Real-World Treatment Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness of Palbociclib Plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as First-Line Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis from the US Syapse Learning Health Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Regimens and Line of Therapy
2.3. Outcomes
2.3.1. Clinical Characteristics
2.3.2. Treatment Patterns
2.3.3. Effectiveness Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
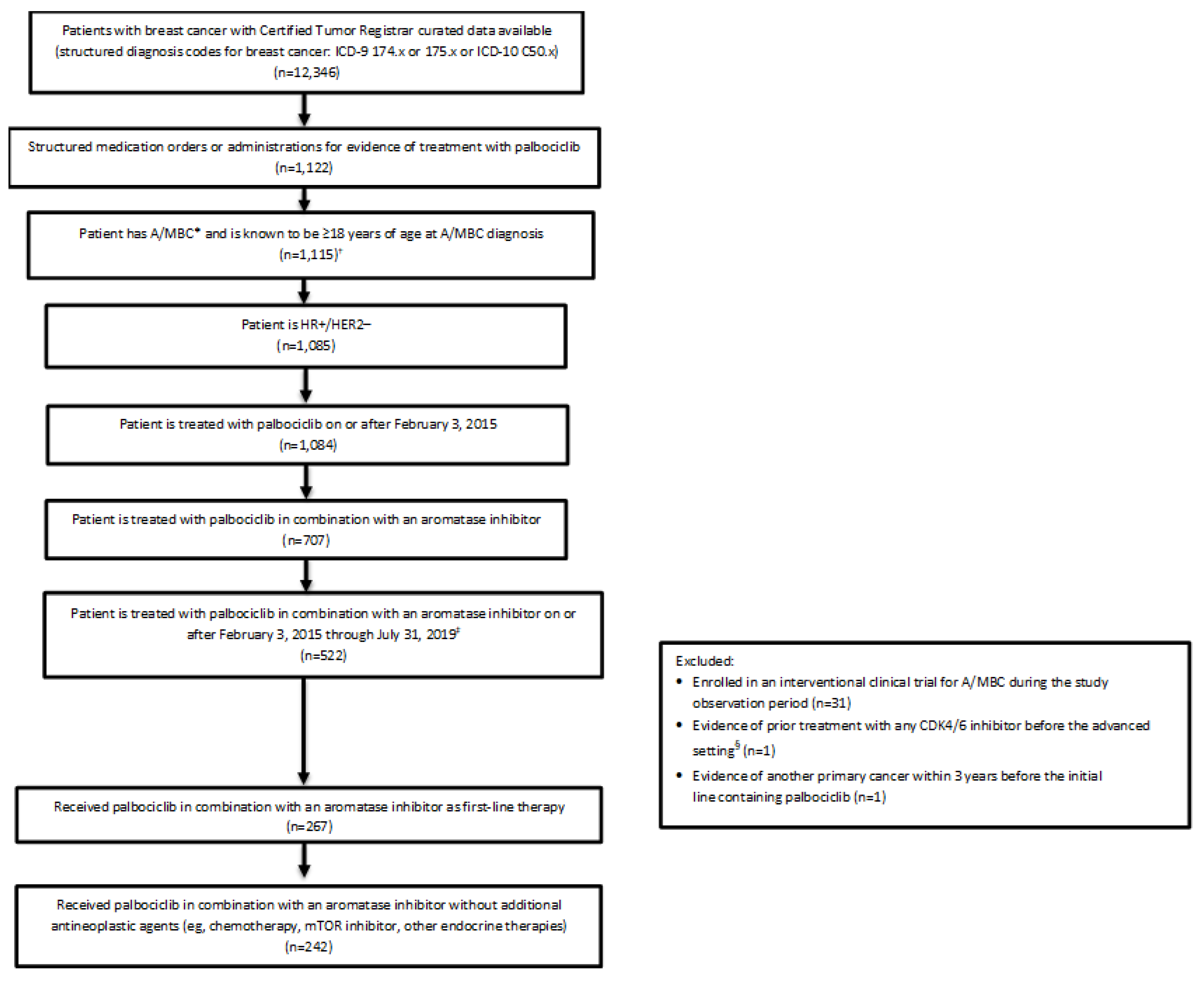
3.1. Patients
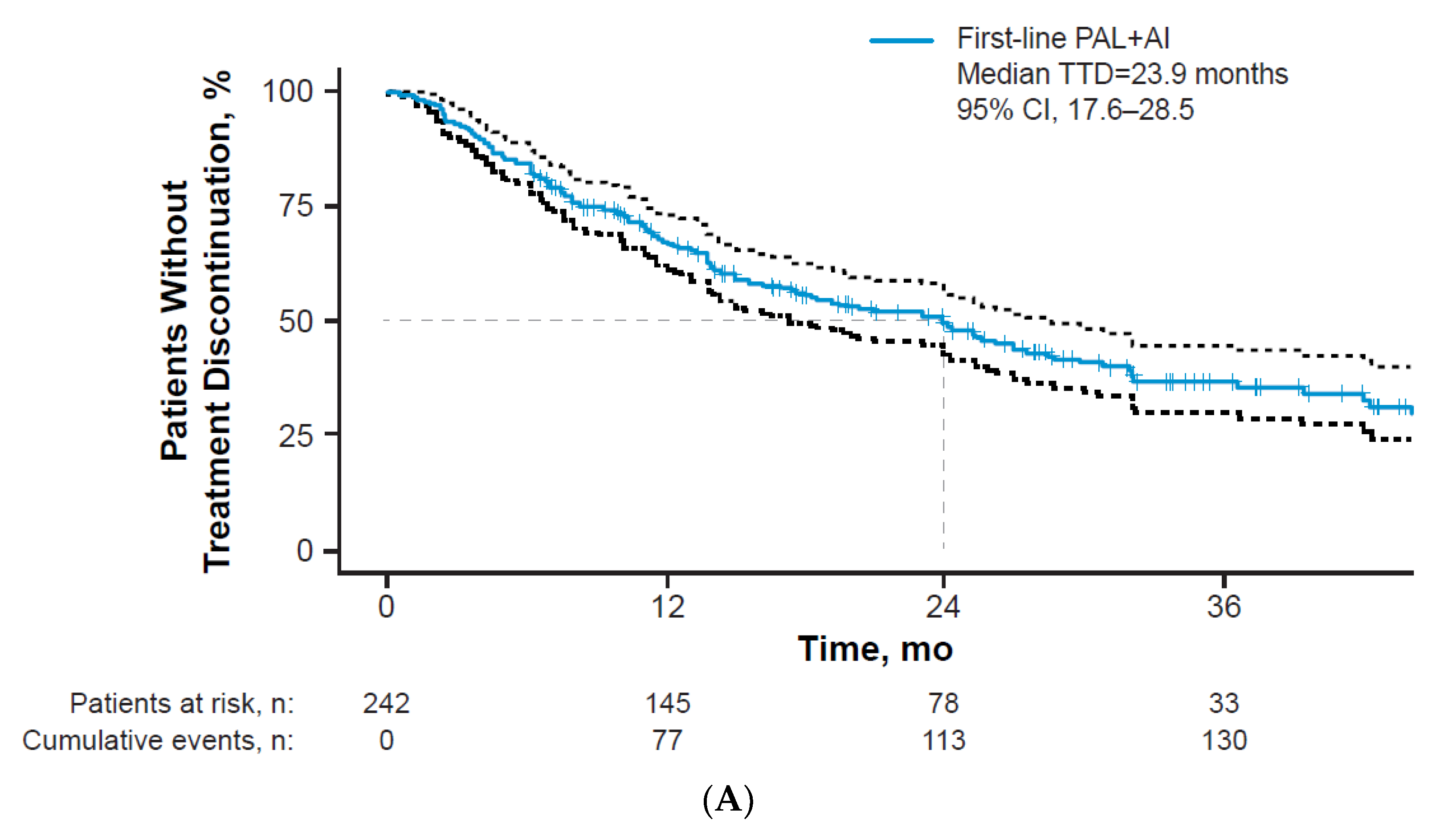
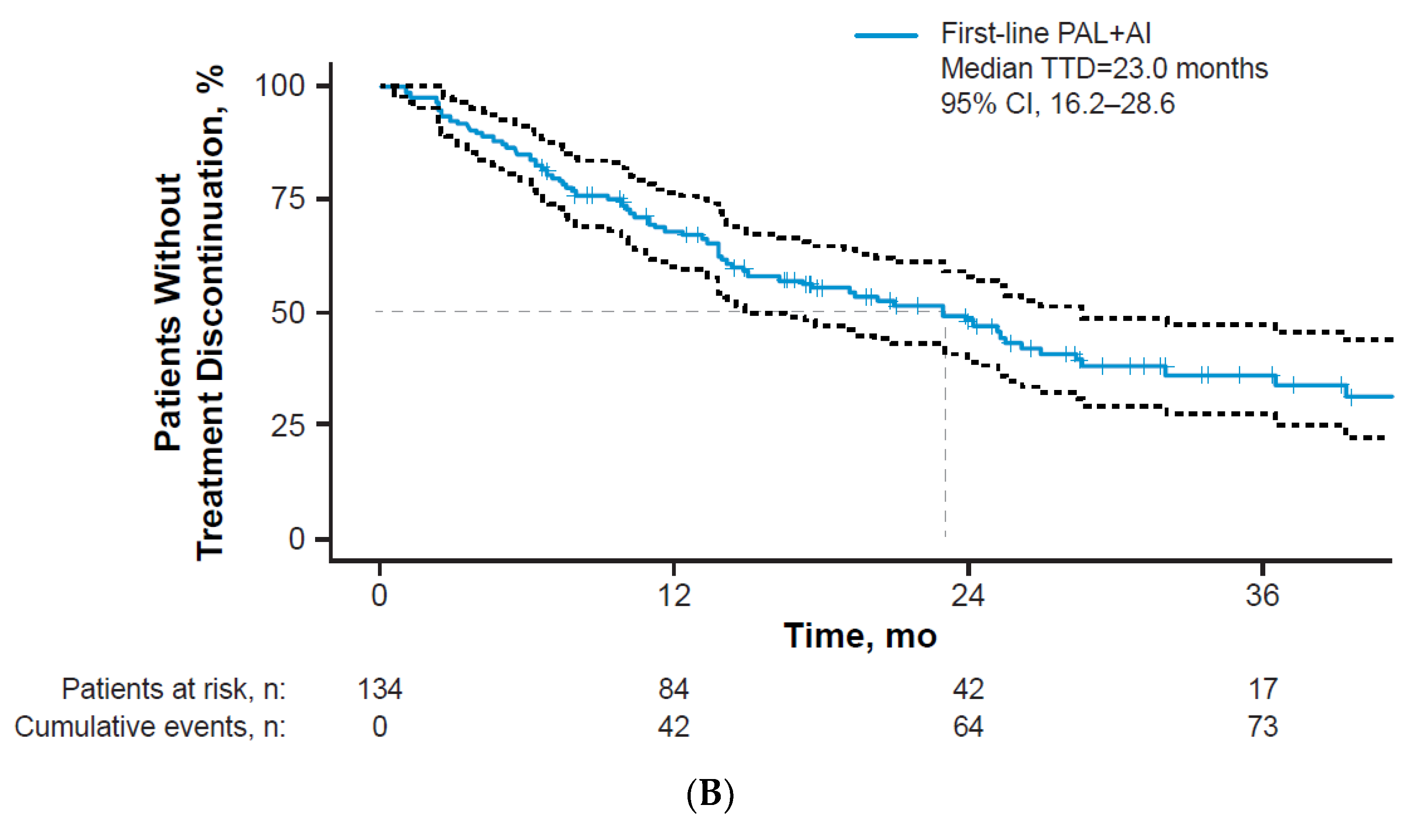
3.2. Treatment Patterns
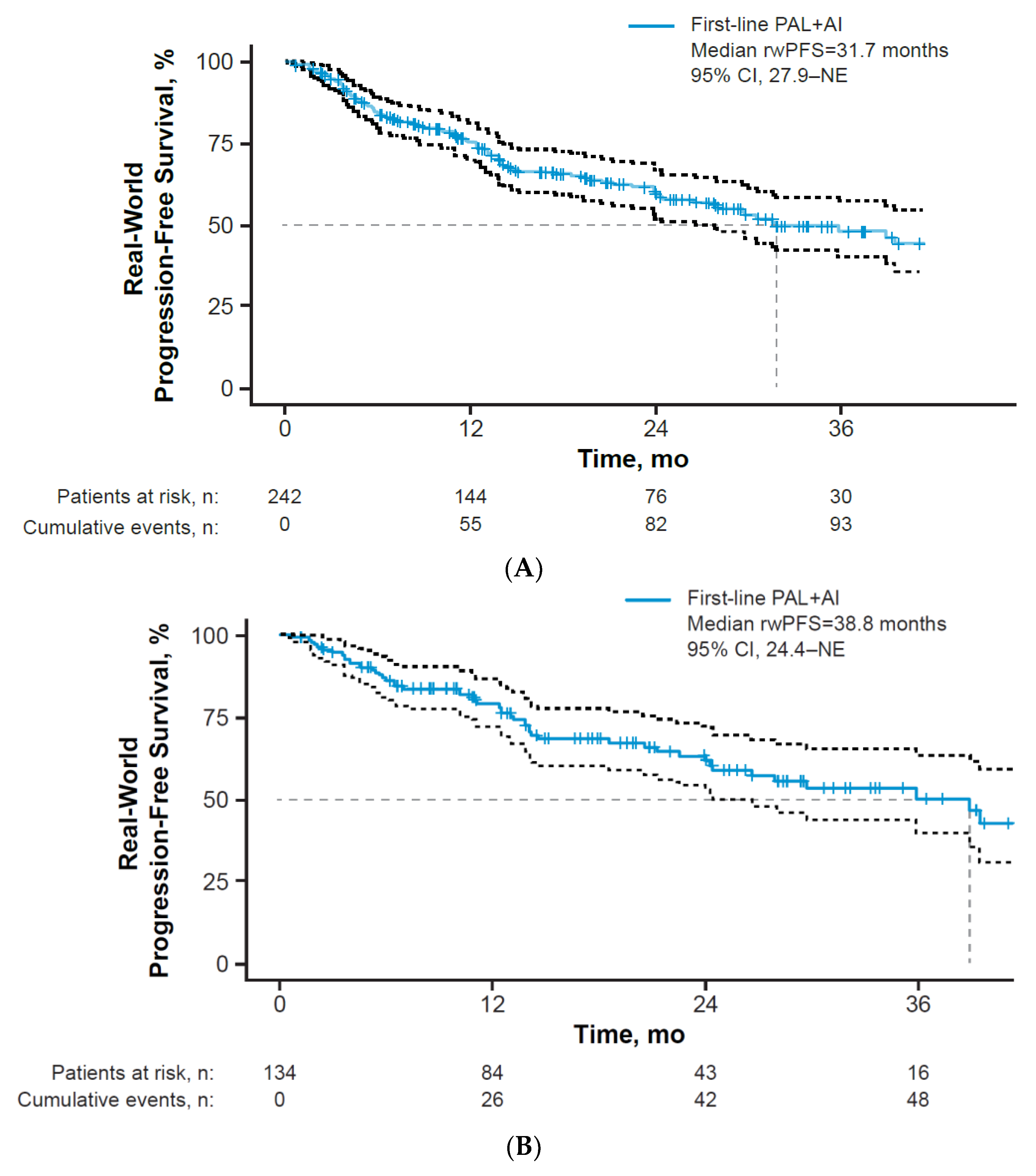
3.3. Clinical Effectiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER) Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts Figures 2019–2020. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures-2019-2020.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Breast Cancer Version 5.2020. Available online: https://www2.tri-kobe.org/nccn/guideline/breast/english/breast.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- IBRANCE® Capsules (palbociclib). Full Prescribing Information; Pfizer Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Beaver, J.A.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Charlab, R.; Chen, W.; Palmby, T.; Tilley, A.; Zirkelbach, J.F.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; et al. FDA approval: Palbociclib for the treatment of postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, A.J.; Wedam, S.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Bloomquist, E.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Chen, W.; Palmby, T.R.; Fourie Zirkelbach, J.; Fu, W.; et al. FDA approval of palbociclib in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4968–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finn, R.S.; Crown, J.P.; Lang, I.; Boer, K.; Bondarenko, I.M.; Kulyk, S.O.; Ettl, J.; Patel, R.; Pinter, T.; Schmidt, M.; et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Ro, J.; André, F.