Abstract
Protein supplements are popular nutritional supplements consumed primarily by physically active individuals with increased protein demands. Despite the increasing consumer demand for protein supplements in Greece, detailed and comparative data on the nutritional profile of such products is scarce. The purpose of this study was to determine the nutritional quality of protein powder supplements available in the Greek market and to compare animal- with plant-based products. Data was extracted from the websites of the major retailers (n = 28). In total, 216 products were identified and grouped as animal- and plant-based, depending on the protein origin. Animal-based products were predominantly (84.0%) produced from whey. Protein content was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in animal-based products, providing 43.5% of the reference intake (RI) for men and 53.2% for women per serving. The content of essential amino acids (EAAs), branched amino acids (BCAAs) and alanine (Ala) was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in animal-based products (median: 11.0, 5.3 and 1.2 g/serving) compared with plant-based alternatives (median: 8.4, 4.0 and 1.0 g/serving size). Plant-based protein supplements contained significantly higher (p < 0.05) content of fiber, fat and salt and were more energy-dense per 100 g. Mean serving size was larger for animal-based products (29.9 ± 0.4 g) compared with the plant-based ones (28.1 ± 0.5 g). Animal-based supplements were more expensive to purchase by 4.3 € per kg. Overall, animal-based protein powder supplements show a more desirable nutritional profile regarding protein content and quality. Results of this study can serve as a tool for consumers to make informed and healthy choices and for health professionals to provide effective and personalized guidance based on the nutritional content of products.
1. Introduction
Protein supplements are common nutritional supplements designed to increase protein intake. These supplements are regularly consumed by individuals engaging in physical activities and particularly by athletes, both amateur and professional. This is due to documented benefits of consumption of protein supplements associated with improved endurance, recovery, training performance and strength [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The recommended daily reference intake of protein for the healthy adult population is 0.8 g of protein per kg of body weight [7]. This recommendation stems from the average requirement of 0.66 g protein/kg body weight per day for healthy adults, regardless of sex, as established by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) [8]. Physically active individuals such as athletes may have elevated physiological protein requirements to maintain adequate protein synthesis and energy production. According to the International Society of Sports Nutrition, these requirements may vary depending on the individual’s training regime but can be as high as 1.4 to 2.0 g of protein per kg of body weight per day [9].
From a product development perspective, protein supplements are processed formulations of concentrated fractions of protein or protein mixtures. These products are often categorized as concentrates, isolates and hydrolysates based on the chemical processing method and the degree of protein concentration [10,11]. Protein isolates are fractions of protein with higher purity in relation to protein concentrates, whereas protein hydrolysates have undergone enzymatic treatment to enhance protein absorption. Protein supplements often contain additives such as fat, lactose, sugar and preservatives to prolong shelf-life and improve palatability [12]. Depending on the protein source, manufacture of such products can involve multiple steps including milling, defatting, extraction and drying [13]. Drying, which is an essential step in protein supplement production, is encountered at the end of the manufacturing process and is typically accomplished by spray-drying or freeze-drying, resulting in a finely soluble powder [14]. It is worth mentioning that powdered protein supplements have traditionally dominated the market share, yet an increase in ready-to-drink protein supplements is recorded over the last years [15].
Most commercially available powder protein supplements originate from animal sources such as dairy, including whey protein and caseins. Globally, there is an increasing consumer demand for dairy products driven by population growth and the improvement of living standards, particularly in developing countries [16]. Animal protein is considered of higher quality compared with plant protein and is often preferred in the context of sports supplementation. Dairy protein for instance, is a good source of essential amino acids (EAAs), which in turn are pivotal for muscle protein synthesis [9]. On the other hand, plant-based alternatives are also becoming increasingly popular in recent years. Plant-based protein supplements typically originate from cereals and legumes such as wheat and soy. The consumption of these products stems from dietary preferences including vegetarianism, food allergies and intolerances, and halal diet [17]. Furthermore, environmental and animal welfare concerns also account for the high market demand for plant-based alternatives [18].
