Abstract
To test the usefulness of the Cancer and Aging Research Group (CARG) predictive tool, it was used to assess elderly cancer patients with prior anticancer therapy. Among patients with solid malignancies aged ≥ 65 years receiving second-line chemotherapy who were admitted to the Department of Medical Oncology/Hematology at Kakogawa Central City Hospital between April 2016 and September 2019, the risk ≥ grade 3 of developing chemotherapy-related adverse events (CRAEs) (low, intermediate, or high) was calculated using the tool. Correlations between grades 3 and 5 CRAE incidence rates in the first course of each regimen and CARG risk score, age, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) were assessed. Included patients (n = 62) had a mean age of 71 years (range, 65–82 years). Severe CRAE incidence in patients with low, medium, or high CARG risk was 27%, 54%, and 71%, respectively (p = 0.026). The incidence of severe non-hematological toxicities was 5%, 35%, and 64%, respectively (p < 0.01). There was no association between age or ECOG PS and chemotherapy toxicity. The results suggest the validity of the CARG predictive tool in elderly cancer patients with prior anticancer therapy. Particularly, the tool showed potential for predicting non-hematological toxicity.
1. Introduction
In the United States, cancer is a disease of the elderly, with approximately 80% of all cancer deaths among individuals aged ≥60 years [1]. Similarly, in Japan, approximately 70% of all cancers are in those aged ≥65 years [2]. As a result, the use of anticancer drug therapy is increasing in the elderly, which increases the risk of chemotherapy-related adverse events (CRAEs) among the elderly population [3,4]. With the newly established use of adjuvant chemotherapy and the development of treatment with various molecular targeted agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors, including biliary tract cancer, CRAEs have also become more varied [5,6]. Nonetheless, few tools that are useful for characterizing chemotherapy-related risks in older patients with solid tumors are in current use.
Regardless of age, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) is used to predict chemotherapy toxicity and the likelihood of survival in patients [7]. However, whether ECOG PS is a valid predictor of toxicity remains unclear. The validity of ECOG PS is especially controversial in the elderly because the measure was validated in young adults, without addressing the health status diversity observed among elderly cancer patients. Therefore, Hurria et al. developed the Cancer and Aging Research Group (CARG) predictive tool, a prediction model for CRAEs of elderly cancer patients [8,9]. The tool facilitates the prediction of grade 3–5 CRAE tumors in elderly patients with solid tumors, which was previously difficult using age and ECOG PS.
However, most patients included in their study were treated with first-line anticancer drugs, and the model was not validated in patients treated with second-line or subsequent anticancer therapies [8,9]. Therefore, it remains unclear whether pre-treatment influences the prediction of adverse events. To test the usefulness of the CARG predictive tool, it was used to assess elderly cancer patients who received prior anticancer therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
Patients aged ≥65 years with solid tumors who received second-line or subsequent chemotherapy were eligible for inclusion in the study. Patients who visited the Department of Medical Oncology/Hematology of Kakogawa Central City Hospital between April 2016 and September 2019 and received a new patient’s anticancer drug regimen were considered. Patients receiving concurrent radiation were excluded.
The study was approved by the institutional review board of Kakogawa Central City Hospital. The study was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the 1963 Declaration of Helsinki and its later versions. Due to the retrospective design of this study, the requirement for patients’ informed consent was waived by our hospital’s institutional review board.
2.2. Study Design
Prior to chemotherapy, patients completed a medical questionnaire that included information regarding the presence of comorbidities, hearing impairment, falls in the past 6 months, walking restriction for 100 m, need for medication assistance, and loss of social activities due to physical and mental health status. In addition, we recorded tumor characteristics (type and stage), pre-treatment laboratory data, line of chemotherapy (second-line or later), use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and first-line chemotherapy drugs and dosage. Chemotherapy dosing for the first cycle of treatment was categorized as either standard or dose-reduced, as per American National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. Grade 3–5 CRAEs during chemotherapy were defined as per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE), version 5.0, via a medical record review. Laboratory-based toxicities were identified based on laboratory values on the date of scheduled chemotherapy or when patients sought medical care for symptoms that presented between chemotherapy cycles.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A chemotherapy toxicity score was calculated for each patient by using 11 prechemotherapy variables included in the CARG predictive tool for chemotherapy toxicity (Table 1) [8,9]. Chemotherapy toxicity risk was categorized as follows: low (0–5 points), moderate (6–9 points), or high (≥10 points) [8,9]. We evaluated the correlation between the incidence of grade ≥3 CRAEs during the first course of each regimen and CARG risk score or the patient characteristics. Toxicity distributions among different risk groups were compared with the ability of ECOG PS or age to predict toxicity. To make this comparison, ECOG PS scores were divided into three groups (0, 1, and ≥2), and patients were also divided into three age groups (65–69 years, 70–74 years, and ≥75 years).

