The Effect of Ergothioneine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Memory, and Sleep in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Protocol Deviations, and Ethics Approval
2.2. Participants, Screening, and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Randomization, Blinding, and Intervention
2.4. Study Procedures
2.5. Sample Size and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
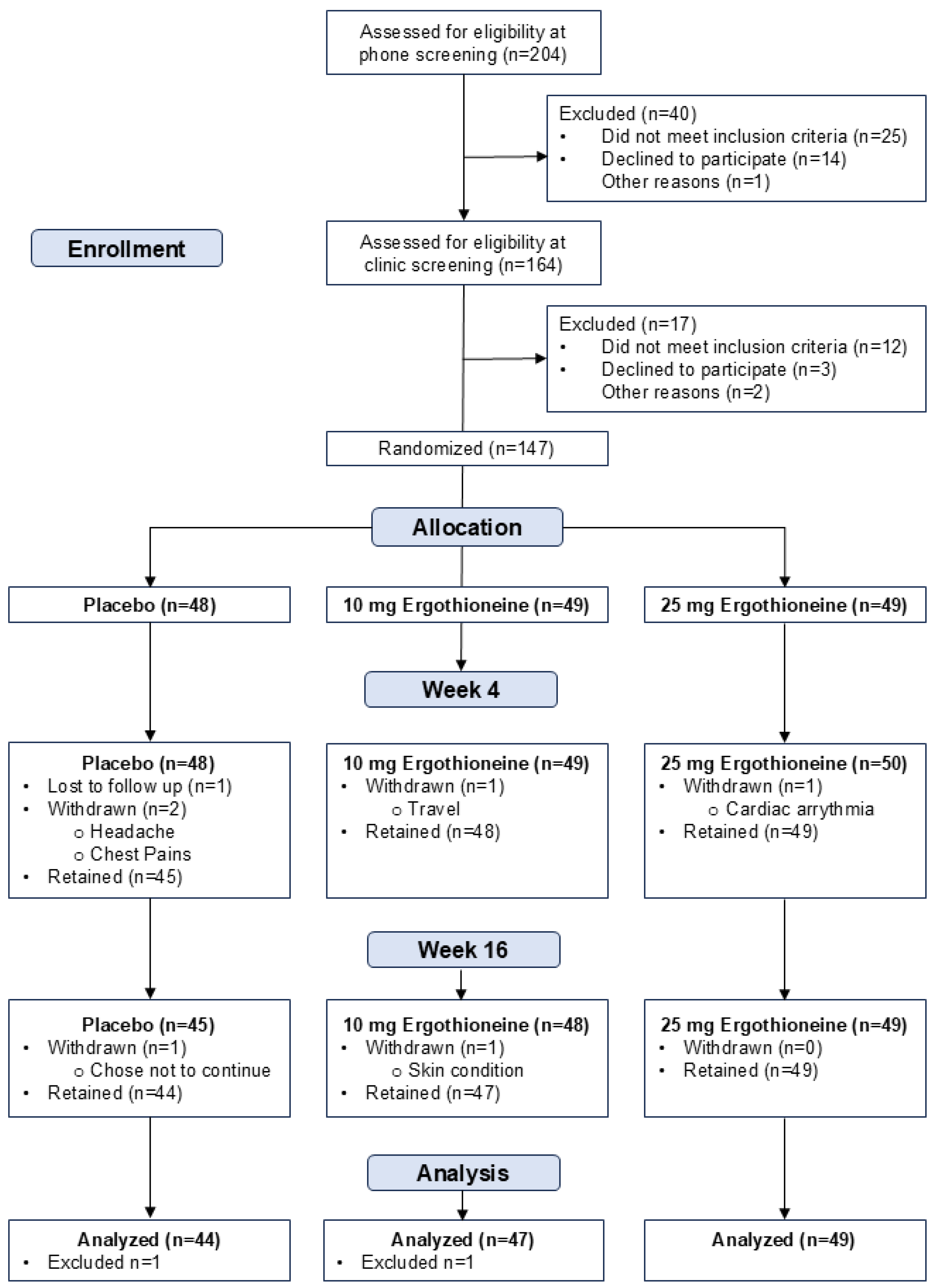
3.1. Participant Characteristics and Recruitment
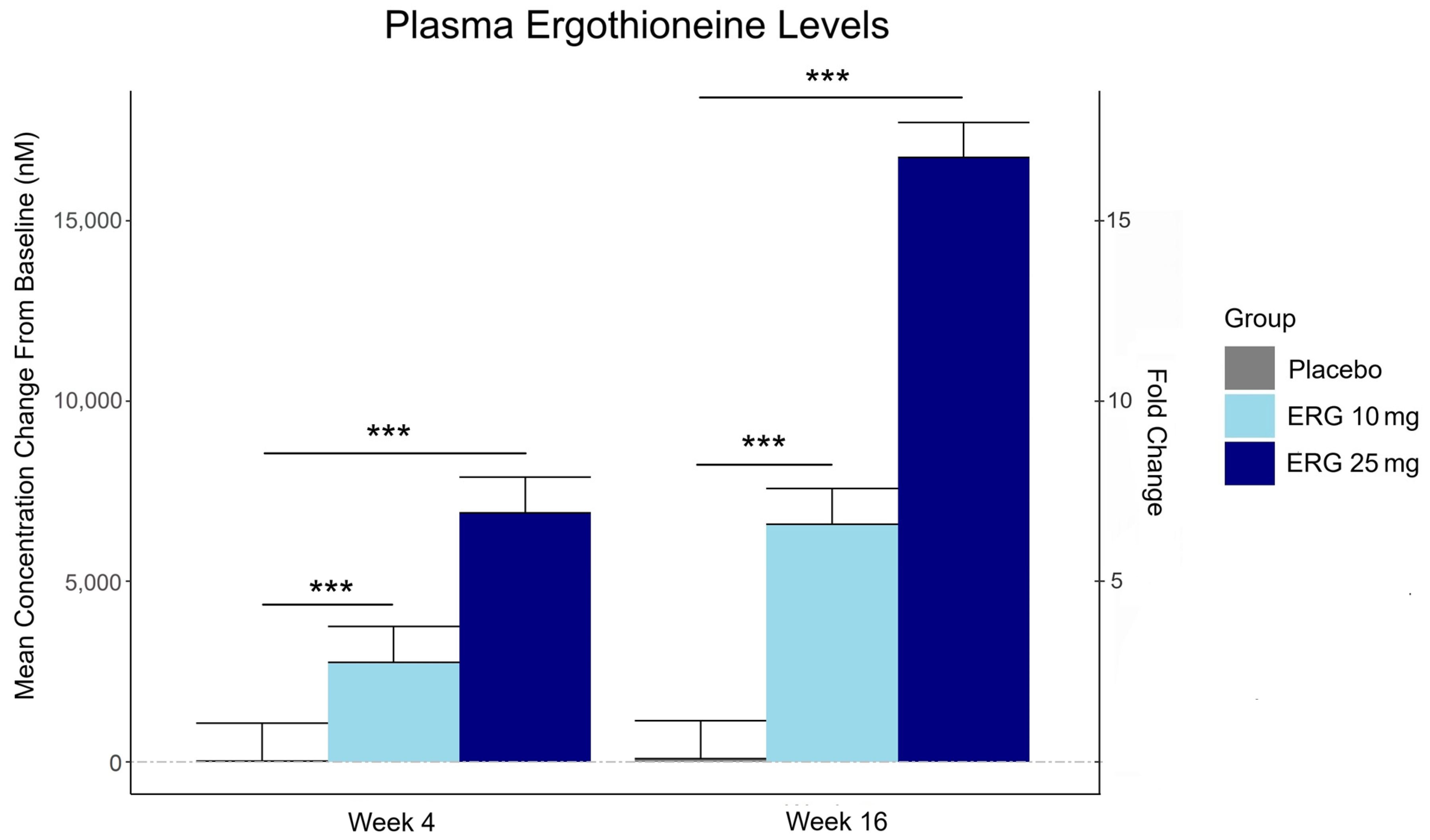
3.2. Plasma Ergothioneine Levels
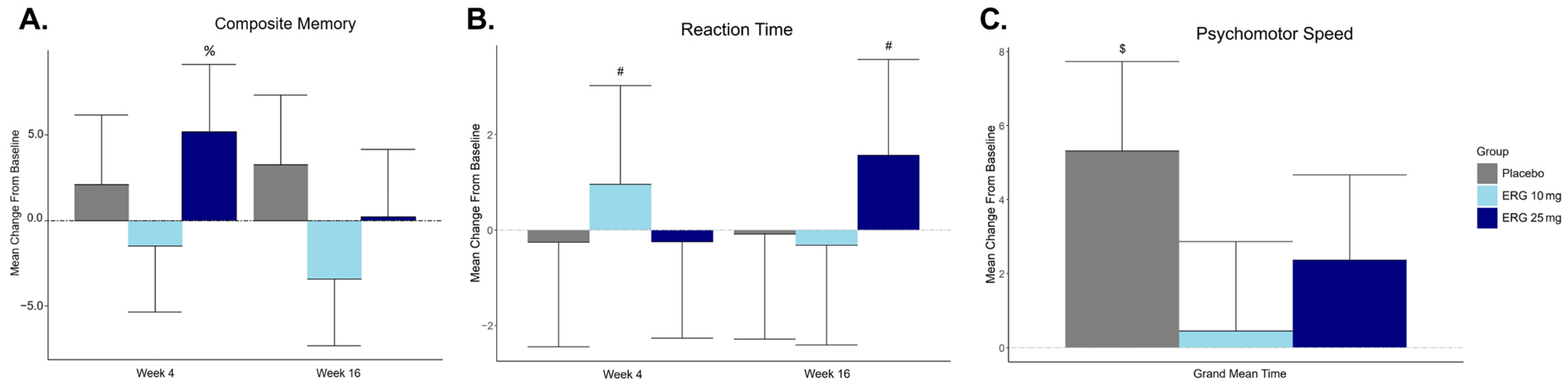
3.3. Primary Outcome: Composite Memory Measured by CNS-VS Composite Memory Score
3.4. Secondary Outcome: Cognitive Function Measured by CNS-VS (All Domains)
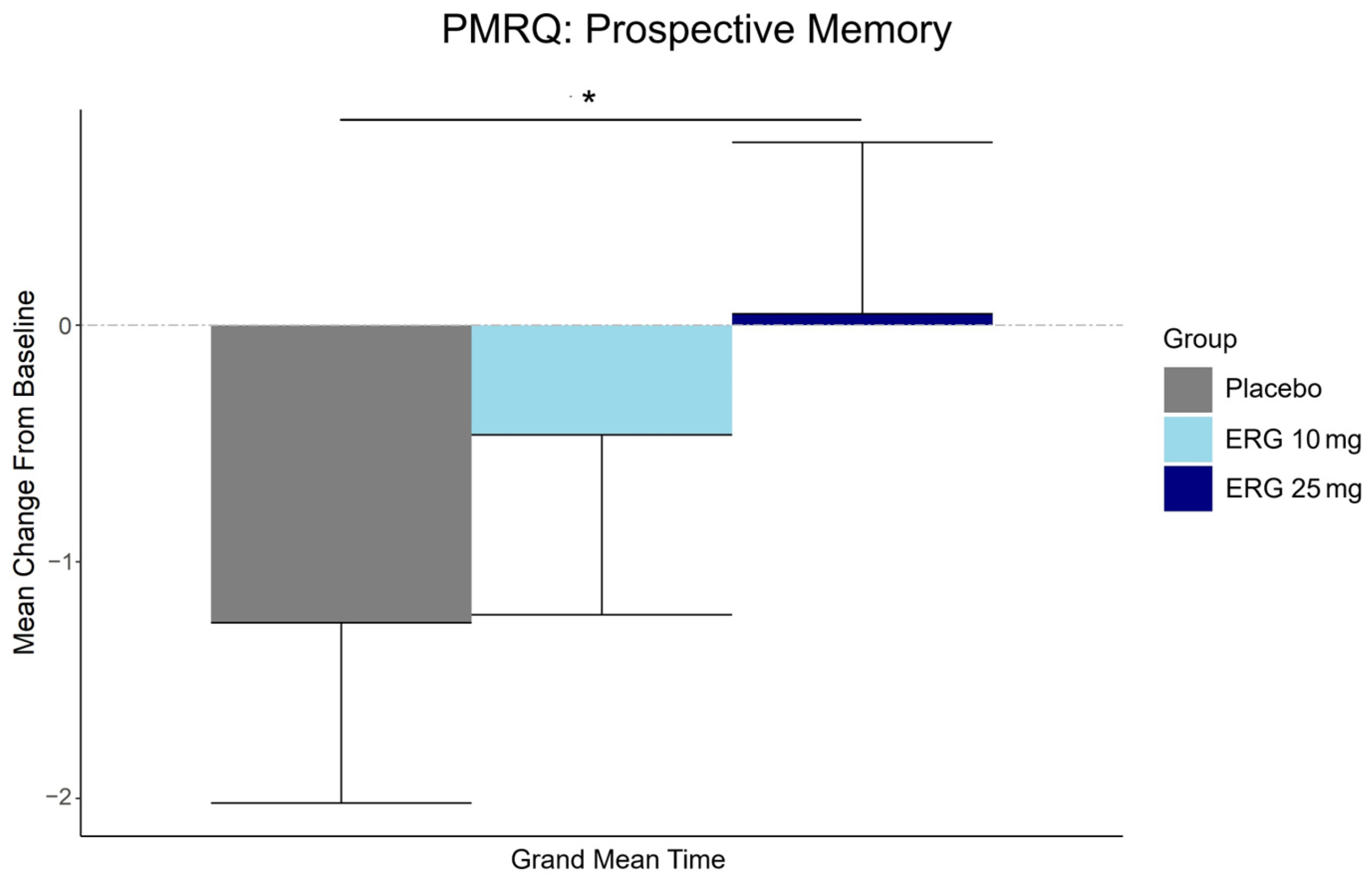
3.5. Secondary Outcome: Subjective Memory
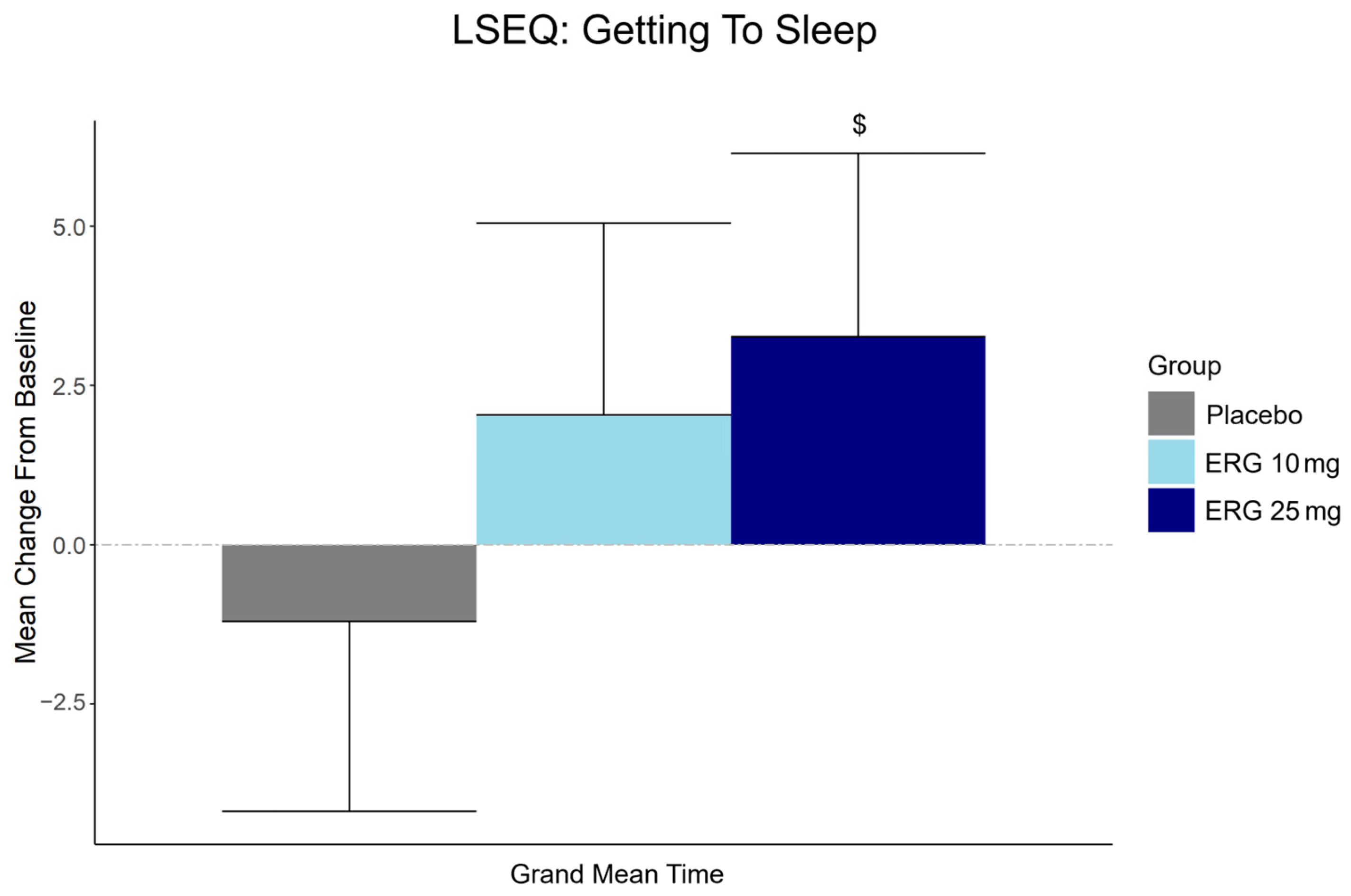
3.6. Secondary Outcome: Subjective Sleep Quality
3.7. Exploratory Biomarker: Leukocyte Telomere Length
3.8. Inflammation
3.9. Safety, Liver Function and TMAO Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DASH | Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension |
| MIND | Mediterranean–DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| CNS-VS | Central Nervous System Vital Signs |
| CSIRO | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization |
| COMPASS | Composite Autonomic Symptom Score |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| MAC-Q | Memory Assessment Clinics Questionnaire |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| ERG | Ergothioneine |
| IWRS | Interactive Web-Based Randomization Service |
| AHTA | Adelaide Health Technology Assessment |
| GRAS | Generally Recognized As Safe |
| cGMP | Current Good Manufacturing Practices |
| PRMQ | Prospective and Retrospective Memory Questionnaire |
| LSEQ | Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| LC-QTof | Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time-of-Flight |
| TMAO | Trimethylamine N-Oxide |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ITT | Intention To Treat |
| PP | Per Protocol |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| MAC-Q | Memory Assessment Clinics Questionnaire |
| HSD | Honestly Significant Difference |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| LSM | Least Squares Mean |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MOCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| GDS | Global Deterioration Scale |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| NCI | Neurocognitive Index |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| TMA | Trimethylamine |
References
