Abstract
Brewer’s spent grain is the residue left after the separation of wort during the beer-brewing process. Although this by-product has been reported to have a high protein content, it is normally treated as waste. This work aims to isolate bioactive hydrolysates from BSG, and then explore their bioactivities. Two groups (A and B) of BSG were subjected to protein extraction using the alkaline extraction method at pH 12, where group A was pre-treated with cellulase, while group B was not pre-treated and was directly extracted. The final isolate yielded 50.18 ± 1.22% recovery of the BSGP from group A and 66.41 ± 0.37% recovery from group B. RP-HPLC profiles showed that the extracted BSGPs are mainly hydrophilic proteins. The proteins extracted by the two methods were hydrolyzed enzymatically using Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin. The hydrolysates obtained displayed blood pressure regulation activity and antioxidant properties, when assayed with angiotensin-converting enzyme assay, 2,2-diphenyl-picryl-hydrazyl assay, and ferric antioxidant power assay. It can be concluded that it is possible to extract good quality proteins from BSG and this by-product presents potential as a source for the extraction of a variety of proteins that might be of interest to the food industries.
1. Introduction
In the food industry, the brewing industry holds an important economic place, with the world beer production exceeding 1.91 billion hectoliters in 2019 [1]. During the brewing process, after wort manufacture, brewers’ spent grain (BSG) is obtained as the barley malt residue, representing approximately 85% of the total brewing waste generated [2]. Annually, around 3.4 million tons of BSG are produced within the European Union, and Ireland contributes approximately 160,000 tons [3]. BSG is a lignocellulosic material, which contains significant amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, phenolics, and minerals and is a valuable source of nutritional substance [4]. The protein components of BSG are mainly albumin, globulin, hordein, and glutenin, of which hordein typically accounts for 50% and a high content of proline and glutamine is also present [5]. These amino acid residues are connected to bioactive peptides, which may play a role in the control of metabolic illnesses, such as cardiovascular disease and type II diabetes [6]. However, despite being readily available, BSG receives little attention and is traditionally only used in cattle feed or sold as ordinary fodder at a low price by beer manufacturers. This underutilization is attributed to the protein being trapped by the complicated carbohydrate composition and high moisture content, which make it difficult to extract it and the other valuable nutrients present [5].
In recent years, many studies have been carried out on the extraction of BSG protein (BSGP), which generally include salt solution extraction, ethanol precipitation, ultrasound-assisted extraction and ultrafiltration treatment, and alkali-soluble acid precipitation and organic solvent extraction, among others [7]. To date, the alkaline-soluble acid precipitation method has been widely used in the extraction of plant-derived proteins, due to the fact that plant proteins are easily soluble in an alkaline environment and precipitate under acidic isoelectric conditions [8]. A number of reports outline the use of carbohydrase pre-treatments to aid in the extraction of nutrients such as protein and phenolic compounds [9], but limited information appears to exist on how the enzymatic pretreatment process impacts the biological activity of the resulting peptide-rich extract.
At present, there is an increasing awareness of the enormous potential for acquiring bioactive hydrolysates from a variety of by-products of the food industry. Many reports have described that extracts from various plants [5], hydrolysates from marine by-products [10], and some probiotics [11] exhibit relatively high bioactivities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory properties, among others. A literature survey shows that only a limited number of studies have compared the physicochemical characteristics and biological properties of BSGPs and their associated hydrolysates generated by the enzyme pretreatment method and direct alkaline extraction method [7].
In developed countries, the use and upcycling of food-derived peptides and protein hydrolysates have received considerable attention, due to their potential health effects beyond a nutritional role [12]. By 2030, an estimated 366 million people will be affected by type II diabetes worldwide, with about 70% of them also suffering from hypertension [13]. ACE is targeted for inhibition during the treatment of hypertension due to its involvement in the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and kinin nitric oxide system (KNOS) [14]. Therefore, excessive action of ACE causes increased vasoconstriction and hypertension. However, pharmacological ACE inhibitors, such as captopril, lisinopril, or enalapril, are associated with a number of side effects, which include angioedema, cough, skin rashes, decreased renal function, and fetal abnormalities [14]. Aside from ACE’s excessive action, oxidative stress, defined as the overproduction of relative oxygen species (ROS) relative to antioxidant defense, also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of numerous chronic diseases, such as diabetes, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease, liver injury, cancer, and immune dysfunction [15]. BSG has been proven to be a valuable source of bioactive peptides, giving it potential as an active component in the diet by integration into functional food products [16]. This would meet environmental protection laws, as well as the current trends among consumers who are chasing the use of natural nutraceuticals [17].
This study aims to (1) extract BSGP using the cellulase pretreatment method and direct alkaline solubilization and isoelectric precipitation method, (2) generate enzymatic hydrolysates from the extracted BSGP using different commercially available food-grade enzyme preparations, (3) characterize both BSGP extracts and their respective hydrolysates and (4) assess the potential antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory properties of the extracted BSGP and its hydrolysates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Representative samples of BSG were kindly provided by Ballykilcavan Brewery Ltd., Co. Laois, Ireland. BSG was blended using a blender (Argos Ltd, Milton Keynes, UK) for 1 min and stored at −20 °C for future use. The solutions for the protein extraction were prepared from a stock solution of hydrochloric acid reagent grade, 37% (Scharlab S.L., Barcelona, Spain) and sodium hydroxide ACS reagent, ≥ 97.0%, pellets (Sigma-Aldrich Ireland Ltd., Wicklow, Ireland). For the protein quantification, Bradford’s reagent (VWR, Solon, OH, USA), bovine serum albumin (BSA), and lyophilized powder (Sigma-Aldrich Ireland Ltd., Wicklow, Ireland) were used. For the reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), acetonitrile (VWR, Solon, Ohio, USA), trifluoroacetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich Ireland Ltd., Wicklow, Ireland) and ultra-pure water were used. Alcalase® 500 mL and Cellulase® were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Merck (Wicklow, Ireland). Alpha-chymotrypsin, 3x crystallized was obtained by MP Biomedicals, LLC (Strasbourg, France). For the TNBS assay, the trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS) reagent was from Biosciences Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). The kits used for the ACE-inhibitory assay, FRAP assay, and DPPH assay were purchased from tebu-bio (Le Perray-en-Yvelines, France). All other reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Merck (Wicklow, Ireland).
2.2. Cellulase Pretreatment
The BSGP samples were generated by alkaline extraction after cellulase pretreatment. Briefly, wet BSG was suspended in distilled H2O (d H2O) (1:4 v/w) and then the mixture was heated to 50 °C in a water bath. The pH was adjusted to 4.5. A ratio of 1:50 of cellulase was then added to the BSG solution and allowed to incubate for 60 min. HCl (1.00 M) or NaOH (1.00 M) was continuously added to the reaction system during the pretreatment to maintain the pH within the set value of pH 4.5 ± 0.1. After the 60 min had elapsed, the suspension was inactivated at 85 °C for 20 min and then centrifuged at 3800× g and 4 °C for 15 min (Hettich Rotanta 460RF centrifuge, Baden-Württemberg, Germany). The supernatant was discarded, and the resulting precipitation was stored at −20 °C for future protein extraction.
