Early Versus Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment in Infective Endocarditis: Similar Findings and No Difference in Clinical Outcome
Summary
Introduction
Methods
Patient Population
Clinical and Laboratory Data
Microbiology Data
Echocardiography
Clinical Outcomes
Statistical Analysis
Results
Patient Population
Microbiological Spectrum
Clinical Findings and Duke Classification
Time Course of IE
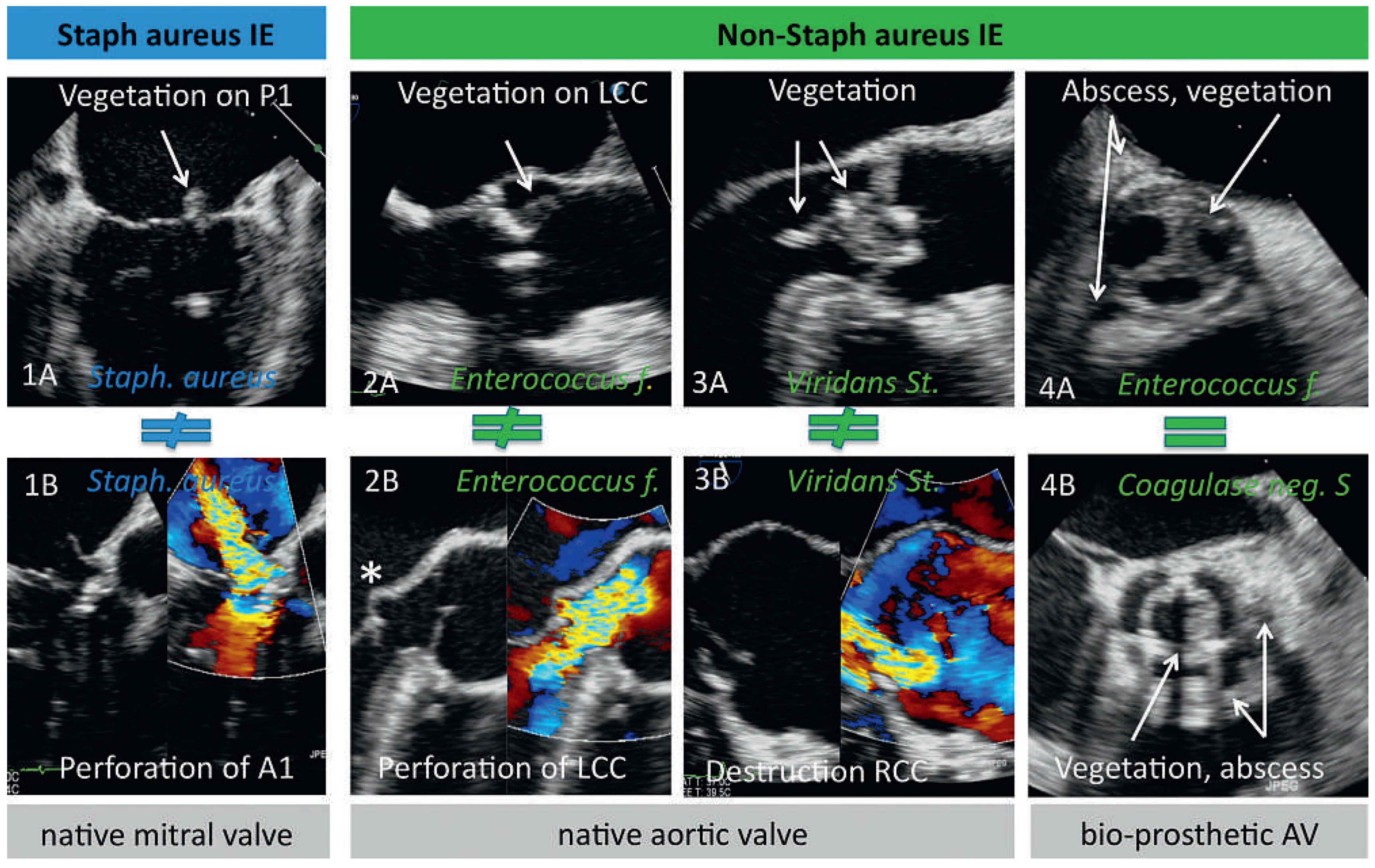
Influence of Microorganisms on Echocardiographic Findings (Table 2)
Early vs Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment
Influences of Microorganisms and Timing of Echocardiography on Outcome
Patients with an Initially False Negative Study
Discussion
Timing of the Initial Echocardiographic Assessment
Patients with Initially Negative Echocardiographic Studies
Association Between IE Causing Organisms and Specific Findings on Echocardiography
Clinical Implications
Limitations
Conclusions
Funding/Potential Competing Interests
References
- Bashore, T.M.; Cabell, C.; Fowler, V., Jr. Update on infective endocarditis. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2006, 31, 274–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D.R.; Corey, G.R.; Hoen, B.; Miro, J.M.; Fowler, V.G.; Jr Bayer, A.S.; et al. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch Intern Med. 2009, 169, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuny, F.; Di Salvo, G.; Belliard, O.; Avierinos, J.F.; Pergola, V.; Rosenberg, V.; et al. Risk of embolism and death in infective endocarditis: prognostic value of echocardiography: a prospective multicenter study. Circulation. 2005, 112, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuny, F.; Grisoli, D.; Collart, F.; Habib, G.; Raoult, D. Management of infective endocarditis: challenges and perspectives. Lancet 2012, 379, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G.; Jr. , Bolger, A.F.; Levison, M.E.; et al. Infective endocarditis: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association: endorsed by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Circulation. 2005, 111, e394–434. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, V.G., Jr. , Miro, J.M.; Hoen, B.; Cabell, C.H.; Abrutyn, E.; Rubinstein, E.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a consequence of medical progress. JAMA. 2005, 293, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirouze, C.; Cabell, C.H.; Fowler, V.G.; Khayat, N.; Olaison, L.; Miro, J.M.; Habib, G.; Abrutyn, E.; Eykyn, S.; Corey, G.R.; et al. Prognostic Factors in 61 Cases of Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis from the International Collaboration on Endocarditis Merged Database. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botelho-Nevers, E.; Thuny, F.; Casalta, J.P.; Richet, H.; Gouriet, F.; Collart, F.; Riberi, A.; Habib, G.; Raoult, D. Dramatic Reduction in Infective Endocarditis–Related Mortality With a Management-Based Approach. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endorsed by the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) and by the International Society of Chemotherapy (ISC) for Infection and Cancer; Habib, G. ; Hoen, B.; Tornos, P.; Thuny, F.; Prendergast, B.; Vilacosta, I.; Moreillon, P.; Antunes, M.d.J.; Thilen, U.; et al. Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infective endocarditis (new version 2009): The Task Force on the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Hear. J. 2009, 30, 2369–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, V.G.; Li, J.; Corey, G.; Boley, J.; A Marr, K.; Gopal, A.K.; Kong, L.K.; Gottlieb, G.; Donovan, C.L.; Sexton, D.J.; et al. Role of Echocardiography in Evaluation of Patients With Staphylococcus aureusBacteremia: Experience in 103 Patients. JACC 1997, 30, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, K.; Mou, D.; Patel, A.; Celermajer, D.S. Clinical criteria and the appropriate use of transthoracic echocardiography for the exclusion of infective endocarditis. Heart 2003, 89, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppu, J.C.; Corretti, M.; Mackowiak, P.; Roghmann, M.-C. Overuse of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Native Valve Endocarditis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Durack, D.T.; Lukes, A.S.; Bright, D.K.; Service, D.E. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am. J. Med. 1994, 96, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Sexton, D.J.; Mick, N.; Nettles, R.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Ryan, T.; Bashore, T.; Corey, G.R. Proposed Modifications to the Duke Criteria for the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, P.P.; Kronenberg, A.; Zbinden, R.; Ruef, C.; Böttger, E.C.; Altwegg, M. Etiologic Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis by Broad-Range Polymerase Chain Reaction: A 3-Year Experience. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampini, S.K.; Bloemberg, G.V.; Keller, P.M.; Buchler, A.C.; Dollenmaier, G.; Speck, R.F.; et al. Broad-range 16S rRNA gene polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of culture-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2011, 53, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, P.; Moura, L.; Pierard, L.A.; Agricola, E.; Popescu, B.A.; Tribouilloy, C.; et al. European Association of Echocardiography recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 2: mitral and tricuspid regurgitation (native valve disease). Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancellotti, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Hagendorff, A.; Moura, L.; Popescu, B.A.; Agricola, E.; et al. European Association of Echocardiography recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 1: aortic and pulmonary regurgitation (native valve disease). Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghbi, W.A.; Chambers, J.B.; Dumesnil, J.G.; Foster, E.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Grayburn, P.A.; et al. Recommendations for evaluation of prosthetic valves with echocardiography and doppler ultrasound: a report From the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Task Force on Prosthetic Valves, developed in conjunction with the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Imaging Committee, Cardiac Imaging Committee of the American Heart Association, the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, the Japanese Society of Echocardiography and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography, endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association, European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, the Japanese Society of Echocardiography, and Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 975–1014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vuille, C.; Nidorf, M.; Weyman, A.E.; Picard, M.H. Natural history of vegetations during successful medical treatment of endocarditis. Am. Heart J. 1994, 128, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohmann, S.; Erbel, R.; Darius, H.; Makowski, T.; Meyer, J. Effect of antibiotic treatment on vegetation size and complication rate in infective endocarditis. Clin. Cardiol. 