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The Global Prevalence of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salthouse, T.A. What and When of Cognitive Aging. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2004, 13, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.C.; DeFazio, R.A.; Bizon, J.L. Characterizing Cognitive Aging of Spatial and Contextual Memory in Animal Models. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2012, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Sun, H.; Dong, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Song, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Executive Dysfunction and Gray Matter Atrophy in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Liu, K.Y.; Costafreda, S.G.; Selbæk, G.; Alladi, S.; Ames, D.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Brayne, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2024 Report of the Lancet Standing Commission. Lancet 2024, 404, 572–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.; Matthews, F.E.; Barnes, D.E.; Yaffe, K.; Brayne, C. Potential for Primary Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis of Population-Based Data. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolappa, K.; Seeher, K. Optimizing Brain Health across the Life Course: WHO Position Paper; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Tang, M.; Mayeux, R.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean Diet and Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Clavero, P.; Toledo, E.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; San Julián, B.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Ros, E.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.Á. Mediterranean Diet Improves Cognition: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA Randomised Trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Babyak, M.A.; Craighead, L.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.A.; Browndyke, J.N.; Strauman, T.A.; Sherwood, A. Effects of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Diet, Exercise, and Caloric Restriction on Neurocognition in Overweight Adults With High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Soest, A.P.; Beers, S.; van de Rest, O.; de Groot, L.C. The Mediterranean-Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diet for the Aging Brain: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-H.; Ho, M.-H.; Wang, C.-S.; Chen, I.-H. Effect of Dietary Patterns on Cognitive Functions of Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 110, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingö, L.; Bergh, C.; Rode, J.; Rubio, M.F.R.; Persson, J.; Johnson, L.B.; Smit, L.H.; Hutchinson, A.N. The Effect of Whole-Diet Interventions on Memory and Cognitive Function in Healthy Older Adults–A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; Sisto, A.; Marzetti, E. Anorexia