Electrochemotherapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Metastases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
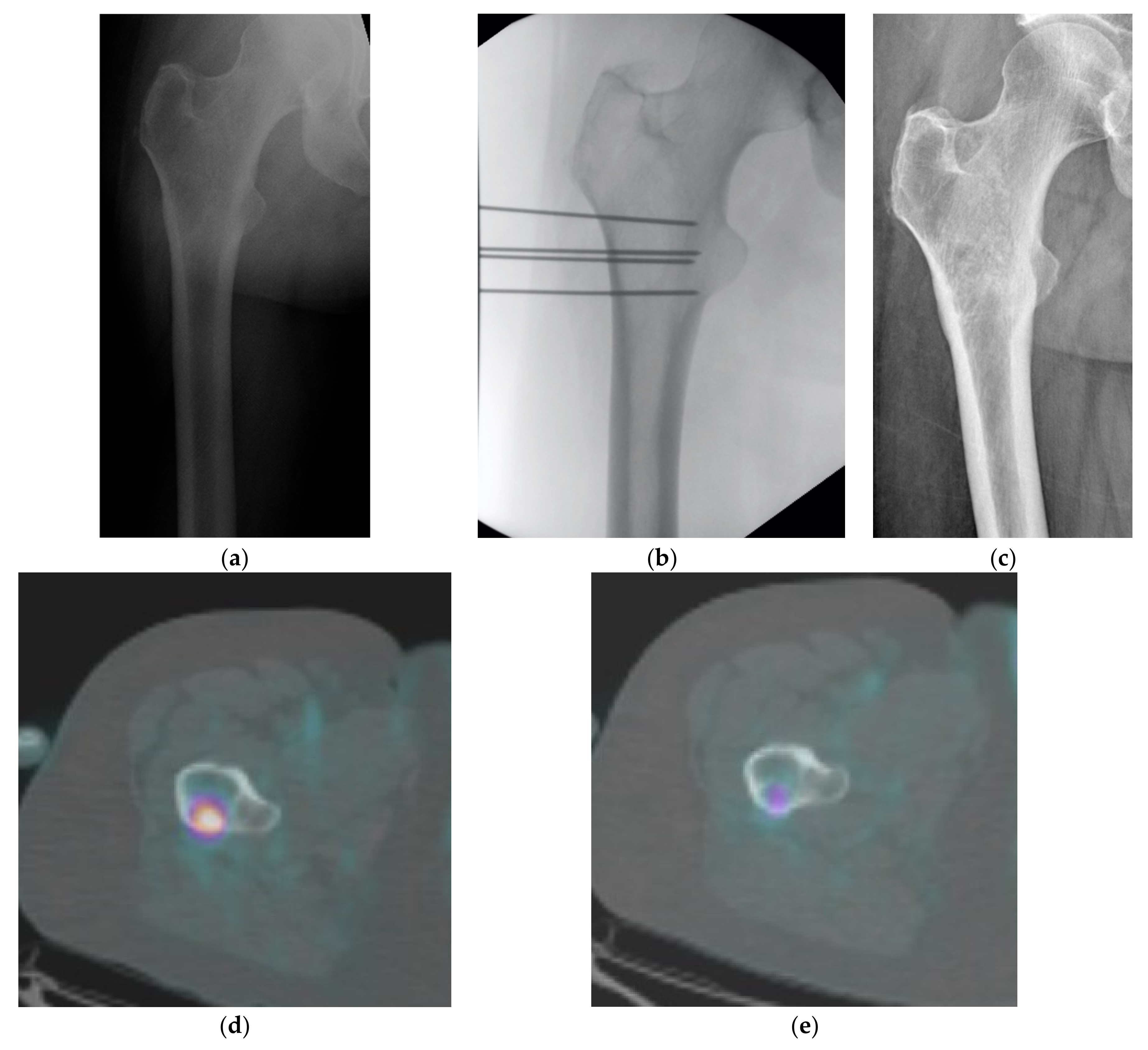
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Current Cancer Epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jörling, M.; Rutzner, S.; Hecht, M.; Fietkau, R.; Distel, L.V. Deterioration of Health-Related Quality of Life Scores under Treatment Predicts Longer Survival. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e3565238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-H.M.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Hoffe, S.E. Overview of diagnosis and management of metastatic disease to bone. Cancer Control. J. Moffitt Cancer Center 2012, 19, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fornetti, J.; Welm, A.L.; Stewart, S.A. Understanding the Bone in Cancer Metastasis. J. Bone Min. Res. 2018, 33, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bickels, J.; Dadia, S.; Lidar, Z. Surgical management of metastatic bone disease. J. Bone Jt. Surg Am. 2009, 91, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, E.; Harris, K.; Fan, G.; Tsao, M.; Sze, W.M. Palliative radiotherapy trials for bone metastases: A systematic review. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Casadei, R.; Bianchi, G.; Romagnoli, C.; Rimondi, E.; Ruggieri, P. Embolisation of bone metastases from renal cancer. Radiol. Medica 2013, 118, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kido, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Facchini, G.; Peta, G.; Rossi, G.; Mavrogenis, A.F. Current Overview of Treatment for Metastatic Bone Disease. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3347–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigi Cazzato, R.; Auloge, P.; De Marini, P.; Rousseau, C.; Chiang, J.B.; Koch, G.; Caudrelier, J.; Rao, P.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous image-guided ablation of bone metastases: Local tumor control in oligometastatic patients. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fini, M.; Salamanna, F.; Parrilli, A.; Martini, L.; Cadossi, M.; Maglio, M.; Borsari, V. Electrochemotherapy is effective in the treatment of rat bone metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Campanacci, L.; Ronchetti, M.; Donati, D. Electrochemotherapy in the Treatment of Bone Metastases: A Phase II Trial. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 3088–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mir, L.M.; Gehl, J.; Sersa, G.; Collins, C.G.; Garbay, J.-R.; Billard, V.; Geertsen, P.F.; Rudolf, Z.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Marty, M. Standard operating procedures of the electrochemotherapy: Instructions for the use of bleomycin or cisplatin administered either systemically or locally and electric pulses delivered by the CliniporatorTM by means of invasive or non-invasive electrodes. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2006, 4, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrič, H.; Kos, B.; Tedesco, G.; Cadossi, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miklavčič, D. Electrochemotherapy of Spinal Metastases Using Transpedicular Approach-A Numerical Feasibility Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533034618770253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritter, P.L.; González, V.M.; Laurent, D.D.; Lorig, K.R. Measurement of pain using the visual numeric scale. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- de Kock, I.; Mirhosseini, M.; Lau, F.; Thai, V.; Downing, M.; Quan, H.; Lesperance, M.; Yang, J. Conversion of Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG) to Palliative Performance Scale (PPS), and the interchangeability of PPS and KPS in prognostic tools. J. Palliat. Care 2013, 29, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O, J.H.; Lodge, M.A.; Wahl, R.L. Practical PERCIST: A Simplified Guide to PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.0. Radiology 2016, 280, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; van Glabbeke, M.