Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
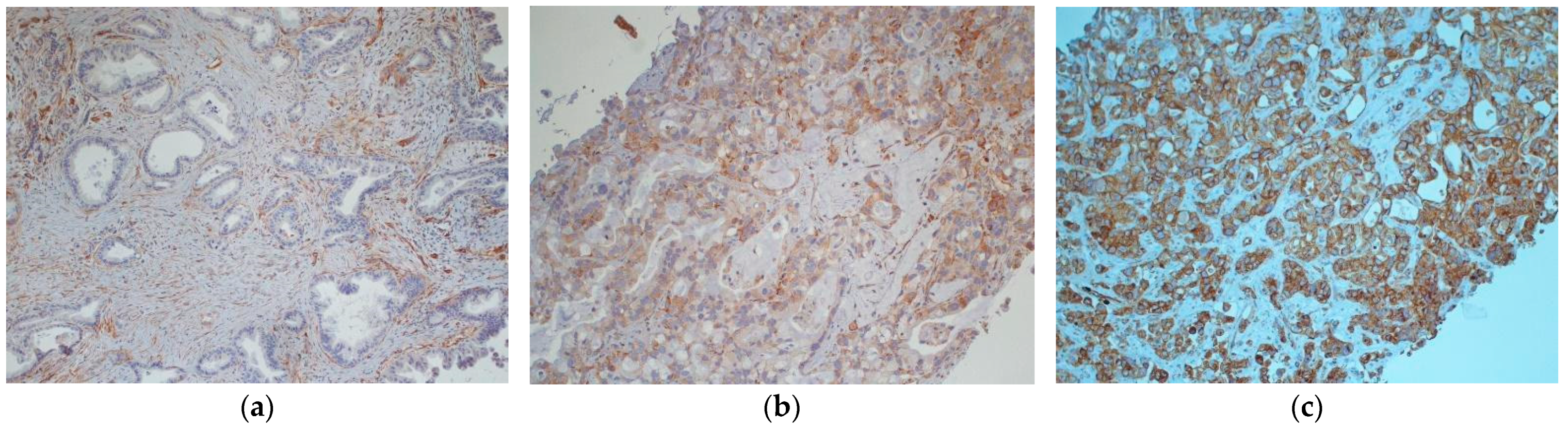
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Patients’ Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting Cancer Incidence and Deaths to 2030: The Unexpected Burden of Thyroid, Liver, and Pancreas Cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Wee Ma, W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased Survival in Pancreatic Cancer with nab-Paclitaxel plus Gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouche, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Becouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardière, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conroy, T.; Hammel, P.; Hebbar, M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Raoul, J.L.; Choné, L.; Francois, E.; Artru, P.; Biagi, J.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.M.; Lisanti, M.P. The Caveolin genes: From cell biology to medicine. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ramírez, C.M.; Aryal, B.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Liu, X.; Diaz, A.; Torrecilla-Parra, M.; Suárez, Y.; Cuervo, A.M.; Sessa, W.C.; et al. Cav-1 (Caveolin-1) Deficiency Increases Autophagy in the Endothelium and Attenuates Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuoki, M.; Miyamoto, M.; Kato, K.; Hiraoka, K.; Oshikiri, T.; Nakakubo, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Shichinohe, T.; Shinohara, T.; Itoh, T.; et al. Impact of caveolin-1 expression on prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; DiVito, M.M.; Merajver, S.D.; Boyanapalli, M.; van Golen, K.L. Regulation of pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by RhoC GTPase and caveolin-1. Mol. Cancer 2005, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.C.; Huang, P.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, P.C.; Hsu, S.M. Up-regulated caveolin-1 accentuates the metastasis capability of lung adenocarcinoma by inducing filopodia formation. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordes, N.; Frick, S.; Brunner, T.B.; Pilarsky, C.; Grutzmann, R.; Sipos, B.; Klöppel, G.