Impact of an Augmented Reality Navigation System (SIRIO) on Bone Percutaneous Procedures: A Comparative Analysis with Standard CT-Guided Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Groups
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Biopsies
2.2.2. Ablations
2.3. SIRIO Augmented Reality Navigation System
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berning, W.; Freyschmidt, J.; Ostertag, H. Percutaneous bone biopsy, techniques and indications. Eur. Radiol. 1996, 6, 875–881. [Google Scholar]
- Monfardini, L.; Preda, L.; Aurilio, G.; Rizzo, S.; Bagnardi, V.; Renne, G.; Maccagnoni, S.; Vigna, P.D.; Davide, D.; Bellomi, M. CT-guided bone biopsy in cancer patients with suspected bone metastases: Retrospective review of 308 procedures. Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, R.F.; Faiella, E.; Luppi, G.; Schena, E.; Giurazza, F.; Del Vescovo, R.; D’Agostino, F.; Cazzato, R.L.; Beomonte Zobel, B. Percutaneous lung biopsy: Comparison between an augmented reality CT navigation system and standard CT-guided technique. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2013, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, M.A.; Brinjikji, W.; Copelan, A.; Venkatesan, A.M. Navigational Tools for Interventional Radiology and Interventional Oncology Applications. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 32, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.J.; Zhang, H.; Durrani, A.; Glossop, N.; Ranjan, S.; Lindisch, D.; Levy, E.; Banovac, F.; Borgert, J.; Krueger, S.; et al. Navigation with electromagnetic tracking for interventional radiology procedures: A feasibility study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. JVIR 2005, 16, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, L.; Sosna, J.; Nissenbaum, Y.; Benshtein, A.; Goldberg, S.N. Electromagnetic navigation system for CT-guided biopsy of small lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruners, P.; Penzkofer, T.; Nagel, M.; Elfring, R.; Gronloh, N.