Clinicopathologic and Treatment Features of Long-Term Surviving Brain Metastasis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Treatment and Follow-up Protocols
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
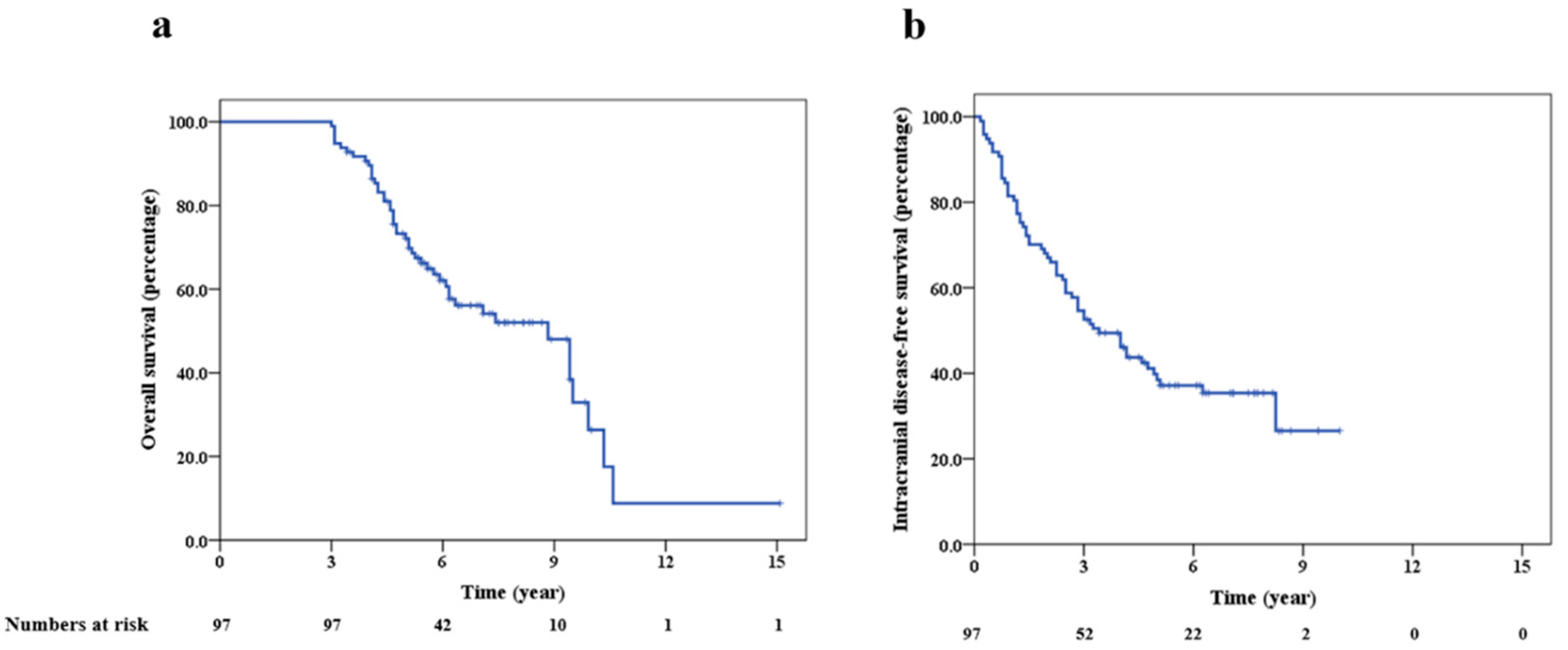
3.1. Survival
3.2. Patient Clinical and Treatment Features
3.3. Intracranial Outcomes
3.4. Long-Term Toxicity
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence Proportions of Brain Metastases in Patients Diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagney, D.N.; Martin, A.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Redig, A.J.; Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y.; Dunn, I.F.; Bi, W.L.; Weiss, S.E.; et al. Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: A population-based study. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvold, N.D.; Lee, E.Q.; Mehta, M.P.; Margolin, K.; Alexander, B.M.; Lin, N.U.; Anders, C.K.; Soffietti, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khan, O.H.; Asher, A.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Gondi, V. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases: Evolution or Revolution? J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G.; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahgal, A.; Aoyama, H.; Kocher, M.; Neupane, B.; Collette, S.; Tago, M.; Shaw, P.; Beyene, J.; Chang, E.L. Phase 3 trials of stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for 1 to 4 brain metastases: Individual patient data meta-analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Diéras, V.; Paul, D.; Lossignol, D.; Christodoulou, C.; Stemmler, H.-J.; Roche, H.; Liu, C.M.H.; Greil, R.; Ciruelos, E.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Lapatinib in Patients with Brain Metastases from HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.K.; Korpanty, G.J.; Tomasini, P.; Alizadeh, M.; Jao, K.; Labbé, C.; Mascaux, C.M.; Martin, P.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Tsao, M.-S.; et al. Treatment options for patients with brain metastases from EGFR/ALK -driven lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Algazi, A.P.; Hamid, O.; Hodi, F.S.; Moschos, S.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lewis, K.; Lao, C.D.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Melanoma Metastatic to the Brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Djalilian, H.R.; Nussbaum, E.S.; Cho, K.H. Long-term survival with metastatic cancer to the brain. Med. Oncol. 2000, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterbach, J.; Bartelt, S.; Ostertag, C. Long-term survival in patients with brain metastases. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 128, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondziolka, D.; Martin, J.J.; Flickinger, J.C.; Friedland, D.M.; Brufsky, A.M.; Baar, J.; Agarwala, S.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Lunsford, L.D. Long-term survivors after gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases. Cancer 2005, 104, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.T.; Barnett, G.H.; Liu, S.W.; Reuther, A.M.; Toms, S.A.