of Aging: Risk Factors, Consequences, and Potential Treatments. Nutrients 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, L.; Folch, A.; Rojas, M.; Cantero, J.L.; Atienza, M.; Folch, J.; Camins, A.; Ruiz, A.; Papandreou, C.; Bulló, M. Effects of Nutrition on Cognitive Function in Adults with or without Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, M.; Lehoczki, A.; Tarantini, S.; Fazekas-Pongor, V.; Csípő, T.; Csizmadia, Z.; Varga, J.T. Improving Cognitive Function with Nutritional Supplements in Aging: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Clinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Vitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants, and Other Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D.; Scholey, A.; White, D.J.; Cohen, N.J.; Cassidy, A.; Gillings, R.; Irvine, M.A.; Kay, C.D.; Kim, M.; King, R.; et al. A Combined DHA-Rich Fish Oil and Cocoa Flavanols Intervention Does Not Improve Cognition or Brain Structure in Older Adults with Memory Complaints: Results from the CANN Randomized, Controlled Parallel-Design Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleztena, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Pardo, M.; Añorbe, T.; Gost, J.I.; Gomez, C.; Ilarregui, B.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Association between Cognitive Function and Supplementation with Omega-3 PUFAs and Other Nutrients in ≥ 75 Years Old Patients: A Randomized Multicenter Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangour, A.D.; Allen, E.; Elbourne, D.; Fasey, N.; Fletcher, A.E.; Hardy, P.; Holder, G.E.; Knight, R.; Letley, L.; Richards, M.; et al. Effect of 2-y N−3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Cognitive Function in Older People: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaras, M.D.; Richie, J.P.; Calcagnotto, A.; Beelman, R.B. Mushrooms: A Rich Source of the Antioxidants Ergothioneine and Glutathione. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ey, J.; Schömig, E.; Taubert, D. Dietary Sources and Antioxidant Effects of Ergothioneine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6466–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Cheah, I.K. Diet-Derived Antioxidants: The Special Case of Ergothioneine. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beelman, R.B.; Phillips, A.T.; Richie, J.P.; Ba, D.M.; Duiker, S.W.; Kalaras, M.D. Health Consequences of Improving the Content of Ergothioneine in the Food Supply. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluccio, M.; Tripicchio, M.; Pochini, L. The Human OCTN Sub-Family: Gene and Protein Structure, Expression, and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Kato, Y. Ergothioneine in the Brain. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Cheah, I. Are Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases Caused by a Lack of the Diet-Derived Compound Ergothioneine? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 217, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, N.; Nakao, S.; Nishiyama, M.; Takeda, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Masuo, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kato, Y. Oral Administration of the Food-Derived Hydrophilic Antioxidant Ergothioneine Enhances Object Recognition Memory in Mice. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 14, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, K. Ergothioneine Improves Cognitive Function by Ameliorating Mitochondrial Damage and Decreasing Neuroinflammation in a <scp>d</Scp> -Galactose-Induced Aging Model. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 11686–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsube, M.; Ishimoto, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Kagami, A.; Shuto, T.; Kato, Y. Ergothioneine Promotes Longevity and Healthy Aging in Male Mice. Geroscience 2024, 46, 3889–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, D.; Slade, L.; Paikopoulos, Y.; D’Andrea, D.; Savic, N.; Stancic, A.; Miljkovic, J.L.; Vignane, T.; Drekolia, M.K.; Mladenovic, D.; et al. Ergothioneine Improves Healthspan of Aged Animals by Enhancing CGPDH Activity through CSE-Dependent Persulfidation. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, H.-G.; Mittenbühler, M.J.; Sun, Y.; Van Vranken, J.G.; Schindler, S.; Jayaraj, A.; Khetarpal, S.A.; Smythers, A.L.; Vargas-Castillo, A.; Puszynska, A.M.; et al. Ergothioneine Controls Mitochondrial Function and Exercise Performance via Direct Activation of MPST. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, Z.W.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Cheah, I.K.-M.; Leow, D.M.K.; Chen, L.; Halliwell, B. Ergothioneine and Mitochondria: An Important Protective Mechanism? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 726, 150269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, I.K.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Yew, T.S.Z.; Lim, K.H.C.; Halliwell, B. Administration of Pure Ergothioneine to Healthy Human Subjects: Uptake, Metabolism, and Effects on Biomarkers of Oxidative Damage and Inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, I.K.; Feng, L.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Lim, K.H.C.; Halliwell, B. Ergothioneine Levels in an Elderly Population Decrease with Age and Incidence of Cognitive Decline; a Risk Factor for Neurodegeneration? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Castellano-Escuder, P.; Carmona, F.; Lefèvre-Arbogast, S.; Low, D.Y.; Du Preez, A.; Ruigrok, S.R.; Manach, C.