Table 1.
Prediction model and scoring algorithm values used to predict chemotherapy toxicity.
The Fisher’s exact test was used to evaluate between-group differences in the incidence of grade 3–5 toxicity. All statistical analyses were performed using EZR software (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan) [10]. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
The study population comprised 62 cancer patients aged ≥65 years (Table 2). The median age of participants was 71 years (range, 65–82 years), and 53% were male. The most common type of cancer was gastrointestinal cancer (58%). Seventy-one percent of all patients received a single agent, and 69% received standard doses of chemotherapy. The number of patients with ECOG PS scores of 0, 1, and 2 was 11, 40, and 11, respectively. When stratified according to the CARG risk score, 22 patients were placed in a low-risk group, 26 in an intermediate-risk group, and 14 in a high-risk group.

Table 2.
Patient characteristics.
3.2. Chemotherapy-Related Adverse Events
The most commonly observed grade 3–5 hematologic toxicities were neutropenia (21%) and leucopenia (15%). Grade 4 hematologic toxicities included neutropenia (8%), leucopenia (2%), and thrombocytopenia (2%). The most commonly observed grade 3–5 nonhematologic toxicities were nausea (18%), fatigue (13%), and oral mucositis (6%). The grade 4 nonhematologic toxicities included hyponatremia (2%) and hypomagnesemia (2%) (Table 3). No patient died due to CRAEs.

Table 3.
Chemotherapy-related adverse events.
3.3. Comparison of CARG, ECOG PS, and Age for Predicting the Occurrence of Grade 3–5 CRAEs
As shown in Table 3, CRAE in patients classified as having low, medium, or high CARG risk scores was 27%, 54%, and 71%, respectively (p = 0.026) (Figure 1a). When classified based on the patient’s ECOG PS score, the incidence of grade 3–5 CRAEs in patients with PS scores of 0, 1, and ≥2 was 36%, 48%, and 64%, respectively (p = 0.50) (Figure 1b). In addition, the incidence of ≥grade 3 CRAEs was 54% for those aged 65–69 years, 44% for those aged 70–74 years, and 44% for those aged ≥75 years or older, with no correlation between age and the incidence of severe CRAEs observed (p = 0.85) (Figure 1c).
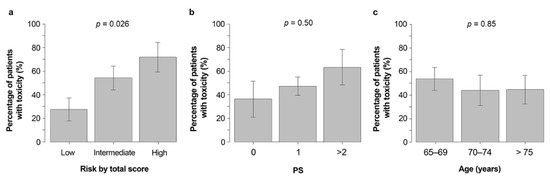
Figure 1.
Grade 3–5 CRAE incidence in those with low, medium and high (a) CARG risk scores, (b) PS, and (c) age classifications. Abbreviations: CARG, Cancer and Aging Research Group; PS, performance status; Gr3–5 CRAEs, grade 3–5 chemotherapy-related adverse events.
The incidence of severe hematological toxicities was 27%, 27%, and 42% in patients with low, medium, and high CARG risk scores, respectively (p = 0.60) (Figure 2a), while the incidence of severe non-hematological toxicities was 5%, 35%, and 64%, respectively (p < 0.01) (Figure 2b).
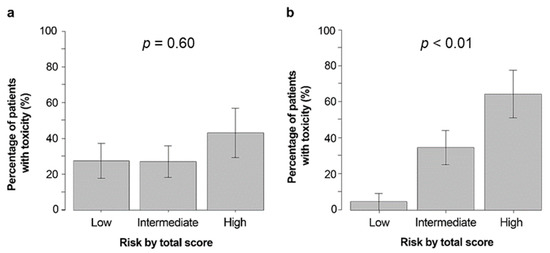
Figure 2.