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Videtic, G.M.; Suh, J.H. Five-year survivors of brain metastases: A single-institution report of 32 patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, M.; Glogowski, M.W.; Tyc-Szczepaniak, D.; Wierzchowski, M.; Kepka, L. Characteristics of long-term survivors of brain metastases from lung cancer. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2011, 16, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, F.; Geisenberger, C.; Jungk, C.; Bermejo, J.L.; Warta, R.; Von Deimling, A.; Herold-Mende, C.; Unterberg, A. Prognostic factors and long-term survival in surgically treated brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 142, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Vogel, S.; Suh, J.H.; Barnett, G.H.; Murphy, E.S.; Reddy, C.A.; Parsons, M.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Angelov, L.; Mohammadi, A.M.; et al. A cure is possible: A study of 10-year survivors of brain metastases. J. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 129, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Berkey, B.; Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.; Curran, W. A New Prognostic Index and Comparison to Three Other Indices for Patients with Brain Metastases: An Analysis of 1,960 Patients in the RTOG Database. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Mehta, M.P. Prognostic indices for brain metastases—Usefulness and challenges. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: An update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Effect of Tumor Subtype on Survival and the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Patients with Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Jiang, W.; Brown, P.D.; Braunstein, S.; Sneed, P.; Wattson, D.A.; Shih, H.A.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Lockney, N.A.; et al. Estimating Survival in Melanoma Patients with Brain Metastases: An Update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Melanoma Using Molecular Markers (Melanoma-molGPA). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary Report on the Graded Prognostic Assessment: An Accurate and Facile Diagnosis-Specific Tool to Estimate Survival for Patients with Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltman, E.; Salvajoli, J.V.; Brandt, R.A.; Hanriot, R.D.M.; Prisco, F.E.; Cruz, J.C.; Borges, S.R.D.O.; Wajsbrot, D.B. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: A score index for predicting prognosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.-T.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Suh, C.; Lee, J. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulli, E.; Legramandi, L.; Salvati, L.; Mandala, M. The impact of targeted therapies and immunotherapy in melanoma brain metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer 2019, 125, 3776–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | Long-Term Survivors (n = 97) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| <60 years | 69 (71%) |
