Re-Irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Radiation Therapy
2.3. Biologically Equivalent Dose
2.4. Systemic Treatment
2.5. Follow Up
2.6. Toxicity
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Re-Irradiation
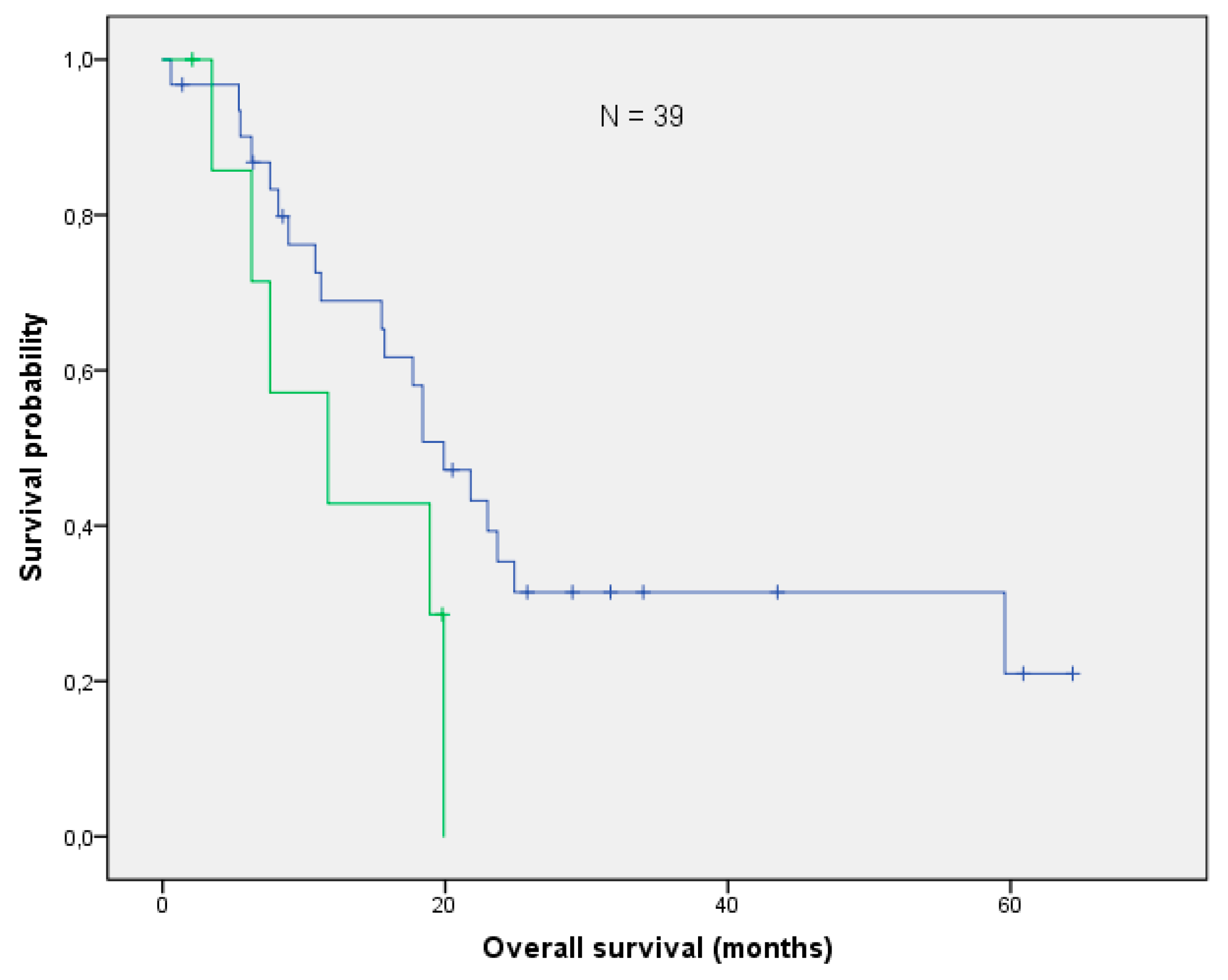
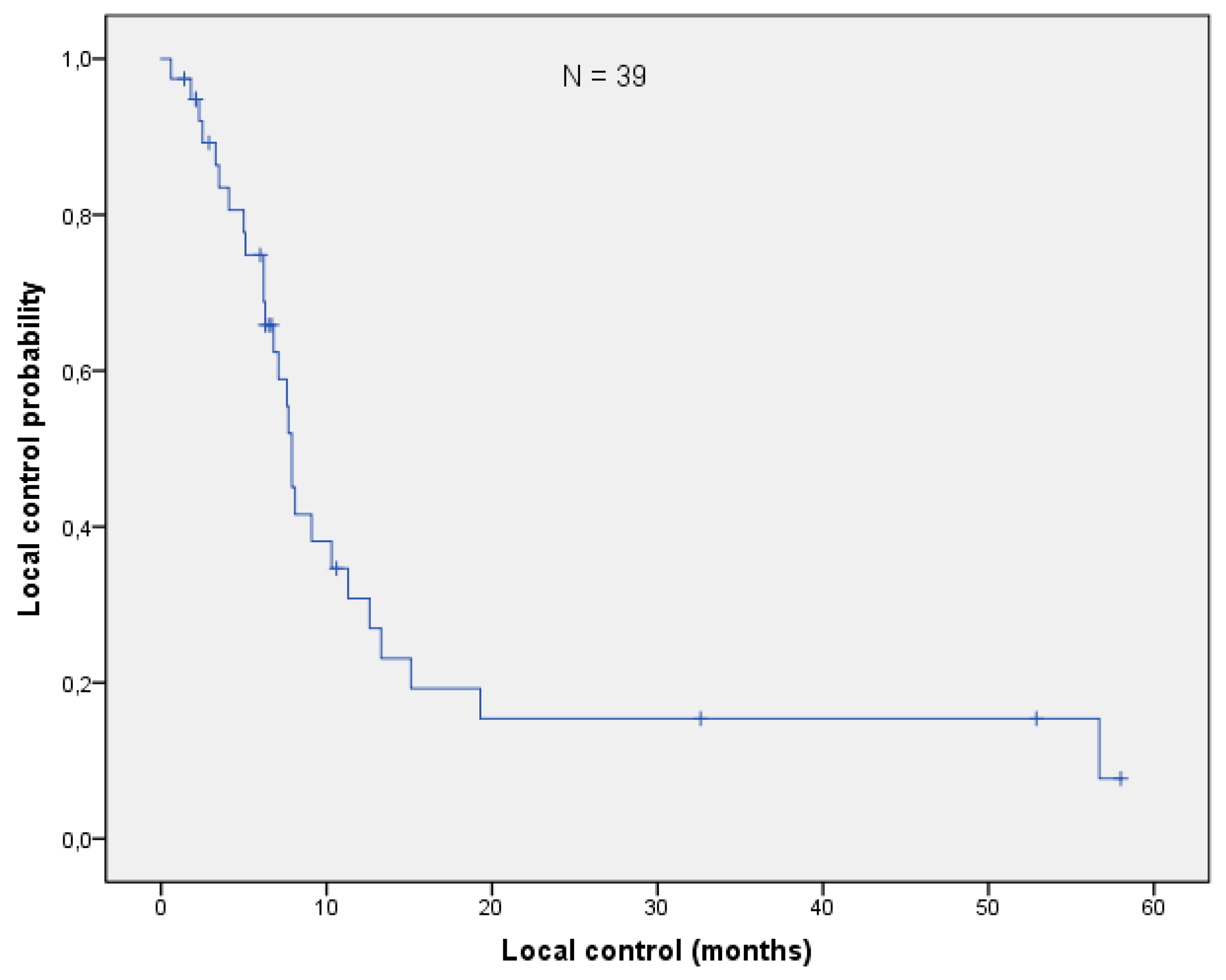
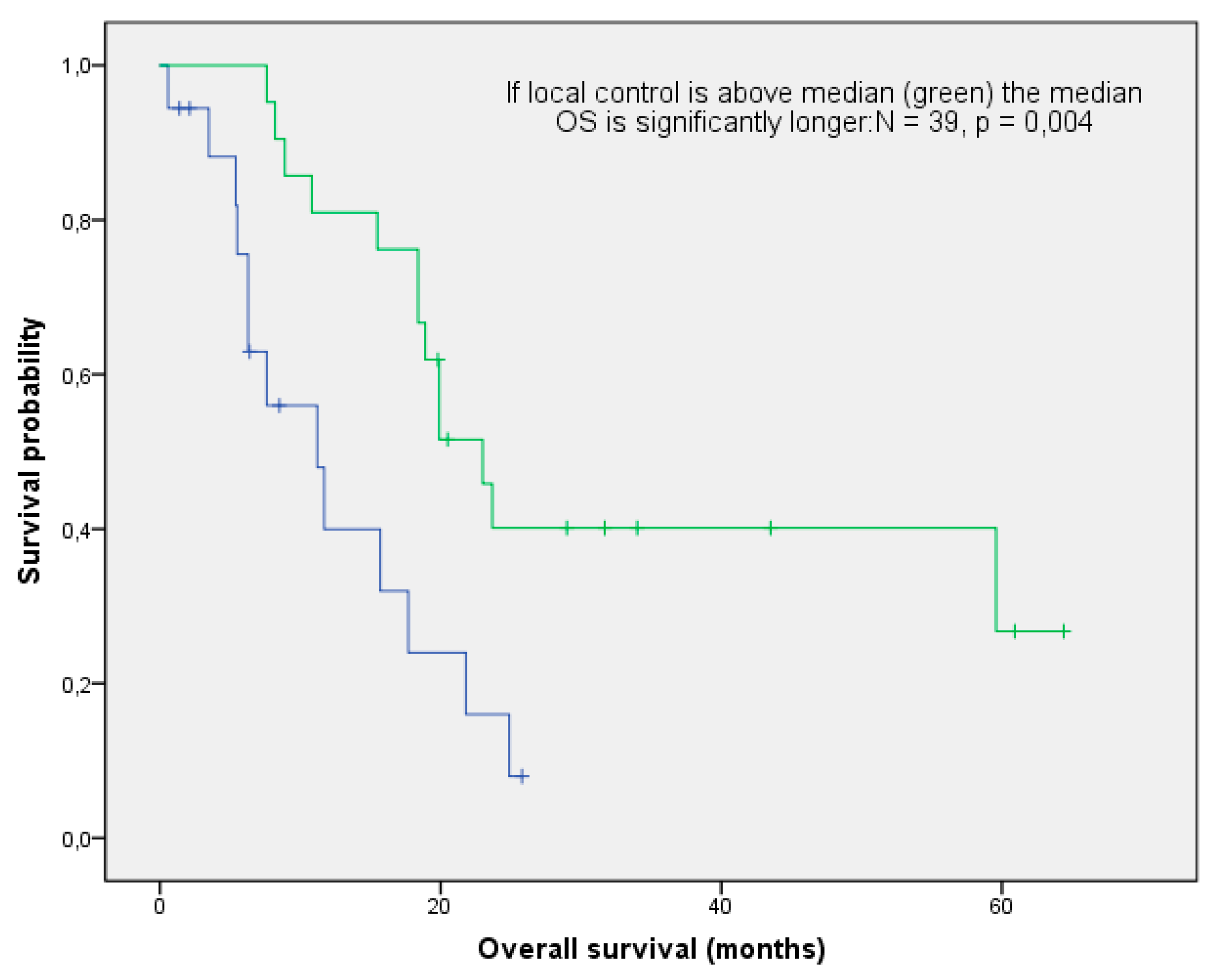
3.3. Overall Survival and Local Control
3.4. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCI | Charlson co-morbidity index |
| CTCAE | Common toxicity criteria for adverse events |
| DART | Dose-differentiated accelerated radiotherapy |
| ECOG | Eastern cooperative oncology group |
| EQD2 | Biologically equivalent dose in 2 Gy fractions |
| IMRT | Intensity modulated radiotherapy |
| LC | Local control |
| mOS | Median overall survival |
| MVA | Multivariate analysis |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OAR | Organs at risk |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PS | Performance score |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| SABR | Stereotactic ablative body therapy |
| SCLC | Small-cell lung cancer |
| UVA | Univariate analysis |
| VMAT | Volumetric intensity modulated arc therapy |
References
- Malvezzi, M.; Carioli, G.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; Vecchia, C.L.; Negri, E. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2019 with focus on breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 307, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohguri, T.; Imada, H.; Yahara, K.; Moon, S.D.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yatera, K.; Mukae, H.; Hanagiri, T.; Tanaka, F.; Korogi, Y. Re-irradiation plus regional hyperthermia for recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: A potential modality for inducing long-term survival in selected patients. Lung Cancer 2012, 771, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkley, M.S.; Hiniker, S.M.; Chaudhuri, A.; Maxim, P.G.; Diehn, M.; Loo, B.W.; Shultz, D.B. Dosimetric Factors and Toxicity in Highly Conformal Thoracic Reirradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 94, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumita, K.; Harada, H.; Asakura, H.; Ogawa, H.; Onoe, T.; Murayama, S.; Nakamura, S.; Tanigawa, N.; Takahashi, T.; Nishimura, T. Re-irradiation for locoregionally recurrent tumors of the thorax: A single-institution, retrospective study. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Jiang, G.