Abstract
Circulating epithelial tumor cells (CETC) are considered to be responsible for the formation of metastases. Therefore, their importance as prognostic and/or predictive markers in breast cancer is being intensively investigated. Here, the reliability of single cell expression analyses in isolated and collected CETC from whole blood samples of patients with early-stage breast cancer before and after radiotherapy (RT) using the maintrac® method was investigated. Single-cell expression analyses were performed with qRT-PCR on a panel of selected genes: GAPDH, EpCAM, NANOG, Bcl-2, TLR 4, COX-2, PIK3CA, Her-2/neu, Vimentin, c-Met, Ki-67. In all patients, viable CETC were detected prior to and at the end of radiotherapy. In 7 of the 9 (77.8%) subjects examined, the CETC number at the end of the radiotherapy series was higher than before. The majority of genes analyzed showed increased expression after completion of radiotherapy compared to baseline. Procedures and methods used in this pilot study proved to be feasible. The method is suitable for further investigation of the underlying molecular biological mechanisms occurring in cells surviving radiotherapy and possibly the development of radiation resistance.
1. Introduction
In breast cancer patients, adjuvant radiotherapy has been shown to reduce not only the risk of locoregional recurrence but also the risk of distant metastases, thus to reducing breast cancer mortality (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative, Darby [1]). Adjuvant irradiation destroys subclinical disease in the breast and possibly in locoregional lymph nodes, which is believed to prevent seeding of tumor cells from persistent reservoirs of locoregional disease and thus avoid metastasis formation.
Tumor cells circulating in the bloodstream (CTC) are considered to be responsible for the formation of metastases [2,3]. Therefore, their importance as prognostic and/or predictive markers in breast cancer is being intensively investigated [4,5,6,7,8,9,10].
The determination of circulating epithelial tumor cells (CETC) promises real-time monitoring of treatment effects—including effects of radiotherapy—as well as longitudinal monitoring of treatment response and early detection of tumor relapse [11]. In patients with metastatic breast cancer, CTC have been proposed as prognostic biomarkers [12,13]. To date, the method has, however, not been implemented in routine clinical practice as a basis to guide treatment decisions, which is partly due to a lack of standardization in analysis approaches [14,15].
Next to the number of CETC, the molecular characterization of CETCs is crucial to relate molecular characteristics of individual CETC to molecular characteristics of the primary tumor, but also to follow the fate of circulating tumor cells during treatment. Equally important is the description of relevant genetic changes that may be caused by treatment-related effects in CETC. However, due to the relative rarity and heterogeneity of circulating tumor cells, their isolation and characterization at the molecular and genetic level is challenging and technically difficult [16,17,18].
In this study the maintrac® method was used to analyze changes in the number of CETC before and after adjuvant radiotherapy in a group of prospectively enrolled patients with breast cancer. The study further investigated changes of molecular characteristics and expression of a panel of selected genes of isolated CETCs before and after the radiotherapy series. The study demonstrates the reproducibility of the method for single cell expression profiling during monitoring of the influence of radiotherapy in preparation of a larger study that will allow inclusion of a higher number of patients.
2. Materials and Methods
The study is designed as a biology-driven translational trial to investigate the feasibility of isolating and collecting circulating epithelial tumor cells from whole blood samples before and after radiotherapy using the maintrac® method, and to analyze possible up- and/or down-regulation of a panel of selected cancer-related genes.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
Patients with histologically-proven, primarily non-metastasized breast cancer were eligible if adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery was planned. Other eligibility criteria were age ≥ 18 y, WHO performance status ≤ 2, no severe concomitant disease, and in particular no additional tumor diseases. There were no restrictions with respect to preceding systemic treatments like (neo)adjuvant cytostatic or antihormonal drugs if indicated according to current guidelines. All patients gave informed consent prior inclusion in the study. The trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Hospital Jena (1 September 2012) under No. 0921-08/02 and is registered (2 May 2019) at trials.gov under NCT03935802.
2.2. Study Procedures
Routine clinical parameters were prospectively collected, including baseline history, breast cancer specific procedures and treatments, as well as radiotherapy. Patients were prospectively followed for local control, metastasis-free survival, and overall survival for a minimum of 5 years after diagnosis.
2.3. Radiotherapy
All patients received adjuvant radiotherapy according to current guidelines [19]. The breast and chest wall were irradiated with a 3D-conformal technique using tangential opposing fields to a total absorbed dose of 50.0 Gy in 25 fractions. In cases where a boost was indicated, the tumor bed received an additional dose of 16.0 Gy in 8 fractions.
2.4. Sample Processing and Analysis
Blood samples were drawn as part of routine laboratory checks on the first and the last day of radiotherapy, where 10 mL blood (EDTA-tube, Sigma-Aldrich Co., Munich, Germany) were additionally taken for analysis within this trial.
Samples were processed for picking viable, epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-positive cells and analysis of selected messenger ribonucleic acids (mRNAs), which are typically found in breast cancer cells, as detailed in Figure 1.
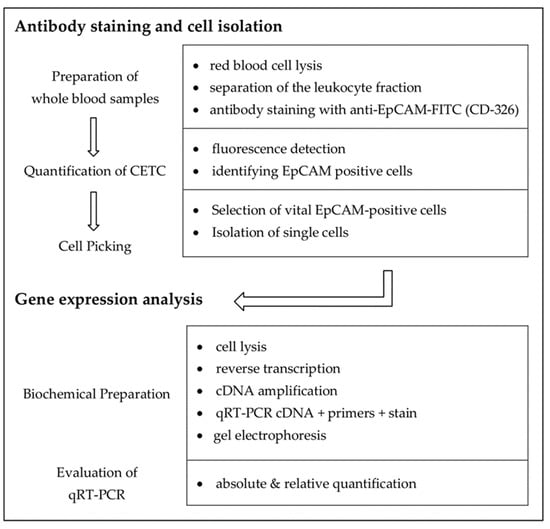
Figure 1.
Workflow of antibody staining, cell isolation, and determination of mRNA contents.
