Real World Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Variables
2.4. Treatment Patterns
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Extensive Stage Disease
3.2. Limited Stage Disease
3.3. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lally, B.E.; Urbanic, J.J.; Blackstock, A.W.; Miller, A.A.; Perry, M.C. Small Cell Lung Cancer: Have We Made Any Progress Over the Last 25 Years? Oncologist 2007, 12, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Evans, W.K.; Stys-Norman, D.; Shepherd, F.A.; The Lung Cancer Disease Site Group of Cancer Care Ontario’s Program in Evidence-based Care. Chemotherapy for Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Practice Guideline. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, R.; Page, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Read, W.; Tierney, R.; Vlahiotis, A.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Piccirillo, J. Changing Epidemiology of Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States Over the Last 30 Years: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiologic, and End Results Database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownson, R.C.; Chang, J.C.; Davis, J.R. Gender and Histologic Type Variations in Smoking-Related Risk of Lung Cancer. Epidemiology 1992, 3, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society AC. Cancer Facts & Figures 2019 Atlanta, GA. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2019/cancer-facts-and-figures-2019.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Varghese, A.M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Yu, H.A.; Won, H.H.; Riely, G.J.; Krug, L.M.; Kris, M.G.; Rekhtman, N.; Ladanyi, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Small-Cell Lung Cancers in Patients Who Never Smoked Cigarettes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, E.; Lilenbaum, R.C. Small Cell Lung Cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 12, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemkerian, G.P. Advances in pharmacotherapy of small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Ihde, D.C. Small-cell lung cancer: Treatment progress and prospects. Oncology 1998, 12, 647–658. [Google Scholar]
- Oze, I.; Hotta, K.; Kiura, K.; Ochi, N.; Takigawa, N.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tabata, M.; Tanimoto, M. Twenty-Seven Years of Phase III Trials for Patients with Extensive Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Disappointing Results. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; López-Martin, J.A.; Bendell, J.; Ott, P.A.; Taylor, M.; Eder, J.P.; Jäger, D.; Pietanza, M.C.; Le, D.T.; De Braud, F.; et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metro, G.; Cappuzzo, F. Emerging drugs for small-cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2009, 14, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Small cell lung cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer 2015, 121, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auperin, A.; Arriagada, R.; Pignon, J.-P.; Le Péchoux, C.; Gregor, A.; Stephens, R.J.; Kristjansen, P.E.; Johnson, B.E.; Ueoka, H.; Wagner, H.; et al. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Complete Remission. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotman, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Kramer, G.; Rankin, E.; Snee, M.; Hatton, M.; Postmus, P.; Collette, L.; Musat, E.; Senan, S.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Seto, T.; Harada, H.; Nokihara, H.; Saka, H.; Nishio, M.; Kaneda, H.; Takayama, K.; Ishimoto, O.