| 60 years or more | 28 (29%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 23 (24%) |
| Female | 74 (76%) |
| ECOG (during diagnosis of BM) | |
| 0–1 | 73 (75%) |
| 2 or more | 13 (14%) |
| Unknown | 11 (11%) |
| Number of intracranial lesions (at time of BM diagnosis) | |
| Single | 63 (65%) |
| Multiple | 34 (35%) |
| Primary | |
| Lung | 51 (52%) |
| Breast | 24 (25%) |
| Thyroid | 6 (7%) |
| Melanoma (skin) | 5 (5%) |
| Kidney | 3 (3%) |
| Unknown primary | 3 (3%) |
| Gynecological malignancies | 2 (2%) |
| Male genitourinary | 1 (1%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 1 (1%) |
| Head neck | 1 (1%) |
| Extracranial disease status (at the time of BM diagnosis) | |
| Controlled | 38 (39%) |
| Uncontrolled | 59 (61%) |
| Interval from cancer diagnosis to detection of BM | |
| Median (range) | 15 (0–266) months |
| First site of metastasis | |
| Brain | 74 (76%) |
| Others | 23 (24%) |
| Molecular characteristics | |
| Targetable mutations | |
| Yes | 38 (39%) |
| No | 51 (53%) |
| Unknown | 8 (8%) |
| Hormonal receptors (among patients with breast cancer) | |
| Yes | 16 (67%) |
| No | 8 (33%) |
| Unknown | 8 (8%) |
| Systemic therapy a | |
| Targeted therapy/Hormonal therapy/Immune therapy | 64 (66%) |
| None of the above/Unknown | 33 (34%) |
| Stereotactic radiosurgery a | |
| Yes | 50 (52%) |
| No | 47 (48%) |
| Whole brain radiotherapy a | |
| Yes | 54 (56%) |
| No | 43 (44%) |
| Surgery a | |
| Yes | 39 (40%) |
| No | 58 (60%) |
| Molecular Characteristics | Long-Term Survivors |
|---|---|
| Lung primary | (n = 51) |
| EGFR mutation | 21 (41%) |
| ALK rearrangement | 4 (8%) |
| EGFR/ALK- | 21 (41%) |
| Unknown | 5 (10%) |
| Breast primary | (n = 24) |
| ER/PR +/Her 2+ | 6 (25%) |
| ER/PR+/Her 2- | 10 (42%) |
| ER/PR-/Her 2+ | 6 (25%) |
| Triple-negative | 2 (8%) |
| Unknown | 0 (0%) |
| Melanoma | (n = 5) |
| BRAF+ | 0 (0%) |
| BRAF- | 2 (40%) |
| Unknown | 3 (60%) |
| Intracranial Treatment | Long-Term Survivors (n = 97) |
|---|---|
| SRS alone | 29 (30%) |
| Surgery alone | 2 (2%) |
| WBRT alone | 15 (15%) |
| Surgery with SRS | 7 (7%) |
| Surgery with WBRT | 25 (26%) |
| SRS and WBRT | 9 (9%) |
| Surgery with SRS and WBRT | 5 (5%) |
| Systemic therapy alone | 5 (5%) |
| Study | Cut-off for LTS | No of Patients | Percentage of Patients | Most Common Primary Sites | Patients Receiving WBRT | Patients Receiving SRS | Patients Undergoing Surgery | Crude rate Neurologic Death | Comments/Prognostic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hall et al. (2000) [11] | 2 years | 51 | 6.9% (2 years) | 1. NSCLC 2. Breast 3. Melanoma/ renal cell carcinoma | 98% | 8% | 57% | 22% | 1. Ovarian carcinoma patients had the highest rate of survival among cohort. 2. Single lesion, surgery, and WBRT were factors associated with LTS. |
| Lutterbach et al. (2002) [12] | 2 years | 2 years-48 3 years-25 5 years-12 | 2.8% (3 years) | 1. NSCLC 2. Breast | 98% | 0% | 73% | NA | 1. For patients with single lesion, radiation boost was considered following WBRT. 2. Survival was best patients with a single brain metastasis |