2.3. Protein Extraction
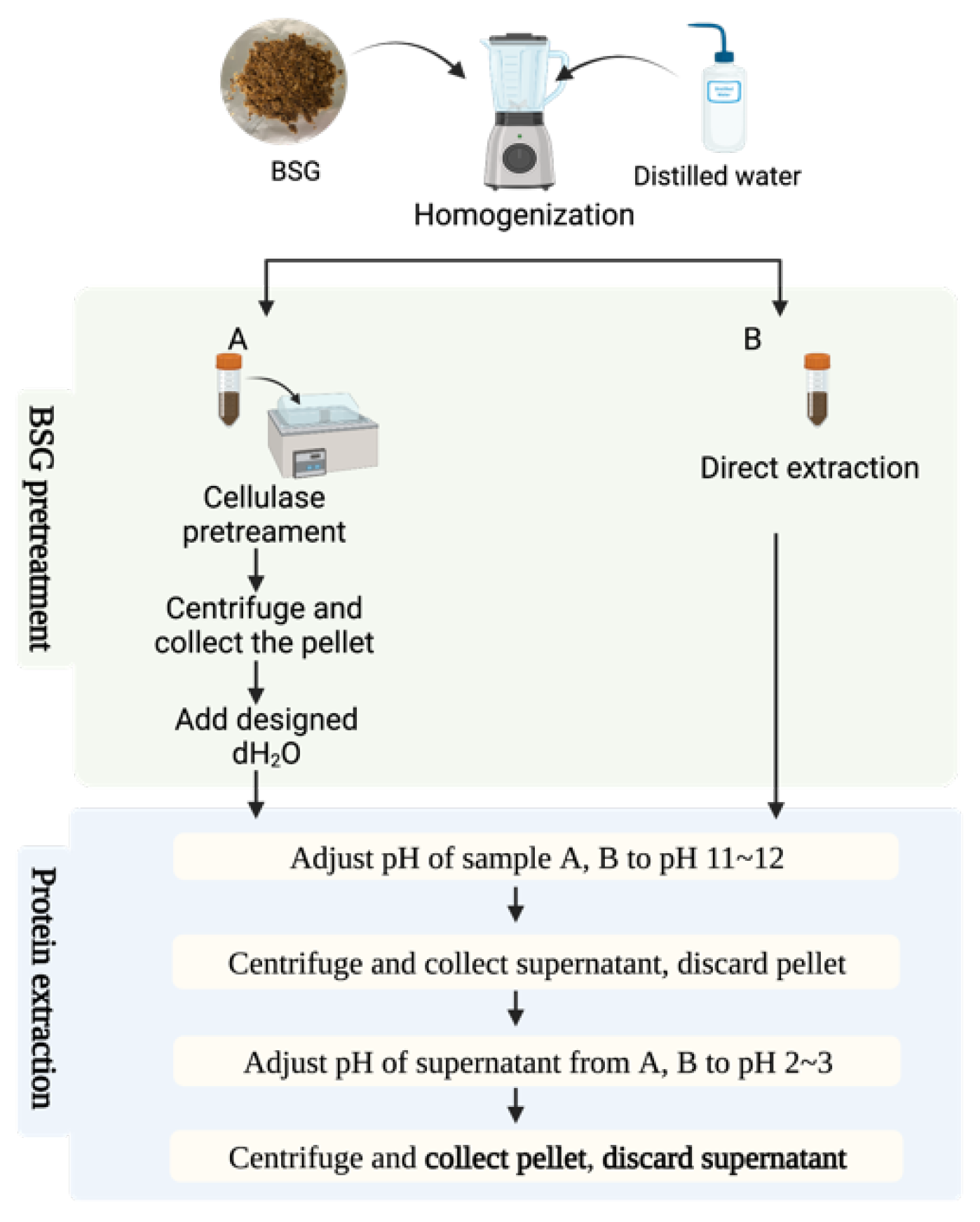
Wet BSG was suspended in dH2O (1:8 w/v). The pH was adjusted to pH 12.0 (using 1.00 M HCl and 1.00 M NaOH) and allowed to react for 60 min. After the 60 min had elapsed, the suspension was centrifuged at 3800× g and 4 °C for 15 min (Hettich Rotanta 460RF centrifuge, Baden-Württemberg, Germany) and the supernatant was collected and then freeze-dried (SP VirTis Advantage Pro Freeze Dryer/Lyophilizer, Cologne, Germany) to obtain BSGP. The methods are outlined in Figure 1.
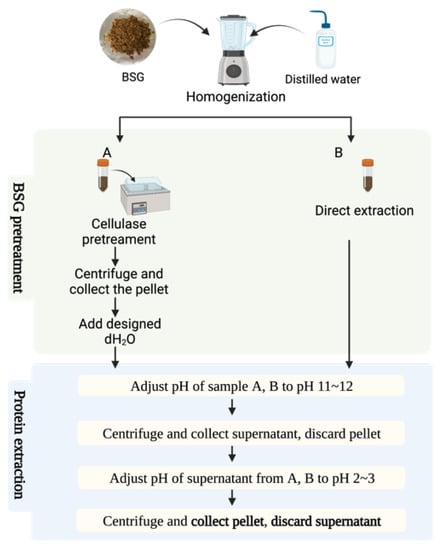
Figure 1.
The extraction method of group A and group B.
2.4. Protein Quantification
The protein content of BSG was quantified using a modification of the Kjeldahl method [18]. The sample (350 g in duplicate) was digested in 50 mL concentrated sulfuric acid with two Kjeldahl catalyst tablets. A value of 6.25 was used as the protein conversion factor [19].
Protein concentration in the extracts was determined in triplicate using the Bradford assay [20], using bovine serum albumin as the standard.
2.5. Generation of Protein Hydrolysates
Enzymatic hydrolysis with Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin was performed according to the protocol outlined by Celus, Brijs [2] with slight modifications. Briefly, a 6.0% (w/v on a protein basis) aqueous dispersion of protein solution was hydrolyzed under the following variables: time, enzyme: substrate ratio, temperature, and pH. Table 1 provides an overview of all the experiments carried out. After the reaction period, the mixture was adjusted to pH 6.0 with 1.00 M HCl and heated to 85 °C for 20 min to inactivate the enzymes. Then, 50 μL of the total hydrolysates obtained after enzymatic hydrolyzing was withdrawn to determine the degree of hydrolysis (DH). The remaining mixture was centrifuged (3800× g, 20 min, 4 °C), resulting in both supernatant and pellet, both of which were freeze-dried (SP VirTis Advantage Pro Freeze Dryer/Lyophilizer, Cologne, Germany) separately and stored for later bioactivity testing.

Table 1.
Different reaction conditions for enzymatic hydrolysis. Note: all the experimental parameters in Table 1 were chosen based on the results of cellulase pretreatment optimization tests (Figure S1 and protein extraction optimization tests Figure S2) as shown in the Supplementary Materials.
2.6. Quantification of Degree Hydrolysis (DH)
The degree of hydrolysis (DH), expressed as the percentage of peptide bonds hydrolyzed, was determined in triplicate using the 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) method following the procedure of [21], as modified by Spellman, McEvoy [22].
The optimal hydrolyzing parameters were chosen based on the results of optimization tests as shown in Figure S3 (Alcalase) and Figure S4 (α-chymotrypsin) in the Supplementary Materials.
2.7. Physicochemical Analysis of Extracted BSGP and Its Enzymatic Hydrolysates
2.7.1. Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
To determine the type of molecules present in BSGP and their respective hydrolysates, high-performance liquid chromatography was performed by SPD-20A Shimadzu (GenTech, New York, NY, USA), as described by Varela, O’Hara [10].
2.7.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
The infrared spectra of the samples were recorded between 4000 and 650 cm−1 at a resolution of 4 cm−1 using a Nicolet iS10 spectrometer (PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) mounted with an attenuated total reflectance (ATR) accessory. The powder was directly placed on a single reflection diamond ATR accessory and pressed to have good contact between the crystal and sample. Spectra processing was performed using the software EZ Omnic (Thermo Electron Corporation, Madison, WI, USA).
2.8. Bioactive Properties Assessment
2.8.1. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Assay
ACE inhibitory activity was tested using a colorimetric detection assay, as described by [23,24]. This detection system measures the amount of 3-hydroxybutyric acid (3HB) produced by ACE from 2-hydroxybutyryl-Gly-Gly-Gly. Experiments were carried out as independent six replicates assayed in triplicate. The ACE-inhibitory ratio was calculated using GraphPad Prism 9 from the sigmoidal dose-response versus the negative control. The values were expressed as the mean ACE inhibition percentage ± standard deviation (n = 3). CaptoprilTM was used as a positive control.
2.8.2. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Antioxidant Assay
The antioxidant properties of recovered BSGP/BSGPH were determined by the DPPH free radical scavenging method using an assay kit (tebu-bio, Le Perray-en-Yvelines, France), based on the DPPH assay improved by [25]. The antioxidant capacity is expressed as the DPPH scavenging percentage when using this kit, a value calculated from the inhibition percentage of the antioxidant samples versus the inhibition percentage of the negative control. Experiments were conducted as independent six replicates assayed in triplicate. DPPH inhibitory ratio was calculated using GraphPad® Prism 9.0 from the sigmoidal dose-response plots of inhibitor concentration (μM) versus % inhibition. The values were presented as the mean DPPH inhibition percentage ± standard deviation (n = 3).
2.8.3. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
FRAP was determined using the assay kit provided by Sigma-Aldrich (Ireland). Briefly, a freshly prepared 10 μL unknown sample solution was added to each well in a 96-well microtiter plate. For the positive control, 4 μL of the FRAP positive control plus 6 μL of FRAP assay buffer were added to the desired wells. Then, 190 μL reaction mix (152 μL FRAP assay buffer, 19 μL FeCl3 solution, and 19 μL FRAP probe) were mixed and added to each well containing the standards, positive control, and test samples. For background correction, the background control mix (171 μL FRAP assay buffer and 19 μL FeCl3) was added to the sample background control well (s) and mixed well. The plate was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min then the absorbance was measured at 594 nm using the endpoint mode. The FRAP reading for each sample was obtained by subtracting the background control reading. Sample FRAP can be obtained by comparing the sample A594 value to the ferrous standard curve to obtain nmol of the reduced ferrous ions generated during the reaction. The mM ferrous equivalent (nmol/μL) of samples was calculated using the following equation:
where B is the ferrous ammonium sulphate amount from the standard curve (nmol), D is the sample dilution factor, and V is the sample volume added into the reaction well (μL).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data were reported as means ± standard deviation of the three independent replicates. The results of the extraction and hydrolyzing yields from two groups were analyzed by t-tests and the results of the ACE-inhibitory test, DPPH inhibition test, and FRAP assay were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with the Tukey post-hoc test using GraphPad Prism, version 9.0 for macOS (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Significant levels were defined as p < 0.05.
