Ibrutinib in c-MYC and HER2 Amplified Oesophagogastric Carcinoma: Results of the Proof-of-Concept iMYC Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Eligibility
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Definition of c-MYC or HER2 Gene Amplification
2.4. Study Assessments and Toxicity
2.5. Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Episodes Observed on Study
2.6. Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Plan
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
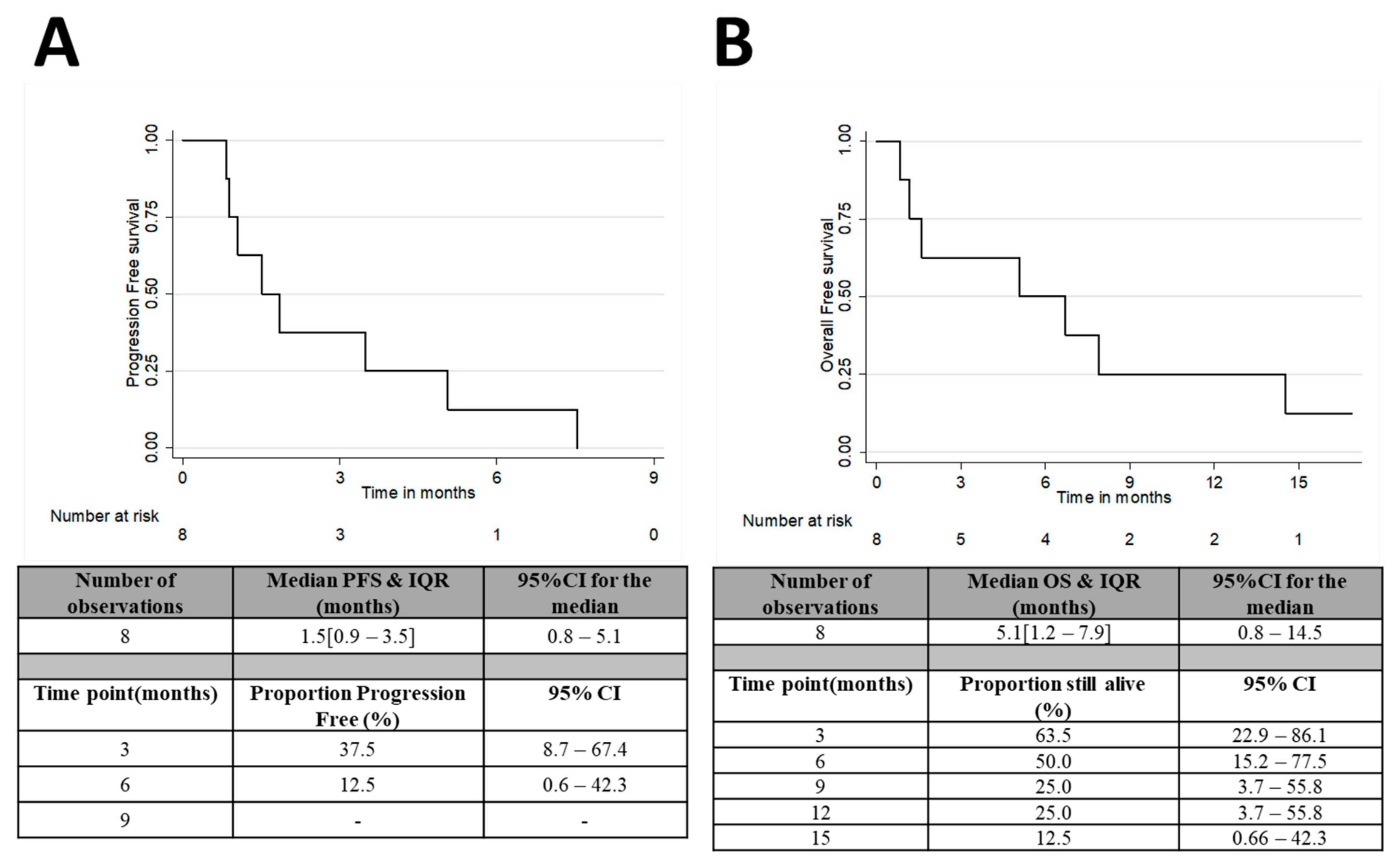
3.2. Therapeutic Response
3.3. Treatment Tolerance and Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, H.E.R.; Marshall, A.; Bridgewater, J.A.; Janowitz, T.; Coxon, F.Y.; Wadsley, J.; Mansoor, W.; Fyfe, D.; Madhusudan, S.; Middleton, G.W.; et al. Docetaxel versus active symptom control for refractory oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (COUGAR-02): An open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordick, F.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chung, H.; Salman, P.; Oh, S.C.; Bodoky, G.; Kurteva, G.; Volovat, C.; Moiseyenko, V.; Gorbunova, V.; et al. Capecitabine and cisplatin with or without cetuximab for patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer (EXPAND): A randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 490–499. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/docview/1346915158?accountid=26535 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Waddell, T.; Chau, I.; Cunningham, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Okines, A.F.C.; Wotherspoon, A.; Saffery, C.; Middleton, G.; Wadsley, J.; Ferry, D.; et al. Epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine with or without panitumumab for patients with previously untreated advanced oesophagogastric cancer (REAL3): A randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 481–489. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/docview/1346915044?accountid=26535 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.A.; Bang, Y.-J.; Lordick, F.; Alsina, M.; Chen, M.; Hack, S.P.; Bruey, J.M.; Smith, D.; McCaffery, I.; Shames, D.S.; et al. Effect of Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin with or without Onartuzumab in HER2-Negative, MET-Positive Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: The METGastric Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, D.V.T.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Davidenko, I.; Murad, A.M.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Ilson, D.H.; Tjulandin, S.; Gotovkin, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Rilotumumab plus epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy in advanced MET-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (RILOMET-1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1467–1482. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470204517305661 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.-J.; Xu, R.-H.; Chin, K.; Lee, K.