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; Iwata, H.; Harbeck, N.; Loibl, S.; Bartlett, C.H.; Zhang, K.; et al. Palbociclib in hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rugo, H.S.; Finn, R.S.; Diéras, V.; Ettl, J.; Lipatov, O.; Joy, A.A.; Harbeck, N.; Castrellon, A.; Iyer, S.; Lu, D.R.; et al. Palbociclib plus letrozole as first-line therapy in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer with extended follow-up. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristofanilli, M.; DeMichele, A.; Giorgetti, C.; Turner, N.C.; Slamon, D.J.; Im, S.-A.; Masuda, N.; Verma, S.; Loi, S.; Colleoni, M.; et al. Predictors of prolonged benefit from palbociclib plus fulvestrant in women with endocrine-resistant hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer in PALOMA-3. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 104, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Im, S.-A.; Slamon, D.J.; Harbeck, N.; Bondarenko, I.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; et al. Overall survival (OS) with palbociclib (PAL) + fulvestrant (FUL) in women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC): Updated analyses from PALOMA-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Boer, K.; Bondarenko, I.; Patel, R.; Pinter, T.; Schmidt, M.; Shparyk, Y.V.; Thummala, A.; Voitko, N.; Bananis, E.; et al. Overall survival results from the randomized phase 2 study of palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone for first-line treatment of ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1, TRIO-18). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 183, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Slamon, D.J.; Ro, J.; Bondarenko, I.; Im, S.-A.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; et al. Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan-Curay, J.; Sacks, L.; Woodcock, J. Real-world evidence and real-world data for evaluating drug safety and effectiveness. JAMA 2018, 320, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, J.K.; Ward, M.A.; Garofalo, D.; Ahmed, H.V.; McRoy, L.; Laney, J.; Zanotti, G.; Braverman, J.; Yu, H.; Feinberg, B.A. Real-world evidence analysis of palbociclib prescribing patterns for patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer treated in community oncology practice in the USA one year post approval. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Du, E.X.; Chu, L.; Peeples, M.; Xie, J.; Barghout, V.; Tang, D.H. Real-world palbociclib dosing patterns and implications for drug costs in the treatment of HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMichele, A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Brufsky, A.; Liu, X.; Mardekian, J.; McRoy, L.; Layman, R.M.; Emir, B.; Torres, M.A.; Rugo, H.S.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of first-line palbociclib plus letrozole versus letrozole alone for HR+/HER2− metastatic breast cancer in US real-world clinical practice. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Stokes, G.; Mitra, D.; Waller, J.; Gibson, K.; Milligan, G.; Iyer, S. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes among patients receiving palbociclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant for HR+/HER2-negative advanced/metastatic breast cancer in real-world settings in the US: Results from the IRIS study. Breast 2019, 43, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chang, E.; Cho-Phan, C.; Hirsch, J.; Thompson, M.A.; Blumenthal, G.; Huang, S.M.; et al. Pneumonitis incidence in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with immunotherapy or chemotherapy in clinical trials and real-world data (abstr CT086). In Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.Y.; Vallejo, J.J.; Gong, Y.; Brown, T.D.; Zhang, C.; Hirsch, J.; Tang, S.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Singh, H.; Kluetz, P.G.; et al. Outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (aNSCLC) and high PD-L1 expression treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy: An FDA-pooled analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Izano, M.A.; Thompson, M.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Weese, J.L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Schrag, A.; Teka, M.; Walters, S.; Wolf, F.M.; et al. Rapid real-world data analysis of patients with cancer, with and without COVID-19, across distinct health systems. Cancer Rep. 2021, 4, e1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, M.H.; Holmes, B.; Hilaire, D.S.; Tran, M.; Rioth, M.; Subramanian, V.; Winzeler, A.M.; Brown, T. Validation of a mortality composite score in the real-world setting: Overcoming source-specific disparities and biases. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2021, 5, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friends of Cancer Research. Considerations for Use of Real-World Evidence in Oncology. Available online: https://friendsofcancerresearch.org/sites/default/files/2020-10/Use_of_Real-World_Evidence_in_Oncology_0.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Lin, J.; McRoy, L.; Fisher, M.D.; Hu, N.; Davis, C.; Mitra, D.; Walker, M.S. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes of palbociclib-based therapy received in US community oncology practices. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Liu, X.; Mardekian, J.; McRoy, L. Palbociclib plus an aromatase inhibitor as first-line therapy for metastatic breast cancer in US clinical practice: Real-world progression-free survival analysis. In Proceedings of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 27 September–1 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Varella, L.; Eziokwu, A.S.; Jia, X.; Kruse, M.; Moore, H.C.F.; Budd, G.T.; Abraham, J.; Montero, A.J. Real-world clinical outcomes and toxicity in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with palbociclib and endocrine therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Oza, A.; Thomas, S.; Ademuyiwa, F.; Weilbaecher, K.; Suresh, R.; Bose, R.; Cherian, M.; Hernandez-Aya, L.; Frith, A.; et al. Retrospective analysis of treatment patterns and effectiveness of palbociclib and subsequent regimens in metastatic breast cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaro, C.; Batra, A.; Lupichuk, S. First-line treatment with a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor plus an aromatase inhibitor for metastatic breast cancer in Alberta. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2270–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, D.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; McRoy, L.; Layman, R.M.; Brufsky, A. Real-world treatment patterns and tumor response of palbociclib plus an aromatase inhibitor for metastatic breast cancer: Flatiron database analysis. In Proceedings of the Miami Breast Cancer Conference, Virtual, 4–7 