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Korosi, A.; et al. Food and Microbiota Metabolites Associate with Cognitive Decline in Older Subjects: A 12-Year Prospective Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-Y.; Kan, C.N.; Cheah, I.K.; Chong, J.R.; Xu, X.; Vrooman, H.; Hilal, S.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Chen, C.P.; Halliwell, B.; et al. Low Plasma Ergothioneine Predicts Cognitive and Functional Decline in an Elderly Cohort Attending Memory Clinics. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Fukuji, Y.; Kondoh, H.; Yanagida, M. Whole-Blood Metabolomics of Dementia Patients Reveal Classes of Disease-Linked Metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022857118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-Y.; Cheah, I.K.; Chong, J.R.; Chai, Y.L.; Tan, J.Y.; Hilal, S.; Vrooman, H.; Chen, C.P.; Halliwell, B.; Lai, M.K.P. Low Plasma Ergothioneine Levels Are Associated with Neurodegeneration and Cerebrovascular Disease in Dementia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Saiki, S.; Okuzumi, A.; Mohney, R.P.; Hattori, N. Identification of Novel Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease by Metabolomic Technologies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, Y.F.; Cheah, I.K.; Mahendran, R.; Tang, R.M.; Chua, R.Y.; Goh, R.E.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Kua, E.H.; Chen, C.; et al. Investigating the Efficacy of Ergothioneine to Delay Cognitive Decline in Mild Cognitively Impaired Subjects: A Pilot Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 102, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, T.H., 3rd; Feher, E.P.; Larrabee, G.J. Assessment of memory complaint in age-associated memory impairment: The MAC-Q. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1992, 4, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.; Lamport, D.J.; Field, D.T.; Butler, L.T.; Williams, C.M. Practice Effects in Nutrition Intervention Studies with Repeated Cognitive Testing. Nutr. Healthy Aging 2018, 4, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, C.; Johnson, L. Reliability and Validity of a Computerized Neurocognitive Test Battery, CNS Vital Signs. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2006, 21, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Smith, G.; Maylor, E.; Della Sala, S.; Logie, R. The Prospective and Retrospective Memory Questionnaire (PRMQ): Normative Data and Latent Structure in a Large Non-Clinical Sample. Memory 2003, 11, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, A.C.; Hindmarch, I. Factor Analysis of a Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire. Psychol. Med. 1978, 8, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Tan, S.B. The Correct Interpretation of Confidence Intervals. Proc. Singap. Healthc. 