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Günther, R.W.; Mahnken, A.H. Electromagnetic tracking for CT-guided spine interventions: Phantom, ex-vivo and in-vivo results. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Meitinger, M.; Nagel, M.; Kalender, W.; Bautz, W.A.; Baum, U. [Computer-assisted navigation system for interventional CT-guided procedures: Results of phantom and clinical studies]. ROFO Fortschr. Geb. Rontgenstr. Nuklearmed. 2008, 180, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghayev, E.; Ebert, L.C.; Christe, A.; Jackowski, C.; Rudolph, T.; Kowal, J.; Vock, P.; Thali, M.J. CT data-based navigation for post-mortem biopsy—A feasibility study. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2008, 15, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Dogan, S.; Maataoui, A.; Gurung, J.; Schiemann, M.; Ackermann, H.; Wesarg, S.; Sakas, G.; Vogl, T.J. Accuracy of biopsy needle navigation using the Medarpa system--computed tomography reality superimposed on the site of intervention. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Dogan, S.; Maataoui, A.; Wesarg, S.; Gurung, J.; Ackermann, H.; Schiemann, M.; Wimmer-Greinecker, G.; Vogl, T.J. Navigation-based needle puncture of a cadaver using a hybrid tracking navigational system. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, G.; Zheng, J.; Wen, S.; Zeng, H.; Hao, W.; Luo, J.; Guo, L. Electromagnetic navigation to assist with computed tomography-guided thermal ablation of liver tumors. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. MITAT Off. J. Soc. Minim. Invasive Ther. 2020, 29, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringe, K.I.; Pöhler, G.H.; Rabeh, H.; Wacker, F. Electromagnetic Navigation System-Guided Microwave Ablation of Hepatic Tumors: A Matched Cohort Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalič, R.; Zdovc, J.; Mohar, J.; Trebše, R. Electromagnetic navigation system for acetabular component placement in total hip arthroplasty is more precise and accurate than the freehand technique: A randomized, controlled trial with 84 patients. Acta Orthop. 