-L.; Qian, H.; Wang, L.-J.; Yang, H.-J.; Fu, X.-L.; Zhao, S. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for locoregionally recurrent lung carcinoma after external beam irradiation: A prospective phase I–II clinical trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 57, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Le Pechoux, C.; Peeters, S.; Belderbos, J. High-dose re-irradiation following radical radiotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e620–e624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulach, R.; Hanna, G.G.; Franks, K.; McAleese, J.; Harrow, S. Re-irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: Evidence, Risks and Benefits. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremic, B.; Videtic, G.M.M. Chest Reirradiation with External Beam Radiotherapy for Locally Recurrent Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 80, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.; Melbye, R.W. Lung-Cancer—Retreatment of Local Recurrence after Definitive Irradiation. Cancer 1982, 49, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, G.H.; Dahele, M.; De Haan, P.F.; Van De Ven, P.M.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S. High-dose, conventionally fractionated thoracic reirradiation for lung tumors. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coon, D.; Gokhale, A.S.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E.; Ozhasoglu, C.; Christie, N. Fractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of primary, recurrent, and metastatic lung tumors: The role of positron emission tomography/computed tomography-based treatment planning. Clin. Lung Cancer 2008, 92, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijneke, T.R.; Petit, S.F.; Wentzler, D.; Hoogeman, M.; Nuyttens, J.J. Reirradiation and stereotactic radiotherapy for tumors in the lung: Dose summation and toxicity. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 107, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, T.; Shioyama, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Sasaki, T.; Ohga, S.; Shinto, M.; Terashima, K.; Asai, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Hirata, H.; et al. Definitive fractionated re-irradiation for local recurrence following stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 5649–5653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wurstbauer, K.; Deutschmann, H.; Dagn, K.; Kopp, P.; Zehentmayr, F.; Lamprecht, B.; Porsch, P.; Wegleitner, B.; Studnicka, M.; Sedlmayer, F. DART-bid (Dose-differentiated accelerated radiation therapy, 1.8 Gy twice daily)–A novel approach for non-resected NSCLC: Final results of a prospective study, correlating radiation dose to tumor volume. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambozov, B.; Wolf, F.; Kaiser, J.; Wass, R.; Fastner, G.; Gaisberger, C.; Rettenbacher, L.; Studnicka, M.; Pirich, C.; Sedlmayer, F.; et al. Pulmonary function decreases moderately after accelerated high-dose irradiation for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 11, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurstbauer, K.; Zehentmayr, F.; Deutschmann, H.; Dagn, K.; Exeli, A.-K.; Kopp, P.; Porsch, P.; Maurer, B.; Studnicka, M.; Sedlmayer, F. DART-bid for loco-regionally advanced NSCLC: Summary of acute and late toxicity with long-term follow-up; experiences with pulmonary dose constraints. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017, 193, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Murakami, M.; Yoden, E.; Sasaki, R.; Okuno, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Kuroda, Y. Reirradiation for locally recurrent lung cancer previously treated with radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 52, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusaris, H.; Storchi, P.R.M.; Brandwijk, R.P.; Nuyttens, J.J. Second re-irradiation: Efficacy, dose and toxicity in patients who received three courses of radiotherapy with overlapping fields. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 99, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, G.; Constine, L.S.; Moiseenko, V.; Correa, C.; Pierce, L.J.; Allen, A.M.; Marks, L.B. Radiation Dose–Volume Effects in the Heart. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 76, S77–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.F.; Tomé, W.A.; Fenwick, J.D.; Mehta, M.P. A challenge to traditional radiation oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 60, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Fukuda, H.; Matsui, K.; Hirashima, T.; Hosono, M.; Takada, Y.; Inoue, Y. Non-small-cell lung cancer: Reirradiation for loco-regional relapse previously treated with radiation therapy. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 10, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlampp, I.; Rieber, J.; Adeberg, S.; Bozorgmehr, F.; Heußel, C.P.; Steins, M.; Kappes, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J.; et al. Re-irradiation in locally recurrent lung cancer patients. Strahlenther Onkol. 