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Extraction of BSGP and Generation of BSGPH
The goal of this research was to create an effective industrial BSG protein extraction protocol for the valuable component of BSG, barley proteins, to be successfully separated and potentially used in a food industrial setting. Because the production of oven-dried grains on a large scale may require a lot of energy, it was decided that this study would investigate the best conditions for protein extraction using wet BSG as a starting material. In general, pretreatment is an important strategy for accomplishing this and increasing protein exposure for functional use [26]. It is critical for increasing the efficiency of the processes involving the valorization of protein from BSG, which should be simple, cost-effective, free of corrosive substances, and the fraction of interest should be safeguarded and should not result in significant losses [27].
Several pre-treatments have been studied by researchers as part of the valorization of BSG. Qin, Johansen [28] assessed different pretreatment strategies for protein extraction from BSG with the highest extraction yields of 95% by sequential alkaline and dilute acid pretreatment, while some others used ultrasonication of BSG as a pretreatment prior to protein extraction [29,30]. However, as stated previously, BSG is lignocellulosic in nature and consists primarily of polysaccharides. The polysaccharides in BSG consist of cellulose and hemicellulose and account for approximately 45% of total dry weight [4]. The high fiber content of BSG limits its applicability without prior fractionation. To effectively use BSG for value-added purposes, techniques that break down the naturally ordered structure of cellulose are required.
Carbohydrases, such as cellulase, may have an advantage in cleaving the linkages within the polysaccharide matrix, and hence may liberate more intercellular constituents, such as protein [31]. To the best of our knowledge, cellulase is mainly used for the production of lactic acid [32], bioethanol [33], and carbohydrates [34] among others, instead of assisting the extraction of protein from BSG. In addition, no existing report appears to compare the effect of pretreatment on the bioactivities of protein/hydrolysates from BSG with and without cellulase. Therefore, in this study, to evaluate the effect of carbohydrases on the extraction yields of BSGP and the bioactivities of the extracted proteins and their related hydrolysates, cellulase was added in the pretreatment step to relieve the cross-linking effect of protein with xylan and phytate, with the aim of increasing protein solubility, and thus protein extraction yield.
The methods of extraction with and without cellulase pre-treatment (group A and group B, respectively) were assessed to compare if the pre-treatment influences the yield and properties of extracted BSGP. With the cellulase pretreatment method, a yield of 50.18 ± 1.22% (w/w, dry base) protein was obtained from BSG, while 66.41 ± 0.37% (w/w, dry base) protein was extracted using direct alkaline solubilization, which is comparable to the yield reported by Connolly, Cermeño [5] for BSGP (63.09 ± 0.27% dry base). The results demonstrate that the direct alkaline extraction method yields significantly more BSGP than the cellulase pre-treated extraction method. To the best of our knowledge, no other study appears to have compared the recovery of protein with/without cellulase pre-treatment prior to the pH-adjusting phase. This result is significant from the viewpoint of industrial processing, as the direct extraction method is conceived to be considerably more scalable, and it greatly decreases resource consumption because it negates the need for the pre-treatment step.
