Everything You Always Wanted to Know about Sarcopenia but Were Afraid to Ask: A Quick Guide for Radiation Oncologists (impAct oF saRcopeniA In raDiotherapy: The AFRAID Project)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Definitions and Concepts
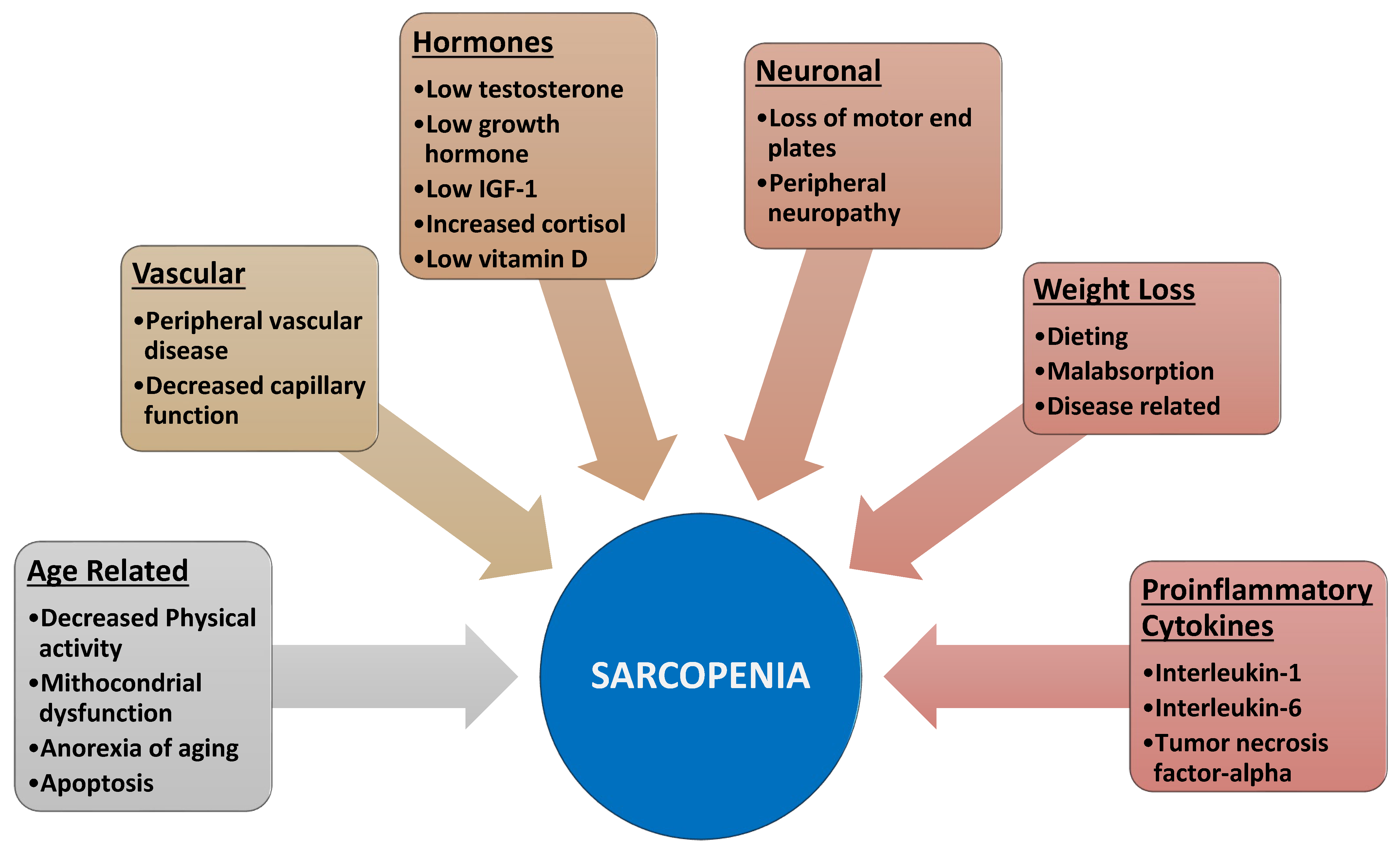
- 1
- 2
- Furthermore, aging is also associated with motor neuron alterations [9] leading to muscle atrophy and decreased muscle function.
- 3
- 4
- Aging and obesity favor a condition of insulin resistance, leading to reduced availability of glucose and proteins needed for muscle anabolism [13].
