Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019 and Analysis Using an Age–Period–Cohort Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in China from 1990 to 2019
3.2. Change in the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in China from 1990 to 2019
3.3. Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019
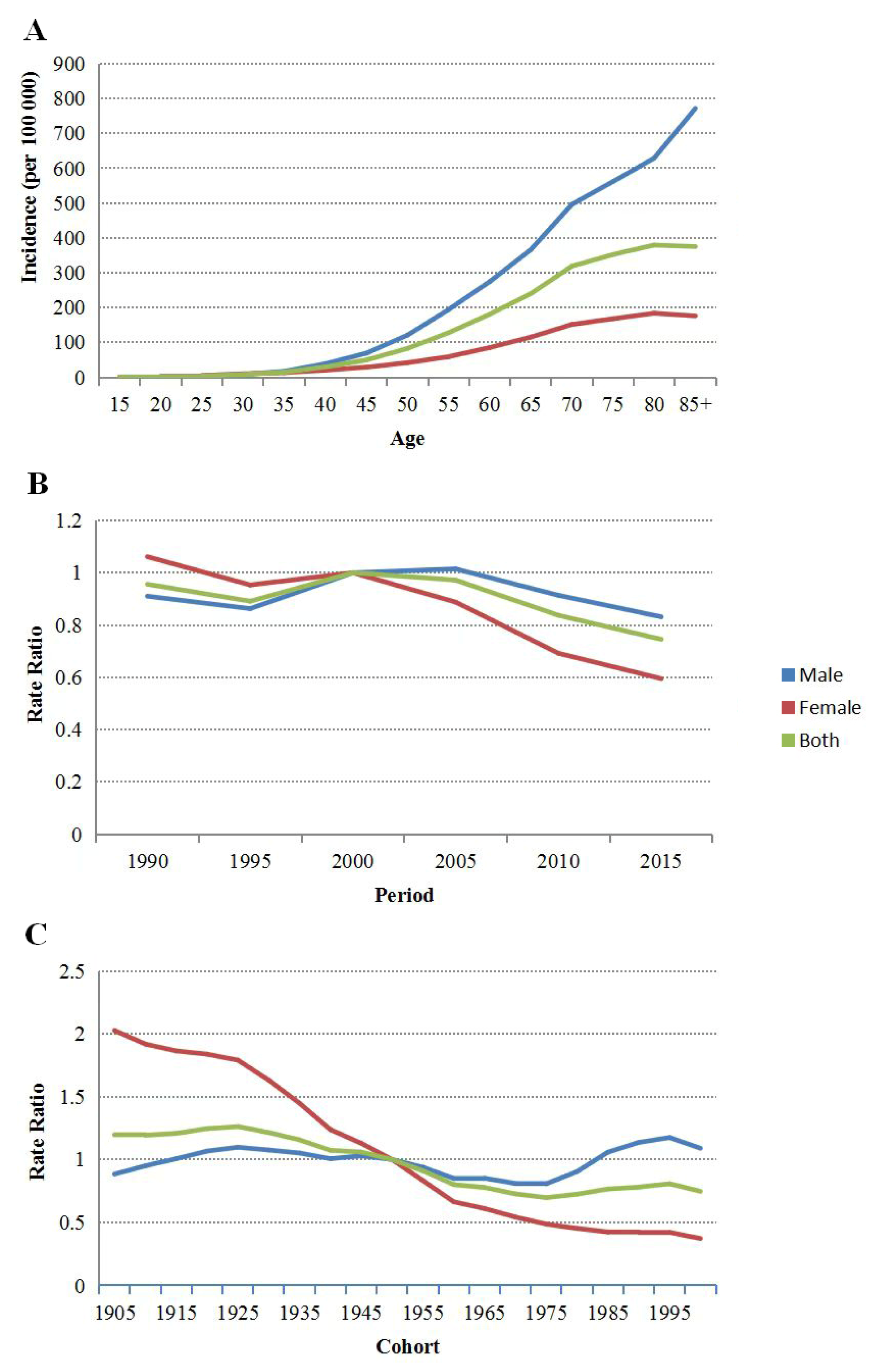
3.4. Age–Period–Cohort Model Analysis of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-populations (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Shen, M.; Xia, R.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, H.; Wei, W.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W. The long-term population impact of endoscopic screening programmes on disease burdens of gastric cancer in China: A mathematical modelling study. J. Theor. Biol. 2020, 484, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Song, G.; Li, B.; Zhao, D.; Hua, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hao, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. Effectiveness of one-time endoscopic screening programme in prevention of upper gastrointestinal cancer in China: A multicentre population-based cohort study. Gut 2021, 70, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, S.; Li, H.; Zou, K.; Li, N.; Tian, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Esophageal cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and screening. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 33, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdollahi, M.; Abedi, P.; Abedi, A.; Abolhassani, H.; et al. Five insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1135–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Fay, M.P.; Feuer, E.J.; Midthune, D.N. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, T.R. An alternative approach to statistical analysis. J. Chronic Dis. 1985, 38, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, T.R. The estimation of age, period and cohort effects for vital rates. Biometrics 1983, 39, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.S.; Check, D.P.; Anderson, W.F. A web tool for age–period–cohort analysis of cancer incidence and mortality rates. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Li, M.; Lei, S.; Zhuang, G.; Wei, W. Gastric and esophageal cancer in China 2000 to 2030: Recent trends and short-term predictions of the future burden. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.S.; Gu, X.Y.; Li, X.T.; Zhang, S.W.; Zeng, H.M.; Sun, K.X.; Zhou, X.N.; Xia, C.F.; Yang, Z.X.; Li, H.; et al. Analysis on the trend of cancer incidence and age change in cancer registry areas of China, 2000 to 2014. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 52, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical Communique. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjgb/ndtjgb/ (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Fang, E.F.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Jahn, H.J.; Li, J.; Ling, L.; Guo, H.; Zhu, X.; Preedy, V.; Lu, H.; Bohr, V.A.; et al. A research agenda for aging in China in the 21st century. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhan, J.; Fu, H. Trends in Smoking Prevalence and Intensity between 2010 and 2018: Implications for Tobacco Control in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Zhao, L.Y.; Fang, H.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Ju, L.H.; Xu, X.L.; Li, S.J.