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotman, B.J.; Van Tinteren, H.; Praag, J.O.; Knegjens, J.L.; El Sharouni, S.Y.; Hatton, M.; Keijser, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Senan, S. Use of thoracic radiotherapy for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, E.M.; Hu, C.; Sun, A.Y.; Grimm, D.F.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Dunlap, N.E.; Higgins, K.A.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Allen, A.M.; Iyengar, P.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study Comparing Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Alone to Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation and Consolidative Extracranial Irradiation for Extensive-Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer (ED SCLC): NRG Oncology RTOG 0937. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, N.; Ohkuni, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Yamaguchi, E.; Kubo, A. Relapsed small cell lung cancer: Treatment options and latest developments. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2014, 6, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Argiris, A.; Murren, J.R. Progress in the therapy of small cell lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2004, 49, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Crowley, J.J.; Van Houtte, P.; Postmus, P.E.; Carney, D.; Chansky, K.; Shaikh, Z.; Goldstraw, P. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals Regarding the Clinical Staging of Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Forthcoming (Seventh) Edition of the Tumor, Node, Metastasis Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Care Ontario. Members of the Lung Cancer Disease Site Group. Chemotherapy for Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. Toronto Program in Evidence-Based Care Evidence-based Series No.: 7-17 Version 2. 2013. Available online: https://www.cancercareontario.ca/en/guidelines-advice/types-of-cancer/801 (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 2.2014. 2014. Available online: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sclc.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- NICE. Topotecan for the Treatment of Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta184 (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Vincent, M.; Evans, B.; Smith, I. First-line chemotherapy rechallenge after relapse in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1988, 21, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, J.L.; McCoy, F.; Scullin, P.; Fennell, D.A. New Advances in the Second-Line Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2009, 14, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcaro, A.; Fischer, B. Current Status of Clinical Trials for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2008, 3, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postmus, P.E.; Berendsen, H.H.; Van Zandwijk, N.; Splinter, T.A.; Burghouts, J.T.M.; Bakker, W. Retreatment with the induction regimen in small cell lung cancer relapsing after an initial response to short term chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1987, 23, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, C.; Postmus, P.; Giaccone, G.; Smit, E. Second-line chemotherapy and its evaluation in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1999, 25, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garassino, M.C.; Torri, V.; Michetti, G.; Dico, M.L.; La