Each sample was analyzed with respect to:
- quantitative immunofluorescence detection of viable CETC and
- quantitative gene expression analysis of single CETC by qRT-PCR to analyze for differential expression of selected genes.
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay and Quantification
Isolation of individual cells from whole blood was carried out by employing a method previously described by Pachmann et al. [11,17,20]. Briefly, 1 mL whole blood drawn into Sarstedt EDTA tubes (SARSTEDT AG & Co., Nümbrecht, Germany) for anti-coagulation was mixed with 10 mL lysis buffer (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) for erythrocyte lysis followed by centrifugation at 300 rcf to separate the cellular fraction from the plasma fraction of blood samples. The cellular fraction was re-suspended in 500 µL phosphate buffered salt solution (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) and incubated with 20 µL of master mix (120 µL EpCAM-FITC, 100 µL 10% BSA, 4 µL 7AAD (500 µg/mL), and 776 µL PBS-EDTA) (fluoroisothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody (CD-326, Miltenyi, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) and 7-Aminoactinomycin D (7AAD, Sigma-Aldrich Co., Taufkirchen, Germany)). Finally, 20 μL of this suspension were transferred to a 96-well plate (Eppendorf twin.tec PCR plate 96, Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany) and mixed with a PE-formalin solution (10% Formalin solution and PBS-EDTA 1:1).
After 1 h of sedimentation, immunofluorescence detection was initiated using a microscope-based imaging platform for fully automated image acquisition (ScanR Olympus IX81 ZDC, Olympus GmbH Hamburg, Germany). Each well was scanned by taking 94 individual images using a 20×-objective and analyzed for the presence of EpCAM-positive cells. Due to the different emission intensities of the markers (515–545 nm for FITC and 635–655 nm for 7AAD), objects with exclusively EpCAM-positive surface staining (viable cells) and combined EpCAM- and 7AAD-stained avital cells could be automatically detected. In addition to the automatic detection and classification (viable vs. nonviable) of cells, up to 100 EpCAM-positive cells per sample were controlled visually in a randomized fashion for accuracy of classification. From the number of viable EpCAM-positive cells detected per well, the number of cells/mL was calculated.
We additionally examined blood samples of 9 healthy subjects without tumor disease as a control group. In none of these subjects, EpCAM-positive cells were detected.
2.6. Single Cell Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
From an aliquot of the above stained cells, single EpCAM-positive cells were separated from other white blood cells using a semi-automated fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Hamburg, Germany). A drop of cell suspension containing cells of possible tumor origin was placed on a microscope slide, and EpCAM-positive cells were detected under the microscope (Figure 2 and Figure 3). To only collect viable cells, cells with morphologically intact cell membrane and nucleus as well as an intense EpCAM signal were selected. The cell suspension was prepared to allow aspiration of only one cell into the capillary. Selected cells were individually aspirated semi-manually with an MMI CellEctor (MMI, Eching, Germany) into 100 nL buffer solution into a glass capillary and transferred into a 100 µL PCR cup, making sure that only this one cell was deposited before being stored individually at −18 °C.

Figure 2.
High-performance stereomicroscope and preparation platform MMI CellEctor plus™ with a three-dimensionally-controllable micromanipulator.
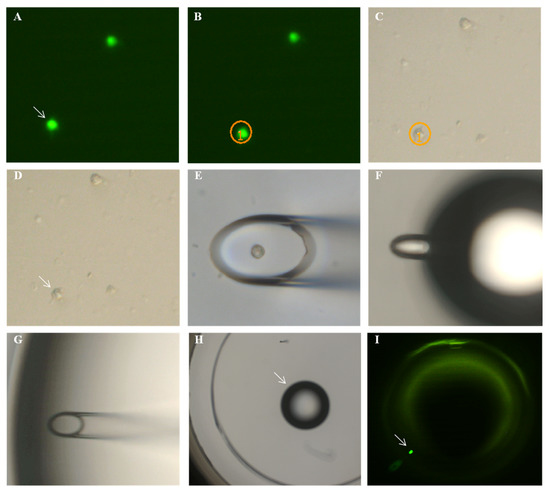
Figure 3.
Steps of micromanipulation: (A) the cell to be picked is located in fluorescent light and (B) is circled by the software. (C,D) The cell is located in transmitted light. (E) The opening of the capillary is positioned over the cell and aspirates the cell. (F) The droplet with the cell is blown out from the capillary (diameter 25 µm), and (G) it is confirmed that the cell is no longer inside the capillary but that it is released with the (H) droplet and can be detected (I) in fluorescent light.
Cell lysis and subsequent cDNA amplification were performed using the whole transcriptome amplification kit according to protocol A of the manufacturer (CellAmp™ Whole Transcriptome amplification kit (Real Time) TaKaRa Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan). cDNA amplification was performed in 21 cycles using a Mastercycler® (Eppendorf realplex4, Mastercycler eppgradient S, Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany). The resulting 25 µL of cDNA amplification reaction mix was stored at −20 °C.
Subsequently, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed in 96 well plates using the LightCyclerR 480 SYBRGreen 1 Master Kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). A known concentration of beta-actin was used in control reactions to calculate absolute values [21]. Following the manufacturer´s instructions, 1 µL of amplified cDNA was pipetted into wells of a 96-well plate, 19 µL of master mix were added, and the sample was cooled to 4 °C. Amplified cDNA from one cell was tested for specific mRNAs in eight separate wells containing one primer pair each. qRT-PCR reactions were performed for 40 cycles. A melting curve was generated for quality control. Absolute quantification and analysis of melting curves were undertaken using the qRT-PCR machine’s software package (Eppendorf realplex4, Mastercycler eppgradient S, Mastercycler ep realplex 2.0, Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany). The resulting gene product was verified by gel electrophoresis. Sequences of the 11 selected primer pairs are summarized in Table 1. All primers were produced individually (Jena Bioscience GmbH, Jena, Germany). Negative control experiments were undertaken using 1 µL RNase-free water.

Table 1.