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J. Human pancreatic tumor cells are sensitized to ionizing radiation by knockdown of caveolin-1. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6851–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ben-Josef, E.; Thomas, D.G.; Morgan, M.A.; Zalupski, M.M.; Khan, G.; Andrew Robinson, C.; Griffith, K.A.; Chen, C.S.; Ludwig, T.; et al. Caveolin-1 is Associated with Tumor Progression and Confers a Multi-Modality Resistance Phenotype in Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hehlgans, S.; Eke, I.; Storch, K.; Haase, M.; Baretton, G.B.; Cordes, N. Caveolin-1 mediated radioresistance of 3D grown pancreatic cancer cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamposioras, K.; Tsimplouli, C.; Verbeke, C.; Anthoney, A.; Daoukopoulou, A.; Papandreou, C.N.; Sakellaridis, N.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Potamianos, S.P.; Liakouli, V.; et al. Silencing of caveolin-1 in fibroblasts as opposed to epithelial tumor cells results in increased tumor growth rate and chemoresistance in a human pancreatic cancer model. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ben-Josef, E.; Robb, R.; Vedaie, M.; Seum, S.; Thirumoorthy, K.; Palanichamy, K.; Harbrecht, M.; Chakravarti, A.; Williams, T.M. Caveolae-Mediated Endocytosis Is Critical for Albumin Cellular Uptake and Response to Albumin-Bound Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5925–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.Y. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eso, Y.; Seno, H. Current status of treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors for gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, and pancreatic cancers. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820948773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J.; Goldstein, D.; Hamm, J.; Figer, A.; Hecht, J.R.; Gallinger, S.; Au, H.J.; Murawa, P.; Walde, D.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faloppi, L.; Bianconi, M.; Giampieri, R.; Sobrero, A.; Labianca, R.; Ferrari, D.; Barni, S.; Aitini, E.; Zaniboni, A.; Boni, C.; et al. Italian Group for the Study of Digestive Tract Cancer (GISCAD). The value of lactate dehydrogenase serum levels as a prognostic and predictive factor for advanced pancreatic cancer patients receiving sorafenib. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35087–35094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amantini, C.; Morelli, M.B.; Nabissi, M.; Piva, F.; Marinelli, O.; Maggi, F.; Bianchi, F.; Bittoni, A.; Berardi, R.; Giampieri, R.; et al. Expression Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Biomarkers Predicting Overall Survival. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscail, E.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Quincy, P.; Cauvin, T.; Chauvet, A.; Degrandi, O.; Caumont, C.; Verdon, S.; Lamrissi, I.; Moranvillier, I.; et al. High Clinical Value of Liquid Biopsy to Detect Circulating Tumor Cells and Tumor Exosomes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients Eligible for Up-Front Surgery. Cancers 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giampieri, R.; Piva, F.; Occhipinti, G.; Bittoni, A.; Righetti, A.; Pagliaretta, S.; Murrone, A.; Bianchi, F.; Amantini, C.; Giulietti, M.; et al. Clinical impact of different exosomes’ protein expression in pancreatic ductal carcinoma patients treated with standard first line palliative chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boscher, C.; Nabi, I.R. Caveolin-1: Role in cell signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 729, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jo, U.; Park, J.K.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, I.; Park, K.H. Caveolin-1 Modulates Docetaxel-Induced Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cell Subtypes through Different Mechanisms. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, E.; Wang, B.; et al. Caveolin-1 expression predicts efficacy of weekly nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer in the phase II clinical trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricci, F.; Le Tourneau, C. Emerging new predictive biomarkers in metastatic breast cancer: Caveolin-1 and weekly nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine, are we on for tomorrow? Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianzen Herrera, D.; Ashai, N.; Perez-Soler, R.; Cheng, H. Nanoparticle albumin bound-paclitaxel for treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An evaluation of the clinical evidence. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Burgos-Ravanal, R.; González, M.F.; Huilcaman, R.; Lobos González, L.; Quest, A.F.G. Cell intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms of caveolin-1- enhanced metastasis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Truong, L.D.; Wheeler, T.M.; Thompson, T.C. Caveolin-1 expression in clinically confined human prostate cancer: A novel prognostic marker. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5719–5723. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xue, B.; Xu, G.Y. Association of Caveolin-1 Expression with Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Oncol. 2021, 10, 562774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobos-González, L.; Aguilar, L.; Diaz, J.; Diaz, N.; Urra, H.; Torres, V.A.; Silva, V.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Lladser, A.; Hoek, K.S.; et al. E-cadherin determines Caveolin-1 tumor suppression or metastasis enhancing function in melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lobos-Gonzalez, L.; Aguilar-Guzmán, L.; Fernandez, J.G.; Muñoz, N.; Hossain, M.; Bieneck, S.; Silva, V.; Burzio, V.; Sviderskaya, E.V.; Bennett, D.C.; et al. Caveolin-1 is a risk factor for postsurgery metastasis in preclinical melanoma models. Melanoma Res. 2014, 24, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, P.; Shen, X.K.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.Y.; Xu, C.H.; Hao, K.K.; Hu, W.; et al. Expression of caveolin-1 is correlated with disease stage and survival in lung adenocarcinomas. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eliyatkin, N.; Aktas, S.; Diniz, G.; Ozgur, H.H.; Ekin, Z.Y.; Kupelioglu, A. Expression of Stromal Caveolin- 1 May Be a Predictor for Aggressive Behaviour of Breast Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, K.; Matsunaga, S.; Nakano, T.; Usui, S.; Hirano, K. Inhibition of Caveolin-1 expression by Incandronate in PC-3 prostate cells. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 2977–2982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gasperi-Campani, A.; Baiocchi, D.; Marti, G.; Rossi, A.M.L.; Roncuzzi, L. Caveolin-1 as a novel target of therapeutic activity of Fenretinide in osteosarcoma and glioblastoma in vitro. Proc. Amer. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1291. [Google Scholar]