Verde, N.; Aglione, S.; Mancuso, A.; Gallerani, E.; Galetta, D.; Martelli, O.; et al. Outcomes of small-cell lung cancer patients treated with second-line chemotherapy: A multi-institutional retrospective analysis. Lung Cancer 2011, 72, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, G. Second line chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 1989, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.H.; Adak, S.; Cella, D.; Devore, R.F., III; Johnson, D.H. Topotecan Versus Observation After Cisplatin Plus Etoposide in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: E7593—A Phase III Trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pawel, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; Fields, S.Z.; Kleisbauer, J.; Chrysson, N.G.; Stewart, D.J.; Clark, P.I.; Palmer, M.C.; Depierre, A.; et al. Topotecan Versus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and Vincristine for the Treatment of Recurrent Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Ott, P.A.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Ready, N.E.; Hann, C.L.; De Braud, F.G.; Antonia, S.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Moreno, V.; Atmaca, A.; et al. Nivolumab (nivo) ± ipilimumab (ipi) in advanced small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): First report of a randomized expansion cohort from CheckMate 032. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, N.E.; Farago, A.F.; De Braud, F.; Atmaca, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Schneider, J.G.; Spigel, D.R.; Moreno, V.; Chau, I.; Hann, C.L.; et al. Third-Line Nivolumab Monotherapy in Recurrent SCLC: CheckMate 032. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Reck, M.; Gettinger, S.N.; Spigel, D.R.; Antonia, S.J.; Rupnow, B.A.; Pieters, A.; Selvaggi, G.; Fairchild, J.P.; Peters, S. LBA5 Efficacy and safety of nivolumab (nivo) monotherapy versus chemotherapy (chemo) in recurrent small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Results from CheckMate 331. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 511. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg, L.; Korytowsky, B.; Penrod, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, T.; Le, T.; Abraham, P.; Selvaggi, G. P1.12-21 Developing a Real-World 3L Comparator to CheckMate 032: Overall Survival (OS) in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S581–S582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simos, D.; Sajjady, G.; Sergi, M.; Liew, M.S.; Califano, R.; Ho, C.; Leighl, N.; White, S.; Summers, Y.; Petrcich, W.; et al. Third-Line Chemotherapy in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An International Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.K.; Hacken, N.H.T.; Groen, H.J. Third-line chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 52, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, B.; Chouaid, C.; Baud, M.; Masanes, M.-J.; Febvre, M. Oral second- and third-line lomustine–etoposide–cyclophosphamide chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ahn, M.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, J.; Hong, Y.S.; Park, B.-B.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, I.G.; Park, J.O.; Lim, H.; et al. Combination chemotherapy with paclitaxel and ifosfamide as the third-line regimen in patients with heavily pretreated small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2007, 58, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ueda, S.; Ono, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; Murakami, H.; Endo, M.; Takahashi, T. Evaluation of the Recommended Dose and Efficacy of Amrubicin as Second- and Third-Line Chemotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, C.