Globally, the size of protein supplements was valued at € 5.0 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach € 10.8 billion by 2030 [15]. In line with the global market growth, the protein supplements market in Greece is also experiencing substantial growth. The protein drinks and bars market account for 33.3% of the Nutrition eCommerce market in Greece. The expected annual growth rate for the next four years (2025–2029) will be 9.1%, resulting in a projected market volume of € 32.7 million by 2029 [19].
Despite the significant growth of the protein supplements market, the legislative framework that regulates the manufacture and marketing of this type of sports supplements is overlooked. In 2016, the European Union agreed that sports nutrition is regulated under the General Foods Law provision, and no specific regulation is needed [6]. Yet, the lack of specific regulations for such products of increasing popularity may impose health risks associated with improper use [4]. Improper use of protein supplements can result in digestive issues, weight gain, allergies, nutrient deficiencies and exposure to harmful contaminants [20]. Furthermore, the presence of undeclared ingredients in supplements has been linked with documented failed doping control tests for athletes [20]. Thus, implementing accurate labeling policy strategies for protein supplements is an effective means to ensure that products are safe and appropriate for meeting the nutritional requirements of consumers.
The purpose of this study was to estimate the sample size of commercially available protein powder supplements in the Greek market and to determine their nutritional content. In this context, a comparative analysis between animal- and plant-based products was attempted, with particular emphasis on protein and amino acid content. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to systematically assess the nutritional quality of protein powder supplements available in the Greek market. Results of this study can provide valuable information to policymakers for implementing policies that regulate the manufacture and marketing of protein supplements, and health professionals for providing personalized guidance for such products. This would enable consumers to choose the products that meet their individual protein requirements depending on their physical condition and make safe and appropriate use following evidence-based protein supplement recommendations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powder Protein Supplement Data Collection
Data was collected exclusively from the websites of the following 28 online stores in Greece: gymbeam.gr, xtr.gr, proteon.gr, bbclub.gr, proteinmax.gr, mrfit.gr, upcyclestore.gr, fitness-store.gr, foxfitness.gr, Myprotein.gr, fitnessmarket.gr, fit1.gr, prozis.com/gr, realgreekdairies.gr, megaproteinstore.gr, muscleclub.gr, bio-logos.com, fitness-sport.gr, physislaboratory.gr, physiolaboratory.com, muscleattack.gr, nutraholic.com/gr, shopflix.gr, skroutz.gr, hollandandbarrett.gr, mybiohouse.gr, pharmanet.gr and mygreektaste.gr. The online stores selected represent the major retailers of protein supplements in Greece. Data was collected into a comprehensive database by accessing the online stores of the retailers between December 2024 and March 2025. Identical products in different stores were identified as duplicates and were removed.
For each product, the following data was recorded from the label: price (Euros/kg), serving size (g), total energy (kcal), protein (g), carbohydrate (g), sugar (g), salt (g), fat (g), saturated fat (g) and fiber (g) content. Essential amino acids (EAAs), branched amino acids (BCAAs) and alanine (Ala) were also recorded per serving size. Because the serving size of products varied, data was recorded both per 100 g and per serving for energy and macronutrient content. Serving size was recorded strictly based on manufacturer recommendations. Values for salt, fiber, essential amino acids (EAAs), branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and alanine (Ala) were recorded only when such information was available on the product label. When BCAAs are reported, the value represents the sum of all three amino acids (valine, leucine and isoleucine) content. For values that were not reported (i.e., additives were not always available in plant-based products), this was left blank in the data sheet. % Reference intake was calculated for energy and protein, based on reference values for men (2500 kcal, 55 g protein) and for women (2000 kcal, 45 g protein) [21]. Qualitative data on additives from the ingredients list were also recorded in the database. A second researcher reviewed all the data entered and confirmed the entries.