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; Gwyther, S.G. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornelis, F.H.; Ben Ammar, M.; Nouri-Neuville, M.; Matton, L.; Benderra, M.A.; Gligorov, J.; Jansa, R.; Plesnik, B.; Bosnjak, M.; Tratar, U.L.; et al. Percutaneous Image-Guided Electrochemotherapy of Spine Metastases: Initial Experience. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, J.S.; Holt, G.E.; Lewis, V.O.; Schwartz, H.S.; Yaszemski, M.J. Metastatic bone disease: Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Wedin, R. Surgical treatment for pathologic fracture. Acta Orthop. Scand. Suppl. 2001, 72, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathan, S.S.; Healey, J.H.; Mellano, D.; Hoang, B.; Lewis, I.; Morris, C.D.; Athanasian, E.A.; Boland, P.J. Survival in patients operated on for pathologic fracture: Implications for end-of-life orthopedic care. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6072–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.S. Painful osseous metastases. Pain Physician 2011, 14, E373–E403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougioumtzopoulou, A.; Zygogianni, A.; Liakouli, Z.; Kypraiou, E.; Kouloulias, V. The role of radiotherapy in bone metastases: A critical review of current literature. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2017, 26, e12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarawal, J.P.; Swangsilpa, T.; van der Linden, Y.; Rades, D.; Jeremic, B.; Hoskin, P.J. The role of external beam radiotherapy in the management of bone metastases. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2006, 18, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callstrom, M.R.; Dupuy, D.E.; Solomon, S.B.; Beres, R.A.; Littrup, P.J.; Davis, K.W.; Paz-Fumagalli, R.; Hoffman, C.; Atwell, T.D.; Charboneau, J.W.; et al. Percutaneous image-guided cryoablation of painful metastases involving bone: Multicenter trial. Cancer 2013, 119, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, C.; Sotgia, B.; Fele, R.M.; Melis, L. Treatment of bone metastases with microwave thermal ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, D.E.; Liu, D.; Hartfeil, D.; Hanna, L.; Blume, J.D.; Ahrar, K.; Lopez, R.; Safran, H.; DiPetrillo, T. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases: A multicenter American College of Radiology Imaging Network trial. Cancer 2010, 116, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, A.-S.; Iannessi, A.; Natale, R.; Beaumont, H.; Patriti, S.; Xiong-Ying, J.; Baudin, G.; Thyss, A. Focused ultrasound for the treatment of bone metastases: Effectiveness and feasibility. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, A.; Fujimoto, H.; Yasuda, S.; Osaka, I.; Goto, N.; Shinozaki, M.; Ito, H. Transcatheter arterial embolization for bone metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, M.; Tschon, M.; Ronchetti, M.; Cavani, F.; Bianchi, G.; Mercuri, M.; Alberghini, M.; Cadossi, R. Ablation of bone cells by electroporation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanacci, L.; Bianchi, G.; Cevolani, L.; Errani, C.; Ciani, G.; Facchini, G.; Spinnato, P.; Tognù, A.; Massari, L.; Cornelis, F.H. Operating procedures for electrochemotherapy in bone metastases: Results from a multicenter prospective study on 102 patients. European. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Descriptive Statistics on 38 Patients | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| SEX | ||
| M | 13 | 34% |
| F | 25 | 66% |
| Primary tumor | ||
| Breast | 6 | 15% |
| Endometrial/uterus | 6 | 15% |
| Lung | 4 | 11% |
| Kidney | 3 | 8% |