-C.; Elender, C.; Hutzschenreuter, U.; Dille, S.; Binninger, A.; Spring, L.; Jänicke, M.; Marschner, N. Treatment and outcome of 432 patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in first, second and third line—Results from the prospective German TLK cohort study. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R. Membership in Sick Funds 2017. Available online: https://www.btl.gov.il/Publications/survey/Documents/seker_303.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Shalev, V.; Chodick, G.; Goren, I.; Silber, H.; Kokia, E.; Heymann, A.D. The use of an automated patient registry to manage and monitor cardiovascular conditions and related outcomes in a large health organization. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 152, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodick, G.; Heymann, A.D.; Shalev, V.; Kookia, E. The epidemiology of diabetes in a large Israeli HMO. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 18, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldshtein, I.; Chandler, J.; Shalev, V.; Ish–Shalom, S.; Nguyen, A.; Rouach, V.; Chodick, G. Osteoporosis in the Community: Findings from a Novel Computerized Registry in a Large Health Organization in Israel. J. Aging Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 4, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Israel Center for Disease Control MoH. Israel National Cancer Registry 2019. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/English/MinistryUnits/HealthDivision/Icdc/Icr/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Characterization and Classification of Geographic Units by the Soci-Economic Level of the Population 2008; Publication No. 1530; Central Bureau of Statistics: Jerusalem, Israel, 2013.
- Crown, J.P.A.; Chahinian, A.P.; Jaffrey, I.S.; Glidewell, O.J.; Kaneko, M.; Holland, J.F. Predictors of 5-year survival and curability in small cell lung cancer. Cancer 1990, 66, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chute, J.P.; Venzon, D.J.; Hankins, L.; Okunieff, P.; Frame, J.N.; Ihde, D.C.; Johnson, B.E. Outcome of Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer During 20 Years of Clinical Research at the US National Cancer Institute. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1997, 72, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.R.; Qi, Y.; Shi, Q.; Krook, J.E.; Kugler, J.W.; Jett, J.R.; Molina, J.R.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A.; Mandrekar, S.J. Tumor response and progression-free survival as potential surrogate endpoints for overall survival in extensive stage small-cell lung cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartarone, A.; Lerose, R.; Ardito, R.; Troiani, L.; Tedesco, B.; Bozza, G.; Cangiano, R.; Aieta, M. Long-term survival in small cell lung cancer: A case report and review of the literature. Futur. Oncol. 2014, 10, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, C.-H.; Chen, P.; Wu, J.-N.; Bao, Q.-L.; Qiu, H.; Li, X.