Protein supplements were initially categorized into two main groups based on their protein source: animal-based (e.g., whey, casein, egg, or their blends) and plant-based (e.g., soy, pea, rice, hemp, or their blends). Υeast is an alternative and sustainable source of protein suitable for vegetarian and vegan diets and therefore yeast protein supplements were classified as plant-based. Subsequently, each group was further subdivided according to the presence or absence of added flavorings, aiming to evaluate both the additives and potential differences in the nutritional profiles of the products. Preference was given to chocolate-flavored products, as this is the most commercially popular flavor; when chocolate-flavored versions were unavailable, the flavored product with the highest protein content was selected. To ensure comparability of the samples, specific inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. Only protein powder supplements commercially available in the Greek market through online retailers were included. A small number of protein powder supplements with protein content <60% on a dry basis were identified and were excluded from the study because their distribution between groups (animal- and plant-based) was skewed. Priority was given to products with complete nutritional labeling and quality certifications (e.g., Informed-Sport, ISO, GMP), although these were not mandatory criteria for inclusion. Products with protein content below 60% or lacking sufficient information on nutritional composition or additives were excluded from the analysis.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables are summarized as the number of products and corresponding percentages. Data variables are presented as median (IQR) and mean (±SE). The Shapiro–Wilk test and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests were used to determine whether the data were normally distributed or not. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 to detect differences between groups and sub-groups, using Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction applied. Results were considered statistically significant (*) if the adjusted p-value was less than 0.006 (per 100 g; 0.05/8) or less than 0.01 (per serving; 0.05/5). Price and serving size were not corrected. Cohen’s d was calculated to determine the effect size between groups.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptives of Protein Powder Supplements
In total, 216 products met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed in this study. Plant-based products slightly outnumbered (50.9%) the animal-based ones (49.1%). This finding indicates the strong presence of plant-based products in the Greek protein supplements market. Market penetration of plant-based alternative products is in line with current consumption trends. A global survey in 2019 reported that 40% of consumers are trying to reduce their consumption of animal proteins [22]. The plant-based meat alternatives global market is projected to increase from € 1.4 billion in 2019 to € 3.0 billion by 2026 [23]. Table 1 presents the global survey and the descriptive characteristics of the powder protein supplements per group. In terms of protein content, most animal-based powders were within the range 80–89%, whereas for plant-based ones, within the range 70–79%. The manufacturing of protein concentrates and isolates involves a variety of processes, including the separation and extraction of proteins. Dry fractionation and wet extraction techniques are the two primary protein extraction and separation methods [24]. Many plant-based alternative proteins, such as pulses, have formulation issues, particularly in the areas of nutrition, sensory function and functionality. For instance, the interaction of other constituents in the plant source with protein not only influences the protein extractability but also its functional properties [24]. However, novel strategies are currently being researched to increase the purity and protein yield from plant sources during the steps of fractionation and extraction. Both animal- and plant-based products were predominantly available as flavored options, yet this effect was less prominent for plant-based powders. With regard to protein type, isolates and blends of isolates with concentrates were higher in number for plant-based powders. On the other hand, concentrates and hydrolyzed animal-based powders were more numerous. The vast majority of animal-based products originated from dairy, whereas plant-based products show a more balanced distribution between blended samples and soy, pea and rice. Milk and dairy products are considered an ideal source for the manufacture of protein supplements due to their well-balanced essential amino acids profile and high bioavailability, protein efficiency ratio and net protein utilization [25].

Table 1.
Descriptives of the protein powders analyzed: numbers and percentages for animal- and plant-based products per category.