- 5
- Finally, obesity and various diseases increase proinflammatory cytokines and thus activate NFkB and ultimately protein catabolism [14].
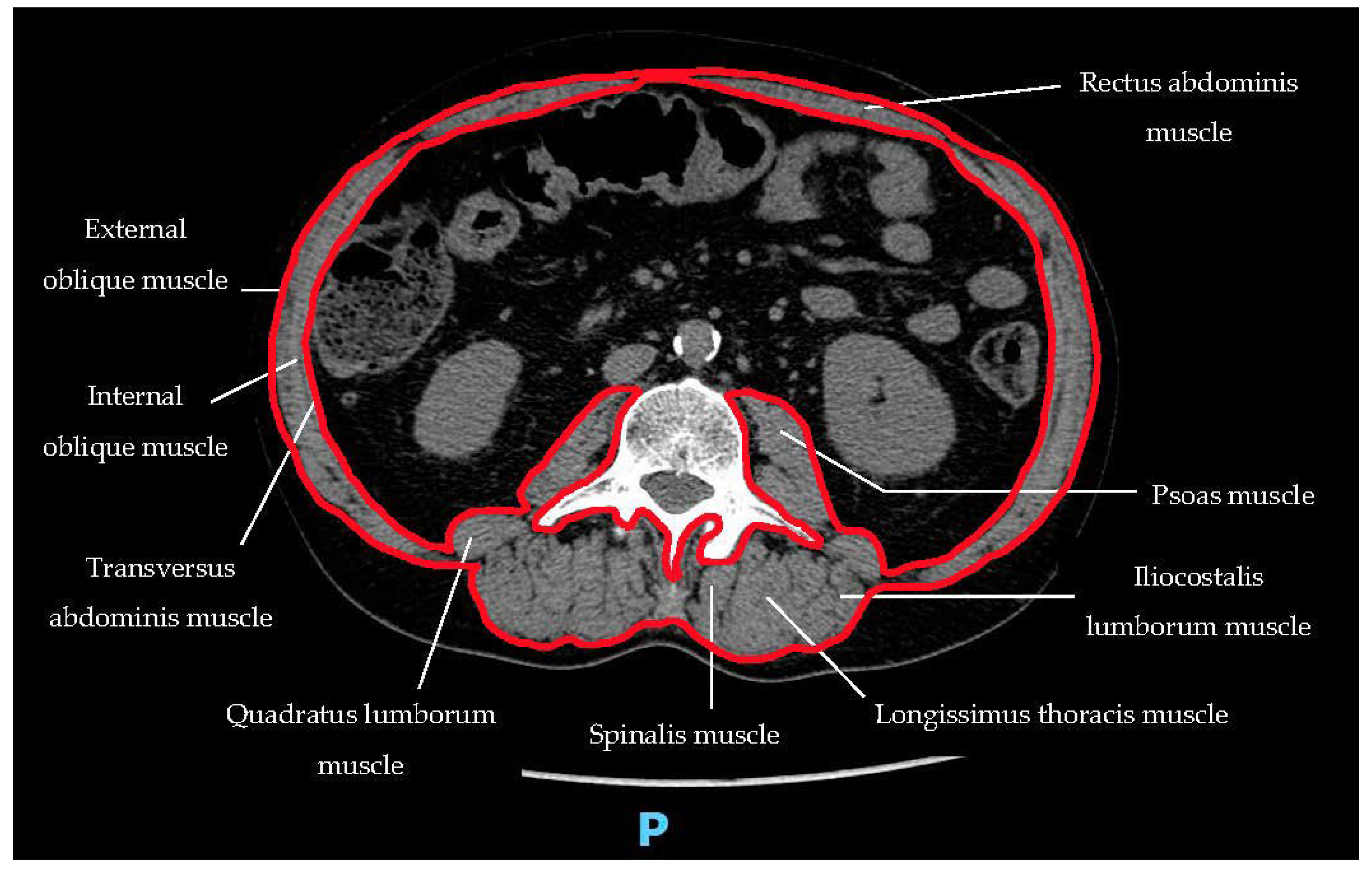
- 1
- 2
- 3
- The loss of muscle mass reduces the secretion of some circulating cytokines, which are produced by muscle cells (myokines: IL-6, IL-8, IL-15) and which hinder tumor progression.