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Porte, B.; Carton, M.; Lerebours, F.; Brain, E.; Loirat, D.; Haroun, L.; Bellesoeur, A.; Hamba, S.B.; Kirova, Y.; Cottu, P. Real life efficacy of palbociclib and endocrine therapy in HR positive, HER2 negative advanced breast cancer. Breast 2020, 54, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, J.A.; Mayer, M.; Atwood, M.K.; Kaplan, H.G. Differential presentation and survival of de novo and recurrent metastatic breast cancer over time: 1990–2010. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 167, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salloum, R.G.; Smith, T.; Jensen, G.A.; Lafata, J.E. Using claims-based measures to predict performance status score in patients with lung cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Characteristic | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 238 (98.3) |
| Male | 4 (1.7) |
| Race | |
| White | 196 (81.0) |
| Black or African American | 29 (12.0) |
| Asian | 10 (4.1) |
| Other or not provided | 7 (2.9) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic-Latino | 15 (6.2) |
| Non-Hispanic/Non-Latino | 225 (93.0) |
| Unknown | 2 (0.8) |
| Region of residence | |
| Midwest | 230 (95.0) |
| South | 10 (4.1) |
| Other | 2 (0.8) |
| Age at A/MBC diagnosis, y | |
| Median (min, max) | 66.0 (31.0–93.0) |
| 50 | 25 (10.3) |
| 50–64 | 86 (35.5) |
| 65–74 | 80 (33.1) |
| 75 | 51 (21.1) |
| Menopausal status at A/MBC diagnosis | |
| Postmenopausal | 207 (85.5) |
| Pre/perimenopausal | 26 (10.7) |
| Unknown/not applicable * | 9 (3.7) |
| Insurance carrier | |
| Medicare/Medicaid | 149 (61.6) |
| Commercial | 69 (28.5) |
| None/Not stated | 24 (9.9) |
| Characteristic | n (%) |
|---|---|
| A/MBC at diagnosis | 137 (56.6) |
| Early stage at diagnosis | 105 (43.4) |
| Setting where first-line palbociclib plus AI was received | |
| Advanced Setting | 6 (2.5) |
| Metastatic Setting | 236 (97.5) |
| ECOG PS | |
| 0 | 57 (23.6) |
| 1 | 58 (24.0) |
| ≥2 | 29 (12.0) |
| Unknown | 98 (40.5) |
| CCI Score | |
| 0 | 158 (65.3) |
| 1 | 47 (19.4) |
| 2 | 22 (9.1) |
| 3 | 9 (3.7) |
| ≥4 | 6 (2.5) |
| Specific comorbidities | |
| Hypertension | 118 (48.8) |
| Diabetes | 53 (21.9) |
| Renal disease | 22 (9.1) |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 14 (5.8) |
