The Role of Surgical Approaches in the Multi-Modal Management of Adult Craniopharyngiomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation
1.2. Radiologic and Histopathologic Features
2. Surgical Principles and Approaches
3. Description of Surgical Techniques
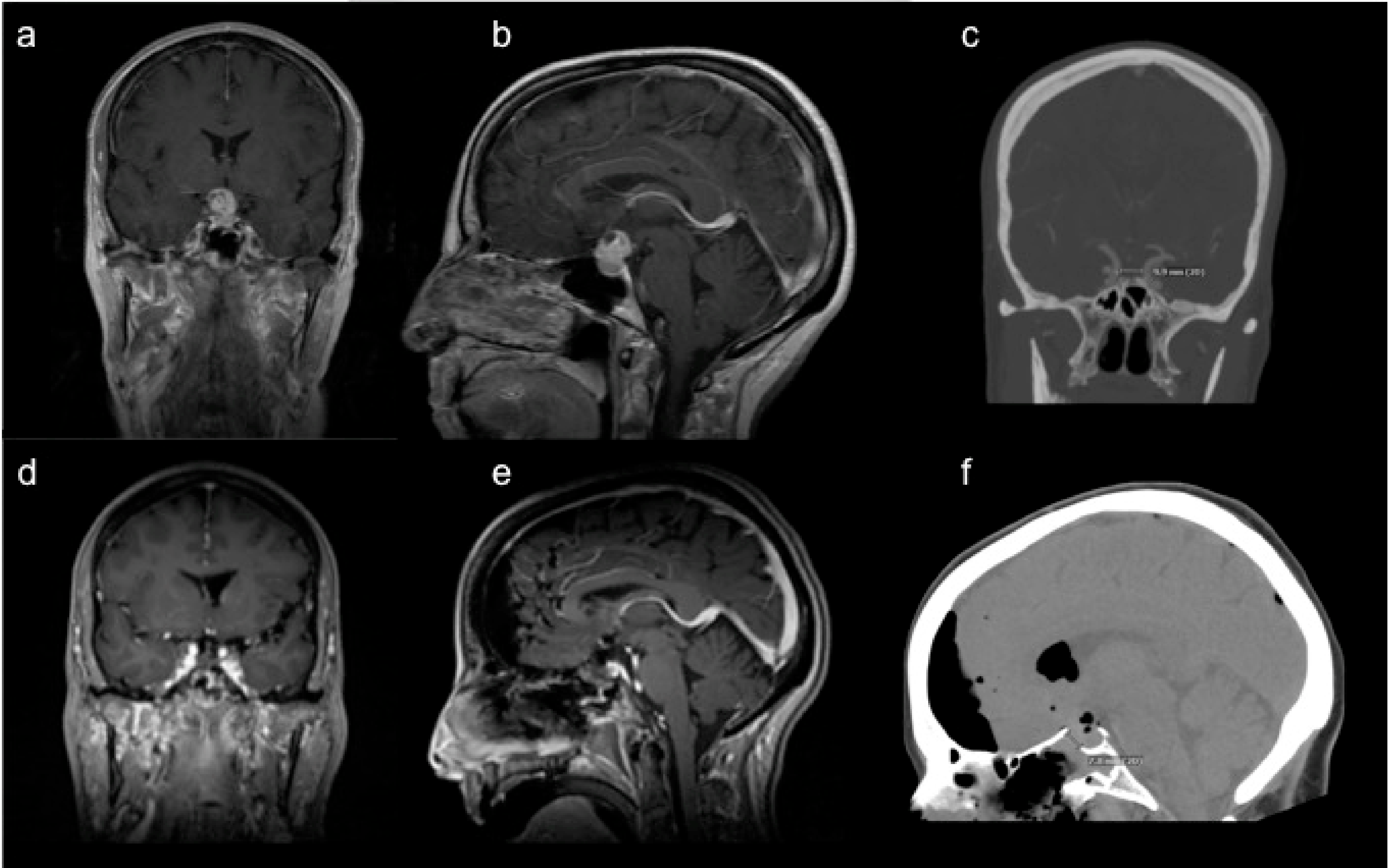
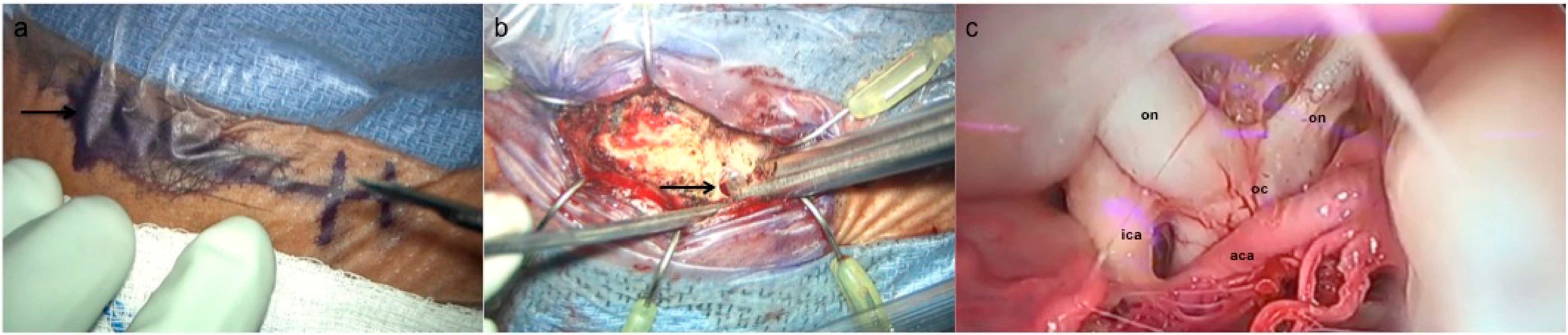
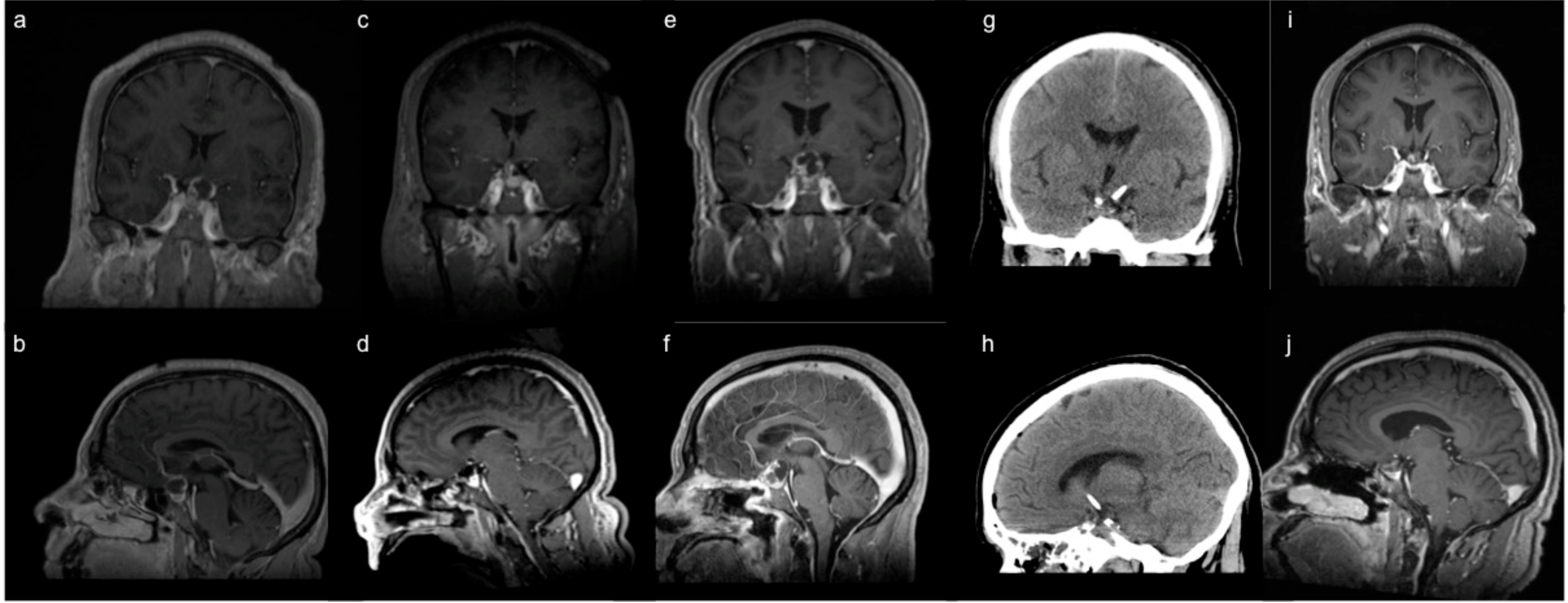
3.1. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach
3.2. Supraorbital Craniotomy
4. Adjunctive Treatment Modalities
4.1. Stereotactic Cyst Decompression
4.2. Radiation
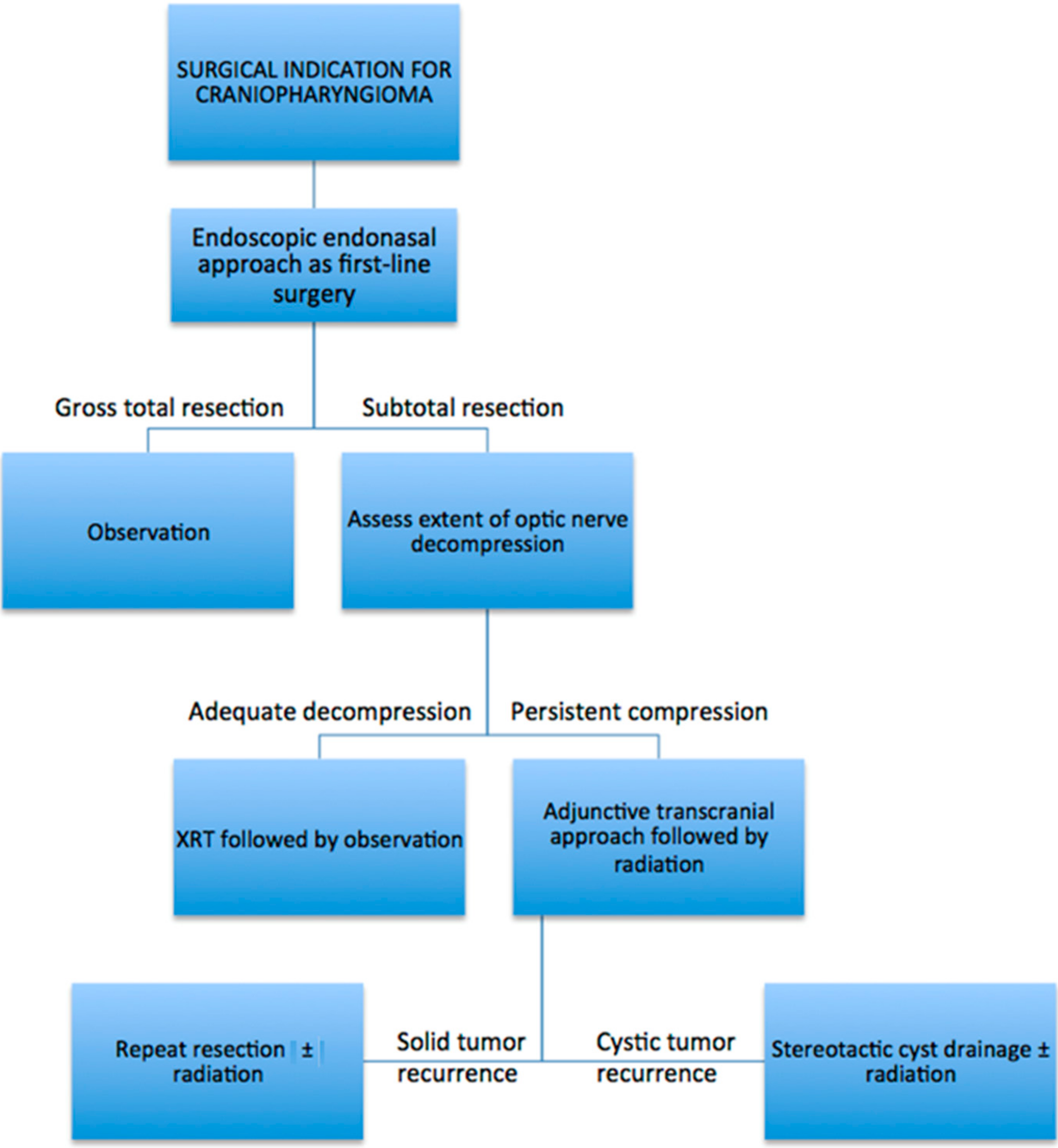
5. Overall Approach to Surgical Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, H.L.; Merchant, T.E.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Martinez-Barbera, J.P.; Puget, S. Craniopharyngioma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, G.R.; Surawicz, T.S.; Witman, P.A.; Preston-Martin, S.; Davis, F.; Bruner, J.M. The descriptive epidemiology of craniopharyngioma. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharia, B.E.; Bruce, S.S.; Goldstein, H.; Malone, H.R.; Neugut, A.I.; Bruce, J.N. Incidence, treatment and survival of patients with craniopharyngioma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zacharia, B.E.; Amine, M.; Anand, V.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic Endonasal Management of Craniopharyngioma. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 49, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitaki, N.; Cudlip, S.; Adams, C.B.; Wass, J.A. Craniopharyngiomas. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omay, S.B.; Chen, Y.N.; Almeida, J.P.; Ruiz-Trevino, A.S.; Boockvar, J.A.; Stieg, P.E.; Greenfield, J.P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Kacker, A.; Pisapia, D.J.; et al. Do craniopharyngioma molecular signatures correlate with clinical characteristics? J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zada, G.; Lin, N.; Ojerholm, E.; Ramkissoon, S.; Laws, E.R. Craniopharyngioma and other cystic epithelial lesions of the sellar region: A review of clinical, imaging, and histopathological relationships. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 28, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekine, S.; Shibata, T.; Kokubu, A.; Morishita, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Craniopharyngiomas of adamantinomatous type harbor beta-catenin gene mutations. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.S.; Omuro, A.; An, Y.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kohli, A.A.; McGuone, D.; Vining, E.M.; Omay, S.B.; Erson-Omay, E.Z. Sporadic adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma with double-hit somatic APC mutations. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Manley, P.E.; Jones, R.T.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Thorner, A.R.; Lawrence, M.S.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Bernardo, L.A.; Schubert, L.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies BRAF mutations in papillary craniopharyngiomas. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juratli, T.A.; Jones, P.S.; Wang, N.; Subramanian, M.; Aylwin, S.J.B.; Odia, Y.; Rostami, E.; Gudjonsson, O.; Shaw, B.L.; Cahill, D.P.; et al. Targeted treatment of papillary craniopharyngiomas harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cancer 2019, 125, 2910–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borrill, R.; Cheesman, E.; Stivaros, S.; Kamaly-Asl, I.D.; Gnanalingham, K.; Kilday, J.P. Papillary craniopharyngioma in a 4-year-old girl with BRAF V600E mutation: A case report and review of the literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crotty, T.B.