2010, 19, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fethney, J. Statistical and Clinical Significance, and How to Use Confidence Intervals to Help Interpret Both. Aust. Crit. Care 2010, 23, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema, D.; Phillips, I.R.; Shephard, E.A. Trimethylamine and Trimethylamine N-Oxide, a Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 (FMO3)-Mediated Host-Microbiome Metabolic Axis Implicated in Health and Disease. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, V.E.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; Casso, A.G.; VanDongen, N.S.; Ziemba, B.P.; Sapinsley, Z.J.; Richey, J.J.; Zigler, M.C.; Neilson, A.P.; Davy, K.P.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Age-Related Vascular Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction in Mice and Healthy Humans. Hypertension 2020, 76, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; DuGar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.-M.; et al. Gut Flora Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine Promotes Cardiovascular Disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Ottosson, F.; Hellstrand, S.; Ericson, U.; Orho-Melander, M.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O. Ergothioneine Is Associated with Reduced Mortality and Decreased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Heart 2020, 106, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, P.; Monti, S.; Lustgarten, M.S.; Song, Z.; Ellis, D.; Tian, Q.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Stancliffe, E.; Leshchyk, A.; Short, M.I.; et al. Metabolite Signatures of Chronological Age, Aging, Survival, and Longevity. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M. Vitamins Associated with Brain Aging, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer Disease: Biomarkers, Epidemiological and Experimental Evidence, Plausible Mechanisms, and Knowledge Gaps. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M.; Coley, N.; Andrieu, S.; Bonhomme, C.; Caubere, J.P.; Cesari, M.; Gautry, J.; Garcia Sanchez, I.; Hugonot, L.; Mansuy, L.; et al. How to Design Nutritional Intervention Trials to Slow Cognitive Decline in Apparently Healthy Populations and Apply for Efficacy Claims: A Statement from the International Academy on Nutrition and Aging Task Force. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Beaumont, H.; Ferguson, D.; Yadegarfar, M.; Stubbs, B. Risk of Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older People with Subjective Memory Complaints: Meta-Analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 130, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, M.E.M.; van Boxtel, M.P.J.; Willems, D.; Jolles, J. Do Subjective Memory Complaints Predict Cognitive Dysfunction over Time? A Six-Year