-Q. Survival and prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2009, 27, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paesmans, M.; Sculier, J.P.; Lecomte, J.; Thiriaux, J.; Libert, P.; Sergysels, R.; Bureau, G.; Dabouis, G.; Cutsem, O.V.; Mommen, P.; et al. Prognostic factors for patients with small cell lung carcinoma: Analysis of a series of 763 patients included in 4 consecutive prospective trials with a minimum follow-up of 5 years. Cancer 2000, 89, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelman, D.; Maurer, L.H.; Ware, J.H.; Perry, M.C.; Chahinian, A.P.; Comis, R.; Eaton, W.; Zimmer, B.; Green, M. Prognostic factors in small-cell carcinoma of the lung: An analysis of 1,521 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parulekar, W.; Murray, N.; Feld, R.; Evans, W.K.; Tu, D.; Shepherd, F.A. Influence of Sex on Toxicity and Treatment Outcome in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundstrøm, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Kaasa, S.; Aasebø, U.; Aamdal, S.; Norwegian Lung Cancer Study Group. Second-line chemotherapy in recurrent small cell lung cancer. Results from a crossover schedule after primary treatment with cisplatin and etoposide (EP-regimen) or cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and vincristin (CEV-regimen). Lung Cancer 2005, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Goto, K.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Kubota, K.; Saijo, N.; Nishiwaki, Y. Performance status and sensitivity to first-line chemotherapy are significant prognostic factors in patients with recurrent small cell lung cancer receiving second-line chemotherapy. Cancer 2008, 113, 2518–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, T.; Seber, S.; Kefeli, U.; Sari, E.; Canhoroz, M.; Oven, B.; Yildirim, E.; Yasar, N.; Aydin, D.; Balvan, O.; et al. Comparison of second-line treatment outcomes between sensitive and refractory small cell lung cancer patients: A retrospective analysis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 15, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niho, S.; Yoshida, T.; Akimoto, T.; Sakamaki, K.; Ono, A.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Hida, T.; Okamoto, H.; et al. Randomized phase II study of chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin + S-1 versus cisplatin + pemetrexed for locally advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: SPECTRA study. Lung Cancer 2020, 141, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genestreti, G.; Tiseo, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Kazushige, W.; Di Battista, M.; Cavallo, G.; Carloni, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Burgio, M.A.; Casanova, C.; et al. Outcomes of Platinum-Sensitive Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Platinum/Etoposide Rechallenge: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, e223–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarin, A.T. Analysis of Long-term Survivors With Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Chest 1993, 103, 440S–444S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoulet, P.; Depierre, A.; Moro, D.; Riviere, A.; Milleron, B.; Quoix, E.; Ranfaing, E.; Anthoine, D.; Lafitte, J.J.; Lebeau, B.; et al. Long-term survivors of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): A French multicenter study. Ann. Oncol. 1997, 8, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total n = 235 | Extensive Stage n = 150 | Limited Stage n = 85 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Variables | |||||
| Sex | Female | 91 (38.7) | 57 (38.0) | 34 (40.0) | 0.870 |
| Age | median (IQR **) | 64.0 (58.0,69.5) | 64.0 (58.0,69.0) | 63.0 (58.0,70.0) | 0.637 |
| 35–64 | 124 (52.8) | 76 (50.7) | 48 (56.5) | 0.684 | |
| 65–74 | 86 (36.6) | 57 (38.0) | 29 (34.1) | ||
| ≥75 | 25 (10.6) | 17 (11.3) | 8 (9.4) | ||