Hydrolysates from cellulase-pretreated BSGP, along with directly alkaline extracted BSGP, obtained using Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin, were generated in order to compare their physicochemical and in vitro bioactive properties. As shown in Table 2, incubation with Alcalase resulted in higher DH in both BSGP (pre-treated BSGPH and directly extracted BSGPH were 6.6 ± 1.01% and 12.6 ± 0.38%, respectively). The DH of BSGPH directly extracted by Alcalase was comparable to the yield reported by Celus, Brijs [35] (13%). The DH of pre-treated BGSPH and directly extracted BSGPH with α-chymotrypsin was 4.7 ± 0.21% and 5.11 ± 1.31%, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, no other studies have reported on the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulase pre-treated BSGP and α-chymotrypsin being used to hydrolyze BGSP has not previously been reported. Further detailed studies that focus on process control would be required to efficiently reduce energy waste and improve extraction yields.

Table 2.
BSGP extraction yield and the degree hydrolysis of BSGP hydrolysates generated with Alcalase and alpha-chymotrypsin.
3.2. Qualification of Extracted BSGP and Its Enzymatic Hydrolysates
3.2.1. RP-HPLC
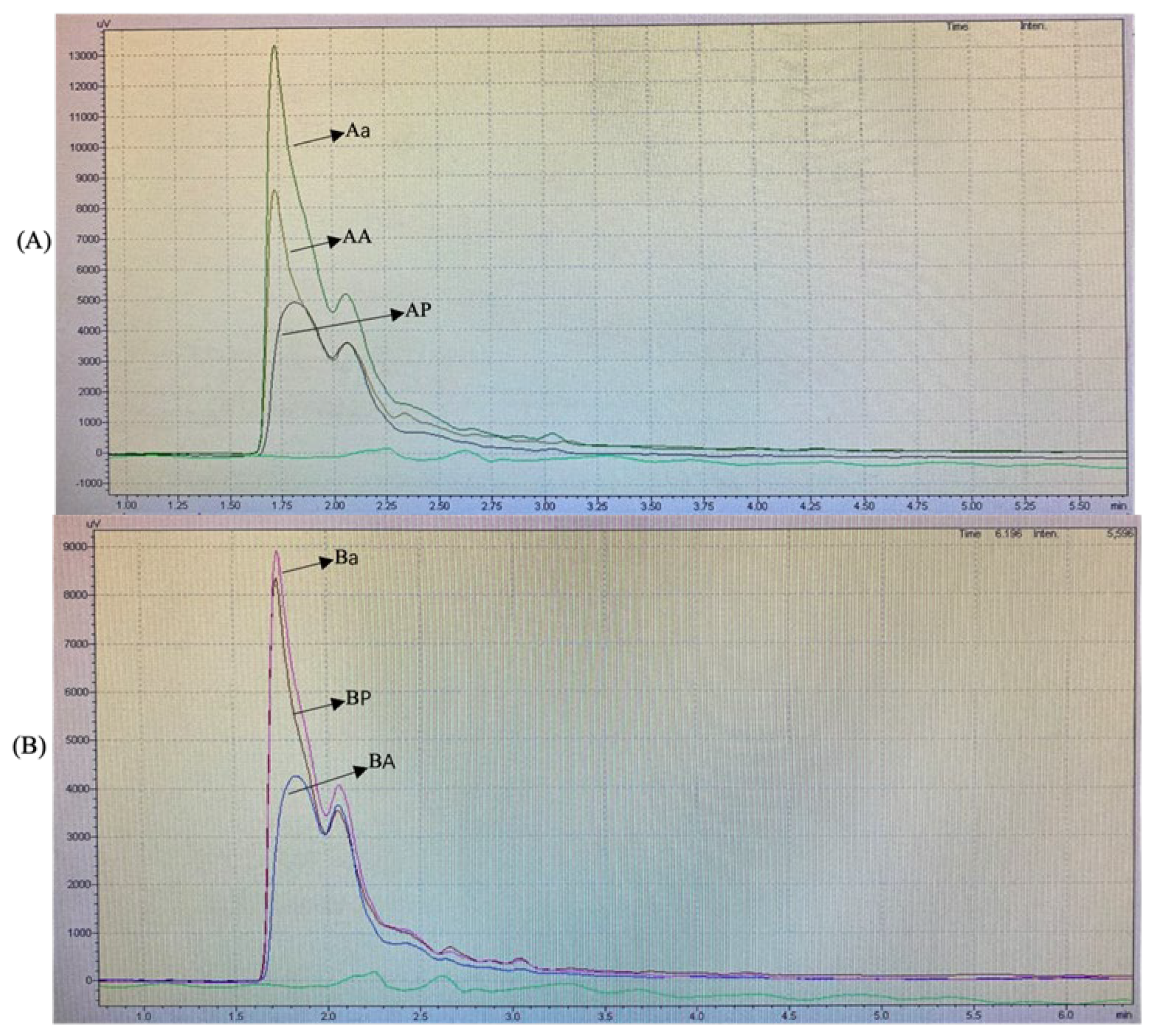
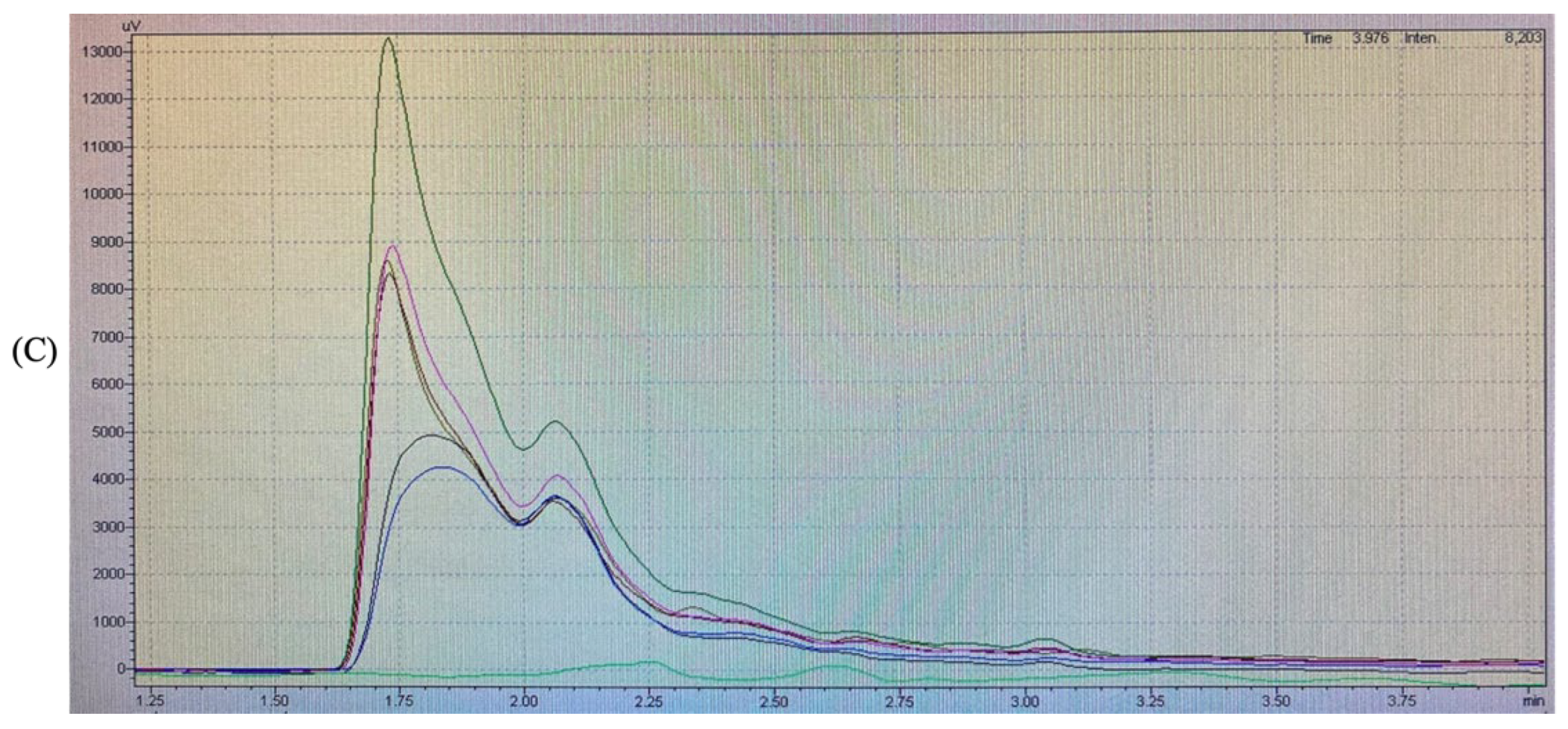
The RP-HPLC analysis was performed with a hydrophobic phase of 70% acetonitrile and a hydrophilic phase of ultra-pure water. The results obtained for each group are shown in Figure 2.
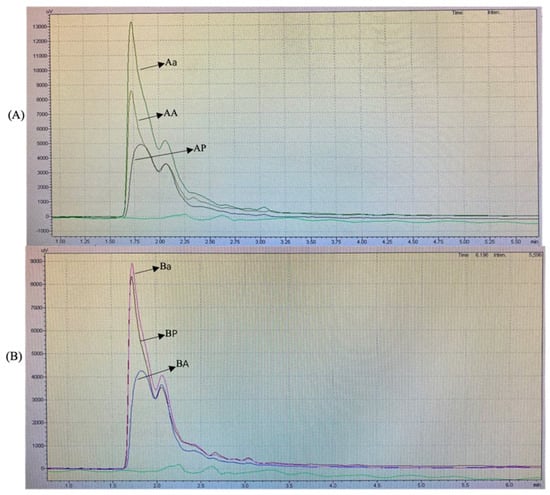
Figure 2.
Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography profiles of (A) cellulase pretreatment BSGP (AP) and its Alcalase hydrolysates (AA) and α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates (Aα), (B) directly extracted BSGP (BP) and its Alcalase hydrolysates (BA) and α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates (Bα), (C) all samples.
The RP-HPLC profiles of BSGPs and their associated hydrolysates generated using Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin were similar in the hydrophilic region of the spectrum at 280 nm. For the cellulase pretreatment BSGP and its associated hydrolysates (AA and Aα), the intensities of the peptide peaks were higher than the protein in group A (Figure 2A). The α-chymotrypsin hydrolysate was found to be the most intense one. No major difference could be detected between the different hydrolysates.
For the directly extracted BSGP and its associated hydrolysates with Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin (BA and Bα), similar peaks were observed in the hydrophilic portion at 280 nm. However, BP showed relatively higher intensity than BA, and α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates from both groups had the most intense peak, while Aα was more intense compared to Bα. No major difference could be detected between the different hydrolysates either.
Similar findings have been reported by Connolly, Cermeño [5], who stated that Alcalase peptides were more intense than protein. To the best of our knowledge, no existing reports about the physicochemical properties of α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates exist. These results suggested that hydrolysates with different hydrophilic intensities may be generated depending on the types of enzymatic preparations used for hydrolysis.
3.2.2. FTIR
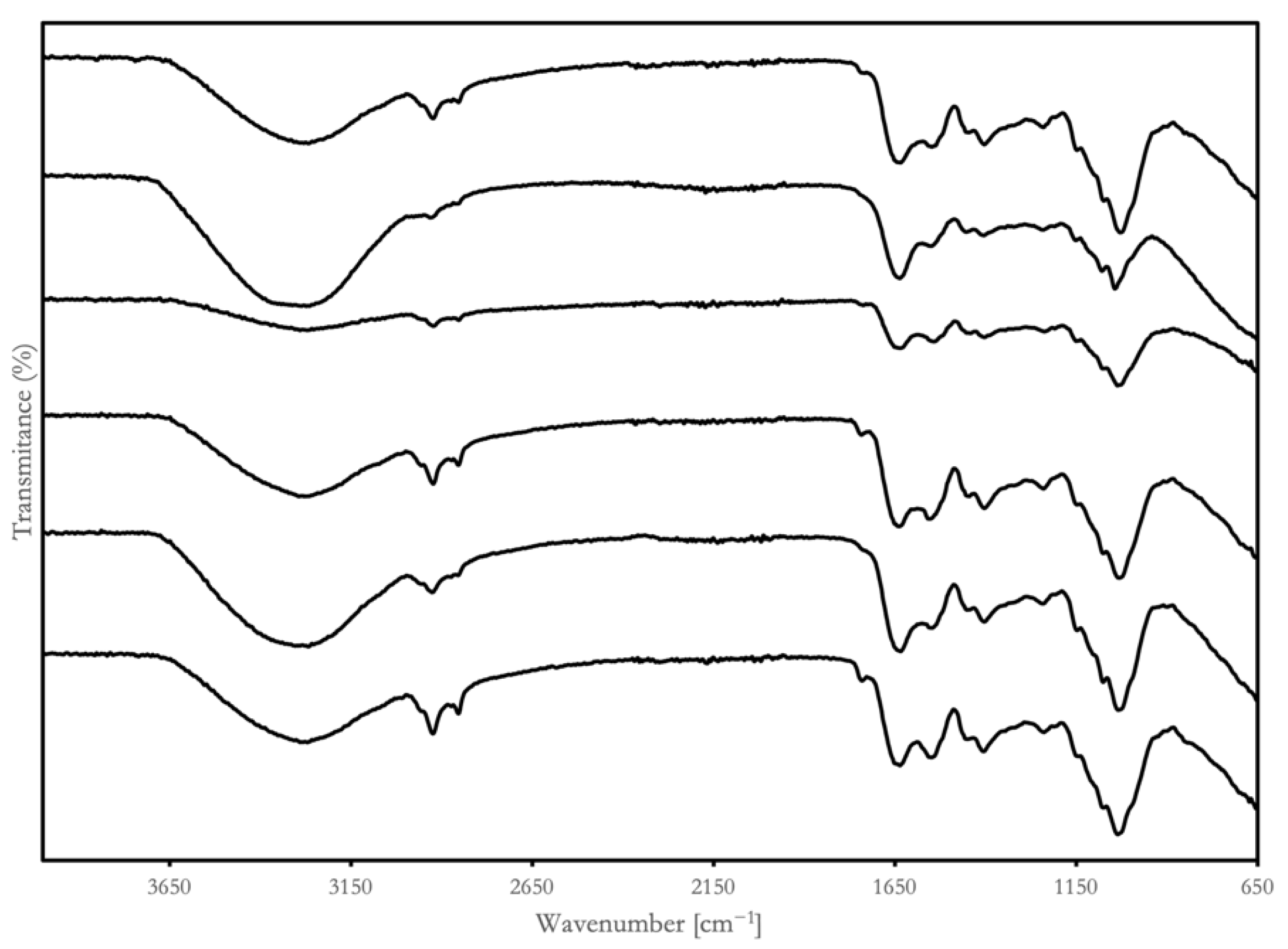
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were used to identify the vibrations of functional groups in macromolecules, molecular structural changes, and protein secondary structures [36]. The characteristic absorbance bands of the BSGPs and their hydrolysates in the range of 4000 to 650 cm−1 are presented in Figure 3.