- Guruswamy, S.; Rao, C.V. Synergistic effects of lovastatin and celecoxib on caveolin-1 and its down-stream signaling molecules: Implications of colon cancer prevention. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristic | N (%) Tot = 39 |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 23 (59%) |
| Female | 16 (41%) |
| Median age (range) | 68 (31–86) |
| ECOG | |
| 0 | 18 (46%) |
| 1 | 14 (36%) |
| 2 | 7 (18%) |
| First Line Chemotherapy Regimen | |
| Gemcitabine plus Abraxane | 27 (69%) |
| FOLFIRINOX or FOLFOX | 5 (12%) |
| Monotherapy | 7 (17%) |
| Stage at diagnosis | |
| Locally advanced | 17 (43%) |
| Metastatic | 22 (67%) |
| Metastatic sites | |
| Liver | 30 (76%) |
| Lung | 8 (20%) |
| Peritoneum | 4 (10%) |
| Bone | 2 (5%) |
| Lymph nodes | 13 (33%) |
| Best Overall Response | N(%) Tot = 39 |
|---|---|
| CR | 0 (0%) |
| PR | 8 (20%) |
| SD | 10 (25%) |
| PD | 17 (43%) |
| unknown | 4 (10%) |
| median OS (months) | 11.93 |
| median PFS (months) | 6.93 |
| Caveolin-1 Expression and Sampling Methods | N (%) Tot = 39 |
|---|---|
| Sites of biopsy | |
| primary tumor | 28 (70%) |
| liver metastasis | 11 (30%) |
| Sampling Method | |
| Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) on primary tumor | 12 (30%) |
| core biopsy on primary tumor | 7 (18%) |
| core biopsy on liver metastasis | 11 (28%) |
| surgical primary tumor sample | 9 (24%) |
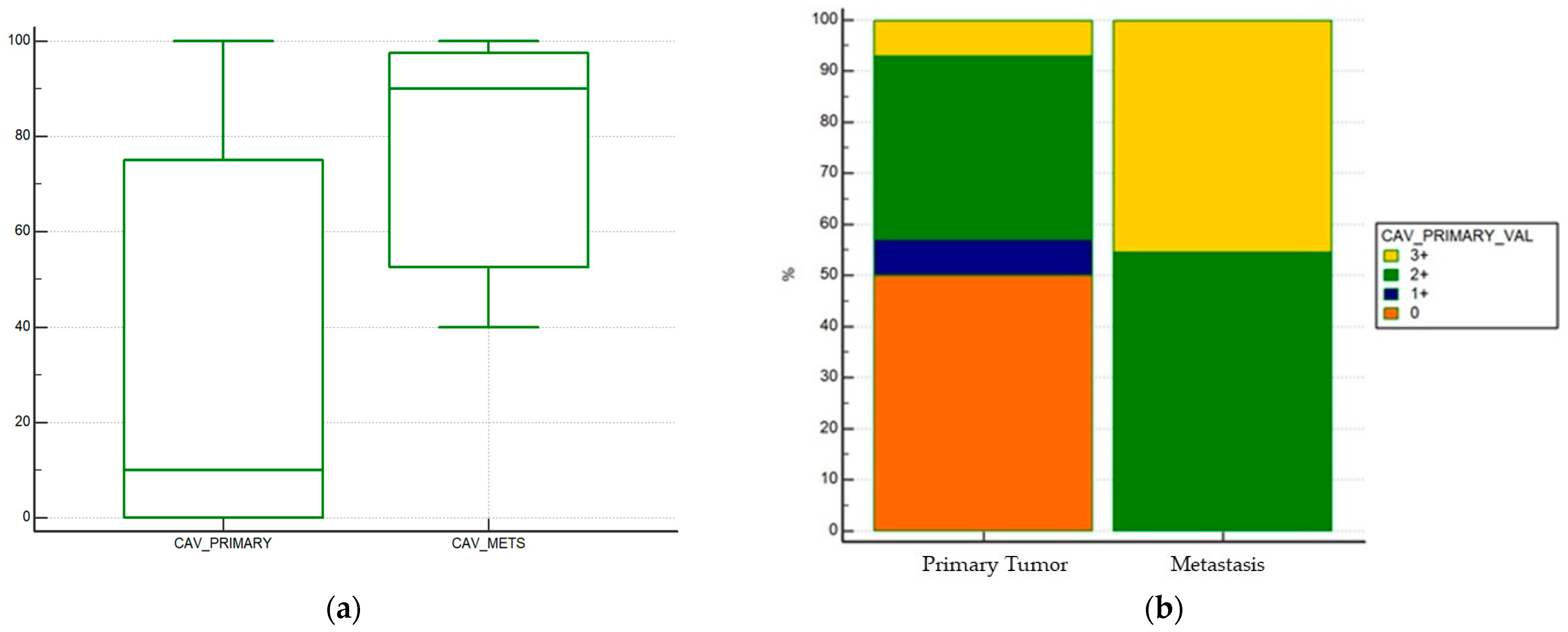
| Tumoral Caveolin-1 expression (primary tumor) | 28 |
| negative | 13 (46%) |
| 1+ | 2 (7%) |
| 2+ | 10 (35%) |
| 3+ | 2 (7%) |
| not evaluable | 1 (4%) |
| Tumoral Caveolin-1 expression (mestastatic sites) | 11 |
| negative | 0 (0%) |
| 1+ | 0 (0%) |
| 2+ | 6 (54%) |
| 3+ | 5 (46%) |
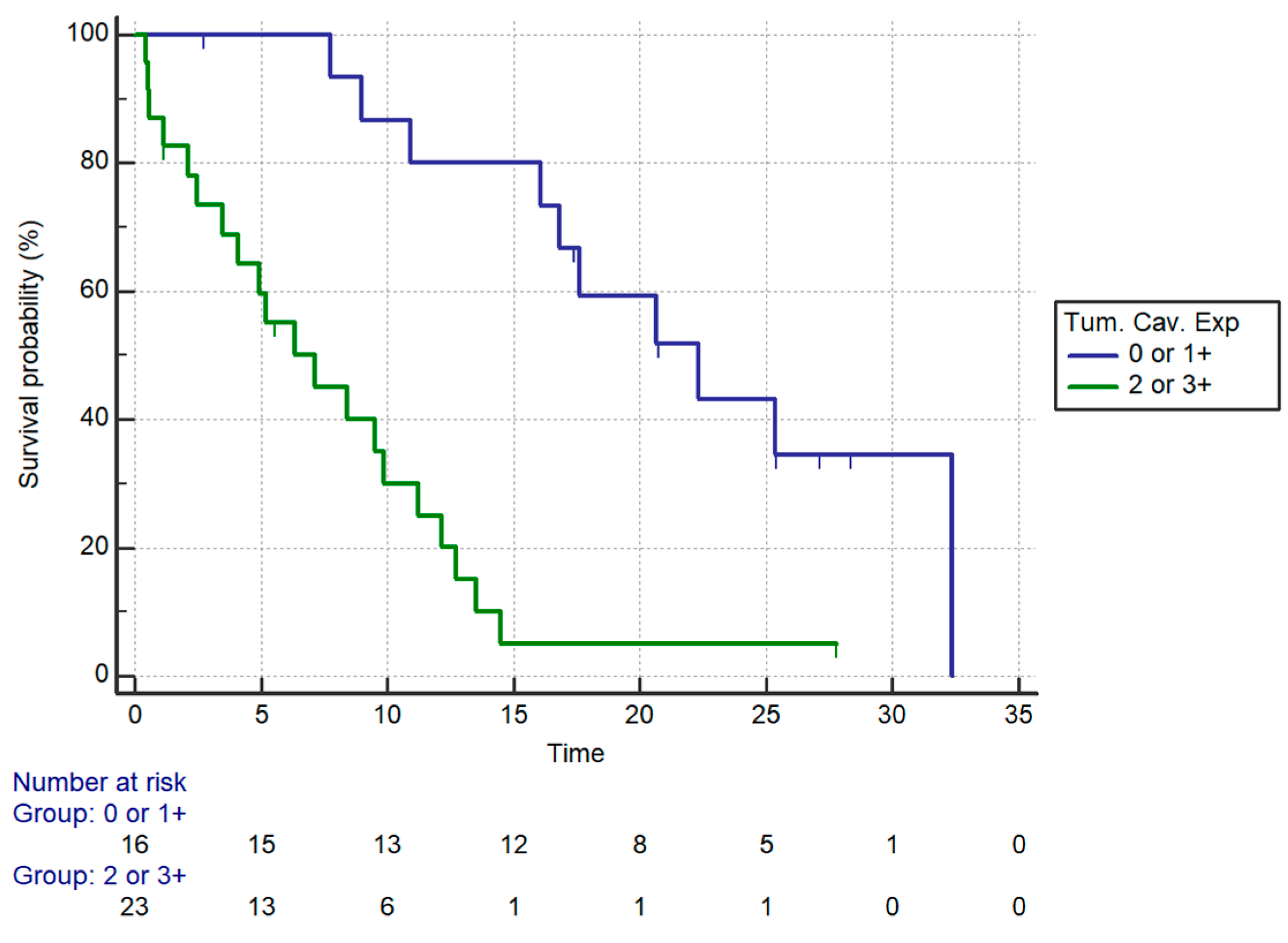
| Patients’ Characteristics | Univariate Analysis (OS) | mOS (Months) | Multivariate Analysis (OS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |||
| Age | <75 | 1.46 (0.56–3.76) | 0.43 | 12.72 | NS | |
| ≥75 | 7.15 | |||||