- 4
- 5
- 6
- SP is associated with increased radiation-induced late toxicity, with possible worsening of prognosis and quality of life [25].
- 1
- Between different muscles (intermuscular),
- 2
- In the extracellular site but within a single muscle (intramuscular),
- 3
- Within the cells (intramiocellular). Furthermore, MS is characterized not only by the accumulation but also by the different chemical compositions of fats normally present in the muscles [30].
3. Detection of Sarcopenia
4. Impact of Sarcopenia
5. Management of Sarcopenia during Radiotherapy
6. Future Studies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Sarcopenia: European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, R.A.; Vellas, B.; Evans, W.J.; Bhasin, S.; Morley, J.E.; Newman, A.B.; Abellan van Kan, G.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Breuille, D.; et al. Sarcopenia: An Undiagnosed Condition in Older Adults. Current Consensus Definition: Prevalence, Etiology, and Consequences. International Working Group on Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Liu, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Hsu, P.-S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shachar, S.S.; Williams, G.R.; Muss, H.B.; Nishijima, T.F. Prognostic Value of Sarcopenia in Adults with Solid Tumours: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2016, 57, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, F.; Bazzocchi, A.; Buwenge, M.; Zamagni, A.; Macchia, G.; Deodato, F.; Cilla, S.; De Iaco, P.; Perrone, A.M.; Strigari, L.; et al. Impact and Treatment of Sarcopenia in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Multidisciplinary, AMSTAR-2 Compliant Review of Systematic Reviews and Metanalyses. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 887156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radiotherapy Sarcopenia—Search Results—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=radiotherapy+sarcopenia&sort=pubdate&size=200 (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Morley, J.E. Weight Loss in Older Persons: New Therapeutic Approaches. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 3637–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntosh, C.; Morley, J.E.; Chapman, I.M. The Anorexia of Aging. Nutrition 2000, 16, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drey, M.; Krieger, B.; Sieber, C.C.; Bauer, J.M.; Hettwer, S.; Bertsch, T.; DISARCO Study Group. Motoneuron Loss Is Associated with Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Waters, D.L.; Gallagher, D.; Morley, J.E.; Garry, P.J. Predictors of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Elderly Men and Women. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1999, 107, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nieschlag, E.; Swerdloff, R.; Behre, H.M.; Hellstrom, W.J.; Gooren, L.J.; Kaufman, J.M.; Legros, J.-J.; Lunenfeld, B.; Morales, A.; et al. International Society of Andrology; International Society for the Study of Aging Male; European Association of Urology; European Academy of Andrology; American Society of Andrology. Investigation, Treatment, and Monitoring of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Males: ISA, ISSAM, EAU, EAA, and ASA Recommendations. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haren, M.T.; Siddiqui, A.M.; Armbrecht, H.J.; Kevorkian, R.T.; Kim, M.J.; Haas, M.J.; Mazza, A.; Kumar, V.B.; Green, M.; Banks, W.A.; et al. Testosterone Modulates Gene Expression Pathways Regulating Nutrient Accumulation, Glucose Metabolism and Protein Turnover in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Int. J. Androl. 2011, 34, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, A.; Morley, J.E.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Paolisso, G.; Bayer, T.; Zeyfang, A.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Vischer, U.; Woo, J.; Chapman, I.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus in Older People: Position Statement on Behalf of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics (IAGG), the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People (EDWPOP), and the International Task Force of Experts in Diabetes. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Haehling, S.; Steinbeck, L.; Doehner, W.; Springer, J.; Anker, S.D. Muscle Wasting in Heart Failure: An Overview. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. Prevalence, Incidence, and Clinical Impact of Sarcopenia: Facts, Numbers, and Epidemiology-Update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, G.; Kang, D.; Cho, J.; Kim, H.K.; Zo, J.I.; Shim, Y.M.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Association between Sarcopenia and Physical Function among Preoperative Lung Cancer Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, B.J.; Kaasa, S.; McMillan, D.C.; Fallon, M.T.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Fayers, P.; Klepstad, P. Prognostic Factors in Patients with Advanced Cancer: A Comparison of Clinicopathological Factors and the Development of an Inflammation-Based Prognostic System. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, S.I.; Pezier, T.F.; Tijink, B.M.; Janssen, L.M.; Braunius, W.W.; de Bree, R. Preoperative Low Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Risk Factor for Pharyngocutaneous Fistula and Decreased Overall Survival in Patients Undergoing Total Laryngectomy. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, E.; Chargi, N.; van Gemert, J.T.M.; van Es, R.J.J.; Dieleman, F.J.; Rosenberg, A.J.W.P.; Van Cann, E.M.; de Bree, R. Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Is a Strong Predictive Factor for Surgical Complications and a Prognostic Factor in Oral Cancer Patients Undergoing Mandibular Reconstruction with a Free Fibula Flap. Oral Oncol. 2020, 101, 104530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiguchi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakamura, H.; Yamatsu, Y.; Hirai, Y.; Shoda, K.; Kurozumi, S.; Ibaragi, S.; Harimoto, N.; Motegi, S.-I.; et al. Evaluation of Overall and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Free Flaps for Oral Cancer Resection. Microsurgery 2020, 40, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.R.; Roh, J.-L.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, S.-H.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Efficacy of Head and Neck Computed Tomography for Skeletal Muscle Mass Estimation in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 95, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, K.; Ueno, T.; Hirai, N.; Komori, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kondo, S.; Wakisaka, N.; Yoshizaki, T. Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Is a Risk Factor for Aspiration Pneumonia During Chemoradiotherapy. The Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1524–E1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huiskamp, L.F.J.; Chargi, N.; Devriese, L.A.; May, A.M.; Huitema, A.D.R.; de Bree, R. The Predictive Value of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Assessed on Cross-Sectional Imaging for Anti-Cancer Drug Toxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shodo, R.; Yamazaki, K.; Ueki, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Horii, A. Sarcopenia Predicts a Poor Treatment Outcome in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Soc. EUFOS Affil. Ger. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2021, 278, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn-Dekker, M.I.; van den Bosch, L.; van den Hoek, J.G.M.; Bijl, H.P.; van Aken, E.S.M.; van der Hoorn, A.; Oosting, S.F.; Halmos, G.B.; Witjes, M.J.H.; van der Laan, H.P.; et al. Impact of Sarcopenia on Survival and Late Toxicity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 147, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, K.; Strasser, F.; Anker, S.D.; Bosaeus, I.; Bruera, E.; Fainsinger, R.L.; Jatoi, A.; Loprinzi, C.; MacDonald, N.; Mantovani, G.; et al. Definition and Classification of Cancer Cachexia: An International Consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, K.; Aoi, W.; Yamaguchi, A. Molecular Mechanism of Sarcopenia and Cachexia: Recent Research Advances. Pflugers Arch. 2017, 469, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.J.; Mozer, M. Differentiating Sarcopenia and Cachexia Among Patients with Cancer. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 32, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Delrio, P.; Mascheroni, A.; Zanetti, M. The Spectrum of Malnutrition/Cachexia/Sarcopenia in Oncology According to Different Cancer Types and Settings: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabowski, A.; Zendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Nawrocki, A.; Górski, J. Not Only Accumulation, but Also Saturation Status of Intramuscular Lipids Is Significantly Affected by PPARγ Activation. Acta Physiol. Oxf. Engl. 2012, 205, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-de-Araujo, R.; Addison, O.; Miljkovic, I.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Bergman, B.C.; Clark, R.V.; Elena, J.W.; Esser, K.A.; Ferrucci, L.; Harris-Love, M.O.; et al. Myosteatosis in the Context of Skeletal Muscle Function Deficit: An Interdisciplinary Workshop at the National Institute on Aging. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Kelley, D.E.; Thaete, F.L.; He, J.; Ross, R. Skeletal Muscle Attenuation Determined by Computed Tomography Is Associated with Skeletal Muscle Lipid Content. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Thaete, F.L.; Kelley, D.E. Thigh Adipose Tissue Distribution Is Associated with Insulin Resistance in Obesity and in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kuk, J.L.; Davidson, L.E.; Hudson, R.; Kilpatrick, K.; Graham, T.E.; Ross, R. Exercise without Weight Loss Is an Effective Strategy for Obesity Reduction in Obese Individuals with and without Type 2 Diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taaffe, D.R.; Henwood, T.R.; Nalls, M.