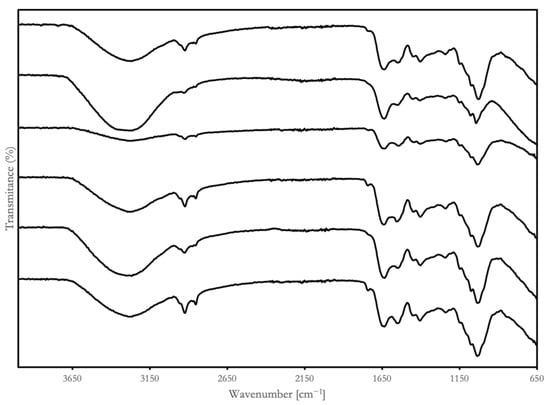
Figure 3.
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) profiles for lyophilized BSGPs and their associated hydrolysates from two groups: group A (cellulase pretreatment): AP (group A BSGP), AA (group A Alcalase hydrolysates), Aα (group A α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates); group B (direct extraction): BP (group B BSGP), BA (group B Alcalase hydrolysates), Bα (group B α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates).
All the samples had wide peaks, ranging from 3500 to 3000 cm−1. The peak intensity and peak width of BP were lower than the other samples and α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates were lower than Alcalase hydrolysates. The FTIR spectra showed a wide and high absorption peak around 3300 cm−1, suggesting the possible presence of substantial intramolecular or intermolecular hydrogen bond forces in the molecular polymers of BSGP hydrolysates.
Two BSGP showed faint peaks in the primary and secondary amine stretch (3500 cm−1 to 3100 cm−1). The Alcalase hydrolysates both displayed significantly stronger peaks in the primary and secondary amine stretch than their non-hydrolyzed counterparts. The peak at 2900 cm−1 of the samples was associated with asymmetric CH2 stretching, which is common in the aliphatic side chain of proteins [36]. All the hydrolysates showed lower tensity at 2900 cm−1, indicating changes in the composition of the aliphatic chains. These findings showed that the microenvironment within BSGP hydrolysates, as well as the hydrophobic zone of the hydrolysates, are modified during enzyme hydrolysis.
Although chymotrypsin prefers aromatic residues, such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, it can hydrolyze other peptide bonds at a slower rate [37]. Chymotrypsin hydrolysis may release aromatic amino acid residues, which may account for the appearance of aromatic overtones in the spectrum, as shown in Figure 3. The α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates also presented stronger peaks in the sp3 alkane segment (3000 to 2850 cm−1) and alkene stretch (1000 to 650 cm−1) than the unhydrolyzed BSGP, which may be because of the fact that the vibrational stretching of the peptide alkanes and alkene may be stronger than in the intact protein molecule.
Alcalase is regarded as a “serine endopeptidase”, which was initially obtained from Bacillus subtilis [38]. It demonstrated broad specificity with an alkaline pH optimum, which is very important from an industrial standpoint, due to its activity and stability at alkaline pH values, having been used largely as additives in detergent formulations [39].
3.3. Bioactivity of Alkaline Extracted Protein and Its Hydrolysates
A number of studies exist in the literature that show the biological activities associated with brewers’ spent grain-derived proteins and their associated hydrolysates. Recently, bioactive peptides from BSGP have been reported to have antioxidant activity, ACE inhibitory activity, and antibacterial activity, among others [40]. In the present study, the intact protein extract and its related hydrolysates were assayed for their ACE, DPPH inhibitory, and FRAP properties.
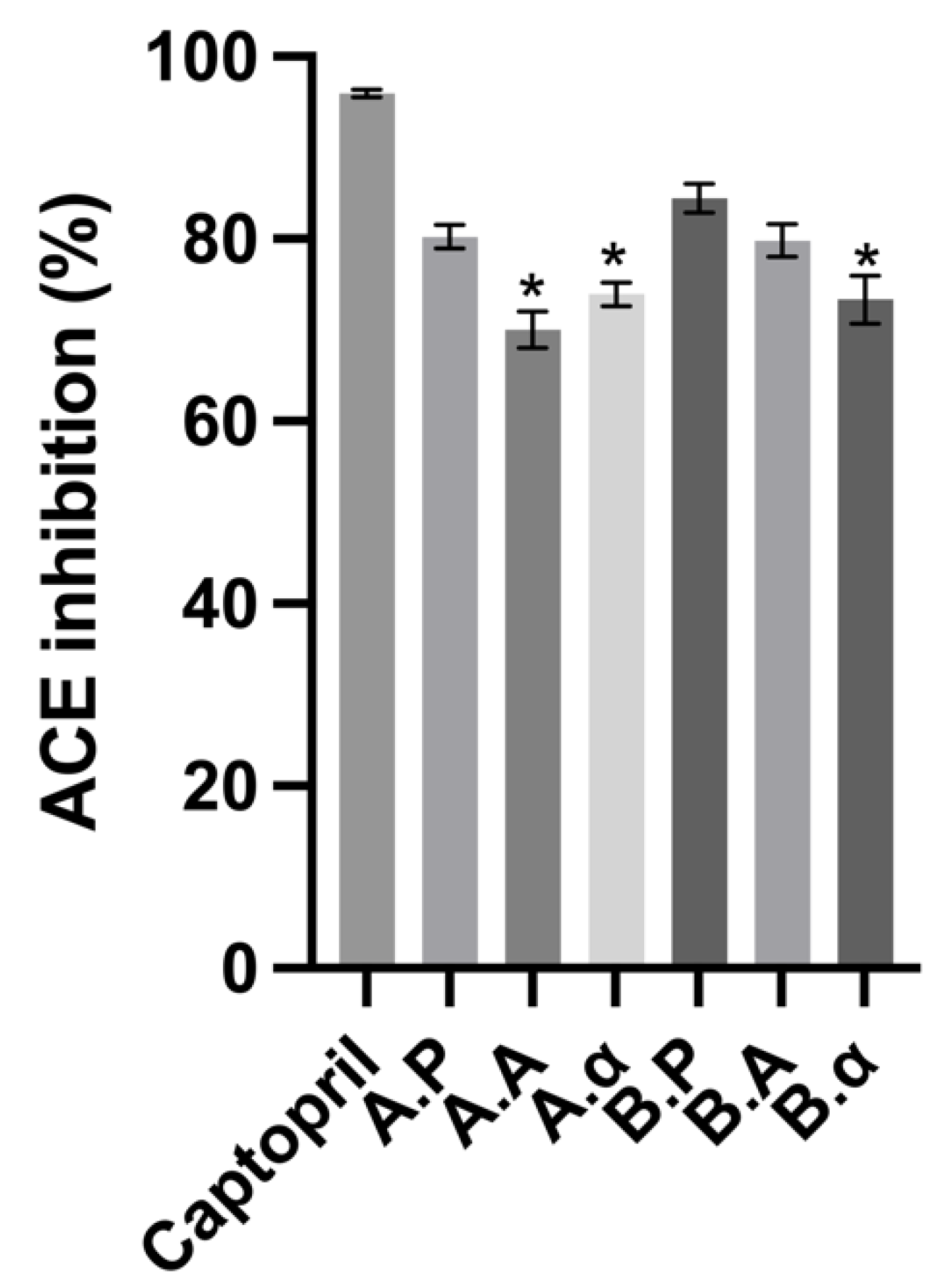
ACE inhibitory peptides have been examined extensively in a variety of protein sources, including cereal, milk, barley, and macroalgae [41,42]. Using ACE activity extracted from bovine lung, the BSGP and its associated hydrolysates were evaluated for their ACE inhibitory capability at 2.5 mg mL−1. The BSGP extracted by the direct alkaline solubilization method and enzyme-pretreated method resulted in 73.35 ± 0.02% and 73.95 ± 0.01% inhibition on a dry weight basis, respectively. Hydrolysis of BSGP all significantly improved ACE inhibition for Alcalase hydrolysates, which in general inhibited ACE to a greater extent than hydrolysates generated with α-chymotrypsin. All samples in this study were found to display significantly higher ACE-inhibitory activity than peanut flour, as reported by Yu, Mikiashvili [43] (46.47 ± 0.80 %), which is a valuable protein source in dietary supplements. Brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysates generated using Alcalase have been shown to inhibit ACE to a greater extent than Flavourzyme and Corolase [44], while Alcalase hydrolysates of macroalgae protein also demonstrated greater ACE inhibition than Flavourzyme [42].