2020, 91, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attivissimo, F.; Lanzolla, A.M.L.; Carlone, S.; Larizza, P.; Brunetti, G. A novel electromagnetic tracking system for surgery navigation. Comput. Assist. Surg. Abingdon Engl. 2018, 23, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, B.; Tselikas, L.; De Baere, T.; Varin, F.; Abed, A.; Debays, L.; Bardoulat, C.; Hakime, A.; Teriitehau, C.; Deschamps, F.; et al. CT guidance assisted by electromagnetic navigation system for percutaneous fixation by internal cemented screws (FICS). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-F.; Jiao, D.-C.; Ren, J.-Z.; Zhang, W.-G.; Han, X.-W. Percutaneous bone biopsy using a flat-panel cone beam computed tomography virtual navigation system. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselikas, L.; Joskin, J.; Roquet, F.; Farouil, G.; Dreuil, S.; Hakimé, A.; Teriitehau, C.; Auperin, A.; de Baere, T.; Deschamps, F. Percutaneous bone biopsies: Comparison between flat-panel cone-beam CT and CT-scan guidance. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 38, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floridi, C.; Carnevale, A.; Fumarola, E.M.; Schampaert, S.; Fontana, F.; De Palma, D.; Del Sole, A.; Giganti, M.; Carrafiello, G. Percutaneous Lung Tumor Biopsy Under CBCT Guidance with PET-CT Fusion Imaging: Preliminary Experience. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, C.; Becker, J.; Deli, M.; Busch, M.; Boehme, M.; Groenemeyer, D.H.W. A novel Laser Navigation System reduces radiation exposure and improves accuracy and workflow of CT-guided spinal interventions: A prospective, randomized, controlled, clinical trial in comparison to conventional freehand puncture. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagadis, G.C.; Katsanos, K.; Karnabatidis, D.; Loudos, G.; Nikiforidis, G.C.; Hendee, W.R. Emerging technologies for image guidance and device navigation in interventional radiology. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 5768–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xiao, Y.