-W.; Park, S.H.; Rha, S.Y.; Shen, L.; Qin, S.; Xu, N.; Im, S.-A.; et al. Olaparib in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced gastric cancer who have progressed following first-line therapy (GOLD): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1637–1651. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470204517306824 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Cho, B.C.; Takahashi, M.; Okada, M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chin, K.; Kadowaki, S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Hamamoto, Y.; Doki, Y.; et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Muro, K.; Francois, E.; Hsu, C.-H.; Moriwaki, T.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, S.-H.; Bennouna, J.; Kato, K.; Lin, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced esophageal cancer: Phase III KEYNOTE-181 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the Path to Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.-H.; Hsieh, L.-L.; Luo, F.-C.; Weinstein, I.B. Amplification of the EGF receptor andc-myc genes in human esophageal cancers. Int. J. Cancer 1988, 42, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitzer, M.; Stahl, M.; Arjumand, J.; Rees, M.; Klump, B.; Heep, H.; Gabbert, H.E.; Sarbia, M. C-myc gene amplification in different stages of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Prognostic value in relation to treatment modality. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brough, R.; Frankum, J.R.; Costa-Cabral, S.; Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. Searching for synthetic lethality in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 34–41. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959437X10001760 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, M.; Howie, H.L.; Imakura, M.; Walsh, R.M.; Annis, J.E.; Chang, A.N.; Frazier, J.; Chau, B.N.; Loboda, A.; Linsley, P.S.; et al. Functional genomics identifies therapeutic targets for MYC-driven cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9545–9550. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22623531 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, I.Y.; Aronson, L.; Bryant, H.; Gulati, A.; Campbell, J.; Elliott, R.; Pettitt, S.; Wilkerson, P.; Lambros, M.B.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; et al. Mapping genetic vulnerabilities reveals BTK as a novel therapeutic target in oesophageal cancer. Gut 2018, 67, 1780–1792. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28830912 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Pala, E.E.; Bayol, U.; Ozguzer, A.; Akman, O. HER2 status in gastric cancer: A comparison of two novel in situ hybridization methods (IQ FISH and dual color SISH) and two immunohistochemistry methods (A0485 and HercepTestTM). Pathol. Res. Pract. 2013, 209, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummukainen, J.K.; Salminen, T.; Lundin, J.; Joensuu, H.; Isola, J.J. Amplification of c-myc Oncogene by Chromogenic and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Archival Breast Cancer Tissue Array Samples. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 1545–15551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Dowsett, M.; McShane, L.M.; Allison, K.H.; Allred, D.C.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.; et al. Recommendations for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3997–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.; Cafferkey, C.; Goode, E.F.; Kouvelakis, K.; Hughes, D.; Reguera, P.; Kalaitzaki, E.; Peckitt, C.; Rao, S.; Watkins, D.; et al. Survival in Advanced Esophagogastric Adenocarcinoma Improves with Use of Multiple Lines of Therapy: Results from an Analysis of More Than 500 Patients. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, 223–230. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1533002818301038 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Rule, S.; Martin, P.; Goy, A.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.S.; Jurczak, W.; Advani, R.; Romaguera, J.E.; Williams, M.E.; et al. Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiron, D.; Di Liberto, M.; Martin, P.; Huang, X.; Sharman, J.; Blecua, P.; Mathew, S.; Vijay, P.; Eng, K.; Ali, S.; et al. Cell-Cycle Reprogramming for PI3K Inhibition Overrides a Relapse-Specific C481S BTK Mutation Revealed by Longitudinal Functional Genomics in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhi, A.D.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Jenkins, R.B.; Lan, F.; Fink, S.R.; Nassar, H.; Vang, R.; Fetting, J.H.; Hicks, J.; Sukumar, S.; et al. MYC gene amplification is often acquired in lethal distant breast cancer metastases of unamplified primary tumors. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 25, 378–387. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/myc-gene-amplification-is-often-acquired-lethal/docview/925048338/se-2 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.; Aronson, L.; Howard-Reeves, J.; Bryant, H.; Cutts, R.J.; Hulkki-Wilson, S.; Kouvelakis, K.; Kalaitzaki, E.; Watkins, D.; Starling, N.; et al. Clonal diversity of MYC amplification evaluated by fluorescent in situ hybridisation and digital droplet polymerase chain reaction in oesophagogastric cancer: Results from a prospective clinical trial screening programme. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowsett, M.; Procter, M.; McCaskill-Stevens, W.; De Azambuja, E.; Dafni, U.; Rueschoff, J.; Jordan, B.; Dolci, S.; Abramovitz, M.; Stoss, O.; et al. Disease-Free Survival According to Degree ofHER2Amplification for Patients Treated with Adjuvant Chemotherapy with or without 1 Year of Trastuzumab: The HERA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2962–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson, A.; Smyth, E.; Babina, I.; Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Tarazona, N.; Peckitt, C.; Kilgour, E.; Smith, N.R.; Geh, C.; Rooney, C.; et al. High-Level Clonal FGFR Amplification and Response to FGFR Inhibition in a Translational Clinical Trial. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 6, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haffner, I.; Schierle, K.; Raimúndez, E.; Geier, B.; Maier, D.; Hasenauer, J.; Luber, B.; Walch, A.; Kolbe, K.; Knorrenschild, J.R.; et al. HER2 Expression, Test Deviations, and Their Impact on Survival in Metastatic Gastric Cancer: Results from the Prospective Multicenter VARIANZ Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Oki, E.; Kashiwada, T.; Arigami, T.; Makiyama, A.; Iwatsuki, M.; Narita, Y.; Satake, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Re-evaluation of HER2 status in patients with HER2-positive advanced or recurrent gastric cancer refractory to trastuzumab (KSCC1604). Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 105, 41–49. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959804918313947 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ibrutinib Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/10041/smpc#gref (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Tempero, M.; Oh, D.-Y.; Tabernero, J.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Hendifar, A.; Waldschmidt, D.-T.; Starling, N.; Bachet, J.-B.; Chang, H.-M.; et al. Ibrutinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Phase III RESOLVE study. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 600–608. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0923753421000983 (accessed on 24 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Maluf-Filho, F.; Martins, B.C.; De Lima, M.S.; Leonardo, D.V.; Retes, F.A.; Kawaguti, F.S.; Sato, C.F.M.; Hondo, F.Y.; Safatle-Ribeiro, A.V.; Ribeiro, U. Etiology, endoscopic management and mortality of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cancer. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2013, 1, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
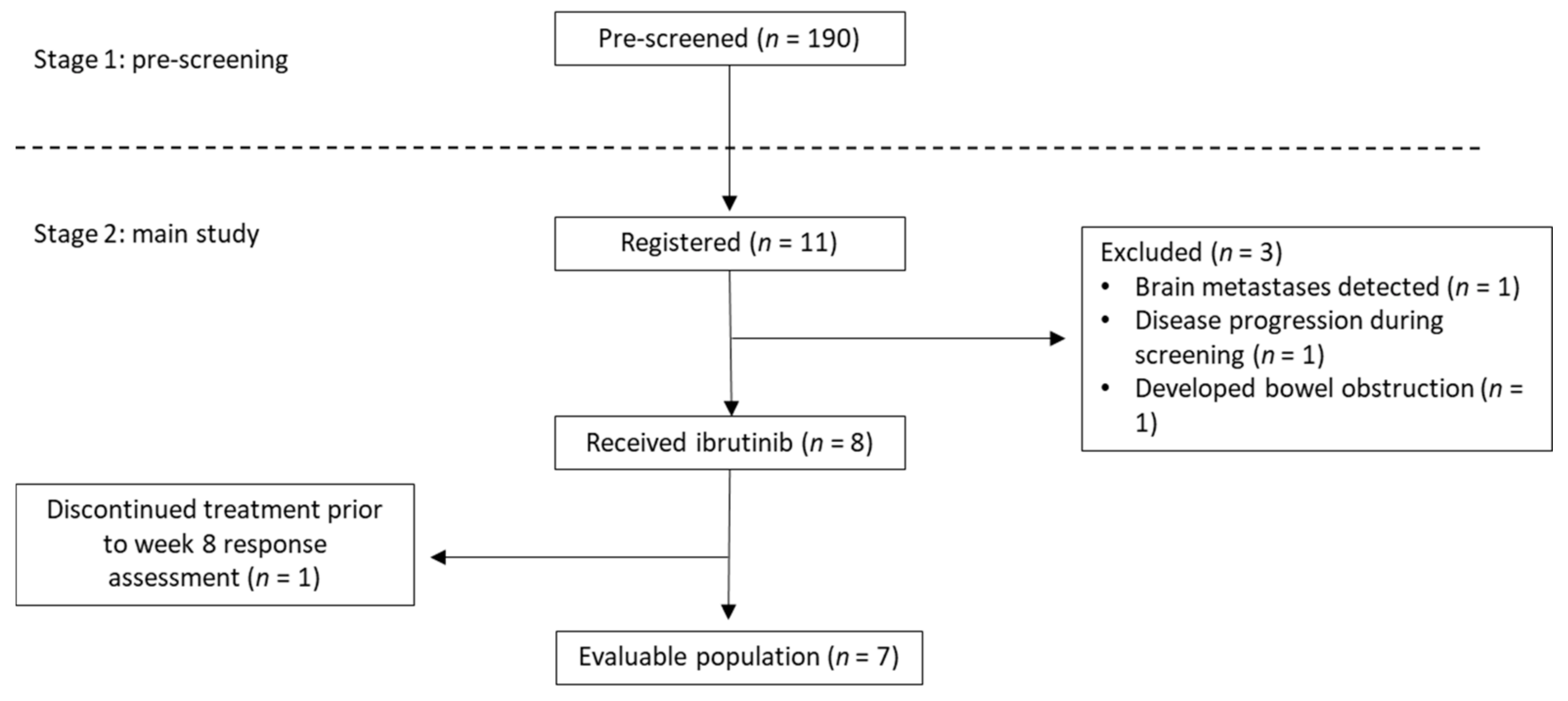
| Pre-Screened (n = 190) | Registered (n = 11) | Patients Starting Ibrutinib (n = 8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at registration, (years) | |||
| Median (IQR) | NA | 63 (58–69) | 62 (58–69) |
| Mean (SD) | NA | 62.3 (9.8) | 63.5 (8.4) |
| Min–Max | NA | 43–79 | 52–79 |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 40 (21) | 2 (18) | 1 (13) |
| Male | 150 (79) | 9 (82) | 7 (87) |
| Histology | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 155 (82) | 8 (73) | 5 (62) |
| Squamous carcinoma | 33 (17) | 3 (27) | 3 (38) |
| Mixed | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| HER2 status | |||
| Negative | 154 (81) | 5 (45) | 3 (38) |
| Positive | 36 (19) | 6 (55) | 5 (62) |
| Cmyc status | |||
| Amplified | 43 (23) | 8 (73) | 6 (75) |
| Not amplified | 120 (63) | 2 (18) | 1 (12) |
| Failed Testing | 25 (13) | 1 (9) | 1 (12) |
| Other | - | - | |
| No tumour | 1 (1) | - | - |
| Not tested | 1 (1) | - | - |
| Coamplified | 8 (2) | 3 (27) | 3 (38) |
| Tumour location | |||
| GOJ | 60 (31) | 4 (36) | 2 (25) |