Gene expression analysis and respective primer sequences.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Single cell analysis is associated with variability of the measured values. The mRNA amount of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in our study showed a large variability between the single cells as expected. Due to the biology of cellular transcription, data normalization using housekeeping genes is not meaningful when quantifying single cells [22]. The absolute values of the cDNA concentrations of the 8 cells per patient as well as the measurement time points were mapped as absolute values. The quotient was then calculated from the values of the 8 cells collected prior to and after radiotherapy for all genes serving as a measure of gene activity and compared to the mean values.
In all examined cells, GAPDH-mRNA could be detected with at least 7.20 copies/μL. This result confirmed selected CETC to be viable cells. We used the SPSS21 software package (IBM Statistics, SPSS Inc., New York, NY, USA) for comparative statistics.
3. Results
Nine eligible patients were included in the trial between September 2011 and September 2012 [23]. All but one patient exhibited estrogen receptor positive tumors and had already received endocrine treatment during the period of radiotherapy. Estrogen receptor positivity was not determined in the circulating tumor cells. The mean follow-up was in 88 months (38 months–100 months). During follow-up, two patients experienced a second tumor diagnosis: patient 2 was diagnosed with colon carcinoma 84 months after radiotherapy, patient 5 suffered from a local relapse, and patient 6 was diagnosed with malignant melanoma 17 months after radiotherapy for breast cancer. All patients were alive at the time of the last visit. Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Patient characteristics.
3.1. Changes in CETC Number
In all patients, viable CETC were detected prior to and at the end of radiotherapy (detection rate: 100%) and the cell number was determined. Blood samples from nine healthy subjects, who volunteered as a control group without tumor disease, were additionally examined. In none of these subjects, EpCAM-positive cells were detected.
In seven of the nine (77.8%) subjects investigated, the CETC number was higher in the blood sample drawn at the end of the radiotherapy series as compared to the CETC number prior to the start of radiotherapy (Table 3). Statistical evaluation showed a significantly increased number of viable CETC at the end of the radiotherapy series compared to the CETC number before start of radiotherapy (p = 0.009). The fold increase (quotient) was moderate as compared to that observed in patients with primary breast cancer under adjuvant chemotherapy (6).

Table 3.
Mean number of CETC.
3.2. Gene Expression Profiles of Single Circulating Epithelial Cells
In two patients, isolation of single cells was not possible due to logistical reasons. In the remaining seven patients, a maximum of eight vital CETC per patient were picked prior to as well as after the end of the radiotherapy series for gene expression analysis. As shown in the materials and methods section, the approach for picking individual cells ensured that only the targeted cell was aspirated and deposited. Previous studies showed that cells isolated in this way carry the same mutations as their corresponding primary tumor and also express its tumor tissue characteristics [17,24].
The expression of a panel of selected genes, which encode for proteins involved in processes necessary for metastatic spread, such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, adhesion, and apoptosis, were analyzed in these individually isolated cells. A total of 1505 individual gene copy numbers were measured (copy number > 0/μL) from 131 EpCAM-positive cells most probably of tumor origin. Each individual cell could be assigned a defined copy number of the respective gene.
A typical example of the heterogeneity in upregulation of gene expression of 11 genes in eight cells from Pat. ID 2 is shown in Table 4. In some cells, several genes were highly upregulated, e.g., cell 6: GAPDH, BCL-2, Cox2, PIK3CA, and TLR 4 whereas EpCAM, NANOG, Her2, Vimentin c-Met, and Ki-67 were only moderately upregulated. In cell 7, GAPDH, Cox-2, and TLR 4 were strikingly highly upregulated.

Table 4.
Copy numbers of Pat. ID 2.
Relative quantification showed that patients exhibiting an increased cell number under radiotherapy also showed overexpression of almost all genes investigated (Table 5). The two patients without an increase in CETC numbers (Pat. ID 4 and ID 5) showed the lowest relative gene expression apart from NANOG in patient ID 4. The extent of increase of expression in selected genes differed considerably between patients.

Table 5.
Quotient (Q) of the CETC number (first row) and quotient of the copy number of genes before and after the end of irradiation.
A decrease of expression for several genes was observed only in one patient whose CETC number decreased after radiotherapy (Pat. ID 4) in comparison to the CETC number prior to radiotherapy.
Since the number of copies in patients ID 2 and ID 4 varied particularly strongly for some genes (especially BCL2, HER2, Vimentin), they were censored in the statistical analysis. Considering the extreme values, a symmetrical distribution of the mean values could be achieved (Shapiro–Wilk test: p ≤ 0.05, boxplot diagram of the mean value difference symmetrical). It was possible to use the T-test for connected samples.
The different expression level of the single cells is shown in the example of NANOG for all patients in Figure 4. The variability of expression between individual cells in the patients is shown. The copy number amplitudes are higher after RT, indicating an increase in gene expression.
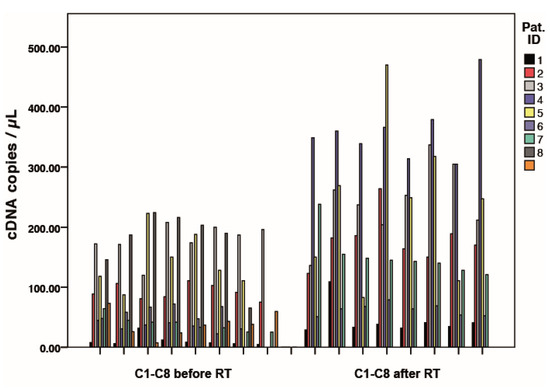
Figure 4.
Results of NANOG expression analysis for eight single cells (C1-8) before and after radiotherapy for all patients. Each bar represents the expression of a single tumor cell/patient.
The distribution of the mRNA copies for each gene is shown below in the box plot diagrams (Figure 5). Although the measured values varied, the mean values of the mRNA copy numbers are higher after irradiation in all the genes investigated. Except for PIK3CA, ERBB2, and Vimentin, statistically significant changes in gene activity could be detected.