2019, 195, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyngold, M.; Wu, A.J.; McLane, A.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, M.; Stein, N.F.; Zhou, Y.; Ho, A.Y.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Yorke, E.D.; et al. Toxicity and outcomes of thoracic re-irradiation using stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaes, R.J. Tumor heterogeneity, tumor size, and radioresistance. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1989, 17, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Balter, P.A.; Rebueno, N.; Sharp, H.J.; Liao, Z.; Komaki, R.; Chang, J.Y. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Patients With Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Thoracic Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 78, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Gomez, D.R.; Amini, A.; Rebueno, N.; Allen, P.K.; Martel, M.K.; Rineer, J.M.; Ang, K.K.; McAvoy, S.; Cox, J.D.; et al. Aortic dose constraints when reirradiating thoracic tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 106, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Vinogradskiy, Y.Y.; Swisher, S.G.; Komaki, R.; Chang, J.Y. Predicting Radiation Pneumonitis After Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Patients Previously Treated with Conventional Thoracic Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 84, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, J.M.; Kuremsky, J.G.; Blackstock, A.W.; Munley, M.; Kearns, W.; Hinson, W.; Lovato, J.; Miller, A.; Petty, W.; Urbanic, J. Thoracic re-irradiation using stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) techniques as first or second course of treatment. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borm, K.J.; Oechsner, M.; Schiller, K.; Peeken, J.C.; Dapper, H.; Munch, S.; Kroll, L.; Combs, S.E.; Duma, M.N. Prognostic factors in stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung metastases. Strahlenther Onkol. 2018, 194, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Mannsaker, B.; Yobuta, R.; Haukland, E. Provider decision regret-a useful method for analysis of palliative thoracic re-irradiation for lung cancer? Strahlenther Onkol. 