Follow-up of the Maastricht Aging Study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl Robertson, F.; Jacova, C. A Systematic Review of Subjective Cognitive Characteristics Predictive of Longitudinal Outcomes in Older Adults. Gerontologist 2023, 63, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsube, M.; Watanabe, H.; Suzuki, K.; Ishimoto, T.; Tatebayashi, Y.; Kato, Y.; Murayama, N. Food-Derived Antioxidant Ergothioneine Improves Sleep Difficulties in Humans. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 95, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Ozawa, N.; Shinozaki, T.; Wakabayashi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kawano, Y.; Ohtsu, I.; Tatebayashi, Y. Ergothioneine, a Metabolite of the Gut Bacterium Lactobacillus Reuteri, Protects against Stress-Induced Sleep Disturbances. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubu, O.M.; Brannick, M.; Mortimer, J.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.; Sebastião, Y.V.; Wen, Y.; Schwartz, S.; Borenstein, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Morgan, D.; et al. Sleep, Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.P.; Kowgier, M.; Yu, L.; Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Sleep Fragmentation and the Risk of Incident Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Decline in Older Persons. Sleep 2013, 36, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R.; Vitiello, M. V Implications of Sleep Disturbance and Inflammation for Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudney, L.E.; Frey, B.N.; McCabe, R.E.; Green, S.M. Investigating the Relationship between Objective Measures of Sleep and Self-Report Sleep Quality in Healthy Adults: A Review. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2022, 18, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, A.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Marx, W.; Turner, M.; McKune, A.; Naumovski, N. The Effects of L-Theanine Consumption on Sleep Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2025, 81, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, P.; Tsapekos, M.; de Pedro, N.; Liu, A.G.; Casey Lippmeier, J.; Chen, S. Ergothioneine Mitigates Telomere Shortening under Oxidative Stress Conditions. J. Diet Suppl. 2022, 19, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, R. Genetic Liability to Human Serum Metabolites Is Causally Linked to Telomere Length: Insights from Genome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Metabolic Pathways Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1458442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Yu, X.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Hou, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; et al. Ergothioneine Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting Glycerophospholipids Metabolism and TGF-β/Smads Signaling Pathway: Based on Metabonomics and Network Pharmacology. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 45, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Guo, H.; Jia, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, S. Supplement of Food Functional Factor Ergothioneine Can Effectively Prevent Liver Injury in Mice. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Placebo (N = 48) | ERG 10 mg (N = 49) | ERG 25 mg (N = 50) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | N | % | N | % | N | % |
| Female | 35 | 72.9 | 36 | 73.5 | 36 | 72 |
| Male | 13 | 27.1 | 13 | 26.5 | 14 | 28 |
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | |
| Age (years) | 70.4 | 6.7 | 68.4 | 7.4 | 69 | 7.9 |
| MOCA | 27 | 2 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 2 |
| MAC-Q | 27 | 2 | 27 | 2 | 27 | 1 |
| GDS | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| SBP | 130.2 | 17.5 | 132.7 | 18 | 125.5 | 15.7 |
| DBP | 78.7 | 13.3 | 78.7 | 9 | 78 | 12 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.6 | 0.3 | 5.6 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 0.3 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 37 | 4 | 37 | 5 | 37 | 4 |
| Height (cm) | 163.5 | 14.3 | 163.4 | 9.7 | 165.3 | 12.5 |
| Weight (kg) | 74 | 16.9 | 73.4 | 13 | 74.5 | 18.6 |
| Body mass index | 27.7 | 5.2 | 27.6 | 5.5 | 26.1 | 5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zajac, I.T.; Kakoschke, N.; Kuhn-Sherlock, B.; May-Zhang, L.S. The Effect of Ergothioneine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Memory, and Sleep in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutraceuticals 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030015
Zajac IT, Kakoschke N, Kuhn-Sherlock B, May-Zhang LS. The Effect of Ergothioneine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Memory, and Sleep in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutraceuticals. 2025; 5(3):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030015
Chicago/Turabian StyleZajac, Ian T., Naomi Kakoschke, Barbara Kuhn-Sherlock, and Linda S. May-Zhang. 2025. "The Effect of Ergothioneine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Memory, and Sleep in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial" Nutraceuticals 5, no. 3: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030015
APA StyleZajac, I. T., Kakoschke, N., Kuhn-Sherlock, B., & May-Zhang, L. S. (2025). The Effect of Ergothioneine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Memory, and Sleep in Older Adults with Subjective Memory Complaints: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutraceuticals, 5(3), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030015