Ruiz, Ramos [45] indicated earlier that Phe, Trp, Tyr, and Pro were found at the C-terminal of the most potent ACE-inhibitory peptides. Proteinases derived from Bacillus licheniformis, such as Alcalase, primarily contain subtilisin endoproteinase with minor glutamyl endopeptidase activity [46]. This activity, combined with the BSG-high PI’s Pro content, could lead to the release of Pro-containing ACE inhibitory peptides. In the sequence of barley hordein, two powerful ACE inhibitors, Trp-Pro and Leu-Gin-Pro, have been found, with the latter sequence occurring as 16 repetitions in the protein structure [41]. As shown in Figure 4, this study has found that α-chymotrypsin and Alcalase have the ability to release peptides that have potent ACE inhibitory activity. There appear to be no existing studies on the ability of α-chymotrypsin BSG protein hydrolysates to inhibit ACE.
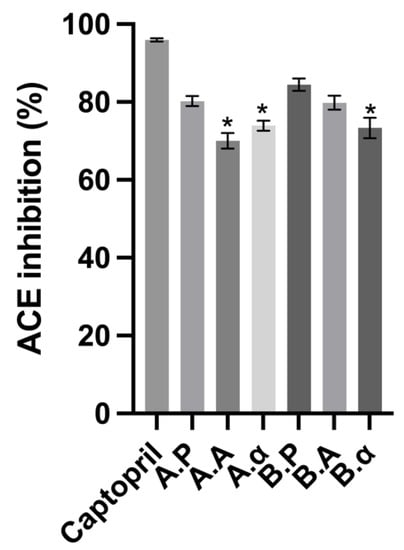
Figure 4.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of brewers’ spent grain protein and associated hydrolysates. Captopril was used as a positive control and was assayed at 2.5 mg mL−1. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). * Denotes inhibition was significantly higher than BSGP at the same concentration (p < 0.05).
It is well noted that the radical system used to examine antioxidants could have an impact on the experimental results; therefore, two or more radical systems are necessary to investigate a sample’s radical-scavenging abilities. As a result, the antioxidant activity of extracts derived from BSG samples was also assessed using DPPH and FRAP in the current study.
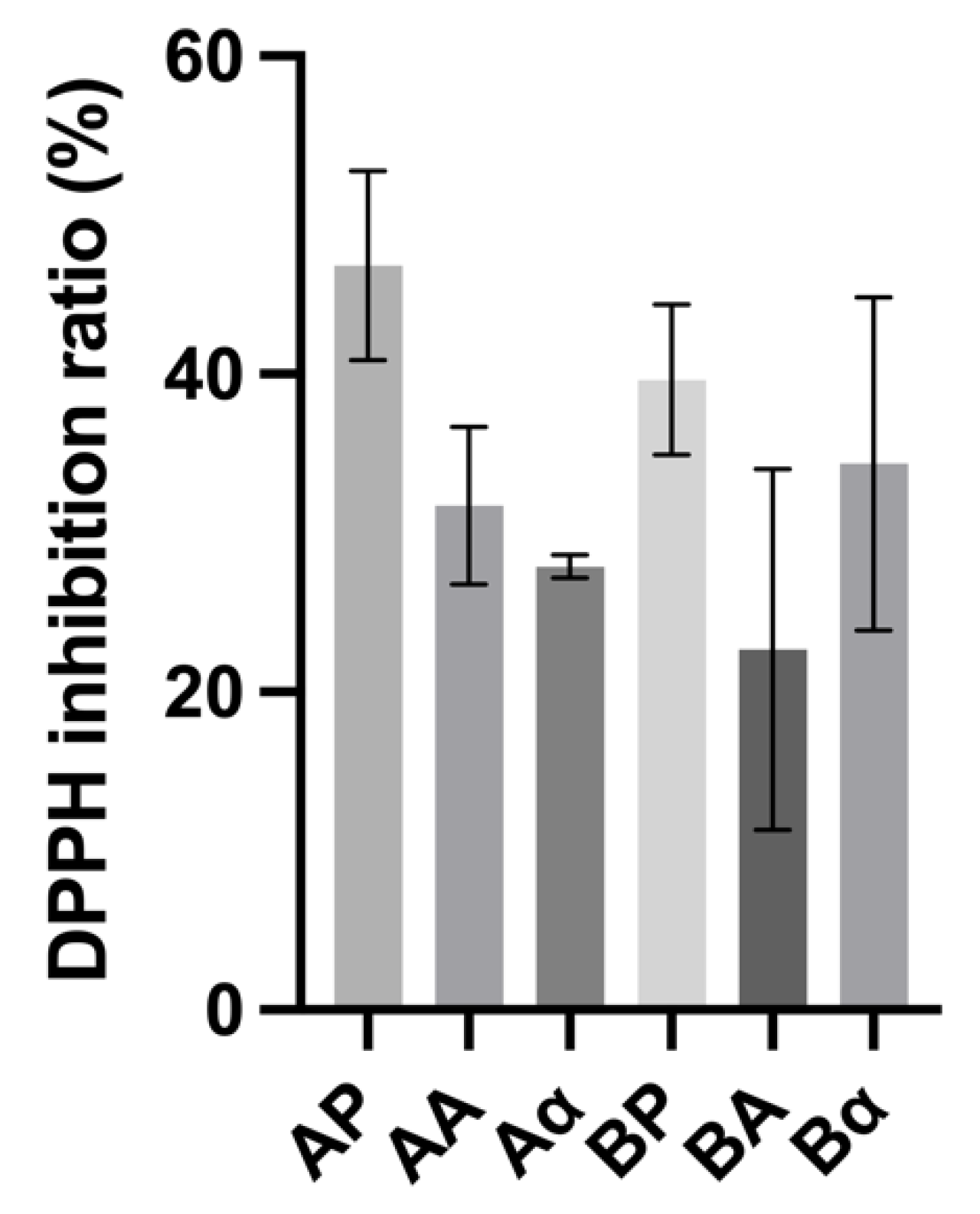
The DPPH inhibitory activity of BSGP and its associated hydrolysates generated with Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin had inhibition values ranging from 22.66 ± 9.26% to 46.87% ± 4.87%. As shown in Figure 5, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were found between BSGP, and the hydrolysates generated using Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin. These activities were significantly higher than light malt extracts (Pilsen, melano, melano 80 and carared) (15 ± 1%) as reported by Moreira, Morais [47]. Generally, the intact BSGP displayed higher DPPH inhibition activity than hydrolysates generated with Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin, which is in accordance with the ACE inhibitory activity obtained. These results indicate that the intact BSGP have been hydrolyzed during the beer fermentation, leading to the release of potent DPPH inhibitory peptides.
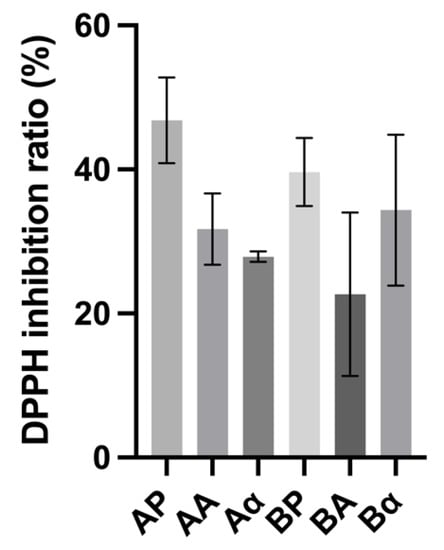
Figure 5.
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) inhibitory activity of brewers’ spent grain protein and associated hydrolysates. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).