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A.-L.; Li, H.-J.; Gao, D.-F. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided percutaneous cryoablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in special regions. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. HBPD INT 2010, 9, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faiella, E.; Frauenfelder, G.; Santucci, D.; Luppi, G.; Schena, E.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Grasso, R.F. Percutaneous low-dose CT-guided lung biopsy with an augmented reality navigation system: Validation of the technique on 496 suspected lesions. Clin. Imaging 2018, 49, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, F.; Bruno, F.; Zugaro, L.; Natella, R.; Cappabianca, S.; Russo, U.; Papapietro, V.R.; Splendiani, A.; Cesare, E.D.; Masciocchi, C.; et al. Developments in the management of bone metastases with interventional radiology. Acta Bio Med. Atenei Parm. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 166. [Google Scholar]
- Huda, W.; Mettler, F.A. Volume CT dose index and dose-length product displayed during CT: What good are they? Radiology 2011, 258, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, L.A.; Jamadar, D.A.; Jacobson, J.A.; DeMaeseneer, M.O.; Ebrahim, F.S.; Sabb, B.J.; Kretschmer, M.T.; Biermann, J.S.; Kim, S.-M. CT-guided biopsy of bone: A radiologist’s perspective. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, W283–W289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.C.B.; Stavas, J.M. Bone and Soft Tissue Ablation. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 31, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guberina, N.; Forsting, M.; Ringelstein, A.; Suntharalingam, S.; Nassenstein, K.; Theysohn, J.; Wetter, A. Radiation exposure during CT-guided biopsies: Recent CT machines provide markedly lower doses. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurban, L.A.; Gomersall, L.; Weir, J.; Wade, P. Fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous lung biopsy: A valuable alternative to computed tomography. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, T.; Lund, T.; Ylikoski, M.; Lohikoski, J.; Schlenzka, D. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with and without computer assistance: A randomised controlled clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Eur. Spine J. Off. Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deform. Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 2000, 9, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, C.; Wigfield, C. Image-guided surgery: Applications to the cervical and thoracic spine and a review of the first 120 procedures. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 92, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, G.; Caivano, R.; Villonio, A.; Semeraro, V.; Lucarelli, N.M.; Ganimede, M.P.; Gisone, V.; Dinardo, G.; Bruno, S.; Macarini, L.; et al. Percutaneous Computed Tomography-Guided Lung Biopsies using a Virtual Navigation Guidance: Our Experience. Cancer Investig. 2018, 36, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, R.F.; Cazzato, R.L.; Luppi, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Schena, E.; Del Vescovo, R.; Giurazza, F.; Faiella, E.; Beomonte Zobel, B. Percutaneous lung biopsies: Performance of an optical CT-based navigation system with a low-dose protocol. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, V.J.; Zhang, J.; Bruner, A.P. Impact of physician practice on patient radiation dose during CT guided biopsy procedures. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2014, 22, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.-D.; Weng, H.-H.; Hsu, S.-L.; Hsu, L.-S.; Lin, W.-M.; Chen, C.-W.; Tsai, Y.-H. Accuracy and complications of CT-guided pulmonary core biopsy in small nodules: A single-center experience. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, H.F.; Yu, J.H.; Xu, X.X. CT-guided percutaneous core needle biopsy for small (≤ 20 mm) pulmonary lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, e43–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Thiruvalluvan, K.; Krzeminski, L.; Moore, W.H.