2020, 196, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruser, T.J.; McCabe, B.P.; Mehta, M.P.; Khuntia, D.; Campbell, T.; Geye, H.; Cannon, G. Reirradiation for locoregionally recurrent lung cancer: Outcomes in small cell and non-small cell lung carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montebello, J.F.; Aron, B.S.; Manatunga, A.K.; Horvath, J.L.; Peyton, F.W. The Reirradiation of Recurrent Bronchogenic Carcinoma with External Beam Irradiation. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 16, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetingoz, R.; Arican-Alicikus, Z.; Nur-Demiral, A.; Durmak-Isman, B.; Bakis-Altas, B.; Kinay, M. Is re-irradiation effective in symptomatic local recurrence of non small cell lung cancer patients? A single institution experience and review of the literature. Int. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2009, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar]

| Patient Characteristics and Treatment Factors | NSCLC N = 31 | SCLC N = 8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Characteristics | Age (years) | median | 66.5 | 66.1 |
| range | 52–83 | 52–73 | ||
| Sex | male | 20 | 5 | |
| female | 11 | 3 | ||
| Weight loss (%) | >5% | 17 | 5 | |
| <5% | 14 | 3 | ||
| ECOG | 0–1 | 27 | 6 | |
| 2 | 4 | 2 | ||
| Histology | SCLC | 0 | 8 | |
| NSCLC | 30 | 0 | ||
| unknown | 1 * | 0 | ||
| T-stage | x | 2 | 1 | |
| 1 | 6 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 16 | 0 | ||
| 3 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 4 | 3 | 2 | ||
| N-stage | 0 | 7 | 0 | |
| 1 | 4 | 2 | ||
| 2 | 16 | 4 | ||
| 3 | 4 | 2 | ||
| M-stage | 0 | 26 | 6 | |
| 1 | 5 | 2 | ||
| UICC-stage | I | 4 | 0 | |
| II | 5 | 1 | ||
| III | 17 | 5 | ||
| IV | 5 | 2 | ||
| FEV1 (%) | median | 72 | 70 | |
| range | 29–100 | 35–100 | ||
| COPD grade | 0 | 13 | 1 | |
| 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 2 | 6 | ||
| 3 | 9 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 4 | 1 | ||
| unknown | 1 | 0 | ||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | median | 6 | 9 | |
| range | 3–10 | 4–10 | ||
| Treatment Related Factors | Re-rad volume (mL) | median | 45 | 48 |
| range | 4–239 | 9–541 | ||
| Tumor location at re-rad (n) | peripheral | 16 | 1 | |
| central | 15 | 7 | ||
| EQD2 (Gy) at first radiation | median | 77 | 47 | |
| range | 50–88 | 40–60 | ||
| EQD2 (Gy) at re-rad | median | 61 | 46 | |
| range | 44–133 | 40–50 | ||
| Cumulative EQD2 (Gy) | median | 135 | 84 | |
| range | 98–211 | 77–193 | ||
| First radiation fractionation | DART-bid | 16 | 4 | |