| ECOG-PS | 0 | 0.0012 | 16.02 | NS | ||
| 1 | 9.87 | |||||
| 2 | 2.46 | |||||
| Chemotherapy regimen | Monotherapy | 0.50 (0.15–1.67) | 0.09 | 10.92 | NS | |
| Combination | 12.72 | |||||
| Caveolin | 2+/3+ | 5.35 (2.38–12.05) | 0.0001 | 7.15 | 4.96 (2.02–12.16) | 0.0005 |
| 0/1+ | 22.3 | |||||
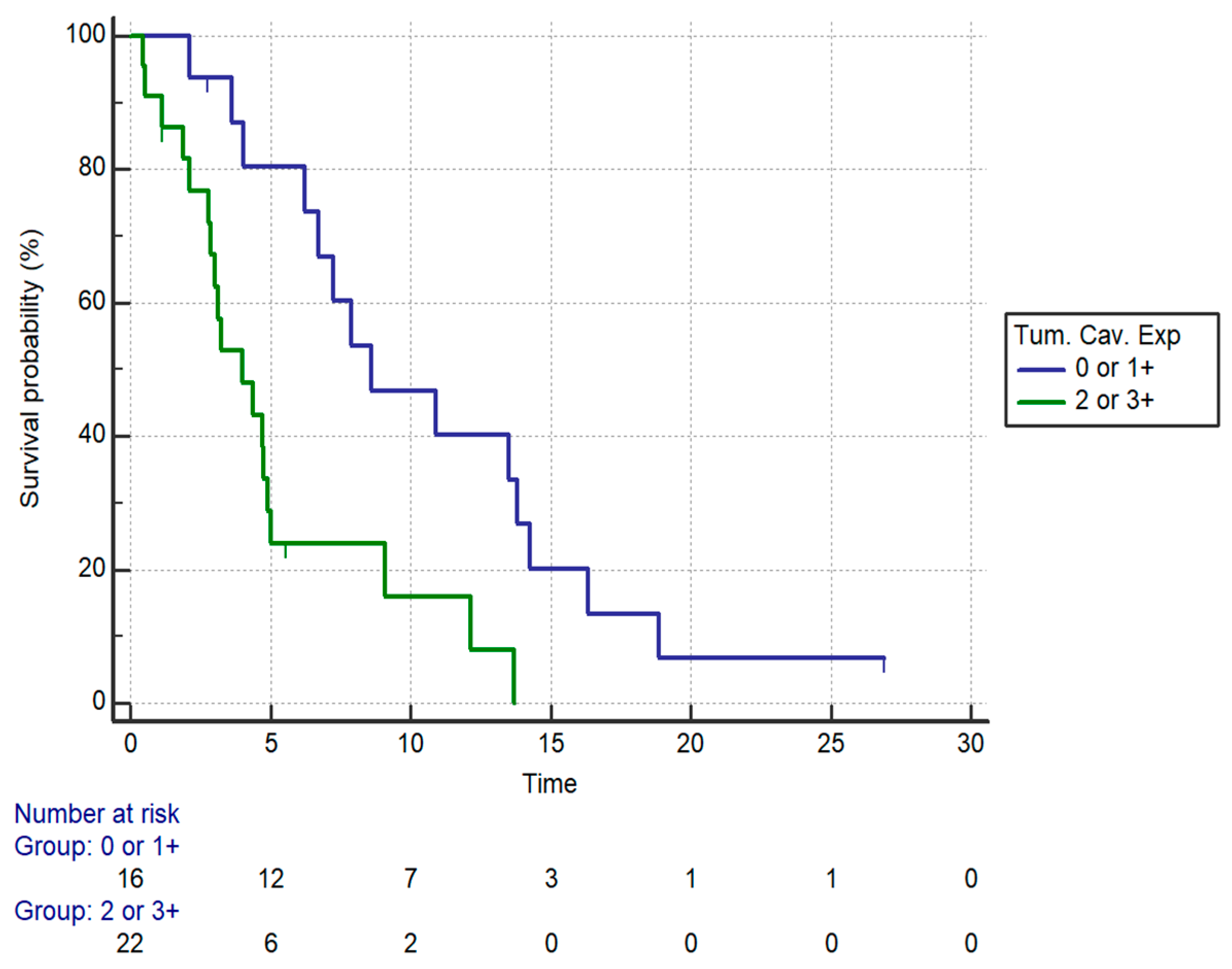
| Patients’ Characteristics | Univariate Analysis (PFS) | mPFS (Months) | Multivariate Analysis (PFS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |||
| Age | <75 | 1.5 (0.64–3.55) | 0.34 | 6.23 | NS | |
| ≥75 | 4.75 | |||||
| ECOG-PS | 0 | 0.0004 | 6.72 | NS | ||
| 1 | 7.87 | |||||
| 2 | 2.10 | |||||
| Chemotherapy regimen | Monotherapy | 0.30 (0.07–1.33) | <0.0001 | 2.79 | 0.3 (0.10–0.9) | 0.03 |
| Combination | 7.25 | |||||
| Caveolin | 2+/3+ | 3.12 (1.44–6.72) | 0.0037 | 4 | 2.81 (1.17–6.76) | 0.019 |
| 0/1+ | 8.59 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bittoni, A.; Giampieri, R.; Pecci, F.; Pinterpe, G.; Mandolesi, A.; Del Prete, M.; Zizzi, A.; Crocetti, S.; Liguori, C.; Mentrasti, G.; et al. Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3525-3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050303
Bittoni A, Giampieri R, Pecci F, Pinterpe G, Mandolesi A, Del Prete M, Zizzi A, Crocetti S, Liguori C, Mentrasti G, et al. Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(5):3525-3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050303
Chicago/Turabian StyleBittoni, Alessandro, Riccardo Giampieri, Federica Pecci, Giada Pinterpe, Alessandra Mandolesi, Michela Del Prete, Antonio Zizzi, Sonia Crocetti, Carolina Liguori, Giulia Mentrasti, and et al. 2021. "Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients" Current Oncology 28, no. 5: 3525-3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050303
APA StyleBittoni, A., Giampieri, R., Pecci, F., Pinterpe, G., Mandolesi, A., Del Prete, M., Zizzi, A., Crocetti, S., Liguori, C., Mentrasti, G., Cantini, L., Pellei, C., Bisonni, R., Scarpelli, M., & Berardi, R. (2021). Retrospective Cohort Study of Caveolin-1 Expression as Prognostic Factor in Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Current Oncology, 28(5), 3525-3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050303