| District | Centre | 155 (66.0) | 104 (69.3) | 51 (60.0) | 0.245 |
| North | 50 (21.3) | 27 (18.0) | 23 (27.1) | ||
| South | 30 (12.8) | 19 (12.7) | 11 (12.9) | ||
| Socio-economic status, groups * | Low | 101 (43.0) | 65 (43.3) | 36 (42.4) | 0.933 |
| Median | 49 (20.9) | 32 (21.3) | 17 (20.0) | ||
| High | 85 (36.2) | 53 (35.3) | 32 (37.6) | ||
| Clinical Variables | |||||
| Co-morbidities | Diabetes mellitus | 70 (29.8) | 45 (30.0) | 25 (29.4) | 1.000 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 72 (30.6) | 48 (32.0) | 24 (28.2) | 0.650 | |
| Hypertension | 132 (56.2) | 83 (55.3) | 49 (57.6) | 0.836 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 40 (17.0) | 27 (18.0) | 13 (15.3) | 0.727 | |
| COPD | 75 (31.9) | 50 (33.3) | 25 (29.4) | 0.635 | |
| Osteoporosis | 43 (18.3) | 29 (19.3) | 14 (16.5) | 0.712 | |
| Smoking | Ever | 224 (95.3) | 141 (94.0) | 83 (97.6) | 0.342 |
| Never | 11 (4.7) | 9 (6.0) | 2 (2.4) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0–1 | 141 (60.0) | 85 (56.7) | 56 (65.9) | 0.039 |
| 2 | 30 (12.8) | 25 (16.7) | 5 (5.9) | ||
| 3–4 | 4 (1.7) | 4 (2.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Unknown | 60 (25.5) | 36 (24.0) | 24 (28.2) | ||
| Brain metastases | 26 (11.1) | 26 (17.3) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 | |
| Prognostic Parameters | N | Events n (%) | Median OS (95% CI) | Alive At 1 Year N (%) | Alive at 2 Years N (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXTENSIVE STAGE, N = 150 | |||||||
| Sex | Male | 93 | 84 (90.3%) | 8.91 (7.96,10.50) | 30.0% (21.8–41.4%) | 3.9% (1.3–11.8%) | 0.13 |
| Female | 57 | 51 (89.5%) | 9.63 (8.61,11.70) | 32.8% (22.6–47.8%) | 13.6% (6.7–27.7%) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0–1 | 85 | 73 (85.9%) | 9.63 (8.65,13.80) | 41.0% (31.6–53.2%) | 11.2% (5.7–22.0%) | 0.09 |
| 2 | 25 | 25 (100.0%) | 8.91 (4.9,11.30) | 20.0% (9.1–43.8%) | - | ||
| 3–4 | 4 | 4 (100.0%) | 8.43 (3.45, NR) | - | - | ||
| Unknown | 36 | 33 (91.7%) | 8.73 (6.94,9.90) | 19.7% (9.9–39.2%) | 6.6% (1.7–24.7%) | ||
| Brain metastases | No | 124 | 111 (89.5%) | 9.17 (8.38,10.30) | 32.1% (24.7–41.8%) | 7.6% (3.8–15.2%) | 0.89 |
| Yes | 26 | 24 (92.3%) | 8.81 (7.27,12.10) | 26.9% (14.3–50.7%) | 7.7% (2.0–29.1%) | ||
| Survival from line | L1 | 150 | 135 (90.0%) | 9.14 (8.38, 10.30) | 31.08% (24.3–39.7%) | 7.70% (4.2–14.2%) | |
| L2 | 62 | 57 (91.9%) | 4.54 (3.19, 6.12) | 9.99% (4.4–22.5%) | |||
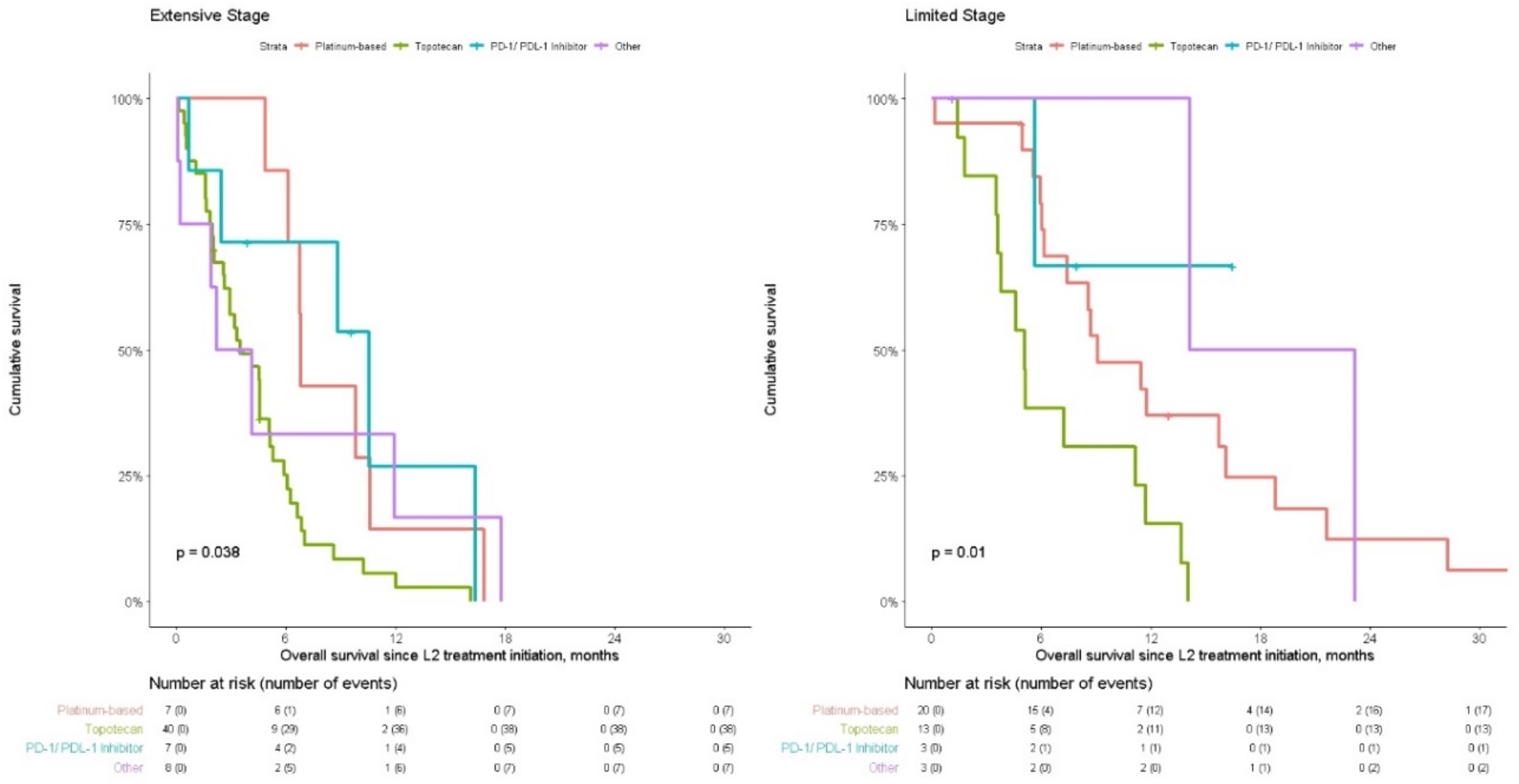
| Treatment pattern at L2 for those sensitive to L1 treatment | Retreatment | 7 | 7 (100.0%) | 6.81 (6.12, NR) | 14.30% (2.3–87.7%) | 0.06 | |
| Treatment switch | 27 | 23 (85.2%) | 4.5 (2.63, 6.61) | 7.06% (1.3%–39.7%) | |||
| LIMITED STAGE, N = 85 | |||||||
| Sex | Male | 51 | 39 (76.5%) | 21.50 (17.60,27.10) | 79.9% (69.4–91.9%) | 38.0% (26.1%55.3%) | 0.03 |
| Female | 34 | 16 (47.1%) | 29.60 (20.4, NR) | 75.8% (62.5–92.0%) | 57.9% (42.5–78.7%) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0–1 | 56 | 33 (58.9%) | 24.50 (20.50,34.90) | 85.0% (75.9–95.2%) | 50.5% (38.0–67.2%) | 0.07 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 (60.0%) | 50.50 (22.10, NR) | 80.0% (51.6–100.0%) | 60.0% (29.3–100.0%) | ||
| Unknown | 24 | 19 (79.2%) | 16.00 (11.70,32.30) | 62.5% (45.8–85.2%) | 31.4% (17.0–58.1%) | ||
| Survival from line | L1 | 85 | 55 (64.7%) | 23.54 (19.40,27.90) | 78.20% (69.8–87.7%) | 45.70% (35.6–58.5%) | |
| L2 | 39 | 33 (84.6%) | 8.68 (6.02, 14.04) | 34.37% (21.9–54.0%) | 7.50% (2.1–27.1%) | ||