Percentage of participants with severe hematologic (a) and non-hematologic (b) toxicities based on CARG predictive tool risk strata. Abbreviations: CARG, Cancer and Aging Research Group.
4. Discussion
In developed countries, cancer incidence and mortality rates are high [11], as is anticancer drug treatment use. In recent years, with the development of anticancer drug therapy, opportunities for the elderly to receive anticancer drug therapy after first-line treatment have increased. However, few methods for predicting CRAEs in elderly patients receiving second-line and subsequent anticancer therapies have been explored [8,9,12,13,14,15]. The CARG predictive tool enables the prediction of the occurrence of grade 3–5 CRAEs in elderly cancer patients receiving first-line treatment, which was previously difficult to predict based on age and ECOG PS [8,9]. Therefore, the American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines recommend the use of this tool [16].
Our study suggests that the CARG tool predicts grade 3–5 CRAEs well in elderly cancer patients who received prior anticancer therapy. In this patient population, it was difficult to predict severe CRAEs based on age or ECOG PS. Another tool for predicting CRAEs is the Chemotherapy Risk Assessment Scale for High-Age Patients (CRASH) score. In the previous study, the CRASH score predicted grade 3–5 CRAEs in cancer patients aged ≥70 years. The CRASH score also allowed the stratification of the risk in hematologic and non-hematologic toxicities [15]. Approximately half of the validation cohort considered, when assessing the ability of CRASH scores to predict CRAEs risk, were patients receiving second-line or subsequent chemotherapy. However, there are no data on CRASH scores and adverse events in previously treated patients only, and it remains unclear whether CRASH scores accurately predict adverse events among this population [15]. Furthermore, the CRASH score does not facilitate the assessment of the toxicity of new treatment.
The current study showed that the CARG risk score correlated more strongly with the incidence of severe non-hematologic toxicity than that of severe hematologic toxicity. Among the study population, a standard anticancer drug dosage rate of approximately 70%, a monotherapy rate of approximately 70%, and a G-CSF use rate of approximately 10% occurred, which might explain the reduced incidence of severe hematologic toxicity observed.
This study had some limitations. First, it was a retrospective study with a relatively small sample size. To produce more generalizable findings, a prospective multicenter study is necessary. Second, the assessment of non-hematologic toxicity might vary among clinicians and nurses more than that of hematologic toxicity. However, since the clinicians involved in this study performed clinical assessments based on NCI-CTCAE, and the number of the clinicians was small, variation was unlikely to be significant. Although a previous study reported that the ECOG PS scores of clinicians, nurses and patients varied, in the present study, clinician evaluations were preferred because they tended to best reflect prognosis [17]. Third, it is currently unknown whether new molecular targeted drugs or immune checkpoint inhibitors can predict toxicity. Therefore, it is necessary to accumulate data from elderly cancer patients receiving new molecular targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors to validate the usefulness of the CARG predictive tool.
Importantly, the extent to which anticancer drug dosage should be reduced in groups classified as high risk using the CARG predictive tool remains unknown. The Geriatric Assessment for Patients 70 years and older (GAP70+), and the Elderly Selection on Geriatric Index Assessment (ESOGIA) 08-02 trials, revealed that the dose adjustment of anticancer drugs using geriatric assessment reduced the incidence of CRAEs but did not improve survival [14,18]. Therefore, the results of the current study suggest that the CARG predictive tool is crucial for managing drug side effects in previously treated cancer patients and might help adjust the dose of anticancer drugs according to the CARG risk scores.
Future efforts are required to accumulate detailed toxicity data using electronic patient-reported outcomes and establish more precise toxicity prediction models using artificial intelligence.
5. Conclusions
This study suggested the utility of the CARG tool for predicting adverse event risk in elderly cancer patients who received prior anticancer therapy. In particular, this tool may facilitate the prediction of non-hematological toxicity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S. and A.O.; methodology, H.S. and A.O.; sample collection, H.S, Y.I., and A.O.; validation, H.S, Y.I., and A.O.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, H.S., Y.I., and A.O.; supervision, A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board Kakogawa Central City Hospital Ethics Committee. The approval code for this study is no.2019079.