3.2. Nutritional Value of Protein Powder Supplements
Table 2 summarizes the descriptive statistics for the continuous variables (price, energy, macronutrients and salt) per 100 g for each product group. Significant differences (p < 0.05) are detected for most variables, apart from saturated fatty acid content and carbohydrates. Animal-based protein powders are significantly more expensive to purchase than plant-based ones. This finding indicates that plant-based protein supplements can offer financial benefits to regular consumers. This is an important conclusion as one of the barriers to adopting a vegetarian diet is the perception that plant-based alternatives are more expensive to purchase [26]. In addition, animal-based products contain significantly higher protein and sugar content. Saturated fatty acid content was higher for animal-based supplements but not at a significant level. On the other hand, plant-based alternatives are more energy-dense and contain significantly higher content of fiber. In recent years, growing scientific evidence has highlighted the diverse health benefits of dietary fiber, which in turn has created a large and expanding market for fiber-rich foods and initiated a trend to find new sources of dietary fibers that can be used in food formulations [27]. There is increasing evidence to suggest that the inclusion of fiber in protein supplements may be desirable from a health perspective [6]. A high fiber intake is recommended for individuals adopting a high protein diet for promoting gut colonization by benign microbes, increasing saccharolytic fermentation and decreasing protein fermentation, controlling gastrointestinal inflammation, and reducing gut permeability reduction [28]. With respect to athletic performance, dietary fiber plays a crucial role by regulating energy release, stabilizing the gut microbiome, and reducing inflammation, all of which are essential for sustained energy, improved immune function, and faster recovery [29]. Recent scientific evidence indicates that moderate fiber intake (17 g/day) in athletes can influence the impact of perceived exertion and thus can positively impact the training-induced perception of fatigue [30].

Table 2.
Price, energy, macronutrients and salt content of animal- and plant-based protein powders. Data are expressed median (25th–75th percentile) and mean ± SE.
There are additional health-related reasons for adopting a vegetarian diet and excluding animal-based products, such as lactose intolerance or cow’s milk protein allergy [31]. Nevertheless, it is worth noting the presence of food enzymes in many of the animal-based dairy supplements, with the aim of reducing or eliminating the amount of lactose [4]. Furthermore, protein isolates from dairy are lactose-free and, therefore, are often preferred as a protein source from lactose-intolerant consumers [13]. Health promotion, animal welfare and reduction in the environmental footprint of the diet can at least partially explain the increasing popularity of plant-based products [32]. Results of this study indicate that plant-based protein supplements contain significantly higher amounts of salt and fat. It is often challenging for food manufacturers to develop plant-based alternatives which recreate the appearance, texture, flavor and mouthfeel of meat products, which in some cases is a prerequisite to meet consumer demands [32]. Taste is a major determinant of product purchase and, as indicated by previous research, consumers refuse to purchase protein alternatives because they “won’t like the taste” [33].
Energy and protein data per serving size for each group is presented in Table 3. All descriptive variables were higher for animal-based products in this case. Interestingly, energy was also higher for animal-based products per serving size, which was not the case when protein powders were compared per 100 g (Table 2). This is explained by the significantly higher serving size for animal-based products (29.9 ± 0.4 g vs. 28.1 ± 0.5 g) recommended by the manufacturers on the product label. Both animal- and plant-based products provide above 20 g of protein per serving size, which is within the recommendations for protein intake per dose (20 g < protein < 40 g) [9,34]. Protein quality is largely determined by the amino acid composition and its ability to be digested, absorbed and utilized to meet the body’s physiological needs [35,36]. Animal protein is considered as “high quality” since it provides all the essential amino acids (EAAs) in sufficient quantities and tends to be well digested [37]. EAAs are known to stimulate the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway, triggering an increase in muscle protein synthesis [38,39]. The consensus in relation to EAAs in the context of sports nutrition is that consumption of between 6 and 12 g of EAAs is recommended after training [9,40]. Data of the present study suggest that this criterion is met both by animal- and plant-based powder supplements (11 vs. 8.4 g, respectively). On the other hand, plant protein has a lower content of EAAs and is generally less digestible than animal protein, most likely due to differences in protein structure [41]. Data of the present study indicates that animal-based protein supplements are a better source of EAAs, providing a median excess of 2.6 g of EAAs per serving size, compared with the plant-based alternatives. This finding agrees with the previous work suggesting that animal- and especially dairy-based proteins have the highest content of EAA when compared to plant proteins, which are typically low in one or more EAAs [42]. The presence and amounts of BCAAs are also indicators of protein quality. BCAAs (valine, leucine and isoleucine) are pivotal in modulating muscle protein biosynthesis. This influence stems from their ability to stimulate glutamine and alanine synthesis, which in turn are known to promote muscle protein synthesis, decrease central fatigue and improve performance [5,43,44]. Furthermore, BCAAs may have a role in regulating some brain neurotransmitter production, which can affect fatigue development during training [45]. BCAAs content was significantly higher for animal-based products, with a median of 18.0 g/100 g, compared with 14.7 g/100 g for plant-based ones. Similar findings are reported from previous studies with an estimated content of 16–26 g of BCAAs per 100 g of products for dairy protein supplements and 13–18 g per 100 g of products for plant protein products [4]. Thus, although there is no current recommendation for BCAAs consumption in relation to training, vegetable protein supplements contain lower levels of BCAAs compared with animal protein. Ala content was also significantly higher in animal-based protein supplements by 0.2 g per serving size. This effect is expected as higher BCAA levels can lead to increased alanine production through metabolic processes [46].