1997, 20, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Sochowski, R.; Chan, K.-L. Implication of negative results on a monoplane transesophageal echocardiographic study in patients with suspected infective endocarditis. JACC 1993, 21, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shively, B.K.; Gurule, F.T.; Roldan, C.A.; Leggett, J.H.; Schiller, N.B. Diagnostic value of transesophageal compared with transthoracic echocardiography in infective endocarditis. JACC 1991, 18, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, R.O.-M.; Zollinger, E.; Seiler, C.; Cerny, A. Infective endocarditis: clinical spectrum, presentation and outcome. An analysis of 212 cases 1980-1995. Heart 2000, 84, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohmann, S.; Erbel, R.; Darius, H.; Görge, G.; Makowski, T.; Zotz, R.; Mohr-Kahaly, S.; Nixdorff, U.; Drexler, M.; Meyer, J. Prediction of Rapid versus Prolonged Healing of Infective Endocarditis by Monitoring Vegetation Size. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 1991, 4, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckelberg, J.M.; Murphy, J.G.; Ballard, D.; Bailey, K.; Tajik, A.J.; Taliercio, C.P.; Giuliani, E.R.; Wilson, W.R. Emboli in Infective Endocarditis: The Prognostic Value of Echocardiography. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 114, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, A.; Gonzalez-Alujas, M.T. Echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Heart 2004, 90, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, A.J.; Picard, M.H.; Newell, J.B.; Rosas, E.; Davidoff, R.; Thomas, J.D.; Weyman, A.E. Echocardiographic assessment of patients with infectious endocarditis: Prediction of risk for complications. JACC 1991, 18, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuny, F.; Beurtheret, S.; Mancini, J.; Gariboldi, V.; Casalta, J.-P.; Riberi, A.; Giorgi, R.; Gouriet, F.; Tafanelli, L.; Avierinos, J.-F.; et al. The timing of surgery influences mortality and morbidity in adults with severe complicated infective endocarditis: a propensity analysis. Eur. Hear. J. 2009, 32, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, W.G.; Erbel, R.; Kasper, W.; A Visser, C.; Engberding, R.; Sutherland, G.R.; Grube, E.; Hanrath, P.; Maisch, B.; Dennig, K. Safety of transesophageal echocardiography. A multicenter survey of 10,419 examinations. Circulation 1991, 83, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, D.G.; Bansal, R.C.; Hauck, A.J.; Ross, J.J.J.; Applegate, P.M.; Jutzy, K.R.; Mintz, G.S.; Chandrasekaran, K. Transesophageal echocardiographic recognition of subaortic complications in aortic valve endocarditis. Clinical and surgical implications. Circulation 1992, 86, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, W.G.; Mügge, A.; Martin, R.P.; Lindert, O.; Hausmann, D.; Nonnast-Daniel, B.; Laas, J.; Lichtlen, P.R. Improvement in the Diagnosis of Abscesses Associated with Endocarditis by Transesophageal Echocardiography. New Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All patients (n = 274) | SA group (n = 84) |
Non-SA
group
(n = 190) | p | |
| Mean age (years) | 53 ± 17 | 50 ± 6 | 53 ± 6 | 0.19 |
| Women, n (%) | 70 (26) | 18 (21) | 52 (27) | 0.30 |