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Young, W.F., Jr.; Davis, D.H.; Shaw, E.G.; Miller, G.M.; Burger, P.C. Papillary craniopharyngioma: A clinicopathological study of 48 cases. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, A.; Cama, A.; Consales, A.; Gandolfo, C.; Garre, M.L.; Milanaccio, C.; Pavanello, M.; Piatelli, G.; Ravegnani, M.; Tortori-Donati, P. Neuroimaging of pediatric craniopharyngiomas: A pictorial essay. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 19 (Suppl. 1), 299–319. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.P.; Kalyvas, A.; Mohan, N.; Oswari, S.; Takami, H.; Velasquez, C.; Asha, M.; Zadeh, G.; Gentili, F. Current Results of Surgical Treatment of Craniopharyngiomas: The Impact of Endoscopic Endonasal Approaches. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, L.M.; Frank, G.; Cappabianca, P.; Solari, D.; Mazzatenta, D.; Villa, A.; Zoli, M.; D’Enza, A.I.; Esposito, F.; Pasquini, E. The endoscopic endonasal approach for the management of craniopharyngiomas: A series of 103 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dho, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Se, Y.B.; Han, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, C.K.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, D.G. Endoscopic endonasal approach for craniopharyngioma: The importance of the relationship between pituitary stalk and tumor. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichev, D.; Kalinin, P.; Kutin, M.; Sharipov, O. Extended Transsphenoidal Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery of Suprasellar Craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutourousiou, M.; Gardner, P.A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Wang, E.W.; Snyderman, C.H. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for craniopharyngiomas: Surgical outcome in 64 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, J.; Wang, X.; Huo, G.; Ruan, L.; Jin, K.; Tan, S.; Wang, F.; Hua, H.; Yang, G. Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery for Craniopharyngiomas: A Series of 60 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, e424–e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez-Rubiano, E.G.; Forbes, J.A.; Morgenstern, P.F.; Arko, L.; Dobri, G.A.; Greenfield, J.P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Anand, V.K.; Kacker, A.; et al. Preserve or sacrifice the stalk? Endocrinological outcomes, extent of resection, and recurrence rates following endoscopic endonasal resection of craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.R.; Kshettry, V.R.; Farrell, C.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Won, T.B.; Han, D.H.; Do, H.; Nyguist, G.; Rosen, M.; et al. Clinical Outcome After Extended Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Craniopharyngiomas: Two-Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovanovic, I.; Dehdashti, A.R.; Turel, M.K.; Almeida, J.P.; Godoy, B.L.; Doglietto, F.; Vescan, A.D.; Zadeh, G.; Gentili, F. Expanded Endonasal Endoscopic Surgery in Suprasellar Craniopharyngiomas: A Retrospective Analysis of 43 Surgeries Including Recurrent Cases. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 17, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Xiao, L.; Xie, S.; Huang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, E.; Hong, T. Extended endoscopic endonasal approach for recurrent or residual symptomatic craniopharyngiomas. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 168, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnazzo, F.; Zoli, M.; Mazzatenta, D.; Gompel, J.J.V. Endoscopic and Microscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery of Craniopharyngiomas: A Systematic Review of Surgical Outcomes Over Two Decades. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2018, 79, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, R.H. Hypothalamic obesity after craniopharyngioma: Mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, S.M.; Lunsford, L.D.; Niranjan, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C. Stereotactic radiosurgery of residual or recurrent craniopharyngioma, after surgery, with or without radiation therapy. Neuro-Oncology 2001, 3, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stripp, D.C.; Maity, A.; Janss, A.J.; Belasco, J.B.; Tochner, Z.A.; Goldwein, J.W.; Moshang, T.; Rorke, L.B.; Phillips, P.C.; Sutton, L.N.; et al. Surgery with or without radiation therapy in the management of craniopharyngiomas in children and young adults. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 58, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Bowman, R.M. Craniopharyngiomas in children: Surgical experience at Children’s Memorial Hospital. Child Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.; Pekmezci, M.; Barnes, M.J.; Tihan, T.; Gupta, N.; Lamborn, K.R.; Banerjee, A.; Mueller, S.; Chang, S.; Berger, M.S.; et al. The superiority of conservative resection and adjuvant radiation for craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 108, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasargil, M.G.; Curcic, M.; Kis, M.; Siegenthaler, G.; Teddy, P.J.; Roth, P. Total removal of craniopharyngiomas. Approaches and long-term results in 144 patients. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 73, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasargil, M.G.; Krayenbuhl, H. The use of the binocular microscope in neurosurgery. Bibl. Ophthalmol. 1970, 81, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.K.; Sevak, I.A.; Carmel, P.W.; Eloy, J.A. Microscopic versus endoscopic approaches for craniopharyngiomas: Choosing the optimal surgical corridor for maximizing extent of resection and complication avoidance using a personalized, tailored approach. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leng, L.Z.; Greenfield, J.P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic, endonasal resection of craniopharyngiomas: Analysis of outcome including extent of resection, cerebrospinal fluid leak, return to preoperative productivity, and body mass index. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omay, S.B.; Almeida, J.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Shetty, S.R.; Liang, B.; Ni, S.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Is the chiasm-pituitary corridor size important for achieving gross-total resection during endonasal endoscopic resection of craniopharyngiomas? J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chibbaro, S.; Signorelli, F.; Milani, D.; Cebula, H.; Scibilia, A.; Bozzi, M.T.; Messina, R.; Zaed, I.; Todeschi, J.; Ollivier, I.; et al. Primary Endoscopic Endonasal Management of Giant Pituitary Adenomas: Outcome and Pitfalls from a Large Prospective Multicenter Experience. Cancers 2021, 13, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komotar, R.J.; Starke, R.M.; Raper, D.M.