Table 3.
Energy, protein, essential amino acids (EAA), branched amino acids (BCAA) and alanine content of animal- and plant-based protein powders per serving size. Data are expressed median (25th–75th percentile) and mean ± SE.
The % reference intakes (%RI’s) for energy and protein content per serving size are presented in Figure 1. As expected, animal-based protein powder supplements provide significantly higher energy (p < 0.001) for men (4.6%/serving) and women (5.7%/serving) compared with the plant-based ones for men (4.5%/serving) and women (5.3%/serving). The same effect was observed for the % protein reference intake for both sexes. Animal-based protein powder supplements provide significantly higher protein (p < 0.001) for men (43.5%/serving) and women (53.2%/per serving) compared with the plant-based ones for men (39.2%/serving) and women (47.9%/serving). The animal-based supplements’ contributions to energy and protein intake are higher compared with the contribution of plant-based ones. This is expected as protein and energy content of animal-based supplements per serving size is higher than of the plant-based alternatives. This effect between animal-based and plant-based products is more profound for women’s % RI’s because energy and protein reference intakes are lower for adult women than men. Reference intakes are set at 2500 kcal/day and 55 g of protein for men, and 2000 kcal/day and 45 g of protein for women [21].
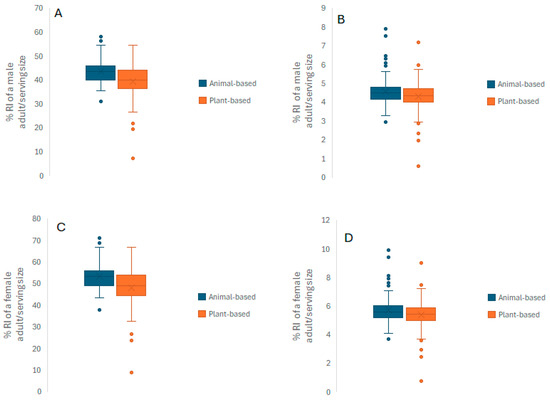
Figure 1.
Energy and protein content of animal- and plant-based protein powders. Data are expressed as % reference intake of protein (A–C) and energy (B–D) per serving size. Data is calculated based on Nutrient Reference Values (NRVs) of 55 g protein and 2500 kcal energy for an adult male and of 45 g protein and 2000 kcal energy for an adult female [24]. Medians are outlined with an X.