| SABR | 9 | 0 | ||
| Hypofracionated-RT | 3 | 3 | ||
| Conventional-RT | 3 | 1 | ||
| Re-rad fractionation | DART-bid | 17 | 3 | |
| SABR | 9 | 1 | ||
| Hypofracionated-RT | 2 | 3 | ||
| Conventional-RT | 2 | 2 | ||
| Systemic therapy at first radiation (n) | yes | 23 | 8 | |
| no | 8 | 0 | ||
| Systemic therapy at re-rad (n) | yes | 16 | 2 | |
| no | 15 | 6 | ||
| Interval between radiation courses (months) | median | 21 | 16 | |
| range | 9–80 | 6–145 | ||
| V20 total lung (%) at re-rad | median | 27 | 27 | |
| range | 3–43 | 3–53 | ||
| V25 heart (%) at re-rad | median | 4 | 1.5 | |
| range | 1–75 | 1–16.5 | ||
| Toxicity (N = 39) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Toxicity | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Grade 5 | |
| Acute | Esophagitis | n.a. | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Pneumonitis | n.a. | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Heart | n.a. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Late | Esophagitis | n.a. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pneumonitis | n.a. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hemorrhage | n.a. | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grambozov, B.; Nussdorfer, E.; Kaiser, J.; Gerum, S.; Fastner, G.; Stana, M.; Gaisberger, C.; Wass, R.; Studnicka, M.; Sedlmayer, F.; et al. Re-Irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1835-1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030170
Grambozov B, Nussdorfer E, Kaiser J, Gerum S, Fastner G, Stana M, Gaisberger C, Wass R, Studnicka M, Sedlmayer F, et al. Re-Irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(3):1835-1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030170
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrambozov, Brane, Evelyn Nussdorfer, Julia Kaiser, Sabine Gerum, Gerd Fastner, Markus Stana, Christoph Gaisberger, Romana Wass, Michael Studnicka, Felix Sedlmayer, and et al. 2021. "Re-Irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis" Current Oncology 28, no. 3: 1835-1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030170
APA StyleGrambozov, B., Nussdorfer, E., Kaiser, J., Gerum, S., Fastner, G., Stana, M., Gaisberger, C., Wass, R., Studnicka, M., Sedlmayer, F., & Zehentmayr, F. (2021). Re-Irradiation for Locally Recurrent Lung Cancer: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis. Current Oncology, 28(3), 1835-1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030170