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.M. Current situation of drinking behaviors of adults aged 18 and over in China. Food Nutr. China 2021, 27, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.; Obi, K.O.; Rubenstein, J.H. The synergistic effects of alcohol and tobacco consumption on the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Huang, K.Y.; Yang, L. Analysis on health literacy and its influencing factors about cancer prevention and control among urban residents in Guangxi. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2019, 23, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipponen, P.; Correa, P. Delayed rise in incidence of gastric cancer in females results in unique sex ratio (M/F) pattern: Etiologic hypothesis. Gastric Cancer 2002, 5, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackaman, C.; Tomay, F.; Duong, L.; AbdolRazak, N.B.; Pixley, F.J.; Metharom, P.; Nelson, D.J. Aging and cancer: The role of macrophages and neutrophils. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.M.; Li, H.; Sun, D.Q.; He, S.Y.; Yu, Y.W.; Li, J.; Chen, H.D.; Shi, J.F.; Ren, J.S.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer screening in China: The current status, challenges, and suggestions. Cancer Lett. 2021, 506, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Dai, M.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, N. Cancer trends in China. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 40, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Kong, L.; Wu, F.; Bai, Y.; Burton, R. Preventing chronic diseases in China. Lancet 2005, 366, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Ji, J.S.; Zou, X.; Xia, C.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003–15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e555–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, P.E.; Strasser-Weippl, K.; Lee-Bychkovsky, B.L.; Fan, L.; Li, J.; Chavarri-Guerra, Y.; Liedke, P.E.R.; Pramesh, C.S.; Badovinac-Crnjevic, T.; Sheikine, Y.; et al. Challenges to effective cancer control in China, India, and Russia. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 489–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Kamangar, F.; Fan, J.H.; Abnet, C.C.; Sun, X.-D.; Johnson, L.L.; Gail, M.H.; Dong, Z.W.; Yu, B.; et al. Total and cancer mortality after supplementation with vitamins and minerals: Follow-up of the Linxian General Population Nutrition Intervention Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Q.; Zuo, T.T. Initial effect achievement of battles on upper digestive tract cancer in China. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 51, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Hao, C.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.K.; Guo, L.W.; Quan, P.L.; Germain, P.; et al. Effectiveness evaluation of organized screening for esophageal cancer: A case-control study in Linzhou city, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Hao, C.-Q.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.K.; Guo, L.W.; Quan, P.L.; Zhao, N.; et al. Effectiveness of endoscopic gastric cancer screening in a rural area of Linzhou, China: Results from a case-control study. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Wei, W.Q. A new transition of the screening, early diagnosis and early treatment project of the upper gastrointestinal cancer: Opportunistic screening. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 53, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Kakiuchi, N.; Yoshizato, T.; Nannya, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Shiozawa, Y.; Sato, Y.; Aoki, K.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Age-relatedremodelling of oesophageal epithelia by mutated cancer drivers. Nature 2019, 565, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, P.; Islami, F.