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lang, T.F.; Harris, T.B. Alterations in Muscle Attenuation Following Detraining and Retraining in Resistance-Trained Older Adults. Gerontology 2009, 55, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.A.; Mourtzakis, M.; Chu, Q.S.C.; Baracos, V.E.; Reiman, T.; Mazurak, V.C. Nutritional Intervention with Fish Oil Provides a Benefit over Standard of Care for Weight and Skeletal Muscle Mass in Patients with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy. Cancer 2011, 117, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubrey, J.; Esfandiari, N.; Baracos, V.E.; Buteau, F.A.; Frenette, J.; Putman, C.T.; Mazurak, V.C. Measurement of Skeletal Muscle Radiation Attenuation and Basis of Its Biological Variation. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baracos, V.E.; Arribas, L. Sarcopenic Obesity: Hidden Muscle Wasting and Its Impact for Survival and Complications of Cancer Therapy. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S2), ii1–ii9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishigori, T.; Obama, K.; Sakai, Y. Assessment of Body Composition and Impact of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Margioris, A.N. Sarcopenic Obesity. Horm. Athens Greece 2018, 17, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A Symptom Score to Predict Persons with Sarcopenia at Risk for Poor Functional Outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.; Tanaka, T.; Shibasaki, K.; Ouchi, Y.; Kikutani, T.; Higashiguchi, T.; Obuchi, S.P.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Hirano, H.; Kawai, H.; et al. Development of a Simple Screening Test for Sarcopenia in Older Adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2014, 14 (Suppl. S1), 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.C.; Denison, H.J.; Martin, H.J.; Patel, H.P.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. A Review of the Measurement of Grip Strength in Clinical and Epidemiological Studies: Towards a Standardised Approach. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Five Time Sit to Stand Test (FTSST); 2017.
- Mitsiopoulos, N.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lyons, W.; Gallagher, D.; Ross, R. Cadaver Validation of Skeletal Muscle Measurement by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computerized Tomography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Smith, R.; Aulet, M.; Bensen, B.; Lichtman, S.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N. Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass: Measurement by Dual-Photon Absorptiometry. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, A.; Langius, J.A.E.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Nurmohamed, S.A.; van der Pant, K.A.M.I.; Blauwhoff-Buskermolen, S.; Wierdsma, N.J. Percentiles for Skeletal Muscle Index, Area and Radiation Attenuation Based on Computed Tomography Imaging in a Healthy Caucasian Population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derstine, B.A.; Holcombe, S.A.; Ross, B.E.; Wang, N.C.; Su, G.L.; Wang, S.C. Skeletal Muscle Cutoff Values for Sarcopenia Diagnosis Using T10 to L5 Measurements in a Healthy US Population. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Roubenoff, R.; Mayer, J.; Nair, K.S. Sarcopenia. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2001, 137, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, B.; Boyle, S.P.; Boutin, R.D.; Lenchik, L. Approaches to Assessment of Muscle Mass and Myosteatosis on Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Punyanitya, M.; Wang, Z.; Gallagher, D.; St-Onge, M.-P.; Albu, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heshka, S. Total Body Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue Volumes: Estimation from a Single Abdominal Cross-Sectional Image. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Sawyer, M.B.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and Clinical Implications of Sarcopenic Obesity in Patients with Solid Tumours of the Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Tracts: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molwitz, I.; Leiderer, M.; McDonough, R.; Fischer, R.; Ozga, A.-K.; Ozden, C.; Tahir, E.; Koehler, D.; Adam, G.; Yamamura, J. Skeletal Muscle Fat Quantification by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Comparison with 3T MR Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 7529–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Birdsell, L.; Macdonald, N.; Reiman, T.; Clandinin, M.T.; McCargar, L.J.; Murphy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Cancer Cachexia in the Age of Obesity: Skeletal Muscle Depletion Is a Powerful Prognostic Factor, Independent of Body Mass Index. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangelov, B.; Bauer, J.; Kotevski, D.; Smee, R.I. The Use of Alternate Vertebral Levels to L3 in Computed Tomography Scans for Skeletal Muscle Mass Evaluation and Sarcopenia Assessment in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vugt, J.L.A.