| Clinical sings of infective endocarditis | ||||
| Fever (>38 °C) | 206 (75) | 71 (85) | 135 (71) | 0.02 |
| Vascular complicationsa | 141 (52) | 56 (67) | 85 (45) | 0.001 |
| Cerebral complications n (%) | 70 (26) | 33 (39) | 37 (20) | <0.001 |
| Immunologic complicationsb | 21 (8) | 6 (7) | 15 (8) | 0.83 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| Leucocyte count (103/μl) | 11.6 ± 6.3 | 11.8 ± 7.3 | 11.5 ± 5.8 | 0.71 |
| Thrombocyte count (103/μl) | 226 | 181 (14–755) | 237 (6–1601) | 0.007 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/l) | 100 | 155 (3–508) | 81 (1–384) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (μmol/l) | 96 | 115 (49–526) | 91 (44–767) | <0.001 |
| Clinical risk factors for IE | ||||
| Previous valve surgery | 59 (22) | 13 (16) | 46 (24) | 0.11 |
| Intravenous drug abuse, n (%) | 52 (19) | 31 (37) | 21 (11) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 35 (13) | 17 (20) | 18 (10) | 0.01 |
| HIV, n (%) | 22 (8) | 11 (13) | 11 (6) | 0.04 |
| Central venous catheter, n (%) | 18 (7) | 6 (7) | 12 (6) | 0.80 |
| Immunosuppressive therapy, n (%) | 10 (4) | 5 (6) | 5 (3) | 0.17 |
| Timing of initial echocardiography | ||||
| Days of antibiotic use before echo | 3 (0–50) | 4 (0–50) | 3 (0–34) | 0.17 |
| Early infectionc post OP: days to echo | 95 (18–180) | 99 (55–180) | 95 (18–179) | 0.53 |
| Late infectionc post OP: years to echo | 6.4 (0.7–44.6) | 9.0 (0.9–22) | 5.4 (0.7–44.6) | 0.18 |
| Echocardiographic modality used | ||||
| TTE only, n (%) | 121 (44) | 37 (44) | 84 (44) | 0.10 |
| TEE only, n (%) | 62 (23) | 25 (30) | 37 (20) | 0.10 |
| TTE and TEE, n (%) | 91 (33) | 22 (26) | 69 (36) | 0.10 |
| IE = infective endocarditis; SA = Staphylococcus aureus. a Vascular complications includes septic arterial embolisation (cerebral, abdominal, lungs) and Janeway lesions. b Immunologic complications includes Osler nods, Roth’s spots and IE associated glomerulonephritis. c Early and late infection post OP: defined as infective endocarditis occurring ≤ and > than 6 months post prior heart valve surgery, respectively. | ||||
| All patients (n = 274) | SA goup (n = 84) |
Non-SA
group
(n = 190) | p * | |
| Site of endocarditis | ||||
| Native valve endocarditisa | 251 (92) | 84 (100) | 167 (88) | 0.07 |
| – Aortic, all | 106 (39) | 27 (32) | 79 (42) | 0.09 |
| – Aortic, bicuspid | 30 (11) | 8 (10) | 22 (12) | 0.65 |
| – Mitral | 109 (40) | 40 (48) | 69 (36) | 0.06 |
| – Tricuspid | 35 (13) | 17 (20) | 18 (9) | 0.01 |
| – Pulmonic | 1 (<1) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.5) | 0.51 |
| Repaired mitral valve | 9 (3) | 5 (6) | 4 (2) | 0.09 |
| Prosthetic valve endocarditisa | 53 (19) | 10 (12) | 43 (22) | 0.006 |
| – Mechanical prosthesis | 28 (10) | 6 (7) | 22 (12) | 0.28 |
| – Biological prosthesis | 25 (9) | 4 (5) | 21 (11) | 0.10 |
| Pacemaker leadsb | 6 (2) | 2 (2) | 4 (2) | 0.30 |
| Double valve endocarditis | 45 (16) | 17 (20) | 28 (15) | 0.23 |
| Specific findings | ||||
| Vegetations | 242 (88) | 79 (94) | 163 (86) | 0.05 |
| – Size of vegetations, cm | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.32 |
| Paravalvular abscess | 64 (23) | 17 (20) | 47 (25) | 0.42 |
| – Native valve | 40 (15) | 14 (17) | 26 (14) | 0.52 |
| – Prosthetic valve | 24 (9) | 3 (4) | 21 (11) | 0.04 |
| Valve destruction | 111 (41) | 35 (42) | 76 (40) | 0.80 |
| – Chordal rupture | 32 (12) | 6 (7) | 26 (4) | 0.12 |
| – Leaflet or cusp rupture | 15 (5) | 4 (5) | 11 (6) | 0.73 |
| – Valve perforation | 70 (26) | 25 (30) | 45 (24) | 0.29 |