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Freedman, N.D.; Kamangar, F. Gastric cancer: Descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collatuzzo, G.; Pelucchi, C.; Negri, E.; López-Carrillo, L.; Tsugane, S.; Hidaka, A.; Shigueaki Hamada, G.; Hernández-Ramírez, R.U.; López-Cervantes, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; et al. Exploring the interactions between Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection and other risk factors of gastric cancer: A pooled analysis in the Stomach cancer Pooling (StoP) Project. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.M.; Zong, Y.N.; Cao, S.M.; Xu, R.H. Current cancer situation in China: Good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeing H, Epidemiological research in stomach cancer: Progress over the last ten years. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 117, 133–143. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, L.S.; Wang, K.B. Secular trends in salt and soy sauce intake among Chinese adults, 1997–2011. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.J.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, M.G.; Zhao, Z.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, L.M. Vegetable and Fruit Consumption among Chinese Adults and Associated Factors: A Nationally Representative Study of 170,847 Adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.T.; Su, C.; Ouyang, Y.F.; Zhang, B. Trends of vegetables and fruits consumption among Chinese adults aged 18 to 44 years old from 1991 to 2011. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howson, C.P.; Hiyama, T.; Wynder, E.L. The decline in gastric cancer: Epidemiology of an unplanned triumph. Epidemiol. Rev. 1986, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Cai, P.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, T.P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Gu, Y.L.; Wei, L.Q.; Yan, C.W.; Jin, G.F. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Meng, L.H.; Chiolero, A.; Ma, C.W.; Xi, B. Trends in smoking prevalence and attributable mortality in China, 1991–2011. Prev. Med. 2016, 93, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, J.L.; Steck, S.E.; Bradshaw, P.T.; Trivers, K.F.; Abrahamson, P.E.; Engel, L.S.; He, K.; Chow, W.-H.; Mayne, S.T.; Risch, H.A.; et al. Dietary intake of flavonoids and oesophageal and gastric cancer: Incidence and survival in the United States of America (USA). Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Kong, L.Z.; Zhao, W.H.; Wan, X.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, L.C.; Koplan, J.P. Emergence of chronic non-communicable diseases in China. Lancet 2008, 372, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, P.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Deng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Jin, D.; et al. Prevalence and Ethnic Pattern of Diabetes and Prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA 2017, 317, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Y.; Lu, J.M.; Weng, J.P.; Jia, W.P.; Ji, L.N.; Xiao, J.Z.; Shan, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.M.; Ji, Q.H.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes among Men and Women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Disease Control and Prevention of National Health and Family Planning Commission. In Report on Chinese Residents’ Chronic Diseases and Nutrition 2015; Peking: People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1–116.