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Z. CT-guided robotic needle biopsy of lung nodules with respiratory motion—Experimental system and preliminary test. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. MRCAS 2013, 9, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.M. Perspective on Precision Medicine in Oncology. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 37, 988–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, I.R.; Fuchs, O.; Hansen, G.; von Mutius, E.; Kopp, M.V. What is precision medicine? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswami, R.; Bayer, R.; Galea, S. Precision Medicine from a Public Health Perspective. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, A.R. Precision Medicine. Health Aff. Proj. Hope 2018, 37, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
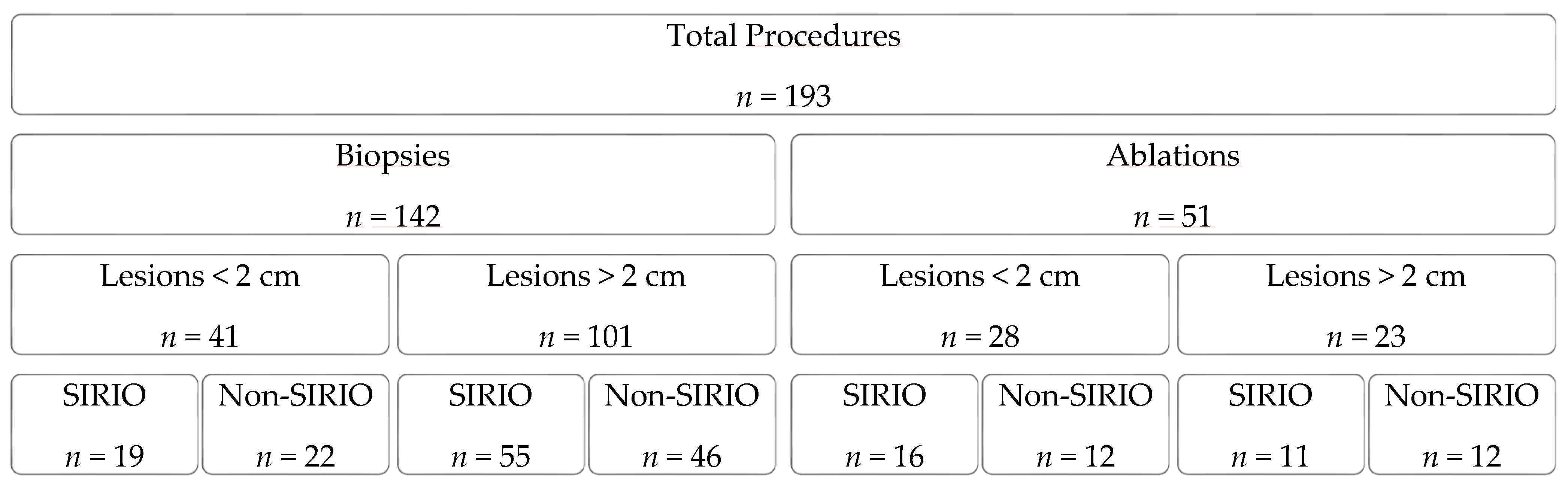
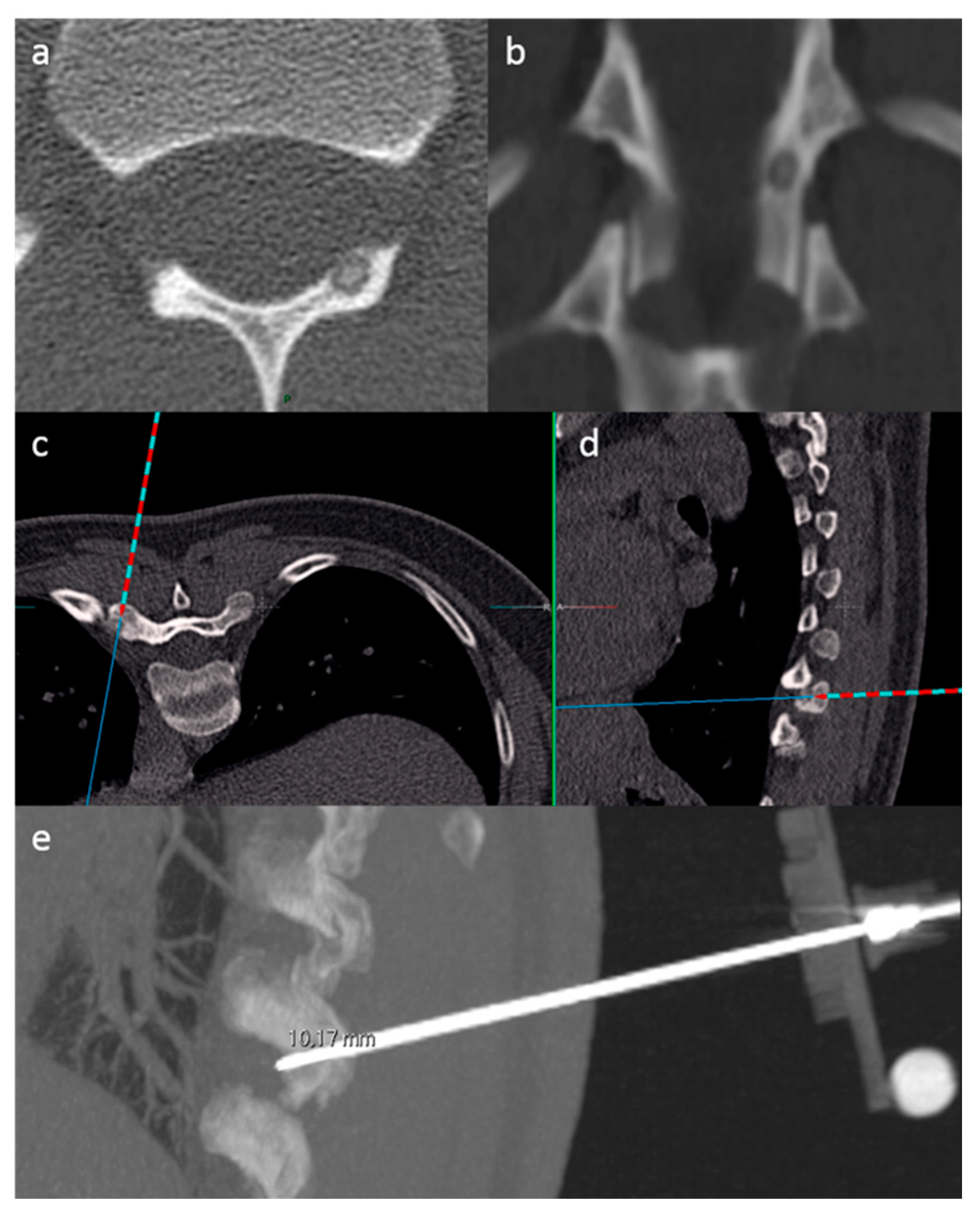
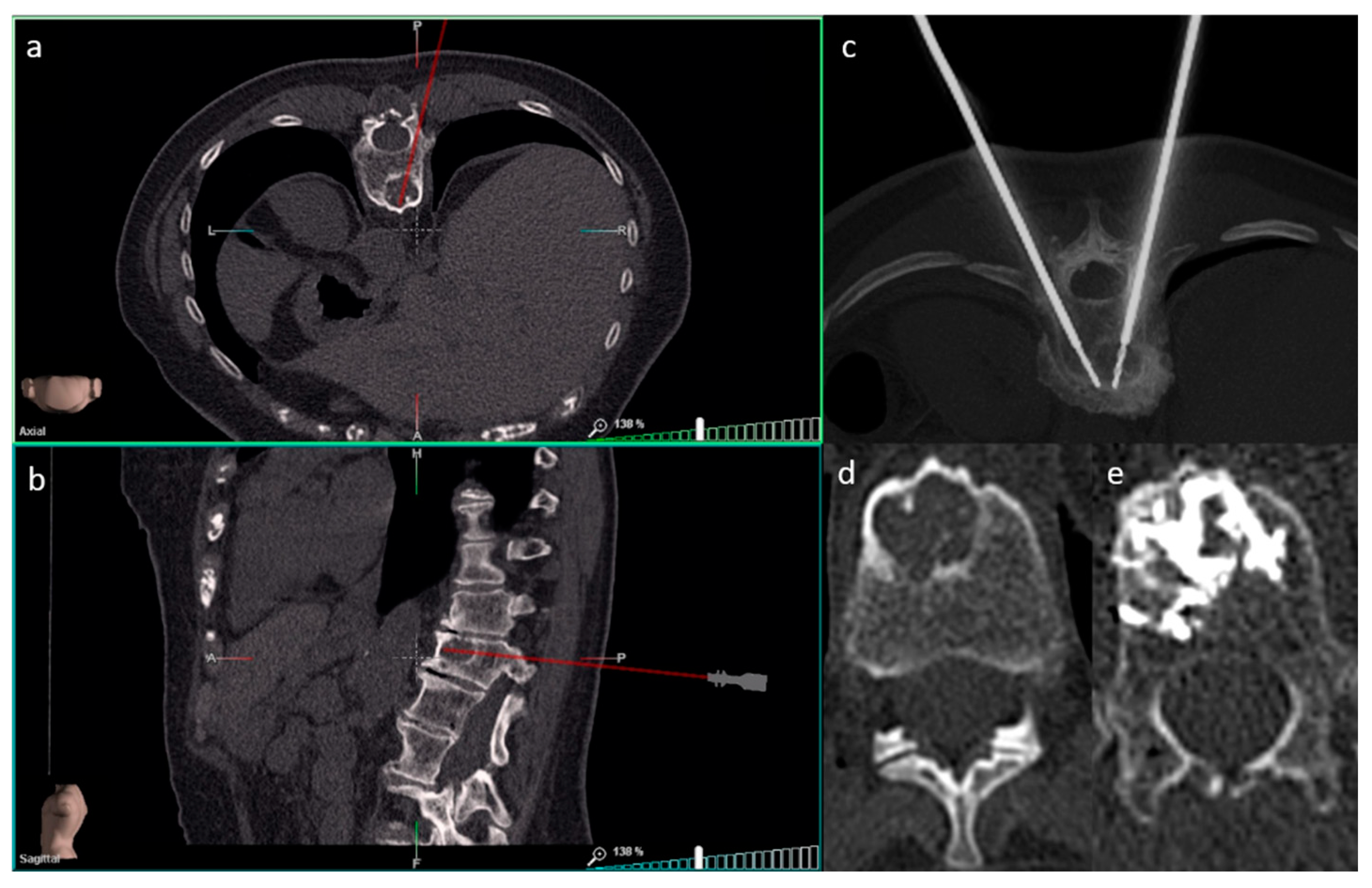
| Biopsies | SIRIO | Non-SIRIO |
|---|---|---|
| <2 cm | ||
| n (males; females) | 19 (7; 12) | 22 (10; 12) |
| Age (mean) ± SD | 61.4 ± 11.9 | 56.8 ± 13.9 |
| >2 cm | ||
| n (males; females) | 55 (22; 33) | 46 (15; 31) |
| Age (mean) ± SD | 60.9 ± 15.4 | 61.3 ± 15.3 |
| Ablations | ||
| <2 cm | ||
| n (males; females) | 16 (12; 4) | 12 (6; 6) |
| Age (mean) ± SD | 29.4 ± 16.4 | 29.7 ± 11.1 |
| >2 cm | ||
| n (males; females) | 11 (5; 6) | 12 (5; 7) |
| Age (mean) ± SD | 65.9 ± 8.7 | 55.5 ± 18.1 |
| Lesion Characteristics | n |
|---|---|
| Lesion Site | |
| Vertebrae | 56 |
| Sternum/Ribs | 19 |
| Pelvic bones | 63 |
| Upper limb bones | 12 |
| Lower limb bones | 43 |
| Lesion Types | |
| Metastases | 100 |
| Osteoid osteomas | 31 |
| Multiple myelomas | 4 |
| Osteoblastoma | 1 |
| Infectious/inflammatory | 8 |
| Other non-malignant | 35 |
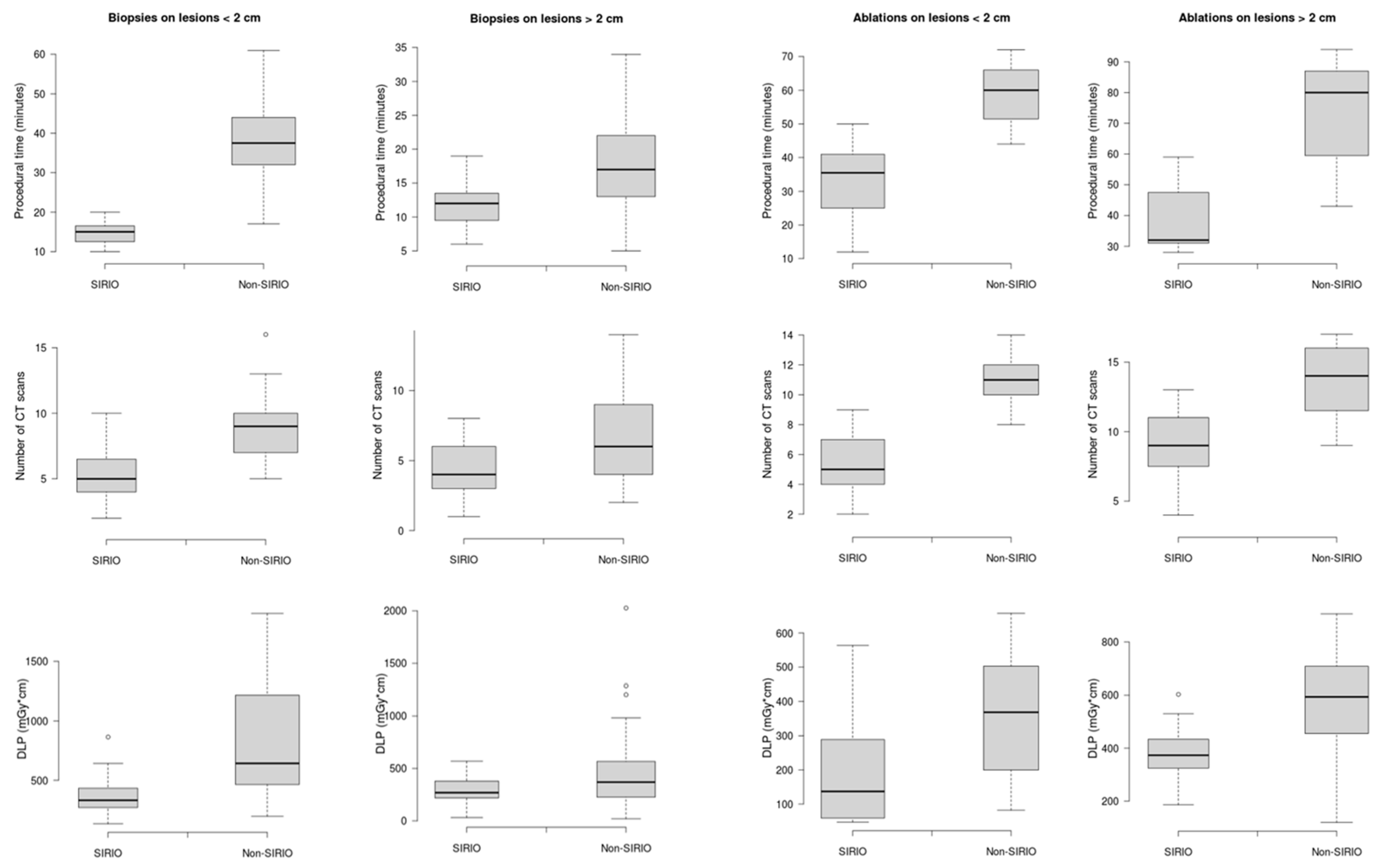
| Variables | Biopsies | Ablations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 cm | >2 cm | <2 cm | >2 cm | |||||