Informed Consent Statement
Due to the retrospective design of this study, the requirement for patients’ informed consent was waived by our hospital’s institutional review board.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the medical staff of the Department of Medical Oncology/Hematology, Kakogawa Central City Hospital for their support during this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Matsuda, T.; Shibata, A.; Katanoda, K.; Sobue, T.; Nishimoto, H. Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2009: A study of 32 population-based cancer registries for the Monitoring of Cancer Incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurria, A.; Hurria, A.; Brogan, K.; Panageas, K.S.; Pearce, C.; Norton, L.; Jakubowski, A.; Howard, J.; Hudis, C. Effect of creatinine clearance on patterns of toxicity in older patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Drugs Aging 2005, 22, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repetto, L. Greater risks of chemotherapy toxicity in elderly patients with cancer. J. Support. Oncol. 2003, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Brandi, G. Pitfalls, challenges, and updates in adjuvant systemic treatment for resected biliary tract cancer. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Ricci, A.D.; Tober, N.; Nigro, M.C.; Mosca, M.; Palloni, A.; Abbati, F.; Frega, G.; De Lorenzo, S.; Tavolari, S.; et al. Second-line Treatment in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer: Today and Tomorrow. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 3013–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albain, K.S.; Crowley, J.J.; LeBlanc, M.; Livingston, R.B. Survival determinants in extensive-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: The Southwest Oncology Group experience. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurria, A.; Togawa, K.; Mohile, S.G.; Owusu, C.; Klepin, H.D.; Gross, C.P.; Lichtman, S.M.; Gajra, A.; Bhatia, S.; Katheria, V.; et al. Predicting chemotherapy toxicity in older adults with cancer: A prospective multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3457–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurria, A.; Mohile, S.; Gajra, A.; Klepin, H.; Muss, H.; Chapman, A.; Feng, T.; Smith, D.; Sun, C.L.; De Glas, N.; et al. Validation of a Prediction Tool for Chemotherapy Toxicity in Older Adults with Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2366–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN stimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Q.; Bai, C. Predicting chemotherapy toxicity in older adults with lung cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2013, 4, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.F.; Deal, A.M.; Williams, G.R.; Sanoff, H.K.; Nyrop, K.A.; Muss, H.B. Chemotherapy Toxicity Risk Score for Treatment Decisions in Older Adults with Advanced Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2018, 23, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohile, S.G.; Mohamed, M.R.; Xu, H.; Culakova, E.; Loh, K.P.; Magnuson, A.; Flannery, M.A.; Obrecht, S.; Gilmore, N.; Ramsdale, E.; et al. Evaluation of geriatric assessment and management on the toxic effects of cancer treatment (GAP70+): A cluster-randomised study. Lancet 2021, 398, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extermann, M.; Boler, I.; Reich, R.R.; Lyman, G.H.; Brown, R.H.; DeFelice, J.; Levine, R.M.; Lubiner, E.T.; Reyes, P.; Schreiber, F.J., 3rd; et al. Predicting the risk of chemotherapy toxicity in older patients: The Chemotherapy Risk Assessment Scale for High-Age Patients (CRASH) score. Cancer 2012, 118, 3377–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohile, S.G.; Dale, W.; Somerfield, M.R.; Schonberg, M.A.; Boyd, C.M.; Burhenn, P.S.; Canin, B.; Cohen, H.J.; Holmes, H.M.; Hopkins, J.O.; et al. Practical Assessment and Management of Vulnerabilities in Older Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: ASCO Guideline for Geriatric Oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2326–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, M.; Ando, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Shimokata, K.; Minami, H.; Wakai, K.; Ohno, Y.; Sakai, S. Prognostic value of performance status assessed by patients themselves, nurses, and oncologists in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corre, R.; Greillier, L.; Le Caër, H.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Baize, N.; Bérard, H.; Falchero, L.; Monnet, I.; Dansin, E.; Vergnenègre, A.; et al. Use of a Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment for the Management of Elderly Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase III Randomized ESOGIA-GFPC-GECP 08-02 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).