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.J.; Schippers, H.J.W.; Veen, K.M.; Levolger, S.; de Bruin, R.W.F.; Koek, M.; Niessen, W.J.; IJzermans, J.N.M.; Willemsen, F.E.J.A. Contrast-Enhancement Influences Skeletal Muscle Density, but Not Skeletal Muscle Mass, Measurements on Computed Tomography. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2018, 37, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grande, M.; Rizzo, S.; Nicolino, G.M.; Colombo, I.; Rossi, L.; Manganaro, L.; Del Grande, F. Computed Tomography-Based Body Composition in Patients With Ovarian Cancer: Association With Chemotoxicity and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 718815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powrózek, T.; Dziwota, J.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Nutritional Deficiencies in Radiotherapy-Treated Head and Neck Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, M.; White, K.; Lai, M.; Luo, D.; Bauer, J.D. The Association Between Computed Tomography-Defined Sarcopenia and Outcomes in Adult Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy of Curative Intent for Head and Neck Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 1330–1347.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, M.; White, K.; Brown, C.; Bauer, J.D. Nutritional Status and Skeletal Muscle Status in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Impact on Outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Takemoto, N.; Oya, R.; Inohara, H. Prognostic Impact of Sarcopenia in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Treated with Surgery or Radiation: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganju, R.G.; Morse, R.; Hoover, A.; TenNapel, M.; Lominska, C.E. The Impact of Sarcopenia on Tolerance of Radiation and Outcome in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Receiving Chemoradiation. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 137, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, R.; Modzelewski, R.; Lequesne, J.; Mihailescu, S.; Decazes, P.; Auvray, H.; Benyoucef, A.; Di Fiore, F.; Vera, P.; Dubray, B.; et al. Prognostic Value of Sarcopenia in Patients Treated by Radiochemotherapy for Locally Advanced Oesophageal Cancer. Radiat. Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2020, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardi, P.; Giani, A.; Maggi, G.; Braga, M. Relation between Skeletal Muscle Volume and Prognosis in Rectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Therapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.; Hui, D.; Bidaut, L.; Lem, K.; Del Fabbro, E.; Crane, C.; Reyes-Gibby, C.C.; Bedi, D.; Bruera, E. Relationships among Body Mass Index, Longitudinal Body Composition Alterations, and Survival in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Receiving Chemoradiation: A Pilot Study. J. Pain Symptom Manage 2012, 44, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyotoki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Haraga, J.; Omichi, C.; Ida, N.; Saijo, M.; Nishida, T.; Kusumoto, T.; Masuyama, H. Sarcopenia Is an Important Prognostic Factor in Patients with Cervical Cancer Undergoing Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2018, 28, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsui, K.; Ogata, T.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshio, K.; Kuroda, M.; Hiraki, T.; Kiura, K.; Maeda, Y.; Toyooka, S.; Kanazawa, S. Publisher Correction: Sarcopenia Is Associated with Poor Prognosis after Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.-L.; Wang, H.-H.; Lin, H.-S.; Liu, W.-S.; Chen, L.-M.; Chou, F.-H. Body Composition Early Identifies Cancer Patients with Radiotherapy at Risk for Malnutrition. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2018, 55, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op den Kamp, C.M.H.; De Ruysscher, D.K.M.; van den Heuvel, M.; Elferink, M.; Houben, R.M.A.; Oberije, C.J.G.; Bootsma, G.P.; Geraedts, W.H.; Pitz, C.C.M.; Langen, R.C.; et al. Early Body Weight Loss during Concurrent Chemo-Radiotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, E.; Brown, T.E.; Campbell, L.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Banks, M.D.; Lin, C.Y.; Kenny, L.M.; Bauer, J.D. Impact of Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis on Survival Outcomes for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing Curative-Intent Treatment. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.A.; Elliott, J.A.; McIntyre, T.V.; Barnes, M.E.; Donlon, N.E.; Umair, M.; Gillis, A.E.; Ridgway, P.F. Body Composition Is Associated with Operative and Oncologic Outcomes in the Management of Retroperitoneal and Trunk Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 223, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.-B.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Dai, J.; Xia, L.; Peng, J.; Zhou, F.-X.; Wei, Y.-C.; Shi, H.