The Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Pros and Cons
Abstract
Introduction
Description of the Therapy
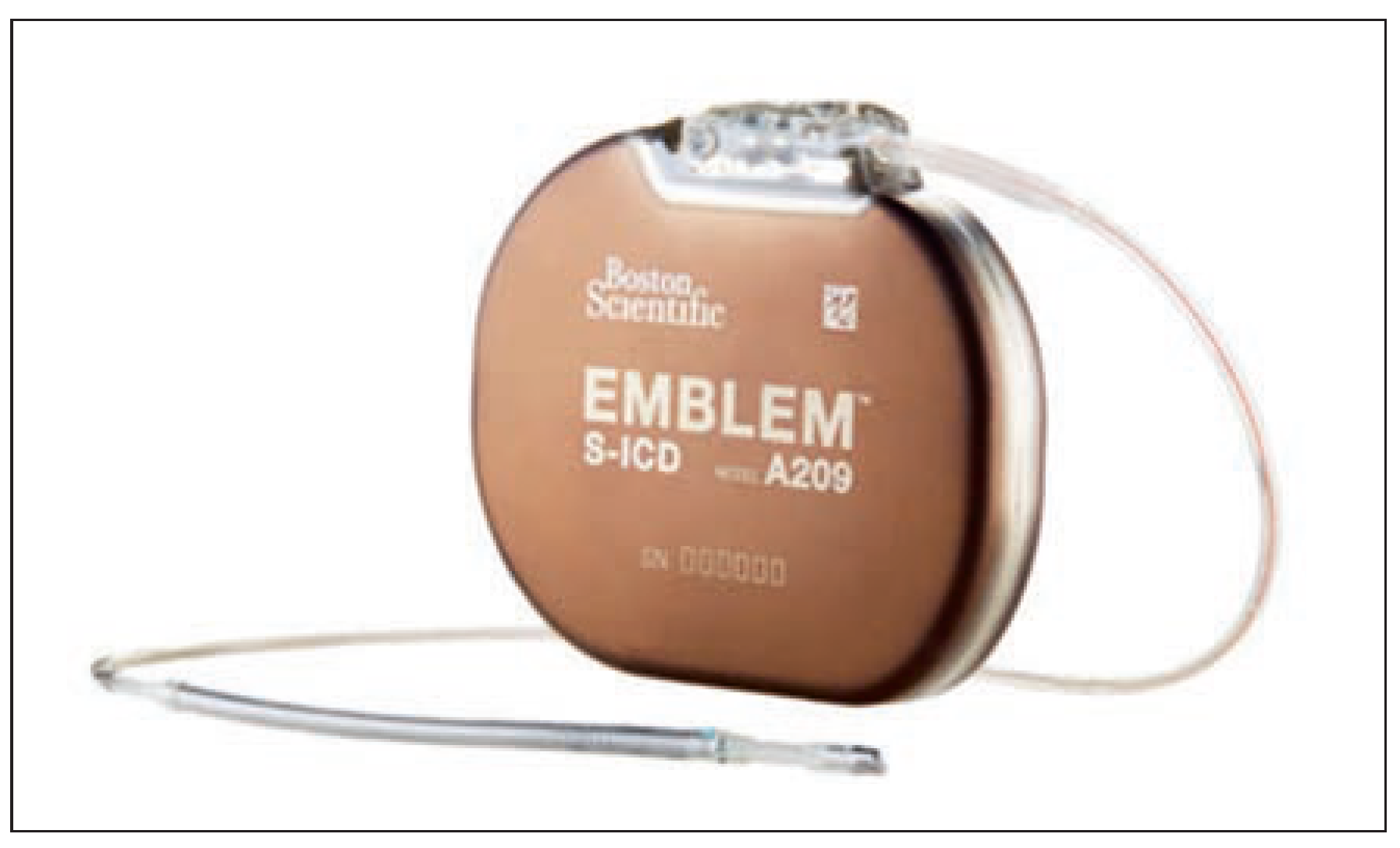
The S-ICD Device
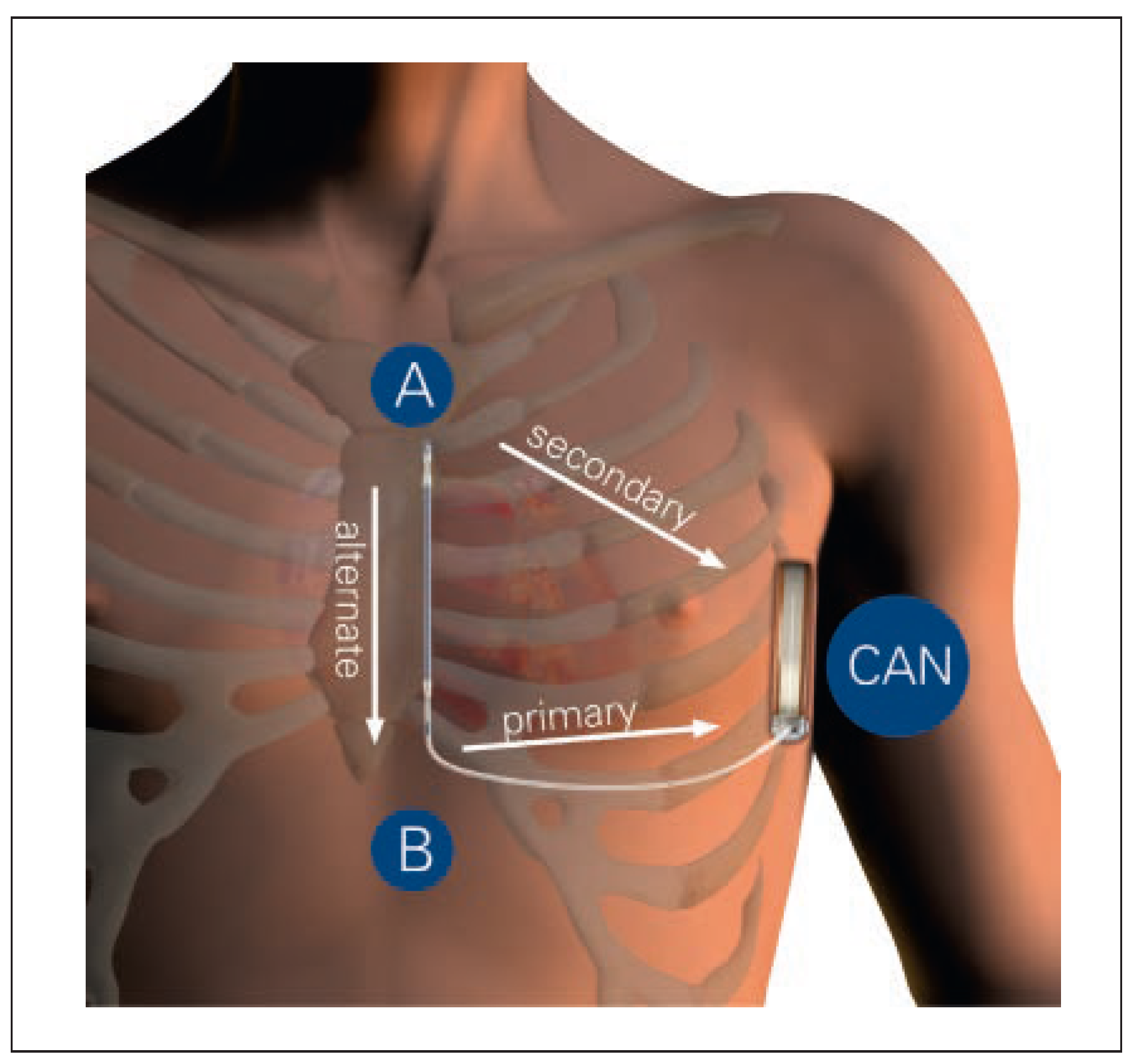
Implantation Procedure
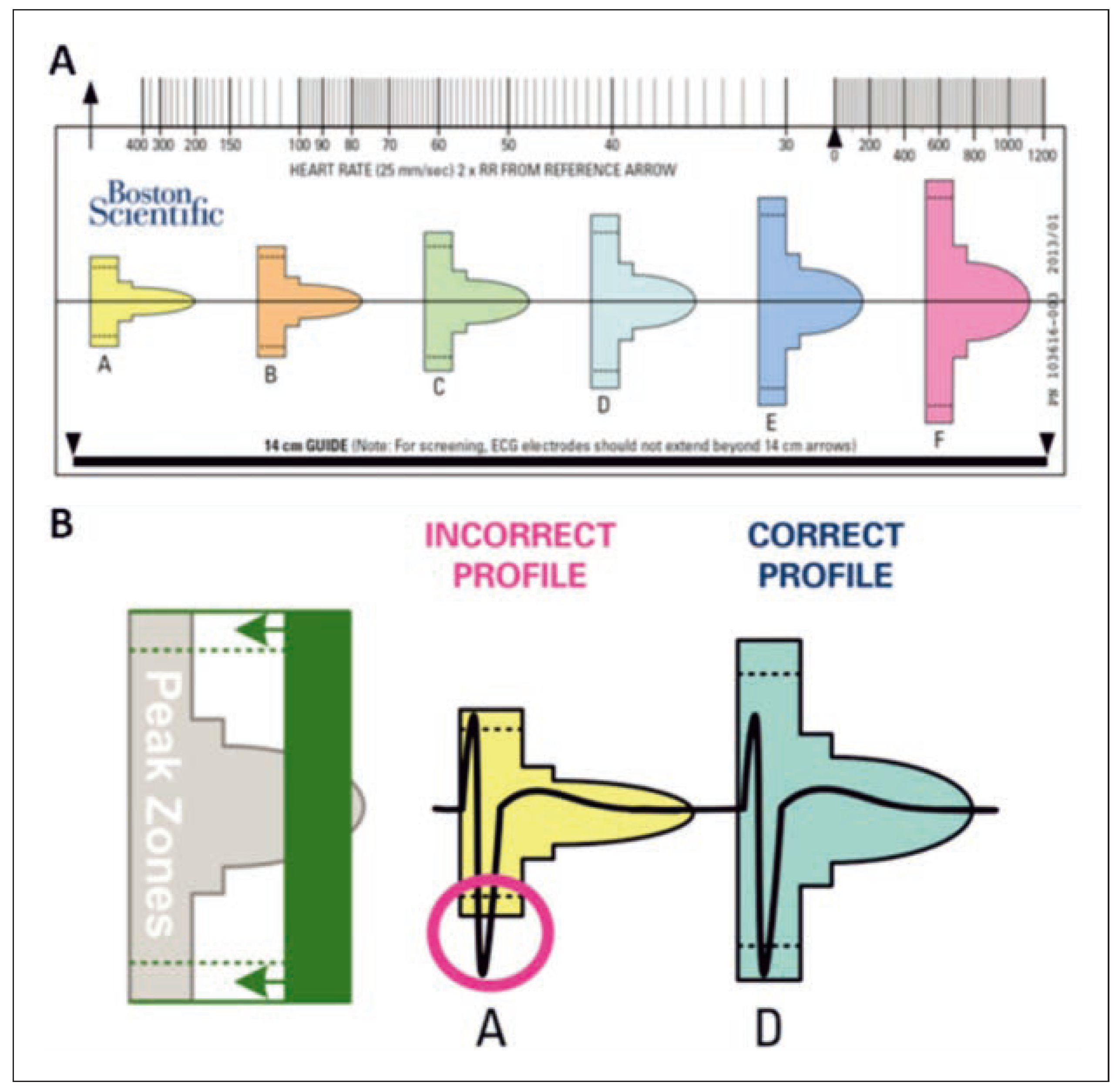
Preimplantation Screening
Arrhythmia Detection
Shock Delivery
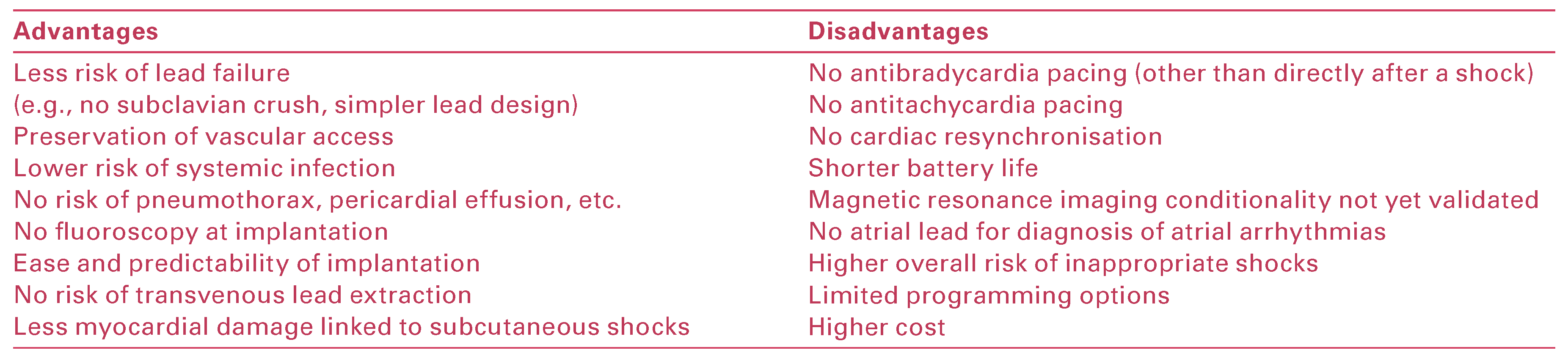
Advantages and Disadvantages of the S-ICD
Indications for the S-ICD
Current Evidence
Eligibility for S-ICD Implantation
Sensitivity and Specificity of Arrhythmia Detection
Shock Efficacy
Inappropriate Shocks
Strategies to Reduce IAS
Safety and Complications
S-ICD in Switzerland
Conclusions
Disclosure Statement
References
- Mirowski, M.; Reid, P.R.; Mower, M.M.; Watkins, L.; Gott, V.L.; Schauble, J.F.; et al. Termination of malignant ventricular arrhythmias with an implanted automatic defibrillator in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980, 303, 322–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Zareba, W.; Hall, W.J.; Klein, H.; Wilber, D.J.; Cannom, D.S.; et al. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002, 346, 877–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardy, G.H.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B.; Poole, J.E.; Packer, D.L.; Boineau, R.; et al. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005, 352, 225–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A comparison of antiarrhythmic-drug therapy with implantable defibrillators in patients resuscitated from near-fatal ventricular arrhythmias. The Antiarrhythmics versus Implantable Defibrillators (AVID) Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1997, 337, 1576–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kuck, K.H.; Cappato, R.; Siebels, J.; Ruppel, R. Randomized comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy with implantable defibrillators in patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest: the Cardiac Arrest Study Hamburg (CASH). Circulation. 2000, 102, 748–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammill, S.C.; Kremers, M.S.; Stevenson, L.W.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Lang, C.M.; Curtis, J.P.; et al. Review of the registry’s fourth year, incorporating lead data and pediatric ICD procedures, and use as a national performance measure. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 1340–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkfeldt, R.E.; Johansen, J.B.; Nohr, E.A.; Moller, M.; Arnsbo, P.; Nielsen, J.C. Risk factors for lead complications in cardiac pacing: a population-based cohort study of 28,860 Danish patients. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1622–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rees, J.B.; de Bie, M.K.; Thijssen, J.; Borleffs, C.J.; Schalij, M.J.; van Erven, L. Implantation-related complications of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization therapy devices: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 58, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, J.; Koller, M.T.; Zabel, M.; Kalusche, D.; Schaer, B.A.; Osswald, S.; et al. Necessity for surgical revision of defibrillator leads implanted long-term: causes and management. Circulation. 2008, 117, 2727–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorni, M.G. Long-term results on transvenous lead extraction in Europe. European Society of Cardiology Annual Scientific -Sessions, Milano. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berul, C.I.; Triedman, J.K.; Forbess, J.; Bevilacqua, L.M.; Alexander, M.E.; Dahlby, D.; et al. Minimally invasive cardioverter defibrillator -implantation for children: an animal model and pediatric case report. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001, 24, 1789–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedemann, M.; Hund, K.; Stertmann, W.; Michel-Behnke, I.; Gonzales, M.; Akintuerk, H.; et al. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a child using a single subcutaneous array lead and an abdominal active can. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2004, 27, 117–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, N.; Gaynor, J.W.; Tanel, R.; Cohen, M.; Nicholson, S.; Vetter, V.; et al. Single-finger subcutaneous defibrillation lead and “active can”: a novel minimally invasive defibrillation configuration for implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation in a young child. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003, 126, 1657–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, K.A.; McLean, A. Implantation of a fully subcutaneous ICD in children. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, e20–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.; Knight, B.P.; Gold, M.R.; Leon, A.R.; Herre, J.M.; Hood, M.; et al. -Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation. 2013, 128, 944–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, P.D.; Barr, C.; Theuns, D.A.; Knops, R.; Neuzil, P.; Johansen, J.B.; et al. Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from the EFFORTLESS S-ICD Registry. Eur Heart J. 2014, 35, 1657–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.; Regoli, F.R.; Moccetti, T.A.A. Subcutaneous cardioverter--defibrillator and drug-induced Brugada syndrome: the importance of repeat morphology analysis during ajmaline challenge. Eur Heart J. in press.