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic endonasal compared with microscopic transsphenoidal and open transcranial resection of craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2012, 77, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.; Luther, E.M.; Morell, A.A.; Burks, J.D.; King, H.; Eichberg, D.G.; Lu, V.M.; Shah, A.H.; Kaur, G.; Komotar, R.J.; et al. Perioperative Complications in Endoscopic Endonasal versus Transcranial Resections of Adult Craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2021, 152, e729–e737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Raza, S.M.; McCoul, E.D.; Patrona, A.; Greenfield, J.P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Long-term quality of life after endonasal endoscopic resection of adult craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peraio, S.; Chumas, P.; Nix, P.; Phillips, N.; Tyagi, A. From above or from below? That is the question. Comparison of the supraorbital approach with the endonasal approach. A cadaveric study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 32, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, N.; Dusick, J.R.; de Paiva Neto, M.A.; Malkasian, D.; Kelly, D.F. Endonasal versus supraorbital keyhole removal of craniopharyngiomas and tuberculum sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nagatani, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Chu, J.; Wakabayashi, T. Fully endoscopic combined transsphenoidal and supraorbital keyhole approach for parasellar lesions. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banu, M.A.; Mehta, A.; Ottenhausen, M.; Fraser, J.F.; Patel, K.S.; Szentirmai, O.; Anand, V.K.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscope-assisted endonasal versus supraorbital keyhole resection of olfactory groove meningiomas: Comparison and combination of 2 minimally invasive approaches. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallo, L.M.; de Divitiis, O.; Aydin, S.; Messina, A.; Esposito, F.; Iaconetta, G.; Talat, K.; Cappabianca, P.; Tschabitscher, M. Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the suprasellar area: Anatomic considerations—part 1. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conger, A.R.; Lucas, J.; Zada, G.; Schwartz, T.H.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. Endoscopic extended transsphenoidal resection of craniopharyngiomas: Nuances of neurosurgical technique. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassam, A.B.; Gardner, P.A.; Snyderman, C.H.; Carrau, R.L.; Mintz, A.H.; Prevedello, D.M. Expanded endonasal approach, a fully endoscopic transnasal approach for the resection of midline suprasellar craniopharyngiomas: A new classification based on the infundibulum. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luginbuhl, A.J.; Campbell, P.G.; Evans, J.; Rosen, M. Endoscopic repair of high-flow cranial base defects using a bilayer button. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, A.K.M.; Bhatia, S.; Tantawy, M.H.; Sekula, R.; Keller, J.T.; Froelich, S.; Happ, E. Minimally invasive transpalpebral “eyelid” approach to the anterior cranial base. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, ons195–ons207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jane, J.A.; Park, T.S.; Pobereskin, L.H.; Winn, H.R.; Butler, A.B. The supraorbital approach: Technical note. Neurosurgery 1982, 11, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemayer, H.; Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Wiedemayer, H.; Stolke, D. The supraorbital keyhole approach via an eyebrow incision for resection of tumors around the sella and the anterior skull base. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2004, 47, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frio, F.; Solari, D.; Cavallo, L.M.; Cappabianca, P.; Raverot, G.; Jouanneau, E. Ommaya Reservoir System for the Treatment of Cystic Craniopharyngiomas: Surgical Results in a Series of 11 Adult Patients and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e869–e877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavitaki, N. Management of craniopharyngiomas. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowczynski, O.D.; Langan, S.T.; Rizk, E.B. Craniopharyngiomas: A systematic review and evaluation of the current intratumoral treatment landscape. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 166, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.; Parkes, J. Intracystic interferon therapy in childhood craniopharyngioma: Who, when and how? Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Cai, B.W.; Xu, J.G.; You, C. Intracystic bleomycin for cystic craniopharyngiomas in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 7, CD008890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbok, P.; Hukin, J. Intracystic treatments for craniopharyngioma. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 28, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, A. Intracavitary therapeutic options in the management of cystic craniopharyngioma. Child Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, M.M.; Cardeal, D.D.; Teixeira, M.J.; Lucio, J.; Sanders, F.H.; Kuromoto, R.K.; Matushita, H. Brachytherapy in paediatric craniopharyngiomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis of recent literature. Child Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backlund, E.O. Colloidal radioisotopes as part of a multi-modality treatment of craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 1989, 33, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T.; Kondziolka, D.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Lunsford, L.D. Management of cystic craniopharyngiomas with phosphorus-32 intracavitary irradiation. Neurosurgery 2004, 54, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannalfi, A.; Fragkandrea, I.; Brock, J.; Saran, F. Radiotherapy in craniopharyngiomas. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julow, J.; Backlund, E.O.; Lanyi, F.; Hajda, M.; Balint, K.; Nyary, I.; Szeifert, G.T. Long-term results and late complications after intracavitary yttrium-90 colloid irradiation of recurrent cystic craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, B.E.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Levine, G.; Flickinger, J.C. Phosphorus-32 intracavitary irradiation of cystic craniopharyngiomas: Current technique and long-term results. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 33, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretti, L.; Legninda Sop, F.Y.; Pallini, R.; Fernandez, E.; D’Alessandris, Q.G. Neuroendoscopic Treatment of Cystic Craniopharyngiomas: A Case Series with Systematic Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, e367–e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, A.H.; Kerasha, A.A.; Mahmoud, M.E. Surprising outcome of ommaya reservoir in treating cystic craniopharyngioma: A retrospective study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 27, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiert, C.; Grauvogel, J.; Roelz, R.; Demerath, T.; Schnell, D.; Beck, J.; Coenen, V.A.; Reinacher, P.C. Stereotactic cysto-ventricular catheters in craniopharyngiomas: An effective minimally invasive method to improve visual impairment and achieve long-term cyst volume reduction. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinalli, G.; Spennato, P.; Cianciulli, E.; Fiorillo, A.; Di Maio, S.; Maggi, G. The role of transventricular neuroendoscopy in the management of craniopharyngiomas: Three patient reports and review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 19 (Suppl. 1), 341–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enayet, A.E.R.; Atteya, M.M.E.; Taha, H.; Zaghloul, M.S.; Refaat, A.; Maher, E.; Abdelaziz, A.; El Beltagy, M.A. Management of pediatric craniopharyngioma: 10-year experience from high-flow center. Child Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldine, M.H.A.; Khodmehr, S.; Sabahi, M.; Alikhani, P.; Jallo, G.I.; Arjipour, M. Neuroendoscopic Transventricular Approach for Cystic Craniopharyngioma. Cureus 2021, 13, e18123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D. Transcortical Transventricular Endoscopic Approach and Ommaya Reservoir Placement for Cystic Craniopharyngioma. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2015, 50, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarebi, M.; Coutte, A.; Bartier, F.; Khormi, Y.; Peltier, J.; Lefranc, M. A Novel, Hybrid, Stereotactic Approach (Radiosurgery and Dual Ommaya Reservoirs) for the Treatment of Mixed (Polycystic and Solid) Craniopharyngioma. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2019, 97, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndukuba, K.; Ogiwara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Abe, D.; Ichinose, S.; Horiuchi, T.; Ohaegbulam, S.; Hongo, K. Cyst fenestration and Ommaya reservoir placement in endoscopic transcortical transventricular approach for recurrent suprasellar cystic craniopharyngioma without ventriculomegaly. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.S.; Chang, J.H.; Park, Y.G.; Kim, D.S. Recurrence rates after neuroendoscopic fenestration and Gamma Knife surgery in comparison with subtotal resection and Gamma Knife surgery for the treatment of cystic craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmathulla, G.; Barnett, G.H. Minimally invasive management of adult craniopharyngiomas: An analysis of our series and review of literature. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S411–S421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, S.; Akutsu, H.; Mizumoto, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsuboi, K.; Matsumura, A. Neuroendoscopy Followed by Radiotherapy in Cystic Craniopharyngiomas—A Long-Term Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolato, A.; Foroni, R.; Rosta, L.; Gerosa, M.; Bricolo, A. Multimodality stereotactic approach to the treatment of cystic craniopharyngiomas. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2004, 47, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, A.; Coutte, A.; Capel, C.; Maroote, J.; Lefranc, M. Dosimetric and volumetric outcomes of combining cyst puncture through an Ommaya reservoir with index-optimized hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of craniopharyngioma. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 23, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeberg, S.; Harrabi, S.B.; Bougatf, N.; Verma, V.; Windisch, P.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Herfarth, K.; Debus, J.; Rieken, S. Dosimetric Comparison of Proton Radiation Therapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy, and Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy Based on Intracranial Tumor Location. Cancers 2018, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habrand, J.L.; Ganry, O.; Couanet, D.; Rouxel, V.; Levy-Piedbois, C.; Pierre-Kahn, A.; Kalifa, C. The role of radiation therapy in the management of craniopharyngioma: A 25-year experience and review of the literature. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 44, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.B.; Ahmed, S.; Johnson, A.; Thomas, H.; Depauw, N.; Horick, N.; Tansky, J.; Evans, C.L.; Pulsifer, M.; Ebb, D.; et al. Proton Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kida, Y.; Mori, Y.; Hasegawa, T. Long-term results of gamma knife surgery for the treatment of craniopharyngioma in 98 consecutive cases. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 103, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tsugawa, T.; Hashizume, C.; Takahashi, H. Prognostic factors for tumor recurrence after gamma knife radiosurgery of partially resected and recurrent craniopharyngiomas. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, C.J.; Hung, Y.C.; Wu, H.M.; Shiau, C.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Pan, D.H.; Chung, W.Y.; Liu, K.D. Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngioma: Report on a 20-year experience. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121 (Suppl. 2), 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niranjan, A.; Kano, H.; Mathieu, D.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Radiosurgery for craniopharyngioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikis, S.; Mantziaris, G.; Lavezzo, K.; Dabhi, N.; Sheehan, J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Iwai, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashi, M.; Kenai, H.; Kano, T.; Mori, H.; et al. Gamma Knife Surgery for Residual or Recurrent Craniopharyngioma After Surgical Resection: A Multi-institutional Retrospective Study in Japan. Cureus 2020, 12, e6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Yen, C.P.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J. Outcomes of Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, A.; Niranjan, A.; Kano, H.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Optimizing stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with recurrent or residual craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 154, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, F.; Kawamoto, S.; Abe, Y.; Kim, P.; Ueki, K. Effectiveness of a 1-day aspiration plus Gamma Knife surgery procedure for metastatic brain tumor with a cystic component. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Jia, Q.; Zheng, L.; Xu, D. Same-day stereotactic aspiration and Gamma Knife surgery for cystic intracranial tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.J.; Niranjan, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Kano, H.; Castillo, P.; Matchett, J.C.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Combining brain diagnosis and therapy in a single strategy: The safety, reliability, and cost implications using same-day versus separate-day stereotactic procedures. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2011, 89, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.J.; De Silva, M.; Humphreys, R.P.; Drake, J.M.; Smith, M.L.; Blaser, S.I. Aggressive surgical management of craniopharyngiomas in children. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 76, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.L.; El Naqa, I.; Leonard, J.R.; Park, T.S.; Hollander, A.S.; Michalski, J.M.; Mansur, D.B. Long-term outcome in children treated for craniopharyngioma with and without radiotherapy. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2008, 1, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, G.L.; Fan, J. Growth patterns of craniopharyngiomas: Clinical analysis of 226 patients. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 17, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Combs, S.E.; Thilmann, C.; Huber, P.E.; Hoess, A.; Debus, J.; Schulz-Ertner, D. Achievement of long-term local control in patients with craniopharyngiomas using high precision stereotactic radiotherapy. Cancer 2007, 109, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Saran, F.; Traish, D.; Soomal, R.; Sardell, S.; Gonsalves, A.; Ashley, S.; Warrington, J.; Burke, K.; Mosleh-Shirazi, A.; et al. Fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy following conservative surgery in the control of craniopharyngiomas. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 82, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, B.; Ashley, S.; Gorman, C.; Jose, C.C.; Horwich, A.; Bloom, H.J.; Marsh, H.; Brada, M. Craniopharyngioma—Long-term results following limited surgery and radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 1993, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlotto, J.M.; Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Deutsch, M. External beam irradiation of craniopharyngiomas: Long-term analysis of tumor control and morbidity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 54, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, A.L.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Pollack, I.F.; Adelson, P.D. Individualized treatment of pediatric craniopharyngiomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.Y.; Pan, D.H.; Shiau, C.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Wang, L.W. Gamma knife radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlotto, J.; DiMaio, C.; Grassberger, C.; Tangel, M.; Mackley, H.; Pavelic, M.; Specht, C.; Sogge, S.; Nguyen, D.; Glantz, M.; et al. Multi-modality management of craniopharyngioma: A review of various treatments and their outcomes. Neurooncol. Pract. 2016, 3, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Minimally invasive leading to faster recovery, shorter hospital stay | Higher rates of CSF leak |
| Higher rates of gross total resection | Limited reach to purely third ventricular tumors, which may be more amenable unilateral subfrontal or midline transcallosal approaches |
| Higher rates of improved visual outcomes | Limited reach to tumors with significant lateral extension, which may be more amenable to unilateral pterional/orbitozygomatic/supraorbital approaches |
| Lower endocrine complication rates | Steep learning curve, may require two surgeons fluent with endoscopic techniques |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, C.S.; Omay, S.B. The Role of Surgical Approaches in the Multi-Modal Management of Adult Craniopharyngiomas. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1408-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030118
Hong CS, Omay SB. The Role of Surgical Approaches in the Multi-Modal Management of Adult Craniopharyngiomas. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(3):1408-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030118
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Christopher S., and Sacit Bulent Omay. 2022. "The Role of Surgical Approaches in the Multi-Modal Management of Adult Craniopharyngiomas" Current Oncology 29, no. 3: 1408-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030118
APA StyleHong, C. S., & Omay, S. B. (2022). The Role of Surgical Approaches in the Multi-Modal Management of Adult Craniopharyngiomas. Current Oncology, 29(3), 1408-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030118