| New insufficiency ≥moderate | 214 (78) | 63 (75) | 151 (79) | 0.41 |
| a Including 45 double valve infective endocarditis (native and/or prosthetic): aortic + mitral valves (n = 33), aortic + tricuspid valves (n = 5), mitral + tricuspid valves (n = 5) and aortic + pulmonic valve (n = 2). b Including: 2 patients with isolated pacemaker IE, 2 patients with concomitant mechanical aortic prosthesis IE, 2 patients with concomitant native valve IE (1 × tricuspide valve, 1 × mitral valve). SA = Staphylococcus aureus. | ||||
| Initial echocardiography after antibiotic treatment of | |||
| ≤2 days | >2 days | ||
| (n = 119)* | (n = 144)* | p | |
| Time of antibiotic therapy to echo, days | 1 (0–2) | 9 (3–50) | <0.001 |
| Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis, n (%) | 32 (27) | 51 (35) | 0.14 |
| Vegetations, n (%) | 108 (91) | 124 (86) | 0.25 |
| Vegetation size (cm) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 0.83 |
| Paravalvular abscess, n (%) | 28 (24) | 35 (24) | 0.88 |
| Valve destruction, n (%) | 52 (44) | 51 (35) | 0.17 |
| New insufficiency ≥ moderate, n (%) | 94 (79) | 110 (76) | 0.62 |
| Native valve endocarditis, n (%) | 100 (84) | 114 (79) | 0.31 |
| Repaired mitral valve endocarditis, n (%) | 3 (3) | 6 (4) | 0.47 |
| Prosthetic valve endocarditis, n (%) | 19 (16) | 32 (22) | 0.20 |
| Pacemaker lead endocarditis, n (%) | 2 (2) | 4 (3) | 0.55 |
| Heart surgery for endocarditis, n (%) | 72 (61) | 76 (53) | 0.21 |
| In-hospital death due to endocarditis, n (%) | 10 (8) | 16 (11) | 0.46 |
| * In 11 patients, the time of antibiotic treatment before the initial echocardiography could not be reconstructed. | |||
© 2012 by the author. Attribution-Non-Commercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Bonetti, N.R.; Namdar, M.; Guenthard, H.F.; Gruner, C.; Greutmann, M.; Steffel, J.; Huerlimann, D.; Ruef, C.; Tanner, F.C.; Jenni, R.; et al. Early Versus Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment in Infective Endocarditis: Similar Findings and No Difference in Clinical Outcome. Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 15, 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.00115
Bonetti NR, Namdar M, Guenthard HF, Gruner C, Greutmann M, Steffel J, Huerlimann D, Ruef C, Tanner FC, Jenni R, et al. Early Versus Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment in Infective Endocarditis: Similar Findings and No Difference in Clinical Outcome. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2012; 15(11):317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.00115
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonetti, Nicole R., Mehdi Namdar, Huldrych F. Guenthard, Christiane Gruner, Matthias Greutmann, Jan Steffel, David Huerlimann, Christian Ruef, Felix C. Tanner, Rolf Jenni, and et al. 2012. "Early Versus Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment in Infective Endocarditis: Similar Findings and No Difference in Clinical Outcome" Cardiovascular Medicine 15, no. 11: 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.00115
APA StyleBonetti, N. R., Namdar, M., Guenthard, H. F., Gruner, C., Greutmann, M., Steffel, J., Huerlimann, D., Ruef, C., Tanner, F. C., Jenni, R., & Biaggi, P. (2012). Early Versus Late Initial Echocardiographic Assessment in Infective Endocarditis: Similar Findings and No Difference in Clinical Outcome. Cardiovascular Medicine, 15(11), 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.00115