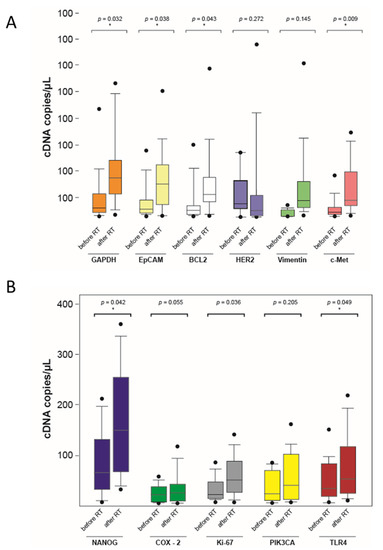
Figure 5.
Mean mRNA copy number before and after the end of radiotherapy in a boxplot diagram (* significant, p < 0.05) (A,B).
All results of the RT-PCR were verified by gel-electrophoresis where the corresponding gene product could be detected.
4. Discussion
Potential changes of the tumor cell activation during the course of a disease render longitudinal analysis of circulating tumor cells promising for a more complete understanding of the complex processes underlying treatment response or relapse. Consequently, CETC numbers and their relevance as prognostic or predictive factors were investigated in numerous studies [4,11,25,26]. Further characterization of CETC on a molecular and genetic level may reveal their potential role as an indicator of response to treatment [27,28,29]. Molecular characterization of CETC is, however, technically challenging as is their unequivocal mapping with cells of the primary tumor or even metastases. Hence, following the fate of tumor (sub-)clones during the course of disease is not currently possible [30].
Therefore, in this study, radiation-related changes in CETC numbers after curative breast-conserving surgery and alterations in expression of selected genes in individual EpCAM-positive CETC were prospectively investigated using the maintrac® method.
Since this was a feasibility study, both the number of patients included and the number of cells studied were considered sufficient. The number of patients included so far allows a first description of the observed effects, but is not high enough for definite conclusions. Confounding factors could influence CETC counts and gene expression profiles in addition to radiotherapy.
4.1. Comparison of Methods for Detection of CETC
Different approaches exist for the identification and characterization of circulating tumor cells, where genetic and immunological methods need to be distinguished. A frequently used enrichment method is immunomagnetic separation using the CellSearch™ system. It has been approved by the FDA as a tool for the detection of CTC in metastatic breast cancer [31,32,33]. The CellSearch™ system variably defines a threshold of 1–5 cells/7.5 mL blood (≥0.67 cells/mL blood) in patients with primary or metastasized tumors as a sign of poor prognosis [34,35].
In contrast to the method used in this work, the CellSearch™ system aspirates the blood into special CellSave tubes with additional fixation solution instead of standard EDTA monovettes. The fixation solution in the CellSave tubes seems to strongly influence the detectable amount of circulating tumor cells. It has been shown that the use of CellSave tubes reduces the detection of EpCAM-positive cells by more than 10-fold compared to the maintrac® method. According to other studies, a high proportion of cell fragments is detected using the CellSearch™ method, which is, however, attributed the same prognostic significance as intact, vital cells [36].
In our study using the maintrac® method, an approach omitting fixation and enrichment steps, the number of EpCAM-positive cells was much higher with 1220 and 18,070 cells/mL blood in clinically non-metastatic women. This included cells with very low EpCAM expression, which may be lost by enrichment steps. In spite of confirmed metastatic breast cancer, the CellSearch™ method detects circulating tumor cells in only 10–60% of cases in blood or bone marrow [37]. The maintrac® method detects CETC in 90% of cases of primary non-metastatic breast cancer and an increase in these numbers during therapy is highly significantly correlated with relapse [11].
The number of circulating tumor cells determined by various methods is controversially discussed [38]. Given the heterogeneous results concerning the number of detected circulating tumor cells with various methods of analysis, standardization of test methods is of utmost importance [39]. The high number of CETC detected with the method applied here is advantageous with respect to micromanipulation for isolation of individual cells in patients with early breast cancer [17,29,40] to analyze intra-individual changes in CETC numbers during the course of treatment and to amplify mRNA from the individually isolated cells.
The possibility of false positive results in light of the high detection rate must be considered. However, the fact that mRNA of the candidate genes could be amplified from the individually isolated cells suggests that these cells are viable.
4.2. Expression Pattern of EpCAM
The EpCAM antigen used in the maintrac® process is not exclusively expressed on the surface of breast cancer cells, but also on normal epithelial cells, e.g., of the gut and the lung. EpCAM overexpression in breast cancer correlates with tumor mass, lymph node status, and the presence of estrogen receptors [41]. The EpCAM antigen is also found in other cancers such as lung or colorectal carcinoma [42,43,44]. Therefore, the detected cells comprise circulating tumor cells but the presence of additional nonmalignant cells cannot be completely excluded. EpCAM-positive cells are usually not detectable in healthy subjects, as confirmed in our study in blood samples from healthy subjects.
By labeling the CETC with EpCAM and subsequently picking EpCAM-positive cells, PCR results could be assigned exclusively to the respective cells. It has been assumed in the past that the detection of tissue-specific mRNA in peripheral blood indicates the presence of circulating tumor cells [45,46]. However, irrespective of the enrichment method used, samples are contaminated with white blood cells, resulting in reduced specificity, especially in the analysis of mixed populations of cells allowing only for cross-sectional information. In contrast, our analysis of individual cells displays the heterogeneity of the circulating tumor cells. Since mRNA is transcribed only in viable cells and degraded very rapidly during cell decay, the combination of upstream individual cell isolation and subsequent multiplex PCR using single cells in this study minimized these sources of error and increased sensitivity and specificity [7,18,47].
4.3. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
With regard to the qRT-PCR results, difficulties arise especially with genes which are expressed at low levels. Intercellular differences in gene expression can be large, and extreme values of individual cells can largely influence the mean value [48]. As expected, the number of gene copies detected in single cells in this study varied considerably between undetectable (HER2 for Pat. ID 1) and 379.0 copies/µL (NANOG for Pat. ID 4). This led to large standard deviations.
Nonetheless, the averaged gene copy numbers in up to eight analyzed single cells was significantly increased for most genes after irradiation in comparison to the average copy number in cells before irradiation.
In this study, analysis of single circulating cells by qRT-PCR allowed for discerning heterogeneities in gene activity between individual CETC of a patient, and additionally determined changes in gene activation during therapy to provide a starting point for in-depth research of a higher number of patients.