- Gold, M.R.; Theuns, D.A.; Knight, B.P.; Sturdivant, J.L.; Sanghera, R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of arrhythmia discrimination performance of subcutaneous and transvenous ICD -arrhythmia detection algorithms: the START study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 359–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Hartel, F.; Schluter, M.; Butter, C.; Kobe, J.; Seifert, M.; et al. Shock efficacy of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for prevention of sudden cardiac death: initial multicenter experience. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 913–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.C.; Gold, M.R.; Knight, B.P.; Barr, C.S.; Theuns, D.A.; Boersma, L.V.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the Totally Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillator: 2-Year Results From a Pooled Analysis of the IDE Study and EFFORTLESS Registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1605–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarman, J.W.; Todd, D.M. United Kingdom national experience of entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator technology: important lessons to learn. Europace. 2013, 15, 1158–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardy, G.H.; Smith, W.M.; Hood, M.A.; Crozier, I.G.; Melton, I.C.; Jordaens, L.; et al. An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N Engl J Med. 2010, 363, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killingsworth, C.R.; Melnick, S.B.; Litovsky, S.H.; Ideker, R.E.; Walcott, G.P. Evaluation of acute cardiac and chest wall damage after shocks with a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in Swine. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 1265–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathen, M.S.; DeGroot, P.J.; Sweeney, M.O.; Stark, A.J.; Otterness, M.F.; -Adkisson, W.O.; et al. Prospective randomized multicenter trial of empirical antitachycardia pacing versus shocks for spontaneous rapid ventricular tachycardia in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: Pacing Fast Ventricular Tachycardia Reduces Shock Therapies (PainFREE Rx II) trial results. Circulation. 2004, 110, 2591–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Sherfesee, L.; DeGroot, P.J.; Wathen, M.S.; Wilkoff, B.L. Differences in effects of electrical therapy type for ventricular -arrhythmias on mortality in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 353–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authors/Task Force, M.; Priori, S.G.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Mazzanti, A.; Blom, N.; Borggrefe, M.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the -management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur Heart J. 2015.