| Colon | 4 | 11% |
| Vescica | 3 | 8% |
| Liver | 3 | 8% |
| Prostate | 1 | 3% |
| Other * | 8 | 21% |
| Presence of visceral metastases | ||
| Yes | 24 | 63% |
| No | 14 | 37% |
| Pattern of metastatic disease | ||
| Solitary bone mts | 10 | 26% |
| Multiple bone mts | 4 | 11% |
| Bone and visceral (non-lung) | 8 | 22% |
| Bone and pulmonary | 9 | 24% |
| Bone, visceral, pulmonary | 7 | 17% |
| Pathologic fractures | ||
| Yes | 7 | 18% |
| No | 31 | 82% |
| Type of lesions | ||
| Lytic | 29 | 76% |
| Sclerotic | 1 | 3% |
| Mixed | 8 | 21% |
| Previous treatments for metastases | ||
| Chemotherapy | 19 | 50% |
| Hormonal therapy | 5 | 13% |
| Radiotherapy | 12 | 32% |
| Other | 6 | 16% |
| Performance status | ||
| Fully active | 3 | 8% |
| Restricted in physically strenuous activity | 12 | 31% |
| Ambulatory capable but unable to work | 16 | 42% |
| Capable of only limited self-care | 6 | 16% |
| Completely disabled | 1 | 3% |
| N° | % | Median | Range | Mean ± St. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion localization | |||||
| Lower limbs, of which | |||||
| Tibia | 7 | 18% | |||
| Femur | 6 | 16% | |||
| Tarsus | 1 | 3% | |||
| Upper limbs, of which | |||||
| Ulna | 1 | 3% | |||
| Scapula | 3 | 8% | |||
| Humerus | 2 | 6% | |||
| Trunk/pelvis, of which | |||||
| Iliac wing (+ pelvis) | 10 | 25% | |||
| Acetabulum | 2 | 5% | |||
| Sacrum | 3 | 8% | |||
| Pubic ramus | 2 | 5% | |||
| Costo-vertebral | 1 | 3% | |||
| Size | |||||
| Volume (cm3) | 102 | 3.328 ± 138.2400 | 273.505 ± 34.9730 | ||
| Axial direction (mm) | 49 | 13–140 | 51 ± 27 | ||
| Coronal direction (mm) | 52 | 16–120 | 59 ± 29 | ||
| Sagittal direction (mm) | 50 | 16–120 | 58 ± 29 | ||
| Duration of procedure (min) | 42 | 18–80 | 46 ± 16 | ||
| GUIDANCE | |||||
| Intensifier | 22 | 58% | |||
| CT | 16 | 42% | |||
| Number of electrodes used (39) | |||||
| 3 | 2 | 5% | |||
| 4 | 8 | 21% | |||
| 5 | 5 | 13% | |||
| 6 | 19 | 50% | |||
| 7 | 1 | 3% | |||
| 8 | 1 | 3% | |||
| 11 | 2 | 5% | |||
| Anesthesia | |||||
| Locoregional + deep sedation | 31 | 82% | |||
| General | 4 | 10% | |||
| Locoregional | 2 | 5% | |||
| Deep sedation | 1 | 3% | |||
| Completely covered lesion | |||||
| Yes | 22 | 58% | |||
| No | 16 | 42% | |||
| ECT sessions | |||||
| 1 | 37 | 95% | |||
| 2 | 1 | 5% |
| RECIST | PERCIST | Pain | Before ECT | Early FU | Late FU | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| CR | 3 | 9% | 5 | 14% | no | 4 | 11% | 8 | 27% | 7 | 47% |
| PR | 6 | 16% | 8 | 22% | mild | 3 | 8% | 13 | 43% | 5 | 33% |
| SD | 22 | 59% | 5 | 14% | moderate | 18 | 47% | 6 | 20% | 1 | 7% |
| PD | 6 | 16% | 19 | 50% | severe | 13 | 34% | 3 | 10% | 2 | 13% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanacci, L.; Cevolani, L.; De Terlizzi, F.; Saenz, L.; Alì, N.; Bianchi, G.; Donati, D.M. Electrochemotherapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1672-1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030139
Campanacci L, Cevolani L, De Terlizzi F, Saenz L, Alì N, Bianchi G, Donati DM. Electrochemotherapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Metastases. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(3):1672-1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030139
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanacci, Laura, Luca Cevolani, Francesca De Terlizzi, Laura Saenz, Nikolin Alì, Giuseppe Bianchi, and Davide Maria Donati. 2022. "Electrochemotherapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Metastases" Current Oncology 29, no. 3: 1672-1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030139
APA StyleCampanacci, L., Cevolani, L., De Terlizzi, F., Saenz, L., Alì, N., Bianchi, G., & Donati, D. M. (2022). Electrochemotherapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Metastases. Current Oncology, 29(3), 1672-1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030139