- Tan, X.D.; Liu, X.X.; Shao, H.Y. Healthy China 2030: A Vision for Health Care. Value Health Reg. Issues 2017, 12, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Trend | Year | APC (95% CI) | p-Value | AAPC (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | |||||
| Male | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | 0.68 (0.32, 1.04) | <0.05 | 1.93 (1.71, 2.12) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 6.96 (6.28, 7.64) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2017 | 0.22 (0.07, 0.37) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2017–2019 | 3.22 (0.79, 5.70) | <0.05 | ||
| Female | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | 0.21 (−0.03, 0.44) | 0.09 | 0.44 (0.25, 0.65) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 4.43 (3.97, 4.89) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2015 | −2.31 (−2.45, −2.16) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2015–2019 | 2.58 (1.96, 3.21) | <0.05 | ||
| Both | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | 0.52 (0.25, 0.80) | <0.05 | 1.42 (1.23, 1.59) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 6.07 (5.54, 6.60) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2016 | −0.49 (−0.63, −0.36) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2016–2019 | 2.66 (1.65, 3.68) | <0.05 | ||
| ASIR | |||||
| Male | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | −1.17 (−1.55, −0.78) | <0.05 | −0.56 (−0.81, −0.31) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 4.11 (3.40, 4.82) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2017 | −2.44 (−2.59, −2.28) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2017–2019 | 0.15 (−2.34, 2.69) | 0.90 | ||
| Female | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | −1.71 (−1.95, −1.47) | <0.05 | −2.07 (−2.20, −1.94) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 2.09 (1.63, 2.56) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2015 | −5.14 (−5.28, −4.99) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2015–2019 | −0.49 (−1.12, 0.16) | 0.13 | ||
| Both | |||||
| Trend I | 1990–1998 | −1.32 (−1.60, −1.03) | <0.05 | −1.12 (−1.21, −0.94) | <0.05 |
| Trend II | 1998–2004 | 3.48 (2.94, 4.02) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend III | 2004–2016 | −3.30 (−3.40, −3.11) | <0.05 | ||
| Trend IV | 2016–2019 | −0.33 (−1.34, 0.70) | 0.51 |
| Null Hypothesis | Male | Female | Both | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | df | p-Value | χ2 | df | p-Value | χ2 | df | p-Value | |
| Net drift = 0 | 4.12 | 1 | <0.05 | 282.43 | 1 | <0.05 | 76.92 | 1 | <0.05 |
| All age deviations = 0 | 2156.5 | 13 | <0.05 | 772.96 | 13 | <0.05 | 3113.23 | 13 | <0.05 |
| All period deviations = 0 | 240.48 | 4 | <0.05 | 164.66 | 4 | <0.05 | 350.02 | 4 | <0.05 |
| All cohort deviations = 0 | 83.19 | 18 | <0.05 | 109.23 | 18 | <0.05 | 123.94 | 18 | <0.05 |
| All period RR = 1 | 251.47 | 5 | <0.05 | 492.88 | 5 | <0.05 | 474.64 | 5 | <0.05 |
| All cohort RR = 1 | 131.49 | 19 | <0.05 | 1027.18 | 19 | <0.05 | 511.54 | 19 | <0.05 |
| All local drifts = net drift | 77.05 | 15 | <0.05 | 99.69 | 15 | <0.05 | 113.61 | 15 | <0.05 |
| Net drift (95% CI) | −0.21 (−0.39, −0.02) | −2.25 (−2.51, −1.99) | −0.83 (−1.02, −0.64) | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Guo, Z.; Huang, S.; Ma, J.; Xiang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W. Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019 and Analysis Using an Age–Period–Cohort Model. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7470-7481. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100588
Lin Y, Guo Z, Huang S, Ma J, Xiang Z, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Chen W. Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019 and Analysis Using an Age–Period–Cohort Model. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7470-7481. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100588
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yongtian, Zengqing Guo, Shuna Huang, Jingyu Ma, Zhisheng Xiang, Yongying Huang, Yan Zhou, and Wanqing Chen. 2022. "Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019 and Analysis Using an Age–Period–Cohort Model" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7470-7481. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100588
APA StyleLin, Y., Guo, Z., Huang, S., Ma, J., Xiang, Z., Huang, Y., Zhou, Y., & Chen, W. (2022). Time Trend of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Incidence in China from 1990 to 2019 and Analysis Using an Age–Period–Cohort Model. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7470-7481. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100588