- Kobe, J.; Reinke, F.; Meyer, C.; Shin, D.I.; Martens, E.; Kaab, S.; et al. Implantation and follow-up of totally subcutaneous versus conventional implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: a multicenter case-control study. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olde Nordkamp, L.R.; Dabiri Abkenari, L.; Boersma, L.V.; Maass, A.H.; de Groot, J.R.; van Oostrom, A.J.; et al. The entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: initial clinical experience in a large Dutch cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1933–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri Abkenari, L.; Theuns, D.A.; Valk, S.D.; Van Belle, Y.; de Groot, N.M.; Haitsma, D.; et al. Clinical experience with a novel subcutaneous implantable defibrillator system in a single center. Clin Res Cardiol. 2011, 100, 737–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Nordkamp, L.R.; Knops, R.E.; Bardy, G.H.; Blaauw, Y.; Boersma, L.V.; Bos, J.S.; et al. Rationale and design of the PRAETORIAN trial: a Prospective, RAndomizEd comparison of subcuTaneOus and tRansvenous ImplANtable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy. Am Heart J. 2012, 163, 753–60.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, C.A.; Sharma, S.; Pelchovitz, D.J.; Bhave, P.D.; Rhyner, J.; Verma, N.; et al. Use of an electrocardiographic screening tool to determine candidacy for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1361–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olde Nordkamp, L.R.; Warnaars, J.L.; Kooiman, K.M.; de Groot, J.R.; Rosenmoller, B.R.; Wilde, A.A.; et al. Which patients are not suitable for a subcutaneous ICD: incidence and predictors of failed QRS-T-wave morphology screening. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 494–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randles, D.A.; Hawkins, N.M.; Shaw, M.; Patwala, A.Y.; Pettit, S.J.; Wright, D.J. How many patients fulfil the surface electrocardiogram criteria for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation? Europace. 2014, 16, 1015–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bie, M.K.; Thijssen, J.; van Rees, J.B.; Putter, H.; van der Velde, E.T.; Schalij, M.J.; et al. Suitability for subcutaneous defibrillator implantation: results based on data from routine clinical practice. Heart. 2013, 99, 1018–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, J.A.; Poole, J.E.; Johnson, G.W.; Callans, D.J.; Raitt, M.H.; Reddy, R.K.; et al. No benefit from defibrillation threshold testing in the SCD-HeFT (Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008, 52, 551–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutyifa, V.; Huth Ruwald, A.C.; Aktas, M.K.; Jons, C.; McNitt, S.; Polonsky, B.; et al. Clinical impact, safety, and efficacy of single versus dual-coil ICD leads in MADIT-CRT. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 1246–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J.; Schuger, C.; Beck, C.A.; Brown, M.W.; Cannom, D.S.; Daubert, J.P.; et al. Reduction in inappropriate therapy and mortality through ICD programming. N Engl J Med. 2012, 367, 2275–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Williamson, B.D.; Stern, R.S.; Moore, S.L.; Lu, F.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Strategic programming of detection and therapy parameters in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators reduces shocks in primary prevention patients: results from the PREPARE (Primary Prevention Parameters Evaluation) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008, 52, 541–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auricchio, A.; Schloss, E.J.; Kurita, T.; Meijer, A.; Gerritse, B.; Zweibel, S.; et al. Low inappropriate shock rates in patients with single-and dual/triple-chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillators using a novel suite of detection algorithms: PainFree SST trial primary results. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, 926–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarman, J.W.; Lascelles, K.; Wong, T.; Markides, V.; Clague, J.R.; Till, J. Clinical experience of entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in children and adults: cause for caution. Eur Heart J. 2012, 33, 1351–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.R.; Weiss, R.; Theuns, D.A.; Smith, W.; Leon, A.; Knight, B.P.; et al. Use of a discrimination algorithm to reduce inappropriate shocks with a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1352–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooiman, K.M.; Knops, R.E.; Olde Nordkamp, L.; Wilde, A.A.; de Groot, J.R. Inappropriate subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks due to T-wave oversensing can be prevented: implications for management. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 426–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisben, A.J.; Burke, M.C.; Knight, B.P.; Hahn, S.J.; Herrmann, K.L.; Allavatam, V.; et al. A new algorithm to reduce inappropriate therapy in the S-ICD system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 417–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.V.; Wang, Y.; Curtis, J.P.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Hlatky, M.A. Physician procedure volume and complications of cardioverter-defibrillator implantation. Circulation. 2012, 125, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Dayal, N.; Burri, H.; Sticherling, C.; Auricchio, A. The Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Pros and Cons. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 19, 121. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00396
Dayal N, Burri H, Sticherling C, Auricchio A. The Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Pros and Cons. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2016; 19(4):121. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00396
Chicago/Turabian StyleDayal, Nicolas, Haran Burri, Christian Sticherling, and Angelo Auricchio. 2016. "The Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Pros and Cons" Cardiovascular Medicine 19, no. 4: 121. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00396
APA StyleDayal, N., Burri, H., Sticherling, C., & Auricchio, A. (2016). The Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Pros and Cons. Cardiovascular Medicine, 19(4), 121. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00396