| SIRIO | Non-SIRIO | SIRIO | Non-SIRIO | SIRIO | Non-SIRIO | SIRIO | Non-SIRIO | |
| Procedural time (min) | 14.6 ± 3 | 38.1 ± 11.4 | 12.1 ± 2.8 | 14 ± 4 | 33.2 ± 10.7 | 58.8 ± 9.4 | 38 ± 10.5 | 73.6 ± 1.2 |
| CT-s | 5 ± 2 | 9 ± 3 | 3 ± 2 | 5 ± 3 | 5 ± 2 | 11 ± 2 | 9 ± 3 | 14 ± 3 |
| DLP (mGy*cm) | 369.8 ± 178.8 | 829.3 ± 475.1 | 313.9 ± 132.4 | 446 ± 371.2 | 190.3 ± 168.6 | 360.4 ± 192.3 | 383.1 ± 117.3 | 555.8 ± 237.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faiella, E.; Castiello, G.; Bernetti, C.; Pacella, G.; Altomare, C.; Andresciani, F.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Grasso, R.F. Impact of an Augmented Reality Navigation System (SIRIO) on Bone Percutaneous Procedures: A Comparative Analysis with Standard CT-Guided Technique. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1751-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030163
Faiella E, Castiello G, Bernetti C, Pacella G, Altomare C, Andresciani F, Beomonte Zobel B, Grasso RF. Impact of an Augmented Reality Navigation System (SIRIO) on Bone Percutaneous Procedures: A Comparative Analysis with Standard CT-Guided Technique. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(3):1751-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030163
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaiella, Eliodoro, Gennaro Castiello, Caterina Bernetti, Giuseppina Pacella, Carlo Altomare, Flavio Andresciani, Bruno Beomonte Zobel, and Rosario Francesco Grasso. 2021. "Impact of an Augmented Reality Navigation System (SIRIO) on Bone Percutaneous Procedures: A Comparative Analysis with Standard CT-Guided Technique" Current Oncology 28, no. 3: 1751-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030163
APA StyleFaiella, E., Castiello, G., Bernetti, C., Pacella, G., Altomare, C., Andresciani, F., Beomonte Zobel, B., & Grasso, R. F. (2021). Impact of an Augmented Reality Navigation System (SIRIO) on Bone Percutaneous Procedures: A Comparative Analysis with Standard CT-Guided Technique. Current Oncology, 28(3), 1751-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28030163