4.4. Quantitative Measurement of the CETC
In seven of the nine patients (77.8%) the number of CETC was higher after radiotherapy as compared to the CETC number before start of radiotherapy. On average, a doubling of CETC numbers was observed. One possible explanation for this observation is the release of cells from occult residues, which subsequently enter the microenvironment and the bloodstream [49,50,51]. These could represent cells that have survived radiation and may be a sign of radioresistant cell clones already present prior to the radiotherapy series [52]. The changes in the local and systemic environment, such as inflammation induced by radiotherapy, may stimulate the expansion of the cells that are circulating in blood [53]. It is controversially discussed whether the cells found in blood are derived directly from the primary tumor [54,55,56]. Further investigations including analysis of molecular markers of the CETC at serial time points during treatment are necessary to clarify this question.
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
In patients with increased CETC numbers after radiotherapy, we also found an increased expression of the majority of genes in single CETC of the respective patients.
The examined genes encode proteins involved in cell metabolism, but also in inflammatory and immunological processes, cell proliferation, adhesion, differentiation, and migration as well as angiogenesis, apoptosis inhibition, and preservation of cellular pluripotency [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67].
It is known that irradiation causes dose-dependent effects, leading to DNA damage by direct or indirect ionization and additionally by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby destroying cancer cells. Ionizing irradiation can however also promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis, invasion, and finally metastasis formation [68,69,70,71,72,73]. As an example, PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling regulates cell growth and proliferation apoptosis and DNA damage response but also acts as a main driver of cellular survival mechanisms after irradiation. In addition, ionizing radiation increases Akt phosphorylation in numerous tumor entities, possibly causing resistance to therapy. The gene activation after radiotherapy observed in this trial is therefore is not surprising, however its relevance and underlying molecular mechanisms are unclear. Despite the small patient and cell numbers explored in this study as well as the variability of the measured values, differences between pre-radiation and post-radiation cells were significant in 5 out of 11 genes over all patients. It might well be that effects mediated by radiation therapy itself could be responsible for the upregulation of gene expression.
In addition to direct impact ionization at the cellular level, immunomodulatory phenomena are known which are dose-, time-, and volume-dependent and can occur both locally and systemically [74,75]. Radiotherapy leads to cell death in some of the cells, thereby evoking phagocytosis of these cells and again inducing an immune response. This particularly underlines the activation of TLR4 and COX-2 observed in this study, suggesting that increased cytokine and chemokine production suppresses an adaptive immune response and promotes metastatic processes [76,77]. It is also possible that the detected CETC are radio-resistant tumor stem cells or subclones with pronounced differentiation potential, which can survive treatment (especially if such cells circulating with the blood stream do not receive the total radiation dose applied locally to the breast/chest wall) and lead to a selected subpopulation of CETC with increased malignant potential [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88]. The strong activation of NANOG in all patients seems to support this hypothesis [82]. With regard to the genes described, these surviving cells would then represent a particular risk for the development of distant metastases [89].
Based on the present pilot study, further investigations are currently being performed on a larger number of patients and single cells in order to investigate the molecular biological and functional effects of radiotherapy on CETC in more detail. In order to identify prognostic and predictive biomarkers, a prospective follow-up study of the group will investigate the impact of radiotherapy on CETC, its gene expression profile, and immunophenotype over the course of treatment including follow-up (study number NCT03935802).
4.6. Influence of Endocrine Therapy
Endocrine therapy might influence changes in the numbers of CETCs as well as gene expression as a confounding factor [87]. This and other confounders cannot be eliminated as patients were treated according to current guidelines. In all examined patients in this study, endocrine therapy was started already prior to RT.
Data on the effect of endocrine treatments on CETC number are scarce. It is known that patients whose CETC count increases after endocrine therapy are significantly more likely to suffer a relapse [90]. However, to what extent endocrine therapy has a direct influence on the single CETCs is not clear so far.
4.7. Clinical Follow-Up
The only patient who suffered a local relapse within five years after RT was patient ID 5. The number of CETC was slightly decreased after RT and the gene expression increase was only moderate. This indicates that local relapse may not necessarily be directly related to CETC number changes and gene expression levels.
Two of the nine patients examined developed a second malignancy. This is a strikingly high number but attributed to a random statistical effect. The patient with the highest increase in activity of COX-2, PIK3CA, HER2, and Vimentin was diagnosed with colon cancer 84 months after treatment of breast cancer. It is unclear to what extent the CETC detected in the study are related to the development of colon cancer as EpCAM used in our method is also overexpressed in colon cancer [91]. Pat. ID 6 was diagnosed with malignant melanoma 17 month after treatment of breast cancer. This patient also showed only a moderate increase in CETC count and gene expression.
5. Conclusions
Procedures and methods used in this study proved to be feasible. We were able to detect changes in the CETC numbers of patients with early-stage breast cancer before radiotherapy in comparison to the end of radiotherapy.
Gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR of single CETC showed that there was an increase in the expression of selected genes involved in metastatic processes in the majority of CETC analyzed under radiotherapy. Because of the heterogeneity of results in gene expression in individual cells, further characterization of the biological and functional effects of radiotherapy is needed. The findings of this pilot study provide an important basis for a prospective follow-up study with larger numbers of patients and cells (NCT03935802).
Author Contributions
Study design, conceptualization M.M. and K.P.; investigation, formal analysis, interpretation of data, writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; supervision, project administration, T.W.; project administration, writing—review and editing, K.P.; data curation, writing—review and editing, A.W., visualization, D.S. This work includes results from the medical thesis of M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the, commercial. M.M. was supported by the DFG through the OrganAge programme for clinical scientists (WI 830/12-1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Hospital Jena (No. 0921-08/02).