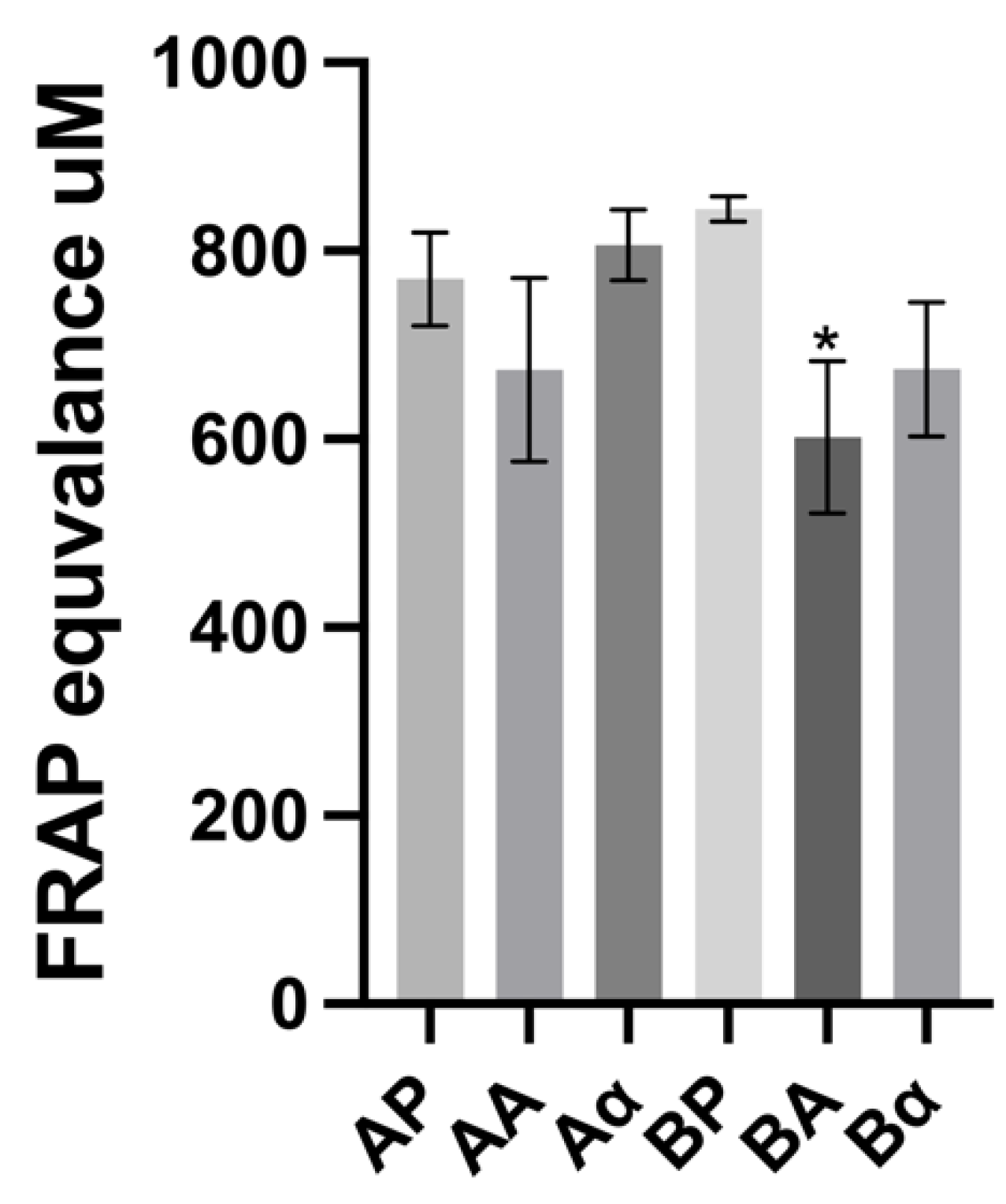
The FRAP assay was also used for in vitro assessment of antioxidant properties; the relative ability of ferric reducing power has been compared with the ferrous standard. The results from this assay were similar to those obtained for the DPPH assay, with intact BSGP exhibiting a stronger ferric reducing antioxidant power (except for the α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates from enzyme-pretreated BSGP), as shown in Figure 5. The BSGP and its related hydrolysates displayed relatively high FRAP values. As can be observed in Figure 6, significant differences were observed for the Alcalase hydrolysate from directly alkaline extracted protein, where the FRAP value for BSGP hydrolysates (601.90 ± 65.82 μM) was significantly lower (p < 0.05) than the corresponding BSGP (844.63 ± 11.12 μM). The ferric-reducing activity found in BSGP and its hydrolysates was higher than rice bran protein hydrolysates (125.09 ± 1.45 µmoL Fe2+ equivalent/g sample) reported by Phongthai, D’Amico [48]. The α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates resulted in higher FRAP values than Alcalase hydrolysates in both groups of BSGP. The proteolytic preparation used for the generation of hydrolysates clearly had an impact on the antioxidant activity obtained. No previous research appears to have reported on the comparative antioxidant assays between cellulase-pretreated BSGP and its associated hydrolysates, or directly extracted BSGP and its related hydrolysates.
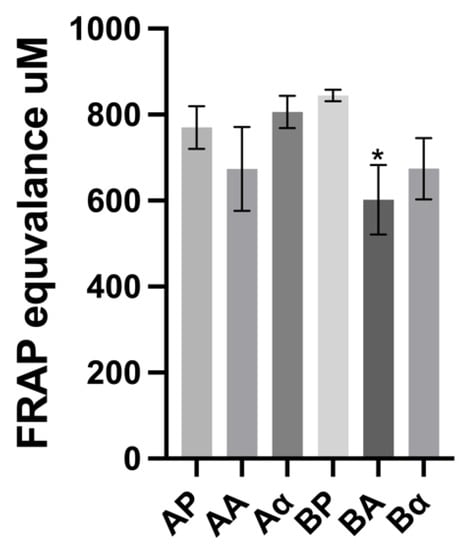
Figure 6.
Ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) of brewers’ spent grain protein and associated hydrolysates. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). * Denotes inhibition was significantly higher than BSGP at the same concentration (p < 0.05).
This study found that intact BSGPs extracted with two different methods led to higher biological activities when compared to their Alcalase hydrolysates and α-chymotrypsin hydrolysates, except for the intact protein from group A in the FRAP assay, which showed lower antioxidant capacity than its related α-chymotrypsin hydrolysate. However, there is no statistical difference between the intact protein and its associated hydrolysates from group A.
The reason for the low effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the biological activity of BGSP is thought to be related to the original protein that has been partially hydrolyzed. The protein was obtained as a by-product of the brewing industry and was left in the processing line (under humid and warm conditions) for a period of time, before being frozen prior to the experiments. This can result in some hydrolysis/fermentation, and the extracted protein is no longer a fully intact protein, but rather smaller peptides. Smaller peptides have less bond breakage when they come into contact with the enzymes. Therefore, the results suggest that hydrolysates with potent in-vitro antihypertensive and antioxidant properties can be generated without enzymatic hydrolysis. This may be of interest and importance in the brewing industry, as the fermentation process is much less expensive than the enzymatic hydrolysis process.
The studies indicate that the protein and hydrolysates generated in this study could be used as ingredients in functional nutraceuticals, with the potential to enhance consumers’ health through antioxidant and antihypertension management. However, further investigation of bio protein and the associated hydrolysates in cell culture models and in vivo is required to validate the findings reported here. Moreover, it would be interesting to investigate the effects of fermentation and enzymatic hydrolyzation on the bioactive capacities of BSG-derived protein and peptides.
4. Conclusions
This research compares the extraction methods and physicochemical and bioactivity properties of hydrolysates generated from BSGP. The extraction of protein via the direct alkaline solubilization method and cellulase pre-treatment method was not significantly different in terms of the extraction yield. This demonstrates that the direct alkaline extraction method is a less resource-intensive process and will be adopted for BSGP extraction in future studies. This result is significantly important from the industrial processing perspective, as it is considerably more relevant in terms of production cost and energy consumption.
The intact BSGP and its associated hydrolysates had similar FTIR and RP-HPLC profiles. Both BSGPs displayed significantly higher ACE-inhibitory properties than their related hydrolysates, except for the Alcalase hydrolysates generated from directly extracted BSGP, which were lower. The DPPH and FRAP activities of BSGP and its associated hydrolysates were not significantly different, again with the exception of Alcalase hydrolysates generated from directly extracted BSGP, which had lower values for the FRAP activities compared to the intact BSGP. The findings revealed that the BSGP already exhibited relatively high biological activity without further enzymatic hydrolysis. In addition, the cellulase pretreatment did not show any significant effect on the biological properties of the BSGP and BSGPH. These results are valuable to the industry, since the direct extraction of bioactive BSGP without hydrolyzation can shorten the production time, decrease solvent consumption, improve the utilization of protein in the residue and reduce the waste of resources and environmental pollution.
The results of this study demonstrated that the extraction of bioactive peptides from wet BSG by direct alkaline solubilization is a potentially viable method for the processing of BSG without enzymatic hydrolysis. Additionally, this research showed that BSGP and hydrolysates generated with Alcalase and α-chymotrypsin have the potential to be used in the nutraceutical industry, as an added-value ingredient with multi-functional bioactive properties.