| Treatment pattern at L2 for those sensitive to L1 treatment | Retreatment | 20 | 17 (85.0%) | 9.11 (7.40, 18.80) | 36.94% (20.5–66.5%) | 12.31% (3.4–44.1%) | 0.14 |
| Treatment switch | 13 | 12 (92.3%) | 6.43 (5.06, NA) | 25.00% (9.4–66.6%) | |||
| Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| EXTENSIVE STAGE, N = 150 | |||||
| Age | years | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 0.191 |
| Sex | Male vs. female | 1.32 | 0.92 | 1.92 | 0.136 |
| Socio-economic status, groups * | low (Ref.) | ||||
| Medium | 0.77 | 0.47 | 1.25 | 0.283 | |
| High | 0.78 | 0.53 | 1.16 | 0.225 | |
| ECOG PS | 0–1 (Ref.) | ||||
| 2 | 1.63 | 1.00 | 2.65 | 0.048 | |
| 3–4 | 2.45 | 0.83 | 7.24 | 0.104 | |
| Unknown | 1.53 | 0.99 | 2.35 | 0.054 | |
| Brain metastases | 0.98 | 0.62 | 1.54 | 0.927 | |
| LIMITED STAGE, n = 85 | |||||
| Age | years | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.02 | 0.474 |
| Sex | Male vs. female | 2.17 | 1.12 | 4.20 | 0.022 |
| Socio-economic status, groups * | low (Ref.) | ||||
| Medium | 0.93 | 0.46 | 1.87 | 0.845 | |
| High | 0.71 | 0.36 | 1.42 | 0.337 | |
| ECOG PS | 0–1 (Ref.) | ||||
| 2 | 0.75 | 0.21 | 2.63 | 0.650 | |
| Unknown | 2.42 | 1.31 | 4.47 | 0.005 | |
| Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| EXTENSIVE STAGE, N = 62 | |||||
| Age * | years | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.531 |
| Sex | Female vs. Male | 1.55 | 0.83 | 2.91 | 0.172 |
| ECOG PS * | 0–1 (Ref.) | ||||
| 2 | 2.22 | 1.03 | 4.79 | 0.043 | |
| 3–4 | 3.45 | 0.36 | 33.16 | 0.284 | |
| missing | 1.33 | 0.62 | 2.85 | 0.462 | |
| Brain metastases * | 0.76 | 0.36 | 1.60 | 0.471 | |
| L2 Drug Treatment | Platinum-based regimen (Ref.) | ||||
| Topotecan | 2.79 | 1.05 | 7.39 | 0.039 | |
| PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy | 0.96 | 0.27 | 3.40 | 0.950 | |
| Other | 1.27 | 0.35 | 4.66 | 0.715 | |
| Platinum sensitivity to L1 treatment | 1.18 | 0.64 | 2.2 | 0.592 | |
| LIMITED STAGE, n = 39 | |||||
| Age * | years | 1.01 | 0.95 | 1.07 | 0.762 |
| Sex | Female vs. Male | 1.08 | 0.41 | 2.84 | 0.870 |
| ECOG PS * | 0–1 (Ref.) | ||||
| 2 | 0.3 | 0.03 | 2.63 | 0.274 | |
| missing | 2.28 | 0.89 | 5.86 | 0.087 | |
| L2 Drug Treatment | Platinum-based regimen (Ref.) | ||||
| Topotecan | 2.43 | 0.94 | 6.24 | 0.066 | |
| PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy | 0.19 | 0.02 | 2.24 | 0.186 | |
| Other | 0.23 | 0.04 | 1.17 | 0.076 | |
| Platinum sensitivity to L1 treatment | 0.33 | 0.08 | 1.40 | 0.134 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moser, S.S.; Bar, J.; Kan, I.; Ofek, K.; Cohen, R.; Khandelwal, N.; Shalev, V.; Chodick, G.; Siegelmann-Danieli, N. Real World Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 317-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010036
Moser SS, Bar J, Kan I, Ofek K, Cohen R, Khandelwal N, Shalev V, Chodick G, Siegelmann-Danieli N. Real World Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(1):317-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoser, Sarah Sharman, Jair Bar, Inna Kan, Keren Ofek, Raanan Cohen, Nikhil Khandelwal, Varda Shalev, Gabriel Chodick, and Nava Siegelmann-Danieli. 2021. "Real World Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes" Current Oncology 28, no. 1: 317-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010036
APA StyleMoser, S. S., Bar, J., Kan, I., Ofek, K., Cohen, R., Khandelwal, N., Shalev, V., Chodick, G., & Siegelmann-Danieli, N. (2021). Real World Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes. Current Oncology, 28(1), 317-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010036