Informed Consent Statement
All patients provided written consent for the publication of research performed with their medical data.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the study are not publicly available due to preservation of privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Christoph Schnedermann for the linguistic and editorial revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
K.P. is the holder of the patents for the herein described method maintrac® to detect CETCs. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Glossary
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CETC | Circulating epithelial tumor cells |
| EpCAM | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
| FITC | Fluoroisothiocyanate |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
References
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative, G.; Darby, S.; McGale, P.; Correa, C.; Taylor, C.; Arriagada, R.; Clarke, M.; Cutter, D.; Davies, C.; Ewertz, M.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 378, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Taubert, H.; Blumke, K.; Bilkenroth, U.; Meye, A.; Kutz, A.; Bartel, F.; Lautenschlager, C.; Ulbrich, E.J.; Nass, N.; Holzhausen, H.J.; et al. Detection of disseminated tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer: Correlation to nodal status and occurrence of metastases. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 92, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiewicz, A.; Szostakowska-Rodzos, M.; Zaczek, A.J.; Grzybowska, E.A. Circulating tumor cells in early and advanced breast cancer; biology and prognostic value. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Duffy, M.J. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in breast cancer: Past, present and future. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Muller, V.; Auer, M.; Nusser, N.; Harbeck, N.; Braun, S. Detection and clinical implications of early systemic tumor cell dissemination in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 6326–6334. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, C.R.; Seagle, B.L.; Friedl, T.W.P.; Rack, B.; Lato, K.; Fink, V.; Cristofanilli, M.; Donnelly, E.D.; Janni, W.; Shahabi, S.; et al. Association of circulating tumor cell status with benefit of radiotherapy and survival in early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e180163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinhardt, F.; Franken, A.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Driemel, C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Fischer, J.C.; Niederacher, D.; Ruckhaeberle, E.; Fehm, T.; Neubauer, H. Diagnostic leukapheresis enables reliable transcriptomic profiling of single circulating tumor cells to characterize inter-cellular heterogeneity in terms of endocrine resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, D.H.; Hall, C.; Lucci, A. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020, 215, 127–145. [Google Scholar]
- Janni, W.J.; Rack, B.; Terstappen, L.W.; Pierga, J.Y.; Taran, F.A.; Fehm, T.; Hall, C.; de Groot, M.R.; Bidard, F.C.; Friedl, T.W.; et al. Pooled analysis of the prognostic relevance of circulating tumor cells in primary breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frick, M.A.; Feigenberg, S.J.; Jean-Baptiste, S.R.; Aguarin, L.A.; Mendes, A.; Chinniah, C.; Swisher-McClure, S.; Berman, A.; Levin, W.; Cengel, K.A.; et al. Circulating tumor cells are associated with recurrent disease in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pachmann, K.; Camara, O.; Kavallaris, A.; Krauspe, S.; Malarski, N.; Gajda, M.; Kroll, T.; Jorke, C.; Hammer, U.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; et al. Monitoring the response of circulating epithelial tumor cells to adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer allows detection of patients at risk of early relapse. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bidard, F.C.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nole, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; Grisanti, S.; Generali, D.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Hayes, D.F.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdyntseva, N.V.; Litviakov, N.V.; Denisov, E.V.; Gervas, P.A.; Cherdyntsev, E.S. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer: Functional heterogeneity, pathogenetic and clinical aspects. Exp. Oncol. 2017, 39, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bäuerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Valad, L.; Lucci, A. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer patients. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2016, 21, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorg, S.; Pachmann, K.; Brede-Hekimian, K.; Freesmeyer, M.; Winkens, T. Determining tissue origin of circulating epithelial cells (cec) in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer by real-time pcr using thyroid mrna probes. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, M.; Tjensvoll, K.; Oltedal, S.; Javle, M.; Smaaland, R.; Gilje, B.; Nordgard, O. Single-cell mrna profiling reveals transcriptional heterogeneity among pancreatic circulating tumour cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz, F.; Budach, W. Personalized radiotherapy for invasive breast cancer in 2017 national s3 guidelines and degro and ago recommendations. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017, 193, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachmann, K.; Clement, J.H.; Schneider, C.P.; Willen, B.; Camara, O.; Pachmann, U.; Hoffken, K. Standardized quantification of circulating peripheral tumor cells from lung and breast cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2005, 43, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Hageleit, M. Validities of mrna quantification using recombinant rna and recombinant DNA external calibration curves in real-time rt-pcr. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhlberg, A.; Kubista, M. The workflow of single-cell expression profiling using quantitative real-time pcr. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäurer, M.A. Analysen Zirkulierender Epithelialer Tumorzellen im Periphervenösen blut bei Patientinnen mit Primär nicht Metastasiertem Mammakarzinom unter Adjuvanter Radiotherapie. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, Jena, Germany, 2 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pachmann, K.; Pizon, M.; Zimon, D.; Stein, E.L. Mc13-0080 somatic mutations of the egfr, kras and braf genes: Heterogeneity in circulating epithalial tumor cells (cetc) as determined using the cobas® z 480 analyzer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical applications of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA as liquid biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koonce, N.A.; Juratli, M.A.; Cai, C.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Dent, J.; Quick, C.M.; Dings, R.P.M.; Nedosekin, D.; Zharov, V.; et al. Real-time monitoring of circulating tumor cell (ctc) release after nanodrug or tumor radiotherapy using in vivo flow cytometry. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mu, Z.; Chervoneva, I.; Austin, L.; Ye, Z.; Rossi, G.; Palazzo, J.P.; Sun, C.; Abu-Khalaf, M.; Myers, R.E.; et al. Longitudinally collected ctcs and ctc-clusters and clinical outcomes of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 161, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewes, M.; Aktas, B.; Welt, A.; Mueller, S.; Hauch, S.; Kimmig, R.; Kasimir-Bauer, S. Molecular profiling and predictive value of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: An option for monitoring response to breast cancer related therapies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 115, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pizon, M.; Zimon, D.; Carl, S.; Pachmann, U.; Pachmann, K.; Camara, O. Heterogeneity of circulating epithelial tumour cells from individual patients with respect to expression profiles and clonal growth (sphere formation) in breast cancer. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Bai, F. Molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells-from bench to bedside. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 75, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, V.; Riethdorf, S.; Rack, B.; Janni, W.; Fasching, P.A.; Solomayer, E.; Aktas, B.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Pantel, K.; Fehm, T.; et al. Prognostic impact of circulating tumor cells assessed with the cellsearch system and adnatest breast in metastatic breast cancer patients: The detect study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riethdorf, S.; Fritsche, H.; Muller, V.; Rau, T.; Schindlbeck, C.; Rack, B.; Janni, W.; Coith, C.; Beck, K.; Janicke, F.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with metastatic breast cancer: A validation study of the cellsearch system. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nole, F.; Munzone, E.; Zorzino, L.; Minchella, I.; Salvatici, M.; Botteri, E.; Medici, M.; Verri, E.; Adamoli, L.; Rotmensz, N.; et al. Variation of circulating tumor cell levels during treatment of metastatic breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Herrler, M.; Burgess, D.; Manna, E.; Krag, D.; Burke, J.F. Enrichment with anti-cytokeratin alone or combined with anti-epcam antibodies significantly increases the sensitivity for circulating tumor cell detection in metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Doggen, C.J.M.; Attard, G.; de Bono, J.S.; Terstappen, L. All circulating epcam+ck+cd45- objects predict overall survival in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehm, T.; Muller, V.; Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Micrometastatic spread in breast cancer: Detection, molecular characterization and clinical relevance. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10 (Suppl. 1), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pachmann, U.; Hekimian, K.; Pachmann, K. Comparing sequential steps for detection of circulating tumor cells: More specific or just less sensitive? Oncol. Rep. 2011, 37, 3219–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Gaforio, J.J.; Serrano, M.J.; Sanchez-Rovira, P.; Sirvent, A.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Campos, M.; de la Torre, N.; Algarra, I.; Duenas, R.; Lozano, A. Detection of breast cancer cells in the peripheral blood is positively correlated with estrogen-receptor status and predicts for poor prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankiewicz, S.; Rivero, B.G.; Bocher, O. Quantitative real-time rt-pcr of disseminated tumor cells in combination with immunomagnetic cell enrichment. Mol. Biotechnol. 2006, 34, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A.K.; Clark, G.M.; Chamness, G.C.; McGuire, W.L. Association of the 323/a3 surface glycoprotein with tumor characteristics and behavior in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar]
- Balzar, M.; Winter, M.J.; de Boer, C.J.; Litvinov, S.V. The biology of the 17-1a antigen (ep-cam). J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 1999, 77, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osta, W.A.; Chen, Y.; Mikhitarian, K.; Mitas, M.; Salem, M.; Hannun, Y.A.; Cole, D.J.; Gillanders, W.E. Epcam is overexpressed in breast cancer and is a potential target for breast cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5818–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moldenhauer, G.; Momburg, F.; Moller, P.; Schwartz, R.; Hammerling, G.J. Epithelium-specific surface glycoprotein of mr 34,000 is a widely distributed human carcinoma marker. Br. J. Cancer 1987, 56, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keilholz, U.; Willhauck, M.; Scheibenbogen, C.; deVries, T.J.; Burchill, S. Polymerase chain reaction detection of circulating tumour cells. Melanoma Res. 1997, 7, S133–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvastad, L.; Werne Solnestam, B.; Johansson, E.; Nygren, A.O.; Laddach, N.; Sahlen, P.; Vickovic, S.; Bendigtsen, S.C.; Aaserud, M.; Floer, L.; et al. Single cell analysis of cancer cells using an improved rt-mlpa method has potential for cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalaki, A.; Agelaki, S.; Perraki, M.; Apostolaki, S.; Xenidis, N.; Stathopoulos, E.; Kontopodis, E.; Hatzidaki, D.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V. Detection of cytokeratin-19 mrna-positive cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with operable breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeevan, M.S.; Vernon, S.D.; Taysavang, N.; Unger, E.R. Validation of array-based gene expression profiles by real-time (kinetic) rt-pcr. J. Mol. Diagn. 2001, 3, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehm, T.; Sagalowsky, A.; Clifford, E.; Beitsch, P.; Saboorian, H.; Euhus, D.; Meng, S.; Morrison, L.; Tucker, T.; Lane, N.; et al. Cytogenetic evidence that circulating epithelial cells in patients with carcinoma are malignant. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2073–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.A. Parallel progression of primary tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopp, A.H.; Spaeth, E.L.; Dembinski, J.L.; Woodward, W.A.; Munshi, A.; Meyn, R.E.; Cox, J.D.; Andreeff, M.; Marini, F.C. Tumor irradiation increases the recruitment of circulating mesenchymal stem cells into the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11687–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, O.A.; Anderson, R.L.; Narayan, K.; MacManus, M.P. Does the mobilization of circulating tumour cells during cancer therapy cause metastasis? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, A.D.; von Eyben, R.; Newman, N.B.; Gutkin, P.; Mayer, I.; Horst, K.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Rafat, M. Systemic inflammation after radiation predicts locoregional recurrence, progression, and mortality in stage ii-iii triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 108, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Tripathy, D.; Frenkel, E.P.; Shete, S.; Naftalis, E.Z.; Huth, J.F.; Beitsch, P.D.; Leitch, M.; Hoover, S.; Euhus, D.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in patients with breast cancer dormancy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8152–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Meucci, S.; Sheng, L.; Keilholz, U. Meta-analysis of the mutational status of circulation tumor cells and paired primary tumor tissues from colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 77928–77941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolke, E.; Orth, K.; Gerber, P.A.; Lammering, G.; Mota, R.; Peiper, M.; Matuschek, C.; Budach, W.; Rusnak, E.; Shaikh, S.; et al. Gene expression of circulating tumour cells and its correlation with tumour stage in breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2009, 14, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slamon, D.J.; Godolphin, W.; Jones, L.A.; Holt, J.A.; Wong, S.G.; Keith, D.E.; Levin, W.J.; Stuart, S.G.; Udove, J.; Ullrich, A.; et al. Studies of the her-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989, 244, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, H.; LaRochelle, W.J.; Sharp, R.; Otsuka, T.; Kriebel, P.; Anver, M.; Aaronson, S.A.; Merlino, G. Diverse tumorigenesis associated with aberrant development in mice overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurenzi, I.J. An analytical solution of the stochastic master equation for reversible bimolecular reaction kinetics. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.L.; Botting, R.M.; Hla, T. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: The biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 387–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.Y.; Rong, M.; Grieu, F.; Iacopetta, B. Pik3ca mutations in breast cancer are associated with poor outcome. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 96, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaska, J.; Pallari, H.M.; Nevo, J.; Eriksson, J.E. Novel functions of vimentin in cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzel, D.; Denzel, S.; Mack, B.; Canis, M.; Went, P.; Benk, M.; Kieu, C.; Papior, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Munz, M.; et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen epcam. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Feng, P.; Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Xie, X.; Shen, H.; Zhu, X. Reduced expression of toll-like receptor 4 inhibits human breast cancer cells proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Cao, W.W.; Li, L.; Li, S.P.; Liu, T.; Wan, H.Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. Microrna-519d targets mki67 and suppresses cell growth in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line qgy-7703. Cancer Lett. 2011, 307, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraro, E.; Furlan, C.; Avanzo, M.; Martorelli, D.; Comaro, E.; Rizzo, A.; Fae, D.A.; Berretta, M.; Militello, L.; Del Conte, A.; et al. Local high-dose radiotherapy induces systemic immunomodulating effects of potential therapeutic relevance in oligometastatic breast cancer. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zeng, B.; Yi, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Yu, D. Upregulation of circular rna circatrnl1 to sensitize oral squamous cell carcinoma to irradiation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.M.; Yang, X.L.; Jiang, F.; Pan, Y.C.; Zhang, L. Matrine involves in the progression of gastric cancer through inhibiting mir-93-5p and upregulating the expression of target gene ahnak. J. cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, N.; Nawaz, M.; Rezaie, J. Bystander effects of ionizing radiation: Conditioned media from x-ray irradiated mcf-7 cells increases the angiogenic ability of endothelial cells. Cell commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, E.K.; Ju, M.K.; Jeon, H.M.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Park, H.G.; Han, S.I.; Kang, H.S. Induction of metastasis, cancer stem cell phenotype, and oncogenic metabolism in cancer cells by ionizing radiation. Mol. cancer 2017, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarosz-Biej, M.; Smolarczyk, R.; Cichon, T.; Kulach, N. Tumor microenvironment as a "game changer" in cancer radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eke, I.; Makinde, A.Y.; Aryankalayil, M.J.; Sandfort, V.; Palayoor, S.T.; Rath, B.H.; Liotta, L.; Pierobon, M.; Petricoin, E.F.; Brown, M.F.; et al. Exploiting radiation-induced signaling to increase the susceptibility of resistant cancer cells to targeted drugs: Akt and mtor inhibitors as an example. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leeman, J.E.; Schoenfeld, J.D. Radiation therapy and immune modulation. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, N.L.; Luetragoon, T.; Andersson, B.A.; Oliva, D.; Nilsson, M.; Strandeus, M.; Lofgren, S.; Rutqvist, L.E.; Lewin, F. The influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms and adjuvant radiotherapy on systemic inflammatory proteins, chemokines and cytokines of patients with breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Yusuf, N. Expression of toll-like receptors on breast tumors: Taking a toll on tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 2012, 716564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, G.E.; Cho, N.H.; Pyo, H.R.; Shim, S.J.; Chang, S.K.; Park, H.C.; Suh, C.O.; Park, T.K.; Kim, B.S. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated with radiation and concurrent chemotherapy. Cancer 2002, 95, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, M.; Madjd, Z.; Janani, L.; Rasti, A. Circulating cancer stem cell markers in breast carcinomas: A systematic review protocol. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, L.P.; Zhang, H.M.; Tong, S. Circulating tumor cells and tumor stem cells detection in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of breast cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Cozzi, P.; Hao, J.L.; Beretov, J.; Chang, L.; Duan, W.; Shigdar, S.; Delprado, W.; Graham, P.; Bucci, J.; et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (epcam) is associated with prostate cancer metastasis and chemo/radioresistance via the pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 2013, 45, 2736–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, T.M.; Riethdorf, S.; Nees, J.; Hartkopf, A.D.; Schonfisch, B.; Domschke, C.; Sprick, M.R.; Schutz, F.; Brucker, S.Y.; Stefanovic, S.; et al. Impact of apoptotic circulating tumor cells (actc) in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 160, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzhna, L.; Golubov, A.; Ilnytskyy, S.; Chekhun, V.F.; Kovalchuk, O. Molecular mechanisms of radiation resistance in doxorubicin-resistant breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1692–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badve, S.; Nakshatri, H. Breast-cancer stem cells-beyond semantics. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e43–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Urbano, M.A.; Grinan-Lison, C.; Rios-Arrabal, S.; Artacho-Cordon, F.; Torralbo, A.I.; Lopez-Ruiz, E.; Marchal, J.A.; Nunez, M.I. Radiation and stemness phenotype may influence individual breast cancer outcomes: The crucial role of mmps and microenvironment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saga, R.; Matsuya, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Hasegawa, K.; Date, H.; Hosokawa, Y. Analysis of the high-dose-range radioresistance of prostate cancer cells, including cancer stem cells, based on a stochastic model. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.S.; Pajonk, F.; McCloskey, S.; Low, D.A.; Kupelian, P.; Steinberg, M.; Sheng, K. Radioresistance of the breast tumor is highly correlated to its level of cancer stem cell and its clinical implication for breast irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, D.S.; Pizon, M.; Pachmann, U.; Pachmann, K.; Schobert, R.; Wittig, A.; Mäurer, M. Influence of adjuvant radiotherapy on circulating epithelial tumor cells and circulating cancer stem cells in primary non-metastatic breast cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, M.; Ma, W.; Saxena, D.; Lustig, R.A.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Zhang, Z.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Circulating glioma cells exhibit stem cell-like properties. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6632–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutsch-Wicherek, M. Rcas1, mt, and vimentin as potential markers of tumor microenvironment remodeling. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachmann, K.; Schuster, S. The value of monitoring the behavior of circulating tumor cells at the end of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients. Cancers 2018, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patriarca, C.; Macchi, R.M.; Marschner, A.K.; Mellstedt, H. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (cd326) in cancer: A short review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).