-P. The Combination of Body Composition Conditions and Systemic Inflammatory Markers Has Prognostic Value for Patients with Gastric Cancer Treated with Adjuvant Chemoradiotherapy. Nutrition 2022, 93, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangl-Kremser, J.; D’Andrea, D.; Vartolomei, M.; Abufaraj, M.; Goldner, G.; Baltzer, P.; Shariat, S.F.; Tamandl, D. Prognostic Value of Nutritional Indices and Body Composition Parameters Including Sarcopenia in Patients Treated with Radiotherapy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bye, A.; Sandmael, J.A.; Stene, G.B.; Thorsen, L.; Balstad, T.R.; Solheim, T.S.; Pripp, A.H.; Oldervoll, L.M. Exercise and Nutrition Interventions in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer during Curative Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, E3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitão, C.; Coutinho, D.; Neves, P.M.; Capelas, M.L.; Pimenta, N.M.; Santos, T.; Mäkitie, A.; Ravasco, P. Protein Intake and Muscle Mass Maintenance in Patients with Cancer Types with High Prevalence of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Support. Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Deng, J.-P.; Long, Z.-Q.; Zhang, W.-W.; Huang, X.; Wen, W.; Guo, L.; He, Z.-Y.; Lin, H.-X. Prognostic Significance of the Skeletal Muscle Index and an Inflammation Biomarker in Patients with Breast Cancer Who Underwent Postoperative Adjuvant Radiotherapy. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Yu, J.I.; Lim, D.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.T.; Hong, J.Y.; Kang, W.K.; Jeong, W.K.; Kim, K.-M. Prognostic Impact of Sarcopenia and Radiotherapy in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer Treated With Anti-PD-1 Antibody. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 701668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Deng, J.-P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, J.-Y.; Chi, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.-G.; He, Z.-Y. Prognostic Significance of the Skeletal Muscle Index and Systemic Inflammatory Index in Patients with Lymph Node-Positive Breast Cancer after Radical Mastectomy. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Oh, D.; Noh, J.M.; Yoon, H.G.; Sun, J.-M.; Kim, H.K.; Zo, J.I.; Shim, Y.M.; Ko, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Feasibility of an Interactive Health Coaching Mobile App to Prevent Malnutrition and Muscle Loss in Esophageal Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: Prospective Pilot Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e28695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Purcell, S.A.; Laviano, A. Nutrition Interventions to Treat Low Muscle Mass in Cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Thyagiarajan, M.S.; Hunt, L.P.; Shield, J.P.H.; Stevens, M.C.G.; Crowne, E.C. Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Childhood Survivors of Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is Associated with Lipodystropic and Sarcopenic Phenotypes. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Noguchi, M.; Fukano, R.; Ueda, T.; Taguchi, S.; Yoshimaru, K.; Namie, M.; Shimokawa, M.; Okamura, J. Sarcopenia and Obesity in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Leukemia/Lymphoma: A Report from a Single Institution. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenc, A.; Hamilton-Shield, J.; Perry, R.; Stevens, M.; CTYA HSCT Adipose and Muscle Late Effects Working Group. Body Composition after Allogeneic Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation/Total Body Irradiation in Children and Young People: A Restricted Systematic Review. J. Cancer Surviv. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 624–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Armenian, S.H.; Bhandari, R.; Lee, K.; Ness, K.; Putt, M.; Lindenfeld, L.; Manoukian, S.; Wade, K.; Dedio, A.; et al. Exercise Training and NR Supplementation to Improve Muscle Mass and Fitness in Adolescent and Young Adult Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial {1}. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, M.L.; McDonald, G.B.; Kida, A.; Hingorani, S.; Armenian, S.H.; Cooke, K.R.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Baker, K.S. National Cancer Institute-National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Consortium First International Consensus Conference on Late Effects after Pediatric Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Long-Term Organ Damage and Dysfunction. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011, 17, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, E.; Skerget, M.; Sever, M.; Zupan, I.P.; Ogrinec, M.; Ursic, B.; Kos, N.; Cernelc, P.; Zver, S. Feasibility and Safety of Exercise Training and Nutritional Support Prior to Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Haematologic Malignancies. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.L.; Tolfrey, K.; Jenney, M.; Elson, R.; Stewart, C.; Moss, A.D.; Cornish, J.M.; Stevens, M.C.G.; Crowne, E.C. Combined Resistance and Aerobic Exercise Intervention Improves Fitness, Insulin Resistance and Quality of Life in Survivors of Childhood Haemopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation with Total Body Irradiation. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.J.; Hellerstein, M.; Orwoll, E.; Cummings, S.; Cawthon, P.M. D3 -Creatine Dilution and the Importance of Accuracy in the Assessment of Skeletal Muscle Mass. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Tool (Reference) |