Qualitative data of the types of additives included in the formulation of animal- and plant-based protein powder supplements is presented in Table 4. Overall, animal-based powders show higher frequencies for most additives including sweeteners, artificial sweeteners, flavor enhancers and emulsifiers/stabilizers/acidity regulators/preservatives. This may at least partially explain the significantly higher sugar content of animal-based products. Excessive sugar intake is correlated with an increased risk of developing obesity and the associated metabolic diseases, especially if a higher energy intake is combined with a sedentary lifestyle [47]. In March 2015, WHO released a new guideline which recommends that adults and children reduce their daily intake of free sugars to less than 10% of their total energy intake [48]. This stems from voluminous scientific evidence which suggests that limiting the amount of sugar added to foods would be beneficial in promoting public health, particularly with regard to reducing the risk of dental caries, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease [49]. Interestingly, plant-based products contain significantly higher levels of fat compared with animal-based ones. Again, this may be due to additives included in the formulation and particularly flavor enhancers. Cocoa powder, which is known to contain considerable amounts of fat, was commonly found in both animal- and plant-based protein supplements [50]. From a human health perspective, reducing fat content in processed foods is in line with World Health Organization initiatives, yet it can be challenging for plant-based formulations as fat substitutes need to be carefully selected to compensate for any negative impact on sensory properties such as flavor and texture deterioration [51,52]. On the other hand, fortificants are added in similar frequencies in both groups, except for amino acids, which are more frequently added in plant-based products. The fortification of plant-based protein supplements with amino acids is essential for developing formulations with a balanced amino acid profile. Plant-based proteins are deficient in some essential amino acids (i.e., lysine in cereals, methionine in legumes, cysteine in pea and soy), making them less nutritious than those obtained from animals [53].

Table 4.
Frequencies (%) of ingredients added to animal- and plant-based protein powders according to food labels.
3.3. Limitations of the Study and Future Recommendations
The primary limitation of this study is that calculations rely entirely on the nutritional content as stated on packaging. Additionally, no information on the method adopted by the manufacturers to determine the amount of energy and nutrients is provided on the label. This may lead to calculation errors in the nutritional information of the present study. Verification of the food label data using laboratory methods would be desirable to ensure accuracy of the calculations.
While protein supplements can contribute towards an individual’s protein needs, excessive, chronic or unguided use can have undesirable health effects. The safety and effectiveness of protein supplements depend upon the quality of the product, individual health status, and other medications or nutritional supplements being consumed. From a public health perspective, a legislative framework to monitor the manufacturing and marketing of protein supplements is required at national and international level. Furthermore, detailed guidance regarding recommendations for EAAs and BCAAs intake, combined with accurate labeling, would be beneficial for regular consumers. In vitro analysis of the protein quality can be conducted in future studies to ensure the information provided by the manufacturers on the product label is accurate.
4. Conclusions
In summary, this study suggests that the nutritional content of animal- and plant-based powder protein supplements differs significantly. Animal-based products have a higher protein content and are a better source of EAAs, BCAAs and Ala. Plant-based alternatives also meet the recommendations for daily protein intake and contain higher levels of fiber. Regular consumers of such products including athletes or lifestyle users should consult information on nutrition labels to make informed decisions and ensure products support their health and fitness goals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.R.; methodology, V.R.; formal analysis, M.N., D.I.P. and N.T.; investigation, M.N. and D.I.P.; data curation, M.N., D.I.P. and V.R.; writing—original draft preparation, V.R.; writing—review and editing, V.R., A.M. and N.T.; supervision, V.R.; project administration, V.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EAA | Essential Amino Acids |
| BCAA | Branched Amino Acids |
| Ala | Alanine |
| RI | Reference Intake |
| NRV | Nutrient Reference Values |
References