| None | 89 (36.8) |
| DFI * in patients with early stage disease at diagnosis, mo (n = 105) | |
| 12 | 14 (13.3) |
| 13–24 | 12 (11.4) |
| 25–36 | 10 (9.5) |
| 36 | 69 (65.7) |
| Number of metastatic sites † | |
| 0 | 1 (0.4) ‡ |
| 1 | 147 (60.7) |
| 2 | 45 (18.6) |
| ≥3 | 49 (20.2) |
| Sites of distant metastases § | |
| Bone (bone only or in addition to other sites) | 201 (83.1) |
| Bone only | 123 (50.8) |
| Visceral || | 78 (32.2) |
| Lung | 52 (21.5) |
| Brain | 6 (2.5) |
| Distant lymph nodes | 45 (18.6) |
| Liver | 24 (9.9) |
| Malignant pleural effusion | 25 (10.3) |
| BRCA 1/2 tested | |
| Yes | 46 (19.0) |
| No | 196 (81.0) |
| Dosing Information | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Starting dose, mg | |
| 125 | 217 (89.7) |
| 100 | 18 (7.4) |
| 75 | 3 (1.7) |
| Unknown | 4 (1.2) |
| End dose, mg | |
| 125 | 147 (60.7) |
| 100 | 67 (27.7) |
| 75 | 24 (9.9) |
| Unknown | 4 (1.7) |
| Dose adjustment | |
| None | 162 (66.9) |
| Decrease | 75 (31.0) |
| Increase | 1 (0.4) |
| Unknown | 4 (1.7) |
| Treatment ongoing | |
| Yes | 106 (43.8) |
| No | 136 (56.2) |
| Discontinuation reason | |
| Progression | 64 (26.4) |
| Intolerance/toxicity | 36 (14.9) |
| Other * | 36 (14.9) |
| Subgroup | n | Median rwPFS (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Metastatic disease sites | ||
| Bone only | 123 | 44.9 (39.4–NE) |
| Visceral | 78 | 27.9 (13.8–NE) |
| Stage at breast cancer diagnosis | ||
| Advanced or metastatic (stages IIIb, IIIc, IV) | 137 | 38.8 (26.5–NE) |
| Metastatic (stage IV) | 134 | 38.8 (24.4-NE) |
| Early stage (stages 0, I, II, IIIa) | 89 | 30.5 (17.4–NE) |
| Unknown | 16 | 29.8 (23.9–NE) |
| Age at A/MBC diagnosis, y | ||
| 50 | 25 | NR (13.3–NE) |
| 50–64 | 86 | 26.5 (17.4–NE) |
| 65–74 | 80 | 41.9 (29.8–NE) |
| ≥75 | 51 | 35.8 (21.2–NE) |
| ECOG PS | ||
| 0 | 57 | 29.8 (27.9–NE) |
| 1 | 58 | 31.7 (19.4–NE) |
| 2+ | 29 | 13.8 (5.7–NE) |
| Unknown | 98 | 38.8 (30.5–NE) |
| CCI score | ||
| 0 | 158 | 44.9 (28.0–NE) |
| 1 | 47 | 26.5 (13.3–NE) |
| 2+ | 37 | 29.8 (21.2–NE) |
| DFI among patients with early stage disease at diagnosis, mo | ||
| ≤12 | 14 | 13.3 (3.7–NE) |
| 12 | 91 | 31.6 (23.9–NE) |
| Race | ||
| White | 196 | 35.8 (24.4–NE) |
| Black or African American | 29 | 18.5 (13.8–NE) |