| Gastric | 40 (21) | 1 (9) | 1 (13) |
| Oesophagus | 90 (48) | 6 (55) | 5 (63) |
| Disease status at time of screening | |||
| First-line on treatment | 85 (45) | 5 (45) | 4 (50) |
| First-line completed treatment | 40 (21) | 3 (27) | 2 (25) |
| Second-line on treatment | 27 (14) | 1 (9) | 1 (12) |
| Second-line completed treatment | 21 (11) | 1 (9) | 1 (12) |
| Third-line on treatment | 8 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Third-line completed treatment | 9 (5) | 1 (9) | 0 (0) |
| 8 Weeks (Best Response) | 16 Weeks | 24 Weeks | 32 Weeks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECIST Response | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % |
| CR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SD | 3 | 43% | 2 | 29% | 1 | 14% | 0 | 0 |
| PD | 4 | 57% | 5 | 71% | 6 | 86% | 7 | 100% |
| Toxicity | Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Anaemia | 1 (13) | 6 (75) | |||
| Arrhythmia | 1 (13) | ||||
| Constipation | 2 (25) | 1 (13) | |||
| Diarrhoea | 3 (38) | ||||
| Dry skin | 2 (25) | ||||
| Fatigue | 5 (63) | 1 (13) | |||
| Fever | 2 (25) | 1 (13) | |||
| Infection | 1 (13) | ||||
| Mucositis | 1 (13) | ||||
| Nausea | 1 (13) | 1 (13) | |||
| Neutropenia | 1 (13) | ||||
| Pruritis | 1 (13) | ||||
| Skin rash/desquamation | 1 (13) | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia | 1 (13) | ||||
| Vomiting | 1 (13) | 1 (13) | 1 (13) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turkes, F.; Bryant, A.; Begum, R.; Davidson, M.; Kalaitzaki, E.; Aresu, M.; Lazaro-Alcausi, R.; Bryant, J.; Rana, I.; Chua, S.; et al. Ibrutinib in c-MYC and HER2 Amplified Oesophagogastric Carcinoma: Results of the Proof-of-Concept iMYC Study. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2174-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040176
Turkes F, Bryant A, Begum R, Davidson M, Kalaitzaki E, Aresu M, Lazaro-Alcausi R, Bryant J, Rana I, Chua S, et al. Ibrutinib in c-MYC and HER2 Amplified Oesophagogastric Carcinoma: Results of the Proof-of-Concept iMYC Study. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(4):2174-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurkes, Fiona, Annette Bryant, Ruwaida Begum, Michael Davidson, Eleftheria Kalaitzaki, Maria Aresu, Retchel Lazaro-Alcausi, Jane Bryant, Isma Rana, Sue Chua, and et al. 2022. "Ibrutinib in c-MYC and HER2 Amplified Oesophagogastric Carcinoma: Results of the Proof-of-Concept iMYC Study" Current Oncology 29, no. 4: 2174-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040176
APA StyleTurkes, F., Bryant, A., Begum, R., Davidson, M., Kalaitzaki, E., Aresu, M., Lazaro-Alcausi, R., Bryant, J., Rana, I., Chua, S., Aronson, L., Hulkki-Wilson, S., Fribbens, C., Watkins, D., Rao, S., Starling, N., Cunningham, D., Chong, I. Y., & Chau, I. (2022). Ibrutinib in c-MYC and HER2 Amplified Oesophagogastric Carcinoma: Results of the Proof-of-Concept iMYC Study. Current Oncology, 29(4), 2174-2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040176