|---|---|
| Case finding | SARC-F questionnaire [42] Ishii screening tool [43] |
| Skeletal muscle strength | Grip strength [44]; Chair stand test (chair rise test) (American Academy of Orthotists & Prosthetists) [45] |
| Skeletal muscle mass or skeletal muscle quality | Appendicular skeletal muscle mass by Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry [46]; Whole-body skeletal muscle mass or appendicular skeletal muscle mass predicted by Bioelectrical impedance analysis [47]; Lumbar muscle cross-sectional area by CT or MRI [48,49] |
| Physical performance | Gait speed (NIH Toolbox 4), Meter Walk Gait Speed Test (https://www.nia.nih.gov/research/labs/leps/short-physical-performance-battery-sppb) °; Short physical performance battery (Short Physical Performance Battery Protocol, https://research.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/prove/documents/assessors/outcomeMeasures/SPPB_Protocol.pdf); Timed-up-and-go test [43]; 400-m walk or long-distance corridor walk [44] |
| Skeletal Muscle Index (SMI) | Skeletal Muscle Mean Radiation Attenuation (SMRA) * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | Man | |||
| Prado et al. [53] | ≤38.5 cm2/m2 | ≤52.4 cm2/m2 | ||
| Martin et al. [55] | <41 cm2/m2 | <43 cm2/m2 if BMI < 25 | <53 cm2/m2 if BMI ≥ 25 | |
| Van der Werf et al. [48] | <29 Hounsfield Units | |||
| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| What is sarcopenia? How is it defined? |
|
| What are the causes and mechanisms leading to sarcopenia? |
|
| What are the clinical, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms underlying reduced therapeutic response? |
|
| Why is sarcopenia different from cachexia and myosteatosis? |
|
| What is sarcopenic obesity? Is it worse than sarcopenia? Why? |
|
| How to screen and diagnose sarcopenia? |
|
| What is the impact of sarcopenia in patients treated with radiotherapy? |
|
| What is the impact of radiotherapy on sarcopenia? |
|
| What is the impact of sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis on radiotherapy outcomes? |
|
| Can sarcopenia impact treatment modulation in patients who are candidates for radiotherapy? |
|
| Can we improve the prognostic impact of sarcopenia by including it in predictive models? |
|
| Is it possible to prevent sarcopenia before radiotherapy? |
|
| Is it possible to treat sarcopenia before and during radiotherapy? |
|
| Should we screen for and treat sarcopenia in radiation-treated pediatric patients too? |
|
| Which future studies on sarcopenia in the radiotherapy setting are needed? |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medici, F.; Rizzo, S.; Buwenge, M.; Arcelli, A.; Ferioli, M.; Macchia, G.; Deodato, F.; Cilla, S.; De Iaco, P.; Perrone, A.M.; et al. Everything You Always Wanted to Know about Sarcopenia but Were Afraid to Ask: A Quick Guide for Radiation Oncologists (impAct oF saRcopeniA In raDiotherapy: The AFRAID Project). Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8513-8528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110671
Medici F, Rizzo S, Buwenge M, Arcelli A, Ferioli M, Macchia G, Deodato F, Cilla S, De Iaco P, Perrone AM, et al. Everything You Always Wanted to Know about Sarcopenia but Were Afraid to Ask: A Quick Guide for Radiation Oncologists (impAct oF saRcopeniA In raDiotherapy: The AFRAID Project). Current Oncology. 2022; 29(11):8513-8528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110671
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedici, Federica, Stefania Rizzo, Milly Buwenge, Alessandra Arcelli, Martina Ferioli, Gabriella Macchia, Francesco Deodato, Savino Cilla, Pierandrea De Iaco, Anna Myriam Perrone, and et al. 2022. "Everything You Always Wanted to Know about Sarcopenia but Were Afraid to Ask: A Quick Guide for Radiation Oncologists (impAct oF saRcopeniA In raDiotherapy: The AFRAID Project)" Current Oncology 29, no. 11: 8513-8528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110671
APA StyleMedici, F., Rizzo, S., Buwenge, M., Arcelli, A., Ferioli, M., Macchia, G., Deodato, F., Cilla, S., De Iaco, P., Perrone, A. M., Strolin, S., Strigari, L., Ravegnini, G., Bazzocchi, A., & Morganti, A. G. (2022). Everything You Always Wanted to Know about Sarcopenia but Were Afraid to Ask: A Quick Guide for Radiation Oncologists (impAct oF saRcopeniA In raDiotherapy: The AFRAID Project). Current Oncology, 29(11), 8513-8528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110671