| Kondziolka et al. (2005) [13] | 4 years | 44 | 6.5% a (4 years) | 1. Lung 2. Breast 3. Kidney | 86% | 100% | NA b | 4% | Compared with a cohort of patients surviving < 3 months, LTS had better KPS, fewer metastases, and a lower extracranial disease burden. |
| Chao et al. (2006) [14] | 5 years | 32 | 2.5% (5 years) | 1. NSCLC 2. Breast 3. Melanoma | 66% | 28% | 69% | 0% (for 10-year survivors) | 1. Prognostic factors were compared to patients surviving <5 years. 2. Female gender, RPA class 1, surgery, and SRS were associated with better survival. |
| Niemiec et al. (2011) [15] | 3 years | 19 | 2% c | NSCLC | 79% | 32% | 53% | 33% | 1. Compared with control group of patients with brain metastases from lung cancer. 2. Female sex, RPA class 1, adenocarcinoma, control of primary tumour and no extracranial metastasis was associated with LTS. |
| Enders et al. (2016) [16] | 2 years | 21 | 18% | NSCLC | 81% | 0% | 100% | NR | Surgery for primary tumour was the only significant factor associated with LTS. |
| Kotecha et al. (2016) [17] | 10 years | 5 years-56 10 yrs-23 | 1.2% (10 years) | 1. NSCLC 2. Melanoma 3. Breast/unknown primary | 52% | 30% | 70% | 0% (for 10-year survivors) | Female gender, single brain metastasis and SRS were associated with better overall survival |
| Current study (2020) | 3 years | 3 years-97 5 years-64 | 16% (5 years) | 1. NSCLC 2. Breast 3. Thyroid | 56% | 52% | 40% | 36% d | 71% of the LTS were <60 years, 65% had single BM at the time of diagnosis, 76% had brain as the first site of metastatic disease, 39% had targetable mutations, 66% received targeted/hormonal and immunotherapies. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dasgupta, A.; Co, J.; Winter, J.; Millar, B.-A.; Laperriere, N.; Tsang, D.S.; van Prooijen, M.; Damyanovich, A.; Heaton, R.; Coolens, C.; et al. Clinicopathologic and Treatment Features of Long-Term Surviving Brain Metastasis Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 549-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010054
Dasgupta A, Co J, Winter J, Millar B-A, Laperriere N, Tsang DS, van Prooijen M, Damyanovich A, Heaton R, Coolens C, et al. Clinicopathologic and Treatment Features of Long-Term Surviving Brain Metastasis Patients. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(1):549-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleDasgupta, Archya, Jayson Co, Jeff Winter, Barbara-Ann Millar, Normand Laperriere, Derek S. Tsang, Monique van Prooijen, Andrei Damyanovich, Robert Heaton, Catherine Coolens, and et al. 2021. "Clinicopathologic and Treatment Features of Long-Term Surviving Brain Metastasis Patients" Current Oncology 28, no. 1: 549-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010054
APA StyleDasgupta, A., Co, J., Winter, J., Millar, B.-A., Laperriere, N., Tsang, D. S., van Prooijen, M., Damyanovich, A., Heaton, R., Coolens, C., Bernstein, M., Kongkham, P., Zadeh, G., Berlin, A., Conrad, T., Moraes, F. Y., & Shultz, D. B. (2021). Clinicopathologic and Treatment Features of Long-Term Surviving Brain Metastasis Patients. Current Oncology, 28(1), 549-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010054







