N (%) | All Patients N = 46 (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 28 (61) |
| Female | 18 (39) |
| Age | |
| <65 years | 15 (33) |
| >65 years | 31 (67) |
| ECOG PS at the beginning of 2nd line treatment | |
| 0–1 | 43 (93) |
| >2 | 3 (7) |
| Tumor location | |
| Intrahepatic | 23 (50) |
| Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma | 11 (24) |
| Extrahepatic | 8 (17) |
| Gall bladder | 4 (9) |
| Synchronous metastases | |
| Yes | 23 (50) |
| No | 23 (50) |
| Primary tumor resection | |
| Yes; received adjuvant treatment | 16; 10 (34) |
| No | 30 (66) |
| 1st line chemotherapy | |
| CDDP + Gemcitabine | 30 (66) |
| FOLFOX/XELOX | 6 (14) |
| GEMOX | 4 (8) |
| Gemcitabine monotherapy | 2 (4) |
| Other | 4 (8) |
| 1st line treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | |
| Yes | 17 (37) |
| No | 29 (63) |
| 2nd line chemotherapy | |
| Irinotecan-based | 22 (48) |
| Platinum-based | 24 (52) |
| Laboratory Test | Mean Value | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.65 | 11.45 | 8.7–15.7 |
| Neutrophil count (/mmc) | 5630 | 4495 | 1820–21,270 |
| Lymphocyte count (/mmc) | 1323 | 1210 | 470–2880 |
| Monocyte count (/mmc) | 626 | 525 | 260–1240 |
| Platelets count (/mmc) | 213,000 | 194,500 | 96,000–571,000 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.41–1.36 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.53 | 0.45 | 0.2–1.5 |
| GOT/GPT (U/L) | 32/38 | 26/33 | 7–86/10–105 |
| LDH (U/L) | 260 | 219 | 96–701 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.4 | 3.6 | 2.1–4.5 |
| CEA (ng/mL) | 16.31 | 3.05 | 0.3–246 |
| Ca 19-9 (U/mL) | 7762 | 206 | 2–100,000 |
| Laboratory Test | Best Cut-Off (by Youden J-Index) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | AUC (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | >10 g/dL | 100.0 | 50.0 | 0.763 (0.003) |
| Neutrophil count (/mmc) | ≤5140/mmc | 80.0 | 75.0 | 0.792 (0.001) |
| Lymphocyte count (/mmc) | >1810/mmc | 24.0 | 100.0 | 0.580 (0.424) |
| Monocyte count (/mmc) | ≤510/mmc | 72.0 | 91.7 | 0.835 (<0.001) |
| Platelets count (/mmc) | >262,000/mmc | 28.0 | 91.7 | 0.525 (0.804) |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | ≤0.9 mg/dL | 76.0 | 66.7 | 0.667 (0.132) |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | ≤0.3 mg/dL | 32.0 | 91.7 | 0.625 (0.179) |
| LDH (U/L) | ≤417 U/L | 96.0 | 33.3 | 0.547 (0.690) |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | >3.5 g/dL | 72.0 | 83.3 | 0.785 (0.002) |
| CEA (ng/mL) | ≤3.3 ng/mL | 83.3 | 54.5 | 0.697 (0.061) |
| Ca 19-9 (U/mL) | ≤688 U/mL | 75.0 | 72.7 | 0.723 (0.013) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Test | Median OS (Months) | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Exp (b) (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Hemoglobin > 10 g/dL | |||||
| Yes | 12.31 | 0.014 (0.002–0.09) | <0.0001 | 0.1244 (0.0327–0.4737) | 0.0023 |
| No | 2.26 | ||||
| Neutrophil count ≤ 5140/mmc | |||||
| Yes | 12.62 | 0.23 (0.09–0.58) | <0.0001 | 0.3035 (0.1352–0.6815) | 0.0039 |
| No | 5.67 | ||||
| Monocyte count ≤ 510/mmc | |||||
| Yes | 12.62 | 0.36 (0.15–0.84) | 0.0189 | NA 1 | NA 1 |
| No | 5.97 | ||||
| Serum albumin > 3.5 g/dL | |||||
| Yes | 9.24 | 0.38 (0.16–0.91) | 0.0302 | NA 1 | NA 1 |
| No | 5.97 | ||||
| Ca 19-9 ≤ 688 U/mL | |||||
| Yes | 12.62 | 0.27 (0.10–0.68) | 0.0057 | NA 1 | NA 1 |
| No | 5.97 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liguori, C.; Copparoni, C.; Felicetti, C.; Pecci, F.; Lupi, A.; Pinterpe, G.; Berardi, R.; Giampieri, R. Hemoglobin and Neutrophil Count as Prognostic Factors in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients in 2nd Line Treatment Setting: Results from a Small Monocentric Retrospective Study. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1032-1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010079
Liguori C, Copparoni C, Felicetti C, Pecci F, Lupi A, Pinterpe G, Berardi R, Giampieri R. Hemoglobin and Neutrophil Count as Prognostic Factors in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients in 2nd Line Treatment Setting: Results from a Small Monocentric Retrospective Study. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(1):1032-1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiguori, Carolina, Cecilia Copparoni, Cristiano Felicetti, Federica Pecci, Alessio Lupi, Giada Pinterpe, Rossana Berardi, and Riccardo Giampieri. 2023. "Hemoglobin and Neutrophil Count as Prognostic Factors in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients in 2nd Line Treatment Setting: Results from a Small Monocentric Retrospective Study" Current Oncology 30, no. 1: 1032-1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010079
APA StyleLiguori, C., Copparoni, C., Felicetti, C., Pecci, F., Lupi, A., Pinterpe, G., Berardi, R., & Giampieri, R. (2023). Hemoglobin and Neutrophil Count as Prognostic Factors in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients in 2nd Line Treatment Setting: Results from a Small Monocentric Retrospective Study. Current Oncology, 30(1), 1032-1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010079