| Number of metastatic sites * | ||
| 1 | 147 | 44.9 (29.6–NE) |
| 2 | 45 | 31.6 (14.0–NE) |
| ≥3 | 49 | 14.7 (12.3–NE) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Law, J.W.; Mitra, D.; Kaplan, H.G.; Alfred, T.; Brufsky, A.M.; Emir, B.; McCracken, H.; Liu, X.; Broome, R.G.; Zhang, C.; et al. Real-World Treatment Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness of Palbociclib Plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as First-Line Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis from the US Syapse Learning Health Network. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1047-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29020089
Law JW, Mitra D, Kaplan HG, Alfred T, Brufsky AM, Emir B, McCracken H, Liu X, Broome RG, Zhang C, et al. Real-World Treatment Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness of Palbociclib Plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as First-Line Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis from the US Syapse Learning Health Network. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(2):1047-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaw, Jeanna Wallenta, Debanjali Mitra, Henry G. Kaplan, Tamuno Alfred, Adam M. Brufsky, Birol Emir, Haley McCracken, Xianchen Liu, Ronda G. Broome, Chenan Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Real-World Treatment Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness of Palbociclib Plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as First-Line Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis from the US Syapse Learning Health Network" Current Oncology 29, no. 2: 1047-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29020089
APA StyleLaw, J. W., Mitra, D., Kaplan, H. G., Alfred, T., Brufsky, A. M., Emir, B., McCracken, H., Liu, X., Broome, R. G., Zhang, C., DiCristo, C., & Chen, C. (2022). Real-World Treatment Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness of Palbociclib Plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as First-Line Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis from the US Syapse Learning Health Network. Current Oncology, 29(2), 1047-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29020089