Further evaluation needs to be performed to assess the antioxidant capacity of these proteins and hydrolysates using other in vitro antioxidant assays, as well as in vivo studies. In addition, other studies need to be carried out to investigate the possibility of fermentation to generate the bioactive peptides instead, since this is more economically beneficial and resource effective for the industry.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nutraceuticals2030016/s1, Figure S1: The effect of (a) temperature, (b) pH; (c) enzyme: BSG ratio on the protein extraction. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). The absorbance of the sample is proportional to the concentration of protein in the sample, so the absorbance versus variables is used to represent the trends in the extracted protein content at different variables. Figure S2: The effect of (a) weight/ volume ratio, (b) pH, (c) temperature; (d) reaction time on the extraction of alkaline soluble protein. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). The absorbance of the sample is proportional to the concentration of protein in the sample, so the absorbance versus variables is used to represent the trends in the extracted protein content at different variables, Figure S3: The effect of (a) Alcalase/ protein, (b) pH, (c) temperature; (d) reaction time on the degree of hydrolysis of alkaline soluble protein. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). The absorbance of the sample is proportional to the DH of protein in the sample, so the absorbance versus variables is used to represent the trends of protein DH content at different variables. Figure S4: The effect of (a) α-chymotrypsin/ protein, (b) pH, (c) temperature; (d) reaction time on the degree of hydrolysis of alkaline soluble protein. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). The absorbance of the sample is proportional to the DH of protein in the sample, so the absorbance versus variables is used to represent the trends of protein DH content at different variables [49,50].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.N.; Data curation, J.Z.; Formal analysis, J.Z.; Investigation, J.Z. and A.C.N.; Methodology, J.Z. and A.C.N.; Project administration, A.P.-G. and A.C.N.; Supervision, A.P.-G. and A.C.N.; Validation, A.P.-G.; Visualization, J.Z.; Writing—original draft, J.Z.; Writing—review and editing, A.P.-G. and A.C.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
South East Technological University: PES 1396; Irish Research Council: GOIPG/2022/610.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded under the South East Technological University (Presidents Research Fellowship) and Irish Research Council (GOIPG/2022/610). The authors would like to express their thanks to all the staff at Ballykilcavan Brewing Company for supplying all BSG samples used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
BSG: brewers’ spent grain; BSGP: brewers’ spent grain protein; BSGPH: brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysates; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; RAS: renin-angiotensin system; KNOS: kinin nitric oxide system; ROS: relative oxygen species; HCl: hydrochloric acid; NaOH: sodium hydroxide; dH2O: distilled water; DH: degree of hydrolysis; TNBS: trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; RP-HPLC: reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography; FTIR: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy; 3HB: 3-hydroxybutyric acid; DPPH: 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; FRAP: ferric reducing antioxidant power; FeCl3: ferric chloride; ANOVA: analysis of variance; AP: cellulase pre-treated brewers’ spent grain protein; AA: cellulase pre-treated brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysate generated with Alcalase; Aα: cellulase pre-treated brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysate generated with α-chymotrypsin; BP: alkaline extracted brewers’ spent grain protein; BA: alkaline extracted brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysate generated with Alcalase; Bα: alkaline extracted brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysate generated with α-chymotrypsin; Phe: phenylalanine; Trp: tryptophan; Try: tyrosine; Pro: proline; PI: isoelectric point; M: molarity; μL: microliter.
References
- Török, A.; Szerletics, A.; Jantyik, L.S.J. Factors influencing competitiveness in the global beer trade. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5957. [Google Scholar]
- Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. The effects of malting and mashing on barley protein extractability. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; İbanoğlu, S. The recycling of brewer’s processing by-product into ready-to-eat snacks using extrusion technology. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ spent grain: Generation, characteristics and potential applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Cermeño, M.; Crowley, D.; O’Callaghan, Y.; O’Brien, N.M.; FitzGerald, R.J. Characterisation of the in vitro bioactive properties of alkaline and enzyme extracted brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Food protein-derived bioactive peptides: Production, processing, and potential health benefits. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, R11–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. A Mini-Review on Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein: Isolation, Physicochemical Properties, Application of Protein, and Functional Properties of Hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3330–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ren, J.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B. Effect of denaturation during extraction on the conformational and functional properties of peanut protein isolate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, P.; Martins, D.; Buchert, J.; Faulds, C.B. Pre-hydrolysis with carbohydrases facilitates the release of protein from brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, D.; O’Hara, R.; Neves, A. By-products of the whelk processing industry as valuable source of antioxidant peptides. Proc. World Conf. Waste Manag. 2021, 2, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-J.; Lee, J.-E.; Lim, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Antioxidant and immune-enhancing effects of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum 200655 isolated from kimchi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elam, E.; Feng, J.; Lv, Y.-M.; Ni, Z.-J.; Sun, P.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Ma, Y.-L.; Wei, Z.-J. Recent advances on bioactive food derived anti-diabetic hydrolysates and peptides from natural resources. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycaemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, R.; Casey, F.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Shields, D.; Mooney, C. Predictive modelling of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory dipeptides. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, S.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Microencapsulation of extracted bioactive compounds from brewer’s spent grain to enrich fish-burgers. Food Bioprod. Processing 2016, 100, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M.B. Concepts and strategy of functional food science: The European perspective. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1660S–1664S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J. Characterisation of protein-rich isolates and antioxidative phenolic extracts from pale and black brewers’ spent grain. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.B. Factors for Converting Percentages of Nitrogen in Foods and Feeds into Percentages of Proteins; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Enzymic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers: Barking, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, D.; McEvoy, E.; O’Cuinn, G.; FitzGerald, R. Proteinase and exopeptidase hydrolysis of whey protein: Comparison of the TNBS, OPA and pH stat methods for quantification of degree of hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.H.; Shimamura, T.; Sakaguchi, K.; Noguchi, K.; Ishiyama, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Ukeda, H. Assay of angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibiting activity based on the detection of 3-hydroxybutyric acid. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 364, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.H.; Shimamura, T.; Manabe, S.; Ishiyama, M.; Ukeda, H. Assay of angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibiting activity based on the detection of 3-hydroxybutyrate with water-soluble tetrazolium salt. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Sumikura, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Tada, A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Matsui, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Akiyama, H.; Ukeda, H. Applicability of the DPPH assay for evaluating the antioxidant capacity of food additives–inter-laboratory evaluation study–. Anal. Sci. 2014, 30, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Jaiswal, A.K. A comparative analysis of pretreatment strategies on the properties and hydrolysis of brewers’ spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. A comprehensive review on pre-treatment strategy for lignocellulosic food industry waste: Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of different pretreatment strategies for protein extraction from brewer’s spent grains. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, H.; Coldea, T.E.; Zhao, H. Modification of structural and functional characteristics of brewer’s spent grain protein by ultrasound assisted extraction. LWT 2021, 139, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, R. An integrated study using ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of hydrolysates from rice based distillery byproduct and its characterization. Process Biochem. 2022, 119, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Qi, M.; Burks, W.; Siebenmorgen, T. Preparation and functional properties of rice bran protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Fernandes, M.; Dragone, G.; Mancilha, I.M.; Roberto, I.C. Brewer’s spent grain as raw material for lactic acid production by Lactobacillus delbrueckii. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.S.; Yohannan, B.K.; Walker, G.M. Bioconversion of brewer’s spent grains to bioethanol. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssell, P.; Kontkanen, H.; Schols, H.A.; Hinz, S.; Eijsink, V.G.; Treimo, J.; Robertson, J.A.; Waldron, K.W.; Faulds, C.B.; Buchert, J. Hydrolysis of brewers’ spent grain by carbohydrate degrading enzymes. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of brewers’ spent grain proteins and technofunctional properties of the resulting hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hu, X. Structural characteristics and stability of salmon skin protein hydrolysates obtained with different proteases. LWT 2022, 153, 112460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, D.; O’Hara, R.; Cunha Neves, A. Bioactive Peptides Generated from the By-Products of the Whelk Processing Industry. World J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 102–130. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.; Bateman, A. MEROPS: The database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D503–D509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Siar, E.-H.; Tavano, O.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Use of Alcalase in the production of bioactive peptides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2143–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Boas AA, V.; Coscueta, E.R.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Campos, D.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M. Bioactive extracts from brewer’s spent grain. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8963–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loponen, J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in Finnish cereals: A database survey. Agric. Food Sci. 2004, 13, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Extraction of protein from the macroalga Palmaria palmata. LWT Food. Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Mikiashvili, N.; Bonku, R.; Smith, I.N. Allergenicity, antioxidant activity and ACE-inhibitory activity of protease hydrolyzed peanut flour. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J. In vitro α-glucosidase, angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory properties of brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 56, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.G.; Ramos, M.; Recio, I. Angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory activity of peptides isolated from Manchego cheese. Stability under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyankar, P.; Zhu, Y.-S.; O’Cuinn, G.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Investigation of the substrate specificity of glutamyl endopeptidase using purified bovine β-casein and synthetic peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3193–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, M.M.; Morais, S.; Carvalho, D.O.; Barros, A.A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Guido, L.F. Brewer’s spent grain from different types of malt: Evaluation of the antioxidant activity and identification of the major phenolic compounds. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phongthai, S.; D’Amico, S.; Schoenlechner, R.; Homthawornchoo, W.; Rawdkuen, S. Fractionation and antioxidant properties of rice bran protein hydrolysates stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bals, B.; Balan, V.; Dale, B. Integrating alkaline extraction of proteins with enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose from wet distiller’s grains and solubles. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5876–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaschel, E.; Ebmeier, L. Stabilization of α-Chymotrypsin by DMSO, in Progress in Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).