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Ratamess, N.A.; Tranchina, C.P.; Rashti, S.L.; Kang, J.; Faigenbaum, A.D. Effect of protein-supplement timing on strength, power, and body-composition changes in resistance-trained men. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2009, 19, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, R.J.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Hespel, P. Dietary supplements for athletes: Emerging trends and recurring themes. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, S57–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lopez, P.; Rueda-Robles, A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Blanca-Herrera, R.M.; Quirantes-Piné, R.M.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Lozano-Sánchez, J. Analysis and Screening of Commercialized Protein Supplements for Sports Practice. Foods 2022, 11, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros-Torres, J.M.; Escalante-Aburto, A.; Villarreal-Arce, M.E.; Caballero-Prado, C.J. Exploring the Impact of Protein Supplement Source on Body Composition in Women Practicing Anaerobic Resistance Exercise: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kårlund, A.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Turpeinen, A.M.; Palo-Oja, O.M.; El-Nezami, H.; Kolehmainen, M. Protein Supplements and Their Relation with Nutrition, Microbiota Composition and Health: Is More Protein Always Better for Sportspeople? Nutrients 2019, 11, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G. Dietary protein intake and human health. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for protein. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Kerksick, C.M.; Campbell, B.I.; Cribb, P.J.; Wells, S.D.; Skwiat, T.M.; Purpura, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Ferrando, A.A.; Arent, S.M.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.G.; Drake, M.A. Invited review: The effects of processing parameters on the flavor of whey protein ingredients. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6691–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrange, V.; Whitsett, D.; Burris, C. Global market for dairy proteins. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A16–A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Aggarwal, K.; Dhawan, A.; Singh, B.; Shah, P.; Sawhney, A.; Jain, R. Protein supplementation: The double-edged sword. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2023, 37, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meganaharshini, M.; Sudhakar, V.; Bharathi, N.D.; Deepak, S. Review on recent trends in the application of protein concentrates and isolates—A food industry perspective. Food Humanit. 2023, 1, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayasanthi, J.; Adsare, S.R.; Lamdande, A.G.; Naik, A.; Raghavarao, K.; Prabhakar, G. Recovery of proteins from coconut milk whey employing ultrafiltration and spray drying. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand View Research. Protein Supplements Market Size, Share Industry Trends Report. 2025. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/proteinsupplements-market (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Aili, T.; Yang, J.; Jia, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, L.; Lv, X.; Huang, X. Dual signal light detection of beta-lactoglobulin based on a porous silicon bragg mirror. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 204, 114035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, A.P.; Aluko, R.E. Functional properties of protein fractions obtained from commercial yellow field pea (Pisum sativum L.) seed protein isolate. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolin, L.; Pereira, R.; Pinheiro, A.; Martins, J.; Andrade, C.; Ramos, O.; Vicente, A. Emergent food proteins—Towards sustainability, health and innovation. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eCommerce Revenue Development in the Protein Drinks & Bars Market in Greece. ECDB. Available online: https://ecommercedb.com/markets/gr/protein-drinks-bars (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Maughan, R.J. Quality assurance issues in the use of dietary supplements, with special reference to protein supplements. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1843S–1847S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government Dietary Recommendations. Government Recommendations for Energy and Nutrients for Males and Females Aged 1–18 Years and 19+ Years. Public Health England. 2016. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a749fece5274a44083b82d8/government_dietary_recommendations.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Gantriis, R.F.; Fraga, P.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Plant-Based Food and Protein Trend from a Business Perspective: Markets, Consumers, and the Challenges and Opportunities in the Future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markets and Markets. Meat Substitutes Market by Source (Soy Protein, Wheat Protein, Pea Protein), Type (Concentrates, Isolates, and Textured), Product (Tofu, Tempeh, Seitan, and Quorn), Form (Solid and Liquid), and Region—Global Forecast to 2026. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/meat-substitutes-market-979.html/ (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Fatima, A.; Singh, P.; Pandey, V.K.; Singh, R.; Rustagi, S. Exploring the significance of protein concentrate: A review on sources, extraction methods, and applications. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 5, 1000771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, R.; Barukčić, I.; Lisak, K. Possibilities of whey utilisation. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Corrin, T.; Papadopoulos, A. Understanding the attitudes and perceptions of vegetarian and plant-based diets to shape future health promotion programs. Appetite 2017, 109, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Piao, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. The effects of different extraction methods on physicochemical, functional and physiological properties of soluble and insoluble dietary fiber from Rubus chingii Hu. Fruits. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 93, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanctuary, M.R.; Kain, J.N.; Angkustsiri, K.; German, J.B. Dietary considerations in autism spectrum disorders: The potential role of protein digestion and microbial putrefaction in the gut-brain axis. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancin, L.; Burke, L.M.; Rollo, I. Fibre: The Forgotten Carbohydrate in Sports Nutrition Recommendations. Sports Med. 2025, 55, 1067–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadžić, E.; Starcevic, A.; Rupčić, T.; Zucko, J.; Čvrljak, T.; Renko, I.; Knjaz, D.; Novak, D. Effects of Soluble Dietary Fibre on Exercise Performance and Perception of Fatigue in Young Basketball Players. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 61, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.R.A.; Silva, M.M.N.; Ribeiro, B.D. Health Issues and Technological Aspects of Plant-Based Alternative Milk. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcorta, A.; Porta, A.; Tárrega, A.; Alvarez, M.D.; Vaquero, M.P. Foods for Plant-Based Diets: Challenges and Innovations. Foods 2021, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Hartmann, C.; Siegrist, M. Consumers’ Associations, Perceptions and Acceptance of Meat and Plant-Based Meat Alternatives. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 87, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Wilborn, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.M.; Jäger, R.; Collins, R.; Cooke, M.; Davis, J.N.; Galvan, E.; et al. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sport Nutr. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Boye, J.; Wijesinha-Bettoni, R.; Burlingame, B. Protein quality evaluation twenty years after the introduction of the protein digestibility corrected amino acid score method. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S183–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.C.; Phillips, S.M. Supplemental Protein in Support of Muscle Mass and Health: Advantage Whey. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A8–A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.-A.; Bendsen, N.; Tremblay, A.; Astrup, A. Effect of proteins from different sources on body composition. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, B16–B31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Dreyer, H.C.; Drummond, M.J.; Glynn, E.L.; Cadenas, J.G.; Yoshizawa, F.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Nutrient signalling in the regulation of human muscle protein synthesis. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Mittendorfer, B.; Wolfe, R.R. Essential amino acids are primarily responsible for the amino acid stimulation of muscle protein anabolism in healthy elderly adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M. Dietary protein requirements and adaptive advantages in athletes. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S158–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrazaga, I.; Micard, V.; Gueugneau, M.; Walrand, S. The Role of the Anabolic Properties of Plant- versus Animal-Based Protein Sources in Supporting Muscle Mass Maintenance: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorissen, S.H.; Witard, O.C. Characterising the muscle anabolic potential of dairy, meat and plant-based protein sources in older adults. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Mach, N. Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis and diet: A systematic review for athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, Y.; Murakami, T.; Nakai, N.; Nagasaki, M.; Harris, R.A. Exercise promotes BCAA catabolism: Effects of BCAA supplementation on skeletal muscle during exercise. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1583S–1587S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Santos, C.; Nascimento, F.E.L. Isolated branched-chain amino acid intake and muscle protein synthesis in humans: A biochemical review. Einstein 2019, 17, eRB4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Ferraz, P.L.; Bozza, T.; Nicastro, H.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. Distinct effects of leucine or a mixture of the branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) supplementation on resistance to fatigue, and muscle and liver-glycogen degradation, in trained rats. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.H.; Rossi, M.; Corpe, C.P.; Butterworth, P.J.; Ellis, P.R. The role of sugars and sweeteners in food, diet and health: Alternatives for the future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guideline: Sugar Intakes for Adults and Children. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549028/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Gillespie, K.M.; Kemps, E.; White, M.J.; Bartlett, S.E. The Impact of Free Sugar on Human Health—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razola-Díaz, M.D.C.; Aznar-Ramos, M.J.; Verardo, V.; Melgar-Locatelli, S.; Castilla-Ortega, E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C. Exploring the Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds in Different Cocoa Powders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lv, B.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. Influence of hydrophilic polysaccharide fat replacers on the in vitro digestibility of protein in emulsion-type sausage. Food Res Int. 2023, 170, 113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Shen, H.; Jiao, Y.; Li, T.; Rivadeneira, J.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Donkey myofibrillar protein/sodium alginate-stabilized high internal phase Pickering emulsion as fat substitutes in emulsion-type sausages: Physicochemical, sensory properties and freeze-thaw stability. Food Res. Int. 2025, 222, 117284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoylu Özbek, Z.; Taşkın, B.; Sözeri Atik, D. Fortification of Plant-Based Food Analogs. In Plant-Based Foods: Ingredients, Technology and Health Aspects; Aydar, A.Y., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 35–72. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).